
Enhanced Attention-Based ResNet for Driver Distraction Detection
Premalatha S, S. Jayachitra, Latha B, Santhosh M, Geethambari M and Hari Arulkumar
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering,
Tiruchengode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Driver Distraction, ResNet, Enhanced Attention Mechanism, Driver Monitoring, Deep Learning, AUC
Distracted Driver Dataset, Real-Time Detection, Cognitive Distractions, Visual Distractions, Accuracy.
Abstract: Aim: The research seeks to identify some common drivers' distractions such as texting and eating, looking
aside, by designing an EAB ResNet model for analyzing the face, eye, and hand movements of a person.
Materials and Methods: The image data is preprocessed through resizing normalization, and augmentation. It
is fine-tuned with transfer learning on a large annotated dataset to detect behaviors like phone use and eating.
Group 1: The model was developed using a Convolutional Neural Network method is accurate in 82% of
dealing with the AUC dataset. Crucial elements were accomplished through the use of the Grad-CAM. Group
2: The suggested system is an essential tool for enhancing road safety since it can achieve high accuracy even
in intricate and dynamic driving situations by using the ResNet architecture. Result: ResNet obtains values of
precision above 96% with small variations, high precision ensures that very few normal driving actions. The
ResNet model continuously attains better accuracy, ranging from 90.5% to 96.01%. Statistical Analysis is
also done to ensure that the model works robustly as the mean accuracy returned 95%, the Standard deviation
is 0.92, and the Standard mean Error is 0.239. Conclusion: The Enhanced ResNet achieves accuracy and
precision is outperforming conventional CNNs. Improvements in the coming future include a mental
distraction ability and a rise in real-world adaptability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Driver distraction is one of the main causes of traffic
fatalities worldwide, mainly as a result of texting,
using a phone, eating, and drowsiness (1). Human
observation by some mere monitoring systems cannot
detect the faint indications of distraction in real time.
However, new developments in deep learning and
computer vision now make it possible to
automatically detect using complex algorithms (2).
Among them, ResNet excels in classification tasks
because it learns from deep features of complex
visual data (3). If attention mechanisms are included
in the system, then the system might focus on
important areas, such as face, eyes, and hands, to
enhance accuracy for detecting cognitive and visual
distractions (4). This high-tech approach, with real-
time processing, reduces the number of accidents
resulting from inattention and fatigue, thereby
ensuring that safety among drivers is much better (5).
2 RELATED WORKS
Published studies on Enhanced Attention-Based
ResNet for the Detection of Driver Distractions have
been published across IEEE Xplore, Google Scholar,
Elsevier, SpringerLink, and even ArXiv. Recent
publications based on ResNet architectures, attention
mechanisms, and distraction detection all enhance
accuracy, real-time applicability, and adaptability by
incorporating multimodal data fusion associated with
visual and sensor inputs. These models strengthen the
detection as they amplify some critical features
including eye movement, facial expressions, and
hand gestures that filter the irrelevant information
responsible for improving precision.
According to research, the attention-based
ResNet models prove better than regular CNNs. (6)
concluded a 5% increase in accuracy and added that
multimodal fusion enhanced this to 7%. (6) also
proved the detection in real-time, 90% of which
occurred at 300 ms, and could thus be utilized in self-
driven vehicles. Improved Attention-Based ResNet
S., P., Jayachitra, S., B., L., M., S., M., G. and Arulkumar, H.
Enhanced Attention-Based ResNet for Driver Distraction Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013925400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
213-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
213
Improved with 15% accuracy against conditions such
as texting and talking that are not usually present with
ordinary distractions (7) Confirmed findings of better
lighting, occlusion, motion blurs but minimizes false
positives (7). The ability of ResNet models to
enhance real-time adaptability, reduce false alarms,
and further increase reliability in self-driving
vehicles. Their potential to handle more complex
driving environments makes them more superior
models as compared to other traditional models
which guarantee more precision and robustness in the
detection of driver distraction.
From previous findings, it is found that CNNs are
not able to detect driver distractions as they do not
manage complex real-life driving situations very
well. Because they are not able to generalize well,
their accuracy in spotting distractions drops. In
comparison, ResNet is better because it overcomes
the vanishing gradient problem using deep residual
learning. This permits the training of deeper
networks, ResNet can be more easily used to monitor
drivers in real time more accurately and efficiently.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The experiment was conducted in the Computer Lab,
where the lab setup included optimized high-
performance computing systems for the training of
data set collected from Kaggle.com of driver images
data and it is fine-tuned ResNet model through
transfer learning with a large annotated dataset (8).
The model is trained to identify distracted driving
behaviors such as phone or eating based on visual
observations. ResNet allows the system to be highly
accurate regardless of poor driving conditions
Group 1: The Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN) architecture for driver distraction as a primary
causative factor for road accidents. The model was
developed using AUC Project and State Farm
Distracted Driver Detection competition datasets of
Kaggle.
Enhanced image classification by identifying the
crucial elements was accomplished through the use of
the Grad-CAM method (8). Even as the model itself
was accurate in 82% of dealing with the AUC dataset,
discoveries were seen pointing to avenues where
improvement needed to be achieved.
Group 2: The ResNet architecture algorithm
optimizes the images provided by in-car cameras by
implementing preprocessing mechanisms such as
resizing and normalization.
Having undergone transfer learning for model
training on a massive annotated database, it analyzes
images in real-time continuously, identifying
distracted driving and providing real-time alerts for
enhanced road safety. With its ResNet-based deep
network architecture, it is capable of achieving high
accuracy of 96% even under complex driving
conditions.
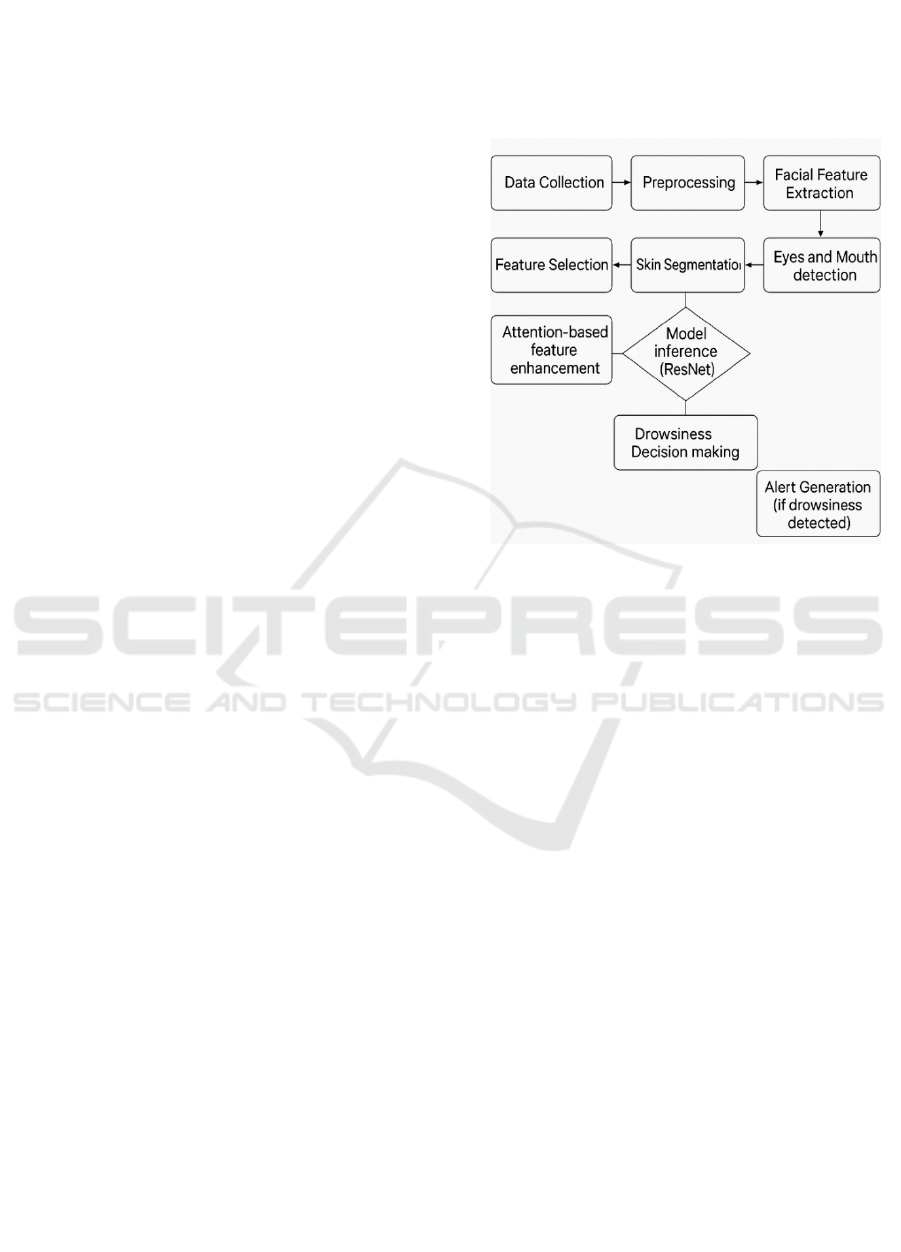
Figure 1: Flowchart of Drowsiness Detection System Using
Attention-Based Feature Enhancement and ResNet Model.
The block diagram Figure 1 Describes a
drowsiness detection process based on facial features
in Data Collection equivalent facial data is taken.
Preprocessing phase which removes noise and gets
the data ready for analysis. Facial Feature Extraction
is performed to identify facial expression. Skin
Segmentation is employed to isolate skin regions,
assisting in the identification of significant facial
features like the eyes and mouth where these features
are detected to identify signs of drowsiness.
Attention-Based Feature Enhancement is
subsequently employed to boost the model's attention
towards important facial features. These boosted
features are subsequently input into the Model
Inference stage, where a ResNet model is employed
to infer drowsiness. Based on the model's inference,
Drowsiness Decision-Making determines whether the
individual exhibits signs of drowsiness. In the event
of drowsiness, the final step is Alert Generation,
where an alert is transmitted to notify the individual
to take appropriate action.
4 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical analysis was conducted by employing the
SPSS tool to assess the performance and significance
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
214
of the model. In the study, The dependent variable
Driver distraction classification and Categorization of
distraction. The independent variable includes
driver’s facial features like eye movement, head
position, facial expressions, Hand positioning on the
steering wheel, Mobile phone usage, Yawning
detection, Environmental factors.
5 RESULTS
The ResNet consistently outperforms CNN in driver
distraction and drowsiness detection tasks and
demonstrates superior performance. In comparison to
the CNN model (85.47%), the ResNet model achieves
a higher mean Accuracy (95.83%) shown in Table 1,
The CNN model shows the lower Precision (82.05%)
as compared with the ResNet (92.43%). Further
evidence of more consistent and trustworthy
predictions comes from the improved model’s
reduced Standard deviation (0.53 vs 0.92) and
Standard Error Mean (0.137 vs 0.239) are shown in
Table 2. Additionally, it states that there existed a
considerable difference between the groups (p<0.05,
independent sample t-test) shown in table 3.
The System flowchart is presented in Figure 1
Preprocessing phase which removes noise and gets
the data ready for analysis. Facial Feature Extraction
is performed to identify facial expression. In Fig.2
Using 15 test cases, The CNN model stays between
80.8% and 86.5%, and the ResNet model
continuously attains better accuracy, ranging from
90.5% to 96.01%. Fig.3 shows that the ResNet
consistently outperforms CNN in recall across
multiple trials. ResNet maintains recall values
predominantly above 92%, with occasional
fluctuations, while CNN lags, showing values
between 80.5% and 83%. Fig.4 ResNet obtains values
of precision above 93% with small variations, while
CNN scores below 79.2% and 82.6%. The significant
reduction shows that the model is able to accurately
and consistently recognize distracted driving in real-
world conditions. The high precision ensures that
very few normal driving actions are classified as
distractions, while the strong recall guarantees that
most cases of driver distraction are correctly
identified.
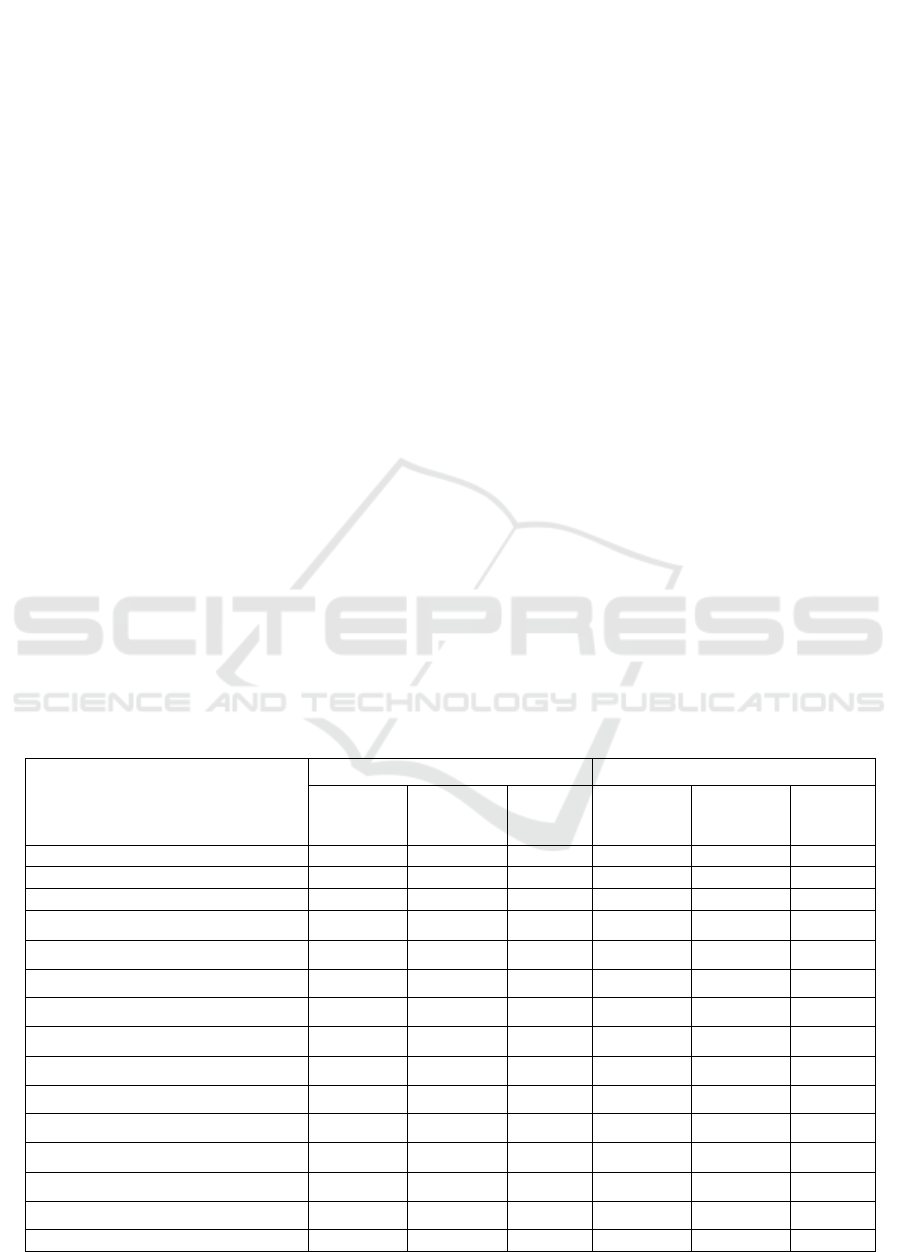
Table 1: The Table 1 Presents the Performance
Metrics of CNN And Resnet Models Across 15 Test
Cases, Comparing Accuracy, Precision, And Recall.
Resnet Consistently Outperforms CNN In All Three
Metrics, With Accuracy Ranging From 92.4% To
95.2%, Precision From 90.7% To 94.2%, And Recall
From 91.5% To 95.5%. In Contrast, CNN Shows
Lower Performance, With Accuracy Between 84.7%
And 86.3%, Precision Between 80.9% And 83.5%,
And Recall Between 80.2% And 82.8%. The Results
Highlight Resnet's Superior Performance in Driver
Distraction Detection Tasks.
Table 1: Performance Comparison of CNN and ResNet Models Based on Accuracy, Precision, and Recall Across Multiple
Test Cases.
Test CasNumber
CNN Model ResNet
Accuracy
(%)
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
Accuracy
(%)
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
1 85.4 82.3 81.9 92.5 90.2 91.8
2 86.1 83.5 82.8 93.1 91.0 92.5
3 84.7 80.9 81.0 94.0 92.3 93.2
4 85.9 82.7 81.5 92.8 91.5 92.0
5 86.3 83.1 82.2 93.6 92.8 93.0
6 85.2 81.8 80.7 94.5 93.1 93.8
7 84.9 81.5 80.3 95.2 94.0 95.5
8 85.5 82.2 81.2 94.7 93.5 94.0
9 86.0 83.0 82.5 92.9 90.8 91.9
10 85.1 81.7 80.9 93.8 92.5 93.6
11 86.2 83.4 82.6 94.3 93.0 93.1
12 85.3 82.0 81.0 95.0 94.2 94.7
13 84.8 81.1 80.2 92.4 90.7 91.5
14 85.6 82.3 81.5 93.9 92.6 93.3
15 85.0 81.9 80.8 94.8 93.8 94.2
Enhanced Attention-Based ResNet for Driver Distraction Detection
215
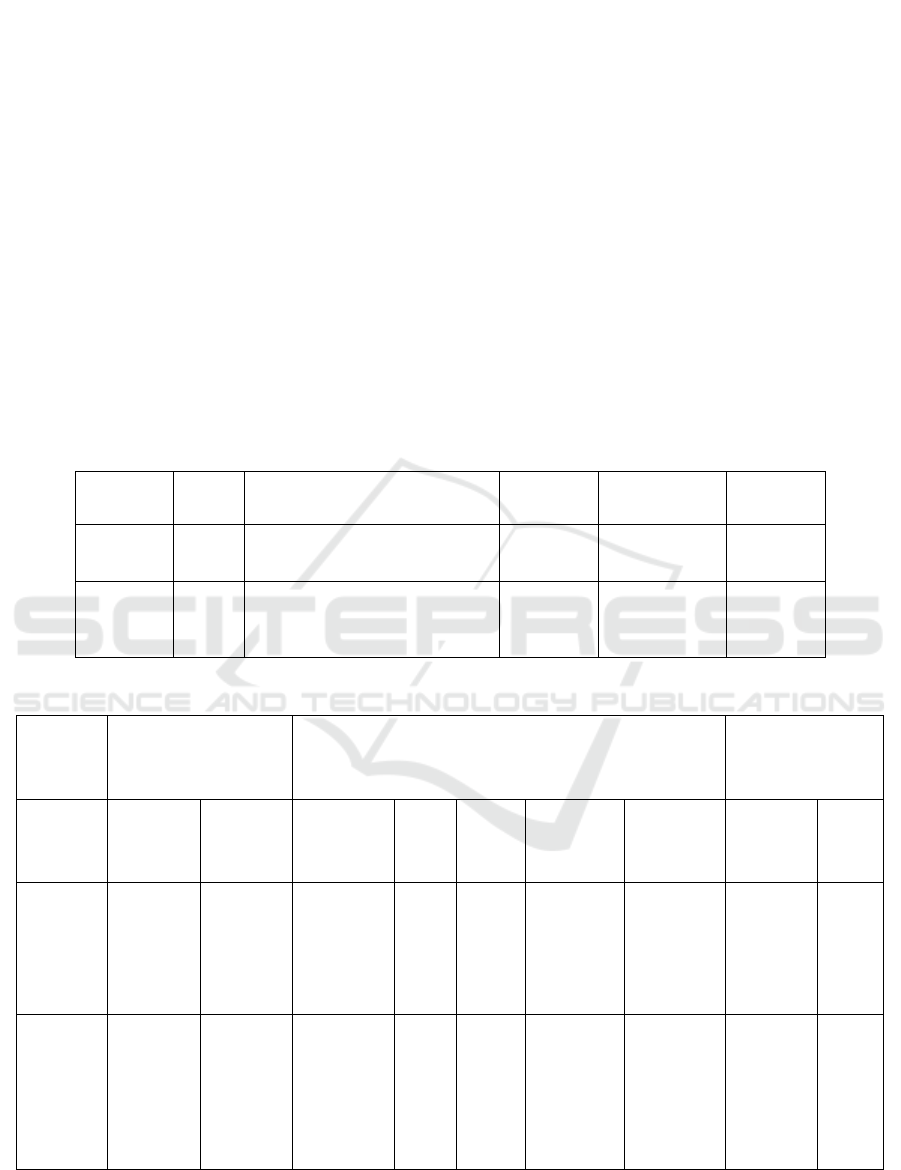
The Table 2 Presents the Performance Statistics
for CNN And Resnet Models. CNN Shows a Mean
Accuracy Of 85.47%, With A Standard Deviation Of
0.92 And A Standard Error Mean Of 0.137. Resnet
Outperforms CNN With a Higher Mean Accuracy Of
93.83%, A Standard Deviation Of 0.53, And A
Standard Error Mean Of 0.239. Both Models
Demonstrate Similar Performance Variability
Despite the Accuracy Difference.
Table 3 Shows the Independent Sample Test T-
Test Comparison of The Accuracy CNN Model and
Resnet Model.
Figure 2 The accuracy comparison indicates a
similar trend, with ResNet achieving higher accuracy
throughout the trials, consistently staying above 92%.
CNN, on the other hand, fluctuates between 85% and
86%. The results suggest that ResNet has better
overall performance in correctly identifying
drowsiness states compared to CNN.
Figure 3 The recall comparison chart
demonstrates that ResNet consistently outperforms
CNN in recall across multiple trials. ResNet
maintains recall values predominantly above 92%,
with occasional fluctuations, while CNN lags,
showing values around 80–83%. This indicates that
ResNet is more effective in capturing true positive
cases, reducing missed detections compared to CNN.
Figure 4 The recall comparison chart
demonstrates that ResNet consistently outperforms
CNN in precision across multiple trials. ResNet
maintains precision values predominantly above
93%, with occasional fluctuations, while CNN lags,
showing values around 80–83%. This indicates that
ResNet is more effective in capturing true positive
cases, reducing missed detections compared to CNN
Table 2: Statistical Summary of CNN and ResNet Model Accuracy with Standard Deviation and Standard Error.
Model N
Mean Accuracy (%)
Standard
Deviation
Standard
Error
mean
Model
CNN 15 85.47 0.92 0.137 CNN
ResNet 15 95.83 0.53 0.239 ResNet
Table 3: Independent Samples Test.
Measure
Levene's Test for
Equality of Variances
Independent Samples Test
95% Confidence
Interval of the
Difference
F Sig. t df
Sig.
(2-
tailed)
Mean
Difference
Std. Error
Difference
Lower Upper
Accuracy
(%) –
Equal
variances
assumed
0.002 0.965 -3.540 28 0.001 -8.36 2.36 -13.20 -3.52
Accuracy
(%) –
Equal
variances
not
assumed
– – -3.540 26.35 0.001 -8.36 2.36 -13.20 -3.52
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
216
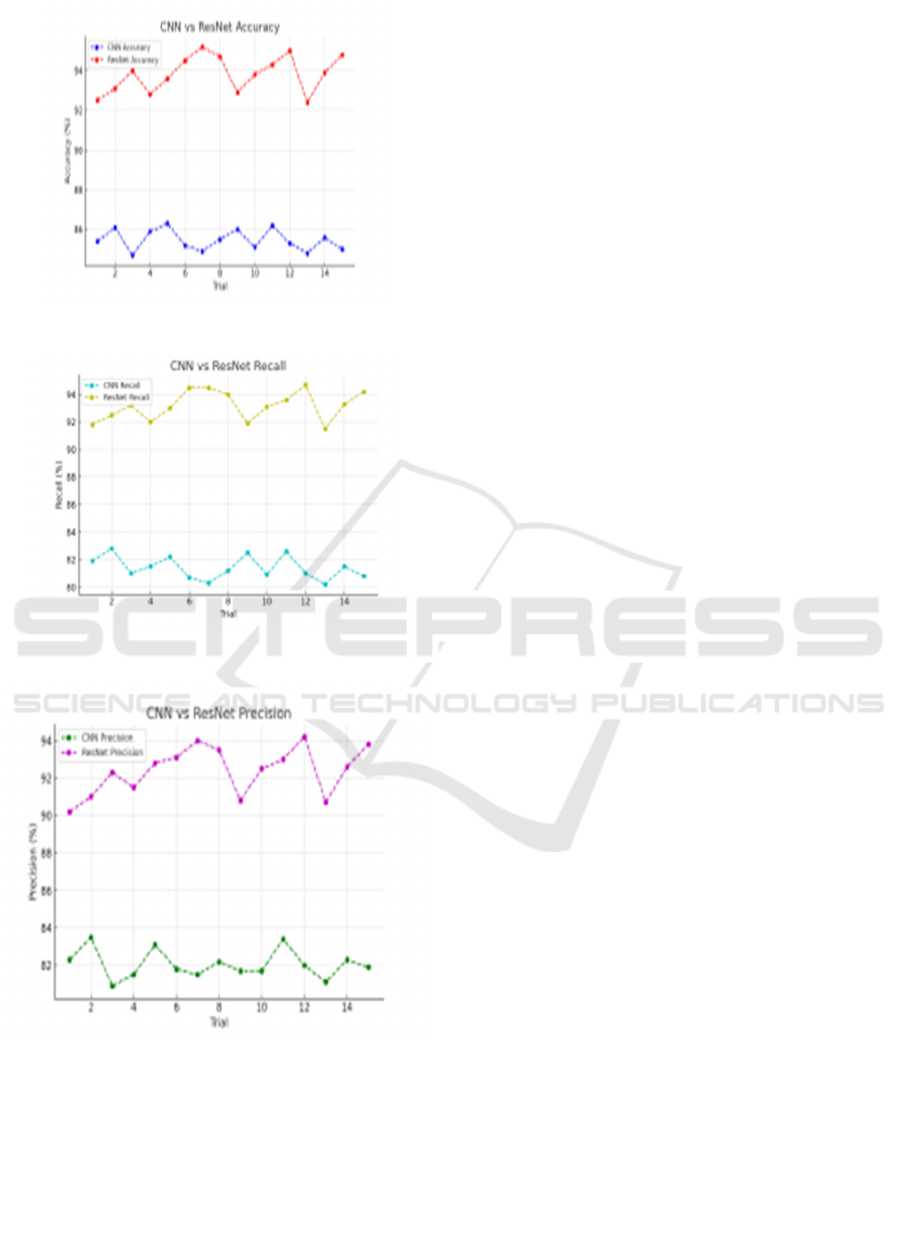
Figure 2: CNN vs ResNet Accuracy.
Figure 3: CNN vs ResNet Recall.
Figure 4: CNN vs ResNet Precision.
6 DISCUSSIONS
Based on the significance value (p<0.05) the research
concluded that the enhanced attention-based ResNet
model significantly improves the detection of driver
distraction. The improvement of attention was
integrated into the ResNet architecture it improved its
performance over CNN models because the attention
mechanism allows the network to focus on relevant
features such as eye gaze and movement of facial
parts (9). A similar work highlighted the importance
of combining attention mechanisms with deep
learning to enhance performance in driver distraction
detection systems, noting that it can help in focusing
on specific facial areas such as the eyes and mouth
(11).
The present study is that the dataset used was
relatively limited, focusing on environmental
conditions and driver profiles. This model showed
great promise; it was not tested in real time driving
scenarios the distractions could be much more
complex. Future studies would expand the dataset
using a more diversified set of drivers and
environmental conditions and include real-time
performance testing to test how the model works in
variable traffic and weather conditions (10). Other
potential areas of future work would include
developing low-latency systems that would offer
instant feedback to the drivers so that the model
would be safe and usable. Exploration into
multimodal sensor used perhaps steering wheel
movement, heart rate variability, or even biometric
sensors inside a vehicle can offer dimensions to
detecting distractions (12).
The limitations of this design are sensitive to
lighting and occlusions, so if there are changes in
lighting in the environment, shadows, or occlusions,
the accuracy can be affected and may result in
misclassification or false negatives in real-world
driving conditions. Motion blur, camera angle
changes, and low-resolution images can also degrade
performance. The model may have difficulty
separating subtle distractions from normal driving
behaviour, leading to more false positives.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The Enhanced ResNet enhances these metrics to 96%
accuracy and 92% precision, whereas Conventional
CNNs generally achieve an accuracy of
approximately 86% with a precision of 82%.
Statistical Analysis is also done to ensure that the
model works robustly as the mean accuracy returned
95%, the Standard deviation is 0.92, and the Standard
mean Error is 0.239. This finding verifies that the
model is useful in enhancing real-time, resource-
effective driver distraction detection, as it improves
scalability.
Enhanced Attention-Based ResNet for Driver Distraction Detection
217

REFERENCES
A Real-time Driving Drowsiness Detection Algorithm with
Indiv Differences Consideration, " by F. You, X.
Li, Y. Gong, H. Wang, and H in IEEE Access, vol. 7,
pp. 179396-179408, 2019,
10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2958667.
Determining Driver Drowsiness Using Condition-Ada
Representation Learning Framework, " by J. Yu,
S. Park, S. Lee, a Jeon, in IEEE Transactions on
Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 20, n pp. 4206-
4218, Nov. 2019, doi:10.1109/TITS.2018.2883823.
In IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 20, no. 7, pp. 3709-3717, 1
April 1, 2 M. Sunagawa, S. Shikii, W.Nakai, M.
Mochizuki, K. Kusukame, an Kitajima published
" Comprehensive Drowsiness Level Detection M
Combining Multimodal Information," doi:
10.1109/JSEN.2019.29601
A Survey on State-of-the-Art Drowsiness Detection
Techniques, & quo M.Ramzan, H. U. Khan,S. M.
Awan, A. Ismail, M. Ilyas, and A. Mahmo IEEE
Access, vol. 7, pp. 61904-61919,
doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914373.
An Effective Hybrid Model for EEG-Based Drowsiness
Detection by U. B V. Bajaj, Y. Akbulut, O. Atila, and
A. Sengur, appeared in IEEE Sensors Jou vol. 19, no.
17, pp. 7624- 7631, September 1, 2 doi:10.1109/JSEN.
2019.2917850.
In IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,vol. 66,
no. 6, pp. 1769–1778, June 2019, K.Fujiwara et al.
published “Heart Rate Variability- Based Driver Dro
wsiness Detection and ItsValidation with EEG”
doi:10.1109/TBME.2018.2879346.
Machine learning aided design and optimization of MEMS
optical phased array with silicon micro mirrors for
nanofabrication S.Premalatha, Himanshu sharma,
Vipul Vekariya, Abhinav Shrivastra, G Ramkumar,
Ahmed Sayed M
In IEEE Tnsactions on Human-Machine Systems, vol. 48,
no. 1, pp. 50-62, February 2018, G.Li and W. Chung
published “Combined EEG-Gyroscope-tDCS Brain
Machine Interface System for Early Management of
Driver Drowsiness," doi:10.1109/THMS.2017.275980
8.
In IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation
Engineering, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 400-406, February
2018, C. Wei, Y. Wang, C. Lin, and T.Jung, "
Towards Drowsiness Detection Using Non-
hair- Bearing EEG- Based Brain- Computer Interfaces
," doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2018.2790359.
Takayuki Katsuki, Kun Zhao, Takayuki Yoshizumi,
"Learning to Estimate Driver Drowsiness from Car
Acceleration Sensors Using Weakly Labeled Data",
ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on
Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP),
pp.3002-3006, 2020.
Rekyan Regasari Mardi Putri, Chin-Chun Chang, Aditya
Fitri Hananta Putra, Setyan Pamungkas, Deron Liang,
"SmartDetect: Safe Driving by Detecting Steering-
Wheel Handling with a Single Smartwatch", IEEE
Sensors Journal, vol.24, no.10, pp.16325-16335, 2024.
Fan, S. Huang, S. Lin, D. Xu, Y. Peng, and S. Yi, ‘‘Types,
risk factors, consequences, and detection methods of
train driver fatigue and distraction,’’ Comput. Intell.
Neurosci., vol. 2022, pp. 1–10, Mar. 2022.
M. Mohana Soundarya, S. Jay Chitra, “An Efficient Code
Compression Technique for Ecg Signal Application
Using Xilinx Software”, International Journal of
Scientific & Technology Research Volume 8, Issue 09,
September 2019 ISSN 2277-8616.
S. Jayachitra, C.Nelson Kennedy Babu “Energy – efficient
Polynomial Time Resource Channelized Framework
for Data Communication in MANET” Asian Journal of
Information Technology, Medwell Journals, vol. 15, no.
12, pp. 1987-1995.2016 ISSN 1682-3915
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
218
