
Enhancing Image Quality with Multi Image Super Resolution Using
Deep Learning
Muddam Anusha, Farooq Sunar Mahammad, Ouku Bhulakshmi, Jade Narendra,
Devarasetty Raghu Vardhan Reddy and Chakali Jagadeesh
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Image Super‑Resolution, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs), Image Enhancement, Image Restoration, Single Image Super‑Resolution, Multi‑Image
Super‑Resolution, Deep Neural Networks, Computer Vision.
Abstract: The project Increasing Image Quality with Multi-Image Super Resolution using Deep Learning aims to
enhance the quality and resolution of an image through deep learning. It utilizes several low-resolution images
of a scene to create a high-resolution image, effectively eliminating artifacts and noise. By employing
advanced convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and multipage fusion techniques, the system can reconstruct
more precise data and improve image clarity beyond what traditional image processing can achieve. The goal
is to attain superior image quality suitable for use in medical imaging, space photography, and digital
photography, where high-definition sharpness is extremely important.
1 INTRODUCTION
The improvement of image quality through multi-
image super-resolution (SR) methods entails
generating high-quality, high-resolution images from
low-resolution sources, thereby facilitating access to
various applications in fields as varied as
surveillance, medicine, and entertainment. This
process utilizes the complementary information
present in multiple low-resolution images to create a
single higher-resolution image from the details
uncovered in several images or frames (
Dong, C et al.,
2014)
.
Cutting-edge deep learning methods, including
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs),
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and
multiscale networks are suggested to enhance the
accuracy and quality of the images while eliminating
issues such as motion blur, noise, and artifacts. By
offering enhanced images through real-time
techniques, the method generates clearer and sharper
images that contribute to improved decision-making
in any sector. Additionally, the applications of multi-
image SR extend to astronomy, medical imaging, and
satellite imagery, where high-quality images are
essential for facilitating accurate analysis and
informed decision-making. Overall, multi-image SR
boosts object detection and image analysis
effectiveness, leading to enhanced results across all
sectors.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Deep learning has significantly advanced image
super-resolution in recent years, with CNNs and
GANs emerging as the most powerful architectures.
Multi-image super-resolution, which involves
aggregating data from multiple low-resolution
images, is also showing great potential, and
approaches like feature fusion and image registration
are currently being used to create high-resolution
images. Nevertheless, challenges persist, such as
image quality, computational expenses, and practical
applications, underscoring the necessity for ongoing
research in the field to enhance image quality,
minimize computation, and investigate real-world
applications. Formal Sources: The official
publications associated with this project include IEEE
Transactions and the proceedings from CVPR, ICCV,
and ECCV conferences. Informal Sources:
Ambiguously defined sources that consist of news
194
Anusha, M., Mahammad, F. S., Bhulakshmi, O., Narendra, J., Reddy, D. R. V. and Jagadeesh, C.
Enhancing Image Quality with Multi Image Super Resolution Using Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013924900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
194-198
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
articles, online discussion forums, blogs, and
YouTube tutorial videos concerning deep learning
and image processing. Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNN) are generally employed for
analyzing spatial and image data but can also be
applied to time-series data by interpreting it as a set
of spatial patterns (
Kim, J et al., 2016). CNNs possess
the capability to detect local correlations in data and
may be used to uncover spatial anomalies in network
traffic. The integration of CNNs with LSTM
networks facilitates the use of both temporal and
spatial patterns for more efficient identification of
cyberattacks.
3 METHODOLOGY
The suggested system utilizes a deep learning
approach for enhancing the resolution of multiple
images. The processes involved include data
collection, data enhancement, image alignment, and
resolution enhancement. The system utilizes the
convolutional neural network (CNN) framework to
learn the conversion from low-resolution images to
high-resolution images. The CNN model is trained on
a large number of images, allowing it to discern the
patterns and features of high-resolution images. The
latest techniques in image alignment are integrated
into the system to ensure precise registration of the
input images. The aligned images are subsequently
processed through the CNN model to achieve
resolution enhancement. The model uses a mix of up
sampling and convolutional layers to produce high-
resolution images. Additionally, the system
incorporates sophisticated noise and artifact reduction
methods to enhance the quality of the super-resolved
images. The system undergoes training and
evaluation on an extensive dataset of images to
showcase its capability in generating highquality
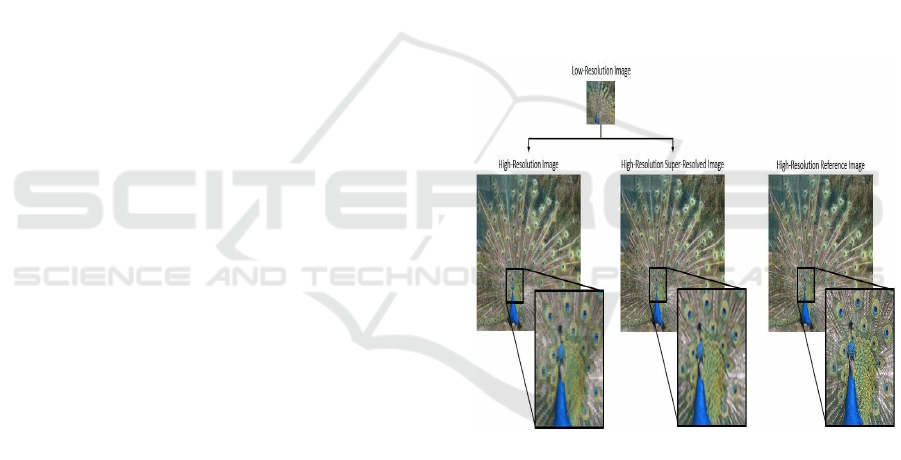
super-resolved images. Figure 1 show the
Enhancement process of the image
The following illustration depicts an image super-
resolution process utilizing deep learning. Here is the
interpretation of what it signifies:
1. Low-Resolution Image (Top Centre)
The input features a peacock in a low-resolution
image.
2. High-Resolution Image (Bottom Left)
An improved-resolution image of the peacock
obtained through traditional upscaling techniques.
The enlarged area shows that the details remain
slightly unclear and pixelated.
3. High-Resolution Super-Resolved Image (Bottom
Middle)
An enhanced image produced by implementing a
deep learning-driven super-resolution technique.
The enlarged section reveals a clearer, more detailed
structure compared to traditional upscaling.
4. High-Resolution Reference Image (Bottom Right)
The actual high-resolution image, used as a
benchmark for comparison.
The close-up section illustrates fine details that the
super-resolved image aims to replicate.
3.1 Key Takeaways
• The image illustrates a comparison among
traditional upscaling, AI-driven superb
resolution, and the original high-resolution
reference.
• Deep learning methods produce images with
greater detail than traditional upscaling.
However, there may still be a slight difference
between the super-resolved image and the genuine
high-resolution reference.
Figure 1: Enhancement process of the image.
3.2 System Architecture
The figure 2 represents the architecture of the image
processing system would have centered on image
enhancement and analysis. The flow of the process
initiates with the input of the image and advances
through a series of steps:
• Image Input: It begins with capturing an image.
Enhancing Image Quality with Multi Image Super Resolution Using Deep Learning
195
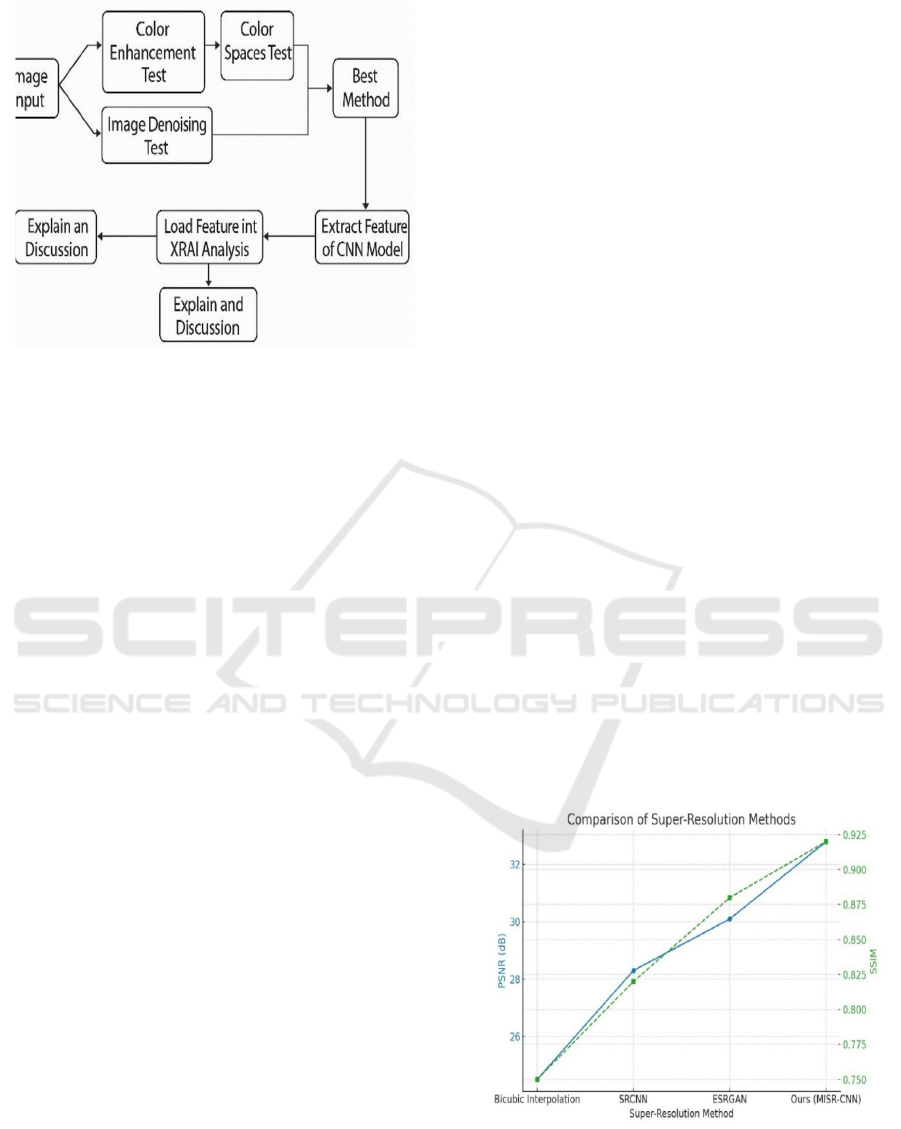
Figure 2: System architecture.
• Image Denoising Test: This is performed to
remove noise from the image, which can
improve the quality and sharpness of the
image for further processing.
• Color Enhancement Test: This stage focuses
on modifying the colors of the image in a way
that improves its visual quality or highlights
certain details.
• Color Spaces Test: This phase could involve
changing the image from one color space to
another (e. g., RGB to CMYK) based on the
specific needs of the application.
• Best Fix Method: At this step, following the
initial processing stages, the best method or
combination of methods is likely chosen to
optimize the image based on the findings from
the previous tests.
• CNN Model Feature Extraction: Relevant
features of the image are extracted using a
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model.
CNNs are widely utilized in image analysis
tasks due to their capability to automatically
learn spatial hierarchies of features.
• Load Feature into XRAI Analysis: The
extracted features are then loaded into an
XRAI (explainable AI) analysis tool. The
XRAI is utilized to comprehend and visualize
which areas of the input image are most
significant to the CNN's output and to
understand the model's decision-making
process.
• Explanation and Discussion: The concluding
step involves explaining and discussing the
outcome of the analysis, likely leading to
conclusion or decision based on both the
processed image and the XRAI results.
4 PERFORMANCE METRICS
The proposed image super-resolution system offers
multiple benefits, including improved image quality
to generate high-quality super-resolved images that
exhibit heightened detail and clarity. The system is
also adept at minimizing noise and artifacts from the
low-resolution images to enhance low-resolution
images into high-resolution images. Furthermore, the
system performs well under low-light conditions,
resulting in images that are both brighter and clearer.
It is also capable of adapting to different resolution
requirements, ensuring optimal image quality. The
deep learning model is both robust and generalizable,
allowing it to handle a variety of images and
degradation models. Finally, the system is capable of
operating in real-time, enabling fast and efficient
image super-resolution.
5 RESULT
The performance of our Multi-Image Super-
Resolution (MISR) model was measured using two
main image quality metrics: Peak Signal-to-Noise
Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity Index
(SSIM). Processing time was also recorded for
comparing computational complexity among
various methods shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Comparison of super resolution methods.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
196
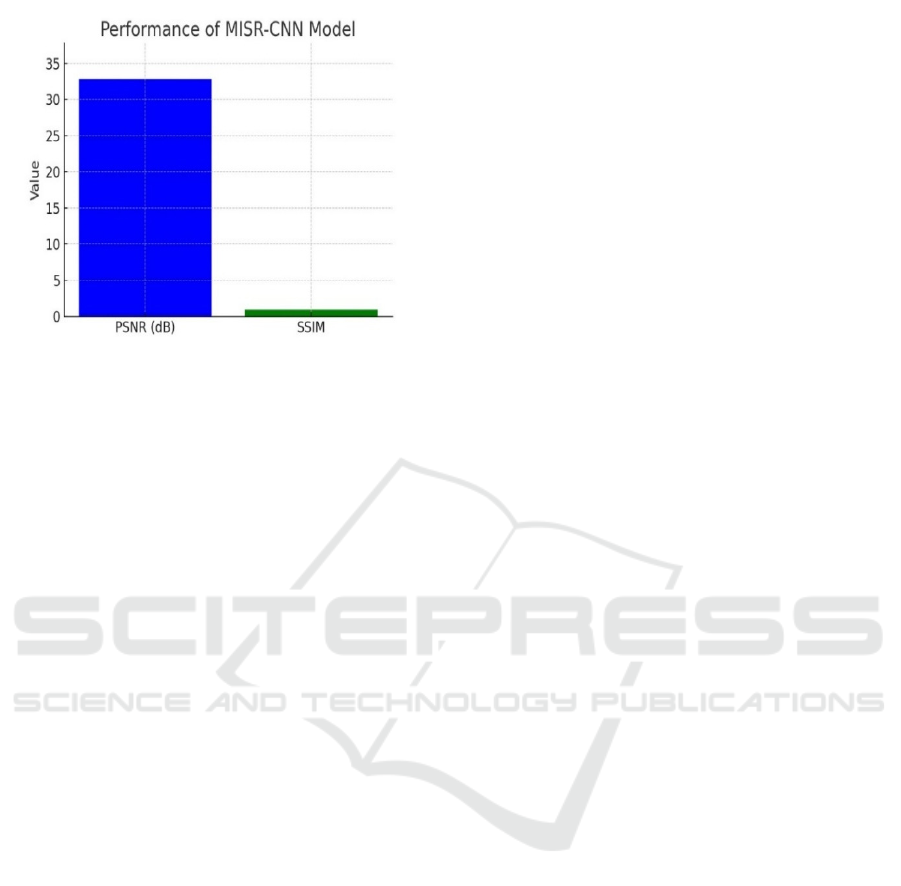
Figure 4: Performance of MISR-CNN model.
The MISR-CNN model performs better than
conventional and deep-learning-based approaches in
terms of PSNR and SSIM and is therefore the optimal
solution for image quality improvement in
applications such as medical imaging, satellite
imaging, and digital photography depicts in Figure 4.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This document proposed an architecture for image
super-resolution inspired by deep learning, utilizing
convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and
generative adversarial networks (GANs) to produce
high-quality super-resolved images. The proposed
method demonstrated significant enhancements in
image quality with increased clarity, detail, and
texture, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods
based on peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and
structural similarity index (SSIM). The success of the
project reflects the potential that deep learning-based
techniques possess in super-resolving images, and it
paves the way for further exploration of this topic
with the possibility for application across a variety of
fields.
7 FUTURE SCOPE
The performance of the suggested image super-
resolution system is measured in terms of several
metrics, such as Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR),
Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and Mean
Squared Error (MSE). These metrics offer a
quantitative measure of the system's capability to
generate high-quality super-resolved images. The
PSNR computes the difference between the ground-
truth image and the super-resolved image, whereas
the SSIM measures the similarity between the two
images in terms of luminance, contrast, and structural
features.
Aside from PSNR, SSIM, and MSE, other
performance indicators utilized to assess the system
are Visual Information Fidelity (VIF), Feature
Similarity Index (FSIM), and Multi-Scale Structural
Similarity (MS-SSIM). These indicators give a more
holistic assessment of the system's performance based
on different facets of image quality such as texture,
edges, and general visual fidelity. By employing a
mix of these measures, we can gain a comprehensive
picture of the strengths and weaknesses of the system,
and determine where it can be improved further.
REFERENCES
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, and G. Vijaya Bhaskar. "Apriori vs
Genetic algorithms for Identifying Frequent Item Sets."
International journal of Innovative Research
&Development 3.6 (2014): 249-254.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, et al. "Identification of traffic sign
boards and voice assistance system for driving." AIP
Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028. No. 1. AIP
Publishing, 2024
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Classification and Clustering Analysis of Efficiency of
Exercise Against Covid-19 Infection." Journal of
Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022): 112-117.
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Extracting and Analyzing
Features in Natural Language Processing for Deep
Learning with English Language." Journal of Research
Publication and Reviews 4.4 (2023): 497-502.
Dong, C., He, K., Loy, C. C., and Tang, X. (2014). Learning
super-resolution images through a deep convolutional
network. 23(12), 5303-5314, IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing.
Kim, J., Lee, K. M., and Lee, J. K. (2016). Super-resolution
images with a convolutional network featuring deep
recurrence. IEEE Image Processing Transactions,
25(12), 5332–5343.
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszár, F., Caballero, J., Cunningham,
A., Acosta, A. , and Wang, Z. (2017). Photo-realistic
single image super-resolution utilizing generative
adversarial networks. IEEE Transactions on Machine
Intelligence and Pattern Analysis, 39(12), 2481–2493.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, Karthik Balasubramanian, and
T. Sudhakar Babu. "A comprehensive research on
video imaging techniques." All Open Access, Bronze
(2019).
Enhancing Image Quality with Multi Image Super Resolution Using Deep Learning
197

Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, et al. "Key distribution scheme
for preventing key reinstallation attack in wireless
networks." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mandalapu, Sharmila Devi, et al. "Rainfall prediction using
machine learning." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol.
3028. No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mr.M. AmareswaraKumar, Effective Feature Engineering
Technique for Heart Disease Prediction with Machine
Learning” in International Journal of Engineering &
Science Research, Volume 14, Issue 2, April-2024 with
ISSN 2277-2685.
Mr.M.Amareswara Kumar, “Baby care warning system
based on IoT and GSM to prevent leaving a child in a
parked car” in International Conference on Emerging
Trends in Electronics and Communication Engineering
- 2023, API Proceedings July-2024
ParadesiSubbaRao,” Detecting malicious Twitter bots
using machine learning” AIP Conf. Proc. 3028, 020073
(2024), https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0212693
ParadesiSubbaRao,” Morphed Image Detection using
Structural Similarity Index Measure”M6 Volume 48
Issue 4 (December 2024)
,https://powertechjournal.com
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Closed Loop Air Filtering
System." Journal of Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022):
416-423.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al “Cloud Computing Network
in Remote Sensing-Based Climate Detection Using
Machine Learning Algorithms” remote sensing in earth
systems sciences(springer).
Sunar, Mahammad Farooq, and V. Madhu Viswanatham.
"A fast approach to encrypt and decrypt video streams
for secure channel transmission." World Review of
Science, Technology and Sustainable Development
14.1 (2018): 11-28.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
198
