
Educhain: Hyperledger‑Powered Decentralized University Services
Management Framework
Suyog A. M., Maheshadithya J., Pavan S. and Sudhir Shenai
Department of Information Science and Engineering, Nitte Meenakshi Institute of Technology, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Keywords: Blockchain Technology, Hyperledger Fabric, Smart Contract, Academic Record Management, Chain Code.
Abstract: In today’s digital age, it is crucial to implement various precautionary measures to ensure the authenticity and
integrity of academic records. This paper suggests Educhain, a blockchain-based structure using Hyperledger
Fabric to establish a system for university and college administration, ensuring data security in a decentralized
way. Educhain enables seamless connectivity between accredited universities and the University Grants
Commission via a secure private blockchain network while ensuring reliability in handling academic
qualifications. UGC oversees the accreditation procedures for this framework, ensuring that only accredited
universities and colleges can participate, thereby decreasing the potential risks, such as fraudulent
accreditation. Educhain provides easy-to-use interfaces or API integrations for institutions without their own
portals to manage faculty data, student enrolments, exam records, and digitally authenticate credentials. The
system improves data security, streamlines administrative processes, and implements restrictions for role-
based access to sensitive data, aiming to address shortcomings in transparency and efficiency in academic
record-keeping. Developing a blockchain solution helps improve trust and security in managing educational
records, ultimately enhancing accountability and operational integrity in academic institutions.
1 INTRODUCTION
The integrity and security of academic records in
modern educational systems are important in
guaranteeing the credibility of the institution and the
value of the student’s qualification. In such a context,
fraudulent academic credentials should not occur.
Digital transformation accelerated this demand to
prevent fraudulent academic credentials. Traditional
record management methods often employ
centralized databases with manual verification
processes. M. Shrivas, et al, 2022, Such techniques
are usually prone to inefficiencies, errors, and security
vulnerabilities. These shortcomings call for creative
approaches to data authenticity, security, and
accessibility.
M. Alam, et al, 2022, Blockchain technology, such
as Hyperledger Fabric, offers a decentralized and
tamper-resistant solution to this challenge. Unlike
public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which
have open access, Hyperledger Fabric rests on
permissioned networks, hence offering a secure and
private environment. The controlled environment in
Hyperledger Fabric implies that only validated
institutions accredited under UGC can take part in this
network, ensuring that only valid users are in control
of academic data.
This paper proposes Educhain a Hyperledger
Fabric-based framework for decentralized university
services management. P. Fernandez and R. Arenas, et
al, 2018, The system enables seamless and secure
communication between colleges and the UGC, while
the latter authorizes and approves the verified
institutes. Educhain facilitates the management of
crucial academic processes, including information
about faculties, student admissions, examination
records, and the issuance of digital certificates.
Marasigan., et al, 2024., It will not only help in
saving them from unauthorized institutions joining the
network, but it will also facilitate the simplification of
administrative workflows and introduce the element
of transparency in the academic record-keeping
process. The introduction of role-based controls
ensures that access and modification privileges are
granted to authenticated users only, hence boosting
the security related to sensitive information. Educhain
is about offering clean records by reducing fraudulent
activities. Amitkumar, et al.,2021 The efficiency and
reliability of academic record management processes
shall continue to increase and hereby finally help
182
M., S. A., J., M., S., P. and Shenai, S.
Educhain: Hyperledger-Powered Decentralized University Services Management Framework.
DOI: 10.5220/0013924600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
182-188
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

educational institutions establish trust and credibility
in their record-keeping.
The technical implementation of Educhain is done
in this paper, reviewing the related literature
concerning blockchain applications to the education
sector, and a comparative analysis of the blockchain
frameworks is done by highlighting the advantages of
Hyperledger Fabric in managing academic
credentials.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
In most cases, such traditional, centralized systems
are increasingly incapable of addressing challenges
related to inefficiency, security vulnerability, and an
increasing number of fraudulent qualifications. Due to
a lack of a secure and standardized framework and
reliance on manual verification processes, the
credibility of institutions and the value of academic
credentials are compromised. These are further
compounded by the fact that there are no open
communications among universities, regulatory
bodies, and third parties, so sensitive data are kept in
a very precarious situation where unauthorized access
and changes to the data can easily be made.
3 RELATED WORK
Starting from the current trends, blockchain
technology is increasingly applied in education to
overcome authenticity, security, and efficiency
challenges at large in managing academic records.
Most traditional systems face inefficiencies, fraud,
and breaches for which blockchain seems nicely
fitted, given its immutability and decentralized nature.
Various works have focused on applications of
blockchain related to certificate management, security
of students’ data, and multi-stakeholder collaboration
within academic environments.
3.1 Blockchain-Based Certificate
Management Systems
H. Gaikwad., et al 2021.; S. Khaleelullah, et al, 2023.
One of the earliest and most prevalent usages of
blockchain in education relates to issues with the
issuance and verification of academic certificates. The
systems conceptualized in make use of permissioned
blockchain networks to generate digital credentials
that are tamper-proof.
Most of these solutions include IPFS, or
decentralized storage methodology, in order to
mitigate large dataset storing challenges on-chain.
This is to ensure that combining the blockchain for
immutability and decentralized storage will definitely
guarantee ease of certificate verification while being
safe from forgery or unauthorized access. Solutions
developed along these lines typically focus narrowly
on certificates and fail to address broader academic
workflows, such as enrolment processes, faculty data
management, and accreditation. Because of this
narrow focus, educational institutions can hardly
adopt blockchain as an integrated solution for their
operational needs.
3.2 Privacy and Security in Blockchain
Applications
As education data is very sensitive, it is really
important to implement privacy-preserving methods
in blockchain adoption. At the same time, numerous
works propose advanced cryptographic mechanisms
for protecting user data. For example, M. Shrives, et
al, 2022, leads the adoption of lattice-based
cryptography so as to protect the blockchain against
quantum computer attacks in the future. Similarly, B.
Sowmiya and E. Poovammal, 2021 leverages
anonymization methods that guarantee personal data
cannot reach subjective persons even in distributed
systems.
While these approaches do have strong privacy
guarantees, many are resource-intensive and complex
to perform at scale. Moreover, solutions like self-
sovereign identities by which users control their
credentials have interoperability issues between
different institutions. These limitations reveal a
further need for a more practical and scalable solution
that efficiently balances privacy and usability.
3.3 Comprehensive Blockchain
Solutions
Other works go further because they are not limited to
only a use case, such as the verification of certificates;
they introduce more general blockchain frameworks
for education. Examples of such include P. Fernandez
and R. Arenas, 2018 , where authors use Hyperledger
Fabric in the implementation of scalable platforms
capable of managing various academic services;
examples include grading, enrolment, and credentials
issuance, which facilitate efficient academic record
management Marasigan., et al, 2024, This system
illustrates the applicability of blockchain in end-to-
end academic management, hence highlighting
Educhain: Hyperledger-Powered Decentralized University Services Management Framework
183
modular architectures capable of being integrated
with existing educational systems. However, many of
them either face regulatory compliance challenges or
stand in conflict with the existing systems. Most
platforms require infrastructure changes, which may
hinder their adoption in resource-constrained
institutions. Also, the limited focus on a particular
region or institution limits the applicability on a larger
scale.
4 METHODOLOGY
Educhain is developed based on Hyperledger Fabric
to establish a decentralized system of university
services management. Five phases are involved in the
development process: system design, blockchain
structure, implementation of modules, integration,
and assessment. These steps make the process of
academic record management secure, transparent, and
efficient and also facilitate easy communication
among universities, colleges, and the University
Grants Commission (UGC).
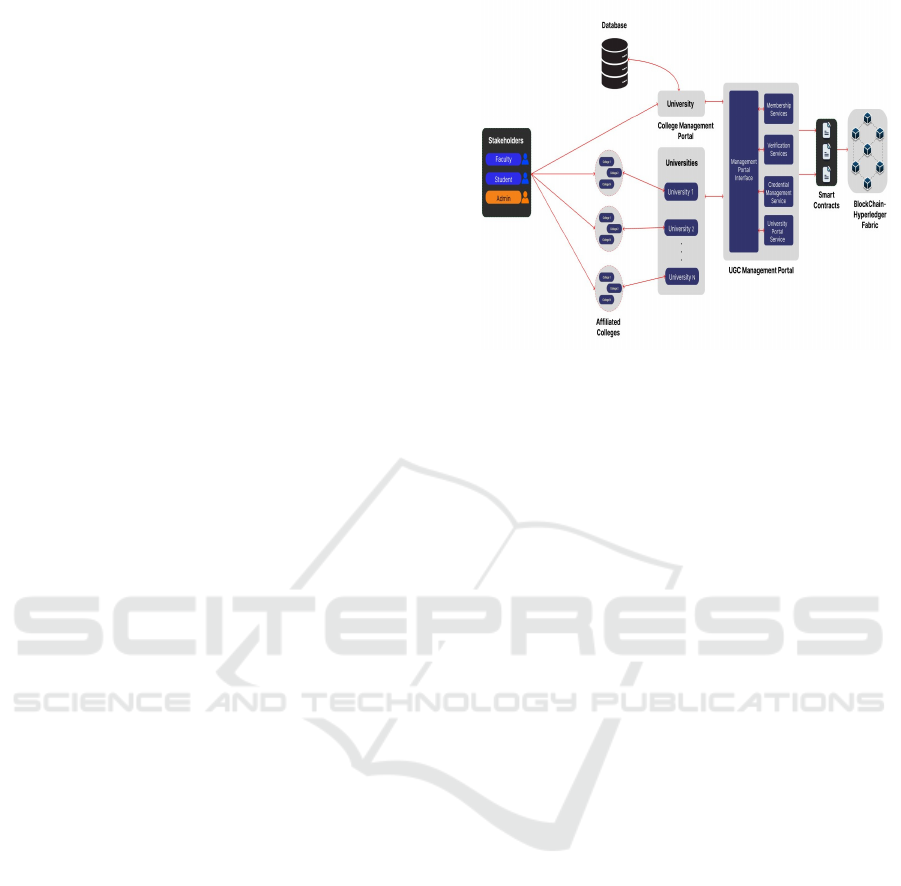
4.1 System Design
The system design begins with an evaluation of the
underlying academic processes and interactions
within the organization, stressing safe data
management and role-based access control.
Comprehensive research stipulates the detailed needs
of the UGC, colleges, universities, and third-party
verifiers. The system automates university
accreditation, administration of academic records, and
issuance of credentials alongside interoperability with
existing institutional systems. A permissioned system
is employed to increase security and transparency.
Numerous users can browse and conduct operations
smoothly due to the user-friendly interface.
Use case modelling dictates primary functions like
university registration, staff and student record
maintenance, credential distribution, and verification.
It is applied in developing how various components of
the system interact and function.
A model of permission is used in allowing only
authorized institutions to be able to view and edit
scholarly data on the blockchain. Frontend is user
experience-oriented, designed to enable
administrators and institutions to leverage required
features like login interfaces, registration monitoring,
and verification modules. Figure 1 shows the
Proposed Framework.
Figure 1: Proposed framework.
4.2 Blockchain Architecture
Educhain’s blockchain is built upon Hyperledger
Fabric in order to authenticate that only sanctioned
members may be granted access to the network. The
existing plan is to deploy a four-system production
network in which various institutions, orders, and
standby nodes are able to communicate with each
other. The current implementation does use the
Hyperledger Fabric Test Network for developing and
testing the fundamental features before it can scale to
full deployment.
A single-channel approach is used within the test
network to manage issuing, verifying, and accrediting
credentials. Chain code automates processes such as
university registration, issuance of credentials, and
reissue. These ensure that things occur as laid down
by predefined business rules to reduce the risk of
errors and fraud. Hyperledger Fabric Certificate
Authority manages the identity and provides
cryptographic certificates used to authenticate
institutions to ensure access or modification only by
accredited institutions of higher education.
4.3 Module Implementation
The system consists of different modules to ensure
smooth development and scalability. The University
and College Registration Module retains institutional
information, accreditation status, and UGC
administrator approvals. The Academic Record
Management Module allows universities and colleges
to store faculty and student information securely, and
institutions with current digital systems integrate via
APIs. The Credential Issuance Module generates
unique identifiers for students and faculty, enabling
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
184

secure digital credentialing. The Verification Module
allows third-party verifiers to verify credentials in
real-time based on student USN or faculty ID.
4.4 Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Educhain uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
to make it possible for approved people only to view
or update academic information. The system
differentiates user permissions according to roles,
such as:
• University/College Administrators – Control
student enrollments, faculty information, and
accreditation.
• Faculty Members – Enter grades, check
attendance, and issue credentials.
• Students – View academic records and order
official transcripts.
• UGC Officials – Track accreditation compliance
and authorize institution participation.
By implementing RBAC, Educhain greatly
minimizes the possibility of unauthorized changes,
making sure that academic records are accurate and
secure.
4.5 Integration
System testing assesses the performance,
functionality, and security of the system. End-to-end
testing confirms university registration, credential
issuance, and verification processes. Transaction
latency, network speed, and scalability are measured
as key performance indicators to confirm that the
system is compliant with academic record-keeping
standards.
4.6 Tools and Technologies
Educhain is created based on the Hyperledger Fabric
Test Network as the blockchain platform. Node.js and
Express.js are used for the backend, and React.js is
used for designing the frontend for a responsive and
dynamic user interface. Docker is used for
containerization so that the system can be easily
deployed and maintained.
5 IMPLEMENTATIONS
Educhain uses Hyperledger Fabric to implement a
private blockchain network with smart contracts
(chaincode) to handle academic information. The
system architecture includes:
• Peer Nodes – Universities and colleges that join
the network.
• Orderer Nodes – Handle blockchain consensus
and transaction verification.
• Membership Service Provider (MSP) – Manages
identity management and authentication.
• Chaincode – Implements smart contract logic to
process secure data.
Institutions communicate with the blockchain via
REST APIs, allowing smooth integration with current
university portals. Data encryption and digital
signatures add another layer of security and protection
against tampering.
Educhain’s strategy for execution includes setting
up a secure blockchain network, developing smart
contracts, creating an intuitive user interface,
implementing external system APIs, and offering
strong security features.
5.1 Blockchain Network Setup
The implementation is currently based on the
Hyperledger Fabric Test Network, which is a pre-
configured test network for testing smart contracts
and blockchain.
The production environment, originally designed
to be a four-system network, will be put in place in
subsequent phases. The test network environment
configuration involves a permissioned blockchain
architecture, orderer and peer nodes for transaction
validation, Certificate Authority (CA) services to
handle identities, and chaincode to control credential
issuing and verification. Figure 2 shows the Setting up
Hyperledger Fabric Test Network.
Figure 2: Setting up Hyperledger fabric test network.
5.2 Chaincode Development
Chaincode, or smart contracts, is written to manage
principal operations. The University Registration
Educhain: Hyperledger-Powered Decentralized University Services Management Framework
185
Chaincode is used to automate registration requests,
allowing UGC administrators to approve institutions
and track their status. The Credential Management
Chaincode offers secure issuance, storage, and
verification of academic credentials with each
credential connected to a unique identifier. The
Accreditation Chaincode tracks accreditation updates,
only allowing accredited institutions to proceed on the
network.
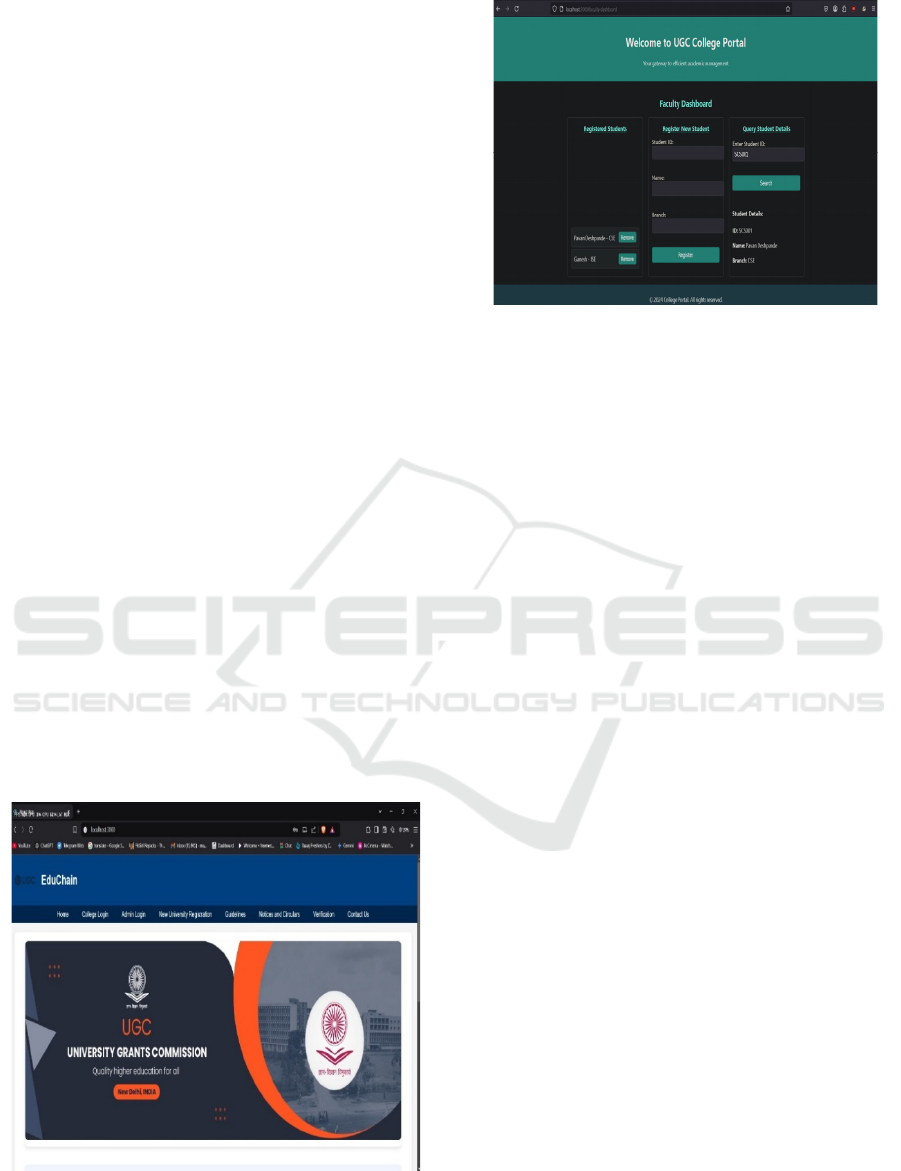
5.3 Frontend Development
The system has user-friendly web portals for different
stakeholders. The UGC Admin Portal gives the
administrators the facility to approve institutions,
handle credentials, and track accreditation status. The
University and College Portal gives the institutions
the facility to manage student information, publish
academic credentials, and validate their enrollment
status. The Third-Party Verification Portal provides
employers or other validators with the facility to
validate credentials in real time without manual
verification.
5.4 API Integration
Educhain integrates with current university
management systems via RESTful APIs. These
enable institutions to bulk-upload faculty and student
records and are
backward compatible with the existing
workflows of the institutions. The APIs support real-
time verification of credentials with a reduced
administrative workload.
Figure 3 shows the UGC
Management Portal.
Figure 4 shows the Credential
Updation Through API.
Figure 3: UGC management portal.
Figure 4: Credential Updation Through Api.
5.5 Testing
All blockchain elements are executed within Docker
containers to have consistency across many
environments. Then the system proceeds with
functionality tests to verify all workflows execute as
expected, performance tests to measure the
transaction execution time, and security tests to
validate data consistency and prevent unapproved
access.
6 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Educhain improves security, transparency, and
efficiency in dealing with academic records. Role-
based access control allows only accredited
institutions to edit information, blocking fake
credentials. Smart contracts automate university
admission, issuing credentials, and credential
verification and minimize human error.
The system enhances administrative processes by
instantiating credential verification and making it
secure. With its blockchain-based architecture,
Educhain enhances trust and accountability between
educational institutions and third-party verifiers.
7 FUTURE WORK
Future work focuses on transitioning from the
Hyperledger Fabric Test Network to a fully deployed
production network with a multi-system architecture,
incorporating distributed peer nodes for improved
scalability and reliability. Enhancements will include
refining smart contracts for better performance
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
186

Figure 5: Content within a block.
and security, expanding API functionalities for
seamless integration with institutional systems, and
introducing additional security measures.
Hyperledger Explorer will be integrated to provide a
user-friendly interface for monitoring transactions and
network activity, improving system transparency and
accessibility. Performance testing will be conducted to
evaluate the system’s efficiency in handling academic
records at scale, ensuring Educhain remains a secure
and efficient solution for decentralized academic
record management. Figure 5 shows the Content
within a Block.
REFERENCES
A. A. Khan, A. A. Laghari, A. A. Shaikh, S. Bourouis, A.
M. Mamlouk, and H. Alshazly,” Educational
blockchain: A secure degree attestation and verification
traceability architecture for higher education
commission,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 112345–
112359, 2021.
A. I. Sanka, A. S. Yahaya, A. R. Ladodo, B. Y. Bichi, S.
Lawal, and F. L. Gambo,” BEdShare: A scalable and
privacy preserving blockchain scheme for education
credentials sharing and verification in Nigeria,” Niger.
J. Comput., Eng. Technol. (NIJOCET), 2022.
A. Rastogi, and D. K. Sinha,” An exploration on
verification of educational assets through blockchain
technology,” Int. Conf. Emerging Research Electronics
(ICERECT), vol. 9, pp. 34–47, 2022.
A. Rustemi, F. Dalipi, v. Atanasovski, and A. Risteski,” A
systematic literature review on blockchain-based
systems for academic certificate verification,” in Proc.
Int. Conf. Blockchain Technol., 2023, pp. 56–68.
Amitkumar, M. I. Sanni, and D. Apriliasari,” Blockchain
technology application: Authentication system in
digital education,” Aptisi Trans. Technopreneurship
(ATT), 2021.
B. Sowmiya and E. Poovammal,” A heuristic k-anonymity-
based privacy preserving for student management
Hyperledger Fabric blockchain,” Wireless Pers.
Commun., vol. 85, pp. 145–165, 2021.
D. Ceke, and N. Buzadija,” Intro basics of modeling user
rights management for the university diploma issuing
process with the support of the Hyperledger Fabric,”
Int. Symposium (INFOTEH-JAHORINA), 2023.
F. R. Vidalm, F. Gouveia, and C.Soares, ”Analysis of
blockchain technology for higher education,” in Proc.
Int. Conf. Cyber Enabled Distributed Computing and
Knowledge Discovery(CyberC), 2021.
H. Gaikwad, N. D’Souza, R. Gupta, and A. K. Tripathy,” A
blockchainbased verification system for academic
certificates,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Syst., Comput., Autom.
Netw. (ICSCAN), 2021, pp. 123–129.
H. Bhosale, R. Kanki, and G. Jaiswal,” Revolutionizing
verification and management of educational certificates
with self-sovereign student identities using
blockchain,” Int. Research Journal of Eng. and
Technology (IRJET), 2023.
M. Nguyen, T.-C. Dao, and B.-L. Do,” Towards a
blockchain-based certificate authentication system in
Vietnam,” PeerJ Comput. Sci., vol. 6, p. e266, Mar.
2020.
M. Alam, S. Hossain, S. Reno, and A. Shekh,” Utilizing
Hyperledger Fabric-based private blockchain and IPFS
to secure educational certificate management,” in Proc.
IEEE Women Eng. Conf. Electr. Comput. Eng.
(WIECON-ECE), 2022, pp. 520–528.
M. Shrivas, S. Kachhwaha, S. V. Singh, and A. Bhansali,”
Quantumresistant university credentials verification
system on blockchain,” in Proc. IEEE Nigercon, 2022,
pp. 342–350.
M. P. M. Sy, R. I. Marasigan, and E. D. Festijo,” Designing,
deploying, and testing a chaincode for educational
credentials verification in a Hyperledger-operated
blockchain network,” International Conference on
Smart Generation Computing, Communication and
Networking (SMART GENCON), 2023.
M. P. M. Sy, R. I. Marasigan, and E. D. Festijo,”
EduCredPH: Towards a permissioned blockchain
network for educational credentials verification
system,” in Proc. 12th Int. Conf. Inf. Educ. Technol.,
2024.
O. S. Saleh, O. Ghazali, and M. E. Rana,” Blockchain-
based framework for educational certificates
verification,” Journal of Critical Reviews, 2020.
P. Fernandez and R. Arenas,” Credence Ledger: A
permissioned blockchain for verifiable academic
credentials,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Eng. Technol.
Innovation (ICE/ITMC), 2018.
S. Mthethwa, T. Singano, L. Ndlovu, R. Khutlang, D.
Shadung, and B. Ngebeni,” Decentralised digital
identity and verifiable credential tracking and
management system,” in Proc. IEEE Global Conf.
Blockchain Appl., 2022, pp. 89–97.
S. A. Jui, M. Ahmed, S. Dilshad, and S. Reno,” Securing
certificate management system using Hyperledger-
Educhain: Hyperledger-Powered Decentralized University Services Management Framework
187

based private blockchain,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Innov.
Sci., Eng. Technol. (ICISET), 2022, pp. 46–52.
S. Khaleelullah, S. Vangapalli, and M. Gaddam,”
Verification of academic records using Hyperledger
Fabric and IPFS,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Pervasive Comput.
Social Netw. (ICPCSN), 2023, pp. 210–220.
Van Duy Tran, Shingo Ata, Thi Hong Tran, Duc Khai Lam,
and Hoai Luan Pham,” Blockchain-powered education:
A sustainable approach for secured and connected
university systems,” Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 15545,
pp. 1–17, 2023.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
188
