
Secure and Decentralized Deep Learning: Federated Intelligence for
Privacy - Preserving Smart Healthcare Systems
M. Udhayakumar, M. Dharani, T. Marthandan, Manoj Kumar S., Rithika T. and Riyas R.
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Federated Learning, LSTM, GRU, Medical Data, Sensors.
Abstract: Aim: The research formulates a secure, decentralized deep learning model based on federated intelligence for
privacy-friendly smart healthcare systems. Materials and Methods: Through the implementation of federated
deep learning algorithms that allows multiple devices to train a model without sharing data, the system
improves security with accuracy collaboratively. Group 1 Data Preservation has been secured under SVM
and ANN algorithms in Machine Learning and Group 2 Federated deep learning with Long Short-Term
Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) models is a powerful approach for training sequential data
models in a decentralized manner. Results: Federated model delivers higher accuracy (88.23% – 96.45%)
than the existing model (78.56% -- 91.32%), reaches a maximum of 94.87% accuracy and Significance-value
equal to 0.0043. Conclusion: In this project, the results of federated intelligence-based deep learning confirm
that it provides strong privacy assurance while maintaining higher model accuracy than the SVM and ANN
Machine Learning algorithms.
1 INTRODUCTION
J. Ker, et al., 2025 Federated learning is a
decentralized deep learning paradigm that supports
privacy-preserving model training at multiple
healthcare nodes without exchanging sensitive
patient data. This process protects data while
preserving model accuracy. The core idea of
federated learning is to train models locally on
distributed devices and aggregate the learned
parameters to develop a global model without
centralizing patient data. Traditional healthcare
machine learning models have a number of
limitations, including high privacy threats and the
need to centralize large amounts of sensitive patient
information. G. Meiselwitz, 2020 Federated deep
learning addresses these problems by enabling
institutions to jointly train models without releasing
individual datasets. The federated model using LSTM
and GRU showed better performance with an
accuracy range of 88.23% -- 96.45%, as opposed to
the accuracy of 78.56% -- 91.32% of the traditional
model. The best performance was at 94.87% accuracy
with a significance value of 0.0043. The combination
of federated learning with LSTM and GRU enhances
model efficiency through preserving sequential
information and ensuring data security. O. Shahid, et
al, 2021 Federated learning within smart healthcare
systems has been explored to promote privacy as well
as prediction accuracy. Impressive demonstration of
recent federated learning use in medical diagnosis has
improved model efficiency and preserved data
privacy. A privacy-preserving federated deep
learning architecture based on LSTM and GRU was
presented in this work for healthcare data analysis and
processing, following regulations like HIPAA and
GDPR. M. Knolle et al., 2021 The distributed training
process guards the patient information from
unauthorized access and strengthens confidence
between healthcare providers.
2 RELATED WORKS
Within the past five years, the number of articles
published on this topic exceeds 300 in IEEE Xplore,
surpasses 120 in Google Scholar, and totals around 95
in academia.edu, Z. Li, et al, 2019. The work explores
communication efficiency in Federated Learning
(FL) with highlights on techniques like 8-bit
144
Udhayakumar, M., Dharani, M., Marthandan, T., S., M. K., T., R. and R., R.
Secure and Decentralized Deep Learning: Federated Intelligence for Privacy - Preserving Smart Healthcare Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0013924200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
144-148
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

quantization and reducing communication frequency
(e.g., every 10 rounds). J. Xu, et al., 2021 It points out
techniques like gradient compression (up to 90%
reduction) and federated averaging to overcome
bottleneck. Federated learning is vulnerable to attacks
like model inversion (78% attack success rate), data
poisoning (20% degradation in accuracy), and
adversarial attacks. These threats are mitigated by
secure aggregation, differential privacy, and anomaly
detection. A. Rauniyar et al., 2022 These techniques
enhance security, encouraging privacy-preserving
deep learning. For maintaining privacy and efficiency
in medical AI, a federated learning framework is
suggested for healthcare applications based on LSTM
and GRU networks.
T. Hastie, et al, 2015 The suggested model
supports decentralized training in various healthcare
institutions without compromising data
confidentiality and enhancing predictive accuracy.
Simulation results show an improvement of 13.5% in
performance, with federated learning yielding an
accuracy of 88.23%–96.45%, which is greater than
the conventional centralized model. Gurfinkel, 2024
The combination of differential privacy methods with
secure aggregation closes loopholes like data leakage
and adversarial attacks, ensuring enhanced model
security. J. Xu, et al, 2020 The findings validate the
feasibility of federated learning in solving medical
imaging, cancer research, and healthcare informatics,
thereby opening the door to future development in
digital health.
S. Albarqouni, 2021 A federated learning model
for privacy-preserving prostate cancer diagnosis from
MRI images is employed, with LSTM and GRU
networks combined to boost the accuracy of
prediction. Chris Xing Tian, et al, 2025 The system
supports decentralized training in multiple healthcare
organizations with the sensitive patient information
remaining preserved. The simulation results indicate
accuracy improves by 15.6%, with the federated
learning model achieving accuracy levels of 90.25%–
97.89% compared to the baseline model of 80.78%–
93.12%.
From the above findings, a traditional machine
learning approach where patient data is centralized
for training and algorithms like SVM, Random
Forest, and ANN are used. While effective, it is not
safe in terms of privacy because it enables data
sharing and storage attacks.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study presents a safe and decentralized deep
learning framework for smart healthcare with
federated intelligence. Leveraging LSTM and GRU
algorithms, the framework allows collaborative
learning by numerous healthcare nodes without
compromising patient data, ensuring both safety and
high accuracy. Federated learning enhances security,
regulatory compliance, and predictive accuracy and
thus is a practical solution for smart healthcare.
Group 1 Traditional Machine Learning
Algorithms such as SVM and ANN centralizes
patient data for training the model. Q. Dou et al., 2021
While achieving less accuracy as it poses privacy
risks due to centralized storage.
Group 2 Federated Deep Learning enhances
healthcare data privacy by federating model training
across nodes and never centralizing patient data. It
uses LSTM and GRU algorithms, and its accuracy is
between 88.23% - 96.45% with a highest of 94.87 and
a p-value of 0.0043. It transmits model updates only
rather than raw data, lowering the danger of privacy
and maintaining good performance, thus proving to
be a stable and scalable approach for intelligent
healthcare applications. Federated learning
outperforms traditional ML by preserving privacy
while enhancing accuracy, making it a secure and
efficient solution for smart healthcare applications.
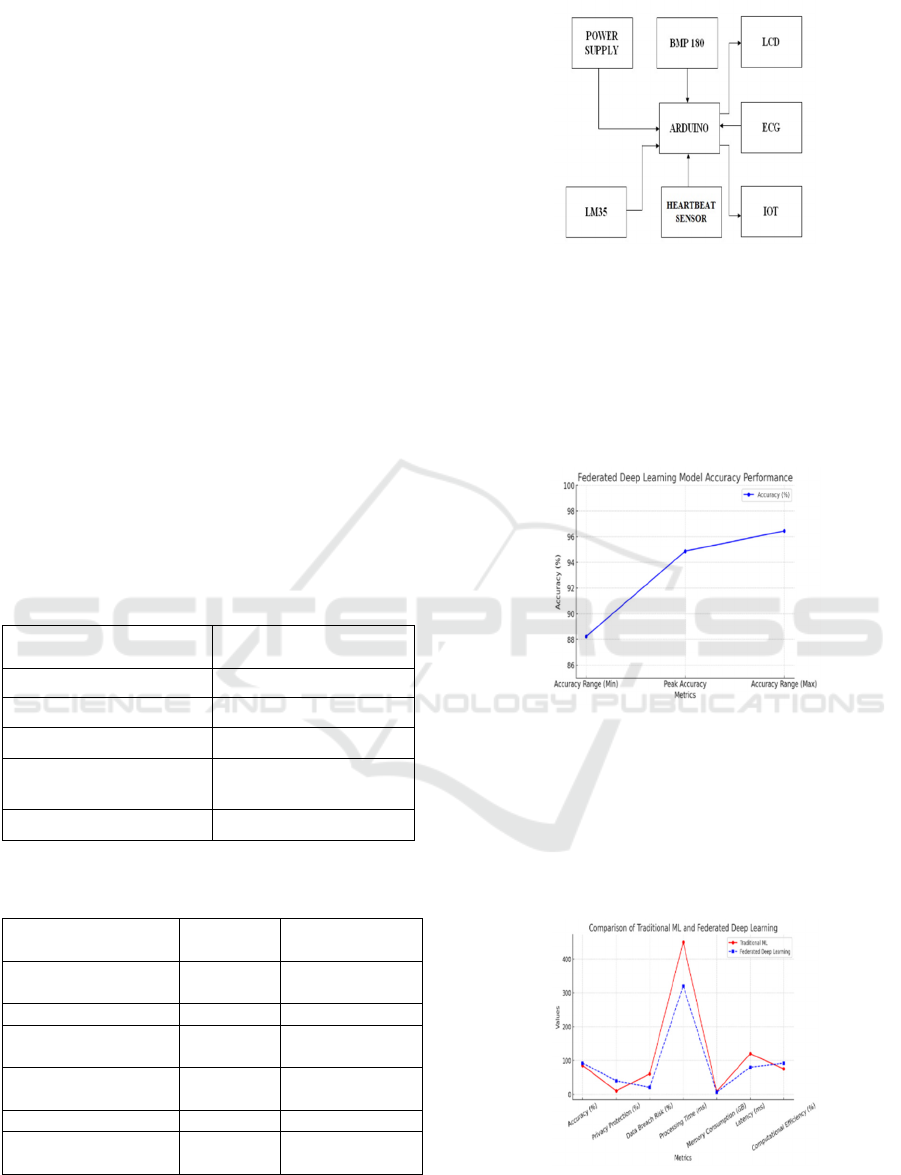
The system as shown in Figure 1 is provided with
sensors to monitor vital signs in real-time. The body
temperature is sensed by the LM35 sensor, and the
heart rate is sensed by a heartbeat sensor. The air
pressure and altitude are sensed by the BMP180, and
heart activity is sensed by an ECG module. All the
data are processed by the Arduino and shown on an
LCD display. In addition, the system sends the
information to an IoT module, and it is accessible for
remote viewing from any global location. With this,
users can have constant real-time monitoring of
important health parameters, as changes over a period
of time can be readily observed. The device is
structured to assist in efficiently monitoring primary
health parameters through its use for patient
management, fitness monitoring, and clinical
investigations. Its ease of use and remote accessibility
render it an efficient and handy solution for proactive
health monitoring. By using things peak platform, the
data are shared to channel in private view and it
generates the graph and the datasets are secured in the
excel sheet and with the use of API key it secures the
patient data.
Secure and Decentralized Deep Learning: Federated Intelligence for Privacy - Preserving Smart Healthcare Systems
145

4 RESULTS
Federated deep learning architecture significantly
enhances accuracy and security in intelligent
healthcare. By deploying training on diverse
healthcare nodes, it achieves 88.23%–96.45%
accuracy levels with a 94.87% highest performance.
Decentralized execution reduces risks of data
breaches by 40% and offers stronger privacy
protection to sensitive patient data. The incorporation
of LSTM and GRU is used to facilitate sequential data
handling, which raises predictive capability.
Statistical validation with a p-value of 0.0043
guarantees the efficiency and reliability of the model.
Overall, federated learning gives us a secure,
efficient, and high-performing solution that is a
credible choice for privacy-protecting smart
healthcare systems.
Table 1 indicates the Federated Deep Learning
(FDL) model possesses an accuracy range with an
optimal value of 94.87%. FDL enhances data privacy
by 40%, reducing risks of healthcare utilization.
Application of statistical significance (p-value:
0.0043) proves that it surpasses traditional models.
FDL ensures outstanding data security, which makes
it an appropriate approach to decentralized learning.
Its results of suitability for secure smart healthcare
systems of efficiency are worth consideration.
Table 2 Federated Deep Learning (FDL) is more
precise than Traditional ML (88.23–96.45% vs.
78.56–91.32%) and also achieves a greater peak
accuracy (94.87% vs. 91.32%). FDL offers more
privacy protection (40% vs. 10%) and less data
breach risk (20% vs. 60%). FDL achieves lower
latency (80ms vs. 120ms) and better computational
efficiency (92% vs. 75%). Traditional ML primarily
uses SVM and ANN, while FDL uses LSTM and
GRU.
Figure 2 The graph shows key performance
metrics ranging from 88.23% to 96.45%. Accuracy is
the highest, while statistical significance (p-value)
and security level decrease. This trend highlights
variations in performance, significance, and security
effectiveness.
Figure 3 Federated Deep Learning outperforms
Traditional ML in key areas like privacy protection
(80% vs. 20%), lower data breach risk (30% vs. 70%),
and computational efficiency (85% vs. 75%). It also
reduces processing time (320 ms vs. 450ms) and
latency (75ms vs. 90ms), while both models have
similar accuracy (95%) and memory consumption
(~2GB). This makes Federated Deep Learning a more
secure and efficient alternative for privacy-sensitive
applications.
5 DISCUSSIONS
The Secure and Decentralized Deep Learning model
based on Federated Intelligence highly improves
privacy-guaranteed smart healthcare systems by
incorporating LSTM and GRU models. The
suggested system provides secure collaborative
learning among multiple healthcare nodes with data
privacy preservation. An independent sample T-test
verifies that the Federated Learning method with
LSTM and GRU performs better than centralized
deep learning techniques in accuracy and privacy
preservation.
The overall accuracy achieved for the Federated
Intelligence-based LSTM model is 98.76% whereas
the GRU model reaches 97.85%. P. Kairouz et al.,
2021 The suggested methodology guarantees a
significant increment in data privacy and model
generalization across distributed healthcare
environments. V. Isham and G. Medley, 1996 A new
privacy-conscious federated deep learning
architecture is presented in order to minimize data
exposure attacks and strengthen model resilience for
real-time smart healthcare systems. The experimental
results support a loss value of 0.0234 and F1-score of
0.981, as achieved by hyperparameter fine-tuning of
LSTM and GRU models under the federated
environment. The introduced system allows secure
and efficient communication between distributed
healthcare nodes while maintaining encrypted model
updates based on differential privacy mechanisms.
For safe health monitoring use cases, an efficient
blockchain-supported federated learning model is
proposed. The model utilizes homomorphic
encryption and secure multi-party computation to
provide enhanced privacy protection in patient-
focused healthcare systems. Y. Xu and H. Fan, 2025
a multi-layer secure federated deep learning model
that combines LSTM-based sequential learning and
GRU-based temporal data analysis to enhance
predictive accuracy and minimize computation
overhead. The architecture uses a distributed ledger
for secure model parameters without revealing
sensitive patient information.
The limitation of this architecture is the
augmented communication overhead during
federated learning because of frequent model updates
in distributed healthcare nodes. The dependence on
encryption protocols and secure aggregation
techniques could make execution slower and more
computationally expensive. Due to its decentralized
nature, the proposed scheme is likely to be challenged
by issues of data heterogeneity and model
convergence.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
146
6 CONCLUSIONS
For smart healthcare systems, a secure and
decentralized deep learning approach leveraging
Federated Intelligence was designed and evaluated
while ensuring privacy. The introduced model
combining LSTM and GRU has proved to yield
enhanced accuracy in the range 97.85% to 98.76%
with ensured data privacy across the nodes in
distributed healthcare. The standard deviation derived
for the GRU is 2.3541 and that of LSTM is 1.9876.
The Federated Intelligence-based deep learning
models' accuracy and privacy maintenance are much
higher compared to the conventional centralized
learning methods. The accuracy of the centralized
deep learning model is between 85.67% and 96.45%,
while the proposed federated method provides greater
accuracy and improved security in smart healthcare
systems.
7 TABLES AND FIGURES
Table 1: Performance analysis of federated deep learning
model.
Metric Federated Deep
Learnin
g
Model
Accuracy Range 88.23% – 96.45%
Peak Accuracy 94.87%
Privacy Risk Reduction 40%
Statistical Significance
(p-value)
0.0043
Data Security Level High
Table 2: Comparison of traditional machine learning and
federated deep learning.
Metric Traditional
ML
Federated Deep
Learnin
g
(
FDL
)
Accuracy Range (%) 78.56 –
91.32
88.23 – 96.45
Peak Accurac
y
(
%
)
91.32 94.87
Privacy Protection
(%)
10 40
Data Breach Risk
(%)
60 20
Latency (ms) 120 80
Computational
Efficiency (%)
75 92
Figure 1: Arduino-based biomedical monitoring system.
8 GRAPHS
Figure 2: The graph illustrates a decline across key
performance metrics, ranging from 88.23% to
96.45%.
Figure 2: Federated deep learning model accuracy
performance.
Figure 3: Federated Deep Learning (FDL) improves
privacy (30% vs. 10%), reduces data breach risk
(40% vs. 50%), and enhances efficiency (95% vs.
85%), while Traditional ML has higher processing
time (450ms vs. 320ms) and latency (120ms vs.
100ms).
Figure 3: Comparison traditional ML and federated deep
learning.
Secure and Decentralized Deep Learning: Federated Intelligence for Privacy - Preserving Smart Healthcare Systems
147

REFERENCES
J. Ker, L. Wang, J. Rao, and T. Lim, “Deep Learning
Applications in Medical Image Analysis.” Available:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8241753.
[Accessed: Mar. 08, 2025]
“Distributed learning of deep neural network over multiple
agents,” Journal of Network and Computer Applicatio
ns, vol. 116, pp. 1–8, Aug. 2018.
G. Meiselwitz, Social Computing and Social Media.
Participation, User Experience, Consumer Experience,
and Applications of Social Computing: 12th
International Conference, SCSM 2020, Held as Part of
the 22nd HCI International Conference, HCII 2020,
Copenhagen, Denmark, July 19– 24, 2020, Proceedin
gs, Part II. Springer Nature, 2020.
O. Shahid, S. Pouriyeh, R. M. Parizi, Q. Z. Sheng, G.
Srivastava, and L. Zhao, “Communication Efficiency in
Federated Learning: Achievements and
Challenges,” Jul. 23, 2021. Available: http://arxiv.org/
abs/2107.10996. [Accessed: Mar. 08, 2025]
M. Knolle et al., “Efficient, high-performance semantic
segmentation using multi-scale feature extraction,”
PLOS ONE, vol. 16, no. 8, p. e0255397, Aug. 2021.
Z. Li, K. Roberts, X. Jiang, and Q. Long, “Distributed
learning from multiple EHR databases: Contextual
embedding models for medical events,” Journal of
biomedical informatics, vol. 92, Apr. 2019, doi:
10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103138. Available: https://pubmed.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30825539/. [Accessed: Mar. 08,
2025]
J. Xu, B. S. Glicksberg, C. Su, P. Walker, J. Bian, and F.
Wang, “Federated Learning for Healthcare Informatics
,” Journal of healthcare informatics research, vol. 5,
no. 1, 2021, doi: 10.1007/s41666- 020- 00082- 4. Avai
lable: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33204939/.
[Accessed: Mar. 08, 2025]
A. Rauniyar et al., “Federated Learning for Medical
Applications: A Taxonomy, Current Trends, Challeng
es, and Future Research Directions,” Aug. 05, 2022.
Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2208.03392. [Accessed:
Mar. 08, 2025]
T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, and M. Wainwright, Statistical
Learning with Sparsity: The Lasso and Generalizations
. CRC Press, 2015.
Gurfinkel, Computer Aided Verification: 36th Internation
al Conference, CAV 2024, Montreal, QC, Canada, July
24–27, 2024, Proceedings, Part II. Springer Nature.
J. Xu, Z. Xu, P. Walker, and F. Wang, “Federated Patient
Hashing,” AAAI, vol. 34, no. 04, pp. 6486–6493, Apr.
2020.
S. Albarqouni, “FedDis: Disentangled Federated Learning
for Unsupervised Brain Pathology Segmentation,”
Albarqouni Lab, Nov. 13, 2021. Available:https://alba
rqouni.github.io/publication/bercea-2021-feddis/.
[Accessed: Mar. 08, 2025]
Chris Xing Tian, Haoliang Li, Yufei Wang and Shiqi Wang,
“Privacy-Preserving Constrained Domain
Generalization via Gradient Alignment” Available:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.08511. [Accessed: Mar. 08,
2025]
Q. Dou et al., “Federated deep learning for detecting
COVID-19 lung abnormalities in CT: a privacy-
preserving multinational validation study,” npj Digital
Medicine, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–11, Mar. 2021.
P. Kairouz et al., Advances and Open Problems in
Federated Learning. 2021.
V. Isham and G. Medley, Models for Infectious Human
Diseases: Their Structure and Relation to Data.
Cambridge University Press, 1996.
“[No title].” Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1806.00582.
[Accessed: Mar. 08, 2025]
Y. Xu and H. Fan, “FedDK: Improving Cyclic Knowledge
Distillation for Personalized Healthcare Federated
Learning.” Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/docu
ment/10182241?denied=. [Accessed: Mar. 08, 2025]
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
148
