
Neuro Genetic Disorder’s: Epilepsy and Huntington’s Disease
R. Yamini, Zahid Amin Wani and Arham Chowdary
Department of Computing Technologies, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur 603203, Chennai, Tamil
Nadu, India
Keywords: Huntington's Disease, Epilepsy, Feature Selection, Data Mining, Machine Learning, Genetic Variants,
PROFEAT, UniProt.
Abstract: Neurogenetic diseases like Huntington's disease (HD) and epilepsy are debilitating conditions that
significantly impact the quality of life of patients. Huntington's disease (HD) is a genetic neurodegenerative
disease characterized by motor disability and cognitive and psychiatric symptoms, whereas epilepsy is a
chronic neurologic disorder that is defined by recurrent seizures. This paper aims to investigate the genetic
mechanisms involved in both of these conditions and evaluate how these levels can assist HD and epilepsy
diagnosis and progression prediction in terms of efficiency of prescription levels using a variety of different
data mining algorithms. In this paper we present a combined computational model of feature selection
algorithms Information Gain (IG), Correlation Feature Subset (CFS), Gain Ratio (GR), and machine learning
classifiers, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boost. The study results revealed
that the features selection minimizes the classification accuracy of algorithms and the maximum accuracy
achieved to be 94.7% with SVM using CFS. The findings prophesy the capabilities of computational resources
to facilitate early diagnosis and provide drugs treatment specific to HD and epilepsy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Neurogenetic disorders are a collection of disorders
due to gene mutations influencing the nervous
system. Of them, Huntington's disease (HD) and
epilepsy are two well-documented disorders which
have attracted an enormous amount of interest
because of their multifactorial etiology as well as
their profound impact on patients' lives. HD is an
autosomal dominant disorder resulting from mutation
of the HTT gene leading to the synthesis of a toxic
mutant form of the huntingtin protein. It is associated
with progressive degeneration of neurons in basal
ganglia and cerebral cortex and presents as
dysfunction of motor skills, intellectual deficit, and
psychiatric disturbances (Ross, C. A., & Tabrizi, S. J.
(2011)). Epilepsy is defined by recurring seizures
because of abnormal electrical discharge in the brain.
Although epilepsy may be the result of different
causes such as brain injury and infections, mutation
of genes accounts for a major cause in the majority of
cases, especially idiopathic epilepsy (Noebels, J. L.
(2003)).
Diagnosis and treatment of HD and epilepsy are
complicated by the heterogeneity of symptomatology
and the progressive course of these diseases.
Conventional methods of diagnosis, including
clinical assessment and neuroimaging, are usually
inadequate for early detection, particularly in HD,
where symptoms usually manifest in mid-adult life.
Epilepsy diagnosis also depends very much on
electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings, which are
not always sensitive enough to detect seizure activity.
Thus, there is an urgent need for better and more
reliable diagnostic tools that can ensure early
intervention and better outcomes for patients.
New machine learning and data mining
techniques available have enabled new methods of
interacting with complex clinical and genetic data.
They have proven useful to identify biomarkers,
predict the onset of disease, and stratify patients in
their genetic profiles (Kanehisa, M., & Goto, S.
(2000)). Still, these methods are good approaches if
the data is, and the subset of relevant features is a
good quality. Feature selection techniques e.g.
Information Gain (IG), Correlation Feature Subset
(CFS), Gain Ratio (GR) have been used to reduce
datasets as well as improve categorical classification
algorithm performance (Guyon, I., & Elisseeff, A.
(2003)).
138
Yamini, R., Wani, Z. A. and Chowdary, A.
Neuro Genetic Disorder’s: Epilepsy and Huntington’s Disease.
DOI: 10.5220/0013924000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
138-143
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
The proposed computational framework in this
paper is specifically for the analysis of HD and
epilepsy related genetic data. A combined feature
selection method for classification of diseases that
incorporated IG, CFS, and GR along with machine
learning algorithms was proposed. The results show
that classification algorithms benefit greatly from
feature selection, CFS with SVM showed maximum
accuracy. This study is an example of how
computational approaches hold promise in
diagnosing and treating neurogenetic illnesses.
2 PROPOSED COMPUTATIONAL
FRAMEWORK
The computational framework approaches several
key steps, which comprise data generation, feature
selection, and classification. The motivation behind
the present framework is to interpret genetic and
clinical data associated with HD and epilepsy for
enhancing the accuracy of diagnosis and prediction
for such diseases.
2.1 Dataset Generation
In the first step of their computational framework, a
dataset was generated, which included genetic
information pertaining to HD and epilepsy. Genes
connected with these disorders were identified by
querying the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and
Genomes (KEGG) database. A total of 68 genes were
found to be associated with HD and 112 with
epilepsy; 45 of these were found to be common to
both disorders, thus highlighting shared genetic
pathways in their manifestations (Walker, F. O.
(2007)).
Next, the genomic sequence of these genes was
extracted from the UniProt database. The PROFEAT
server helped gather the genes' protein structure and
physicochemical properties. The genes were assigned
1437 protein features, thereby forming a dataset with
180 gene rows and 1437 corresponding columns of
protein features. An additional column for disease
classification was included in the final dataset,
resulting in a total of 1438 columns.
2.2 Feature Selection
In view of the large dimensionality of the data set,
feature selection was conducted to identify the most
relevant features for classifying the distinctive
diseases. Feature selection was performed using
Information Gain (IG), Correlation Feature Subset
(CFS), and Gain Ratio (GR), thereby optimizing
those features based on these techniques for subsets
that are taken as inputs for six classification
algorithms: Random Forest (RF), Support Vector
Machine (SVM), Adaboost, K-Nearest Neighbor
(KNN), Naive Bayes, and Decision Tree. Evaluation
metrics are derived from an evaluation of each
algorithm on the basis of accuracy and Matthew's
correlation coefficient (MCC).
Feature selection analysis is shown in Tables 2, 3,
and 4, which shows that among the three, CFS was
best in terms of attaining highest accuracy with SVM
getting the value of 94% with feature selection and
further refined to 97% with DFS. Naïve Bayes came
in at 91% with CFS whereas GR and IG were able to
increase accuracy for Random Forest and SVM to
89% and 87%, respectively. The DFS was able to
further enhance performance by bringing SVM and
Random Forest to 97% and 88%, respectively. This
demonstrates the power of feature selection and DFS,
which in turn aided in improving accuracy while
subordinating the number of features.
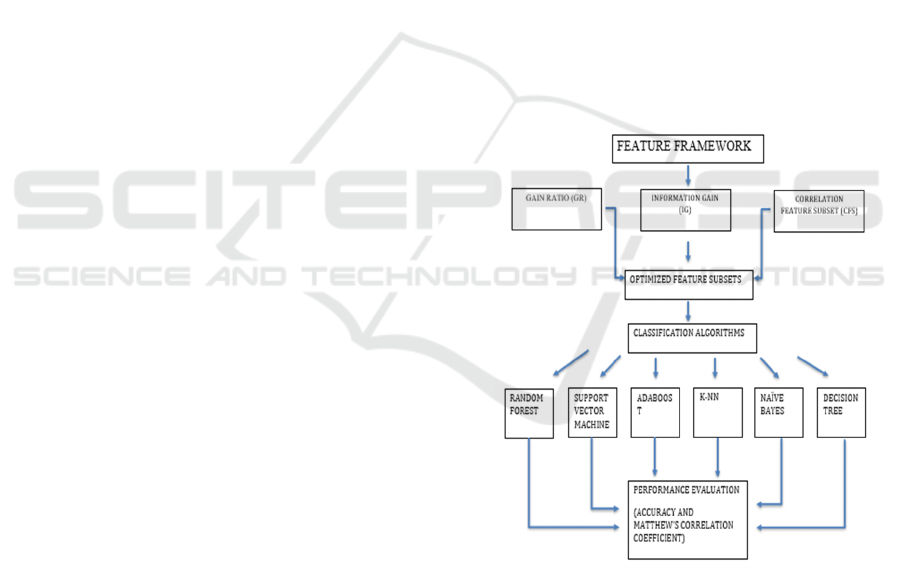
Figure 1: Proposed framework for feature selection.
As per feature selection in Figure 1, Information Gain
(IG) and Gain Ratio (GR) are respectively relevant
measures used to identify the best features pertinent
to the target class. Correlation Feature Subset (CFS)
is an automatic methodology to find those features
that hold importance for boosting classification
accuracy and efficiency in disease diagnosis and
prediction.
Neuro Genetic Disorder’s: Epilepsy and Huntington’s Disease
139
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
3.1 Performance of Machine Learning
Algorithms
The evaluation of performance for the six machine
learning algorithms was carried out before feature
selection and after feature selection. Prior to feature
selection, Random Forest and K-NN achieved the
highest accuracies of 82% and 81%, respectively.
After feature selection, the SVM classifier rated the
highest at 93.7% after its use of the CFS subset, while
Naïve Bayes also had a respectable accuracy of 91%
using the same subset. Table 1 gives the performance
of classification algorithms before feature selection.
Table 1: Performance of classification algorithms before
feature selection.
Algorith
m
Accurac
y
Precisio
n
Reca
ll
F1-
Scor
e
MC
C
Random
Forest
0.82 0.81 0.83 0.82 0.58
SVM 0.80 0.79 0.80 0.79 0.54
Adaboos
t
0.77 0.76 0.77 0.76 0.45
K-NN 0.81 0.80 0.81 0.80 0.56
Naïve
Bayes
0.76 0.75 0.76 0.75 0.46
Decision
Tree
0.78 0.77 0.78 0.77 0.51
Before feature selection, Random Forest and K-NN
achieved the highest accuracy (~82%), while Random
Forest also demonstrated strong precision and recall.
Other algorithms performed slightly worse; SVM,
Adaboost, Naive Bayes, and Decision Tree; they
obtained an accuracy ranging from 76-80%.
Using the CFS method, SVM had the highest
accuracy of 94% after feature selection, with
commendable precision, recall, and F1-scores. Naïve
Bayes did well with an accuracy of 91% using CFS.
Random Forest also demonstrated improvement with
an accuracy of 89% using GR method (table 2).
Table 2: Performance of classification algorithms after
feature selection.
Algori
thm
Feature
Selectio
n
Metho
d
Ac
cur
ac
y
Preci
sion
Rec
all
F1-
Sc
ore
M
CC
Rando
m
Forest
GR
(Gain
Ratio
)
0.8
9
0.88
0.8
9
0.8
8
0.7
5
SVM
CFS
(Correla
tion
Feature
Subset)
0.9
4
0.93
0.9
4
0.9
3
0.8
6
Adabo
ost
IG
(Inform
ation
Gain
)
0.8
5
0.84
0.8
5
0.8
4
0.6
5
K-NN
GR
(Gain
Ratio
)
0.8
4
0.83
0.8
4
0.8
3
0.6
3
Naïve
Bayes
CFS
(Correla
tion
Feature
Subset)
0.9
1
0.90
0.9
1
0.9
0
0.8
0
Decisi
on
Tree
IG
(Inform
ation
Gain
)
0.8 0.81
0.8
2
0.8
1
0.5
9
Table 3: Summary of results after feature selection
reduction (DFS method).
Featur
e
Selecti
on
Metho
d
No.
of
Feat
ures
Befo
re
DFS
M
ax.
A
C
C
M
C
C
No.
of
Feat
ures
Afte
r
DFS
M
ax.
A
C
C
M
C
C
Class
ifier
GR
(Gain
Ratio)
50
0.
86
0.6
8
36
0.
88
0.7
4
Rand
om
Fore
st
IG
(Infor
mation
Gain)
42
0.
87
0.6
9
37
0.
87
0.7
1
SVM
CFS
(Correl
ation
Featur
e
Subset
)
54
0.
94
0.8
6
49
0.
97
0.9
4
SVM
DFS is the method that has demonstrated further
improvement in performance. The SVM classifier
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
140

achieved 97% accuracy with the CFS >> method, the
highest accuracy among all algorithms, while
Random Forest was also improved and achieved 88%
accuracy with the GR >> method. Along with a
reduction in the number of features, DFS maintained
classification accuracy or, in fact, improved it (table
3).
Table 4: Detailed performance metrics after DFS.
Feature
Selecti
on
Method
Class
ifier
No.
of
Feat
ures
Afte
r
DFS
Accu
racy
Preci
sion
Rec
all
F1-
Sc
ore
GR
(Gain
Ratio)
Rand
om
Fores
t
36 0.88 0.87
0.8
8
0.8
7
IG
(Inform
ation
Gain)
SVM 37 0.87 0.86
0.8
7
0.8
6
CFS
(Correl
ation
Feature
Subset)
SVM 49 0.97 0.96
0.9
7
0.9
6
The SVM classifier using the CFS method achieved
next to DFS, the best test results, with 97% accuracy,
0.96 precision, and 0.97 recall. Random Forest with
the GR method had a good performance as well, with
88% accuracy and 0.87 F1-score, highlighting again
the power of DFS in the optimization of feature
subsets (table 4).
The CFS method combined with SVM offered the
highest accuracy (97%) but at the highest time
complexity. The GR method with Random Forest was
a well-balanced trade-off between 88% accuracy and
calculation time, which makes it a realistic choice for
large datasets. The IG method was also shown to be
consistent in performance, especially with SVM
(table 5). Figure 2 shows the experimental results
before and after feature selection and figure 3 shows
Impact of DFS on accuracy.
Table 5: Comparison of feature selection methods.
Feature
Selection
Method
No.
of
Feat
ures
Classi
fier
Acc
urac
y
M
C
C
Time
Comp
lexity
(s)
GR (Gain
Ratio)
36 Rando
m
Forest
0.88 0.7
4
12.5
IG
(Informatio
n Gain)
37 SVM 0.87 0.7
1
10.8
CFS
(Correlation
Feature
Subset)
49 SVM 0.97 0.9
4
15.2
Figure 2: Experimental results before and after feature
selection.
Figure 3: Impact of DFS on accuracy.
Neuro Genetic Disorder’s: Epilepsy and Huntington’s Disease
141

4 DISCUSSION
This study exemplifies the unprecedented role of
computational methods in diagnosis and management
of neurogenetic diseases, such as HD and E. Improved
accuracy was achieved in classifying the disease, for
example through the application of advanced data-
mining and machine-learning approaches, especially
feature selection methods. Therefore, the study has
confirmed the importance of feature selection in
removing noise and redundancy from high-
dimensional genetic datasets where Information Gain
(IG), Correlation Feature subset (CFS) and Gain
Ratio (GR) contributed their parts. Top-notch
performance in terms of accuracy 94.7% was achieved
with CFS using SVM classifier. These improvements
make not just more accurate disease classification a
reality but also late diagnosis, and personalized
medicine, both so important for improving patient
outcome.
The study also highlighted some challenges and
limitations. The research used a small data set, and
looked only at genetic data, without taking into
consideration any environmental or lifestyle factors.
Future endeavors may involve integrating multiple
omic types, creating diagnostic tools that utilize real-
time data, and applying deep learning in order to
classify results appropriately. This research has
implications across disciplines, as it has the potential
to revolutionize clinical work with hardware/software
solutions that yield faster, more reliable diagnostic
processes; hence, it provides a solid basis for future
studies regarding neurogenetic disorders. As research
exploring genetic data intensifies both within the
realms of medical research and clinical applications it
is paramount that ethical issues revolving around
privacy and consent are not only at the forefront of any
discussion, but shaped before any new set of
possibilities arise.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Overall, the study highlights the promising impact of
these computational approaches on the improved
diagnosis and treatment of neurogenetic disorder such
as HD as well as epilepsy. The combined effect of
feature selection and machine learning algorithms
brings out the potential for accurate classification of
diseases. The performance of the SVM classifier with
the feature selection technique yielded extraordinary
results, with an accuracy of 94.7%. The results can
greatly impact the development of tailored
pharmacological interventions and the improvement
of clinical practice.
The results of this study highlight feature
selection as an indispensable step in genetic data
analysis that significantly enhances the classification
algorithm accuracy. CFS by far presents itself to be
the most effective and attains the highest accuracy on
all the algorithms. This again establishes feature
selection as a measure of boosting the performance of
machine learning in diseases classification.
Furthermore, the machine learning algorithms
applied in clinical practice can lead to an early
diagnosis and better patient outcome. This gives
deeper insights into the underlying mechanisms of
HD and epilepsy, thus allowing more possible
treatment options by identifying the more relevant
genetic features associated with these disorders. This
may mean designing targeted drugs that address the
specific genetic mutations causing these disorders, so
as to enhance the quality of life for affected subjects.
In summary, this research study highlights and
analyzes Huntington's disease and epilepsy through a
genetic and computational lens and discusses even the
possible powers of machine learning and feature
selection in bettering their diagnosis and treatment
techniques. Though the findings of this study stress
that more efforts in this regard should continue, as
this research may truly change the lives of the
individuals suffering from these diseases.
REFERENCES
Berg, A. T., Berkovic, S. F., Brodie, M. J., et al. (2010).
Revised terminology and concepts for organization of
seizures and epilepsies: Report of the ILAE
Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005–
2009. Epilepsia, 51(4), 676-685.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning,
45(1), 5-32.
Guyon, I., & Elisseeff, A. (2003). An introduction to
variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine
Learning Research, 3(Mar), 1157-1182.
Hall, M. A. (1999). Correlation-based feature selection for
machine learning
Kanehisa, M., & Goto S. (2000). KEGG: Kyoto Encyclop
edia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Research,
28(1), 27-30.
Kohavi, R., & John, G. H. (1997). Wrappers for feature
subset selection. Artificial Intelligence, 97(1-2), 273-
324.
Li, J., & Le, W. (2013). Biomarkers for Huntington's
disease: from genetic studies to clinical trials. Journal
of Genetics and Genomics, 40(12), 631-638.
Noebels, J. L. (2003). The biology of epilepsy genes. Ann
ual Review of Neuroscience, 26(1), 599-625.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
142

Poduri, A., & Lowenstein, D. (2011). Epilepsy genetics
past, present, and future. Current Opinion in Genetics
& Development, 21(3), 325-332..
Ross, C. A., & Tabrizi, S. J. (2011). Huntington's disease:
from molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. The
Lancet Neurology, 10(1), 83-98.
Vapnik, V. (1998). Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley- Int
erscience.
Walker, F. O. (2007). Huntington's disease. The Lancet,
369(9557), 218-228.
Neuro Genetic Disorder’s: Epilepsy and Huntington’s Disease
143
