
Recommendation System for E‑Learning and E‑Commerce Using
Machine Learning
Shabana, Sreyalakshmi P., Tharun B., Vyshnavi M. and Sameer
Department of CSE (AI & ML), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Anantapur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Recommender Systems, E‑Learning, E‑Commerce, Machine Learning, Personalization, Hybrid Model, Cold
Start Problem, Deep Learning, User Behavior Analysis.
Abstract: Recommender systems have become an essential component of modern e-learning and e-retail platforms,
providing personalized content recommendations to enhance user engagement and satisfaction. Traditional
recommendation techniques, for example, methods like content-based filtering and collaborative filtering,
suffer from drawbacks like the new user problem, limited data density, and overspecialization. To address
these obstacles, this study proposes a combined recommender structure that integrates multiple techniques,
including content-based and collaborative filtering, along with advanced machine learning algorithms. The
proposed system leverages matrix factorization, TF-IDF vectorization, and deep learning models to refine
recommendations and adapt to dynamic user preferences. Experimental evaluation using key performance
indicators like exactness, retrieval rate, F1-measure, and average prediction error (APE) demonstrates that the
hybrid approach significantly improves recommendation accuracy compared to standalone methods. The
findings highlight the potential of hybrid recommender systems in enhancing personalized learning
experiences, optimizing product recommendations, and improving overall platform efficiency. Future
research directions include exploring real-time adaptability, reinforcement learning, and contextual awareness
to further refine recommendation accuracy and user engagement.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the digital age, e-learning and e-retail platforms
generate vast amounts of content and product listings,
making it increasingly challenging for individuals to
discover relevant information efficiently. The
overwhelming number of choices often leads to
decision fatigue, where users struggle to identify
suitable courses or products. Recommender these
setups are crucial for in addressing this challenge by
evaluating user preferences, past interactions, and
product traits to deliver individualized suggestions.
These systems significantly enhance user experience
by ensuring learners access appropriate educational
materials and shoppers discover products adjusted to
their interests.
Classic suggestion frameworks mainly depend on
two approaches: feature-driven filtering and
community-based filtering. Feature-driven filtering
proposes options by assessing their properties and
linking them to a person’s earlier actions. In contrast,
collaborative filtering generates recommendations
based on behavioral patterns among users with
similar interests. While both approaches have been
widely used, they face several limitations, including
the newcomer obstacle (trouble suggesting items to
beginners due to missing past information), data
sparsity (insufficient user- item interactions),
scalability issues, and overspecialization (limited
recommendation diversity). These challenges often
result in inaccurate or repetitive suggestions, reducing
overall effectiveness.
To overcome these limitations, mixed-method
suggestion structures blend various strategies to boost
recommendation precision and versatility. By
merging feature-driven and community-based
filtering with machine learning algorithms, hybrid
models enhance personalization and optimize
recommendation quality. Sophisticated methods like
grid decomposition, TF-IDF vectorization, and deep
learning models help refine user preferences, even in
cases where historical data is limited. These methods
allow the system to learn from user behavior
dynamically, making recommendations more precise
and relevant.
This research aims to develop a hybrid
100
Shabana, , P., S., B., T., M., V. and Sameer,
Recommendation System for E-Learning and E-Commerce Using Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013923400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
100-105
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

recommendation system that effectively addresses the
shortcomings of traditional methods in e-learning and
e-retail domains. The proposed system leverages
advanced machine learning techniques to enhance
recommendation accuracy while ensuring scalability
and real-time adaptability. By evaluating
effectiveness assessed with essential markers such as
exactness, retrieval rate, F1- measure, and average
prediction error (APE), this study demonstrates the
effectiveness of hybrid models in delivering highly
relevant and user-centric recommendations.
As digital platforms continue to evolve, the
demand for intelligent, adaptive, and context-aware
recommendation systems grows. The proposed
hybrid model not only enhances personalized
learning experiences and targeted product
recommendations but also contributes to higher user
engagement, increased sales conversions, and
improved customer satisfaction. Future
advancements could explore reinforcement learning,
contextual awareness, and real-time adaptability to
further refine recommendation accuracy, making
online experiences more intuitive, efficient, and
enjoyable.
2 RELATED WORKS
In 2005, G. Adomavicius and A. Tuzhilin authored
the paper "Toward the Next Generation of
Recommender Systems: A Survey of the State-of-the-
Art and Possible Extensions," which was published in
within IEEE Journal of Knowledge and Data
Engineering (Volume 17, Issue 6). This paper
provided a comprehensive survey of recommender
systems, discussing existing approaches and
proposing possible extensions for future
advancements.
In 2017, X. He, L. Liao, H. Zhang, L. Nie, X. Hu,
and T. S. Chua presented "Neural collaborative
filtering" at the the 26th Global Web Conference
(pages 173-182). Their work introduced deep neural
networks to collaborative filtering, significantly
improving recommendation accuracy by learning
non-linear user-item interactions.
In 2009, Y. Koren, R. Bell, and C. Volinsky
published "Matrix factorization techniques for
recommender systems" in IEEE Computing
Magazine (volume 42, issue 8, pages 30-37). This
research demonstrated how matrix factorization
techniques enhance recommendation accuracy by
capturing latent user- item relationships.
In 2007, A. Paterek contributed "Improving
regularized singular value decomposition for
collaborative filtering" in the Records from the KDD
Cup and Seminar. This study refined singular value
decomposition (SVD) by incorporating regularization
techniques to improve the precision of group- based
filtering-based recommendations.
In 2015, J. McAuley, C. Targett, Q. Shi, and A.
van den Hengel presented "Image-based
recommendations on styles and substitutes" at the
38th Global ACM SIGIR Symposium on Information
Retrieval Research and Development (pages 43-52).
This research introduced image-based
recommendation models that analyze product visual
features to suggest similar styles and substitutes.
In 2009, S. Rendle, C. Freudenthaler, Z. Gantner,
and L. Schmidt-Thieme presented "BPR: Bayesian
personalized ranking from implicit feedback" at the
25th Symposium on Uncertainty in Artificial
Intelligence (pages 452-461). Their work proposed a
Bayesian ranking model that learns personalized
ranking preferences from implicit user feedback.
In 2015, F. Ricci, L. Rokach, and B. Shapira
published Recommendation Systems Guidebook by
Springer, New York, NY. This book serves as a
comprehensive guide on recommender systems,
covering traditional and modern recommendation
techniques.
In 2001, B. Sarwar, G. Karypis, J. Konstan, and J.
Riedl presented "Item-based collaborative filtering
recommendation algorithms" at the 10th Worldwide
Web International Meeting (pages 285-295). Their
research introduced product-focused group filtering,
enhancing suggestion quality scalability and
efficiency.
In 2016, I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, and A.
Courville published Deep Learning in MIT Press,
Cambridge, MA. This book provides foundational
knowledge on advanced neural network methods,
extensively used in suggestion frameworks.
In 2018, H. Fang, Z. Guo, X. Zhang, and J. Zhu
published "A survey on deep learning-based
recommendation systems" within IEEE Open Access
(volume 6, pages 69032-69051). Their work analyzed
various deep learning models used in
recommendation systems, highlighting their strengths
and limitations.
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
Recommendation systems in e-learning and e-
commerce primarily rely on traditional approaches
like attribute-driven filtering and community-based
filtering for provide personalized suggestions.
Content-based filtering analyzes item attributes and
Recommendation System for E-Learning and E-Commerce Using Machine Learning
101

compares them with user preferences, whereas
collaborative filtering generates recommendations by
identifying patterns in user interactions and
behaviors. Despite their widespread use, these
approaches face significant challenges, including the
cold start problem, data sparsity, and limited diversity
in recommendations.
In e-learning, recommendation systems typically
utilize course metadata, student performance, and
engagement metrics to suggest learning materials.
While these systems improve access to relevant
content, they often fail to adapt to individual learning
styles and real-time user engagement. Many
traditional models struggle to provide dynamic
recommendations, leading to repetitive or less
relevant course suggestions. As a result, students may
not receive truly personalized learning experiences,
limiting the effectiveness of the system.
In e-commerce, product recommendation systems
analyze purchase history, browsing behavior, and
customer demographics to suggest relevant products.
While these techniques enhance user experience and
boost sales, they suffer from overspecialization and
inability to capture evolving user interests. The
recommendations often fail to reflect changing
customer preferences, leading to lower engagement
rates. Additionally, traditional models rely on limited
data sources, making it difficult to provide accurate
and adaptable recommendations.
Moreover, standalone recommendation
techniques in both e- learning and e-commerce lack
the ability to integrate multiple sources of user data,
restricting their accuracy and adaptability. This
limitation results in static and less effective
recommendations, making it difficult to cater to
diverse user needs. Consequently, there is a growing
demand for hybrid recommendation systems that can
overcome these challenges by combining multiple
techniques, improving personalization, and ensuring
real-time adaptability in both domains.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed suggestion framework combines
attribute- focused filtering, group-based filtering, and
cutting-edge machine learning methods to improve
recommendation accuracy and user satisfaction.
Traditional recommendation models suffer from
constraints like the initial engagement barrier, limited
data density, and overspecialization, which restrict
their ability to generate diverse and personalized
recommendations. To tackle these issues, the
suggested setup uses machine learning strategies,
such as array decomposition, neural networks, and
adaptive learning, enabling it to dynamically adapt to
user preferences. Unlike conventional models, this
system considers real-time user interactions,
contextual factors like time of access, device type,
and session duration to refine recommendations and
enhance user engagement.
For e-learning applications, the system analyzes
multiple factors, including course completion rates,
time spent on learning modules, assessment scores,
learning pace, and individual engagement patterns.
By leveraging behavioral analytics and real-time
tracking, it provides highly personalized course
recommendations tailored to the learner’s skill level
and interests. Unlike traditional models that primarily
depend on course metadata and predefined tags, this
approach ensures that recommendations evolve
dynamically based on user progress and interaction
patterns. The system incorporates a real-time
feedback mechanism, allowing students to provide
input on recommended materials, which helps refine
the learning pathway. Additionally, the system
supports adaptive learning by identifying weak areas
and suggesting resources to strengthen them, making
education more engaging and effective. It also
considers learning styles, ensuring that
recommendations cater to visual, auditory, or
kinesthetic learners, thus maximizing knowledge
retention.
In the e-commerce domain, the proposed system
enhances item suggestions by evaluating buying
patterns, navigation habits, and user demographics
data, and seasonal trends. Unlike conventional
recommendation models that simply suggest similar
items, this system introduces diverse and trending
products to expand user choices and improve
engagement. By leveraging real-time data processing,
the recommendations remain relevant and up-to-date,
adapting as user preferences shift over time.
Additionally, the system integrates user reviews,
product ratings, and popularity trends to refine
recommendations, increasing customer satisfaction.
To further enhance accuracy, it incorporates
contextual factors, such as purchase frequency, recent
searches, and external influences like ongoing sales
or discounts. Reinforcement learning is used to
continuously improve recommendation precision, as
the system learns from user interactions and fine-
tunes its suggestions accordingly.
Furthermore, the proposed system provides a
hybrid approach that combines multiple
recommendation techniques, ensuring that users
receive more accurate, diverse, and personalized
suggestions. By integrating machine learning-driven
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
102
adaptability, the system reduces bias, mitigates cold
start issues, and effectively handles sparse data,
making it highly efficient and scalable. The inclusion
of context-aware recommendations ensures that users
receive content or product suggestions that are not
only based on historical data but also align with their
current needs and behaviors.
By combining personalization, real-time
adaptability, and contextual awareness, the proposed
system significantly enhances user experience in both
e-learning and e-commerce, making it more intuitive,
effective, and user-centric.
4.1 Architecture
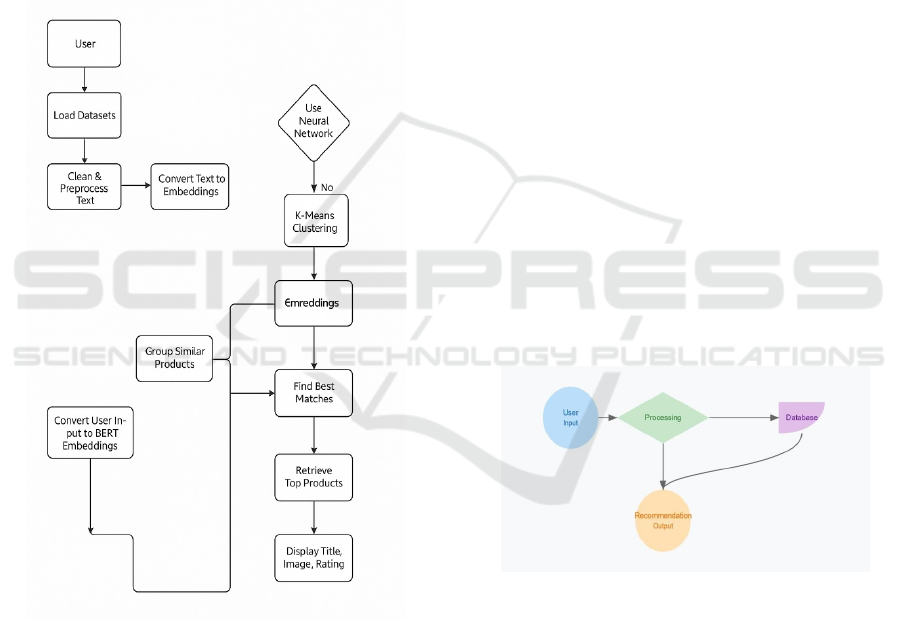
Figure 1: Architecture of the project.
Figure 1 show the given architecture represents a
hybrid recommendation system that utilizes NLP and
machine learning for accurate product
recommendations. It starts by loading datasets and
performing text preprocessing to clean product
information. The system then converts product titles
into embeddings using TF-IDF and NLP methods,
ensuring meaningful feature extraction.
Next, K-Means Clustering groups similar
products into 40 clusters based on textual similarities.
When a user provides input, it is processed using
BERT embeddings, allowing the system to
understand contextual meaning effectively. The
system then finds best matches, retrieves the top 5
recommendations, and displays relevant product
details like title, image, and rating.
This approach enhances recommendation
accuracy, personalization, and user engagement,
making it highly effective for e-commerce and digital
platforms.
5 IMPLEMENTATIONS
The implementation of the recommendation system
follows a structured approach, beginning with data
collection to analyze user behavior and preferences.
In the e-learning domain, data is gathered by tracking
course completion rates, time spent on different
modules, quiz performance, and engagement with
learning materials. Additionally, metadata related to
course content, instructor details, and subject
relevance is considered to refine recommendations.
For e- commerce, the system collects purchase
history, browsing patterns, customer reviews, and
demographic details to understand consumer
preferences. Abandoned carts, product ratings,
frequently viewed items, seasonal trends, and
promotional campaigns further enhance the
recommendation accuracy.
Figure 2: User input and recommendation process flow.
Once data is collected, preprocessing techniques are
applied to clean and transform raw data for effective
model training. Natural language processing methods
like TF-IDF and word embeddings are used for
textual data, while missing values are handled, and
numerical data is normalized. Collaborative filtering
techniques generate user-item interaction matrices,
while content-based filtering analyzes product and
course attributes to build a feature-rich dataset for
training. Figure 2 show the User Input and
Recommendation Process Flow.
Recommendation System for E-Learning and E-Commerce Using Machine Learning
103

Figure 3: User input and recommendation process flow.
The system then employs machine learning models
such as grid decomposition, advanced neural
networks, and adaptive learning to develop the
suggestion engine. Collaborative filtering models
identify patterns based on user behavior, while
content-based filtering focuses on product attributes.
A hybrid model combining both approaches ensures
personalized and diverse suggestions. Figure 3 show
the User Input and Recommendation Process Flow.
The framework steadily adapts through user
engagement, enhancing its suggestions progressively
to boost accuracy and relevance. Following model
training, the system is deployed using cloud-based
APIs, making it scalable and accessible across
multiple platforms. It seamlessly integrates with e-
learning and e-commerce applications to provide real-
time personalized recommendations. Feedback
mechanisms capture user interactions to further
enhance future recommendations. Additionally,
explainability features are incorporated to help users
understand why specific courses or products are
suggested, increasing trust and engagement. This
structured implementation ensures that the
recommendation system is adaptive, accurate, and
user- centric, enhancing user experience across
educational and commercial domains.
6 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The recommendation system for e-learning and retail
platforms is designed to provide personalized
suggestions based on user input and preferences. The
first screen serves as the landing page, where users
can sign up or sign in to access recommendations. It
presents a clean and intuitive interface with a clear
call to action, prompting users to choose a category.
The "Get Recommendations" button directs users to
the recommendation engine, while the "About"
button provides insights into the system’s
functionality. Figure 4 show the Home Page of the
Recommendation System.
Figure 4: Home page of the recommendation system.
The second screen is the product recommendation
interface, allowing users to choose a dataset, enter a
product name, and apply optional filters such as
minimum rating, ASIN, and the number of
recommendations. The interface ensures flexibility,
enabling users to refine their search based on specific
criteria. Once the details are entered, the system
processes the input and provides personalized product
suggestions. The “Home” button allows users to
navigate back to the main page seamlessly, ensuring
a smooth user experience. The visually distinct colors
and structured layout enhance usability, making it
easier for users to interact with the system efficiently.
Figure 5 show the Home Page of the
Recommendation System.
Figure 5: Home page of the recommendation system.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed recommendation system significantly
enhances personalization and user engagement in both
e-learning and e- commerce by leveraging hybrid
techniques and advanced machine learning
algorithms. By addressing challenges like cold start
issues and limited data availability, the setup ensures
accurate and diverse recommendations tailored to
user preferences. Its adaptability allows continuous
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
104

refinement based on user interactions, improving
relevance over time. The cloud- based deployment and
scalable infrastructure enable efficient handling of
large datasets, making the system robust for dynamic
digital platforms. Future advancements, such as
reinforcement learning, real-time analytics, and
context-aware recommendations, will further enhance
its performance, ensuring a more intuitive and
responsive user experience.
8 FUTURE SCOPE
The future of recommendation systems will be driven
by advancements in artificial intelligence,
particularly deep learning, reinforcement learning,
and graph neural networks. These techniques will
improve real-time adaptability, ensuring more accurate
and personalized recommendations. Context- aware
systems that factor in elements such as location, time,
device usage, and sentiment analysis will further
enhance user experience. Additionally, the integration
of multi-modal data, including text, images, videos, and
voice commands, will make recommendations more
interactive and accessible across different platforms.
Security and transparency will also be key
considerations. Explainable AI (XAI) will help users
understand why specific recommendations are made,
increasing trust and engagement. Blockchain
technology can be leveraged to enhance data privacy
and ensure secure transactions, particularly in e-
commerce platforms. Scalability will remain a
priority, with cloud-based and distributed computing
solutions enabling the system to handle vast datasets
efficiently. Future systems will also integrate with
cross-platform services, including IoT devices and
social media, refining recommendations through
broader user interactions, making them more accurate,
dynamic, and user-centric.
REFERENCES
A. Paterek's study, "Improving Regularized Singular Value
Decomposition for Collaborative Filtering," was
presented at the KDD Cup and Workshop in 2007.
B. Sarwar, G. Karypis, J. Konstan, and J. Riedl co-authored
"Item-Based Collaborative Filtering Recommendation
Algorithms," which was published in the Proceedings
of the 10th International Conference on World Wide
Web in 2001 (pp. 285-295).
F. Ricci, L. Rokach, and B. Shapira, Recommender
Systems Handbook. New York, NY: Springer, 2015.
G. Adomavicius and A. Tuzhilin's work, "Toward the Next
Generation of Recommender Systems: A Survey of the
State-of-the-Art and Possible Extensions," was featured
in IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data
Engineering (Vol. 17, No. 6), pp. 734-749, 2005.
H. Fang, Z. Guo, X. Zhang, and J. Zhu, “A survey on deep
learning-based recommendation systems,” IEEE
Access, vol. 6, pp. 69032-69051, 201
I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, and A. Courville, Deep
Learning. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2016.
J. McAuley, C. Targett, Q. Shi, and A. van den Hengel,
“Image-based recommendations on styles and
substitutes,” Proceedings of the 38th International
ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and
Development in Information Retrieval, 2015, pp. 43-
52.
S. Rendle, C. Freudenthaler, Z. Gantner, and L. Schmidt-
Thieme presented "BPR: Bayesian Personalized
Ranking from Implicit Feedback" at the 25th
Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence in
2009 (pp. 452-461).
X. He, L. Liao, H. Zhang, L. Nie, X. Hu, and T. S. Chua,
“Neural collaborative filtering,” Proceedings of the
26th International Conference on World Wide Web,
2017, pp. 173- 182.
Y. Koren, R. Bell, and C. Volinsky contributed to the study
"Matrix Factorization Techniques for Recommender
Systems," which appeared in IEEE Computer (Vol. 42,
No. 8), pp. 30-37, 2009.
Recommendation System for E-Learning and E-Commerce Using Machine Learning
105
