
AI‑Driven Deepfake Detection: A Sequential Learning Approach with
LSTM
Radha Seelaboyina, Karnati Mysanthosh, K. Sri Vishnu Kshiraj and Sourav Kumar
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Geethanjali College of Engineering and Technology,
Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Keywords: Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Spatiotemporal Analysis, Fea-
ture Extraction, Adversarial Training, Sequence Modeling.
Abstract: The rapid advancement of deep learning has made video manipulation techniques, such as deepfakes, widely
accessible. This research investigates the use of Long Short- Term Memory (LSTM) networks for detecting
deepfake videos because of their capacity to learn temporal dependencies from different time intervals be-
tween neighboring frames. Differently from CNN-based approaches that focus on analyzing individual image
frames in isolation, LSTM networks consider sequences of images, which helps normal video frames to reveal
unnatural transitions and inconsistencies in the motion of facial components that are particular for deepfake
videos. The proposed model induced both spatial features, which are artifacts appearing in a single frame, and
temporal artifacts, which are inconsistencies among frames, through the integration of LSTM with CNNs,
thus improving the reliability and precision of deepfake detection.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deepfake technology, the development of artificial
media, has gained interest in recent times. Unlike tra-
ditional editing where face modifications were made
to static images, deepfakes gain true control over fa-
cial appearance in real-time by using modern deep
learning with neural networks: synchronizing lip
movements, changing voice, or manipulating body
position in such ways as to make people say or do
things that they never really did (L. Jiang et al., 2020)
and (Y. Choi et al., 2018). These algorithms may be used
for creative art practices or in education, but the in-
creasing sophistication puts deepfakes into the world
of ethical and security issues. Opponents have used
deepfakes to try to ruin reputations or manipulate
public opinion and dig threats into information secu-
rity (T. Karra et al.,2017), (T. Karras et al., 2019) and
(Zhiqing Guo et al., 2021) With the continuation of
advancements in generative AI, it is becoming more
and more challenging to tell the difference between
real and fake; hence, the development of strong deep-
fake detection methodologies becomes even more
pressing (Belhassen Bayar et al., 2016) and (Richard
Zhang et al., 2018).
Multiple designs for deepfake detection were ex-
plored: CNN-like methods analysis of the spatial fea-
tures in the individual frames (Sheng-Yu Wang et al.,
2020) and (Carlini et al., 2020). However, temporal
inconsistencies and motion anomalies detection were
quite difficult for those methods when processing
deepfake videos (L. Tran et al., 2018) and (Y. Choi et
al., 2020). For this reason, we propose an LSTM in
this study for deepfake detection to address this issue.
LSTMs are a special case of recurrent neural networks
specifically suited for analyzing sequential data,
thereby rendering them able to detect unnatural video
transitions caused by manipulations (Zhou et al., 2018)
and (Frank et al., 2020). Unlike CNNs, which are spa-
tial artifact detectors, LSTMs utilize sequential and
temporal dependencies in a more holistic deepfake
detection schema (McCloskey et al., 2018). Deepfake
detection with Neural Networks has previously been
pursued by many researchers. In the year 2018, feature
learning for the purposes of detecting image manipu-
lation were developed by Zhou et al. with regard to
advancing techniques and merits towards better clas-
sification accuracy (Zhou et al., 2018).
In 2020, Carlini and Farid presented adversarial
attacks on the deepfake detectors, exposing their vul-
nerabilities (Carlini, N. and Farid, H. 2020). In a se-
ries of papers published between the late 2020 and
62
Seelaboyina, R., Mysanthosh, K., Kshiraj, K. S. V. and Kumar, S.
AI-Driven Deepfake Detection: A Sequential Learning Approach with LSTM.
DOI: 10.5220/0013922600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
62-69
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

early 2021, Wang et al. and Guo et al. reiterated the
importance of the convergence of such neural land-
scapes to both spatial and temporal features for deep-
fake detection (Zhiqing Guo et al., 2021) and (Sheng-
Yu Wang et al., 2020). The proposed research incor-
porates CNN-based feature extraction with LSTM
processing to boost detection capabilities.
By fine-tuning the detection mechanism and man-
aging the limitations of the existing methods, this
work intends to augment digital media security and
lessen the dangers posed by deepfake technology.
Moreover, this work endorses the AI-directed forensic
analysis by suggesting a scheme for deepfake detec-
tion addressing the minutiae of inconsistencies in ma-
nipulated video sequences. The method under consid-
eration consists of preprocess-oriented feature extrac-
tion, fusion of CNN-LSTM for better classification,
and the evaluation of the model performance with ex-
isting benchmarks (Marra et al., 2019) and (Yu et al.,
2019).
2 RELATED WORK
The emergence of deep learning-driven methods
helped the field of deepfake detection cross a signifi-
cant milestone. Taeb and Chi performed a thorough
review of current methods, examining their abilities
and drawbacks. Almars systematically categorized
detection strategies based on their machine-learning
dependence, giving insights into the increasing prom-
ise of these paradigms to detect synthetic media. Ab-
dulreda and Obaid stressed that to improve detection,
we should use an interdisciplinary strategy, function-
ality across disciplines. Rana et al. Thresholds are
necessary to determine cut-off points, and these are
defined differently by multiple authors; in a discus-
sion of previous literature and their systematic re-
view, Franke et al. (2037) highlighted accuracy, pre-
cision, recall, and F1-score as the most commonly re-
ported performance metrics, and emphasized the im-
portance of defined and consistent evaluation proto-
cols. Taeb and Chi (2038) performed a comparative
study and advocated a multi-metric approach to ob-
tain a more thorough evaluation of detection models.
3 BACKGROUND AND
OBJECTIVES
Advancements in deepfake system, powered by deep
learning, have led to the easy production of incredibly
lifelike fake videos. These synthetic videos, created
using techniques such at Generative Adversarial Net-
works (GANs), are a considerable risk in spreading
misinformation, identity fraud and cyber-spoofing.
The massive volume of publicly available imagery on
social media has made the execution of such deep-
fake attacks more feasible, hence making the need for
reliable detection systems even more crucial.
Existing deepfake detection frameworks, which
are predominantly based on CNNs, evaluate the data
frame-by-frame but have difficulty generalizing to
new deepfake generation methods. Moreover, they do
not have the ability to model temporal discrepancies,
which are little differences in facial expressions,
movement, and transitions over several frames, lead-
ing to lower detection rates. To overcome these lim-
itations, using temporal features by means of sequen-
tial models such as Long Short-Term Memory
(LSTM) networks are a promising solution.
4 METHODOLOGY AND
PARAMETERS
4.1 Methodology
Structured Approach to Deepfake Detection: The
proposed system follows a thorough approach that
merges spatial and temporal investigation, which
leads to
assured precision and strength of manipu-
lated video content activity. The method is predeter-
mined by the order of tasks to carry out, namely: data
collection (which will be discussed in following sec-
tions), feature extraction,
network design, training,
and deployment. Patch wise CNN for spatiotemporal
feature extraction and
a sequence of RNN, mainly
LSTM, for temporal modelling, synergizes the sys-
tem with a holistic understanding of video sequences.
Dataset Compilation and Preprocessing: Trained
a
good model on a well-annotated and much versatile
dataset. The dataset consists of both authentic and
manipulated videos and covers the
various manipu-
lation techniques in a balanced representation. Cor-
rect labeling demarcates real from
dubiously edited
content. For preprocessing, individual frames are ex-
tracted from
videos, and spatial features are ex-
tracted from frames using a pre-trained CNN model.
These extracted features are then
used for further
temporal analysis.
Temporal Modeling with Recurrent Networks:
The architecture
uses RNNs to model the sequential
dependencies between frames in a video. Because
AI-Driven Deepfake Detection: A Sequential Learning Approach with LSTM
63

long sequences make it important to retain infor-
mation over long inputs, LSTM or Gated Recurrent
Unit (GRU) cells
were initially used to enhance
memory capacity and learning speed. The proposed
approach also makes use
of a bi- directional RNN ar-
chitecture to take both past and future frames into ac-
count, which allows for detection of subtle inconsist-
ences that are characteristic to the specific way in
which the deepfake manipulation will occur.
Combining Spatial and Temporal Features:
RNNs are able to learn temporal dependencies while
CNNs learn spatial features
and combining these sig-
nificantly enhances the detection model’s effective-
ness. By considering the correlation between consec-
utive frames,
this dual-level architecture enables the
system to identify patterns specific to deepfakes that
might not be apparent from analyzing frames in iso-
lation. By utilizing temporal information in conjunc-
tion with spatial cues, our model comprehends video
sequences better by enabling it to recognize real from
fake content.
Hybrid Model Design for Deepfake Detection: The
CNN-RNN based
hybrid model is then used for de-
tection. The CNN module analyzes spatial infor-
mation spatially from the frames to detect structural
vomit and make the difference between natural and
fabricated facial features and
blending artifact. On
the other hand, the recurrent neural network (RNN)
using LSTM or GRU cells can be used to process a
series of frames for abnormal features for motion pat-
tern
or sudden transitions. Using both tasks, we can
build a strong framework which will be able to detect
deepfake content through various ways of manipula-
tion.
Loss Function and Model Training: When we
are doing task of video classification (sequential
task), selecting suitable loss function to optimize per-
formance of model
is also very important. Binary
cross-entropy is the most commonly used loss func-
tion for the binary classification problem which is the
case in our deepfake detection
problem. Since this
model is trained on a balanced dataset, it helps to pre-
vent classification bias, and the
parameters are opti-
mized through backpropagation and gradient descent
techniques to enhance the accuracy of detection.
Preventing Overfitting Through Regularization:
To enhance the model's generalization capability and
prevent overfitting, various regularization techniques
are applied. Dropout layers are incorporated within
the RNN structure to reduce over-reliance on specific
patterns, ensuring the model remains adaptable to un-
seen data. These techniques improve the model's ro-
bustness when deployed in real-world scenarios.
Augmentation for Improved Generalization:
Since real-world videos vary in lighting, facial ex-
pressions, poses, and backgrounds, data augmentation
techniques are applied to introduce diversity into the
dataset. By artificially expanding the dataset, the
model becomes more resilient to different environ-
mental conditions, enhancing its ability to detect
deepfake content across multiple sources and con-
texts.
Optimizing Model Parameters: Fine-tuning
hy-
perparameters
plays
a
crucial
role
in maximizing
the model’s efficiency and accuracy. Key param-
eters, such as learning rate, batch size, the number of
hidden units in the RNN, and CNN filter sizes, are op-
timized through systematic experimentation. Tech-
niques like grid search and other optimization strat-
egies help determine the best combination of param-
eters for peak performance.
Evaluation Metrics and Performance Assessment:
To accurately assess the model’s effectiveness, mul-
tiple evaluation metrics are used, including accuracy,
precision, recall, and F1-score. The model is tested on
an independent dataset containing both real and deep-
fake content to ensure an unbiased evaluation. These
metrics provide insights into the model’s strengths
and highlight areas that require further improvement.
Deployment for Real-Time Applications: Once
trained and validated, the model is deployed in a real-
world environment for practical applications. The de-
ployment phase includes optimizing the model for
real- time or near-real-time processing, allowing effi-
cient video sequence analysis. Techniques like model
compression and inference optimization are applied to
minimize computational overhead while maintaining
high detection accuracy.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Since
deepfake
generation
techniques
are
constantly
evolving, the detection model requires ongoing
monitoring and updates. The system is regularly as-
sessed for performance in real-world scenarios, and
adjustments are made to counter emerging deepfake
techniques. Periodic retraining with new datasets and
model architecture improvements helps maintain the
system’s effectiveness over time.
User
Interaction
and
System
Interface: A
user-friendly interface is developed to ensure acces-
sibility and engagement. This interface allows users
to upload video content for analysis and receive real-
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
64

time feedback on whether the video has been manip-
ulated. Additionally, users can provide feedback to
improve the system’s accuracy over time. This inter-
active component enhances usability and transpar-
ency in deepfake detection applications.
4.2 Parameters
The parameters used in the modelling and ensuring
the efficiency of the detection model consists of in-
consistencies and anomalies in the video content.
Some of those parameters are:
Facial Movement Changes: Unnatural or mismatched
facial expressions often give away deepfake videos.
Real people's faces move in sync when they talk and
show emotion. But deepfake tech sometimes can't get
these subtle movements right so faces look stiff or
over-the-top. You might notice a smile that doesn't
reach the eyes, or a smooth forehead when eyebrows
go up. This happens because the AI learns from sets of
images that don't show all the ways human faces can
move. As a result, the fake face might seem a bit off or
disconnected from what's being said.
Frame Rate and Motion Differences: Real videos
show smooth changes between frames giving a
smooth and lifelike flow of movement. Fake videos,
on the other hand often have problems with how
heads or bodies move from one frame to the next.
This happens because many fake video makers create
each frame on its own, not thinking about how move-
ment should flow between them. Because of this, you
might see a head jump from one spot to another mak-
ing the movement look jerky. Also, the blur you see
during quick moves in real videos might be missing
or look too sharp in fake ones. When you look, these
things can make fake videos stand out.
Eye Blinking Anomalies: People blink in a natural
rhythm, with smooth eyelid movements and a fre-
quency that changes based on focus and surround-
ings. Deepfake videos often struggle to copy this. This
can lead to unnatural blinking rates or long periods
without blinks in the video. This problem happens be-
cause many datasets used to train deepfake systems
have more open-eyed pictures, which causes poor
modelling of blinking. Sometimes, blinks in
these videos might look too quick, sudden, or un-
even between eyes. These odd blinks often give
away AI-made content.
Lighting and Reflection Inconsistencies: Deepfake
models struggle to recreate lighting and reflections.
Real videos show natural changes in shadows and
highlights when people move or light sources shift.
But deepfakes often have strange lighting that doesn't
change with movement. Also, reflections on faces -
like eye glints or skin shine - might not match the
scene's actual lighting. This happens because deep-
fakes focus on creating faces, not on copying how
light works in the real world. As a result, people who
look can spot these odd details more.
Facial Metrics: Everyone has unique facial features,
like symmetry, eye spacing, and skin texture, which
stay the same in real videos. Fake faces made by AI
might not keep these features perfect causing small
changes. For instance, one side of the face could look
a bit different from the other because of mistakes in
face-swapping programs. Skin details such as pores,
lines, and marks, might appear too smooth or have
different sharpness in different parts of the face. Also,
AI models might not line up key face points, like eye
corners and mouth edges right. This can lead to slight
misalignment that face-measuring tools can spot.
Hair and Edge details: Real human hair shows fine
details, with single strands moving as air flows and
the head moves. Deepfake models often can't copy
this level of detail well. Instead, hair might look too
smooth, have odd distortions, or mix with the back-
ground. You'll notice this problem more around the
edges of the head where fake content can create fuzzy,
rough, or flickering borders. When the background
gets complex or the head moves fast, the unnatural
blend between the hairline and surroundings can make
the deepfake stand out more.
Sudden Facial Glitches or Flickering: A clear sign
of a deepfake video is quick facial distortions or flick-
ering around the eyes, nose, or jawline. This happens
when the AI can't create smooth transitions between
frames causing some facial features to warp for a mo-
ment. You'll notice these glitches more during quick
head moves big facial expressions, or in dark settings
where the AI has less info to use. These mistakes ruin
the realistic look and you can spot them by looking at
the video frame by frame.
Neck and Body Mismatch: Deepfake tech changes
faces, but it can have trouble blending the face with
the rest of the body. Sometimes, you might notice the
face's skin tone doesn't quite match the neck or hands
creating obvious color differences. Also, how the
head joins the body can look a bit weird, with small
issues in size or angle. This stands out when a deepfake
puts a new face on someone else's body, as the head
movements can seem out of sync with the original
person's natural stance and movements.
AI-Driven Deepfake Detection: A Sequential Learning Approach with LSTM
65

Unnatural Eye Reflections: In real life, eyes mir-
ror the surroundings, including light sources
and objects nearby Deepfake models often miss
these details leading to eyes that look flat, lack
reflections, or show reflections that don't match
the rest of the video. This problem stands out
more in bright settings or when someone wears
glasses where reflections should change as the
head moves. If the reflections seem too even or
stay the same despite movement, it suggests that
the video has been created.
Unnatural Hand and Face Coordination: When
people talk, their faces and hands work together to
show how they feel and match their words. But in fake
videos, you might see something odd. The face might
not quite fit with what the hands are doing making it
look weird. Picture someone waving their hands to
make a point, but their face stays blank. This happens
because the tech behind these fake videos cares about
getting the face right and doesn't pay much attention
to how the whole body moves together.
5 EXISTING SYSTEM
Current techniques of identifying deepfakes blend
classic forensic analysis with sophisticated machine
learning. Forensic experts first reviewed videos for
abnormal lighting, mismatched shadows, or facial dis-
tortions that seemed artificial (L. Jiang et al.,2020)
and (Y. Choi et al., 2018). These strategies were good
for individual experts but ineffective at larger scope.
This arose from the emergence of feature-based ma-
chine-learning techniques, including lens aberration
detection, JPEG compression artifact analysis, and
demosaicing artifact identification (Seelaboyina et
al., 2023). Although these methods worked well on
still pictures, detecting videos modified using sophis-
ticated AI models including Generative Adversarial
Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders
(VAEs) was very difficult (Zhiqing Guo et al., 2021)
and (Belhassen Bayar et al., 2016).
The next breakthrough was in the detection of fa-
cial modifications thanks to the use of Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs) to extract spatial elements
from single frames. Although they were effective,
CNN-based methods had difficulty identifying chron-
ological discrepancies in deepfake clips. To solve this
problem, scientists investigated Recurrent Neural
Networks (RNNs), specifically Long Short-Term
Memory (LSTM) networks that identify motion
anomalies by analyzing sequential dependencies be-
tween frames (Y. Choi et al., 2020) and (Zhou et al.,
2018). Even though these techniques helped to iden-
tify deepfakes, they still struggled to accurately and
precisely represent motion abnormalities (Frank et
al., 2020 and (McCloskey et al., 2018).
To recap, traditional deepfake detection ap-
proaches work well but are short on scalability, versa-
tility, and scalability as deepfake technology pro-
gresses. Machine learning advancements and AI-
driven models help to improve precision and robust-
ness in deepfake detection, therefore stressing the
need for more refined techniques combining spatial
and temporal analysis (Marra et al., 2019) and (Yu et
al., 2019).
6 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed method is based on Long Short-Term
Memory networks (LSTM) and their potential for se-
quential deepfake detection. Long short-term
memory (LSTM) is a recurrent neural network
(RNN) learning model that can capture signals of a
video sequence’s temporal structure. The suggested
model utilizes the advantages of Convolutional Neu-
ral Networks (CNNs) to extract spatial features and
RNNs to capture temporal features.
Initially, the system gathers a variety of data, in-
cluding both real videos and deepfake videos, with
accurate labelling for training purposes. Each video is
preprocessed consisting of frame extraction and spa-
tial feature extraction using a pre- trained CNN. The
latter is fed into an RNN for temporal modeling of
the frames, utilizing Long Short-Term Memory
(LSTM) or Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) cells for ef-
ficient temporal sequence modeling. By processing
the input in both directions, the RNN provides a
comprehensive understanding of the temporal con-
text, allowing the model to identify subtle temporal
cues characteristic of deepfake manipulation.
Evaluation metrics, including accuracy, precision,
recall, and F1 score, provide a complete assessment of
the model's efficiency in distinguishing between real
and manipulated videos.
This research contributes to the ongoing efforts in
developing sophisticated deepfake detection systems
by using the temporal information encoded in video
sequences efficiently. The proposed model demon-
strates promising results, showcasing its potential to
reduce the risks associated with the rapid increase of
deepfake technology in multimedia content in social
media platforms.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
66
The work of the system is to improve our previ-
ously proposed prediction framework which can help
the law enforcement agencies to predict and detect
crimes in India with improved accuracy and thus re-
duces the crime rate.
Moreover, the application of this deepfake detec-
tion system as part of our formal crime prediction
model improves its overall efficiency in terms of po-
licing. Detection of manipulated videos allows the
potential for policing, law enforcement, and investi-
gative agencies to troubleshoot misinformation which
means that they put faith into evidence that is vali-
dated as being authentic. This enhancement builds in-
tegrity into the video evidence that fluctuates into a
digital crime analysis to inform agency decisions. The
enhanced framework may also be utilized to monitor
social media platforms for threats, scams, or misin-
formation that can lead to violence or disrupt public
order. Adding advanced deepfake detection enhances
our system while helping law enforcement agencies
maintain safety and reduce crime throughout India.
7 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Figure 1: System architecture.
The system architecture for deepfake detection using
LSTM networks has several key components. First,
the video data is collected and analyzed to ensure
model performance. Next, the video data is divided
into training and testing sets. Machine learning mod-
els, such as CNN (Convolutional neural network)
model, LSTM (Long Short-term memory) networks
are trained on the training data to identify patterns and
relationships between features and the underlying
variable. The trained models are evaluated. The da-
taset is tested using metrics such as precision, accu-
racy, recall, F1 score to determine the best model.
Once the model is complete, it is used to detect if the
uploaded video, is a deepfake or not. The system will
determine whether the uploaded video data is a deep-
fake video or not. This architecture ensures a robust,
accurate, and interpretable approach to deepfake de-
tection. The figure 1 shows System Architecture.
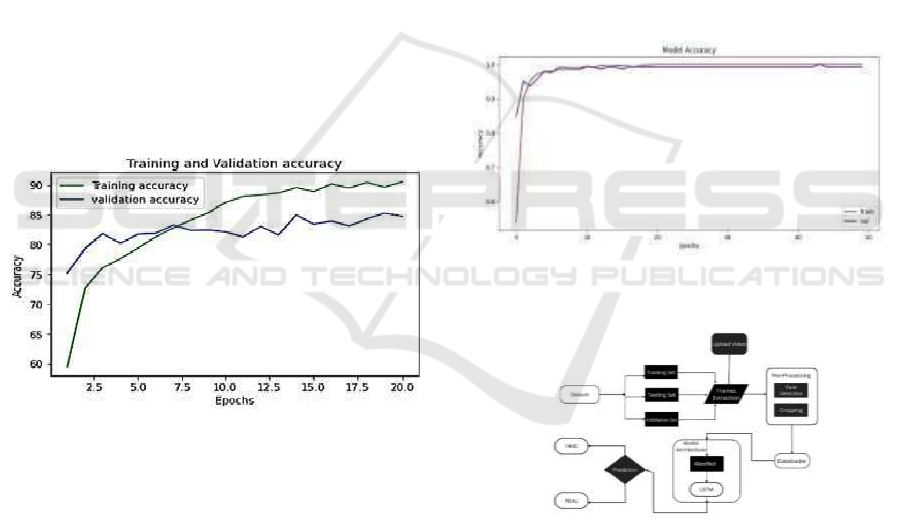
8 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The implementation of the detection system demon-
strated impressive performance. The designed model
was tested for 20 epoch (figure 2) and 40 epoch (fig-
ure 3) due to run time limitation and achieved
84.75 percent and 91.48 percent accuracy respec-
tively. The resultant graphs obtained after implemen-
tation claims the truth that the validation and testing
accuracy increase with increase in number of epochs.
Resultant confusion matrix helps to evaluate the test-
ing accuracy of the system. The figure 3 shows Model
Accuracy Progression Over Epochs.
Figure 2: Graphs of training and validation accuracy for 20
Epoch.
Figure 3: Graphs of training and validation accuracy for 40
Epoch.
AI-Driven Deepfake Detection: A Sequential Learning Approach with LSTM
67
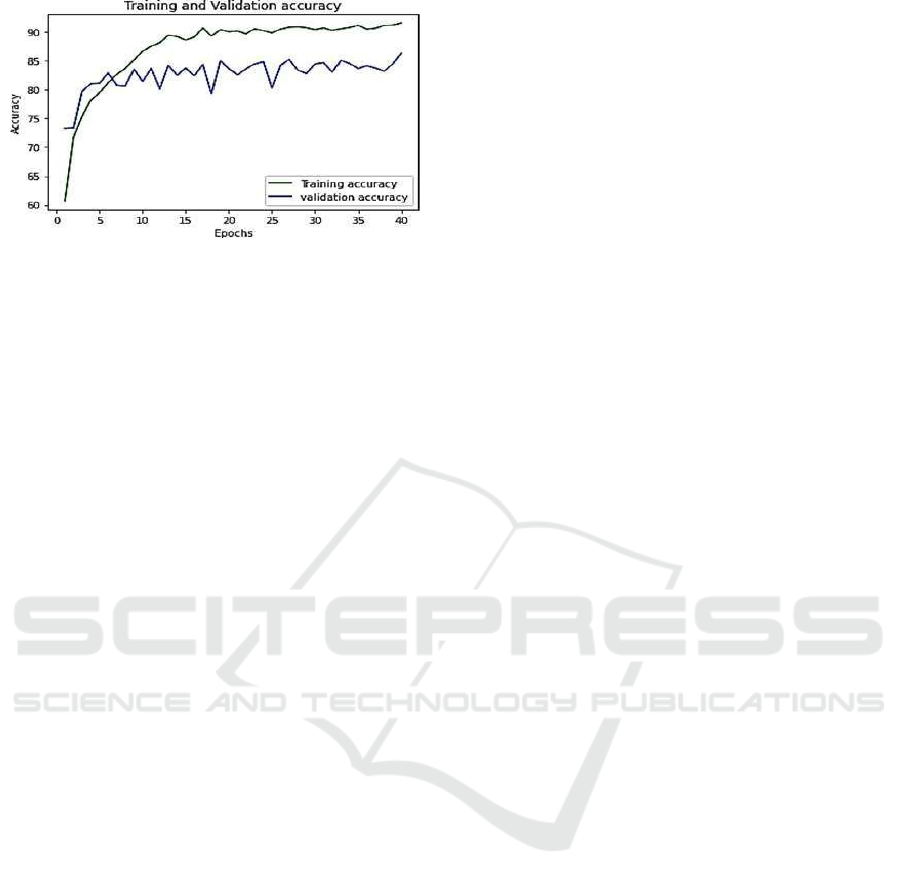
Figure 4: Model accuracy progression over epochs.
9 CONCLUSIONS
The implementation of the detection system demon-
strated impressive performance, validating the effec-
tiveness of combining CNN and RNN models. The ad-
dition of RNNs, similar to something like CNNs but in-
corporating LSTMs, is essential in the accurate deep-
fake placements that are undetected on video se-
quences. Once a LSTM layer is included within a
RNN structure, temporal dependencies of video seg-
ments can easily be captured. RNNs allow for a far
more detailed analysis to be conducted by integrating
both the spatial and the temporal features, thus in-
creasing the resilience of the deepfake detection sys-
tems against highly sophisticated deepfake schemes.
Still the lack of interpretability, as well as problems
with scaling and computational efficiency remain ob-
stacles that need to be solved in order for these strat-
egies to actually work. Multimodal analysis through
audio, text, and action, partnered with real-time social
media interaction along with advanced deepfake tech-
nology offers a lot more in terms of optimization for
RNNs in its future usage. In a broader context, this
means that a real time solution to cybersecurity and
forensic scrutiny would be achieved. Optimizing the
effectiveness of RNN detection systems on various
platforms without compromising accuracy is the best
way to enhance digital security against deepfake tech-
nology and it is these adjustable restrains that deter-
mine the usability of such to provide a flexible solu-
tion. The more challenges and innovations that
emerge from people abusing technology like deepfake
videos and more, the more autonomous, scalable, and
effective defenses against such technology should be
provided.
REFERENCES
Belhassen Bayar and Matthew C. Stamm (2016) “A Deep
Learning Approach to Universal Image Manipulation
Detection Using a New Convolutional Layer” in IH &
MM Sec '16: Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop
on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security.
Carlini, N. and Farid, H. (2020) “Evading deep-fake- image
detectors with white-and black-box attacks” in IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR) Workshops.
Frank, Joel & Eisenhofer, Thorsten & Schönherr, Lea &
Fischer, Asja & Kolossa, Dorothea & Holz, Thorsten.
(2020). Leveraging Frequency Analysis for Deep Fake
Image Recognition.
L. Tran, X. Yin, and X. Liu, “Representation learning by
rotating your faces,” IEEE transactions on pattern anal-
ysis and machine intelligence (TPAMI), vol. 41, pp.
3007:3021, 2018
L. Jiang, R. Li, W. Wu, C. Qian, and C. C. Loy, ‘‘Deeper-
Forensics1.0: A large-scale dataset for real- world face
forgery detection,’’ in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput.
Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), Jun. 2020, pp.
2889:2898.
Marra, F., Gragnaniello, D., Verdoliva, L., and Poggi, G.
Do GANs leave artificial fingerprints? In IEEE Confer-
ence on Multimedia Information Processing and Re-
trieval (MIPR), 2019.
McCloskey, S. and Albright, M. Detecting GAN generated
im agery us ing color cues. arXiv pre print arXiv:1812
.08247, 2018.
Richard Zhang et al., (2018), “Making Convolutional Neu-
ral Networks Shift-Invariant Again” in ICML 2019.
Seelaboyina, Radha, and Rajeev Vishwakarma. "Different
Thresholding Techniques in Image Processing: A Re-
view." In ICDSMLA 2021: Proceedings of the 3rd In-
ternational Conference on Data Science, Machine
Learning and Applications, pp. 23-29. Singapore:
Springer Na ture Singa pore, 2023,https://doi.org/10.1
007/978-981-19-5936-3_3.
Sheng-Yu Wang, Oliver Wang, Richard Zhang, Andrew
Owens, and Alexei A Efros. CNN-generated images are
surprisingly easy to spot...for now. In IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020.
T. Karras, T. Aila, S. Laine, and J. Lehtinen, ‘‘Progressive
growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and
variation,’’ 2017, arXiv:1710.10196.
T. Karras, S. Laine, and T. Aila, ‘‘A style-based generator
architecture for generative adversarial networks,’’ in
Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit.
(CVPR), Jun. 2019, pp. 4401:4410.
Y. Choi, M. Choi, M. Kim, J.-W. Ha, S. Kim, and J. Choo,
‘‘StarGAN: Unified generative adversarial networks
for multi-domain imageto-image translation,’’ in Proc.
IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. pattern Recognit., Jun. 2018,
pp. 8789: 8797.
Y. Choi, Y. Uh, J. Yoo, and J.-W. Ha, “StarGAN v2: Di-
verse image synthesis for multiple domains,” in Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
68

Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020, pp.
8188:8197.
Yu, N., Davis, L. S., and Fritz, M. Attributing fake images
to GANs: Learning and analyzing GAN fingerprints. In
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision
(ICCV), 2019.
Zhiqing Guo, Gaobo Yang, Jiyou Chen, Xingming Sun
(2021) “Fake face detection via adaptive manipulation
traces extraction network” in Computer Vision and Im-
age Understanding-Volume 204.
Zhou, P., Han, X., Morariu, V. I., and Davis, L. S. Learning
rich features for image manipulation detection. In IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV),
2018.
AI-Driven Deepfake Detection: A Sequential Learning Approach with LSTM
69
