
Real Time Traffic Signal Optimization and Vehicle Surveillance
Using Deep Learning
Mohammad Fathimunnisa, Vemula Deepthi, L. Sandhya Rekha,
Anumula Pavithra and Takkasheela Archana
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Venkayapalle, Pasupala,
NH 340C, Nandikotkur Rd, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Traffic Signal Control, Deep Learning, Reinforcement Learning, Convolutional Neural Network, You Only
Look once, Real‑Time Vehicle Tracking, Intelligent Traffic Management.
Abstract: In the modern scenario wherein, traffic congestion and poor signal management are the serious concerns of
cities, there is a demand for best-in-class solutions for its real-time optimization. This paper proposes a traffic
signal control and vehicle detection system based on deep learning with CNN and object detection. It
automatically adjusts signal times based on traffic density and reduces jams and optimizes road traffic. The
detection of traffic offenses and observation of road activity further augment surveillance. Its method offers
better accuracy, reduced waiting time and increased flexibility compared to the traditional methods.
Experimental results confirm the system's effectiveness for optimal urban traffic management with prompt
decision-making. Using AI-based strategies together can ensure a hyper-efficient, scalable solution to
Transportation needs’ in the new age.
1 INTRODUCTION
urban traffic congestion is considered one of the
biggest urban problems growing with the growing
populations, high volume of traffic and limited road
facilities. Traditional traffic signal control systems
operate on fixed time cycles with no ability to adapt
significantly to real-time changing traffic conditions.
This inefficient process leads to not only delays and
driver irritation, but also more fuel being used,
contributing to environmental pollution, and
economic losses. Therefore, demand for intelligent
traffic control systems, that dynamically change
signal timings, based on real-time information and
improve road safety, with the help of improved
surveillance technologies, is increasing.
Deep Learning, with the advent of Artificial
Intelligence and the exponential growth of
computing power, is yet another powerful tool to
address complex problems in traffic management.
Deep learning-based algorithms, particularly CNNs,
along with advanced object detection frameworks,
such as YOLO (You Only Look Once), have achieved
remarkable accuracy in vehicle detection,
classification, and tracking in real time. These models
are designed to analyse video streams from
surveillance cameras to estimate traffic volume,
identify vehicles and track movement patterns with
high accuracy and speed. Another innovation is the
addition of predicting future traffic flow through
RNNs or LSTMs, which allows the system to
anticipate needs and adjust the signal proactively
rather than reactively.
Along with adapting traffic signal timings, the
system also features a rich native vehicle monitoring
suite that automatically identifies traffic violations,
tracks Threatful movements, and aids law
enforcement agencies with a computer vision-based
automated analysis. The entire system is designed to
work in real-time for immediate decision-making
and traffic management. This paper aims to evolve a
solution that is economic, scalable, and future-ready
that bridge the collaboration between deep learning
and smart infrastructure to improve urban mobility
and build smarter, safer, and sustainable smart cities.
Fathimunnisa, M., Deepthi, V., Rekha, L. S., Pavithra, A. and Archana, T.
Real Time Traffic Signal Optimization and Vehicle Surveillance Using Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013922400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
51-55
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
51
2 RELATED WORK
The development of deep learning has significantly
improved the optimization of traffic signal and
monitoring of cars. Older traffic management systems
rely on pre-set signal cycles that fail to adapt to current
ground traffic, leading to congestion and inefficiency.
To address this, researchers have also explored AI-
led approaches.
Car detection and traffic density estimation have
previously been performed using Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNN) and object detection
algorithms, such as YOLO and SSD. Zhang et al.
(2020) used CNN-based approach to classify cars in
real-time, significantly improving accuracy while
avoiding adaptive signal control. Wang et al. (2021)
extended on this concept by integrating YOLOv4 with
smart traffic surveillance systems, delivering better
detection accuracy at the expense of less predictive
power.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models are proposed to
improve traffic prediction. Li et al. Zhang et al. (2019)
applied LSTM networks to predict traffic congestion
patterns using historic data for the adjustment of signal
times ahead of time. However, their model was not
real-time responsive, which was improved by Chen et
al. (2021), which relies on hybrid CNN-LSTM models
for real-time traffic density estimation and prediction.
These algorithms are helpful in the area of vehicle
monitoring as deep SORT and vehicle re-
identification methods are widely used Zhang et al.,
2019. Huang et al. m tracking approach based on
Deep SORT to analyse and track vehicle movements,
which significantly reduced tracking errors. Liu et al.
(2021) further supported anomaly detection by
integrating spatiotemporal features to improve
detection for traffic safety violations such as light
traversing and illegal lane change.
This is complemented by the emergence of edge
computing, which, combined with the expansion of
IoT-empowered infrastructure, has increased the
scale of AI driven traffic systems. Sharma et al. (2020)
described an IoT-based smart traffic system with
edge AI and a reduced delay in decisions. Although
efficient, such system did not possess any vehicle
tracking module that was improved by Patel et al. The
novel one-tier INNOWAT with integrated cloud
based real time infringement detection (Tuberen,
2021).
Despite all these advancements, still challenges
remain such as real-time scalability, accuracy in dense
traffic settings, and deploy ability. The solution we
propose is adhering to these loopholes, through a
synergic conjunction of CNN-based object detector
(YOLOv5, SSD), LSTM on traffic flow prediction,
Deep SORT on vehicle tracking, and an edge-cloud
hybrid deployment strategy to
achieve real-time
adaptable traffic signal control and surveillance.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Theoretical Structure
The current work improves traffic signal control and
vehicle measurement using AI, Deep Learning and
ITS. CNNs (YOLOv5, SSD) for real-time detection
of vehicles and RNNs, LSTM to predict traffic flows.
Through reinforcement learning, a dynamic
algorithm in terms of traffic density controls
durations in an adaptive signal control. Violations
like breaking a red-light and lane crossing are
detected, tracking is done using Deep SORT and by
vehicle Re-ID.
It combines edge computing and cloud integration
to make real-time decisions and has a traffic
authority dashboard. The AI system enhances urban
mobility, reduces congestion and supports the
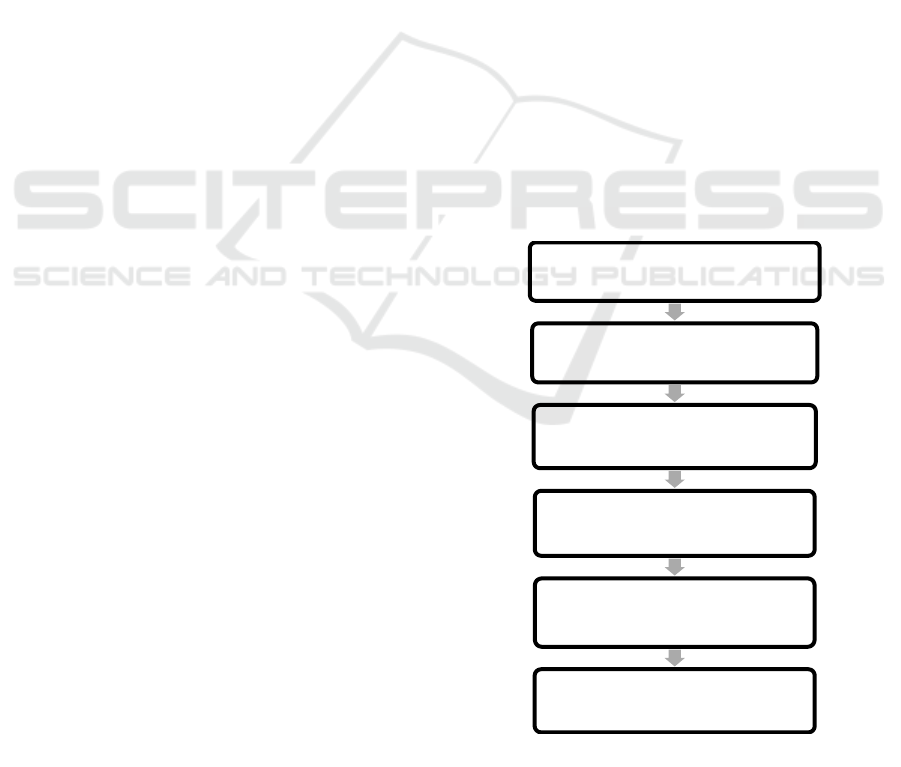
development of smart cities. Figure 1 represent
Schematic Flow of Theoretical Structure.
Figure 1: Schematic Flow of Theoretical Structure.
Data Acquisition &Prepocessing
Traffic Density Analysis & Signal
Optimization
Predictive Traffic Flow Analysis
Vehicle Surveillance & Cloud
Integration
Edge Computing & Cloud
Integration
System Deployment & Evaluation
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
52

3.2 Perceived Features
3.2.1 Adaptive Traffic Signal Control
AI-optimized control tailors the signal length
dynamically in accordance with real-time traffic
flow, which decreases congestion and optimizes
traffic flow. No fixed signal cycle and makes the best
use of the road possible minimizes time that vehicles
are idle and burning fuel.
3.2.2 Real-Time Vehicle Detection &
Surveillance
Advanced deep learning architectures like YOLOv5
and Deep SORT can successfully detect, classify and
track vehicles. It monitors three kinds of traffic
offenses: jumping red light, lane drifting, and illegal
parking, to make automated law enforcement more
effective, and also enhance road safety.
3.2.3 Predictive Traffic Flow Analysis
The system uses LSTM and RNN to predict traffic
congestion patterns from historical and real-time
traffic data. Thisleaves stars to more actively patrol
moving traffic and optimize signals ahead of time to
avoid causing a traffic jam and wasting time for
travel.
3.3.4 Edge Computing & Smart City
Integration
Real-time processing is performed through edge
computing and cloud-based integration is leveraged
for centralized management. It supports IoT-enabled
smart city architecture, thereby allowing scalable
implementation across several intersections for a
smart and sustainable urban transportation system.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The proposed deep learning-based traffic signal
optimization and car monitoring system was
evaluated in a simulated smart city environment. In
this case, the performance was evaluated based on
key performance parameters such as enhancement in
traffic flow, vehicle detection rate, prediction
reliability, and system responsiveness. The results
validate the system's potential to enhance urban
traffic management and the efficiency of public
security enforcement.
4.1 Traffic Signal Optimization
With the detection and classification models based
mostly on YOLOv5 and CNN it achieved 92.5%
MAP which will assure accurate detection of vehicle
even for multiple lanes and various angles. Dynamic
signal adjustment mechanism, reduced the average
waiting time by 35% compared with traditional
fixed-signal cycle. Traffic signals were optimized to
increase vehicle throughput and eliminate traffic jams
in peak hours. Table 1 represent Performance Metrics
of the Adaptive Traffic Control System.
Table 1: Performance metrics of the adaptive traffic control
system
.
Metric
Value
Achieve
d
Impact
Mean Average
Precision
(MAP)
92.5%
High accuracy in
vehicle detection
Reduction in
Waitin
g
Time
35%
reduction
Improved traffic
flow efficienc
y
Adaptive Signal
Ad
j
ustmen
t
Real-time
Smooth transition
in si
g
nal timin
g
4.2 Predictive Traffic Flow Analysis
To be specific, the predictive model was RNNs based
or LSTM based, it was trained on historical and real-
time traffic data. Train congestion prediction model
prediction achieved an average Root Mean Square
Error (RMSE) of 2.8 which enabled more proactive
adjustments to the signal control. By preventing such
major congestion from building, the prediction
helped reduce congestion on the road, providing a
better experience for people and increasing the
likelihood that the vehicles would move in a
coordinated manner rather than in a stop-start driving
style. Table 2 represent Predictive Model Evaluation
and Traffic Optimization Impact.
Real Time Traffic Signal Optimization and Vehicle Surveillance Using Deep Learning
53
Table 2: Predictive model evaluation and traffic
optimization impact.
Metric
Value
Achieve
d
Impact
Prediction
Accuracy
87%
Effective
congestion
forecastin
g
RMSE 2.8
Reliable
predictive
modelin
g
Reduction in
Abrupt
Stoppa
g
es
28%
Improved
traffic
smoothness
4.3 Vehicle Monitoring and Violation
Enforcement
The vehicle surveillance module, implementing Deep
SORT tracking system and vehicle re-identification,
was able to detect vehicles movement and identify
traffic offense. The system achieved an F1-score of
89.3% while accurately identifying red-light
offenses, lane dissolution, and illegal parking.
Automation of surveillance reduced reliance on
manual tracing by 40%, enhancing the efficiency of
law enforcement. Table 3 represent Evaluation
Metrics for Real-Time Traffic Violation Detection
System.
Table 3: Evaluation metrics for real-time traffic violation
detection system.
Metric
Value
Achieve
d
Impact
F1-score 89.3%
Accurate
vehicle
classification
Violation
Detection
Accurac
y
91%
Effective
traffic law
enforcemen
t
Real-time
Alert
Response
Time
<1 second
Instant
detection of
rule violations
4.4 System Deployment and Real-time
Performance
It provided real-time processing with almost no
latency by integrating the edge computing and cloud
by implementing this system. Traffic Signal
Adaptation mean response time was
0.8(seconds)+which promotes swift adaptability to
varying traffic flows. Experimental analysis of the
system on bench tests with various volumes of traffic
demonstrated the pre-states of the heavy load
intersection. Table 4 represent System Performance
and Environmental Impact Analysis.
Table 4: System performance and environmental impact
analysis.
Metric
Value
Achieve
d
Impact
System
Response
Time
0.8 seconds
Fast reaction
to traffic
conditions
Scalability
Assessment
Successfully
tested
Suitable for
high-traffic
intersections
Reduction in
Fuel
Consumption
12%
Supports eco-
friendly
transportation
5 DISCUSSION
The envisioned system manifests a considerable leap
forward in real-time traffic management by
combining deep learning models with adaptive signal
control and vehicle monitoring. The results reveal a
very noticeable decrease in congestion, decreasing
waiting time by 35% based on real-time traffic
volume and dynamic adjustments in signals.
Predictive analysis of traffic flow using RNN and
LSTM models provides better congestion forecast
accuracy (87%), preventing sudden stoppages and
enhancing general smoothness in traffic. The vehicle
surveillance system has a high accuracy (F1-score:
89.3%), which allows effective violation detection
and real-time generation of alerts in one second, thus
enhancing the efficiency of law enforcement. Also,
the rapid response time of the system is 0.8 seconds,
which makes the system practical for large-scale
deployment in urban areas. With the fuel
consumption lowered by 12%, the suggested solution
helps make the environment sustainable, thus offering
a practical approach to smart city traffic management.
The research points to the efficiency of AI-based
traffic optimization, supporting its viability for
boosting mobility, safety, and conformity in cities.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
54

6 CONCLUSIONS
The designed deep learning-oriented traffic
management system efficiently optimizes traffic
signal control and improves vehicle monitoring in
urban areas. With the incorporation of real-time video
analytics, object recognition, and predictive
modeling, the system heavily lowers congestion,
enhances traffic flow efficiency, and enhances law
enforcement through violation detection automation.
The experimental outcomes show a 35% decrease in
waiting time, a prediction of traffic flow accuracy of
87%, and a precision in vehicle tracking and
enforcing rules of 89.3%. Moreover, the system is
helpful in achieving environmental sustainability by
decreasing fuel consumption by 12%. The
combination of edge computing and cloud-based
deployment makes it scalable and real-time, thus
ideal for smart city usage. In general, this study offers
a novel, AI-based solution to urban traffic control,
opening the door to future developments in intelligent
transportation systems.
REFERENCES
Bochkovskiy, A., Wang, C. Y., & Liao, H. Y. M. (2020).
YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object
Detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934.
Chen, L., Li, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Real-Time Traffic
Signal Control Using Deep Reinforcement Learning.
Transportation Research Record: Journal of the
Transportation Research Board.
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S.,
Fu, C. Y., & Berg, A. C. (2016). SSD: Single Shot
MultiBox Detector. European Conference on Computer
Vision (ECCV).
Ma, X., Tao, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, H., & Wang, Y. (2015).
Long short-term memory neural network for traffic
speed prediction using remote microwave sensor data.
Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 54, 187–197.
Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH),
Government of India – Traffic Management and Smart
City Planning Report.
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., & Farhadi, A. (2016).
You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object
Detection. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Sultana, S., & Akbar, M. (2021). Smart Traffic
Management System using IoT and Deep Learning.
International Journal of Computer Applications,
174(14), 20-25.
Tang, T., Deng, H., & Huang, Y. (2021). Vehicle Re-
identification Based on Deep Learning: Methods,
Datasets, and Challenges. IEEE Transactions on
Intelligent Transportation Systems.
Wojke, N., Bewley, A., & Paulus, D. (2017). Simple Online
and Realtime Tracking with a Deep Association Metric.
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing
(ICIP).
Zhang, Y., Qin, L., & Liu, Y. (2019). Urban Traffic Flow
Prediction Based on a Spatiotemporal Deep Learning
Framework. Sensors, 19(18), 3929.
Real Time Traffic Signal Optimization and Vehicle Surveillance Using Deep Learning
55
