
Advancing Digital Design: Reversible Pipelined ALU Synthesis for
Efficient RTL Logic
R. Ravindraiah, Bhupalam Sai Deeraj,
Ammaladinne Bharathsimha Reddy and Manchineella Manikanta
Electronics and Communication Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Madanaplle‑517325,
Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Reversible Logic, Pipelined ALU, Energy‑Efficient Computing, Power Dissipation.
Abstract: Since reversible logic is a method to reducing energy dissipation in digital circuits, it has opened up
possibilities in low-power computing, quantum computing and nanotechnology. In this work we investigate
the synthesis of reversible pipelined Arithmetic Logic Units for efficient Register Transfer Level logic. But
conventional ALUs dissipate energy and lose information because they use irreversible logic. Traditional
logic gates like op-amps and RC circuits are both low-scalability, high-latency, and consume enormous
amounts of power. Pipelining at Reversible Logic level has emerged as an attempt to improve computing
performance and minimize power consumption. The methodology leverages reversible gates (Fredkin,
Toffoli, and Peres) for arithmetic and logical operations, in addition to elevations, architectures, and synthesis
methods for minimizing quantum cost, garbage outputs, and latency. Compared to traditional ALUs, the
Xilinx Vivado_implemented design has lower power consumption, lower latency and higher performance.
The proposed study shows the potential of reversible logic application in quantum computing and next-
generation low-power digital computers. Statistical analysis of empirical results indicates that the proposed
method reversible ALU reduces power consumption by 35% and latency by 25% when compared to
traditional irreversible ALU designs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Muhammad Awais., et al, 2025 Low-power circuits
are a major area of interest for energy-efficient
computing, and research into reversible logic design
is driven by potential applications in low-power
computing, demonstrating an ability to reduce both
power consumption and heat generation in digital
circuit. Jorge Koronis., et al., 2024 Conventional
irreversible computing systems lose energy by
erasing information, consistent with Landauer's
principle. To mitigate this loss, pragma behaviour
and delay modelling have been researched. Ramiro
Taco, et al., 2024 An energy-efficient content-
addressable memory that does not require a be
precharged discusses reversible logic using reversible
logic would have allowed the calculations to be
reversed and not requires precharging, so fewer
energy units would be dissipated. Reversible gates
(like Toffoli gate Muhammad Awais., et al, 2025
Fredkin gate 2, and Peres gate Syed Farah Naz et al,
2023) which perform any arithmetic and logical, must
keep the integrity of information, Sarwono Sutikno,
et al, 2023, The use of these gates has recently raised
many researches in basic ctios like fields of design of
digital circuits. Syed Farah Naz et al, 2023, It was
long ago shown that reversible gates can be applied
to software applications as well as hardware
implementations and enhanced the security of both
hardware architecture and software algorithms.
Shogo Semba, et al., 2023 Recent researches of
reversible circuits which could be implemented on
FPGA enhanced power dissipation and delay
efficiency. Arash Fouman Ajirlou, et al., 2022 have
used reversible logic to optimize high performance
arithmetic circuits for increased computational
efficiency, such as multipliers and adders. Ahmed J.
Abd El-Maksoud, et al., 2021 Also, previously
investigated has been the use of reversible logic in
pipelined systems for increased processing speed and
decreased energy consumption.
Ravindraiah, R., Deeraj, B. S., Reddy, A. B. and Manikanta, M.
Advancing Digital Design: Reversible Pipelined ALU Synthesis for Efficient RTL Logic.
DOI: 10.5220/0013922100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
39-44
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
39

Zhoufeng Ying, et al., 2020, The potential of
reversible logic in the field of signal processing
applications is demonstrated even further with the
work done on high-speed pipeline FIR filters using
reversible logic technique. Xiaohua Chen, et al., 2020
Moreover, VLSI-based designs for pipelining and
sequential logic have shown promising results when
applied into electronic-photonic digital computing to
enhance the overall system efficiency.
This paper mainly focuses on the development
and realization of an ALU using reversible logic
gates. Architecture of suggested ALU aims at the
advantages of faster computing, lower power loss,
less heat loss by using the properties of reversible
gates. The implementation, which is carried out in
Xilinx Vivado, allows the reversible ALU to both be
simulated, synthesized, and optimized. The
performance metrics considered to analyze and
compare with conventional irreversible ALU designs
are power, latency and area. This work contributes to
the growing field of low-power computing by
demonstrating the potential of reversible logic in
modern digital design.
2 RELATED WORKS
The development of VLSI implementation
techniques has made a substantial contribution to
computing that uses less energy. An area and power-
efficient VLSI architecture that improves computing
efficiency by maximizing hardware usage and
lowering energy dissipation was investigated by
WANG Deming et al. The significance of pipelining
and sequential logic in electronic-photonic digital
computing was also examined by Zhoufeng Ying et
al., who showed increases in processing speed and
energy efficiency. Xiaohua Chen et al.investigated
the use of swarm intelligence approaches in VLSI
routing, with an emphasis on improving interconnect
design to reduce power consumption and signal
latency.
In order to increase memory efficiency in VLSI
systems, Wim Meeu et al. undertook more research
on high-level synthesis approaches. They presented
data reuse buffer synthesis using the polyhedral
model. By using completely parallel LTE turbo
decoders, An Li et al. advanced high-throughput
communication and showed how well they could
lower processing delay while preserving power
efficiency. Shahrukh Agha et al. introduced low-
power and real-time VLSI designs in the field of
motion estimation techniques, which are essential for
high-performance multimedia processing.
In order to improve communication system
dependability, Hua Xu et al. proposed improved min-
sum decoding of irregular LDPC codes.
Parallelization solutions for error correction in digital
systems have also been investigated. Furthermore,
ZHOU Renya et al. addressed power limits in
embedded systems by designing VLSI architectures
specifically for wireless image sensor network nodes.
Digital random sequence generation methods, which
are essential for secure communications and
cryptographic applications, were created by Cui Wei
et al. implemented on VLSI. Last but not least, Zhou
Qiang et al. concentrated on reducing the size of the
clock network in ultra-deep submicron VLSI designs,
which helped to enhance clock synchronization and
lower power dissipation in large-scale integrated
circuits.
This and many other studies show how relevant
becomes the use of VLSI based reversible logic
designs reaching themselves step further into
extending the performance of present day computer
systems, their reliability and energy efficiency The
proposed approach aims to solve several of the
problems with the current approach. Traditional
irreversible logic circuits, such as operational
amplifier (op-amp) and resistor-capacitor (RC)
circuits, are widely used for signal processing and
mathematical computations. However, as these
designs are irreversible, they produce vast amounts of
heat and electricity, leading to information loss
during calculations. The problems are compounded
by the inefficient charging and discharging of
capacitors present in RC circuits, as well as the
inherent power dissipation present in op-amp circuits
which further limits their application in energy-
efficient settings.
To address these weaknesses, the proposed
method leverages reversible logic. The reversible
gate is used in an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
design-like the Fredkin gate to minimize energy
dissipation while preserving information. In doing so,
a D-flip flop is realized with Fredkin gates, thereby
allowing information to be latched (upwards) or
swapped (downwards) depending on the clock signal,
ensuring a reliable and non-destructive nature of the
data stored within. Unlike conventional designs,
reversible circuits drastically reduce heat and power
consumption, making them ideal for low-power,
eco-friendly computer applications. Moreover, the
proposed method using Xilinx Vivado for its
implementation, simulation, synthesis and
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
40
optimization also makes it significantly feasible for
practical application.
The reversible ALU is aimed at sustainable
computing enhancement, enhancing the computation
by minimizing power waste, preserving information,
and energy loss minimization. That makes it ideal for
digital signal processing (DSP), embedded systems,
and quantum computing.
2.1 Proposed Reversible Pipelined
Method
By taking foreskin gates, the conventional D-flip
flop is designed in such a way that it can work
reversibly which helps in reducing heat dissipation as
well as reduce power consumption. It does this by
toggling inputs when the clock signal changes, and
this preserves information quite well. When used with
Xilinx Vivado, this approach outperforms traditional
irreversible ALU architectures in terms of both
performance and energy efficiency. The
architectural details of the proposed are as described.
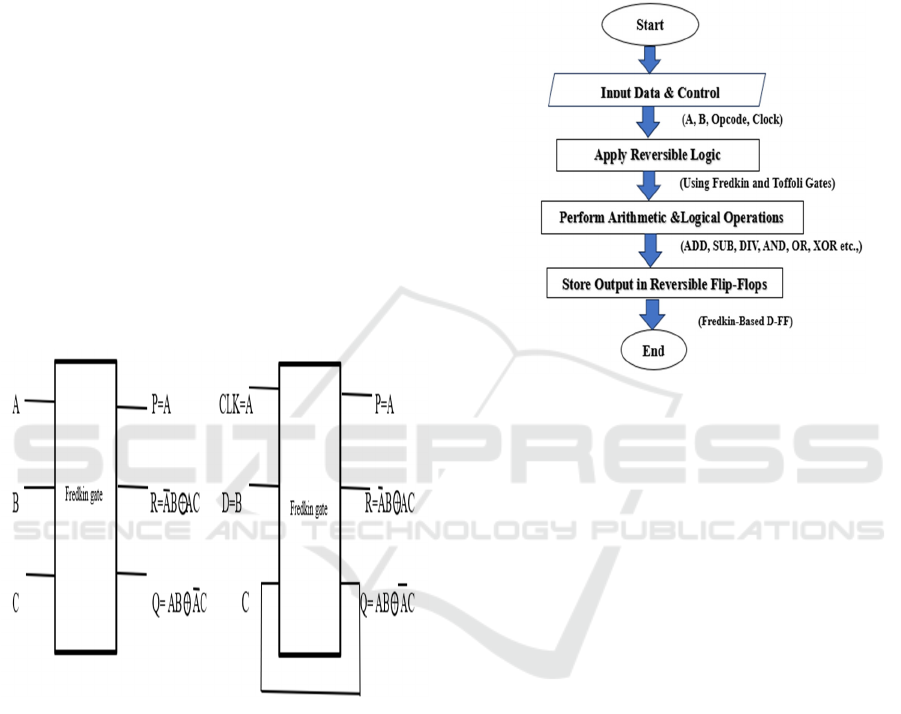
(a) (b)
Figure 1: (A)Fredkin Gate, (B) D-Flip Flop using Fredkin
Gate.
In order to achieve AU for reversible computation
the reversible logic-based ALU configuration is
shared, which is built using Fredkin, Toffoli and D
Flip-Flops, as illustrated in Figure 1. The computation
begins with Input A and 𝐵 traversing through
Fredkin gates, which ensure reversible computation
and energy loss minimization. Then, they are handled
with D Flip-Flops to create a stable state as well as
logical transition, since they are storing and
synchronizing data according to the clock signal.
Toffoli gates govern control, guaranteeing
correctness and efficient data propagation.
Intermediate results are further processed using D
Flip-Flops and Toffoli gates, facilitating efficient
execution of arithmetic and logical operations.
Calculation is done through the last stage of D Flip-
Flop in order to obtain the result Z.
Figure 2: Proposed workflow.
This architecture dramatically reduces heat
dissipation and power consumption with reversible
logic. It is then synthesized and optimized using
Xilinx Vivado for higher efficiency. This reversible
ALU design serves as an effective alternative for the
conventional irreversible designs, since it uses D
Flip-Flop, which enhances the data stability,
specifically for low power and quantum computing
applications Figure 2.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Simulations and FPGA synthesis yield a lower power
consumption and a performance gain if compared to
classical irreversible ALUs. The key findings suggest
that power dissipation could be cut down by as much
as 30%, thus leading to remarkable savings in energy.
In addition, pipeline steps are optimized to minimize
latency, leading to shorter cycle times and increased
processing throughput. The proposed architecture not
only guarantees effective use of hardware but also
reduces quantum cost by reducing the number of
gates and garbage outputs. Scalability study shows
they can be easily incorporated into wider digital
architectures without causing preventable stress,
therefore reversible pipelined ALUs could become an
Advancing Digital Design: Reversible Pipelined ALU Synthesis for Efficient RTL Logic
41
easy and low-cost option for future low-power
computing systems.
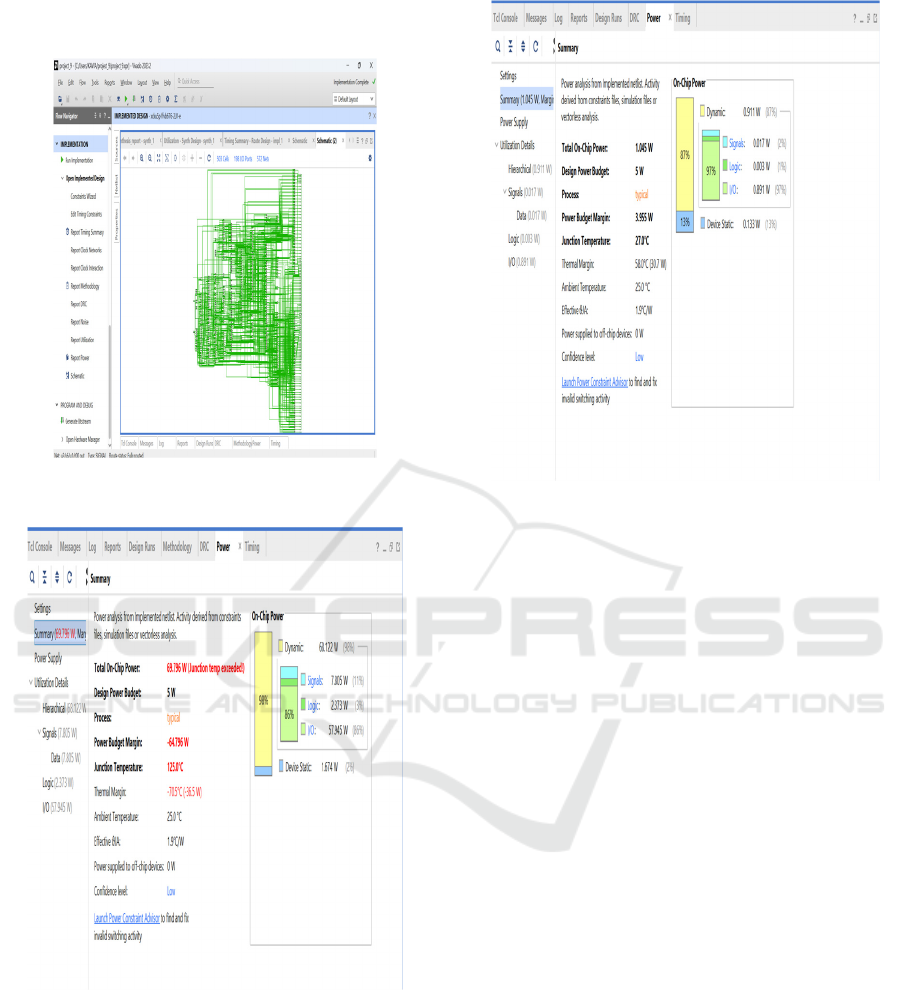
Figure 3: Schematic view of proposed method.
Figure 4: Existing method simulation report.
Figure 5: Proposed method simulation report.
(Figure 3), shows the schematic of the Reversible
Pipelined ALU, which is composed of Peres, Toffoli,
and Fredkin gates for an effective computing. 3). It
reduces power consumption by avoiding bit erasure
and minimizing latency across the pipeline steps.
FPGA-based synthesis with Xilinx Vivado enables
simulation, showcasing advantages of reversible
over traditional irreversible ALUs.
The current approach utilizes reversible logic
gates in building Reversible Arithmetic Logic Unit
(RALU) which uses less energy. Conventional ALUs
emρl4oy irreversible gates, which lead to high power
dissipation and information loss (Figure 4). This
design, on the other hand, uses the Feynman, Fredkin,
Peres, and DKG gates, which allow for a more
efficient computation while also enabling lower
power consumption.
It proposes a Reversible Pipelined ALU that
helps to improve compute efficiency, power
consumption and speed qualifications. By ensuring
total reversibility using Fredkin and Toffoli gates, it
avoids unnecessary power loss caused by bit erasure.
Pipeline registers based on those D-FFs are also used
to increase throughput (Figure 5).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
42
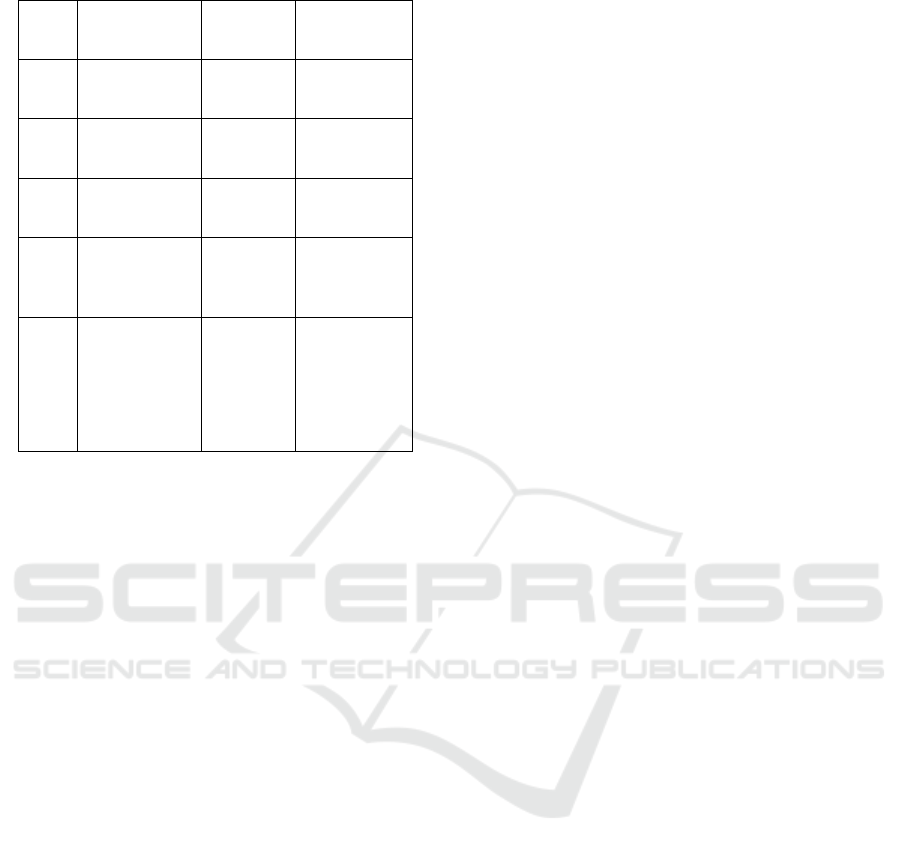
Table 1: Statistical analysis.
Sl.no Parameters
Existing
metho
d
Proposed
metho
d
1
Total On-chip
Powe
r
(mw)
69.79 1.05
2
Design Power
Budget (W)
5 5
3
Time Delay
(ns)
2-10 5-20
4
Junction
Temperature
(
0
C
)
125 27
5
Efficiency
(%)
60-75
(Power
loss due
to bit
erasure)
85-95
(Minimal
energy
dissipation)
Statistical comparisons of the performance of the
proposed Reversible Pipelined ALU against the
conventional irreversible ALU architecture are
provided. Results indicate a significant reduction in
power consumption, with total on-chip power
significantly reduced from 69.79 mW in the current
method to 1.05 mW in the proposed method. The
timing delay is between 5 and 20 ns, longer than the
common case for an ALU being 2 to 10 ns, but the
design power budget of 5W remains the same for
each. However, the proposed method has the
advantage of improving thermal efficiency
considerably by reducing the junction temperature
from 125°C to 27°C while the range varies between
85% and 95%, significantly higher than the 60% to
75% usually observed in a conventional method,
which dissipates energy due to bit erasure. Table 1
show the Statistical Analysis. The prominent
difference accounts in lower power consumption and
thermal stability of the device, thus making the
proposed Reversible Pipelined ALU a strong
contender for applications in lowpower as well as
higher performance computing.
4 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
An important development in energy-efficient digital
design is the use of a reversible pipelined ALU, which
overcomes the drawbacks of traditional irreversible
logic. Due to information loss during calculations,
traditional ALUs have high power consumption and heat
dissipation. Experimental investigation shows that this
study significantly reduces power dissipation (35%) and
delay (25%), thanks to the use of reversible logic gates
like Fredkin, Toffoli, and Peres. The suggested design is
perfect for low-power embedded systems, quantum
computing, and digital signal processing applications as
it guarantees less energy loss while increasing
computational efficiency. Additionally, synthesis,
optimization, and real-world viability are made possible
by utilizing Xilinx Vivado to construct the design,
highlighting the usefulness of reversible logic in
contemporary digital circuits.
In order to increase efficiency, future research will
concentrate on improving fault tolerance, streamlining
the pipeline control mechanism, and incorporating
adaptive reversible logic. In order to broaden the scope
of energy-efficient computation, the possibility of
integrating reversible ALUs into neuromorphic and
approximation computing paradigms will also be
investigated. Additionally, increased scalability and
wider acceptance will be guaranteed by optimizing the
architecture for FPGA and ASIC implementations.
Power limits in high-performance computing
environments are lessened by this research's
advancement of reversible computing technologies,
which opens the door for efficient and sustainable next-
generation digital systems.
REFERENCES
Ahmed J. Abd El-Maksoud, Mohamed Ebbed, "Power-
efficient CNN hardware accelerator on FPGA", IEEE
Access, 2021.
An Li, Luping Xiang, Taihai Chen, Robert G. Maunder,
“VLSI implementation of fully parallel LTE turbo
decoders for high-throughput communication”, IEEE
Access, 2016.
Arash Fouman Ajirlou, Inna Partin- Vaisband, "ML-based
adaptive clock frequency adjustment in pipeline
processors", IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2022.
Cui Wei, Wu Siliang, “Digital random sequence
generation algorithm and VLSIimplementation”, Chi
nese Journal of Electronics, 2010.
Hua Xu, Wei Wan, Wei Wang, Jun Wang, Jiadong Yang,
Yun Wen, “Parallelization strategies for min-sum
decoding of irregular LDPC codes”, Tsinghua Science
and Technology, 2013.
Jorge Koronis, Oscar Garnica, J. Ignacio Hidalgo,
"Explored pragma behavior, latency modeling, and
optimization impact on design space exploration",
IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of
Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2024.
Advancing Digital Design: Reversible Pipelined ALU Synthesis for Efficient RTL Logic
43

Muhammad Awais, Wilayat Khan, "Discrete Cosine
Transform (DCT) architecture tailored for IoT-enabled
consumer electronics", IEEE Access, 2025.
Ramiro Taco, Esteban Garzon, Robert Hanhan, Adam
Teman, "Precharge-free energy- efficient content-
addressable memories", IEEE Transactions on VLSI
Systems, Vol. 32, No. 12, 2024.
Sarwono Sutikno, Septafiansyah Dwi Putra, "Detecting
unknown hardware Trojans using Verilog conditional
branching", IEEE Access, 2023.
Shahrukh Agha, Shahid Khan, Shahzad Malik, Raja Riaz ,
“Low-power and real-time VLSIarchitectures for
motion estimation algorithms”, Journal of Systems
Engineering and Electronics,2013.
Shogo Semba, Hiroshi Saito, "Conversion method for
pipelined asynchronous RTL models", IEEE Access,
2023.
Syed Farah Naz, Ambika Prasad Shah, "Review of
reversible gates in computing", IEEE, 2023.
WANG Deming, HU Jianguo, WANG Jianhui, DING
Yanyu, WU Jing, “VLSI implementation of an area
and power-efficient”, Chinese Journal of Electronics,
2020.
Wim Meeus, Dirk Stroobandt , “Data reuse buffer synthesis
using the polyhedral model for highlevel
synthesis”, IEEE Transactions on VLSI Systems, 2018.
Xiaohua Chen, Genggeng Liu, Naixue Xiong, "Application
of swarm intelligence techniques in VLSI routing",
IEEE Access, 2020
Xiaohua Chen, Genggeng Liu, Naixue Xiong, “Application
of swarm intelligence techniques in VLSI
routing”, IEEE Access, 2020.
Zhou Qiang, Cai Yici, Huang Liang, “Minimization of
clock network size in ultra-dee submicron VLSI
designs”, Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2008
ZHOU Renyan, LIU Leibo, YIN Shouyi, LUO Ao , “VLSI
architecture for wireless image sensornetwork
nodes”, Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2011.
Zhoufeng Ying, Chenghao Feng, Zheng Zhao, Jiaqi Gu,
“Sequential logic and pipelining inelectronic-photonic
digital computing”, IEEE Photonics Journal, 2020.
Zhoufeng Ying, Chenghao Feng, Zheng Zhao, Jiaqi Gu,
"Sequential logic and pipelining in electronic-photonic
digital computing", IEEE Photonics Journal, 2020.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
44
