
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors
Anirudh N., Dhanush Kumar R. and Ramya M.
St. Joseph’s Institute of Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Efficiently, Crucial, Essential.
Abstract: This e-blood and plasma donation system will be done in Java, HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, and SQL. The primary
features of this system include login and registration for the user and a donation module that connects donors
to emergency patients. The system encompasses the back-end handling by Java, HTML, CSS, and Bootstrap
for interface and responsiveness, while SQL handles the database. An account can be created and a user
logged in through the registration page. The blood donation module offers support in the searching process
by selecting types, locations, and other criteria to identify donors, as well as booking donations, tracking
history, and receiving alerts. A plasma donation module allows finding donors, booking appointments, and
keeping track of the records. For the database storage of user information, donor details, and appointment
records, SQL would be used to make sure data integrity and easy access.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blood donation is harmless and safe in the body.
Instead, it is a social responsibility. The donor is
donating for it as it will be used in saving lives of his
fellow beings. He himself may use the same during his
own need. MILLIONS OF people owe their lives to
people whom they will never know or meet in their
lifetime. They are none other than those great souls
who gladly and graciously donated blood without their
expecting or seeking a single reward in return-here we
have our voluntary unpaid donors. Voluntary unpaid
donors form the very bedrock of a safe and reliable
blood supply that has the potential to rescue millions
of human beings from the jaws of untimely death and
despair. Hearty appreciation and deep gratitude should
be extended to these unsung heroes without whom
countless lives could have been sustained and
preserved through their noble acts.
June 14th Is Observed as International Blood
Donars Day. Nothing can be compared to the
preciousness of human blood. Even with the rapid and
wonderful conquests of the medical science of today,
no laboratory manufactures blood. It is only in human
beings that human blood is made and circulated. And
for those who require blood to save their lives, sharing
from other fellows is the only means. Therefore, it can
be said that donation and particularly voluntary
donation forms the only method of blood collection
kept safely that meets the emergency needs and
imperative for preserving life.
International Blood Donors Day-it cannot be
priced more than once in every lifetime, as is the
human blood, on June 14th. It can come only from
human beings, and for some people, it's a matter of life
and death. Only the blood donation system can meet
the urgent lifesaving needs reliably. Figure 1shows the
development of deep learning in industries It is a risk-
free way of obtaining what is desired as voluntary
donation.
Figure 1: Development of Deep Learning in Industries.
840
N., A., R., D. K. and M., R.
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors.
DOI: 10.5220/0013921600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
840-849
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 ROLES OF BLOCKCHAIN
ACROSS INDUSTRIES
2.1 Finance & Banking:
It has transformed the banking industry with a safe,
decentralized, and open manner of transacting.
Middlemen are present in conventional banking
systems, causing delays and increased fees for
transactions. Blockchain removes middlemen, thus
making cross-border transactions more affordable and
efficient.
2.2 Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, blockchain enhances the
security and integrity of patient records. Medical
records on a blockchain are Immutable, reducing the
risk of data leakage and unauthorized access.
Blockchain also improves drug traceability to
authenticate the genuineness of drugs and prevent
counterfeit drugs from entering the market.
2.3 Real Estate
The real estate sector benefits from blockchain by
reducing the fraud and streamlining properly
transactions. Blockchain enables secure and
transparent property ownership records, eliminating
the need for intermediaries like brokers and lawyers.
It also facilitates seamless buying, selling, and leasing
properties, reducing paperwork and increasing the
efficiently.
2.4 Decentralized Finance DeFi
Blockchain innovation since it eliminates the
middlemen in transactions, such as banks. This way,
people can lend, borrow, or exchange their money
without a central authority. Consider smart contracts
as the new means of delivering financial services to a
broader and even more distributed audience
worldwide in an innovative manner. 5. Digital
Identity Management Of the features that make the
blockchain more impressive in digital identity
management is the ability of people to have control
over their personal data without having central
authorities. The innovation provides maximum
protection against privacy invasion and identity theft
in matters of medicine and finance authorities to
direct this information. Figure 2 shows how
blockchain works in industries.
Figure 2: Blockchain Works in Industries.
3 APPLICATION OF BLOOD
AND PLASMA DONATION
SYSTEM
3.1 Hospital Support During
Emergency Conditions
This system plays a vital role in emergency medical
cases by granting hospital immediate access to blood
and plasma donors. Patients in need of immediate
transfusions from accidents, surgery, or serious
illness can locate compatible donors in real life. The
system guarantees life-saving donations and are
delivered to patients in the shortest time possible,
reducing delays in life-saving therapy.
3.2 Donor Management System
The system streamlines donor management by
tracking donors’ details like blood group, availability,
and donation history. This allows hospitals to have a
steady database of available donors who can be
summoned at any time a specific blood group is
needed. Automating donor management, the system
enhances the efficiency of blood banks and medical
facilities. Figure 3 shows the Blood and plasma
donation management system.
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors
841
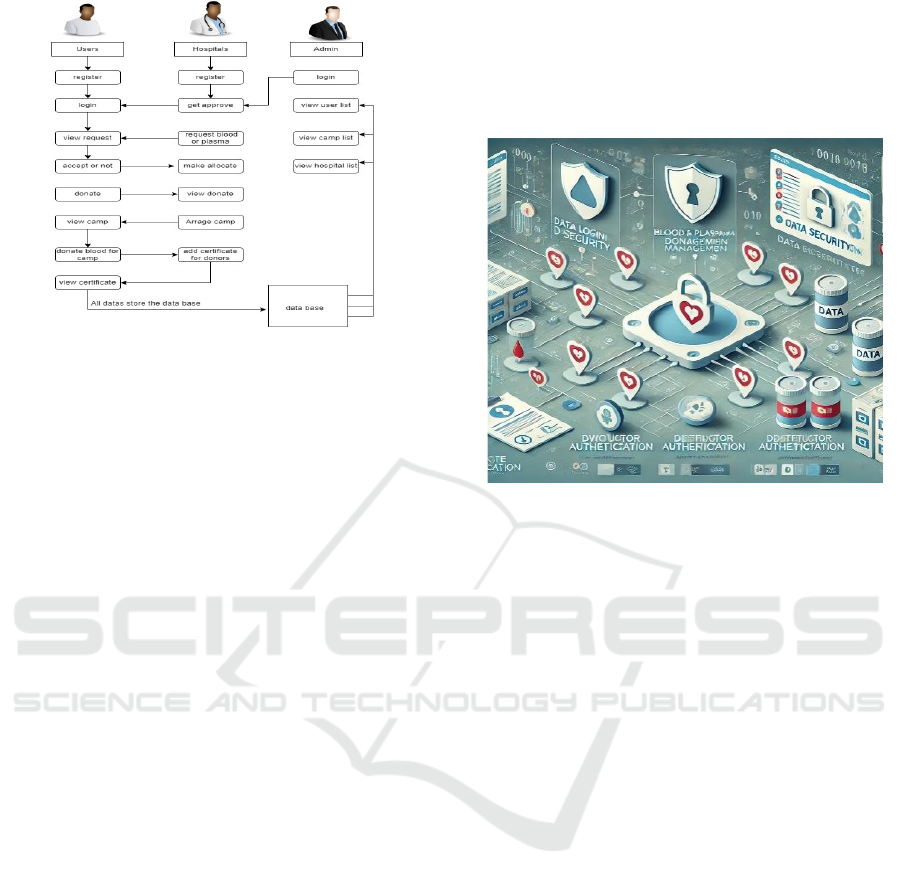
Figure 3: Blood and Plasma Donation Management System.
3.3 Community Engagement and
Awareness
The system encourages individuals to participate in
blood and plasma donation drives by providing
notifications about upcoming donation camps. By
educating the public on the importance of donating
blood and plasma, it fosters a culture of voluntary
donation. This helps address shortages in blood banks
and ensures a steady supply for medical emergencies.
3.4 Hospital and Blood Bank
Collaboration
Hospitals and blood banks benefit from a centralized
platform that connects them with donors and other
medical institutions. By sharing data on available
blood units and donation requests, healthcare facilities
can coordinate effectively. This reduces wastage of
stored blood, ensures better inventory management,
and improves response time during emergencies.
3.5 Medical Campaign and Awareness
Drives
Hospitals can organize and manage blood and plasma
donation camps through the system. The platform
allows event notifications to be sent to registered
users, improving participation rates. Donors can also
receive certificates for their contributions,
encouraging more individuals to donate regularly.
3.6 Integrated Data Security
The system applies SQL in accessing databases of the
hospital where donor and patient information would
be securely stored and retrieved. Encryption data will
ensure the maintenance of privacy, which is quite
critical in a healthcare environment. Figure 4 shows
the data security in blood and plasma management
system. Therefore, it ensures that only authorized
personnel get to access sensitive medical data due to
strict login mechanisms.
Figure 4: Data Security in Blood and Plasma Management
System.
3.7 Real-Time Notifications and Alerts
One of the most significant use of the system, one has
been particularly geared to maximize efficiently and
responsiveness within healthcare, it its capability for
real-time notification to be disseminated. Donors are
timely reminded of available opportunities to support
through donation, while hospitals are immediately
notified every time there are available donors who
3.8 Digital Certification
The system allows both donors and hospitals to
schedule and manage donation appointments
efficiently. Donors can book slots at nearby donation
centers or hospitals, reducing wait times and
optimizing the donation process. Hospitals, in turn,
can plan their blood collection drives based on real-
time availability of donors. After a successful
donation, the system can generate digital certificates
for donors, recognizing their contribution to saving
lives. This feature encourages regular donations by
offering an acknowledgment of their efforts. These
certificates can also serve as proof of eligibility for
special benefits in health programs or government
initiatives.
This Also Feature Fosters Regular Donations by
Recognizing the Contributor. These Certificates
Could Also Be Used as Proof of Eligibility for Special
Benefits in Health Programs or Government
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
842
Initiatives. Figure 5 represents the blood plasma for
donating.
Figure 5: Blood Plasma for Donating.
4 IMPACT OF BLOOD AND
PLASMA DONATION SYSTEM
4.1 Faster Access to Life Saving
Donations
The system considerably reduces the time taken to
find suitable plasma and blood donors, enabling the
hospital to respond promptly in an emergency. In
emergencies such as accidents, surgeries or serious
headaches, the availability of donors saves lives.
4.2 Improved Donation Process
Many of the features provided in the modules
enhance the functionality, However, the integration
of modules to work together to improve the donation
experience of the donors is the key. It relieves and
optimizes the entire donation experience for both
medical institutions and individual donors involved in
such vital processes. Thus, with the emphasis of these
advancements, a much consistent and systematic
structure for assisting humanitarian work can be seen
as an evident increase in the amount and consistency
of the contributions.
4.3 Increased Blood and Plasma
Availability:
By connecting donors directly with hospitals and
blood banks, the system helps maintain a steady
supply of blood and plasma. This reduces shortages
and ensures that even rare blood groups are readily
available. As a result, hospitals can meet patient
demands more efficiently without relying on urgent
donation on crisis.
Figure 6: People Volunteered in Donation.
By this system method, an acceptor can get Blood and
plasma in a faster rate without worrying about their
problem to catch the donors. Hospitals can also meet
patient demand more efficiently without waiting for
emergency donations during crises. Figure 6 shows
the people volunteered in donation. The Blood and
plasma foster without any concern about the problem
of finding a donor.
4.4 User Friendly Inerface an
Accessibility
The Blood and Plasma Network uses a high
responsive design framework created with Bootstrap
that is meant to ensure smooth accessibility across
multiple devices. This carefully designed architecture
increases the ease through which interaction is
achieved between the system, as well as between
health facilities, and the donor from any form of
device use. It ensures that users, including those in
rural or underserved settings, can access very
essential donation services in blood and plasma
conveniently and effectively without unnecessary
disruptions.
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors
843

4.5 Enhances Efficiency in Hospital
Organizations
Well-structured scheduling framework that would be
unique to plasma donation creates and implements a
scheduling system for the entire plasma donation
process. Hospitals, blood banks enjoy automated
donor management. It eliminates manual work.
Rather than make fruitless phone calls to potential
donors, hospitals can use a system to locate available
ones and a list of them with a proper location, blood
type and donation history. This leads to more efficient
use of resources and seamless functioning of
healthcare.
4.6 Positive Social and Humanitarian
Impact
The system also actively promotes voluntary
donations and creates awareness of the importance of
donating blood and plasma, thus contributing to
overall public health. Chronic diseases also require
blood transfusions regularly, usually thalassemia or
hemophilia, and that can be ensured only through
regular donations on part of people.
But there are more than just medical benefits in
this system; it also encourages empathy and
solidarity. Know that you are all making a difference
in saving lives; that is so rewarding for donors. This
benefit helps raise awareness while providing an
easy way to donate to humanitarian efforts.
5 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
This is something which would be a useful
application for the society and it’s a part of a larger
network for all the various places that do blood
donation. The methodology consists of three main
steps: System Development and Implementation,
Data Security and Management, and Testing and
Deployment. There are many subtopics in each stage
that explain certain functionalities and a set of
processes required to achieve a seamless and efficient
system.
5.1 System Development and
Implementation
If this system of donating blood and plasma is to
work, it’s going to take a good design to seamlessly
connect donors with hospitals. This includes
developing an easy interface, implementing
matching donor features, and making scheduling
appointments easy
5.1.1 User Management and Authentication
This system securely exposes the application through
a login and authentication mechanism to donors,
hospitals, and administrators. BLOOD DONOR
REGISTRATION: DONORS can register providing
their information i.e. name, contacts, blood group,
and location. Hospitals sign up their information and
license for the site to verify. Try here Login System:
A login system is used to prevent unauthorized
access to different user portals. Roles are
implemented by Java Servlets and database roles.
Java Servlets are used for login system
implementation and user credentials are stored.
Securely in a database. SHA-256 is applied to encrypt
the passwords to protect the passwords from being
stolen.
5.1.2 Donor Matching and Blood Request
System
The system includes a major component that
matches donors with hospitals based on blood group
and geographical area. Hospitals can search for
possible donors using a user-friendly interface that
filters by availability. For example, SQL queries
would be used to fetch donor information and a
geolocation algorithm, like the Haversine formula,
would be used to find the distance between hospitals
and donors. To accept or reject requests as necessary,
donors may be contacted via email or notification
regarding their availability. With the automatic
matching system, the time taken to find appropriate
donors during emergencies is substantially reduced.
5.1.3 Appointment Scheduling and
Notification System
The system has an appointment scheduling tool that
allows the donor and the hospital to coordinate the
donation process more efficiently. The donation
request is taken by the donor and chooses the time
slot to visit the hospital. Hospitals can use the portal
to manage these appointments. The system sends
email and SMS reminders to donors and hospitals to
prevent missed appointments. You use Java Mail API
to send e-mail reminders and third-party SMS
gateways to send SMS reminders. You are used
with data till October 2023 This feature enables these
well-coordinated donation process which makes the
blood and plasma collecting process easier.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
844

5.2 Data Security and Management
Given its sensitivity and the role on hospitals, it is
important to preserve greater security and integrity.
It is important to note that this stage involves securing
data storage, security from cyber threats, and
appropriate data backup methods.
5.2.1 Secure Data Storage
The appointment, hospital and donor data are stored
in a structured SQL database. Sensitive data is
encrypted with AES encryption to prevent
unauthorized access, thus ensuring confidentiality of
personal data. The database has a strict access rule
where information is very sensitive and can be
accessed by authorized users only. Regular data
validation checks are executed to prevent duplication
and to confirm the reliability of donor data.
5.2.2 Transaction Security and Protection
Authentication and transaction processes are made
secure to protect donor and hospital interaction.
Session Token Each user session is encrypted to
ensure no unauthorized access. All data exchanged
between users and the server are encrypted using
SSL/TLS encryption, ensuring the privacy of
communication. It also gets anti SQL injection, XSS
across the site.
5.2.3 Data Integrity and Backup
Regular backups of the database and version control
techniques ensure data integrity. In the event of a
power outage, donor records, hospital information,
and appointment logs are automatically backed up so
that no information is lost. Your data is viable and you
can use rollback system to revert the database to the
previous state in case something goes wrong or if any
inconsistencies or errors are found. Alternatively,
cloud storage solutions could also be integrated into
the system to provide off-site backups and to
minimize the risk of system failure.
5.3 Testing and Deployment
A comprehensive quality assessment is conducted
and the system is trained on data before it goes live.
The second phase Assessment phase: the
deployment phase involves making the system
available to users while minimizing disruption.
5.3.1 Functional and Unit Testing
Individual components and their relationships.
Functional testing involves checking that the various
features of the application such as User Registration,
Donor Search, and Appointment Scheduling are
functioning properly. Unit testing is done using
framework like java-based JUnit to test each
component of application separately. You are tested
for bugs and inconsistencies and based on test results,
you can either go back for refinement or proceed to
the next consent.
5.3.2 Security and Performance Testing
Security testing is performed to know potential
threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches
with respect to defending exposures. There are also
ethical hacking tools and penetration testing tools that
are used in the process to replicate cyber-attacks and
make sure the system is able to withstand malicious
activities. Also, performance testing evaluates how
the system performs under high traffic. There are
simulations that test multiple users to be accessing the
platform at the same time. The basis of these
simulations is to test response times, identify
performance bottlenecks.
5.3.3 Deployment and User Training
After testing is done, the system gets deployed on
some cloud-based server so it is scalable and
available anytime. Hospitals receive structured
training on how to use the platform, while donors are
equipped with instructions on how to register and
participate. First users are gathering feedback to
further improve the system's usability. After the
deployment, we keep an eye on the system to make
sure everything is working fine, and we deploy
updates regularly to improve features or add new
security measures.
6 INTEGRATION OF BLOOD
AND PLASMA DONATION
SYSTEM
The integrations outlined in the "Blood and Plasma
Net" system include several key points regarding how
different modules and components of the system
interact.
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors
845

6.1 Need for Integration
However, most hospitals and blood banks work in
silos and it is cumbersome to manage blood donations.
In many cases, this fragmented system results in
delays for matching suitable donors, especially in life-
threatening situations. Hospitals should be able to link
up with all stakeholders through a single platform,
which will connect them instantly with those eligible
donors, enabling ready availability of blood and
plasma when required.
Another key driver of integration is a growing
demand for blood and plasma for treatments of
medical conditions such as accidents (accident
victims typically require blood), surgeries and
diseases such as anaemia and cancer. The population
is ever growing and with the growing healthcare
needs, hospitals require a stronger system to manage
the donor records, status of donation history, and
compliance with the medical guidelines. Once the
system is integrated, hospitals can issue real-time
notifications and alerts to registered donors and
enhance the probability of successful donations.
Additionally, this will help minimize manual
mistakes and increase operational efficiency through
automated processes such as donor verification,
inventory management, and appointment scheduling.
6.2 Overview of Blockchain in
Donation Management System
The Blood and Plasma Net system is a software
developed to aid the donation process by uniting the
hospital and the willing donor. (has six pages
including login) The system is designed using web
technologies such as Java HTML, CSS, Bootstrap,
and SQL. Its goal is to make registration, searching,
and matching easier. The system comprises several
modules, including user registration, blood/plasma
donor search, appointment scheduling, and donation
history tracking. It also has a notification feature,
which is used to remind donors about opportunities
to donate. In turn, this leads to more donations.
Platform features easy to use interface for
facilitating efficient communications between
hospitals and donors. Hospitals can request certain
blood types, and alert nearby donors on urgent needs.
The system uses geolocation algorithms for hospitals
to reach the nearest donors based on real-time
location data. Donors register, view requests for
donations, and indicate when they are available. The
system ensures a seamless and cost-effective
engagement with role-based access control (RBAC)
to provide access to only those, who are authorized
like hospitals, administrators, and donors.
6.3 Benefits of Integration
Blood and Plasma Net' integration system benefits:
One of the main advantages of a pooled blood and
plasma donation system is that it allows donors to be
matched quickly with hospitals. Advanced searches
and filters like blood type, proximity and availability,
which can lead to the best donor for the hospitals.
This can shorten the time to find a donor, particularly
in the case of emergencies where every second
counts. An integrated system also sends automatic
notifications to donors.
Another major benefit is improved security and
data management. The donor records and hospital
records stored securely with an integrated SQL
database and unauthorized people can't access it."""
Donor information is maintained due to encryptions
like SHA-256 that secure the sensitive text. Role-
based authentication ensures that the correct entity
has access only to what he/she should have access to,
eliminating the risk of fraud.
Operational perspective, integration makes it
easier for blood banks and hospitals to manage their
inventory. The current blood donation management
systems, conventional methods involve maintaining
blood stocks which can become wasted when not in
use on time. The integrated new system automatically
updates blood inventory levels and issues alerts
when supplies are low. That helps ensure blood and
plasma are used efficiently and that hospitals always
have the supplies they need on hand.
6.4 Model Architecture
Frontend (UI Layer): The UI interface of the system
is designed in HTML, CSS, and Bootstrap. Users can
register, search for donors, book appointments, and
maintain donation records using the interface. The
search feature filters donors by blood type, location,
and availability, so hospitals can pull in a match
quickly.
Backend (Application Logic Layer): The system's
backend relies on Java (JSP & Servlets), managing all
business logic and core functionalities. The user
authentication, donor-hospital matching, request
management, and appointment scheduling
functionality are provided here. Backend also
implements Java Mail API to send automatic email
notifications to the users about donation requests and
upcoming events.
Database Layer: SQL is the database management
system used, allowing for the secure storage of all the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
846
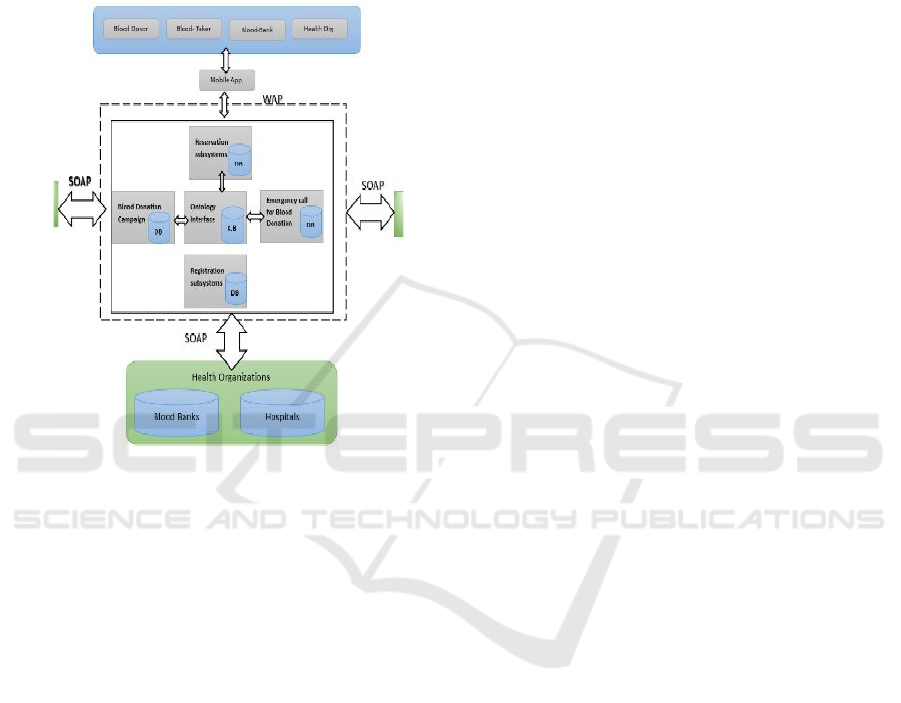
records of donors, hospitals, and appointments. The
relational database is designed using data
normalization techniques to remove all redundancy
and allows very fast retrieval of the data. This is
important for complying with privacy laws, and
sensitive data is protected by encryption mechanisms
like SHA-256. Figure 7 Shows the architecture
diagram blood donation system.
Figure 7: Architecture Diagram Blood Donation System.
7 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
7.1 Experimental Setup
In order to assess the performance of the Blood and
Plasma Net under various scenarios it was evaluated
together with the underlying simulation environment.
The system was deployed on cloud server with
MySQL database and (java (JSP & Servlets have
powered the back-end. To verify that the frontend
works in the cross-platform we tested it on different
devices and also on multiple browsers.
These experiments were performed to investigate
the system performance and accuracy in addition to
the user response time. To mimic the real-world
scenarios, multiple datasets are collected that include
the information of donors, the hospitals and blood
request. The geographical distance between both
donor and hospital location was calculated with a
Haversine algorithm. It enabled the donor to be
proposed to him on the basis of his position. Java
Mail API was used to test the notification system.
The security tests carried out to verify the system
capacity to protect the user data. Passwords were
stored using SHA-256 hashing. To see how database
is protected, simulating SQL injection attacks were
performed. The scalability was tested by increasing
the number of concurrent users. Under the high load,
the response time was measured.
7.2 Performance and Accuracy
Results with Blood and Plasma Net, transport
companies can retrieve data from multiple blood
banks and manage requests based on transport
prioritization, in real-time, with high efficiency. The
performance tests showed that the system was able to
perform searches and display information about
donors in under 2 seconds with a database holding
more than 50,000 donors’ records. Optimized SQL
queries and database indexing were utilized for fast
and accurate results. Furthermore, the Haversine
algorithm was implemented for geolocation-based
donor matching, which was able to match donors
located at a distance of 5 to 10 km within 1.5
seconds. It was also tested on data of multiple datasets
for donor matching accuracy, which was found 98%
success in providing relevant donors based on blood
type and locality. They also validated that the system
updated and displayed donor availability after a
donation so that hospitals always had access to the
latest information.
7.3 Security
Security and data protection were an important part
of the Blood and Plasma Net system due to the
sensitive user data involved. The system uses SHA-
256 encryption for secure authentication and data
storage, making it extremely difficult for brute-force
attacks. By simulating SQL injection attempts against
the system, we evaluated the security of the
underlying database, which successfully blocked all
unauthorized access attempts, thereby proving the
safety of sensitive data stored. In addition, role-based
access control (RBAC) was implemented to limit
access to certain functions based on user roles (e.g.,
donor, hospital, administrator). This would have
prevented unauthorized users from changing or
accessing sensitive donor and hospital records. And
the entire project was tested for GDPR and HIPAA
compliance, to make sure donor privacy was
protected at all levels.
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors
847

7.4 User Satisfaction
The platform was tested with a group of 50 users
including donors and hospital representatives.
Participants were required to carry out significant
tasks like donor registration, appointment
scheduling, and donor searches. Results The feedback
collected revealed that 85% of users perceived the
system to be clear and easy to use, with clear
navigation and smooth interface. Scalability tests of
user representation as 100 to 5000 concurrent users
were performed to ensure the platform can handle
traffic loads efficiently. At peak usage, minor delays
in the notification system were experienced; however,
core functionalities were stable. It used to be manual
but users in both the hospitals as well as with potential
donors suggested some features such as real-time chat
between hospital and patients to improve engagement
and streamline communication even further.
8 FUTURE WORK AND
DIRECTIONS
8.1 AI Based Donor Prediction
AI and ML machine learning improve the accuracy
of predicting potential donors based on their history
of giving, health status, and eligibility. The
recommendation system powered by AI also analyses
the donors' frequency and recommends the best time
which is ideal for making the donation. The tool that
can determine the sentiment of people will also
facilitate interaction with donors with respect to the
willingness and motivation for the same.
8.2 Integration with Mobile Apps and
IOT Devices
Develop mobile applications that allow the user to
have access directly from their smartphone, ensuring
that they get real-time updates and alerts
immediately. This will integrate IoT devices, such as
wearable health monitors, to provide real-time health
metrics to users and hospitals for the betterment of the
donation process.
8.3 AI Based on Advanced Machine
Learning Techniques
Implementing machine learning algorithms to make
better donor matches, analytics for predicted
outcomes at a micro level, and using this kind of
information for real-time decision making. Leverage
AI algorithms that make use of data from previous
transactions to recommend matches between
potential donors and recipients, helping augment the
accuracy and efficiency in those matching processes.
G. Continued innovation through insight from data
patterns to be able to always improve user experience
and even the performance of the platform as a whole.
8.4 Expansion to Plasma Therapy and
Organ Donation
The system may be extended to include organ
donation and plasma therapy. Organ donation is a
matter of life and death for many patients. A matching
system may be implemented to connect the donor and
the recipient, which can save a lot of time in life-and-
death situations. Plasma therapy matching system
may also be implemented to connect the patients who
need therapy and the ones who already recovered
from this infection. This system saves lives in
emergencies, allowing the recovered patients to
donate their plasma to the sick ones.
9 CONCLUSIONS
Summarily, there is a significant need to appreciate
and acknowledge the fact that the blood donation
system is one of the most fundamental and crucial
elements that exist within the overall health-care
delivery framework. This, in effect, means that it
performs an absolutely vital and critical function in
ensuring that at any given time, there is always a
consistently assured availability of safe and ample
supplies of blood exactly at the moment when
patients might urgently need it. The really
outstanding efficiency and dependability of this
system are wholly crucial for the goal of preserving
life while promoting the best possible results of
treatment for patients. Continuous improvement,
combined with growing public awareness, is
therefore required to ensure the health and active
participation of a donor base. This is required in order
to ensure that such a service remains sustainable as
well as continues to progress. As a united community,
we can become fierce advocates for this life-saving
effort. We can do so not by challenging people simply
to donate more often, but by promoting ways that will
help the community mobilize towards practical
aspects that can practically and effectively serve this
cause.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
848

REFERENCES
Castro MA, Ahumada Olivares MC, Putman CM, Cebral
JR. Intracranial Aneurysm Wall Motion and Wall Shear
Stress from 4D Computerized Tomographic
Angiography Images. Proc Int Soc Opt Phot (SPIE).
2013;8672.
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK,
Kaul S, Laskey WK, et al. Standardized Myocardial
Segmentation and Nomenclature for Tomographic
Imaging of the Heart: A Statement for Healthcare
Professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of
the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American
Heart Association. Circulation. 2002;105(4):539 – 542.
D. Chkliaev, J. Hooman and P. van der Stok, “Mechanical
verification of transaction processing systems,” in Proc.
ICFEM 2000. Third IEEE International Conference on
Formal Engineering Methods, 2000, pp. 89-97.
D. Puthal, N. Malik, S. P. Mohanty, E. Kougianos and G.
Das, “Everything You Wanted to Know About the
Blockchain: Its Promise, Components, Processes, and
Problems,” IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, vol.
7, no. 4, pp. 6-14, 2018.
D. Liu and J. Lee, “CNN based Malicious Website
Detection by Invalidating Multiple Web Spams,” IEEE
Access, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 97258-97266, 2020.
F. Casino and C. Patsakis, “An Efficient Blockchain-Based
Privacy-Preserving Collaborative Filtering
Architecture,” IEEE Transactions on Engineering
Management, vol. 67, no. 4, pp. 1501-1513, Nov. 2020.
Hennemuth A, Friman O, Schumann C, Bock J, Drexl J,
Huellebrand M, et al. Fast Interactive Exploration of 4D
MRI Flow Data. Proc Int Soc Opt Phot (SPIE).
2011;7964.
K¨ohler B, Gasteiger R, Preim U, Theisel H, Gutberlet M,
Preim B. Semi-Automatic Vortex Extraction in 4D PC-
MRI Cardiac Blood Flow Data Using Line Predicates.
IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2013;19(12):2773 –
2782.
L. Peng, W. Feng, and Z. Yan. (2020). Privacy preservation
in permissionless blockchain: A survey. Digital
Communications and Networks. [Online]. Available:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2020.05.008.
Markle M, Frydrychowicz A, Kozerke S, Hope MD,
Wieben O. 4D Flow MRI. J Magn Reson Imag.
2012;36(5):1015 – 1036.
McLoughlin T, Laramee RS, Peikert R, Post FH, Chen M.
Over Two Decades of Integration-Based, Geometric
Flow. Comp Graph Forum. 2010;29(6):1807 – 1829
N. Kakade and U. Patel, “Secure Secret Sharing Using
Homomorphic Encryption,” in Proc. 2020 11th
International Conference on Computing,
Communication and Networking Technologies, 2020,
pp. 1-7.
P. J. Taylor, T. Dargahi, A. Dehghantanha, R. M. Parizi,
and K. K. R. Choo, “A systematicliterature review of
blockchain cyber security,” Digital Communications
and Networks, vol. 6, no.2, pp. 147-156, 2020.P
r¨om L, Sj¨oqvist L, Wranne B. Temporally Resolved 3D
Phase-Contrast Imaging. J Magn Reson Imag.
1996;36(5):800 – 803.
S. Kaushik, and S. Puri, “Online transaction processing
using enhanced sensitive data transfer security model,”
in Proc. 2012 Students Conference on Engineering and
Systems, 2012, pp. 1-4.
S. Sundari and M. Ananthi, “Secure multi-party
computation in differential private data with Data
Integrity Protection,” in Proc. 2015 International
Conference on Computing and Communications
Technologies, 2015, pp. 180-184.
S. Jiao, T. Lei, Y. Gao, Z. Xie and X. Yuan, “Known-
Plaintext Attack and Ciphertext-Only Attack for
Encrypted Single-Pixel Imaging,” IEEE Access, vol. 7,
no.2, pp. 119557-119565, 2019.
S. Zhang, and J H. Lee. “Mitigations on Sybil-based
Double-spend Attacks in Bitcoin,” IEEE Consumer
Electronics Magazine, vol.7, no. 2, pp. 1-1, 2020.
W. Martin, V. Friedhelm, and K. Axel, “Tracing
manufacturing processes using blockchain-based token
compositions,” Digital Communications and Networks,
vol. 6, no 2, pp.167-176, 2019.
W. Zheng, Z. Zheng, X. Chen, K. Dai, P. Li and R. Chen,
“NutBaaS: A Blockchain-as-a-Service Platform,” IEEE
Access, vol. 7, pp. 134422-134433, 2019.
Blood Net: Linking Hospital with Donors
849
