
Optimizing Resource Management and Load Balancing in Supply
Chain through Integrating Digital Technologies to Enhance Resource
Efficiency and Workload Management in Manufacturing Firms
Janmejai Kumar Shah
1
, Sudhanshu Joshi
2
and Manu Sharma
1
1
Department of Management Studies, Graphic Era Deemed to be University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
2
School of Management, Doon University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
Keywords: Digital Technologies, Supply Chain Management Resource Management and Load Balancing.
Abstract: Digital integration across supply chains offers significantly improved resource management and load
balance in industrial enterprises. This study aims to examine the favorable effects of Industry 4.0
technologies, enterprise resource management systems, blockchain, and dynamic capabilities on resource
efficiency and workload optimization. The research employs a descriptive literature analysis to identify
principal themes, including sustainability, operational resilience, and performance enhancement, with an
emphasis on green supply chain practices and agility. The paper portrays the limitations associated with
fragmented research, the dynamic technology landscape, and supply chain procedures that are sometimes
context-specific, thereby limiting their universal applicability. The findings support theoretical frameworks
that illustrate the collaborative impact of digital technology in fostering sustainable and efficient supply
chains. The research provides practical recommendations for manufacturing companies to efficiently
leverage digital tools to maintain competitiveness, enhance decision-making, and foster resilience. We
present a conceptual framework for the application of digital technology in supply chain processes and offer
organized techniques to address resource optimization concerns. Research indicates that digital
transformation of supply chains can effectively facilitate the achievement of sustainability objectives.
Ultimately, it indicates prospective research avenues, including sector-specific analyses and emerging
technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, to enhance the adaptability and resilience
of supply chains. This study offers a thorough foundation for resource management and optimization of load
balancing through digital innovation in manufacturing supply chains.
1 INTRODUCTION
Balancing workloads and managing resources
remains a significant issue with many manufacturing
firms facing inconsistencies in their operations due to
the complexities of modern day supply chains,
especially in a world that is perpetually changing.
This fact has spurred interest in some digital
technologies that could help to increase resource
efficiency and better manage workloads. The
technologies discussed here have shown to improve
the utilization of resources, promote sustainability
and increase resilience in the supply chain
infrastructure (Rouhani, S., & Deters, R. 2019),
(Kesidou, S., & Sovacool, B. K. 2019) and (Belhadi
et al., 2022). Although important, there is still a lack
of holistic frameworks for the implementation of
digital technologies in supply chains (Di Vaio, A., &
Varriale, L. 2020). We seek to address this gap by
reviewing literature on this subject, reviewing how
long-term practice evolves and adapts following the
impact of technology upon it, and proposing themes
which encourage the introduction of digital solutions.
While this article contributes to building such a
comprehensive view, certain limitations need to be
acknowledged: The literature studied is
predominantly biased towards certain technologies
or elements of the supply chain management cycle,
without being able to provide a comprehensive or
holistic view. Because these have been generated on
a very specific aspect, thus, the knowledge acquired
is not generalizable (Patil et al., 2022) and (Trujillo-
Gallego et al., 2022). In addition, digital technologies
are always developing; therefore, it is difficult to
fully understand their influence, or to forecast the
818
Shah, J. K., Joshi, S. and Sharma, M.
Optimizing Resource Management and Load Balancing in Supply Chain through Integrating Digital Technologies to Enhance Resource Efficiency and Workload Management in Manufacturing
Firms.
DOI: 10.5220/0013921300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
818-825
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

consequences of their further development (Kesidou,
S., & Sovacool, B. K. 2019), (Bui et al., 2023). A
significant number of studies depend on case studies
from regions or industries and lack empirical
evidence, which restricts the practicality of their
findings (Murguia et al., 2023) and (Noor, Z. Z.
2023). Moreover, practices and challenges within
supply chains differ greatly between industries and
regions, complicating the development of universally
applicable frameworks (de Oliveira-Dias et al.,
2023). Ultimately, there is a lack of longitudinal
studies that investigate the enduring effects of digital
transformation on resource efficiency and workload
management over extended times (Di Vaio, A., &
Varriale, L. (2020) and (Sugianto et al., 2023).
1.1 Objectives
This study focuses on exploring the integration of
digital technologies in supply chain operations to
tackle challenges related to resource management
and workload optimization.
(RO1): Grasp the impact of digital technologies on
supply chain resource management and workload
optimization, integrate and analyze the existing
literature.
(RO2): Examine the ways in which digital
technologies transform and enhance supply chain
practices following their implementation.
(RO3): Develop Themes for Integration to support
manufacturing companies in the effective
implementation of digital technologies within their
supply chain operations.
1.2 Significance
This study enhances the existing understanding of
supply chain innovation by addressing significant
gaps in the knowledge of digital integration. This
offers practical insights for professionals aiming to
enhance resource utilization and workload
management. It also outlines potential avenues for
further investigation for scholars. This study offers
valuable insights for policymakers by guiding the
creation of conducive environments for technology
adoption; it emphasizes that digital transformation
should enhance sustainable and resilient supply
chains (Rodríguez-González et al., 2023) and (Luo
et al., 2024).
1.3 Approach
The objectives of the study are approached through a
descriptive and thematic analysis. This study
conducts a descriptive review of existing literature
utilizing R Studio and thematic analysis through
VOS viewer to identify patterns, trends, and themes
in the application of digital technology within supply
chains. This systematic approach allows the study to
concentrate on significant inquiries, while also
striving to encompass a broad range of insights
(Noor, Z. Z. 2023) and (Fiorini et al., 2022). This
study compiles insights on supply chain practices
from previous investigations, aiming to chart the
progression of these practices while offering
actionable suggestions for manufacturing companies
to utilize digital technologies for achieving resource
efficiency and optimizing workloads.
The study comprises five sections: section 2
consists of literature review followed by
methodology in section 3 and then Implication in
section 4 and Discussion, Conclusion, and Future
Scope in section 5.
2 SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE
REVIEW
A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a
structured approach for thorough evaluation of
literature within one or more specialized study
domains. This methodology facilitates the
identification of trends, limits, and prospective
opportunities for future research, hence enhancing
the understanding of the topic. This research
specifically analyses digital technologies and their
impact on supply chain resource management and
workload distribution.
2.1 Select Database and Keywords
This study utilized the Scopus database due to its
extensive compilation of peer-reviewed journals
featuring high-quality scientific papers. Historically,
we employed a more focused search query utilizing
keywords associated with “Digital,” “Supply
Chain,” “Resource Management,” “Load
Balancing,” and “Performance.” This combination is
specifically intended to discover research that
examine the interface of digital technology and
supply chain optimization.
2.2 Criteria for Acceptance and
Rejection
Strict inclusion and exclusion criteria were
implemented in this review of papers to ensure the
Optimizing Resource Management and Load Balancing in Supply Chain through Integrating Digital Technologies to Enhance Resource
Efficiency and Workload Management in Manufacturing Firms
819
inclusion of pertinent and high-quality research. The
criteria for inclusion were Articles and review
papers published between 2019 and 2024. Research
disseminated in the English language. Research
papers focused on supply chains and digital
technologies, emphasizing resource management,
workload optimization, and performance
enhancement. Studies were omitted if they: They
lacked empirical proof or were not peer-reviewed.
Concerning various topics that are either irrelevant
or pertain to general discourse on digital
technologies. Initially, there were 57 results. Forty-
four studies were evaluated for relevance, and
duplicates were eliminated. Following a
comprehensive content analysis, we refined the
selection to 33 high-quality publications that
constituted the foundation of this study. Table 1
shows the SLR Approach.
Table 1: SLR Approach.
Heads Details
Database Sco
p
us
Search Query
(TITLE-ABS-KEY ("Digital") AND TITLE-ABS-KEY ("supply chain") AND TITLE-ABS-
KEY ("resource management") OR TITLE-ABS-KEY ("load balancing") AND TITLE-ABS-
KEY ("performance"))
Filters Applied Publication years (2019–2024), document type (articles and reviews), language (English)
Initial Search Results 57 studies
First Screening Excluded irrelevant studies, leaving 44 papers
Final Screening Removed duplicates and non-specific studies, resulting in 33 high-quality papers
3 METHODOLOGY
The study achieves this purpose through a
systematic and structured methodology that uses
descriptive and thematic analyses to investigate the
incorporation of digital technology in supply chain
management to optimize resource management and
load balancing. The technique comprises two
essential components: A comprehensive evaluation
of the current literature was initially performed
utilizing bibliometric methods in R Studio. This step
involved producing a quantitative analysis of the
patterns, trends, and publishing dynamics in the
fields. The descriptive review consolidates existing
research by examining the prevalence of pertinent
studies, citation networks, and the distribution of
research findings. On the other hand, a thematic
analysis using VOS viewer as a cutting-edge
visualization software for text analysis was
performed to uncover the patterns and clusters found
in the implementation of digital technology. The
study aims to clarify prominence themes visualized,
elucidate important concepts correlated and
highlight emergent themes and research gaps with
the help of VOS viewer. It is an amalgamation of the
two methodologies, helping in a holistic
understanding of the matter. The descriptive review
section gives a global overview of the research topic,
while in the thematic analysis section specific
themes and patterns are being analyzed in order to
make them actionable. Simultaneously, the dual
framework bolsters both the reliability and
comprehensiveness of the study and remedies major
gaps in the existing literature. This approach not
only encapsulates the existing knowledge into an
integrated synthesis but also provides the
evolutionary journey of digital technologies within
supply chains and a systematic framework to
incorporate them into resource management and
workload optimization.
3.1 Descriptive analysis
Table 2: Year wise evolution.
YEAR ARTICLES
2019 2
2020 1
2021 0
2022 6
2023 10
2024 14
Table 2 shows the year wise evolution. Research on
the integration of digital technologies in supply
chains to enhance resource management and load
balancing has significantly increased throughout the
2019–2024 timeframe, emphasizing resource
management and workload optimization. In 2019
and 2020, only two and one articles were published,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
820
respectively, indicating preliminary investigation
(Patil et al., 2022) and (Trujillo-Gallego et al., 2022)
In 2022, there was a significant increase to six
articles, escalating in 2023 to ten articles, and
culminating in 2024 with fourteen articles as
innovations in Blockchain and Industry 4.0
progressed rapidly (Murguia et al., 2023) and
(Sugianto et al., 2023). It is also associated with
several global supply chain challenges and
sustainability objectives, highlighting the
significance of this domain and the study's purpose
(Kesidou, S., & Sovacool, B. K. 2019), (Patil., et al.,
2022) and (Bui et al.,2023) Table 3 shows the
geographical contribution.
Table 3: Geographical Contribution.
Country TC Average citations
Canada 210 210.00
France 100 50.00
United Kingdom 72 36.00
Colombia 60 60.00
Italy 60 20.00
Sweden 51 51.00
Spain 49 24.50
China 44 6.30
Indonesia 15 5.00
India 13 13.00
Investigations into the application of digital
technology for the optimization of resource
management and load balancing in supply chains
yield diverse contributions from various nations.
Canada possesses the most total citations (TC) at
210, with an average TC of 210.00, attributed to its
advanced emphasis on digital solutions for resource
efficiency (referenced as (Patil., et al., 2022) and
(Murguia et al., 2023). Conversely, France (100 TC,
50.00 average) and the United Kingdom (72 TC,
36.00 average) emphasize significant studies on
integrating digital technology to enhance workload
management (Trujillo-Gallego et al., 2022) and
(Sugianto et al., 2023). Colombia and Sweden
exhibit specialized research initiatives, with TCs of
60 and 51, respectively, suggesting that the
application of digital tools for industrial enterprises
should be prioritized (Bui et al.,2023) and (de
Oliveira-Dias et al., 2023). China (44 TC, 6.30 avg.)
and India (13 TC, 13.00 avg.) exemplify regional
stakeholders' aspiration to enhance efficiency, hence
facilitating additional engagement from rising
contributors (Kesidou, S., & Sovacool, B. K. 2019)
and (Noor, Z. Z. 2023). Research is a global
phenomenon that underscores the importance of
incorporating digital technologies into supply
networks. Prominent contributors, such as Canada
and Sweden, are providing exemplary frameworks
for resource management and load balancing;
concurrently, developing participants are indicating
the potential for regional innovation and cross-
border collaboration. These results highlight the
imperative for manufacturing organizations to adopt
internationally scalable systems that are resource-
efficient and promote sustainable workload
management techniques. Figure 1 shows the
geographic collaboration network.
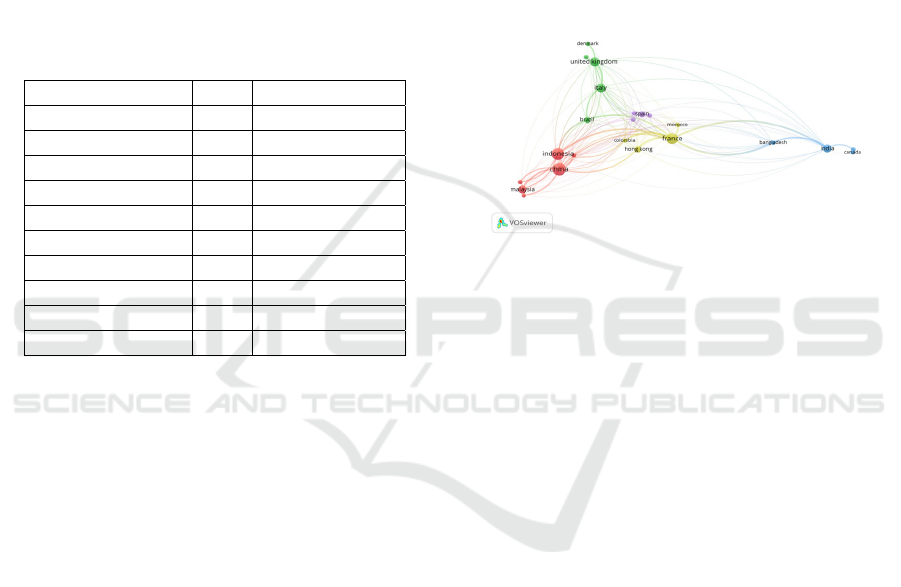
Figure 1: Geographic Collaboration Network.
The visualization illustrates global collaboration
patterns in the integration of digital technologies for
optimizing resource management and load balancing
within the supply chain. Node size represents the
relative contribution of countries, with major
regional and inter-regional links apparent. Canada is
a big part of that, forming key partnerships with
India and Bangladesh. This also matched with
Canada's aim of fostering supply chain innovation
and digital adoption, with an emphasis on
developing nations (Kesidou, S., & Sovacool, B. K.
2019) and (Patil., et al., 2022). Specifically, the
European Countries (UK, France, Italy) show an
intuitive and dense network architecture with
focused powered optimization and digitalization of
supply chains (Trujillo-Gallego et al., 2022) and
(Murguia et al., 2023). They are centers of
innovation, deploying the latest technologies to
improve resource efficiency and workloads.
Emerging economies, in particular, Indonesia and
China, also play essential roles in the network and
connect regional peers in Asia such as Malaysia and
Hong Kong. This suggests that these nations are
employing digital technologies as a means of
overcoming supply chain resilience and operational
efficiency challenges (de Oliveira-Dias et al., 2023)
and (Rodríguez-González et al., 2023). So that goes
back to what I said, which is the need to solution
Optimizing Resource Management and Load Balancing in Supply Chain through Integrating Digital Technologies to Enhance Resource
Efficiency and Workload Management in Manufacturing Firms
821
from all over the world, bring the best ideas and the
best technology and habits over to address the
problems. Drawing linkages between developed and
developing countries provides an opportunity for
cooperation in creating scalable solutions along the
knowledge-sharing process by all stakeholders.
These unprecedented findings, presented on the
network, highlight the importance of international
collaborative frameworks to enable the incorporation
of digital technology into supply chains. With this
in mind, cross-border affiliations help countries
implement comprehensive strategies for improving
resource management and workload repartition in
industrial businesses. Such global intermingling
means that these solutions can be steered for a wide
variety of operational settings, ensuring resilience,
sustainability and efficiency in supply chain
practices. Moreover, such partnerships can bridge
the technological gap between developed and
developing economies, enabling inclusive growth
and innovation. Table 4 gives the key research
focus areas.
Table 4: Key Research Focus areas.
Terms Frequenc
y
Supply chains 16
Su
pp
l
y
chain mana
g
ement 11
Enter
p
rise resource mana
g
ement 10
D
y
namics ca
p
abilit
y
8
Human resource management 8
Industry 4 0 6
Performance 6
Sustainable develo
p
ment 6
Di
g
ital technolo
g
ies 5
Resource management 5
Environmental management 4
Information management 4
Com
p
etition 3
Decision makin
g
3
Digital technology integration in supply chain
management to optimize resources and manage
workload are examined in detail. Recent research
has focused on optimizing "supply chains" (Kandpal
et al., 2024). The cases emphasize digital innovation
to understand and improve supply chain operations
(Kesidou, S., & Sovacool, B. K. 2019) and (Patil., et
al., 2022). These include 11 supply chain
management and 10 enterprise resource management
incidents, which address managerial and operational
standards for efficient resource usage. This
emphasizes automating and streamlining supply
chain processes (de Oliveira-Dias et al., 2023) and
(Trujillo-Gallego et al., 2022). Ideas that innovate
Digital transformation should emphasize agile
methods and human resources, according to
'dynamic capability' and 'human resource
management'. Agile and skilled workers are needed
to implement and maintain digital tools in supply
chain ecosystems (Murguia et al., 2023) and
(Sugianto et al., 2023). The continuous reference of
"Industry 4.0" and "Sustainable development"
emphasizes technology-driven innovation and
supply chain sustainability. Smart technologies like
IoT and AI help green and streamline supply
networks (Bui et al., 2023) and (Rodríguez-
González et al., 2023). Other names like "Digital
techniques," "Resource management," and
"Environmental management" show supply chain
digitization ambitions. These statements stress using
technology to achieve environmental sustainability
and resource optimization. Supply chain
management and resource optimization are
becoming more important, along with dynamic
capabilities, human resource integration, and
sustainability. Thus, strategic and environmental
engagement must accompany technological
advances to restructure the supply chain. The results
reveal that firms must develop comprehensive
digital strategies to improve operational efficiency,
personnel preparation, and sustainability to stay
competitive and resilient. Sustainable development
goals require international cooperation and supply
chain alignment to address global issues.
3.2 Thematic Analysis
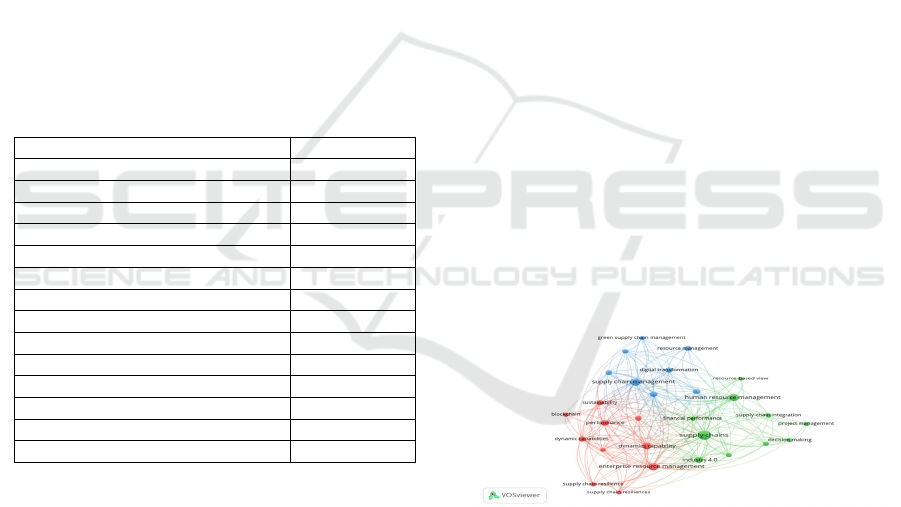
Figure 2: Thematic network.
The visualization of the network map of themes
highlights the connections between key subjects and
organizes related terms into distinct groups, aligning
with the focal directions observed in recent years
within both academic and industrial discussions
(figure 2). The connections illustrate the co-
occurrence relationship between these themes, with
their size indicating the frequency of occurrence for
each theme. Table 5 shows the themes develop for
resource and load management.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
822
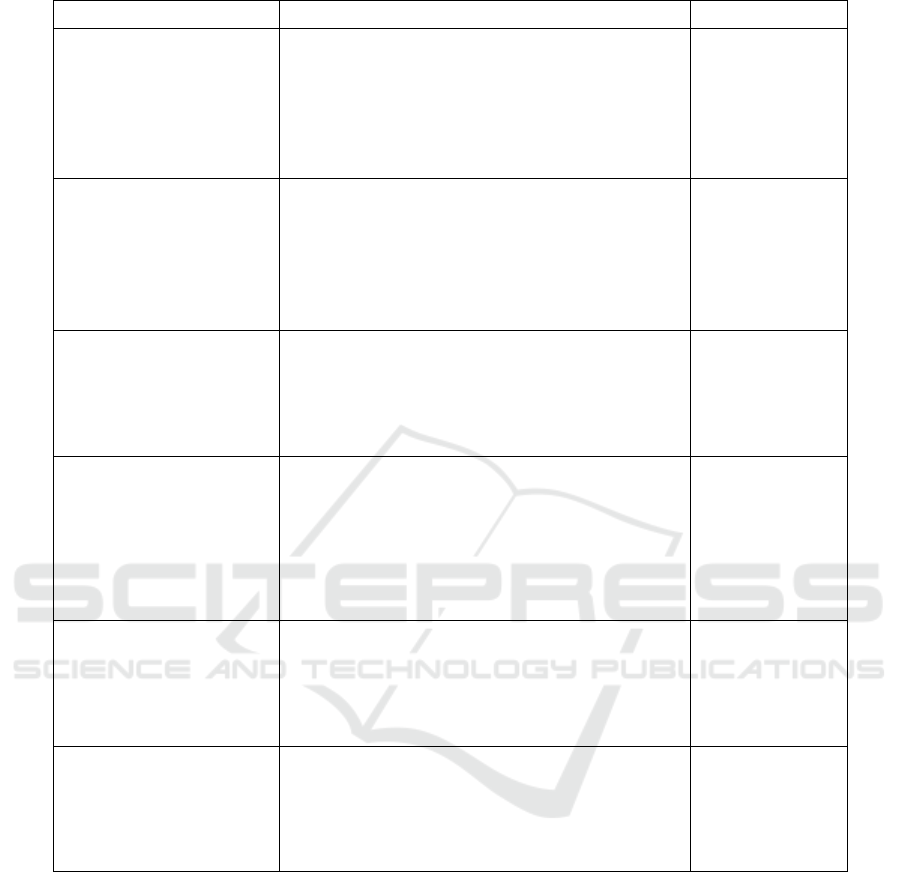
Table 5: Themes develop for resource and load management.
Theme Key Insights References
Enhancing Connections and
Efficiency in Digital Supply
Chain Integration
Digital technologies like Blockchain, IoT, and cloud
platforms improve inventory management, logistics
transparency, and demand forecasting. Industry 4.0
streamlines decision-making, enhances connectivity,
and fosters green innovation for sustainability
compliance.
Di Vaio, A., &
Varriale, L.
(2020), de
Oliveira-Dias ET
AL., 2023 and
Luo, S., Xiong, Z.,
& Liu, J. (2024).
Resource and
Environmental Efficiency:
Addressing Errors to Foster
Positive Progress Towards
Sustainability
AI, predictive analytics, and energy optimization
systems enable resource efficiency and waste
reduction. Circular supply chains and green
initiatives are critical for sustainability in industries
like textiles. Emerging technologies enhance
operational efficiency while reducing environmental
impact.
(Trujillo-Gallego
et al., 2022), (Bui
et al., 2023) and
(Fiorini et al.,
2022).
Human-Centric Digital
Transformation:
Empowering the Workforce
Workforce upskilling and digital HRM facilitate the
effective use of AI and IoT. Green HRM
competencies support green supply chain
management (GSCM) and enhance operational
performance while focusing on environmental
objectives.
(Trujillo-Gallego
et al., 2022),
(Fiorini et al.,
2022) and (Verma
et al., 2022).
Industry 4.0 and
Performance Enhancement:
Employing Innovative
Technology
Robotics, blockchain, and digital twins improve
operational efficiency and resource management.
Technologies enhance performance assessment
systems and bolster supply chain resilience and
adaptability. Additive manufacturing drives dynamic
capabilities for greater efficiency.
(Belhadi et al.,
2022), (Patil et al.,
2022), (de
Oliveira-Dias et
al.,2023) and
(Kandpal et al.,
2024).
Resilience and Adaptability
in Supply Chains:
Readiness for Disruptions
Digital culture and absorptive capacity drive supply
chain resilience. Technologies enable firms to
respond dynamically to market changes, ensuring
continuity during disruptions, as seen in the
Indonesian trucking industry.
(Belhadi et al.,
2022), (Sugianto
et al., 2023) and
(Rodríguez-
González et al.,
2023).
Sustainable Development
and Competitive
Advantage: Efficiency vs
Sustainability
Balancing efficiency and sustainability are key.
Green digital technologies enhance resource
efficiency, boost brand reputation, and drive long-
term competitiveness. Supply chain digitalization
fosters green innovation and ensures adherence to
environmental standards.
(Fiorini et al.,
2022) and (Jauhar
et al., 2021).
4 IMPLICATIONS
4.1 Theoretical Implications
This study applies dynamic capacity theory to
supply networks and demonstrates how digital
technologies enhance adaptability to unforeseen
conditions (de Oliveira-Dias et al., 2023). Industry
4.0 concepts like IoT, blockchain, and AI help
explain how technology innovation improves
resource management and task balancing. Digital
tools improve sustainability by linking resource
efficiency to supply chain environmental
performance. HRM also facilitates technology
adoption and boosts supply chain labor efficiency,
creativity, and innovation (Trujillo-Gallego et al.,
2022) and (Fiorini et al., 2022).
4.2 Practical Implications
The research (Bui et al., 2023) state’s various
themes regarding digital technology to enhance
resource utilization, waste reduction, and cost
effectiveness in industrial enterprises. Live analytics
Optimizing Resource Management and Load Balancing in Supply Chain through Integrating Digital Technologies to Enhance Resource
Efficiency and Workload Management in Manufacturing Firms
823

and predictive modeling increase supply chain
performance by balancing workloads. Green digital
technology will help firms meet sustainability goals,
follow environmental laws, and compete (Fiorini et
al., 2022). IoT, AI, and blockchain allow
transparency, monitoring, and predictive
environmental impact assessments. Effective
integration of digital solutions requires workforce
upskilling to enhance decision-making and
productivity (Rodríguez-González et al., 2023).
5 DISCUSSION, CONCLUSION AND
FUTURE SCOPE
This study explores the ways in which digital
technologies can revolutionize resource management
and load balancing within manufacturing supply
chains. The theoretical contributions emphasize the
interplay between digital tools, including Industry
4.0, dynamic capabilities, and enterprise resource
management, in enhancing resource efficiency,
operational resilience, and sustainability. The
findings indicate that these technologies enable
organizations to enhance decision-making, improve
agility, and address challenges related to resource
allocation and workload optimization. The findings
contribute practically by showing that advanced
digital technologies facilitate leaner operations,
enhance sustainability, and bolster resilience against
disruptions, as evidenced by supply chain
competitiveness. This study proposes a conceptual
framework for the adoption of digital technology
aimed at enhancing efficiency and promoting
sustainable practices. This highlights the importance
of connecting sustainable and flexible policies,
offering practical guidance for manufacturers
preparing to thrive in an increasingly unpredictable
supply chain landscape. Further investigation is
necessary to explore the distinct applications and
challenges of digital transformation through sector-
specific studies. An in-depth investigation into the
incorporation of emerging technologies like artificial
intelligence, IoT, or blockchain into supply chain
optimization can provide valuable insights.
Furthermore, one can establish a trajectory for
sustainable and competitive supply chain strategies
globally by examining the effects of digital
transformation over the long term, as well as by
integrating digital transformation to enhance circular
economies and achieve carbon neutrality.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
“We extend our gratitude to the department of
management studies at Graphic Era deemed to be
University for providing us with the opportunity and
encouragement to conduct this study.” “The contributions
and dedicated engagement were essential to making this
achievement a reality.”
REFERENCES
Rouhani, S., & Deters, R. (2019). Security, performance,
and applications of smart contracts: A systematic
survey. IEEE Access, 7, 50759-50779.
Kesidou, S., & Sovacool, B. K. (2019). Supply chain
integration for low carbon buildings: A critical interdis
ciplinary review. Renewable and sustainable energy
reviews, 113, 109274.
Belhadi, A., Kamble, S. S., Venkatesh, M., Jabbour, C. J.
C., & Benkhati, I. (2022). Building supply chain
resilience and efficiency through additive manufacturi
ng: An ambidextrous perspective on the dynamic
capability view. International Journal of Production
Economics, 249, 108516.
Di Vaio, A., & Varriale, L. (2020). Digitalization in the
sea-land supply chain: experiences from Italy in
rethinking the port operations within inter organization
al relationships. Production Planning & Control, 31(2
-3), 220-232.
Patil, A., Madaan, J., Chan, F. T., & Charan, P. (2022).
Advancement of performance measurement system in
the humanitarian supply chain. Expert Systems with
Applications, 206, 117844.
Trujillo-Gallego, M., Sarache, W., & de Sousa Jabbour, A.
B. L. (2022). Digital technologies and green human
resource management: Capabilities for GSCM adoptio
n and enhanced performance. International Journal of
Production Economics, 249, 108531.
Bui, T. D., Tseng, J. W., Aminah, H., Sulistiawan, J., Ali,
M. H., & Tseng, M. L. (2023). Causality of total
resource management in circular supply chain implem
entation under uncertainty: a context of textile industry
in Indonesia. Annals of Operations Research, 1-41.
Murguia, D., Vasquez, C., Demian, P., & Soetanto, R.
(2023). BIM adoption among contractors: a longitudin
al study in Peru. Journal of Construction Engineering
and Management, 149(1), 04022140.
Noor, Z. Z. (2023). Examining the role and position of the
digital human resource management in economic
development. Економічний часопис-ХХІ, 205(9-10),
39-43.
de Oliveira-Dias, D., Maqueira-Marin, J. M., Moyano-
Fuentes, J., & Carvalho, H. (2023). Implications of
using Industry 4.0 base technologies for lean and agile
supply chains and performance. International Journal
of Production Economics, 262, 108916.
Sugianto, I. M., Pujawan, I. N., & Purnomo, J. D. T.
(2023). A study of the Indonesian trucking business:
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
824

Survival framework for land transport during the
Covid-19 pandemic. International Journal of Disaster
Risk Reduction, 84, 103451.
Rodríguez-González, R. M., Madrid-Guijarro, A., &
Maldonado Guzmán, G.
(2023). Digital organizational
culture and absorptive capacity as precursors to
supply chain resilience and sustainable performance. J
ournal of Cleaner Production, 420, 138411.
Luo, S., Xiong, Z., & Liu, J. (2024). How does supply
chain digitization affect green innovation? Evidence
from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy
Economics, 136, 107745.
Fiorini, P. C., Jabbour, C. J. C., Latan, H., de Sousa
Jabbour, A. B. L., & Mariano, E. B. (2022). Green
emerging digital technologies, green supply chains,
and the performance of environmentally friendly
firms: the underpinning role of human resources. IEEE
Transactions on Engineering Management.
Verma, P., Kumar, V., Daim, T., Sharma, N. K., & Mittal,
A. (2022). Identifying and prioritizing impediments of
industry 4.0 to sustainable digital manufacturing: A
mixed method approach. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 356, 131639.
Kandpal, V., Jaswal, A., Santibanez Gonzalez, E. D., &
Agarwal, N. (2024). Sustainable Energy Transition,
Circular Economy, and ESG Practices. In Sustainable
Energy Transition: Circular Economy and Sustainable
Financing for Environmental, Social and Governance
(ESG) Practices (pp. 1-51). Cham: Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Jauhar, S. K., Pant, M., Kumar, V., Sharma, N. K., &
Verma, P. (2021). Supply chain and the sustainability
management: selection of suppliers for sustainable
operations in the manufacturing industry. In Sustainab
ility in Industry 4.0 (pp. 75-93). CRC Press.
Optimizing Resource Management and Load Balancing in Supply Chain through Integrating Digital Technologies to Enhance Resource
Efficiency and Workload Management in Manufacturing Firms
825
