
AI Powered Personal Health Assistant
Sivapuram Lakshmi Poojitha, Jakkulety Sindhu, Gunda Lakshmi Jyoshna,
Nara Indu Priya and Ravi Bolleddula
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (DS), Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Venkayapally,
Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Generative Artificial Intelligence, Medical Education, LLMs, Med‑PaLM, DeepHealth.
Abstract: The development of sophisticated healthcare system that increase the accuracy level of predicting illness
based on logistic regression and decision tree algorithm is the aim in this project. Depending on how well you
clean the dataset (missing values, categorical data encoding and getting rid of unnecessary variables) the
model's performance will reduce. The system will also include predictive analytics and an interactive
multilingual chatbot that can understand both voice and text in English as well as Tamil. This roundup of
digital health apps and chatbots offering advice and support to people during the COVID-19 pandemic will
help users find information that is vetted by doctors and vetted for accuracy.AI that creates: including systems
like ChatGPT, DALLꞏE, and Bard Rush to contribute: in everyday life and for health Internists are receiving
a COVID-19 mass hysteria data dump: we need them finding the most important info amidst it all AI that
creates Those who continue with work and home needs while trying to build new things are using services
such as ChatGPT or DALLꞏE. Medical AI can help process imaging data, design treatments and expedite
clinical trials. Furthermore, AI-based applications are changing medicine education, simulation and
rehabilitation. However, the challenges remain especially in privacy of data, bias reduction and retaining
medical professional expertise.The proposed project aims at an advanced, fully integrated AI-enabled
healthcare framework using a combination of predictive modeling, conversational intelligence and ethical AI
design that offers personalized and accurate medical advice in an accessible way to the masses for improved
healthcare service delivery in the era of artificial intelligence.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) and
machine learning (ML) technologies has completely
restructured the healthcare industry by enhancing the
efficiency, personalization, and precision of medical
diagnostics. The development of intelligent health
aides is one of the most promising applications of AI.
These healthcare AI systems aim to assist individuals
facing problems relating to the Healthcare sector by
interpreting medical data, predicting diseases, and
offering valuable suggestions for treatment and care.
In the realm of artificial intelligence called
“generative AI,” models and algorithms leverage the
patterns they have identified in the available data to
assist in creating new content. One of the more
popular designs, Generative Adversarial Networks
(GAN), consist of two neural networks, a
discriminator and a generator, that work together to
generate new content.
The generator creates new data, while the
discriminator evaluates the quality of the generated
data and provides the generator with feedback to
improve it. If you use a popular generative AI model,
another one is the Variational Auto encoder (VAE),
which learns, not a deterministic function mapping
input to output, but rather a probabilistic
representation of the training data to generate new data
by sampling from this distribution. Over the past few
decades, the range of tools rooted in artificial
intelligence has grown progressively, all while
generative AI emerges as a powerful tool in that field.
Generative AI utilizes natural language processing
(NLP), deep neural networks and machine learning
techniques to extract features and patterns from
extensive datasets and generate output that closely
resembles text, images or similar output created by
humans. And the output can be generated in different
formats such as text, audio, or video based on the
requirement.
Poojitha, S. L., Sindhu, J., Jyoshna, G. L., Priya, N. I. and Bolleddula, R.
AI Powered Personal Health Assistant.
DOI: 10.5220/0013920500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
767-772
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
767
ChatGPT, a language model that can generate
seemingly human-like responses to textual prompts,
was developed by Open AI. It is one of the most used
GAI models and it is based on transformer model. In
the similar vein of GPT series, Transformers is a
generative model which is commonly used for
Natural Language Generation (NLG). The
transformers are increasingly used to other cognitive
activities like audio and vision. The AI-powered
personal health assistant system incorporates various
technologies, such as data processing, machine
learning models, natural language processing, and
geolocation services, to provide comprehensive
healthcare assistance.
An AI-powered personal health assistant aims to
enable each person to use an interactive platform for
entering personal health records, talking to the system
via speech or text, and receiving personalized health
information. The system can assist with early illness
identification, selection of doctors and departments,
and even recommendations of therapy.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Existing System
Current Naive Bayes classifier-based Clinical
Decision Support Systems (CDSS) suffer with few
disadvantages. In complex healthcare scenarios
where symptoms and patient traits are
interdependently linked, Naive Bayes' assumption of
feature independence does not hold (Naive Bayes)
despite being simple and adequate when handling
large datasets with categorical features. This
assumption may lead to unfounded forecasts if
characteristics are associated, since it disregards the
complex interactions between mit multiple health
markers. In addition, Naive Bayes models may make
biassed predictions in cases where certain ailments
are underrepresented within an unbalanced dataset.
The accuracy of the output, also, was significantly
influenced by the completeness and quality of the
input data; noisy or missing data can substantially
decrease its accuracy.
In addition, if Naive Bayes is computationally
efficient, it does not exploit sequential or temporal
patterns in the patient data, critical for understanding
the evolution of a disease or chronic conditions.
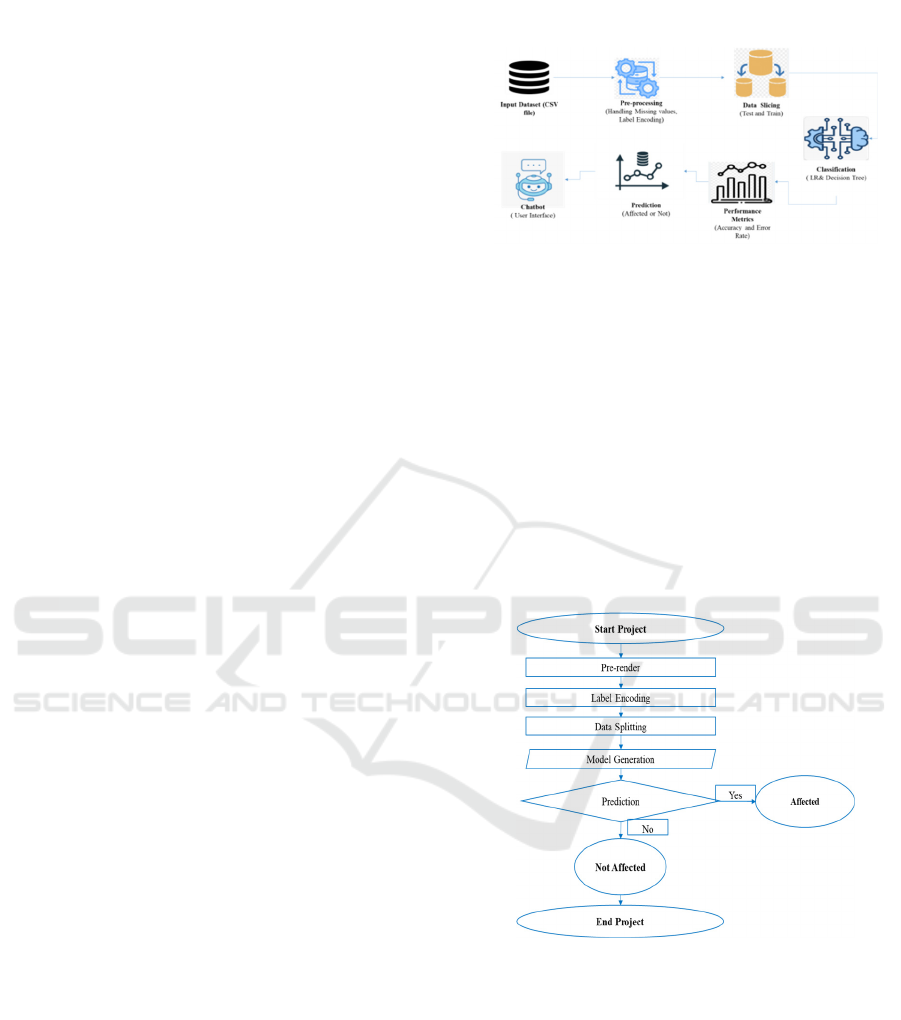
2.2 System Architecture
Figure 1: System Architecture.
2.3 Flow Diagram
A flow diagram (figure 2) is a representative diagram
that illustrates a process or a system. By illustrating
the movement of decisions, actions, and information,
it helps to understand and break down complex
processes. Process representation: In process
representation, a customized illustration is made to
show the various stages or phases or actions in a
process using pre-defined notations (e.g., diamonds
for decisions and arrows representing flow direction
and rectangles for process). The figure 2 shows Flow
Diagram.
Figure 2: Flow Diagram.
2.4 Proposed System
The "AI-based Individual Health Tutor" designed
utilizes state-of-the-art AI and natural language
processing capabilities to transform the way
healthcare is interacted with (google.com) It accepts
voice or text input from a user, processes medical data
and makes predictions about potential diseases. It is
used to predict the illness precisely using a healthcare
dataset including crucial medical features such as
symptoms, medical history, and demographic
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
768

features. It preprocesses and processes this data as
needed, which includes remedial techniques for
filling in blanks and encoding of categorical
attributes, thus ensuring proper accuracy and utility.
The AI Model Predict possible Diagnoses based on
this data using Classification methods such as
Decision Trees and Logistic Regression.
2.5 Working Process
(Near real time): Users can respond in their favourite
way to voice inputs/ yes or no questions through the
chatbot interface (in Tamil, English etc.). The system
recommends personalized medical department,
doctors and treatments. It also offers location-based
services that recommend healthcare facilities near-by
to ensure that consumers can easily access the
healthcare services they need. By combining AI,
machine learning, and geolocation, the system aspires
to deliver better healthcare, promote early disease
detection, and broaden access to medical services.
proposed a new approach for running clinical trials
using the Variational Autoencoder Modular Bayesian
Network (VAMBN) model along with longitudinal
clinical research data.
Theoretical validation concerning data protection
was gained through fake patient data. It can facilitate
data sharing and assist with trial design. GAI can
select and optimize outcomes for clinical studies. It
can identify clinical outcomes and endpoints by
analyzing previous data analytics that identify other
major trends for patients, researchers, and regulatory
bodies. The use of GAI to optimize clinical trials
might dramatically enhance trial efficiency, facilitate
stratification of patients, reduce cost, and deliver
reliable, generalizable results. Researchers may use
the GAI to identify opportunities to improve trial
procedures, which could help enhance patient care
and tailor treatment.
Label Encoding: Label encoding is used to convert
categorical data (such as gender and emotions) into
numerical representation. This process allows for the
efficient handling of these variables by machine
learning algorithms by assigning a unique integer to
each category. The first step is to check for missing
values in the dataset. Depending on the extent and
type of how much does data is missing.
2.5.1 Input Data
The input data for the disease prediction model comes
from an illness prediction dataset available on the
Kaggle platform: Label Encoding: Label encoding is
implemented to convert categorical data (like gender
and emotions) into numerical form. This process
assigns a separate integer for every category allowing
machine learning algorithms to process these
variables. We first check for any missing values in
the dataset. Depending on depending on the extent
and nature of the missing values, techniques such as
mean/median imputation, forward/backward filling,
or dropping records with missing values are applied.
Category is translated through label encoding.
This dataset usually includes symptoms, medical
history, patient demographics, and test results, all of
which are potentially useful for predicting disease.
The data comes from various sources and can include
both unstructured (written descriptions) and
structured (numbers and categories) content. The
dataset serves as the backbone to train and evaluate
predictive models. To ensure the accuracy and utility
of the data, it is crucial to perform a preliminary
inspection and understand the history of each feature
and its role in predicting disease outcomes.
2.5.2 Pre-Processing
Data preparation is a critical step to ensure that the
dataset is clean, and ready for analysis. Preprocessing
is an important process to prepare illness prediction
dataset for analysis. The first step in handling
missing values is to identify any missing or
incomplete data items in the dataset. Common
approaches to tackle this issue include imputation
whereby the missing values are substituted with the
mean, median or mode, or simply deleting records
that have too many missing values.
Dealing with Missing Values: Identifying ways of
missing values can make the analysis wrong. To
address these missing values in the data, methods like
imputation replacing missing values with the mean,
median, or mode and simply removing records that
have missing values are utilized, due to the fact that
machine learning algorithms require numerical input.
2.5.3 Data Splitting
In order for learning to occur throughout the machine
learning process, data is required. Test data are
necessary to assess the algorithm's performance and
determine how well it functions, in addition to the
data needed for training. We regarded 70% of the
input dataset as training data and the remaining 30%
as testing data in our procedure. The process of
dividing accessible data into two halves, typically for
cross-validator reasons, is known as data splitting.
AI Powered Personal Health Assistant
769

2.5.4 Categorization
Classification is the procedure of forecasting what
kind of disease applies Decision Trees and Logistic
Regression to the pre-processed dataset.
DTs, or decision trees
Decision tree (DT) is a popular machine learning
technique for classification and regression problems.
Decision trees divide a dataset into subsets
according to feature values in a recursive manner and
create a tree-like model of decisions and their
possible consequences. Each internal node represents
a characteristic or attribute, each branch represents a
decision rule, and each leaf node represents an
outcome or class label.
RNN and Decision Tree Comparison
Data Types Decision trees are optimal for tabular data
(where associations between features are not
sequential), while RNNs are optimal for sequential
and time-dependent data.
RNNs vs Decision Tree: Compared to a simple
Decision Tree algorithm, RNNs involve more
complex calculations and more trainable weight.
Decision Trees can be implemented faster and are
straightforward, but in turn may overfit our data if
hyper-parameters are not properly tuned.
Interpretability: RNNs are staid to be a "black box"
due to the complexities of its internal processes,
Decision Trees have better interpretability hence
easier to understand and explain. Logistic regression
is a statistical method used for binary classification
problems, where we need to predict one of two
possible outcomes. Logistic regression is more
suitable for conditions with a categorical response
variable (e.g., disease vs. no disease, yes vs. no)
rather than a regression (linear regression explodes
continuous values). For Logistic regression, it
predicts the probability of an event. Logistic
regression's defining idea is the use of the logistic
function referred to as the sigmoid function to
communicate how a dependent variable (the
outcome) relates to one or more independent
variables (predictors or features).
It maps any input value to a probability between 0
and 7 using the logistic function.
2.5.5 Prediction
The prediction phase uses the trained LR and
Decision Tree models to classify the disease type
based on fresh or unknown patient data. The
sequential data is passed through the network in
order for the LR to provide predictions that
correspond to the probability of certain illnesses. On
the other hand, the Decision Tree you learn
classification rules to diagnosis illness according to
feature value. The results from these models give
predictions which can be indirectly used to assess the
possibility of a specific illness or a diagnosis for it.
Finally, a model evaluation by comparing the
predictions with the real diagnosis is conducted.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Figure 3: Enter into Dashboard.
Figure 4: Fill the registration form.
The figure 3 Enter into Dashboard and figure 4
shows Fill the registration form.
Figure 5: login page.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
770
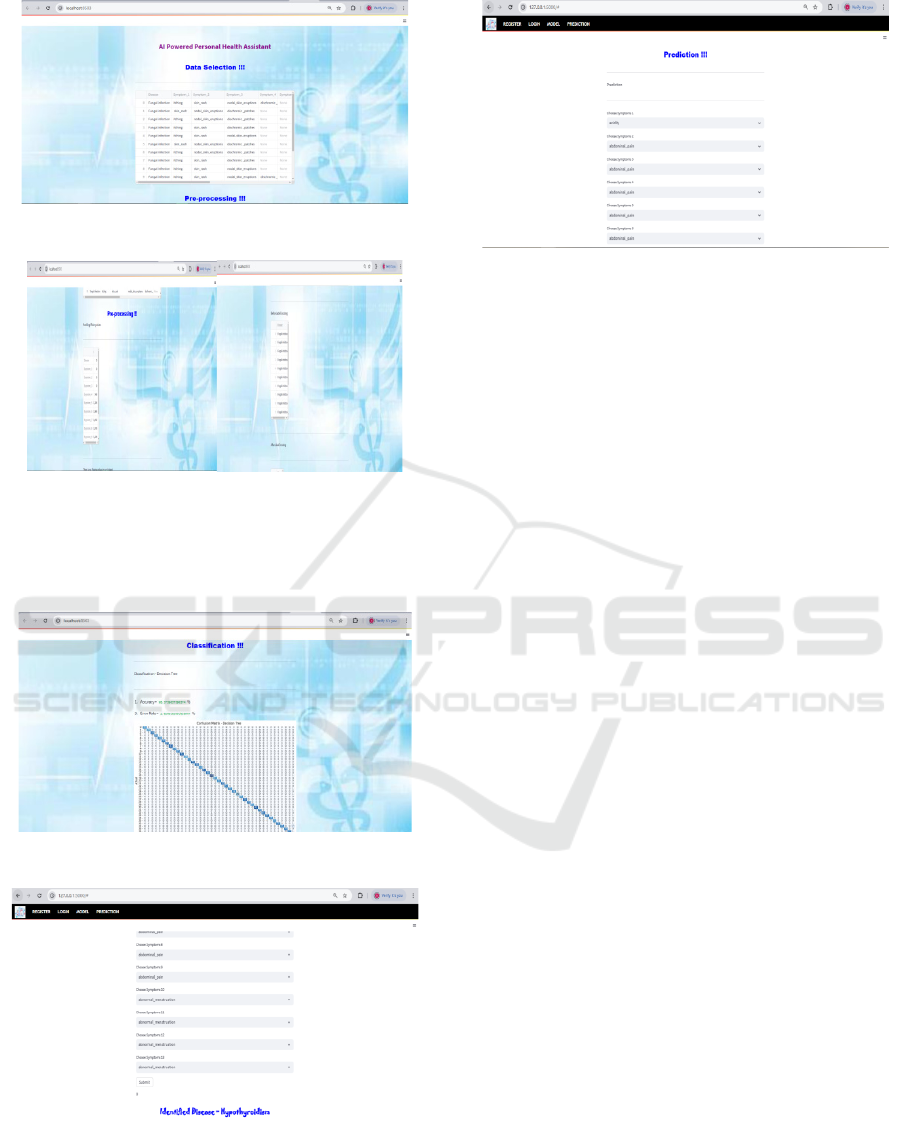
Figure 6: upload dataset.
Figure 7: Preprocessing and encoding.
The figure 5 shows login page and Figure 6 shows
upload dataset. The figure 7 shows Preprocessing and
encoding.
Figure 8: Classification report.
Figure 9(a): Prediction results.
Figure 9(b): Prediction results.
The figure 8 shows Classification report and
figure 9a ,b shows Prediction results.
4 CONCLUSIONS
An advanced personal health assistant powered by
AI, it is designed to improve the quality of medical
decision-making and make healthcare more
accessible. It uses ML algorithms such as logistic
regression and decision trees, enabling it to
accurately predict potential medical problems using
the user input it captures. The assistant will assess
symptoms, medical history and other health
characteristics to generate predictions from
information users provide by voice or text. The
system also provides customized recommendations
on treatment procedures, doctors, and medical
establishments, to ensure that everyone gets quality
care. The chatbot interface enhances user interaction
by offering voice input for hands-free use and
multilingual support. The AI assistant could
furthermore suggest local healthcare facilities based
on the user's location to ensure that medical services
are easily accessed.
REFERENCES
García, A., & Martinez, E. (2023). "Integration of RNNs for
Real-Time Patient Monitoring and Prediction." IEEE
Acess, 11, 1234512355. doi:10.1109/ACESS.2023.32
98745
Harris, L., & Green, M. (2024). "Hybrid Models
Combining RNNs and Decision Trees for Accurate
Disease Predictions." BMC Medical Informatics and
Decision Making, 24(1), 30. doi:10.1186/s12911-024-
02059-8
Johnson, R., & Davis, T. (2023). "Leveraging Natural
Language Processing for Chatbots in Healthcare."
AI Powered Personal Health Assistant
771

Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 140, 104-113. doi:
10.1016/j.jbi.2023.104203
Lee, K., & Park, H. (2024). "Enhancing Clinical Decision
Support with Hybrid RNN-Decision Tree Models."
Journal of Medical Systems, 48(2), 1-12.
doi:10.1007/s10916-023- 01964-4
Miller, J., & Edwards, N. (2024). "A Comprehensive
Review of Decision Trees in Clinical Decision Support
Systems." Computers in Biology and Medicine, 149,
105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.105067
Mohebbanaaz, M. Jyothirmai, K. Mounika, E. Sravani and
B. Mounika, "Detection and Identification of Fake
Images using Conditional Generative Adversarial
Networks (CGANs)," 2024 IEEE 16th International
Conference on Computational Intelligence and
Communication Networks (CICN), Indore, India, 2024,
pp. 606- 610, doi: 10.1109/CICN63059.2024.108473
79.
Mohebbanaaz, Sai, Y.P. & Kumari, L.V.R. A novel
inference system for detecting cardiac arrhythmia using
deep learning framework. Neural Comput &
Applic (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-025-
11092-x.
Mohebbanaaz, Y. P. Sai and L. V. R. Kumari, "Automated
Detection of Cardiac Arrhythmia using Recurrent
Neural Network," 2021 6th IEEE International
Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in
Engineering (ICRAIE), Kedah, Malaysia, 2021, pp. 1-
6, doi: 10.1109/ICRAIE52900.2021.9703995.
Nguyen, H., & Lee, J. (2023). "Real-Time Health
Monitoring Systems Using GRU-Based RNNs." IEEE
Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning
Systems, 34(8), 1543- 1552. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.202
3.315674
Patel, M., & Kumar, S. (2024). "Decision Trees for
Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: A Review." Health
Information Science and Systems, 12(1), 45-58.
doi:10.1186/s13755-024-00023-y
Singh, P., & Gupta, R. (2024). "Evaluating Multilingual
Chatbot Systems for Medical Diagnostics." Journal of
Med cal Itenet Rsearch, 26(3), e34567.doi:10.2196/34
567
Smith, J., & Roberts, A. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of
RNN and LSTM Networks in Disease Prediction
Models." Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 122, 102-
110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2023.102002
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., & Yang, X. (2023). "Advances in
Recurrent Neural Networks for Medical Data
Analysis." Journal of Healthcare Informatics Research,
7(2), 215-229. doi:10.1007/s41666-023-00123-5
Wright, T., & Zhang, X. (2023). "Advancements in Chatbot
Technologies for Personalized Healthcare." Journal of
Artificial Intelligence Research, 72, 567-586.
doi:10.1613/jair.1.12644
Zhang, L., & Chen, Y. (2023). "Deep Learning for Disease
Outcome Prediction: RNNs and Beyond." IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 70(5), 1234-
1245. doi:10.1109/TBME.2023.3154289
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
772
