
Adaptive Post‑Quantum Biometric Authentication Framework for
Decentralized Systems
K. Venkatesh, R. Darasan, S. Dushyanth and R. M. Ragu
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education, Krishnankoil –
626126, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Biometric Authentication, Post‑Quantum Cryptography, Blockchain, Data Security, Industry, Innovation,
Infrastructure (SDG 9), Sustainable Cities, Communities (SDG 11), Peace, Justice, Strong Institutions (SDG
16).
Abstract: Physical attacks against the traditional systems that provide biometric authentication have become a staple of
modern security systems, yet even these systems can leave individuals vulnerable to the risk of data breaches,
quantum computing attacks, and PIN hopping. The first paper is a secure and decentralized biometric
authentication system using post-quantum cryptography and blockchain. The combination of lattice-based
encryption and extensive decentralized storage mechanisms offers an approach to protecting data against
quantum attacks and at the same time achieving data integrity and privacy. Dovetailing with Sustainable
Development Goals (SDGs) and its prospected Goal 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure), Goal 16
(Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions) and Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), the proposed
approach creates an avenue for resilient infrastructure while working with SDGs to streamline security
provisions for the digital landscape and towards cities, ensuring that cities remain safe and resilient for all.
1 INTRODUCTION
Biometric authentication is broadly used today as it
provides a secure and easy to use method of
validating your identity by using unique human
characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition
and retina scans. Biometric authentication also
reduces the chance of hacking, as they are usually
harder to guess and steal than passwords. It is now
being implemented in banking, healthcare, and other
Verticals to Secure Security. However, biometric data
remains a significant concern, as it cannot be altered
like your password if exposed.
The second type of hacking is what we call
traditional hacking where the attacker uses common
user authentication methods such as passwords and
even multi-factor authentication (MFA) that are
riddled with vulnerabilities. Not only that, but weak
or repeated passwords seem to be a problem that most
people have, making them easy pickings for hackers.
Even one-time passwords (OTPs) and security tokens
can be phished and social engineered. While
biometric authentication is stronger, it is not
infallible. The privacy risks involved are serious, as
in recent years major data breaches of companies
have resulted in biometric records being stolen. This
being said, there is a more secure way to process
biometric data.
Like, if we need our fingerprints to unlock our
smartphones, what if they get compromised? To
avert this situation, post-quantum cryptography
needs to be devised to ensure the future security of
biometric data. Blockchain-based authentication is
another emerging solution that also alleviates the
need for storing biometric data in central data banks
and prevents mass data breaches. This allows
biometric verification to be done securely and in a
decentralized way. Providing secure biometric
authentication system based on blockchain and post
quantum cryptography.
2 EXISTING METHODOLOGY
• Current Biometric Authentication Systems:
Discuss centralized and decentralized models.
Security Limitations: Explain vulnerabilities
such as data breaches, replay attacks, and
quantum threats. The figure 1 illustrated the
Data Breaches by Company in Years.
Venkatesh, K., Darasan, R., Dushyanth, S. and Ragu, R. M.
Adaptive Post-Quantum Biometric Authentication Framework for Decentralized Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0013919500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
703-707
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
703
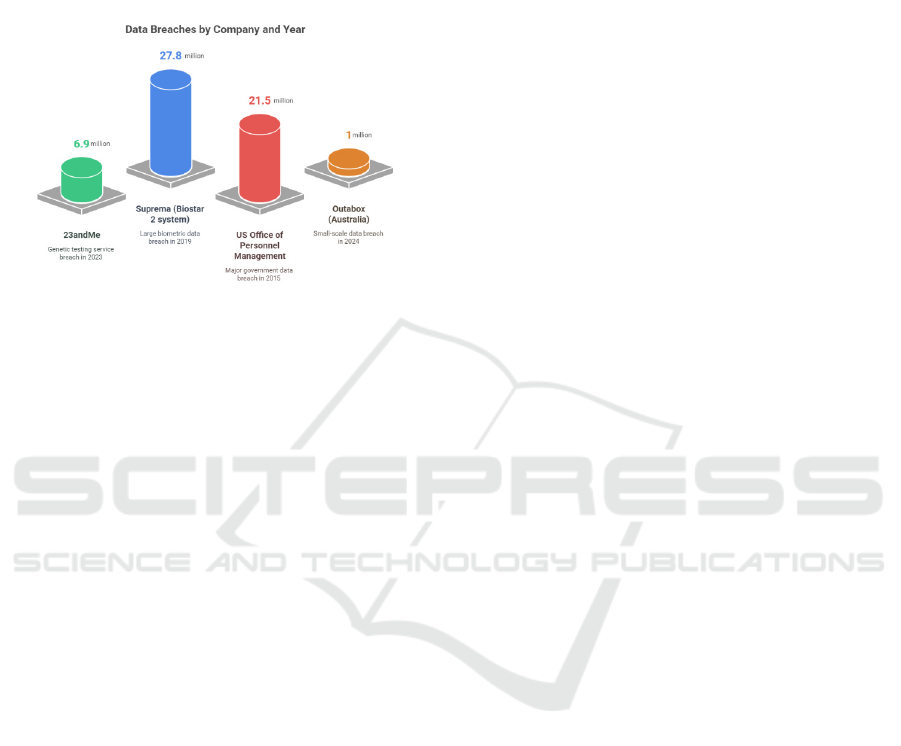
• Tools Used: Describe conventional
cryptographic techniques like RSA, AES, and
ECC.
• Research Gap: Identify the shortcomings in
scalability, security, and computational
efficiency.
Figure 1: Data breaches by company in years.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The following research articles were reviewed to
establish the foundation of our study:
1. The Horcrux Protocol: A Method for
Decentralized Biometric-based Self-sovereign
Identity - Asem Othman, John Callahan.
Proposes decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and
self-sovereign identity concepts to eliminate
single points of compromise.
2. Decentralized Biometric Authentication based
on Fuzzy Commitments and Blockchain -
Nibras Abo Alzahab et al. Introduces a
blockchain-based biometric authentication
protocol leveraging fuzzy commitment
schemes for privacy.
3. Post Quantum Cryptography: Techniques,
Challenges, Standardization, and Directions
for Future Research - Ritik Bavdekar et al.
Discusses vulnerabilities of classical
cryptosystems in the quantum era.
4. Combining Blockchain and Biometrics: A
Survey on Technical Aspects and a First Legal
Analysis - Mahdi Ghafourian et al. Surveys
the integration of blockchain and biometrics,
highlighting technical and legal consideration
5. Companies Prepare to Fight Quantum Hackers
- Catherine Stupp. Discusses corporate efforts
to transition to post-quantum cryptographic
algorithms.
6. A Survey on Post-Quantum Cryptography for
Constrained Devices - Sujoy Sinha Roy, Ingrid
Verbauwhede. Reviews postquantum cryptog
raphic algorithms suitable for resource-limited
devices.
7. BlockchainBased DecentralizedManageme
nt of IoT Access Control: A Survey - Lei Xu
et al. Explores how blockchain enhances
decentralized access control, relevant to
biometric authentication.
8. A Survey on Biometric-based Cryptographic
Key Generation Schemes - Surya Nepal et
al. Discusses cryptographic key generation
from biometric data.
9. Post-Quantum Cryptography: Current State
and Quantum Mitigation - Michele Mosca,
Marco Piani. Analyzes the current state of
post-quantum cryptography and mitigation
strategies.
10. Decentralized Authentication UsingBlockc
hain and Biometrics - S. S. Dash et al.
Proposes a decentralized authentication
framework combining blockchain with
biometrics.
11. Post-Quantum Cryptography: NIST's Plan
for the Future - Dustin Moody et al. Details
NIST’s efforts in standardizing post-
quantum cryptographic algorithms.
12. Blockchain-Based Decentralized Storage
Networks: A Survey - Mohammad Ali Dorri
et al. Surveys decentralized storage
solutions using blockchain.
13. A Survey on Biometric Recognition and Its
Integration with Blockchain Technology - R.
Tolosana et al. Discusses applications and
challenges in integrating biometric recognit
ion with blockchain.
14. Post-Quantum Cryptography: Survey and
Open Research Challenges - Jintai Ding,
Albrecht Petzoldt. Provides a comprehensiv
e survey of post-quantum cryptographic
algorithms.
4 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
• Our Approach: Introduce the novel
combination of post-quantum cryptography
and blockchain storage (IPFS) for secure
biometric authentication. The figure2
illustrated the Causes of Biometric Data
Breaches in India
• Algorithm Used: Explain the steps for
biometric feature extraction, encryption, and
decentralized verification.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
704

• Performance Metrics: Define security
robustness, latency, and system scalability.
Figure 2: Causes of biometric data breaches in India.
5 TOOLS AND TECHNOLOGIES
USED
Here are the tools and technologies used in this
project and there uses.
Table 1: Tools and technologies used for fingerprint data
processing and blockchain integration.
Tool/Techn
ology
Description & Usage
Kali Linux Primary OS for running
fingerprint scanning,
cryptographic operations, and
ADB tools.
Python 3 Core programming language
used for fingerprint data capture
and processing.
PyFingerpri
nt
Python library used to interface
with the fingerprint scanner for
reading and processing
fingerprint data.
PyCryptodo
me
Used for cryptographic
operations like encrypting and
hashing fingerprint data securely.
Web3.py Enables interaction with the
Ethereum blockchain for storing
and verifying fingerprint hashes.
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 3: Secure biometric data management with
blockchain.
Comparison with Existing Methods: Highlight
performance improvements in security, speed, and
decentralization. Security Against Quantum Attacks:
Demonstrate encryption resistance to quantum
decryption attempts. The figure 5 shows the Finger
Print Data Capture & storage. Practical
Implementation & Testing: Discuss real-world
application feasibility and computational efficiency.
1. Connect & Test Fingerprint Scanner
a. Check if the fingerprint scanner is
detected:
lsusb
b. Run this command to test serial device
access:
dmesg | grep tty
c. If detected as /dev/ttyUSB0, proceed with
fingerprint capture.
Figure 4: Connect & test fingerprint scanner.
2. Fingerprint Data Capture & Storage:
a. The fingerprint scanner was successfully
connected and tested using the
pyfingerprint library.
b. Raw fingerprint data was captured and
securely stored in a text file
(fingerprint_raw.txt).
Adaptive Post-Quantum Biometric Authentication Framework for Decentralized Systems
705

Figure 5: Finger print data capture & storage.
3. Secure Transfer & Hashing:
a. Fingerprint data logs were retrieved from an
Android device using ADB and stored on a
Kali Linux system.
b. adb pull /sdcard/fingerprint_log.txt. This will
save fingerprint_log.txt in your current Kali
directory.the figure 3 illustrated theSecure
Biometric Data Management with Blockchan.
c. To ensure data integrity, a SHA-256 hash of
the fingerprint log file was generated and
stored securely. the Figure4 illustrated the
Connect & Test Fingerprint Scanner.
sha256sum fingerprint_log.txt > fingerprint
_hash.txt
d. Verify it’s there: ls -lh fingerprint_log.txt
4. Decentralized Storage on IPFS:
a. The fingerprint hash was uploaded to IPFS,
providing a decentralized, immutable, and
tamper-proof storage mechanism. the figure 6
Illustrated the Secure Transfer & Hashing.
b. The stored hash can be retrieved later using the
CID (Content Identifier) for verification,
ensuring data authenticity.
Figure 6: Secure transfer & hashing.
7 CONCLUSION
The proposed biometric authentication system
enhances security by integrating post-quantum
cryptographic algorithms with blockchain-based
storage. By eliminating centralized vulnerabilities
and ensuring data integrity, our approach aligns with
SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure),
SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions), and
SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). These
goals contribute to the development of resilient digital
infrastructure, safeguarding personal data, and
creating a more secure digital society. Future research
will explore optimizing performance metrics and
real-world deployment.
REFERENCES
A. K. Das, P. Sharma, S. Chatterjee, and M. Conti, "A
Dynamic Password-Based User Authentication Scheme
for Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Networks," Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, vol. 35, no. 5, pp.
1646–1656, 2012.
A.Shamir, "Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature
Schemes," in Advances in Cryptology, G. R. Blakley
and D. Chaum, Eds. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1985,
pp. 47–53.
Attila A. Yavuz, Saleh Darzi, and Saif E. Nouma,
"LiteQSign: Lightweight and Scalable Post-Quantum
Authentication for Heterogeneous IoT Applications,"
arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.18674, March 2025.
C. P. Schnorr, "Efficient Signature Generation by Smart
Cards," Journal of Cryptology, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 161–
174, 1991.
D. Chaum and E. van Heyst, "Group Signatures," in
Advances in Cryptology EUROCRYPT '91, D. W.
Davies, Ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1991,
pp. 257–265.
D.Boneh and M. Franklin, "Identity-Based Encryption from
the Weil Pairing," in Advances in Cryptology CRYPTO
2001, J. Kilian, Ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-
Verlag, 2001, pp. 213–229.
J. Liu, Z. Chen, and F. Xiao, "A Survey on Blockchain-
Based Identity Management Systems," Frontiers of
Computer Science, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2021.
J.Camenisch and A. Lysyanskaya, "An Efficient System for
Non-transferable Anonymous Credentials with
Optional Anonymity Revocation," in Advances in
Cryptology EUROCRYPT 2001, B. Pfitzmann, Ed.
Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2001, pp. 93–118.
K. R. Raghavendra and S. B. D. Kumar, "A Secure and
Efficient Biometric Authentication Scheme for
Multiserver Environments Using Elliptic
Curve Cryptography," Security andCommunication
Networks, vol. 2018, Article ID 4241520, 2018.
L. Lamport, "Password Authentication with Insecure
Communication," Communications of the ACM, vol.
24, no. 11, pp. 770–772, 1981.
M. Bellare and P. Rogaway, "Random Oracles are
Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient
Protocols," in Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference
on Computer and Communications Security, Fairfax,
Virginia, USA, 1993, pp. 62–73.
M. Conti, S. Kumar, C. Lal, and S. Ruj, "A Survey on
Security and Privacy Issues of Bitcoin," IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 20, no. 4,
pp. 3416–3452, 2018.
N. Kaaniche and M. Laurent, "A Blockchain-Based Data
Usage Auditing Architecture with Enhanced Privacy
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
706

and Availability," in Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE
Trustcom/BigDataSE/ICESS, Sydney, NSW,
Australia, August 2017, pp. 875–882.
Nibras Abo Alzahab, Giulia Rafaiani, Massimo Battaglioni,
Franco Chiaraluce, and Marco Baldi, "Decentralized
Biometric Authentication based on Fuzzy
Commitments and Blockchain," arXiv preprint
arXiv:2409.11303, September 2024.
Pranadeep Katari, Venkat Rama Raju Alluri, Ashok Kumar
Pamidi Vankata, Leeladhar Gudala, and Sai Ganesh
Reddy, "Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: Practical
Implementations for Post-Quantum Security," Asian
Journal of Multidisciplinary Research & Review, vol.
4, no. 1, 2023.
R. L. Rivest, A. Shamir, and L. Adleman, "A Method for
Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key
Cryptosystems," Communications of the ACM, vol. 21,
no. 2, pp. 120–126, 1978.
Rosario Arjona, Paula López-González, Roberto Román,
and Iluminada Baturone, "Post-Quantum Biometric
Authentication Based on Homomorphic Encryption and
Classic McEliece," Applied Sciences, vol. 13, no. 2, p.
757, January 2023.
S. Nakamoto, "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash
System," 2008. [Online
T. ElGamal, "A Public Key Cryptosystem and a Signature
Scheme Based on Discrete Logarithms," IEEE
Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 31, no. 4, pp.
469–472, 1985.
W. Diffie and M. E. Hellman, "New Directions in
Cryptography," IEEE Transactions on Information
Theory, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 644–654, 1976.
Adaptive Post-Quantum Biometric Authentication Framework for Decentralized Systems
707
