
The Future Role of Team Creativity and Individual Effectiveness in
Innovation Management and Leadership
N. Vinodh and A. K. Subramani
Saveetha School of Management, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University,
Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Creative Thinking, Leadership, Competitiveness, Risk, Strategy, Innovative Management.
Abstract: The study offers an examination of both personal and professional attributes that aid in the creation of the best
methods for resolving work-related issues. It also outlines leadership tactics that are based on inspiring
employees to act and think outside the box while also considering the team's overall creative output. The
inventions and character traits of persons who develop them and provide methods for putting them into
practice affect the success of contemporary communities. Innovations originate within individuals rather than
in businesses and corporations. The pursuit of methods to enhance management is highly pertinent. The
foundation of the operations of businesses aiming for success in a rapidly evolving business environment is
creativity and innovation. Certain prerequisites must be met for innovative activity: a well-thought-out plan
for the entire company, a welcoming environment, driven staff, and capable management. There are
established methods for overseeing an organization's creative growth. A growth in customer demand, a rise
in product quality, intense competition, and the organization's general sustainability are all influenced by the
relationship between a successful strategy and workers' inventiveness. Techniques for implementing projects
include theoretical (systematization, idealization, modeling) and practical observation, comparison).
Businesses are said to need to be very determined, risk-taking, broad-minded, and imaginative in order to
engage in innovative activities. Popular initiatives rely on the creative ideas of all the experts working on
them to be implemented successfully. Innovative solution implementation techniques are organized. The
prerequisites for cultivating creative thinking and inspiring inventive staff members are outlined.
1 INTRODUCTION
The twenty-first century is a period of constant
invention and transformation. These days, stability is
more likely to surprise than innovation. Furthermore,
the new is invariably linked to advancement and
forward motion(N. F. Al Mass,et.al., 2024). A single
or group of people's actions are what cause any
changes. However, the leader's and his team's actions
carry out the overall plan for the organization's growth
and are contingent upon the circumstances that give
rise to innovative and promising ideas. The necessity
of innovation was part of the general strategy and the
corporate creed of prosperous Indian enterprises. The
emphasis on quality, the price-quality ratio, and the
rejection of phony super profits are examples of
"market values" that have historically taken center
stage(H. Liu, et.al., 2024). Qualitatively novel
products and services that satisfy customer demands
were examples of innovations. The mechanism behind
these advancements indicates that the company's
overall market effect was influenced by consumer
demand. However, competition is the foundation of
success. Predicting market movements, being
prepared for modifications to current management
structures, and inspiring innovative staff members
who contribute to the creation of new innovations are
all critical. Studies conducted by psychologists the
revealed that most persons possess the traits required
to carry out creative endeavors(S. Aziz and N. A.
Rahim, 2023). The challenge lies in out how to
"translate the potential into the actual." External social
factors have the power to either foster or stifle
innovation, "kill it in the bud." Innovation-birthing
reefs are both psychological (the urge for inventive
activity and the environment for its realization) and
economic (material base).One important factor is the
fear of changes, such as the typical stereotype of
human life. Potential innovators must exercise
prudence because this dread instills anxieties and
638
Vinodh, N. and Subramani, A. K.
The Future Role of Team Creativity and Individual Effectiveness in Innovation Management and Leadership.
DOI: 10.5220/0013918100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
638-644
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

discourages daring, proactive acts. It has been
determined that the individual themselves is the
psychological obstacle to introducing something
novel. As a result, inventions originate within each of
us and are realized or not under the circumstances that
life presents. They are not formed in businesses and
corporations.
2 RELATED WORK
In order to successfully apply innovation, one must be
able to recognize its position and importance in the
production process as a whole. Innovation can
transform a condition that no longer meets the needs
of the present. These days, technology has a
significant influence on an organization's strategy,
which is ineffective without a commensurate change
in organizational and production structures. Here, the
organization's selected innovation approach and the
interdependence of subsequent structural changes are
crucial factors. Organization of innovation activities is
based on inevitable managerial changes. The total
level of innovation has increased as a result of these
improvements, both in respect to its prior level and to
competitors (Sharma,et.al., 2024). Any company that
wants to take its operations in a different direction
must alter its labor and management structure and
establish a new division that modifies the management
model to take innovations into consideration.
Selecting the best management style and approach for
a given situation is a crucial step in planning
innovative initiatives. There isn't a single, all-
encompassing organizational structure that works well
for implementing innovative activities. The following
are some of the factors that influence the choice of an
effective organizational model preparedness for
drastic changes long-term technological strategy of
the organization favorable environmental conditions
for the emergence of innovative ideas and availability
of a material base for their implementation ability to
respond to changes in the external environment state
of communications organizational climate as a
guarantee of a healthy working setting. The following
are the new organizational models of innovation
management creation of a departmental organization
that addresses every facet of innovative
activity(Zhang and S. Li,2022). The range of
capabilities for each department is defined; the level
of accountability within the organization's structure
and with regard to partners is established; and the
amount of work within innovative departments is
distributed. At the same time, it's critical to remember
the company's activity profile when organizing an
innovation activity (G. He and Y. Song ,2022). The
following are differentiated based on the
organizational foundation of innovation management
organizations with specialized structures
organizations with mixed structures and a distinct
service that interacts with all departments due to its
authority and competency organizations where
traditional departments handle innovation
management (R. S. Ali,et.al.,2023).
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The level of contact between all of the company's
production units determines how well innovation
management works (L. Gao,et.al.,2012). The overall
inventive impact of the activity is determined by
increasing the level of engagement from each of
them.In big businesses with their own production and
scientific foundation, the third type of innovation
management structure is the most logical and effective
(S. Menon,et.al.,2023). The use of "innovative"
structures, the division of projected development
services, the use of strategic market structures, and the
creation of horizontal management are thought to be
the most successful models of innovation
management. The selection of the best solution
determines how innovation management is
organized(K. K. Ramachandran, et.al.,2024). A
collection of intra-organizational units; unique sectors
for the development of new goods; and industrial units
that permit the fusion of routine and inventive
processes are the three categories into which
innovation development is separated in real-world
practice. Techniques for putting innovations into
practice .The world is changing for objective reasons,
many of which are beyond our control: climate
change, population growth and its corresponding
demands, the need for communication and movement
(migration), and the need to extend and enhance life
expectancy. Any organization cannot function well
over the long run in the ever-changing socioeconomic
landscape without making creative adjustments (N.
Govil, et.al.,2023). If external (natural) circumstances
necessitate such adjustments, the organization will
cease to exist if they are ignored. Techniques for
putting innovations into practice. Finding solutions to
enhance management that take into account social
dynamics is a pressing issue in the modern world(K.
Chandar, et.al.,2024). The challenge of developing
new and upgrading current management structures as
well as planning innovations is brought on by the
growing role of inventive activity in the management
process(Ali Rastgar,et.al.,2024). Knowledge of
The Future Role of Team Creativity and Individual Effectiveness in Innovation Management and Leadership
639
progressive development management theory and
methodology, as well as its creative application and
enrichment, is the methodological foundation of
management (De Silva,et.al.,2024).Scientific study
offers a variety of strategies and a categorization of
techniques for putting creative solutions into
practice.These are the most pertinent ones models of
problem-solving procedures and models of altering
the management system are the most important
models for overseeing an organization's growth (S.
Vella and S. Shariah, 2024).
4 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The original problem scenario was the main focus of
the decision-making process. These issues are
categorized according to the following criteria the
domains they pertain to (technical, economic, and
organizational) the type of impact they have on the
organizational system (strategic, operational, and
current)the degree of uniqueness standard and non-
standard the degree of clarity of the structure
including whether it is well or poorly described; the
degree of feasibility of a solution, such as
algorithmically solvable and not intractable (P.
Pandey,et.al.,2024).The steps listed in constitute a
universal framework for putting innovations into
practice universal mechanism for applying
innovations stage content organizing innovations
unfreezing creative breakthroughs.Performing
creative work freezing innovations that have been put
into practice.
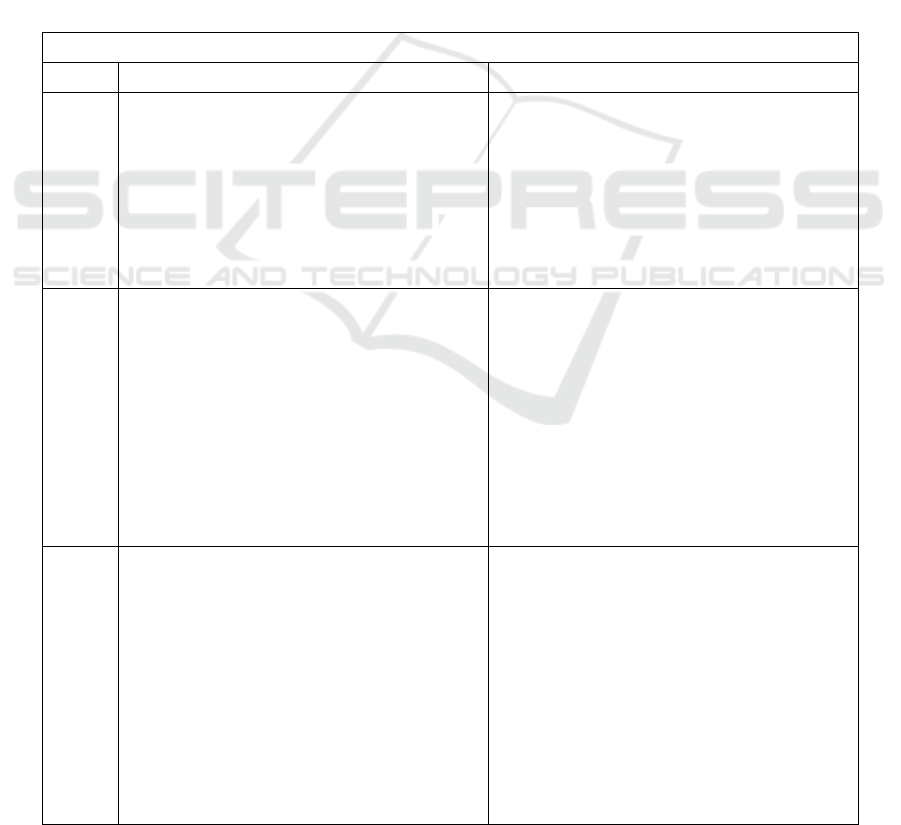
Table 1: Leadership organization.
Innovation
S. No Employee Training
1
The many approaches to putting creative
changes into effect the coerced approach an
inflexible and compelled implementation It
entails implementing ideas quickly. Its
advantage is how quickly innovative
modifications may occur. The drawback is that
the parties concerned have shown strong
opposition to implementing innovation. The
method of ada
p
tation.
A progressive rollout of innovations Its use is
contingent upon the lack of urgency in
achieving an objective. This approach has the
benefit of little resistance to innovations; on the
other hand, the result's potential is delayed. The
approach to crisis management relevant in
situations where the organization's survival is in
jeopardy, innovations are seen as a means of
resolvin
g
a
p
articular issue.
2
The weak resistance is a benefit time constraints
and failure risk are disadvantages. The strategy
for managing resistance. A sophisticated fusion
of the adaptation method and the coercive
method. It is employed when advances must be
implemented immediately. The flexibility to
adjust to a particular circumstance is a benefit;
the intricacy of use is a drawback. The process
of implementing innovations partially
comparable to the adaptive approach the
application of creative elements in certain
de
p
artments, sections, and divisions
The process of implementing innovations in
parallel the concurrent use of innovations and
the earlier methods of work and technology. It
can select the best solution for the work style
using this way. Infrastructure, innovation scale,
and specialist training and retraining are all
critical to the successful adoption of
innovations. However, the organization's
overall lack of readiness for significant changes
and a lack of the required material resources are
linked to the challenges of implementing
innovations.
3
Employee opposition is a unique obstacle to
innovation.
Opposition to innovations.There are two
primary categories of explanations for
opposition to innovations:
Economic and financial fears of unemployment
fears of losing social standing fears of
innovations, changes in the demands and
circumstances of labor, and loss of money. One
economic element impeding innovation to
preserve stability, even if such stability is only
apparent, is the threat of unemployment
. For psychological and personal reasons. The
employee learns that his or her experience,
which has been gathered over many years of
arduous effort, is no longer worth as much
because of inventive advancements. At work,
the situation gets unclear. This is the reason
why workers over 50 are not excited about new
ideas. The socio-psychological basis of
resistance to innovations is confirmed by the
fact that skepticism about innovations is more
prevalent in countries with usually low levels of
economic development, while it can equally
exist in those with high levels
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
640

5 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
The function and demand for an organization's
operations in the social and professional spheres, as
well as the new demands of society, are reflected in
innovative organizational transformations. The Table
1 offering employees a clear image of the
innovations, the steps involved, the anticipated
outcome, details regarding staff placement, and pay is
crucial to preventing resistance to creative
improvements. Official management representatives
and unofficial leaders should encourage innovation.
Innovations can only be successfully adopted in a
favorable socio psychological environment.
Implementing innovations makes the organization's
unseen processes more visible and intensifies both the
team's positive and negative aspects of life.
Innovations have the potential to exacerbate tensions
both horizontally and vertically and damage team
relationships. In the context of innovations, the
manager is fully accountable for the outcomes and
challenges of innovations and is seen as an
impersonal administrator enforcing his will. There is
an increase in criticism directed at the manager and
the overall circumstance. Individual efficacy in
invention. The quest for novel qualitative changes is
one way that innovativeness shows up. This personal
quality is fundamental to the process of coming up
with and putting into practice new ideas, for both
team members and leaders. It stimulates the person's
capacity for original thought. The capacity to come
up with concepts that will serve as the foundation for
breakthroughs is one way that creativity shows up.
Innovativeness is defined as the capacity to manage
novel situations and apply imaginative concepts,
necessitating the proficiency and output of the
individual at every stage. Not all people who are very
creative are also highly innovative. It is challenging
for creative thinkers to put other people's original
ideas into practice. When coming up with fresh
ideas, an organizer-innovator could not be creative.
Therefore, someone who is creative is not always
inventive, and vice versa. An effective organizer-
innovator can understand novel, unconventional
concepts with ease. It is his or her responsibility to
effectively oversee a creative team member's winning
concept and see it through to completion.
6 INNOVATION
CLASSIFICATION
Innovation in the senses the need to relish the sense
of danger, consciousness of the situation's
importance, and unconventional behavior Innovation
in cognition The need to learn new things, satiate
curiosity, look for patterns in everyday objects, and
comprehend intricate but underdeveloped scientific
fields natural inventiveness appears in daily life,
during work, and during active leisure.
Acknowledged innovation In particular acts based
on the circumstances and individual preference.
Personality categories based on the notion of
diffusion of innovations' degree of efficiency in
invention processes. They were ahead of the curve.
The type of inventor who anticipates something
novel, interprets it as meaningful, and is willing to
take chances. Adapting to the times. those who can
engage with advances yet are not risk-takers. Those
who arrive late those who came to the last-minute
realization that changes were necessary. Since the
"human factor" affects how quickly new ideas spread,
the theory of innovation diffusion.
The ability and potential of an organization to
develop and foster innovations is known as
organizational innovativeness. If the organization
adopts conservative stances, such potential might
never materialize. Numerous elements influence
organizational innovativeness, including the
existence of a creative leader, the individual traits of
experts, company values, and the team's
psychological environment.
7 INNOVATION AND
LEADERSHIP
An organization's innovative actions are greatly
influenced by the leadership phenomenon, which also
determines the dynamics and direction of the team's
efforts to solve work-related issues. When it comes to
innovative actions, there are two kinds of leadership.
These come in two varieties: transformational and
transactional. The majority of firms employ the old,
classic transactional style of leadership. The manager
who serves as the team's leader provides clear
instructions on what and how to do, supports or
reprimands subordinates, and enforces rules from
above. Work is still organized in the same way, and
employees carry out their duties as they have in the
past. Innovative development is sparked by
transformational leadership. The leader motivates
The Future Role of Team Creativity and Individual Effectiveness in Innovation Management and Leadership
641

staff to accomplish new goals and transforms the
organizational environment. Workers are influenced
by the leader's example and their perception of the
boundaries of potential change. In addition, the
leader's charm is also quite significant.
A leader needs to be driven, enthusiastic, and
show examples of intellectual innovation. It is the
responsibility of the leader to identify innovative
workers, foster the ideal environments for their
professional and personal growth, and offer tangible
rewards for their efforts. The team's elite should be
composed of regular innovators.The main goal of a
leader is to make positive progress along the route of
inventive development. There are numerous
leadership and management techniques that support
an organization's innovation and creativity. The
following tactics are acknowledged as the most
effective Promoting variety diverse viewpoints
generate innovative concepts. Leaders need to foster
an environment where everyone's viewpoint matters.
Offering materials for innovation and idea generation
to be successful, resources including time, money,
and technology are required. By assembling creative
teams, setting up creative labs, and offering training
to enhance staff members inventive skills, leaders
foster creativity and innovation. Acknowledging the
benefits of innovation.
Team members' innovative contributions should
be rewarded and acknowledged by managers and
leaders, who should also highlight their
accomplishments to inspire them to work more. The
organization's ideals and objectives should be
reflected in rewards and recognition. Workplace
example for the team as a whole, leaders must be
willing to take chances, set an example of desired
conduct, and view setbacks as opportunities for
improvement.A creative approach of thinking
Practical action always comes after thought.
Innovative thinking generates novel, unconventional,
and non-existing concepts. It's a creative process of
coming up with concepts and looking for fresh ways
to tackle issues that need answers.
The ability to integrate intelligence and social
skills in a unique way to extract the precise
information that will lead to the desired solution from
the information field is the foundation of innovative
thinking (N. Govil, et.al.,2023).If a business's team is
led by a leader who thinks creatively and has
proactive, creative people, then the organization is on
an innovative path. The following characteristics are
implied by an innovative way of thinking developed
critical thinking innate curiosity originality
sociability, willingness to share ideas respect for
others' viewpoints, a healthy attitude toward criticism
determination and willpower observation, ability to
conduct thorough analysis individuality, a unique
perspective on commonplace phenomena.
Innovative thinking enables you to generate the
best ideas that can outperform all earlier and
implemented ones identify original solutions in the
social, professional, and personal domains engage
others (friends, family, and coworkers) in your field
of endeavor raise your level of competence by
continuously learning new things and observing and
analyzing innovations value teamwork and combine
the efforts of many into one big one.
These days, the capacity to think creatively is
highly valued in the job market. The creative process
holds a significant position in innovative thought. The
foundation of innovation is creativity integrated into
work procedures. The development of flexibility in
thinking, the invention of new ideas, the pursuit of
new solutions, and enhanced teamwork are all greatly
aided by specific activities designed to foster creative
abilities and inventive thinking. Like brilliance in any
industry, the capacity for innovation is frequently
inherited. However, one may cultivate the ability to
think creatively.
By using a certain algorithm, one can cultivate
creative and imaginative thinking. Prepare, gather the
relevant data regarding the issue, and create a number
of potential solutions. After taking into account the
apparent solution, come up with additional, less time-
consuming, but more effective solutions. Compile a
list of the best concepts. Compile the ideas into a
separate list.Test the outcome to see if anything can
be altered. Through a variety of exercises utilizing
specific strategies, people of all ages can cultivate
their capacity for innovative thinking. The online tool
"TRIZ in Practice" is one of these methods. It has the
greatest algorithms for resolving creative issues in all
aspect of life.
The Table 2 develop your creative skills and learn
how to use innovative algorithms to tackle problems
that call for intricate and unconventional solutions
using this program. Start with the basics if you want
to understand how to develop and apply innovations
in your life. Take in a range of information and gather
inspiration anywhere. in various social media
platforms or blogs.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
642
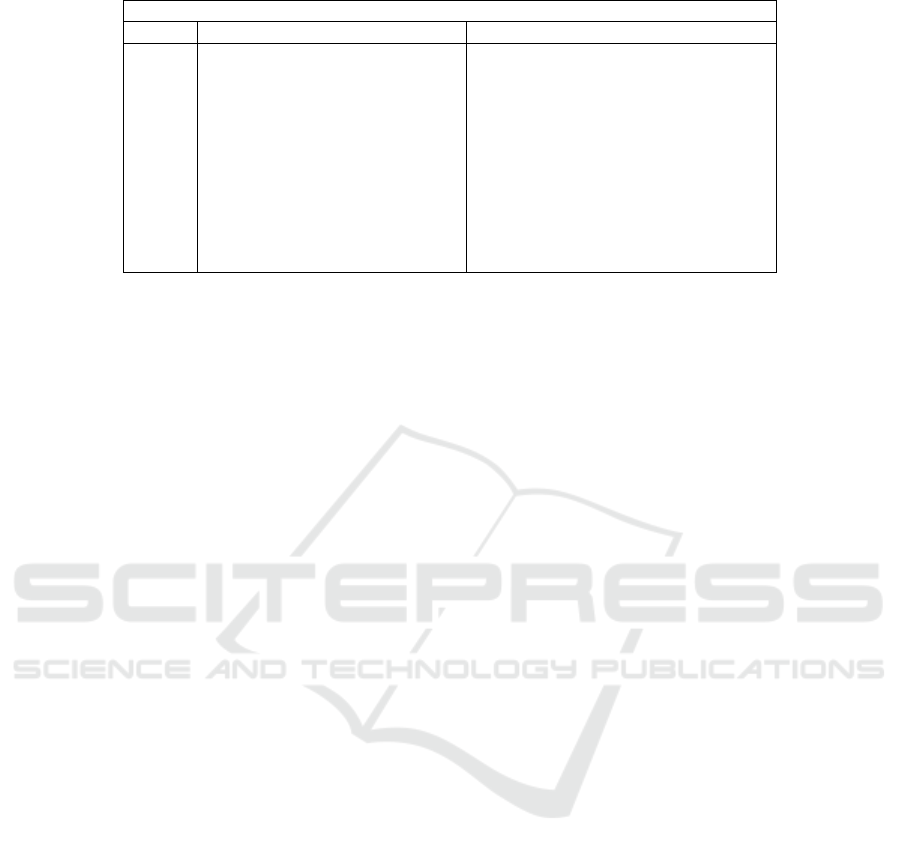
Table 2: Creative skill Management.
Innovation
S. No Tea
m
Leadershi
p
1
Modify the way you absorb
content by utilizing several media
formats, such as text, audio,
video, e-books, and infographics.
Pay attention to the market trends
that are now and will emerge in
the future. Stay abreast of fashion
trends, comprehend the workings
of the field you are interested in,
and identify the sources of
advances
Try everything you've never tried
before and create something new every
day. Think and act creatively, alter your
working approach, and take your job
into consideration from several angles;
defy convention and standard operating
procedures; be fearless in failing and
growing from your mistake and
overcome this obstacle by being
innovative.
When engaging in original creation, consider the
following what would happen if I made this change.
What will occur if I am unable to resolve the
issue.What occurs if I'm headed in the wrong
direction. If I were going to utilize it in 10 years, what
would I change about it. If I had limitless money, how
would I spend it.Depending on their line of work and
way of thinking, each individual from regular
employees to leaders in an organization must create
their own strategy for innovation.Like any other
ability, innovative thinking requires ongoing
development. The organization and its owner can both
gain from an innovative way of thinking .
8 CONCLUSIONS
The able to draw the following conclusions from our
examination of leadership and problem-solving in the
planning of an organization's creative activities.
There are many different models of inventive
processes that are still applicable today, ranging from
a network of intricate coupled system interactions to a
traditional linear series of events. Organizational
innovativeness is the ongoing pursuit of novel
approaches to enhance the company's innovative
climate and capabilities, which aids in fostering the
development of fresh, creative ideas and igniting
inventive activity. The observe the individual
effectiveness of each team member in the innovative
development of the organization by using suggested
models of personality type classification based on
effectiveness of manifestation in innovative activities.
This can create a team that views innovation as a
fundamental aspect of professional activity.
The determined the fundamental traits of an
individual's inventive thinking and put forth an
algorithm for the growth of an original, creative way
of thinking. Understanding the socio-psychological
aspects of innovation resistance and how to effectively
employ them in management will lower the risks
associated with innovations within the company.
Effective management and leadership techniques
that foster innovation and unconventional methods for
resolving production issues, assembling creative
teams, and setting up creative labs have been found.
Finding employees who can become effective leaders
and organizers and who can come up with original
ideas for team promotion is the goal of the suggested
analysis of personal effectiveness in innovative
activities. This will increase the organization's
competitiveness and sustainability.
REFERENCES
N. F. AlMass, A. Arbab, H. M. A. Deeb and A. Shatat,
"Leadership Styles and Their Relationship to Job
Performance: Evidence from Bahrain," 2024
International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and
Applications (DASA), Manama, Bahrain, 2024, pp. 1-4,
doi: 10.1109/DASA63652.2024.10836541.
H. Liu, Y. F. Chin and Y. Ma, "Unraveling the
Experimental Effects of Machine Learning Based
Leadership and Administration on Microsystems
Technology," 2024 International Conference on
Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied
Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 2024, pp. 1-6,
doi: 10.1109/ACCAI61061.2024.10602397.
S. Aziz and N. A. Rahim, "A Review of Ambidextrous
Leadership in Technology Start-Ups: Insights and
Directions," 2023 IEEE Technology & Engineering
Management Conference - Asia Pacific (TEMSCON-
ASPAC), Bengaluru, India, 2023, pp. 1-8, doi:
10.1109/TEMSCON-ASPAC59527.2023.10531350.
A. Sharma, T. R. Barik, D. Daniel and U. Khatari,
"Bibliometric Examination of Spiritual Leadership
Trends in Contemporary Organizations," 2024 IEEE
International Students' Conference on Electrical,
Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), Bhopal,
The Future Role of Team Creativity and Individual Effectiveness in Innovation Management and Leadership
643

India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:10.1109/SCEECS61402.202
4.10482122.
C. Zhang and S. Li, "Impact of Transformational
Leadership and Big Data Analytics Capability on
Supply Chain Innovativeness," 2022 International
Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and
Automation (ICCNEA), Xi'an, China, 2022, pp. 36-39,
doi: 10.1109/ICCNEA57056.2022.00019.
G. He and Y. Song, "Leadership in Community
Organizations: Comparison of the Performance of
Multilayer Network Centrality Algorithms," 2024
International Conference on Interactive Intelligent
Systems and Techniques (IIST), Bhubaneswar, India,
2024, pp. 774-777, doi: 10.1109 /IIST625 26.2024.000
04.
R. S. Ali, B. Rianto, T. Sriwidadi and H. Prabowo, "How
Do Transformational Leadership and The Work
Environment Affects Employee Retention?," 2023 8th
International Conference on Business and Industrial
Research (ICBIR), Bangkok, Thailand, 2023, pp. 1056-
1061, doi: 10.1109/ICBIR57571.2023.10 14769 5 .
L. Gao, R. Qu, K. Shi and J. Lu, "Transactional Leadership
and Employee Creativity: The mediation role of Career
Satisfaction," 2012 International Conference on
Information Management, Innovation Management
and Industrial Engineering, Sanya,
China, 2012, pp. 133-136, doi: 10.1109/ICIII.2012.63
39796.
S. Menon, J. Yadav and A. Chopra, "A Perspective on
Leadership and innovation in a Knowledge-based
economy- Shaping the sustainable workplace," 2023
International Conference on Computational
Intelligence and Knowledge Economy (ICCIKE),
Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2023, pp. 281-286, doi:
10.1109/ICCIKE58312.2023.10131802.
K. K. Ramachandran, S. Takhar, M. K. Jha, J. D. Patel, N.
Randhawa and M. Lourens, "Revolutionising Industries
and Empowering Human Potential with Artificial
Intelligence Tools and Applications," 2024
International Conference on Trends in Quantum
Computing and Emerging Business Technologies,
Pune, India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/TQCEBT
59414.2024.10545285.
N. Govil, N. Batra, D. Thakral, S. Garg and S. Jain,
"Analysis of Information Technology Outsourcing
Services as Future Scope in Indian IT Industries," 2023
2nd International Conference on Applied Artificial
Intelligence and Computing (ICAAIC), Salem, India,
2023, pp. 757-760, doi:
10.1109/ICAAIC56838.2023.10140406.
K. Chandar, V. J and C. K, "Comparative Analysis of Soft
Computing Algorithms for Predicting Employee
Turnover in IT Industry," 2024 3rd International
Conference on Automation, Computing and Renewable
Systems (ICACRS), Pudukkottai, India, 2024, pp. 1643-
1647, doi: 10.110 9/ICACRS 62842.2 024.10841707.
A. Ali Rastgar, M. Basouli and B. Kolahi, "Digital Human
Resource Management: A Mix Method to Identifying
Technical Components," 2024 10th International
Conference on Web Research (ICWR), Tehran, Iran,
Islamic Republic of, 2024, pp. 255-262, doi:
10.1109/ICWR61162.2024.10533367.
D. De Silva, H. Huijser, S. Cunningham and N. Press,
"Essential Professional Skills and Competencies for
Future Information Technology Graduates: Meeting IT
Industry Demands," 2024 International Conference on
Engineering Management of Communication and
Technology (EMCTECH), Vienna, Austria, 2024, pp. 1-
8, doi: 10.1109/EMCTECH63049.2024.10741786.
S. Vella and S. Shariah, "All You Need is Knowledge,
Experience and Tools: A Framework for Integrating
Digital Labour With White Collar Work," 2024 4th
Interdisciplinary Conference on Electrics and
Computer (INTCEC), Chicago, IL, USA, 2024, pp. 1-7,
doi: 10.1109/INTCEC61833.2024.10602875.
P. Pandey, A. Pandey, A. Srivastava, S. Naqvi, S. Bisht and
N. Mahajan, "Intelligent HR Systems in Global
Organizations: Embracing Industry 4.0 for a Smart
Future," 2024 International Conference on Signal
Processing and Advance Research in Computing
(SPARC), LUCKNOW, India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/SPARC61891.2024.10829147.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
644
