
The Impact of Social Media on Elements of Fashion Brands among
Generation Z
Jiji George and Ebenezer Paul Rajan T. Y
Department of Management, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education (KAHE), Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Generation Z, Social media, Privacy, Personal.
Abstract: The current digital age, social media has become a crucial component of Generation Z's lives, influencing
and characterizing their online experiences. Research has shown that social Gen Z is beginning to give up
on media. Previous research has mostly concentrated on the social media usage characteristics of a larger
population, frequently ignoring the variables affecting Generation Z's social media participation. Thus, the
goal of this study is to identify key elements using a novel framework that combines behavioral factors and
the Internet Users' Information Privacy Concerns model with Perceived Risk and consequential variables
like "Social Media Engagement" and social media trust. In order to ensure a broad representation from a
range of backgrounds, the study's quantitative method approach and snowball sampling technique were
applied to 889 Generation Z participants throughout India. The data was gathered from a questionnaire-
based survey was used in conjunction with a number of technologies, including Google Forms and Smart
PLS, to analyze the intricate interactions between variables affecting this group's use of social media. The
intricate relationship between privacy concerns, trust, and risk perception has been clarified by findings,
which ultimately affect the crucial choice to use social media. The results provide crucial information for
social media companies and legislators, indicating that increasing user trust and minimizing risks over
personal information can lessen the likelihood that users will stop using social media. By shedding light on
social media use and digital privacy, this study paves the way for further research into the complex
dynamics of Generation Z's online activity.
1 INTRODUCTION
The current digital age, social media has become a
crucial component of Generation Z's lives,
influencing and characterizing their online
experiences. Research has shown that social Gen Z
is beginning to give up on media. Previous research
has mostly concentrated on the social media usage
characteristics of a larger population, frequently
ignoring the variables affecting Generation Z's social
media participation. Thus, the goal of this study is to
identify key elements using a novel framework that
combines behavioral factors and the Internet Users'
Information Privacy Concerns model with Perceived
Risk and consequential variables like "Social Media
Engagement" and social media trust. In order to
ensure a broad representation from a range of
backgrounds, the study's quantitative method
approach and snowball sampling technique were
applied to 889 Generation Z participants throughout
India.Nonetheless, there is still a significant
knowledge vacuum on the precise elements
influencing Generation Z's use of these platforms.
Although earlier studies have examined social
media's benefits and wider demographics little is
known about how these elements interact particularly
for Generation Z. This study aims to close this gap by
examining the key variables affecting Generation Z's
use of social media. The essential factors influencing
social media engagement among Generation Z serves
as the research question that directs this study. A
snowball sampling strategy was used in quantitative
research to overcome this. A thorough poll with a 6-
point Likert scale was created using Google Forms
and disseminated via open Indian groups and emails.
Gen Z from a range of backgrounds were gathered
throughout India, guaranteeing a diverse range of
socioeconomic and cultural demographics and
producing a thorough knowledge. Additionally,
utilizing structural equation modeling (SEM) [and
Smart PLS 3 as a computational tool, the data was
analyzed. Salience, tolerance, mood modification,
610
George, J. and Y., E. P. R. T.
The Impact of Social Media on Elements of Fashion Brands among Generation Z.
DOI: 10.5220/0013917700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
610-616
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

relapse, withdrawal, conflict, and the IUIPC
constructs of awareness, control, and collection were
all included in this model (G. S. Kumar et al, 2023).
Notably, perceived risk to control (74.2% influence),
control to social media trust (64.6%), and awareness
of social media involvement (62.4%) are the most
important and influential characteristics identified.
The results of this study highlight the importance of
privacy in regulating the distinct social media habits
of Generation Z. The results have important
ramifications that range from theoretical
understandings that fill in current research gaps to
useful tactics for social media companies looking to
increase interaction with this group. The background
and importance of the research are established first in
this article, which is then followed by a literature
review that assesses earlier research critically and
points out any shortcomings. The methodology is
described in depth, the results are shown, and their
applicability is discussed in the following sections.
Lastly, we wrap off with thoughts on the significance
of our investigation and recommendations for
additional research.
2 RELATED WORK
The essential for comprehending privacy issues in the
digital era. The three dimensions of the model are
awareness, control, and collection. Awareness refers
to users' understanding of privacy policies, control
refers to users' capacity to manage their information,
and collection refers to the volume of personal data
collected by social media platforms .This
methodology has been useful in evaluating privacy-
related concerns and how they affect the use of social
media.
2.1 Combining Models and Theories
The incorporating behavioral characteristics like
conflict, tolerance, and salience into the IUIPC model
salience is the importance of social media in a
person's life; tolerance is the degree to which a user
accepts the negative features of social media use; and
conflict is the overuse of social media that leads to
disputes.
2.2 Trust on Social Media
The degree to which a social media platform may be
deemed reliable in terms of safeguarding user
personal information is known as social media trust.
When there are possible privacy hazards, social
media trust plays a crucial role in defending people'
decisions to quit or continue using social media (S.
A. M. Saleem and S. M. B. Naseem,2023)
Consequently, social media trust is a resultant aspect
that arises from user behavior that raises privacy
concerns.
2.3 Risk Perception
Social media users' awareness of the possible
drawbacks of disclosing personal information, like
privacy violations, is a component of perceived risk.
It represents users' assessments of how these risks
outweigh the advantages of using social media,
which may result in lower involvement and support
for privacy-protective measures .
2.4 Participation in Social Media
The measurement of people's interactions with social
media material is known as social media
engagement. A degree of interaction .which is made
up of behavioral, cognitive, and affective
components . This also covers a variety of actions,
ranging from passive ones like reading or watching
postings to active ones like sharing, liking,
commenting, and following. The last significant
component is social media engagement, which shows
how eager and interested consumers are in interacting
with social media.
2.5 Model of Research
Based on a thorough evaluation of the literature, this
study offers a social media engagement model that
incorporates risk perception, behavioral components,
and the IUIPC model, Conflict, salience, and
tolerance. An inventive method of comprehending
the dynamics of social media engagement is
demonstrated by the incorporation of social media
trust, perceived risk, and social media engagement. It
is believed that these constructs will interact and
affect how Generation Z uses social media.
2.6 Development of Hypotheses
Addiction to IUIPC on Social Media Previous studies
use behavioral and psychological perspectives,
particularly salience, tolerance, and conflict, to
analyze social media addiction. These elements,
which come from the literature on addiction (E.
Nitasha et al, K. Nair et al) are used to comprehend
user engagement through the constructs of
awareness, control, and collection in the IUIPC
The Impact of Social Media on Elements of Fashion Brands among Generation Z
611
model. Thus, the following are the hypotheses
collection is influenced by salience Awareness is
influenced by Salience affects control collection is
influenced by tolerance control is influenced by
tolerance influences of tolerance being conscious
collection is influenced by conflict control is
influenced by conflict .Awareness is influenced by
conflict.
2.7 IUIPC Perceived Risk
Users are generally more conscious of privacy issues
when they perceive a significant level of danger
related to information privacy .Given the growing
significance of data privacy, it is imperative to
investigate this link. All aspects of IUIPC are thought
to be influenced by perceived risk. Thus, the
following are the hypothesis.Collection is influenced
by perceived risk control is influenced by perceived
risk. Awareness is influenced by perceived risk .
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The IPC component on social media trust is based on
the following figure 1 hypotheses social media trust
is affected by collection social media trust is
influenced by control social media trust is influenced
by awareness IUIPC to participation in social media
considering people' growing privacy worries about
social networking services. Users may react
differently to these worries depending on their
behavioral objectives, risk views, and trust beliefs
.Thus, the following are the hypotheses prior research
has demonstrated a direct correlation between trust
and a user's social media activity .Users' social media
involvement is said to be influenced by their level of
social media trust. because social media users that
have a high level of trust also typically have high
levels of engagement.
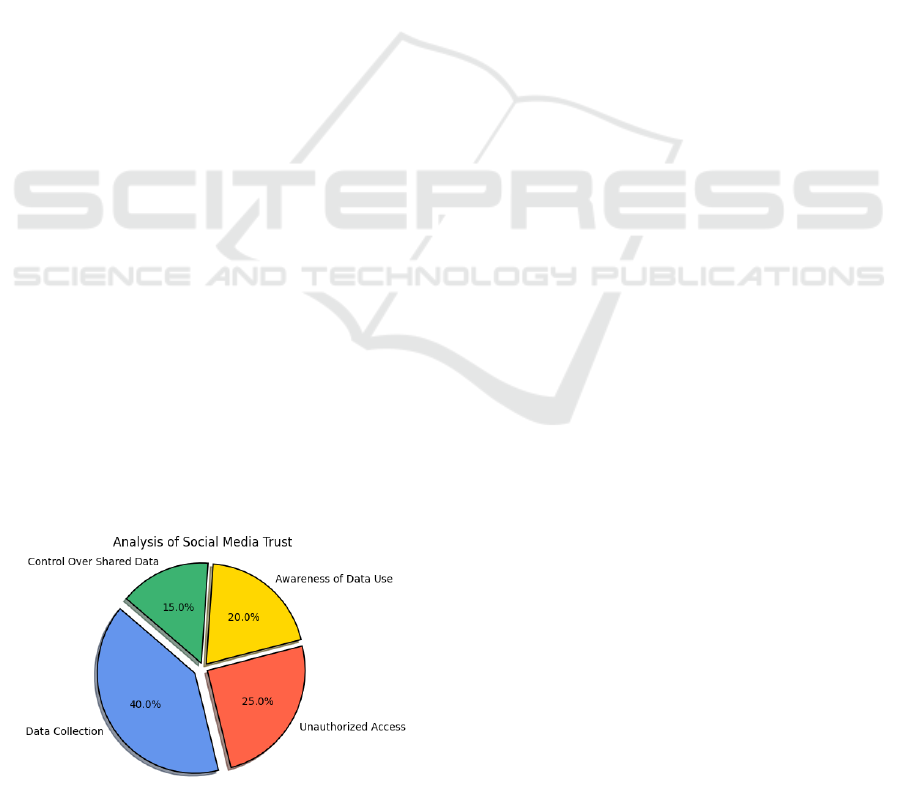
Figure 1: Analysis of Social Media Trust.
Thus, the following are the hypotheses social
media engagement is influenced by social media
trust. The method of data collection an online survey
using a 6-point Likert scale created with Google
Forms was used to collect the data. Demographics
(age, gender, education, and occupation), behavioral
and psychological constructs (salience, tolerance,
mood modification, withdrawal, and conflict) IUIPC
components, social media trust risk perception and
social media engagement were the sections that made
up the questionnaire. The study employed a snowball
sampling technique, which was useful for reaching a
large number of people but may have introduced bias
because of network recruitment. In order to address
this, the poll was dispersed around numerous Indian
communities, guaranteeing that people from a range
of socioeconomic backgrounds were represented.
The following are the demographics of the people
who answered the online survey: 179 respondents
(20.1%) were men, and 710 respondents (79.9%)
were women.The final sample size was 853 since
respondents who were born before 1998 or after 2015
did not fit the Gen Z age range and were not included
in the analysis Sixty-one percent were high school
students, with educational levels ranging from
elementary school to doctorates. The information
gathered from the survey was coded in Microsoft
Excel before the evaluation. The robustness of PLS-
SEM makes it easier to examine intricate model
structures and evaluate the direct and indirect effects
between constructs, giving rise to a more nuanced
understanding of the variables involved.
4 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
The result computation utilizing the Smart PLS
program is thorough explanation of the outcome will
be covered below. A. Validity and reliability of
constructs A minimum Outer Loading score of 0.60
is required for acceptable indicators, and constructs
are considered validated if their Average Variance
Extracted value is greater than 0.50 .It used to assess
the constructs' reliability, which is based on these
validity measures conversation the results show that
trust, risk perception, and privacy concerns interact in
a complicated way to affect Generation Z's use of
social media. Users' awareness and sense of control
are impacted by perceived risks and privacy issues,
but engagement levels are unaffected. Rather, despite
privacy concerns, engagement is improved by greater
awareness and trust. This provides fresh perspectives
on Generation Z's digital habits and is consistent with
previous research, highlighting the value of trust and
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
612
informed knowledge in resolving the privacy-
engagement conundrum.
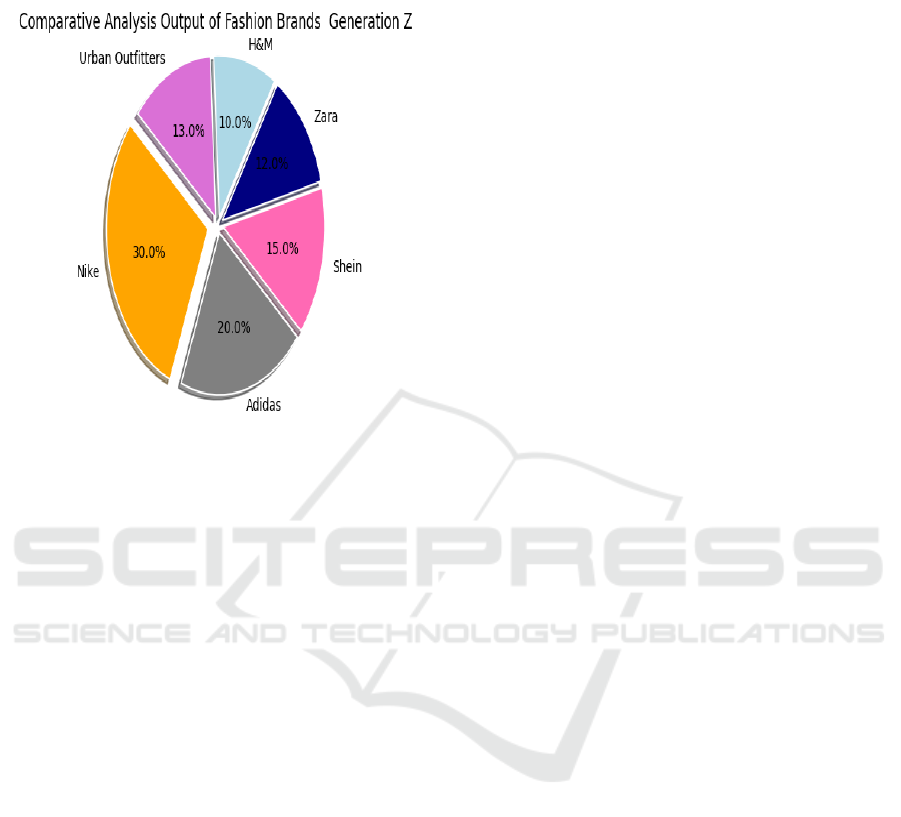
Figure 2: Comparative Analysis Output of Fashion
Brands Generation Z.
The figure 2 first states that salience influences
collection this theory is validated. The findings
suggest that individuals who are more involved in
social media may be less concerned about privacy, as
there is a 12.3% fall in personal data collecting
concerns for every unit of significance placed on
social media. The idea that salience can affect user
behavior has also been validated by earlier research
.Hypothesis control is influenced by salience."There
is no evidence to support this theory. According to
earlier research, users' perceived control over their
information may not be impacted by social media,
despite its importance (D. Jaitly and K. Desai, 2024)
Users' sense of helplessness over data management
may be the source of this, suggesting a disconnect
between perceived control and usage relevance. The
circumstances in which salience might affect control
should be investigated further, taking platform
policies and user education into account.
5 SOCIAL MEDIA
Awareness is influenced by salience this theory is
validated. The findings indicate that a 23.4% rise in
awareness of privacy concerns is correlated with a
larger emphasis on social media, suggesting that
users who are more involved in social media are also
more cognizant of privacy hazards. Another study
concurs .The Collection is influenced by tolerance.
This theory is validated. The findings indicate that a
13.8% reduction in worries about the gathering of
personal data is correlated with a higher tolerance for
social media use. This implies that those who feel
more comfortable interacting on social media on a
daily basis are less concerned about having their data
collected. As mentioned by the frequency of use
may be the reason of this. Control is influenced by
tolerance. There is no evidence to support this theory.
Contrary to research that suggests a direct correlation
between comfort and control, users' comfort level
with social media does not guarantee that they feel in
control of their data. This perception may be
influenced by elements such as platform policies,
user education, and comprehension of data practices.
Better user education on data control is necessary
since users may feel at ease but yet mistrust data
management. Awareness is influenced by tolerance.
This theory is validated the findings indicate that
individuals who are more at peace with heavy social
media usage are also more cognizant of privacy
dangers, with a 21.8% rise in awareness of privacy
risks correlated with greater tolerance for social
media use. Previous research concurs as well
collection is influenced by conflict.
This theory is validated. According to the results,
social media conflicts result in a 54.4% rise in
privacy concerns afterward, which is consistent with
earlier research showing that unfavorable online
interactions raise sensitivity to data privacy .Control
is influenced by conflict" is this theory is validated.
According to the results, conflict resulting from
social media use raises users' concerns about
controlling their personal data by 18%, indicating
that unfavorable experiences lead to greater worries
about privacy management. Another study concurs
.Awareness is influenced by conflict is There is no
evidence to support this theory. Conflict has no
discernible impact on users' knowledge of privacy.
Conflict does not always raise awareness of privacy,
even though it can raise issues with control and
collecting. Users may prioritize pressing problems
over more general privacy procedures. This stands in
contrast to research that suggests unpleasant
experiences increase privacy awareness, highlighting
the necessity for a more thorough investigation of
situational aspects and user responses. "Perceived
Risk influences Collection is This theory is validated.
The findings indicate that greater perceived risks are
associated with a 48.7% increase in concerns about
the gathering of personal data, indicating that risk
awareness increases reluctance to share personal
information online. This idea has been validated by
The Impact of Social Media on Elements of Fashion Brands among Generation Z
613
earlier research .The states that "Control is influenced
by perceived risk." This theory is validated. The
findings indicate a clear link between risk awareness
and proactive privacy management, with users'
control over their privacy increasing by 74.2% when
they perceive social media threats. This is consistent
with research on privacy control and trust in digital
contexts and represents users' defensive reactions to
perceived threats. The states that "Awareness is
influenced by perceived risk." This theory is
validated. The findings indicate a strong correlation
between risk perception and awareness, with
perceived hazards leading to a 35.6% rise in privacy
awareness. This is consistent with earlier studies
collection influences social media trust is there is no
evidence to support this theory. This is consistent
with research from which showed that trust and
usage intentions were unaffected by privacy
knowledge. Furthermore, offers context for these
results by speculating that people might not connect
social media trust with data gathering. Users may
choose to keep their worries about data gathering
apart from their general trust in the platform, placing
more emphasis on platform conduct and openness
than just data procedures.
6 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
The Control affects trust on social media this theory
is validated. The findings indicate that 64.6% of the
variation in social media trust can be explained by
"Control." This strengthens platform trust by
highlighting how crucial it is that consumers feel
empowered to manage their data.
These results are consistent with previous
research on the crucial role user control plays in
determining social media credibility .Awareness
influences social media trust is This theory is
validated. The findings indicate that 29.2% of the
variation in social media trust may be explained by
awareness. This supports research that shows how
privacy awareness affects user trust and emphasizes
the crucial role that awareness plays in boosting
social media trust.
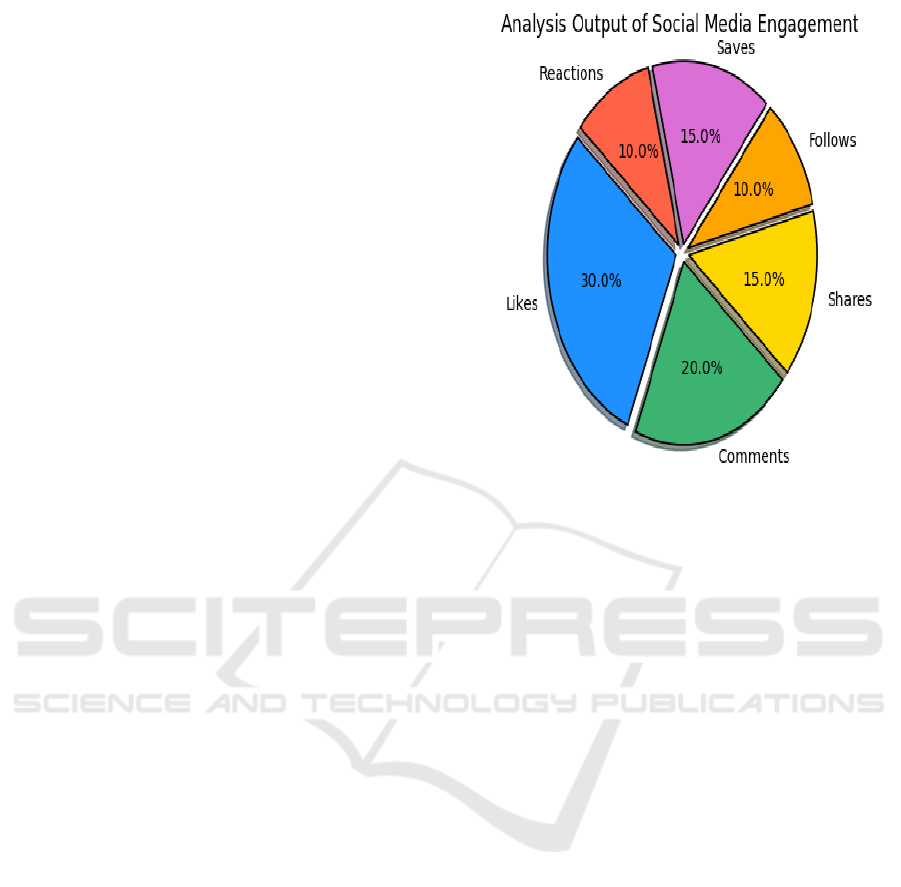
The figure 3 collection influences Social Media
Engagement" is this theory is validated. As a result of
data gathering issues, social media engagement has
decreased by 28.4%. This demonstrates how
transparency affects engagement, which is
corroborated by research in social media engagement
is influenced by control." There is no evidence to
support this theory.
Figure 3: Analysis Output of Social Media Engagement.
7 FUTURE SCOPE
Social media participation is not substantially
impacted by privacy control, suggesting that other
factors might be more important. This is consistent
with indicating that privacy knowledge has little
effect on engagement, similar to control. Instead of
data control, users may interact based on instant
gratification and perceived advantages.
Conditions where control affects engagement
require more investigation. Awareness influences
social media engagement is this theory is validated.
As a result of increased awareness, social media
engagement increased by 62.4%.
This supports which holds that knowledgeable
users are more likely to interact with platforms
actively, and emphasizes the significance of
awareness in affecting user interactions. Social media
trust influences social media trust is this theory is
validated. According to the results, trust has a
significant 31.1% influence on social media
participation.
This figure 4 highlights how crucial trust is as a
motivator for user activity on these platforms, which
is supported by earlier research that emphasizes trust
as a fundamental component of digital engagement.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
614
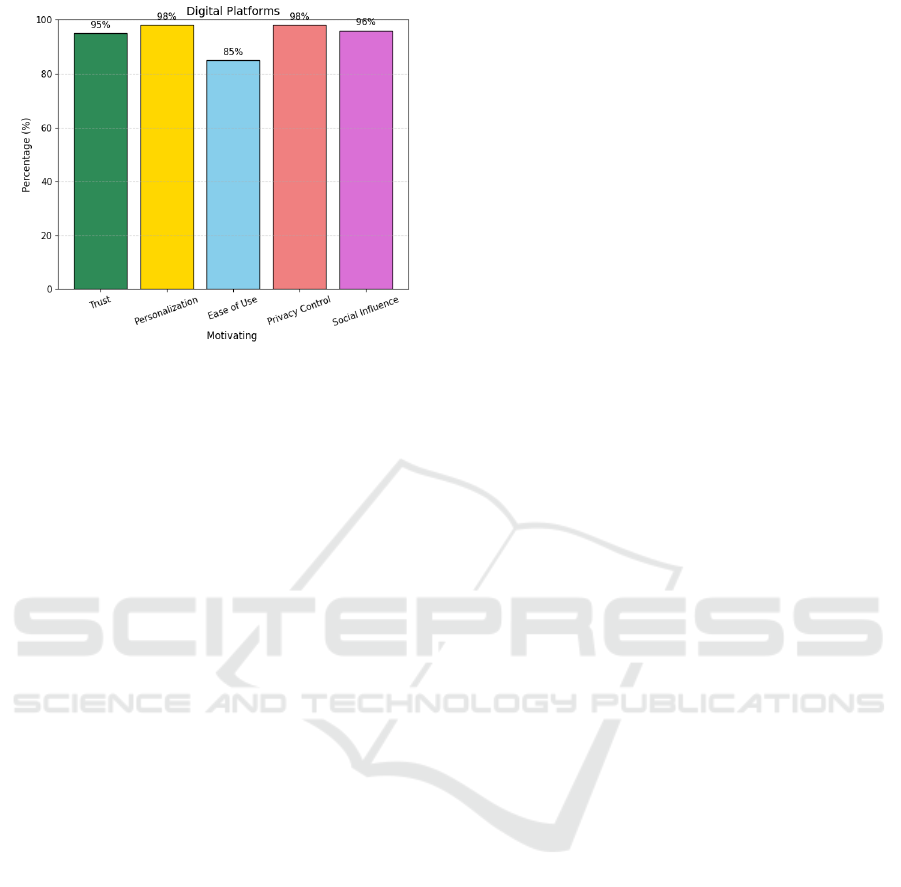
Figure 4: Digital Platforms.
8 CONCLUSIONS
Using the IUIPC model, this study investigates the
intricate connections among India Generation Z's
privacy concerns, perceived risks, social media trust,
and involvement. It concludes that although users'
control and knowledge are impacted by privacy
concerns and perceived risks, engagement is not
decreased. Rather, despite privacy concerns,
engagement was boosted by more understanding and
trust, underscoring the significance of these factors in
resolving the privacy engagement conundrum. The
study offers guidance to legislators and social media
companies, highlighting the necessity of open, user-
centered privacy policies and steps to foster trust.
User involvement and trust can be increased by
addressing privacy concerns with knowledge and
transparency. Even though the study's
generalizability may be limited by its use of snowball
sampling, more varied approaches should be used in
future studies to improve representativeness.
Furthermore, the study's cross-sectional design
provides a moment in time that might not adequately
reflect changing patterns in Generation Z's social
media usage. In light of increased privacy concerns,
this study adds to the conversation around digital
privacy and engagement and provides helpful advice
for enhancing user experience.
REFERENCES
V. Jabade, H. Shrivastav, N. Harak and A. Jadhav,
"Generative AI for Custom Fashion Design Integrating
AI with E Commerce Platforms," 2024 5
th
Internation
al Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive
P. Singh, S. Jaiswal, S. Srivastava, M. L. Azad, V. Mishra
and A. Nautiyal, "Fashion Forward: Exploring the
Influence of AI on Modern Fashion Trends," 2024 7th
International Conference on Contemporary Computin
g and Informatics (IC3I), Greater Noida, India, 2024,
pp. 864-869, doi: 10.1109/IC3I61595.2024.10829054.
S. Huang and Z. Zhang, "The Application of Interactive
AI-Based Narrative Translation Model in Fashion
Design," 2024 International Conference on Interactive
Intelligent Systems and Techniques (IIST), Bhubanesw
ar, India, 2024, pp. 326331, doi: 10.1109/IIST62526.2
024.00024.
H. Y. Wang, W. Rueangsirarak and S. Utama, "Evaluation
of Generative AI Fashion Images using CNN Classifi
cation and Regression," 2024 23
rd
International Sympo
sium on Communications and Information Technologi
es (ISCIT), Bangkok, Thailand, 2024, pp. 146-151,
doi: 10.1109/ISCIT63075.2024.10793532.
W. Lu, J. Wu, H. Li, J. Lu and X. Wang, "Enhancing
Personalized Cultural Product Design Through An AI-
Driven Intelligent Design System," 2024 2
nd
Internatio
nal Conference on Design Science (ICDS), Shanghai,
China, 2024, pp. 16, doi: 10.1109/ICDS62420.2024.1
0751707.
S. A. M. Saleem and S. M. B. Naseem, "A Case Study of
MyntraTM Enhancing E-Commerce Retailing with
Multiple AI Solutions," 2023 6
th
International Confere
nce on Advances in Science and Technology (ICAST),
Mumbai, India, 2023, pp. 5762, doi: 10.1109/ICAST5
9062.2023.10454917.
D. Jaitly and K. Desai, "Artificial Intelligence and the
Future of Fashion: A Systematic Review on Sustainabl
e and Circular Practices," 2024 International Conferen
ce on Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computatio
n-Based Sensor Application (ICAIQSA), Nagpur,
India, 2024, pp. 18, doi: 10.1109/ICAIQSA64000.202
4.10882435.
T. S. Dinesh, K. Ammaiyappan, G. Janav, S. Gopikumar,
R. S. Krishnan and A. Srinivasan, "A Novel AI
Driven Recommendation System for Eco Conscious Cons
umers," 2024 8
th
International Conference on Inventiv
e Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India,
2024, pp. 376382, doi: 10.1109/ICISC62624.2024.00
071.
G. Menon, A. P. Peter, E. Jomon, J. Varghese and M.
Anly Antony, "Apparel Customization Using Generati
ve AI," 2024 10
th
International Conference on Advan
ced Computing and Communication Systems
(ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2024, pp. 1486-1490,
doi: 10.1109/ICACCS60874.2024.10717142.
E. Nitasha, S. Kumari, A. Kumar, R. Bhardwaj, V.
Maddheshiya and A. Khan, "Future of Fashion: AI-
Powered Virtual Dressing for E Commerce Applicatio
ns," 2024 International Conference on Emerging
Innovations and Advanced Computing (INNOCOMP),
Sonipat, India, 2024, pp. 138150, doi: 10.1109/INNO
COMP63224.2024.00031.
The Impact of Social Media on Elements of Fashion Brands among Generation Z
615

G. S. Kumar, S. Hari Krishna, R. Prasad, S. Naredla, P. H.
Navinbhai and P. S. Costume, "Revolutionizing Busin
ess Decision Making: An Analysis of AI Based Servic
es," 2023 3rd International Conference on Advance
Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineerin
g (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 2023, pp. 2751275
6, doi: 10.1109/ICACITE57410.2023.10183274.
K. Nair, K. K. Moenardy, S. R. Jaladi, Y. Supiyanto, K.
Suleimenova and Y. Popov, "A Model based on
Embedded Artificial Intelligence for Retail Industry,"
2022 Sixth International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT
in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC),
Dharan, Nepal, 2022, pp. 663-672, doi: 10.1109/I-
SMAC55078.2022.9987402.
W. -C. Chien, H. -H. Cho and S. Zeadally, "Human-
Centric GenAI Garment Designer: 3D Fashion Design
Recommendations," in IEEE Consumer Electronics
Magazine, doi: 10.1109/MCE.2024.3492510
R. S. Bisht, S. Jain, N. Sharma and D. Sahoo, "Indian
Handloom Exports to the US Market: A Centralized
Platform-Based Business Model Framework Powered
by AI," 2024 International Conference on Communica
tion, Computer Sciences and Engineering (IC3SE),
Gautam Buddha Nagar, India, 2024, pp. 564-570, doi:
10.1109/IC3SE62002.2024.10593304.
Y. Liu and L. Wang, "MYCloth: Towards Intelligent and
Interactive Online T-Shirt Customization based on
User’s Preference," 2024 IEEE Conference on Artifici
al Intelligence (CAI), Singapore, Singapore, 2024, pp.
955-962, doi: 10.1109/CAI59869.2024.00175.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
616
