
Smart Retail: Integrating IoT for Enhanced Shopping
V. S. Nishok, Raja S, Aadhi Piranav R T, Dinesh Kumar S, Enbaraj R and Hariharan R M
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SNS College of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: RFID, IoT, Shopping, Error Detection, Financial Accuracy, Internet of Things.
Abstract: In this work, a smart shopping cart's hardware and software implementation is developed with an emphasis
on affordability, modularity, and usability. Once this solution has been adjusted, traders can immediately
begin using it. It usually tries to satisfy as many end-user requirements as it can. The growing growth of the
Internet of Things has mostly resulted in the automation and optimization of repetitive activities. As a result,
people have more time for their hobbies and careers. Shopping is one of the most time-consuming activities
people perform, particularly in congested areas. Even though e-commerce is undoubtedly growing in
popularity, consumers typically feel compelled to scrutinize the products they purchase and consider any in-
store discounts. In these situations, people are compelled to wait in queues, which can occasionally grow
rather long. Standing in line can lead to a number of stressors and discomforts. Every transaction has an
affordable RFID tag that can be promptly read by a smart shopping cart equipped with an RFID reader.
Another potential addition to this system is smart shelving, which uses RFID scanners and can track inventory
while possibly updating a central server. Because RFID technology can automatically read every item and
determine whether a product's expiration date has gone, it also makes inventory management easier. The IOT
website will be updated with all of the new material.
1 INTRODUCTION
An automatic billing system is a high-end solution
that automates the creation, sending, and
management of invoices according to the billing
flows of businesses. It provides a convenient way of
making payments without allowing humans to enter
calculations and documentation. It is cheaper,
quicker, and more efficient. ABS is crucial to a
number of industries such as e-commerce, energy,
telecom and subscription services. Main Features of
an Automated Billing System. The system automates
essential tasks such as notifying customers of
impending or overdue payments, collecting money
via linked payment gateways, and creating invoices
based on usage or subscription plans. It also tracks
payment history, generates comprehensive reports
and maintains patient data to provide insights for
financial decisions and planning. ABS minimizes
human error and wastes and saves time as well as
administrative costs. It improves the customer
experience through features such as real-time
updates, online payments and easily accessible billing
information. Moreover, it can easily scale to
accommodate a larger number of transactions as the
business expands. The long-term benefits outweigh
the challenges, ensuring improved cash flow and
operational efficiency even though the initial setup
and integration may be expensive. In the present
digital era, it is an essential tool for businesses trying
to optimize their billing processes and deliver
faultless customer service.
2 EXISTING METHOD
The product's quantity is verified using a barcode
scanner. Data is transferred to the PC via ZigBee. To
verify the load on another cart, it lacks a load sensor.
Because the system uses tally for billing and ZigBee
for communication, it operates quite slowly. Every
day, thousands of people go to a supermarket or mall
to buy a variety of goods. Nowadays, in order to buy
a variety of goods at supermarkets or shopping
centers, a trolley is necessary. The process of
purchasing a product might be difficult. The
consumer has to pull the cart each time to retrieve the
items and put them inside. He is also in charge of
managing the cost computation. Customers have to
wait in a long line to pay their bills and scan their
Nishok, V. S., S., R., T., A. P. R., S., D. K., R., E. and M., H. R.
Smart Retail: Integrating IoT for Enhanced Shopping.
DOI: 10.5220/0013916700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
561-564
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
561
purchases after completing a transaction. To avoid
this, we're coming up with a smart shopping strategy.
Each and every item has an RFID tag attached to it.
The smart trolley will include an RFID reader and
transmitter. When the customer scans and adds any
item to the cart, the product name and price will show
up. The total cost of all the products will be included
in the final bill, which will be stored in the micro
controller's memory. The product details of the items
in the cart will be wirelessly transmitted to the main
computer via a transmitter. Consequently, one must
always keep the budget in mind while avoiding the
charging line. Figure 1 shows the flowchart of
existing method.
Figure 1: Existing Method
.
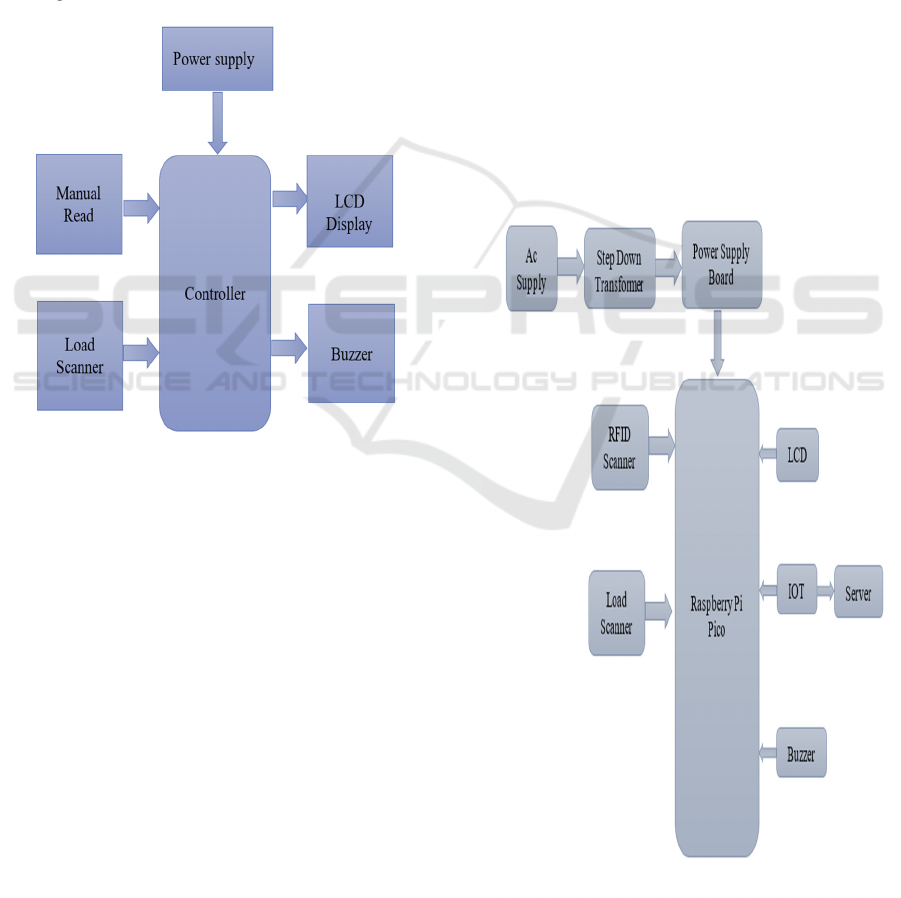
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The smart shopping cart system uses RFID and
weight scanning technology to enhance both the
shopping experience and business operations. The
RFID reader instantaneously confirms a product's
name, price, and quantity when it is put to the cart.
The cart can track the total number of products and
their details in real time because each one has an
RFID sticker that the scanner can read. A weight
scanner is installed inside the cart to determine the
overall weight of the items in order to make sure that
the load does not exceed its capacity. This is vital for
logistics and inventory control and helps store
workers keep an eye on what the cart contains.
NodeMCU simplifies integration with the store's
backend system by sending all of the RFID and
weight scanner data to an Internet of Things website.
This includes product information, the total weight of
the basket, any relevant changes in product demand
or stock levels, etc. An LCD fitted to the cart displays
the purchases, the total weight, and other crucial
details. The method is meant to alert the customer
with a buzzer when a product is ready to expire. This
helps you avoid buying things that should not be sold.
The store has two different IoT sites that show real-
time updates on the demand for products, as well as
supply management and which products to keep an
eye on are in high demand. This smart cart system
makes the shopping experience for customers more
efficient, in addition to improving overall retail
operation efficiency, reducing waste, and maximizing
inventory control. RFID, IoT and weight scanning
have their part to play in making modern purchasing
more efficient and convenient. Figure 2, 3 and 4
shows the prosed method of flowchart and circuit
diagram.
Figure 2: Proposed Method.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
562
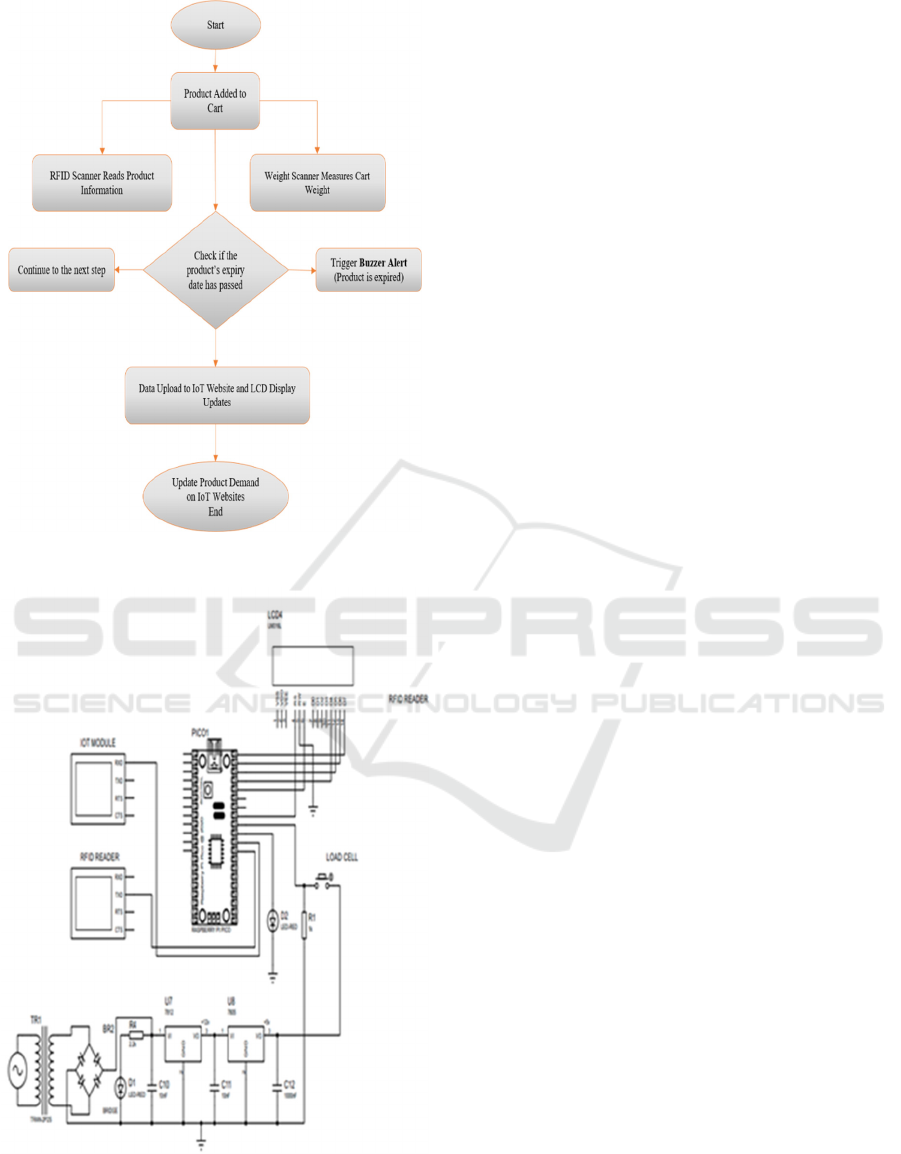
Figure 3: Flowchart of Proposed Method.
Figure 4: Circuit Diagram of Proposed Method.
4 RESULT
In terms of improving the shopping experience and
streamlining store operations, the Internet of Things-
based smart retail system has demonstrated notable
advancements. The usage of RFID improved
customer satisfaction by speeding up and
streamlining processes. Customers were able to make
well-informed selections thanks to real-time
notifications regarding product expirations and
payment restrictions. By using tailored advertising to
notify customers of overloaded carts, the weight
tracking technology improved safety.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We propose a safe smart retail system based on RFID
in this article. UHF RFID is being used for the first
time to enhance the shopping experience while
addressing security concerns as part of a smart retail
system. We build a prototype to assess the system's
performance after carefully developing the entire
system. We create a secure communication protocol
and offer security research and performance
assessments. Our research is at the forefront of
developing a smart shopping system, and we believe
that RFID technology will be utilized in stores in the
future. Future study will concentrate on enhancing the
current system to increase efficiency. For instance, it
will examine methods to lower computational
overhead at the smart cart side and enhance
connectivity without compromising security aspects.
6 FUTURE SCOPE
Mobile App Integration: Link a mobile app to the
system to provide real-time tracking and alerts.
Improved Inventory Control: AI can be used to
forecast supply requirements and update inventory
automatically. Self-Checkout expedites the checkout
process by enabling customers to pay straight through
the cart. Tailored product suggestions according to
the user's previous purchases. Adaptability Features
that help cut down on waste include tracking product
expiration dates and offering discounts on things that
are about to expire.
Smart Retail: Integrating IoT for Enhanced Shopping
563

REFERENCES
K. V. S. H. Gayatri Sarman and Srilakshmi Gubbala,
"Voice based Objects Detection for Visually
Challenged using Active Rfid Technology",
International Conference on Cognitive Computing and
Cyber Physical Systems, Pp. 170-179, 2022.
N.P. Challa, J.S.S. Mohan, V.S. Deepthi and S.
Rajeyyagari, "Smart Irrigation System using Internet of
Things", Proceedings of the 17th Indiacom; 2023 10th
International Conference on Computing for
Sustainable Global Development Indiacom 2023.
V.P. Matta, R.S. Miriyala, K.V.S.H. Gayatri Sarman, M
K.V.S. Reddy, a M.V Pathi and C. Venkateswara Rao,
"Energy Efficient Smart Street Light System based on
Pulse Width Modulation and Arduino", 2023
International Conference on Computer Communication
and Informatics Iccci 2023.
a. Sawant, a. Parashar, S. Saxena and S. Shukla, "Rfid-
based Smart Shopping Cart System", International
Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology,
Vol. 9, No. 1, October 2019.
Rudra Narayan Dash, Akshay Kumar Rathore, Vinod
Khadkikar, Ranjeeta Patel and Manoj Debnath, "Smart
Technologies for Power and Green Energy",
Proceedings of Stpge 2022, Vol. 443, 2022.
S. Naveen, "Smart Shopping Trolley using Qr Code and
Esp32cam", Grenze International Journal of
Engineering & Technology (Gijet), Vol. 8, No. 2, 2022.
T. Naveenprabu, B. Mahalakshmi, T. Nagaraj, N. K Sp and
M. Jagadesh, "Iot based Smart Billing and Direction
Controlled Trolley", in 2020 6th International
Conference on Advanced Computing and
Communication Systems (Icaccs), Pp. 426-429, 2020,
March.
R. Raffik, D. Rakesh, M. Venkatesh and P. Samvasan,
"Supply Chain Control and Inventory Tracking System
using Industrial Automation Tools and Iiot", in 2021
International Conference on Advancements in
Electrical Electronics Communication Computing and
Automation (Icaeca), Pp. 1-5, 2021, October.
M. Sanap, P. Chimurkar and N. Bhagat, "Smart-Smart
Mobile Autonomous Robotic Trolley", in 2020 4th
International Conference on Intelligent Computing and
Control Systems (Iciccs), Pp. 430-437, 2020, May.
P. Satheesan, S. Nilaxshan, J. Alosius, R. Thisanthan, P.
Raveendran and J. Tharmaseelan, "Enhancement of
Supermarket using Smart Trolley", International
Journal of Computer Applications, Vol. 975, Pp. 8887,
2021
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
564
