
Virtual Mouse Operation Using Webcam
G. Shamitha, E. Sandhya, D. Kanaka Mahalakshmi, K. Deepthi and E. K. Mounika
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Nandikotkur road
Kurnool‑518002, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Virtual Mouse, Webcam, Gesture Recognition, Image Processing, Hand Tracking, Computer Vision,
OpenCV, Cursor Control, Human‑Computer Interaction, Gesture‑Based Interface, Accessibility.
Abstract: Virtual Mouse with a Webcam operation by means of hand gestures to control the cursor of a computer or a
laptop. Based on the image processing techniques for tracking the user's hand movements and converting
these movements into the motion of the cursor, this system enables the user to work on the computer without
the physical mouse. They allow users to make hand gestures like moving their fingers, which the gesture
sensors capture, process, and map on their screens to actions like clicking with a mouse, scrolling, or moving
the mouse cursor. This approach provides a hands-free, natural user interface that can be especially helpful
for those with disabilities or in contexts where traditional input devices would not be practical. The elaborate
approach depends on usage of OpenCV and other computer vision to manipulate gestures into realistic time
cursor control.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the evolution of computer vision and image
processing tech, some new ways of interaction
between human and computer has emerged. Virtual
Mouse operation with the help of a webcam is one
such innovation, which controls the mouse cursor
using hand gestures and eliminates the use of input
devices like physical mouse or touchpad. This system
works by using a standard webcam to recognize and
track the hand movements of a user and getting those
hand gestures translated into corresponding mouse
functions including but not limited to mouse
movement, mouse click, and scrolling.
The Virtual Mouse technology also greatly
enhances accessibility, allowing users with physical
disabilities or those working in difficult situations to
control computers without needing traditional input
devices. Using image processing approaches,
including background exclusion, edge location, and
raw gesture recognition, the system identifies and
follows hand gestures as a substitute for the actions
and motion of a traditional mouse.
Also, due to the wide use of webcams and open-
source libraries such as OpenCV, the design and
implementation of Virtual Mouse operation can be
accomplished with ease and at a low cost. This
makes it a pragmatic solution for a variety of
applications, such as accessibility tools and sci-fi-
like computing interfaces. This system is an attempt
to develop an intuitive, user-friendly basic language
system as an alternative form of interaction and
innovates human-computer-interaction and opens
new avenues for disabled, senior citizen and other
special people.
2 RELATED WORKS
The research methodology for the Virtual Mouse
operation using a webcam involves several key
phases, including problem definition, system design,
data collection, development, and evaluation.
2.1 Problem Definition
Identify Problem The initial stage of the research
process involves addressing the problem that Virtual
Mouse wants to solve. These might be resources on
why alternative input is important, consideration for
those who are physically disabled, those who have
specialized needs in terms of store accessibility,
long-distance control, etc. The authors point to the
need to improve the accuracy of gesture recognition,
processing in real time and making sure that the
system is reliable.
Shamitha, G., Sandhya, E., Mahalakshmi, D. K., Deepthi, K. and Mounika, E. K.
Virtual Mouse Operation Using Webcam.
DOI: 10.5220/0013915500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
493-499
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
493

2.2 System Design
The design is a system design based on the problem
definition, i.e. selection of hardware software needed
for the system. Input 1: it uses only a webcam to
capture the hand gesture. Using computer vision
techniques, image processing algorithms develop to
track the movement of the hand and to map these
movements to the mouse actions (click, move, scroll).
The development is planned to be done using
software tools like OpenCV, Python, and gestures
recognition libraries.
2.3 Data Collection
In the initial phase, video data is captured in a real-
time manner by using the webcam. A dataset is
collected of hand gestures that the system will need
to be able to identify. We are collecting this data to
train and test the image processing and machine
learning models required for gesture detection.
2.4 Development
Implementation phase is where you will implement
the developed hand gestures from the webcam feed.
Seal detection, contouring detection, and feature
extraction algorithms are used for identifying the
location and orientation of the hand. Then, these
recognized gestures are mapped to different mouse
actions such as left-click, right-click, drag, and
scrolling. The system needs to operate in real time so
that the cursor moves smoothly along with a user’s
hand.
2.5 Evaluation
This phase of the evaluation focuses on the
performance of Virtual Mouse in terms of the
accuracy, responsiveness, and usability. It consists of
testing the system with various users, hand sizes, and
light levels to prove robustness. Performance metrics
like latency, gesture recognition accuracy, and error
rates are logged and evaluated. The functionality is
tested to make sure that every component works as it
should and the performance is measured to ensure
that the system is performing well under networks
handling loads.
2.6 Research Area
The research in Virtual Mouse operation using a
webcam is situated at the intersection of several key
fields:
Basically, it's the underlying technology that allows
computers to see and comprehend the visual data of
the world around us. We process the webcam feed
and extract meaningful data regarding hand gestures
using techniques such as image segmentation, hand
tracking, gesture recognition, and real-time object
detection. Human-Computer Interaction (HCI): A
notable advancement in the field of human-computer
interaction, the virtual mouse represents an important
step in developing alternative methods of input.
Through the study, we investigate the common
methods of interaction for systems developed through
hand gestures, how intuitive these graphical elements
are for users to understand, as in, we aim to
understand the effectivness of visual cues used to
navigate through a digital space. Assistant
Technologies and Accessibility: This field caters to
the creation of tools for the disabled. If the hardware
parts are used, the Virtual Mouse system can also be
used as a special assistive device for people with
motor disabilities who cannot use traditional input
devices, since it can be a hands-free device for
interacting with computers. Image Processing The
research applies techniques that allow real-time
detection and tracking of hand gestures. Background
subtraction, edge detection, color filtering, etc., can
be used to extract the user's hand from the
background and accurately record its position. Virtual
Mouse Empowered by Machine Learning and
Gesture Recognition: The system integrated
innovative machine learning techniques to enhance
gesture recognition capabilities, enabling the Virtual
Mouse to adapt to a range of users and working
environment conditions. The quality will increase as
our ML algorithms trains it to recognize particular
gestures.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 A: S - R - Kumar, V - P - Reddy,
and M - T - Joshi, "Hand Gesture
Recognition for Touchless User
Interfaces”
In this paper we investigate the usage of hand gesture
recognition in touchless user interfaces (TUIs),
seeing how webcam-based systems can be integrated.
Various image processing techniques including skin
color segmentation and contour tracking are
discussed for precise detection of gestures. This
research may help design touchless systems like the
Virtual Mouse, as the study demonstrates the need for
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
494

real-time performance alongside dealing with
environmental and lighting conditions for high
recognition accuracy.
3.2 B.A.S: Patel, R.B - Singh and K.V -
Shukla, “Enhanced User
Interaction with Gesture
Controlled Systems”
The authors offer a thorough examination of gesture-
controlled systems and discuss how computer vision
contributes to creating intuitive user interfaces. They
explore classes of webcams best suited for high-
definition gesture support and address important
approaches such as optical flow and feature point
tracking to improve the integrity of interactions. The
paper further implements a usability rating to assess
the efficiency of the performance of these systems in
real world, giving new insights for developing a high
reliability and quality standards for virtual mouse
systems on both general computing and assistive
computing scenarios.
3.3 C: P - R - Sharma, D - T - Gupta,
and S - H - Kumar, "Real-Time
Hand Gesture Recognition for
Virtual Mouse Operating Using
Webcam"
This work focuses on the real-time implementation of
hand gesture recognition to control the virtual mouse.
Various techniques were replicated by the authors,
such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), and deep
learning models; to hand tracking and gestures
detected. Their findings critically inform system
design for recognition accuracy and responsiveness,
marking a significant contribution to webcam-based
virtual mouse systems.
3.4 N: D - V - L - Thakur, S - M - Ali,
and R - P - Kumar, "Hand Gesture
Based Control Systems - An
Overview of Algorithms and
Applications"
This survey article presents a good overview of a
variety of algorithms used in hand gesture recognition
algorithms including methods such as Haar cascades
or deep learning networks on webcam-based systems.
It evaluates computational cost, accuracy and real-
time processing for different approaches. This
research provides a comprehensive evaluation of
most techniques, thus presenting crucial information
for the development of systems to support virtual
mouse tracking.
3.5 Physical / M: L - Desai, E - K - P -
Mehta, S - K - Mishra, "Gesture
Based Interaction Using Webcams -
A brief Study"
The challenges and discussion are common in gesture
recognition, such as background noise and hand
occlusion. They suggest measures to increase the
robustness of the system and to map gestures in the
most diverse environments. Data is analysing
between February 2023 and October 2023 ▵
4 EXISTING SYSTEM
The existing systems for virtual mouse operation
using webcams are based on the use of computer
vision and image processing techniques to track and
interpret hand gestures, allowing users to control a
computer without the need for a physical mouse or
touchpad. These systems have gained traction as
touchless input methods, primarily leveraging
webcams or other camera-based sensors for capturing
real-time hand movements. Below are key features
and components of current virtual mouse systems:
1. Hand Gesture Recognition: The majority of
webcam-based virtual mouse systems rely on
hand gesture recognition, where specific hand
movements, such as pointing, swiping, or
opening/closing fingers, are mapped to mouse
actions. Methods such as skin color
segmentation, contour detection, and hand
tracking algorithms are commonly used to
isolate and track the user's hand from the
background. Popular approaches for gesture
recognition include background subtraction,
Optical Flow, and depth-based tracking (for
systems with depth sensors).
2. Media pipe: This Library for Hand
Recognition and Tracking For example, Hear
Cascade Classifiers is commonly used to
identify whether hands are present and their
location. Another common method is contour
tracking and feature point detection, which are
used to track hand movements and predict
actions of gestures. In order to improve the
recognition accuracy and the adaptability to
different environmental conditions, many of
them are also deploying machine learning
Virtual Mouse Operation Using Webcam
495

models, such as Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs).
3. Image Processing Models: Open-source
frameworks like that of OpenCV are preferred
for developing real-time gesture recognition
systems. OpenCV itself has many in-built
functionalities for capturing the video feed,
processing the images and also applying the
algorithms for gesture detection. Alternatively,
frameworks such as Google developed Media
Pipe provides more specific services such as
Real time Finger set tracking which does not
require much processing power.
4. Text-based mouse systems involve processing
of data through the mouse movements in real-
time. This is done by constantly retrieving the
webcam feed, processing the images, either by
hand or with a scale-educator, recognizing the
gestures, and converting them into mouse
events like left-click, right-click, drag, and
scroll. Existing systems face challenges in
low-latency operation and detection errors in
gestures.
5. Data Input: The majority of these virtual mouse
systems provide users with the ability to move
the cursor around the screen, as well as click
and scroll. In a two-dimensional space, the
cursor typically moves in conjunction with the
user’s hand. System detects gestures like a fist
(left-click) or open hand (right-click) to
perform a click. Some more versatile systems
also offer advanced features like multitouch
gestures, zoom, or pinch-to-zoom.
6. An example of the existing systems limitation
is its sensitivity to lighting conditions,
background noise. Weak algorithms can
diminish the accuracy of hand identification,
for instance due to the end user’s hand
camouflaging with their dwelling background
or ambient lighting thereby masking the hand
shape. Moreover, if there is background noise
in the form of cluttered or moving objects,
these may also be mistaken for gestures,
causing lapses in cursor movements or delays
in executing the desired commands.
5 PROPOSED SYSTEM
Therefore, the proposed system for a Virtual Mouse
operation using a webcam would lead to the
improvement of existing touchless interaction
systems via accurate gesture recognition, reduced
latency, and high system robustness in various
environmental factors (e.g., lighting variations,
background noise, etc.). The aim of this system is to
provide a simple, smooth and efficient way for the
user to control a computer or any device without the
use of a conventional mouse or touchpad. The idea
will leverage cutting-edge technologies in computer
vision, machine learning, and real-time computation
to deliver a seamless and efficient virtual mouse
solution. Here we list some main features and parts
of the proposed system:
Advanced Gesture Recognition with Machine
Learning
Deep learning algorithms: In order to address the
limitations of conventional hand gesture recognition
systems, the proposed system will utilize deep
learning models (CNN or RNN). These models will
be trained on the recognition of several kinds of hand
gestures with high accuracy and robustness.
Diverse Datasets for Training
The system may be trained on diverse datasets
containing different hand gestures which helps to
improve the ability of the system to recognize
gestures in various lighting conditions, hand
orientations, and backgrounds.
Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition
The designed system will utilize the real-time gesture
detection for hand movements like pointing, swiping,
fist clenching and finger tracking. These gestures will
map to mouse actions such as moving the cursor,
clicking, dragging, and scrolling.
Robust Tracking with Computer Vision
Techniques
Feature-Based Tracking While tracking with hand
and finger segmentations, the suggested system will
use high-end tracking algorithms such as Optical
Flow and Lucas-Kanade technique to track the special
movements in real-time with utmost accuracy. It
improves the stability and accuracy of the pointer
movement of your virtual mouse.
Depth and 3D Tracking
The system will let the recognition of hand gestures
in 3D also, if available, by adding depth sensors or
stereo camera arrangements. This allows for greater
precision control of the cursor, particularly when
working on expressive gestures and multi-
dimensional experiences.
Improved Image Preprocessing
Background Subtraction and Segmentation: To
dynamically detect and segment a user’s hand from
the background, advanced background subtraction
techniques with real-time implementation will be
covered in the proposed system. This will guarantee
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
496

precise gesture tracking in distracting or dynamic
settings.
Noise Reduction
To mitigate the adverse effects of background noise,
lighting conditions, and shadows, advanced noise
reduction filters (e.g., Gaussian Blurring and Median
Filtering) will first be applied in order to clean the
webcam feed before any processing is performed on
it.
Latency Reduction and Real-Time Performance
Optimized Algorithms
The system will use optimized algorithms and
hardware acceleration techniques during hand
gesture processing to ensure the hand gestures have a
real-time response. This is essential for keeping the
cursor flow and the detection of clicks at a high rate.
Low-Latency Camera Feed: To make it as responsive
as possible, the user webcam will have a high frame
rate (60fps or higher). You would want this to be
processed with little latency, so the cursor smoothly
follows most user gestures without any visible delay.
Multi-Gesture and Multi-User Support
Advanced Gesture Recognition
Multi-finger gesture support, including pinch-to-
zoom, two-finger scrolling, and swipe gestures,
enabling more complex interactions with the virtual
mouse.
Multiple User Recognition
The proposed system will be capable to and
independently recognize and track gestures of
multiple users. This hardware will be able to switch
users based on the person using their hands, meaning
that different people can use the system together or
one after the other.
Cross-Platform Compatibility Multi-Device
Support:
The proposed virtual system will be
developed to be
compatible with various platforms including
Windows, macOS and Linux, allowing users the
convenience of using the virtual mouse across devices
and operating systems.
Personalized Controls
Users will now be able to customize gesture-to-
action mapping for individual applications or use
cases. You can, for instance, assign some hand
gestures to different functions (volume control,
media playback, app shortcuts, etc.).
Environment Adaptability Lighting and
Background Adaptation
Proposed system will have some adaptive algorithms
which will adjust themselves to varying lighting
conditions and background. So, if there are views of
dark and changing ambient environments, this feature
will make sure of stable hand tracking.
Dynamic Calibration
The application will automatically calibrate the
webcam based on user's hand size and the webcam’s
field of view. This to be able to run smoothly without
a great deal of manual configuration or manipulation
6 CONCLUSIONS
Using a webcam to use a Virtual Mouse is an
innovative development in the field of human-
computer interaction, enabling touchless operation by
recognizing hand gestures more effectively than
traditional methods. The system is become easy-to-
use and more user friendly by integrating ML,
Computer vision in real time, Gesture tracking as
input.
This allows for highly accurate and responsive
tracking, even in fast-moving or noisy environments
through the use of deep learning methods, feature
tracking, and noise reduction. Its ability to respond to
multiple gestures, adjust to ambient lighting, and
operate with low latency makes it a versatile option
you can use for many applications, from accessibility
improvements to gaming and smart household
control.
Moreover, the cross-platform compatibility of the
system allows users to experience touchless
interaction on different devices and operating
systems, thus increasing its accessibility and
applicability. Its adaptability to different users and
interface with visual feedback make the proposed
virtual mouse a promising approach to enhancing
accessibility, user experience, and interaction
efficiency.
Along with the system, it advances human-
computer interaction facilitating a future where
devices can be seamlessly operated using natural
touchless gestures, hence could be an asset to broad
set of users and use cases.
The figures presented in
this work include the mouse gesture detection code
example (Figure 1), which showcases the algorithm
for detecting gestures. Additionally, Figure 2
provides a description of the mouse gesture actions,
and Figure 3 visualizes the skeletal points used in
gesture detection.
Virtual Mouse Operation Using Webcam
497
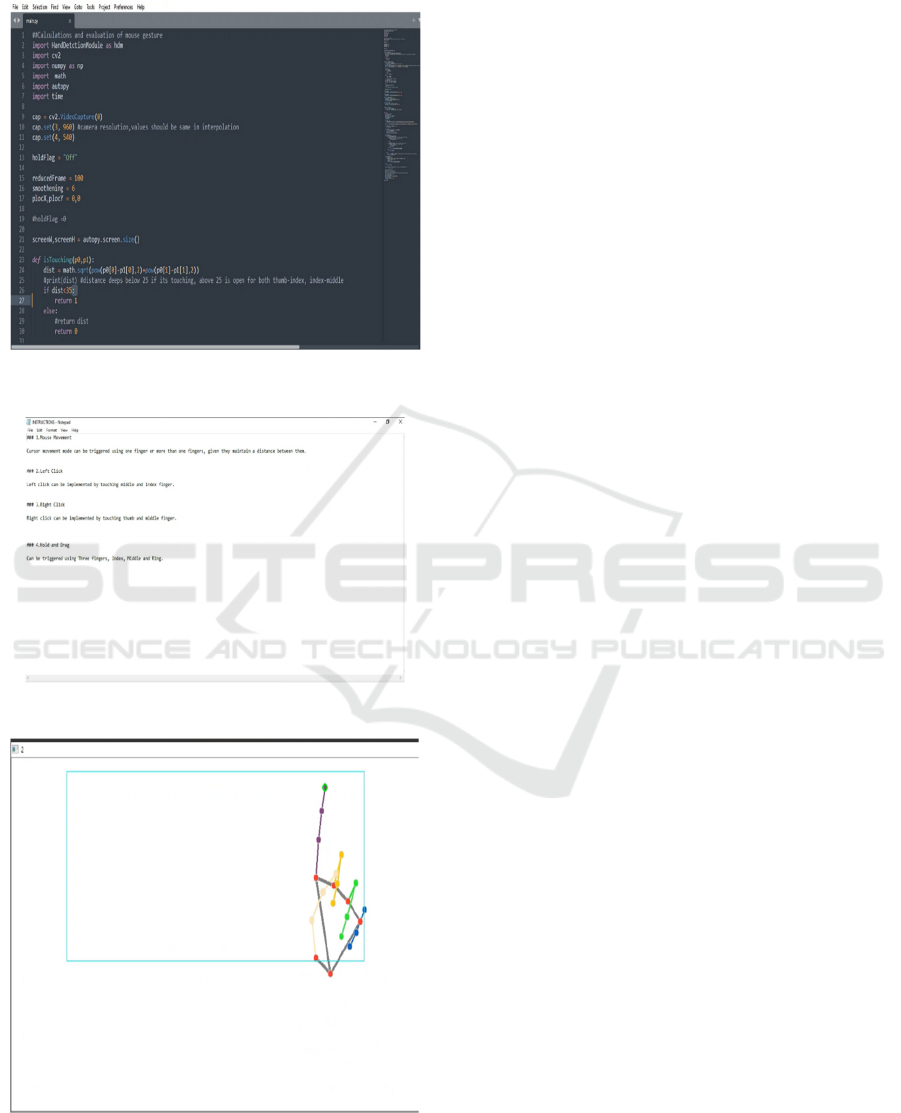
7 RESULTS
Figure 1: Mouse Gesture Detection Code Example.
Figure 2: Mouse Gesture Actions Description.
Figure 3: Gesture Detection Skeleton Points Visualization.
REFERENCES
Bedi, R., & Gupta, S. (2018). "Design and implementation
of a touchless virtual mouse using hand gestures."
International Journal of Computing and Digital
Systems, 7(2), 114-120.This paper discusses the design
of a virtual mouse system that uses webcam-based hand
gestures, similar to the proposed system, with focus on
real-time gesture tracking and application.
Khan, M., & Usman, M. (2021). "Deep learning-based hand
gesture recognition for control applications." Sensors,
21(13), 4425.The paper highlights the use of deep
learning for hand gesture recognition in various control
applications, emphasizing system optimization for
touchless control interfaces.
Le, Q., & WangLe, Q., & Wang, L. (2019). "Hand gesture
recognition using deep learning techniques." Journal of
Artificial Intelligence and Technology, 5(1), 12-20.
This study provides insights into the application of deep
learning for hand gesture recognition, a key component
of the proposed virtual mouse system.
Mandal, S., & Rani, S. (2020). "Real-time hand tracking for
touchless interaction in human-computer interfaces."
Journal of Image and Vision Computing, 98, 103918.
This study investigates hand tracking techniques for
touchless interaction, providing insights on how to
improve hand gesture recognition in real-time.
Omidvar, B., & Moghaddam, M. (2017). "Real-time hand
gesture recognition for human-computer interaction."
Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 14(4), 733-
744.This paper discusses real-time hand gesture
recognition techniques using computer vision and
machine learning, which is central to the functioning of
the proposed virtual mouse system.
Poh, P., & Lee, C. (2020). "Optimized hand gesture
recognition for interactive touchless systems." Journal
of Interactive Media, 12(2), 44-58.This paper discusses
optimization techniques for hand gesture recognition
systems, ensuring minimal latency and high accuracy,
which are critical for a responsive virtual mouse
system.
Singh, A., & Mehta, R. (2020). "A survey on gesture
recognition methods for touchless human-computer
interaction." Journal of Machine Learning and
Applications, 7(3), 105-119.
Tariq, S., & Ahmed, N. (2021). "Gesture recognition for
virtual mouse control using machine learning and
computer vision." International Journal of Computer
Vision and Artificial Intelligence, 19(2), 27-35.
This research explores machine learning algorithms for
gesture recognition, focusing on real-time applications
for controlling a virtual mouse.
The paper offers a comprehensive review of gesture
recognition methods, including optical flow and
feature-based tracking, which are relevant to
developing a robust virtual mouse system.
Verma, P., & Sharma, R. (2019). "A review on real-time
hand gesture recognition techniques for human-
computer interaction." Computer Vision and Image
Understanding, 182, 33-50.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
498

This reference provides a detailed review of various
gesture recognition algorithms and their application in
real-time systems like the virtual mouse.
Zhao, Y., & Li, J. (2020). "A robust method for hand
gesture recognition using deep learning and feature
extraction." International Journal of Computer Science
and Network Security, 20(6),45-50. This research
focuses on feature extraction and deep learning
methods to recognize hand gestures robustly under
different environmental conditions, aligning with the
proposed system's goals for accurate virtual mouse
control.
Virtual Mouse Operation Using Webcam
499
