
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive
Review
Gowri Sankar P. A.
1
, Shanmuga Priya S. R.
2
, Karthikumar K.
3
and Suba S.
4
1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Embedded System Technology, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and
Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Mahendra Engineering College, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Electric Vehicle, Battery Management System, Battery Charging, Batter Technology, Battery Mechanism.
Abstract: The Battery Management System (BMS) plays a critical role in enhancing the performance, safety, and
longevity of Electric Vehicles (EVs). The BMS continuously monitors various parameters such as current,
temperature, and overall battery health, ensuring that the battery operates within optimal conditions. The BMS
collects real-time data from sensors embedded within the EV, providing insights into battery status, charge
levels, and temperature fluctuations. By tracking these parameters, the BMS prevents overcharging,
overheating, and deep discharging, all of which can negatively impact battery life and performance. In this
article, we present an extensive literature review about the recent three year what are the advantages,
techniques, mechanism, AI/ML algorithm used for the Battery Management System (BMS) is presented. This
review paper plays a vital role for the research who pursuing his research especially in the BMS for advancing
sustainable transportation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Electric vehicles offer significant advantages to the
environment, cheaper to run, and offer a smoother,
quieter ride. Electric vehicles are eco-friendly, cost-
effective, and provide a smoother, quieter driving
experience. Recent EV trends include rapid sales
growth, tech innovations, and a focus on
sustainability. Electric vehicle sales increased by 27%
in 2024 relative to the previous year. Battery aging
significantly impacts fuel economy, drivability, and
electric range (Anselma, P. G, et, al 2022)
Demonstrated effectiveness through simulations and
experiments, showing improved fuel cell durability
and reduced hydrogen consumption across various
driving conditions (Yuan, H,et, al, 2022) Develop a
comprehensive methodology for estimating the
duration of lithium battery packs of electric vehicles
(EVs) (Ceraolo, M, et, al, 2024)Energy management
strategy using model-based reinforcement learning
(MBRL) and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) Lee,
H., & Cha, S. W. (2021). Efficient energy use, battery
life reduction due to charge cycles, and cybersecurity
threats. Novel taxonomy for battery optimization,
demand-side management, revenue maximization,
and machine learning applications (Colucci, R, et, al,
2024) Rolling resistance increases significantly with
speed. Aerodynamic drag is influenced by gradient.
Proposed a hybrid Pneumatic-Liquid Thermal
Management System to battery temperature control
(Agrawal, A, et, al, 2023) Classifies EMS
methodologies into rule-based, dynamic
optimization-based, and learning-based strategies.
Emphasizes lifetime optimization of fuel cell systems
and batteries (Rudolf, T, et, al, 2021)
Examines the critical role of the Battery
Management Systems (BMS) in battery-powered
UAVs. Identifies nine key areas categorized into:
Charging and discharging strategies, Battery state
estimation (SOC, SOH, RUL), System components
and safety issues (Jiao, S, et, al, 2023) Developing the
Model Predictive Control (MPC) based Energy
Management System (EMS) for series hybrid electric
agricultural tractor. Achieved 7.2% fuel reduction,
improved battery state of health (SoH), and better
thermal management relative to the conventional
rule-based EMS (Curiel-Olivares, G, et, al, 2023).
Historical safety concerns with Li-ion batteries across
402
A., G. S. P., R., S. P. S., K., K. and S., S.
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0013914000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
402-412
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

various applications. Lack of customer safety
consideration; corrective actions insufficient to
address root causes. Suggestions for improved safety
measures in future EV battery implementations
(Aalund, R, et, al 2021). The article explores the
electrification of road freight in India, focusing on
battery-electric trucks (BETs) and their potential to
address health, ecological and energy security issues
related to conventional transportation. It presents the
usage of energy simulation study tailored to Indian
conditions, analysing key components such as
powertrain systems, battery technologies, and
charging infrastructure. The findings aim to inform
future research on the feasibility and practicality of
BETs in India, ultimately supporting the transition
towards sustainable transportation solutions
(Madichetty, S, et, al, 2022)
Utilizes LSTM for real-time velocity prediction
and a neural network-optimized rule-based energy
management strategy. Prolonged battery lifespan by
26.85%. Reduced total energy losses by 22.25%.
Improved efficiency and energy throughput for
supercapacitors (Udeogu, C. U, et, al, 2022). The
proposed system significantly reduces peak load
demand and operational costs in real distribution
networks. Utilizes real load patterns, various EV
types, and financial analysis to validate performance
against prediction-based techniques (Das, N, et, al,
2023). Utilizes MATLAB/Simulink for system
configuration and Mixed Integer Programming (MIP)
for cost calculations. Two test cases demonstrate the
model's effectiveness in both regulated and
deregulated environments. Findings indicate notable
economic savings and efficient battery state of charge
(SOC) management. The framework is applicable to
various operational environments, enhancing the
feasibility of OLEV systems (Nisar, F, et, al, 2021).
Developed a battery model using real-world data;
integrated into an optimization scheme. Advanced
thermal models are crucial in charging power > 7 Kw.
Ignoring battery aging can underestimate operating
costs by up to 30%. Effective Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
services require consideration of battery aging costs
and dynamic electricity tariffs (Schwenk, K, et, al,
2021). Figure 1 shows Battery Management System
(BMS) for electric vehicles, where sensors attached
to the battery module measure current, voltage, and
temperature. This data is then processed by the BMS,
which calculates and communicates state of charge
(SOC), state of health (SOH), thermal management,
and power optimization to a display unit, ensuring the
safety and optimal performance of the battery pack.
Figure 1: Battery management system (BMS).
2 BATTERY MANAGEMENT
SYSTEM
2.1 Literature Review
Research on the electric vehicle charging safety
warning system (Diao, X, et, al, 2023). This paper
discusses the model predicts voltage changes during
charging, dynamically adjusts warning thresholds,
and effectively identifies abnormal charging data,
enhancing safety and reducing risks of fire incidents.
In this paper, the limitations of the study regarding
data acquisition for EV charging, is founded upon the
limitations in data acquisition concerning the State of
Health (SOH) of the battery cell and the lack of
complete life cycle EV charging data. Additionally,
the collected charging information lacked any fault
data, which could affect the robustness of the early
warning model. Further research is suggested to
explore these areas in greater depth.
Machine learning-based on the battery
management system for the electric vehicle
(Duraisamy, T, 2021). This paper focuses on
improving battery management systems (BMS) for
electric vehicles through an optimal cell balancing
mechanism. It employs machine learning algorithms
to select balancing resistors based on factors such as
cell imbalance, balancing time, and temperature,
resulting in enhanced balancing speed, reduced power
loss, and better thermal management compared to
traditional methods. The effectiveness of the
suggested mechanism is evaluated using BPNN,
RBNN, and LSTM models, showcasing superior
accuracy and efficiency. The main categories of the
machine learning methods used in battery
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive Review
403

management system applications are categorized into
supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-
supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
Review of cloud-based lithium-ion battery
management systems for the electric vehicle (Ismail,
M., & Ahmed, R. 2024). The Cloud computing
enhances BMS efficiency and reliability. Identified
research gaps include online learning, connectivity,
and security. Future work should integrate recent
cloud advancements to improve BMS functionality.
Battery Management Systems (BMS) face challenges
such as limited onboard computational resources,
which restrict the use of accurate state estimation
techniques and lead to energy inefficiencies.
Additionally, BMS cannot be updated remotely,
making it difficult to adapt to changes in battery
behaviour due to aging and preventing manufacturers
from offering new features. These limitations hinder
the overall performance and reliability of BMS in
electric vehicles.
Energy management in hybrid electric and hybrid
energy storage system vehicles (Maghfiroh, H, 2024).
This paper emphasizes the environmental benefits of
HEVs and HESS EVs while discussing various types
of FLC and their practical applications. Additionally,
the review analyses the advantages and challenges
associated with FLC EMS and outlines future
research directions in this field. The benefits of using
Fuzzy Logic Controllers in managing energy
consumption in hybrid vehicles, Fuzzy Logic
Controllers (FLC) in effective energy management in
hybrid vehicles brings numerous advantages, such as
enhanced adaptability to varying driving conditions,
leading to enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced
power consumption. They outperform traditional
control methods, such as Proportional-Integral (PI)
and Sliding Mode Control (SMC), in areas like
voltage regulation and energy management.
Additionally, FLCs can be combined with other
methods to address limitations and optimize
performance, contributing to more efficient and
sustainable transportation solutions.
Development of fuzzy logic and ANFIS control
for the energy management in electric vehicle
(Suhail, M., et, al, 2024) This study centres on the
development of the fuzzy logic and Adaptive Neuro-
Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) controllers for
managing energy consumption in hybrid electric
vehicles (HEVs). The primary goal is to improve the
state of charge (SOC) of battery to enhance vehicle
autonomy and efficiency. Results indicate that the
ANFIS controller outperforms the fuzzy logic
controller in maintaining higher SOC levels,
suggesting better energy management strategies for
HEVs. The ANFIS controller improves the SOC
profile of hybrid electric vehicles by utilizing precise
fuzzy modelling and real-time data to adaptively
control the battery charging process. It analyses input
variables such as state of charge (SOC) and engine
speed to adjust the forward gain, optimizing the
quantity of generated torque utilized for the battery
charging. This leads to a smoother SOC curve and an
increased SOC levels by the conclusion of the drive
cycle, enhancing overall energy efficiency and
performance.
Prediction of the battery state using the digital
twin framework (Jafari, S, et, al, 2022). The
methodology employs Extreme Gradient Boost
(XGBoost) and Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) to
achieve accurate battery state estimation. The
findings indicate that the DT model significantly
improves the reliability, optimization, and accuracy
of battery management, ultimately extending battery
life through effective monitoring and predictive
maintenance. The main types of battery cell models
discussed in the paper are Equivalent Circuit Models
(ECM), electrochemical models, and machine
learning models. Each model boasts unique strengths
and limitations, playing different roles in the battery
system digital twin. ECMs are particularly used for
accurately monitoring the battery cell, state of charge
(SOC), and state of health (SOH).
Online data-driven efficient energy management
of the hybrid electric vehicle (Lee, H, et, al, 2020):
The proposed framework is designed to learn driving
conditions and adapt control policies in real-time,
resulting in simulation outcomes that demonstrate
near-optimal fuel economy, surpassing conventional
rule-based strategies. This work enhances the
understanding of HEV control and offers a robust,
explainable approach to energy management, with
future efforts aimed at experimental validation and
balancing computational efficiency with fuel
economy performance. The proposed Q-learning
algorithm enhances fuel economy in hybrid electric
vehicles by utilizing a model-based approach that
learns from real-time driving data to optimize control
policies. It effectively separates the internal
powertrain dynamics from external driving
conditions, allowing for a more tailored and efficient
energy management strategy. Furthermore, the
algorithm's ability to update the vehicle state
approximation model through interactions helps
refine decision-making, leading to improved fuel
efficiency over time.
Battery management techniques for an electric
vehicle traction system (Abdelaal, A. S, et, al, 2022):
This paper focuses on the implementation of Battery
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
404

Energy Management (BEM) techniques in electric
vehicle (EV) traction systems, specifically utilizing
conventional Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC) and the
Model Predictive Control (MPC) alongside a
Cascaded FLC (CSFLC) to enhance battery longevity
and minimize current fluctuations. The findings
suggest that the CSFLC technique improved battery
lifetime by 5.6% during the New European Driving
Cycle (NEDC) & 6.1% during the US06 cycle, while
also demonstrating lower battery current
consumption compared to the traditional FLC
approach. Overall, the study highlights the efficiency
of advanced control strategies in optimizing energy
use for EV traction systems. The Fuzzy MPC (FMPC)
technique contributes to battery energy management
in EVs by generating a reference current signal for
motor speed regulation while dynamically adjusting
the input weight in the MPC depending on the
battery's state of charge (SOC) and its variations. This
approach minimizes battery energy consumption and
degradation by optimizing the current signal in real-
time, leading to extended battery runtime and
lifetime. Additionally, FMPC exhibits lower
computational effort compared to traditional
methods, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Energy management system for hybrid renewable
energy (Karmaker, A, et, al, 2023). The document
discusses the operation and maintenance costs
(Co&m) associated using Electric Vehicle Charging
Stations (EVCS) and highlights the payback period
(PBP) for charging station owners, which is relatively
short, indicating profitability. It emphasizes the use of
a SIMULINK model to optimize power generation
and charging costs, resulting in a 74.67% reduction in
energy costs compared to flat rate tariffs.
Additionally, the integration of hybrid renewable
resources significantly lowers greenhouse gas
emissions. The integration of renewable resources in
EV charging stations leads to a significant reduction
in charging costs, especially during off-peak hours,
with savings of up to 74.67% compared to
conventional rates. Additionally, it results in a CO2
emission reduction of up to 54.86% when 84% of the
energy is sourced from renewables, thereby
enhancing environmental sustainability. Overall,
increased renewable utilization decreases both
charging costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Development of optimal power-distribution-
management algorithm (Lee, H, et, al, 2021): This
research is dedicated to developing an ideal allocation
of power control algorithm for the 4WD electric
vehicles to enhance improving battery efficiency and
driving range. Simulations demonstrated
improvements in battery efficiency improved by
0.2% under the specified conditions urban driving
and 2.52% on highways compared to a comparison
model, with increased driving efficiency at high-
speed and high-torque ranges. Future efforts will aim
to refine the power allocation ratio contingent on
actual driving behaviour and environmental factors to
further improve the performance of the 4WD electric
vehicles. The study employed urban and simulations
of highway driving based on EPA standards for
analysing battery performance. It utilized dynamic
programming and Pontryagin’s minimum principle
for optimizing power distribution, and
MATLAB/Simulink for modelling the vehicle's
dynamic characteristics. Performance comparisons
were conducted between the proposed optimal power
distribution algorithm and a comparison model to
assess battery efficiency and power consumption.
Energy management of the hybrid electric
vehicles by sequential programming (Ghandriz, T, et,
al, 2021): The document discusses a sequential
programming and gear optimization algorithm for
hybrid powertrains, focusing on minimizing energy
consumption by selecting optimal gears based on
vehicle speed and force. It outlines the constraints and
equations governing the system, including power
balance among various components like internal
combustion engine (ICE) and electric motor (EM).
Additionally, it highlights the importance of
preventing frequent gear shifts to enhance fuel
efficiency and overall performance. The study
utilized sequential linear programming (SLP) and
compared it with sequential quadratic programming
(SQP) to address the predictive control problem. It
also mentioned the application of dynamic
programming (DP) and Pontryagin’s minimum
principle (PMP) as model-based solution methods for
optimal control. These methods were employed to
address the challenges of real-time predictive energy
management for the hybrid electric vehicles.
Driving cycle recognition for the hybrid electric
vehicles (Chen, D, et, al, 2022): This paper focuses
on developing an adaptive equivalent consumption
minimization strategy (A-ECMS) for the hybrid
electric vehicles (HEVs) by employing driving cycle
recognition. The authors utilize a learning vector
quantization (LVQ) neural network, achieving a
recognition accuracy of 98%. The results demonstrate
that A-ECMS enhances fuel economy by 3.8% in the
New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) and 3.6% in
the China Heavy-duty Truck Cycle (CHTC-LT)
compared to traditional logic-based energy
management strategies. The primary goal of the study
on A-ECMS for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) is to
create an adaptive equivalent consumption
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive Review
405

minimization strategy that optimizes fuel
consumption by recognizing driving cycles, thereby
improving energy management and overall fuel
economy.
Comparative performance of the machine
learning algorithm for predicting electric vehicles
energy consumption (Ullah, I, et, al, 2022): The
research assesses a range of machine learning (ML)
frameworks for forecasting electric vehicle (EV)
energy usage, utilizing data derived from 38,362 trips
in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. Advanced ML models,
specifically XGBOOST and Light GBM,
demonstrated superior prediction accuracy compared
to conventional frameworks such as multiple linear
regression (MLR) and artificial neural networks
(ANN). Key factors impacting energy consumption
include trip distance, heater and A/C usage, and road
gradient, with Light GBM achieving the best
performance, reflected by an R² of 0.98, highlighting
its effectiveness in this domain. The dataset was split
into two sections: 80% for training and 20% for
testing. This division is crucial for evaluating the
efficacy of the proposed machine learning algorithms.
Additionally, a 10-fold cross-validation method was
utilized to improve the robustness and efficacy of the
prediction models.
A real-time energy management strategy for the
hybrid electric vehicles (Lee, W, et, al, 2021) It
highlights the potential of HEVs to enhance fuel
efficiency significantly while addressing the
challenges of transitioning to zero-emission vehicles.
The suggested approach showcases enhanced
performance compared to existing adaptive Energy
Consumption Management Strategies (ECMS),
achieving fuel efficiency improvements of 0.5% to
1.5% across different driving cycles. Future driving
information is crucial in the proposed control strategy
as it allows the intelligent control part to estimate the
optimal costate in real-time, enhancing decision-
making for energy management. By predicting
factors such as vehicle power demand, speed, and
acceleration, the strategy can adjust the costate to
optimize the distribution of energy between fuel and
electricity, leading to improved fuel efficiency. This
predictive capability enables the vehicle to
proactively manage its energy resources, ensuring
better performance under varying driving conditions.
Battery management system of electric vehicle
using an artificial neural network (Afzal, M, et, al,
2024) This paper presents an innovative Battery
Management System (BMS) that combines artificial
neural networks (ANN) and fuzzy logic. This new
system features decentralized control and
communication-free operation, leading to improved
reliability, a 15% increase in energy efficiency, and a
20% enhancement in battery life. The BMS was
validated through simulations and experimental
prototypes utilizing a 100kWh lithium-ion battery
pack, representing a substantial advancement in
electric vehicle battery management. The key
innovations in the new Battery Management System
(BMS) for electric vehicles include the application of
artificial neural networks (ANN) and fuzzy logic for
decentralized control and communication-free
operation. It features adaptive virtual admittance for
even load sharing, leading to improved reliability, a
15% increase in energy efficiency, and a 20%
enhancement in battery life.
Energy modelling for the electric vehicles
building on real driving cycles Mądziel, M. (2024).
The study analyses real driving cycles across varying
temperatures, yielding a summer model with an R² of
0.86 and MSE of 1.4, and a winter model with an R²
of 0.89 and MSE of 2.8. The findings are intended to
assist city planners in optimizing charging
infrastructure and enhancing the understanding of EV
energy behaviour in different environmental
conditions. The neural network method performs
comparably to gradient boosting in predicting energy
values for electric vehicles, with superior validation
results, particularly for the test set. While the random
forest technique shows slightly better performance,
the neural network method is recognized as the best
due to its lower error rates and effective predictions.
Overall, the neural network method is favoured for its
simplicity and satisfactory results in energy
consumption modelling.
AI models for energy efficiency in hybrid and
electric vehicles Mądziel, M., & Campisi, T. (2024).
The model demonstrates high accuracy in forecasting
energy usage based on vehicle velocity and
acceleration, which can significantly aid in
optimizing charging infrastructure and energy
management. The findings support sustainable
transport policies and provide valuable insights for
decision-making among EV users. This study
contributes to intelligent optimizing energy usage in
electric vehicles (EVs) by accurately predicting
energy consumption based on driving conditions,
such as velocity and acceleration. This anticipatory
feature enables better strategic planning regarding the
deployment of charging stations and the
incorporation of renewable energy sources into the
grid. Additionally, it enhances the understanding of
vehicle operation for users, ultimately supporting
environmental protection and optimizing energy use
goals.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
406
Role of generative artificial intelligence in
internet of the electric vehicles (Zhang, H, et, al,
2024): The paper explores GAN-based methods,
especially WGAN-GP, for addressing uncertainties in
EV charging load analysis using data from 32 stations
in Zhejiang. It highlights the limited comparative
studies with other Generative AI methods and
introduces CopulaGAN for generating diverse
vehicle types. These approaches aim to improve EV
charging behaviour generation and data augmentation
for better scheduling. The purpose of the WGAN-GP
approach in EV charging load analysis is to tackle
spatial-temporal uncertainty by generating realistic
EV charging scenarios without relying on uniform
probability assumptions across charging stations. It
aims to explore load dynamics and improve the
accuracy of load forecasting at various nodes in the
distribution network. This method enhances the
understanding of EV charging behaviours and their
impact on the power grid.
Artificial intelligence for the electric vehicle
energy systems integration (Hua, W, et, al, 2023):
The paper discusses the incorporation of electric
vehicles (EVs) into energy systems through the
application of artificial intelligence (AI). It highlights
challenges such as battery production, charging
infrastructure, and grid demand, while reviewing AI's
role in optimizing EV integration, including range
prediction and load management. Additionally, it
identifies limitations like gaps in real-world
validation and consumer trust, and suggests future
research directions focusing on advancements in AI
algorithms, explainability, and peer-to-peer energy
trading. The main technical challenges faced by
electric vehicles (EVs) include battery technology
issues such as capacity, range, charging efficiency,
lifespan, and cost. Additionally, developing sufficient
charging infrastructure and decarbonizing the battery
supply chain are significant hurdles. Public opinion
and high costs also impact EV adoption.
Recent AI applications in electrical vehicles for
sustainability (Reddy, K, et, al, 2024): The paper
discusses the function of artificial intelligence (AI) in
electric vehicles (EVs) to enhance sustainability by
improving vehicle control, energy management, and
battery design. It notes significant reductions in
greenhouse gas emissions but highlights challenges
like data security and regulatory issues. The authors
emphasize the necessity for future research to tackle
these challenges and improve infrastructure for AI in
EVs. AI contributes the energy management of the
electric vehicles (EVs) by optimizing charging
schedules, predicting energy usage, and enhancing
battery management systems. It utilizes algorithms
for range prediction, smart charging, and grid
integration, which help reduce peak grid loads and
improve overall efficiency. Additionally, AI enables
real-time monitoring and control of energy
consumption, ultimately maximizing driving range
and minimizing operating costs. Table 1 show the
Authors, Features, Mechanism Used, Advantages and
Disadvantages.
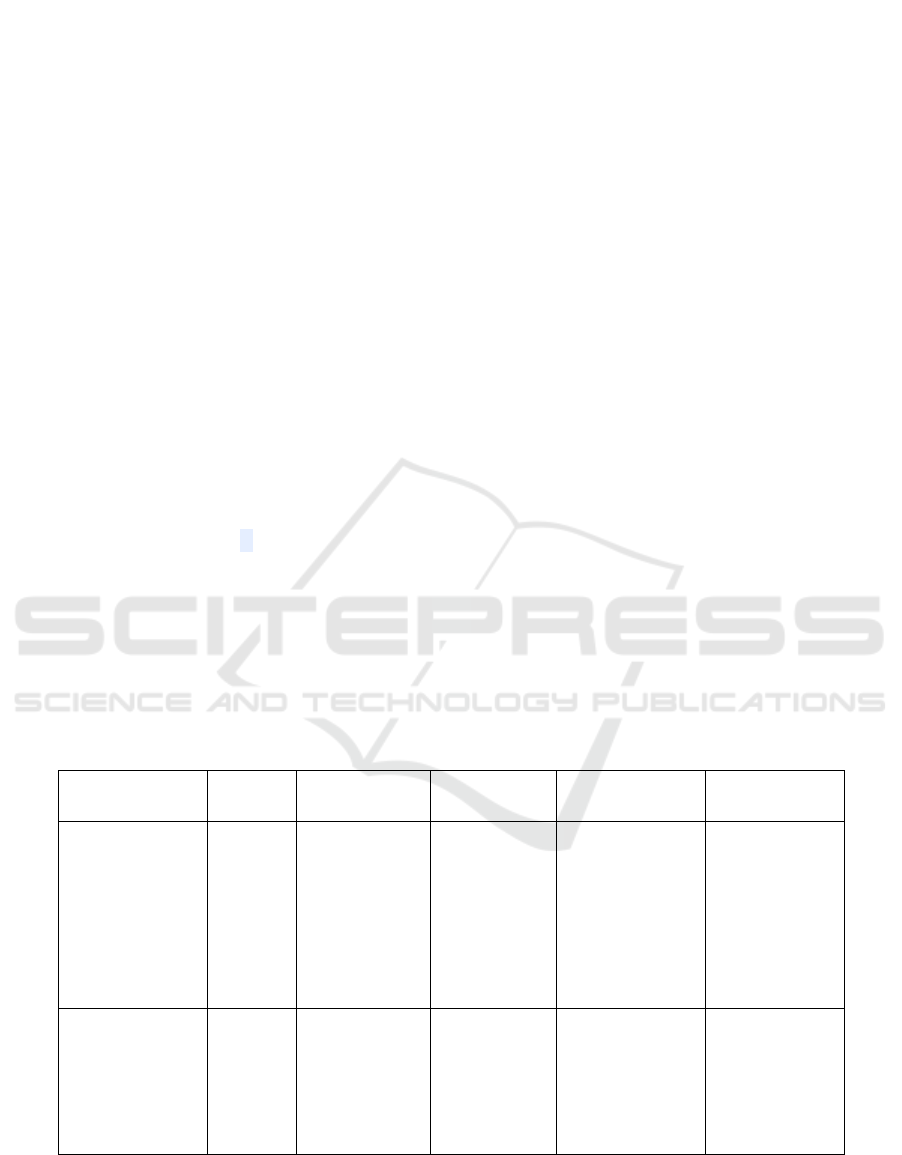
Table 1: Authors, features, mechanism used, advantages and disadvantages.
Reference
Paper
Year Features
Control
Technique
Advantages Disadvantages
Xiaohong Diao,
et. al.
2023
- Early
warning
system for EV
charging safety
- Prediction of
voltage
changes
Adaptive
Long Short-
Term
Memory (A-
LSTM)
algorithm
- Accurate
prediction of
voltage changes -
Dynamic
adjustment of
warning
thresholds
- Real-time
warnings
- Requires
extensive
historical
charging data
- Potential for
false alarms if
data is not
accurate
Thiruvonasundari
et. al.
2021
- Optimal cell
balancing for
EV batteries
- Improved
balancing time
and power loss
mana
g
ement
Machine
Learning
(ML)
algorithms
(BPNN,
RBNN,
LSTM
)
- Enhanced
battery run time
and lifespan
- Optimized
power loss
management
- Requires
accurate data
for effective
balancing
-
Implementation
com
p
lexit
y
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive Review
407
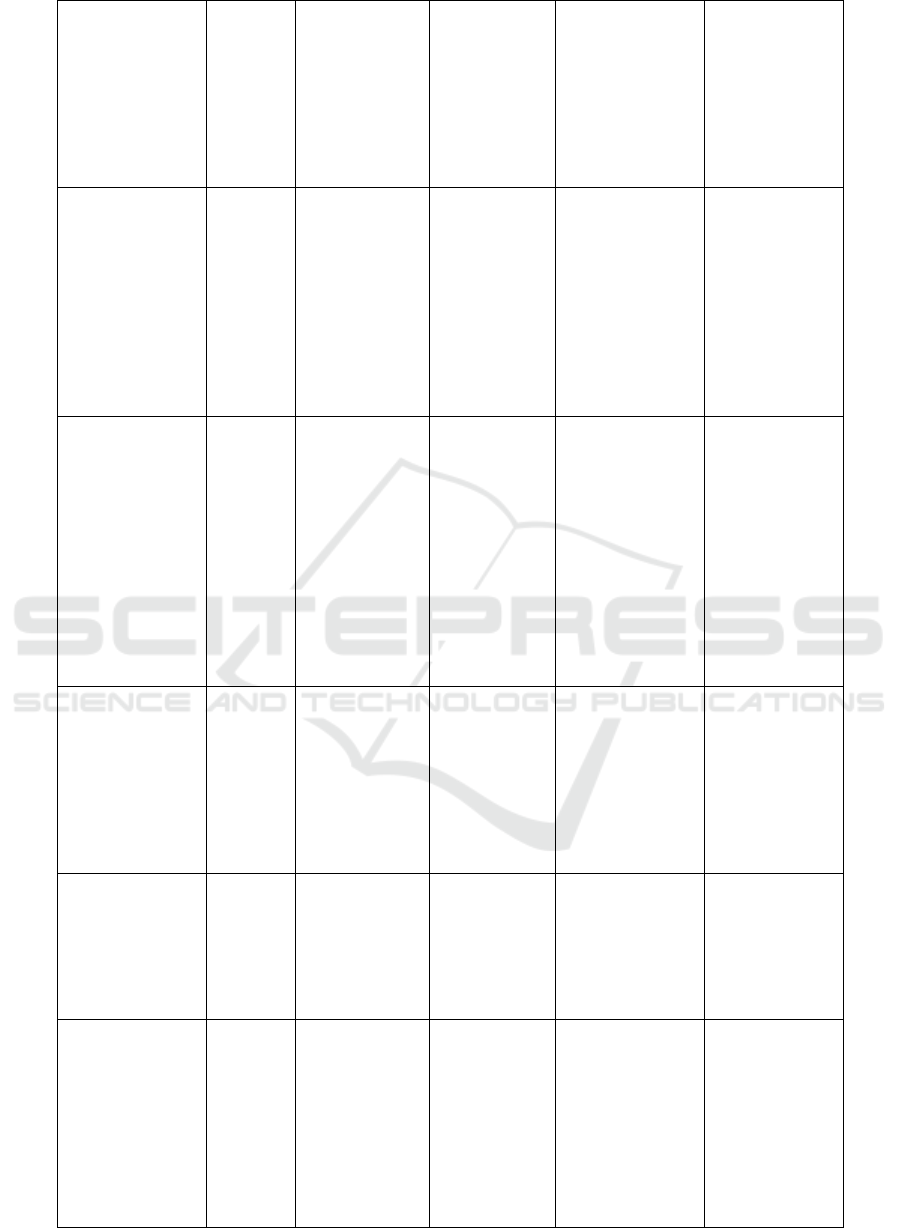
Mohanad Ismail,
et. al.
2024
- Integration
with cloud
computing
- Enhanced
data analysis
and monitoring
- Real-time
battery
management
Cloud-based
data
processing
and analytics
- Improved
battery
performance and
lifespan
- Enhanced
predictive
maintenance
- Better resource
utilization
- Dependency
on internet
connectivity
- Potential data
privacy
concerns
-
Implementation
complexit
y
Hari Maghfiroh,
et. al.
2024
- Efficient
energy
utilization in
hybrid electric
and hybrid
energy storage
system
vehicles
- Fuzzy logic
controller
(FLC)
Fuzzy Logic
Controller
(FLC)
- Efficient energy
storage and
power flow
regulation
- Improved
performance and
stability
- Complexity in
designing and
modelling
- Requires
accurate rule
definition
Mohammad
Suhail, et. al.
2021
- Progressive
fuzzy logic
- Adaptive
Neuro-Fuzzy
Inference
System
(ANFIS)
- Efficient
energy
utilization for
plug-in hybrid
electric
vehicles
Fuzzy Logic
Controller
(FLC) and
ANFIS
- Improved
battery
performance
- Enhanced
energy
management
- Better fuel
efficiency
- Complexity in
designing and
modelling
- Requires
accurate rule
definition
Sadiqa Jafari, et.
al.
2022
- Digital Twin
framework
- State of
Health (SOH)
& State of
Charge (SOC)
prediction
Extreme
Gradient
Boost
(XGBoost)
and Extended
Kalman Filter
(EKF)
- Enhanced
situational
awareness
- Accurate SOH
and SOC
estimation
- Improved
battery
maintenance
- Requires
accurate data
for effective
predictions
- Complexity in
implementation
Heeyun Lee, et.
al.
2020
- Online data-
driven energy
management
- Model-based
Q-learning
Model-Based
Q-Learning
- Adaptive to
driving
environment
- Near optimal
control solution
- Improved fuel
econom
y
- Requires
accurate model
of vehicle
dynamics
- Complexity in
implementation
Ahmed Sayed
Abdelaal, et. al.
2022
- Two battery
energy
management
(BEM)
techniques
- Indirect field-
oriented (IFO)
induction
motor (IM)
drive syste
m
- Cascaded
Fuzzy Logic
Controllers
(CSFLC)
- Fuzzy
Tuned Model
Predictive
Control
(FMPC)
- Regulates
motor speed
- Minimizes
battery pack state
of charge (SOC)
reduction and
state of health
(SOH)
degradation
- Requires
accurate battery
information
- Higher
computational
burden for
CSFLC
compared to
FMPC
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
408
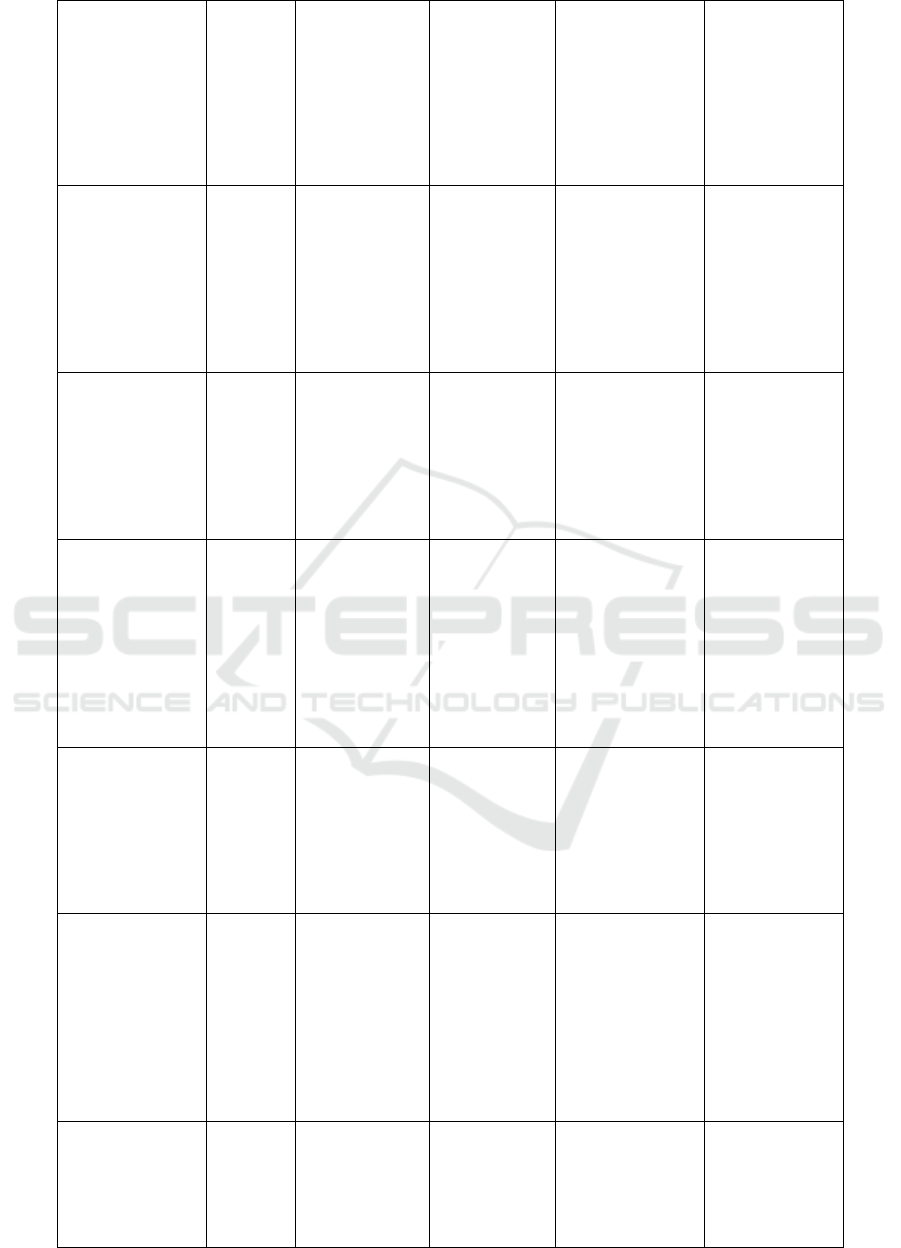
- Prolongs
battery runtime
and lifetime
Ashish Kumar
Karmaker, et. al.
2023
- Hybrid solar
and biogas-
based EV
charging
station
- Fuzzy
inference
system
Fuzzy Logic
Controller
(FLC)
- Optimizes real-
time charging
costs
- Enhances
renewable energy
utilization
- Reduces
greenhouse gas
emissions
- Requires
accurate data
for effective
management
- Dependency
on renewable
energy sources
Hae-Sol Lee, et.
al
2021
- Optimal
power
distribution for
4WD EVs
- Improved
battery
efficiency
Power-
distribution-
management
optimization
algorithm
- Increased
vehicle battery
range
- Reduced power
loss
- Enhanced
driving energy
efficienc
y
- Requires
accurate vehicle
driving
condition data
- Complexity in
implementation
Toheed
Ghandriz, et. al.
2021
- Real-time
predictive
energy
management
- Optimal
control
strategy
- Sequential
linear
p
rogramming
Model
Predictive
Control
(MPC) and
Sequential
Linear
Programming
- Reduced fuel
consumption
- Optimal power
split between
vehicle power
sources and
brakes
- Enhanced
vehicle
p
erformance
- Requires high-
fidelity vehicle
model for
accurate
predictions
- Complexity in
real-time
implementation
Dongdong Chen,
Tie Wang, et. al.
2022
- Adaptive
Equivalent
Consumption
Minimization
Strategy
(ECMS)
- Driving cycle
reco
g
nition
Neural
networks and
optimization
algorithms
- Improved fuel
economy
- Enhanced
adaptability to
driving
conditions
- Better energy
mana
g
ement
- Requires
accurate driving
cycle data
- Complexity in
implementation
Irfan Ullah et. al.
2022
- Comparative
performance of
ML algorithms
- Prediction of
EV energy
consumption
Extreme
Gradient
Boosting
(XGBoost)
and Light
Gradient
Boosting
Machine
(LightGBM)
- Higher
accuracy in
prediction
- Better
performance
compared to
traditional
models
- Enhanced
sustainabilit
y
- Necessitates
substantial data
for training
purposes
- Complexity in
implementation
Woong Lee, et.
al.
2021
- Real-time
intelligent
energy
management
-
Reinforcement
Deep Q-
Networks
(DQN)
- Improved
energy efficiency
- Optimal control
parameter
determination
- Requires
extensive
training data
- Complexity in
implementation
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive Review
409
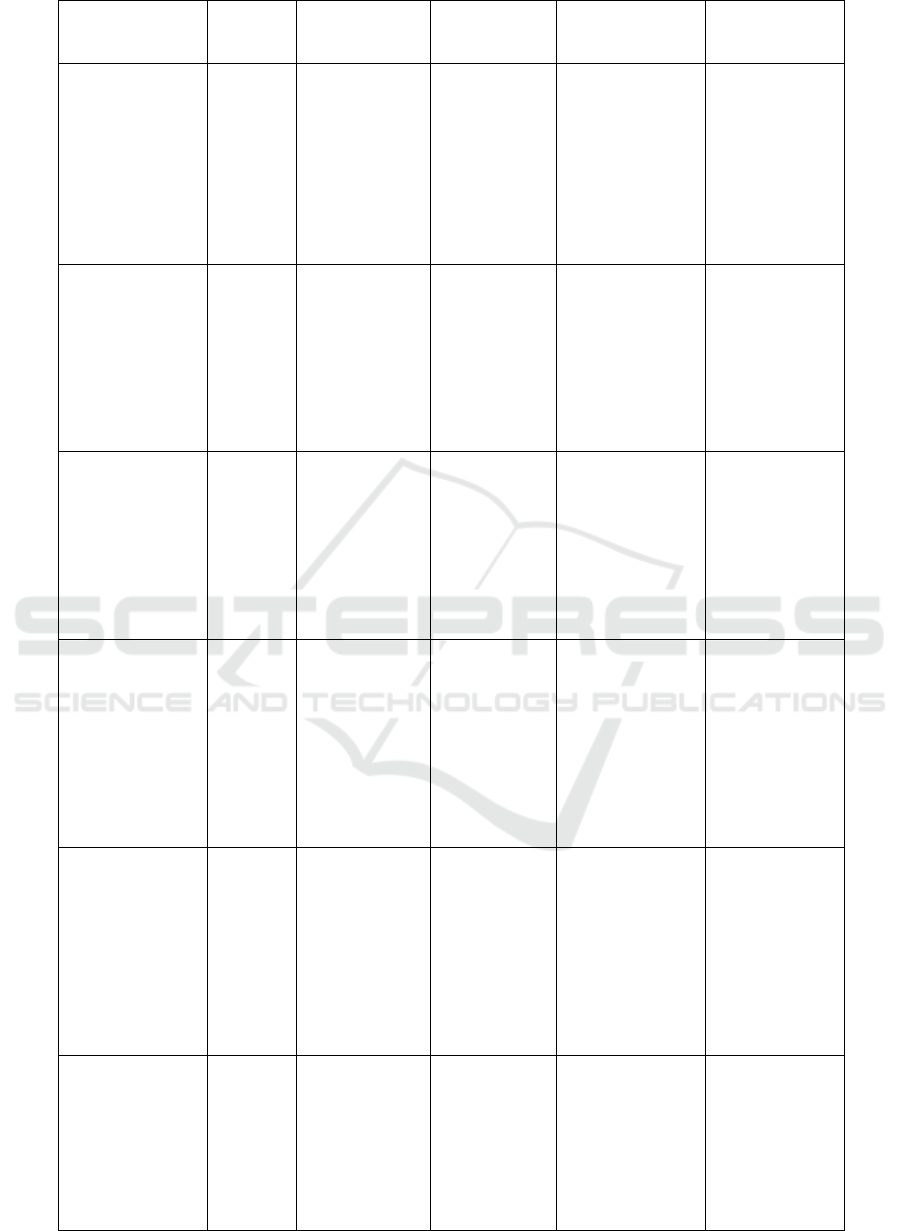
learning (Deep
Q-Networks)
- Enhanced
vehicle
p
erformance
Muhammad
Zeshan Afzal, et.
al.
2023
- ANN-based
adaptive droop
control theory
- Improved
load
distribution
- Enhanced
battery
performance
Artificial
Neural
Network
(ANN) and
Fuzzy Logic
- Decentralized
control
architecture
-
Communication-
free capability
- Improved
reliability and
efficiency
- Requires
accurate SOC
data
- Complexity in
implementation
Maksymilian
Mądziel et. al.
2024
- AI-based
energy
modelling
- Real driving
cycles
- Microscale
analysis
Neural
Networks
- High precision
in energy
consumption
prediction
- Rapid
generation of
results
- Creation of
energy maps
- Necessitates
substantial data
for training
purposes
- Complexity in
implementation
Maksymilian
Mądziel, et. al.
2024
- AI-based
energy
efficiency
models
- Real driving
cycles
- Microscale
analysis
Deep Neural
Network
(DNN)
- High accuracy
in energy
consumption
prediction
- Versatility in
application
- Useful for
transport policy
p
lanning
- Necessitates
substantial data
for training
purposes
- Complexity in
implementation
Hanwen Zhang,
Dusit Niyato, et.
al.
2024
- Generative
AI in IoEV
- Applications
across multiple
layers
Generative AI
techniques
- Enhanced
charging
management
- Improved
cyber-attack
prevention
- Versatile
applications
across different
layers
- Requires
extensive data
for training
- Complexity in
implementation
Weiqi Hua,
Daniel Mullen,
et. al.
2024
- AI for EV
energy systems
integration
- Addressing
integration
challenges
Various AI
techniques
- Enhanced
integration of
EVs into energy
systems
- Improved
energy
management
- Support for
global Net Zero
transition
- Necessitates
substantial data
for training
purposes
- Complexity in
implementation
K. Balaji Nanda,
et. al.
2024
- AI
applications in
EVs
Sustainable
transportation
solutions
Various AI
techniques
- Improved
vehicle control
- Enhanced
energy
management
- Reduced
greenhouse gas
emissions
- Requires
extensive data
for training
- Complexity in
implementation
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
410

3 CONCLUSIONS
This paper's primary goal is to provide an in-depth
analysis of the battery management systems that are
already in use for different types of electric vehicles.
The review article summarizes the various methods,
algorithm proposed for the BMS and provide a clear
knowledge for the unconfiguring researchers and
methods for the new BMS. One of the fundamental
components of electrical energy storage systems is
the BMS. The components, topology, operation, and
functionality of BMS for energy storage systems are
all covered in detail in this study. Although the BMS
can have a variety of configurations depending on the
application, its fundamental operating objective and
safety feature never change. The research offers BMS
suggestions for the present market and battery
technologies.
REFERENCES
Aalund, R., Diao, W., Kong, L., & Pecht, M. (2021).
Understanding the non-collision related battery safety
risks in electric vehicles a case study in electric vehicle
recalls and the LG chem battery. IEEE Access, 9,
89527-89532.
Abdelaal, A. S., Mukhopadhyay, S., & Rehman, H. (2022).
Battery energy management techniques for an electric
vehicle traction system. IEEE Access, 10, 84015-
84037.
Afzal, M. Z., Aurangzeb, M., Iqbal, S., Pushkarna, M.,
Rehman, A. U., Kotb, H., ... & Bereznychenko, V.
(2023). A Novel Electric Vehicle Battery Management
System Using an Artificial Neural Network‐Based
Adaptive Droop Control Theory. International Journal
of Energy Research, 2023(1), 2581729.
Agrawal, A., Singh, R., Kumar, N., Singh, V. P., Alotaibi,
M. A., Malik, H., ... & Hossaini, M. A. (2023).
Mathematical Modeling of Driving Forces of an
Electric Vehicle for Sustainable Operation. IEEE
Access, 11, 95278-95294.
Anselma, P. G., Kollmeyer, P. J., Feraco, S., Bonfitto, A.,
Belingardi, G., Emadi, A., ... & Tonoli, A. (2022).
Economic Payback Time of Battery Pack Replacement
for Hybrid and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE
Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 9(1),
1021-1033.
Ceraolo, M., Fioriti, D., Lutzemberger, G., Quilici, F. G.,
Scarpelli, C., & Bianchi, F. (2024). Electro-Thermal
Modeling and aging evaluation of Lithium Battery
Packs for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access.
Chen, D., Wang, T., Qiao, T., Yang, T., & Ji, Z. (2022).
Driving cycle recognition based adaptive equivalent
consumption minimization strategy for hybrid electric
vehicles. IEEE Access, 10, 77732-77743.
Colucci, R., Mahgoub, I., Yousefizadeh, H., & Al-Najada,
H. (2024). Survey of strategies to optimize battery
operation to minimize the electricity cost in a microgrid
with renewable energy sources and electric
vehicles. IEEE Access.
Curiel-Olivares, G., Johnson, S., Escobar, G., & Schacht-
Rodríguez, R. (2023). Model Predictive Control-Based
Energy Management System for a Hybrid Electric
Agricultural Tractor. IEEE Access, 11, 118801-
118811.
Das, N., Haque, A., Zaman, H., Morsalin, S., & Islam, S.
(2023). Domestic load management with coordinated
photovoltaics, battery storage and electric vehicle
operation. IEEE Access, 11, 12075-12087.
Diao, X., Jiang, L., Gao, T., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., Wang, L.,
& Wu, Q. (2023). Research on Electric Vehicle
Charging Safety Warning Based on A-LSTM
Algorithm. IEEE Access, 11, 55081-55093.
Duraisamy, T., & Kaliyaperumal, D. (2021). Machine
learning-based optimal cell balancing mechanism for
electric vehicle battery management system. IEEE
Access, 9, 132846-132861.
Ghandriz, T., Jacobson, B., Murgovski, N., Nilsson, P., &
Laine, L. (2021). Real-time predictive energy
management of hybrid electric heavy vehicles by
sequential programming. IEEE Transactions on
Vehicular Technology, 70(5), 4113-4128.
Hua, W., Mullen, D., Wahid, A., Sitabkhan, K., & Mason,
K. (2023, September). An overview of artificial
intelligence for electric vehicle energy systems
integration. In European Conference on Artificial
Intelligence (pp. 178-186). Cham: Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Ismail, M., & Ahmed, R. (2024). A Comprehensive Review
of Cloud-Based Lithium-Ion Battery Management
Systems for Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE
Access.
Jafari, S., & Byun, Y. C. (2022). Prediction of the battery
state using the digital twin framework based on the
battery management system. IEEE Access, 10, 124685-
124696.
Jiao, S., Zhang, G., Zhou, M., & Li, G. (2023). A
Comprehensive Review of Research Hotspots on
Battery Management Systems for UAVs. IEEE Access.
Karmaker, A. K., Hossain, M. A., Pota, H. R., Onen, A., &
Jung, J. (2023). Energy management system for hybrid
renewable energy-based electric vehicle charging
station. IEEE Access, 11, 27793-27805.
Lee, H., Kang, C., Park, Y. I., Kim, N., & Cha, S. W.
(2020). Online data-driven energy management of a
hybrid electric vehicle using model-based Q-
learning. IEEE Access, 8, 84444-84454.
Lee, H. S., Hwang, M. H., & Cha, H. R. (2021).
Development of an optimal power-distribution-
management algorithm for four-wheel-drive electric
vehicles. IEEE Access, 9, 99731-99741.
Lee, H., & Cha, S. W. (2021). Energy management strategy
of fuel cell electric vehicles using model-based
reinforcement learning with data-driven model
update. IEEE Access, 9, 59244-59254.
Electric Vehicle Battery Management System: A Comprehensive Review
411

Lee, W., Jeoung, H., Park, D., Kim, T., Lee, H., & Kim, N.
(2021). A real-time intelligent energy management
strategy for hybrid electric vehicles using
reinforcement learning. IEEE Access, 9, 72759-72768.
Madichetty, S., Neroth, A. J., Mishra, S., & Babu, B. C.
(2022). Route towards road freight electrification in
India: examining battery electric truck powertrain and
energy consumption. Chinese Journal of Electrical
Engineering, 8(3), 57-75.
Mądziel, M., & Campisi, T. (2024). Predictive AI Models
for Energy Efficiency in Hybrid and Electric Vehicles:
Analysis for Enna, Sicily.
Mądziel, M. (2024). Energy Modeling for Electric Vehicles
Based on Real Driving Cycles: An Artificial
Intelligence Approach for Microscale
Analyses. Energies, 17(5), 1148.
Maghfiroh, H., Wahyunggoro, O., & Cahyadi, A. I. (2024).
Energy Management in Hybrid Electric and Hybrid
Energy Storage System Vehicles: A Fuzzy Logic
Controller Review. IEEE Access.
Nisar, F., Haider, S., Alam, I., Waqar, A., Ahmed, T., &
Usman, M. (2021). Parametic Model for Optimization
of Battery Capacity and Power Transmitters of On-line
Electric Vehicles in Closed/Open Environments. CSEE
Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 9(1), 185-196.
Reddy, K. B. N. K., Pratyusha, D., Sravanthi, B., & Reddy,
E. J. Recent AI Applications in Electrical Vehicles for
Sustainability, International Journal of Mechanical
Engineering, Volume 11 Issue 3, Year of Publication:
2024.
Rudolf, T., Schürmann, T., Schwab, S., & Hohmann, S.
(2021). Toward holistic energy management strategies
for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles in heavy-duty
applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 109(6), 1094-
1114.
Schwenk, K., Meisenbacher, S., Briegel, B., Harr, T.,
Hagenmeyer, V., & Mikut, R. (2021). Integrating
battery aging in the optimization for bidirectional
charging of electric vehicles. IEEE Transactions on
Smart Grid, 12(6), 5135-5145.
Suhail, M., Akhtar, I., Kirmani, S., & Jameel, M. (2021).
Development of progressive fuzzy logic and ANFIS
control for energy management of plug-in hybrid
electric vehicle. Ieee Access, 9, 62219-62231.
Udeogu, C. U., & Lim, W. (2022). Improved deep learning-
based energy management strategy for battery-
supercapacitor hybrid electric vehicle with adaptive
velocity prediction. IEEE Access, 10, 133789-133802.
Ullah, I., Liu, K., Yamamoto, T., Al Mamlook, R. E., &
Jamal, A. (2022). A comparative performance of
machine learning algorithm to predict electric vehicles
energy consumption: A path towards
sustainability. Energy & Environment, 33(8), 1583-
1612.
Yuan, H. B., Zou, W. J., Jung, S., & Kim, Y. B. (2022). A
real-time rule-based energy management strategy with
multi-objective optimization for a fuel cell hybrid
electric vehicle. IEEE Access, 10, 102618-102628.
Zhang, H., Niyato, D., Zhang, W., Zhao, C., Du, H.,
Jamalipour, A., ... & Pei, Y. (2024). The roles of
generative artificial intelligence in internet of electric
vehicles. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.15750.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
412
