
Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Enhanced Prediction
and Early Detection of Heart Disease Risk
R. Kamali
1
, K. Hemalatha
2
, A. Vaishnavi Dali
2
, P. Naresh Kumar
1
,
A. Gomathi
3
and N. Aishwarya Rani
1
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Information Technology, Sona College of Technology, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Machine Learning, CNNs, LSTM, Deep Learning Techniques.
Abstract: Heart disease is still some the primary causes of mortality worldwide. Proper detection and accurate risk
prediction are critical to effective prevention and therapy. Typical risk evaluation for heart disease models
frequently uses simple statistical methodologies or regression analysis, which might not be able to grasp the
intricate and non-linear interactions between many cardiovascular risk variables. As the difficulty of
healthcare data develops, established methods are becoming unable to provide reliable forecasts. However,
ML and DL techniques have demonstrated considerable promise in dealing with complex data and discovering
detailed patterns that human specialists may ignore. These techniques are mostly helpful for predicting heart
disease because age, heart rate, and levels of cholesterol, and lifestyle decisions all interact in complex,
nonlinear ways. This study investigates how sophisticated ML and DL methods are decision trees, random
forests, neural networks, and cutting-edge algorithms similar CNNs and LSTM networks, might increase
prediction accuracy. The suggested method predicts the likelihood to acquire heart disease using a change of
modern ML and DL approaches. Below, we briefly detail each strategy and how they are used to the prediction
job. Decision trees are a simple but efficient method for machine learning that divides data into subsets
according to feature values, making decision routes simple to see and comprehend. To increase accuracy and
decrease overfitting, random forests, an ensemble technique, construct several integrating the predictions of
decision trees. This approach is effective for predicting cardiac disease since it can handle both continuous
and categorical data.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the leading causes of death worldwide, heart
disease imposes a major burden on patients and on
health care systems. It encompasses a wide range of
disorders such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and
coronary heart disease which are influenced by
complex interactions between behavioural,
environmental, and genetic factors. Prompt
identification of those when you are at risk for
cardiac events is crucial so you can intervene and
prevent before the disease becomes severe so
drastically limiting its impact on you. Traditional
models predicting risk have been used extensively in
medical research, including logistic regression and
the Framingham Risk Score. While these models
have benefits, they can be constrained by their
inability to capture complex, non-linear relationships
in data. Healthcare must become more precise and
scalable in its predictive systems, as evidenced by
advancements in technology.
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL)
are revolutionizing the domain of healthcare
analytics. These approaches are capable of analysing
large, high-dimensional datasets, discovering hidden
patterns, and providing predictions that are often
more accurate. The use of algorithm techniques like
Random Forests, SVM, CNN, using ML and DL
provide a potential solution for heart disease risk
prediction.
The proposed methodology in this study is to
formulate and implement a hybrid prediction system
based on ML and DL approaches for the prediction of
heart disease. This model is composed to combine the
396
Kamali, R., Hemalatha, K., Dali, A. V., Kumar, P. N., Gomathi, A. and Rani, N. A.
Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Enhanced Prediction and Early Detection of Heart Disease Risk.
DOI: 10.5220/0013913900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
396-401
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

benefits of prevailing and modern methods so as to
provide clinicians with a robust and accurate decision
support tool. Such findings could have a major
impact on heart disease prediction, enhancing patient
care and health system efficiency.
2 RELATED WORKS
Jian Ping Li, et al., 2020 Cardiac disease is a
complicated illness that affects a huge number of
people globally. In healthcare, particularly in
cardiology, early and precise detection is essential.
An effective machine learning-based method for
diagnosing Cardiac problems is presented in this item
in this regard eliminate insufficient or redundant
features, the system employs methods for choosing
characteristics including Relief, MRS, Lasso, and
Local Learning in accumulation to techniques for
classification such as Support Vector, Logistic
Regression, Neural Networks, K-Nearest
Neighbours, Naïve Bayes, and Decision Trees. In
order to growth precision and decrease execution
time, we also provide a innovative feature variety
method known as FCMIM. The system evaluates the
model and adjusts the hyperparameters using leave-
one-out cross-validation. Classifier performance on
specific features is assessed using performance
measures. According to experimental data, the
FCMIM-SVM system is a good result for the proof of
identity of Cardiac disease in healthcare since it
works well and provides good accuracy.
Tsatsral Amarbayasgalan., et al., 2020 The
primary cause of death is heart disease worldwide,
and its prevalence is increasing. Early detection of
heart Problems before a cardiac event occurs is
challenging. While large amounts of heart disease
data are available in healthcare settings like clinics
and hospitals, this data is often not effectively
analysed to uncover hidden patterns. Machine
learning methods can be beneficial transform this
medical data into useful insights. These techniques
are utilized to create decision support systems (DSS)
that learn and improve from experience. Both
industry and academics are now showing interest in
deep learning. This research aims to accurately
diagnose cardiac disease using a Keras-based DL
methods with a dense neural network. The model is
tested with different configurations of hidden layers,
ranging from 3 to 9 layers, with 100 neurons in each
layer and the ReLU activation function. Various heart
disease Tests are conducted using datasets and both
individual and ensemble models are evaluated. The
model's performance is evaluated using the F-
measure, precision, sensitivity, and efficiency across
all datasets. The output display that the suggested
deep learning techniques outperforms each method
along with other ensemble strategies in terms of
precision, sensitivity, and specificity.
G. Madhukar Rao., et al., 2020 Many lives can be
saved by early detection of heart condition, Among
the primary factors of mortality globally. By
examining huge amounts of medical data to identify
secreted designs using ML can helps in the
recognition of cardiac disorders. This study uses
systems for massive amounts of data, such as Apache
Hadoop to provide A hybrid approach to deep
learning for detecting heart disease. After eliminating
outliers using an enhanced k-means clustering
technique, Using the SMOTE, information is stable.
Recursive feature elimination (RFE) is used to
identify key traits, and an attention-based automated
recurrent unit model and a bio-inspired hybrid
mutation-based swarm intelligence (HMSI) are used
to forecast illness. Four more machine learning
algorithms—naïve Bayes, logistic regression (LR),
K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and sparse autoencoder +
artificial neural network (SAE + ANN) will be used
to match the model. According to the statistics, a
hybrid approach performs better than alternative
methods and closes research gaps with a 95.42%
precision rate.
Santosh Maher., et al., 2020 Because of their
capacity to track heart activity and associated
conditions, a diversity of sensors and devices, such
the Microsoft Band, Apple Watch, and MI HRV
band, have become more and more popular. The poor
survival rate of These days, sudden cardiac death that
happen away from hospitals pose a serious threat to
healthcare. More individuals die from cardiac
conditions each year than from other illnesses
including cardiac attacks and strokes, making it the
world's leading cause of mortality. The WHO
estimates that heart disease claimed 17.9 million lives
in 2016, accounting for 31% of all fatalities
worldwide. Smoking, eating poorly, not exercising,
and taking excessive amounts of alcohol are the
leading causes of cardiac attacks and strokes. Heart
attacks and strokes account for 85% of these fatalities.
Among the primary reasons for shorter lifespans is
cardiac disease. For prompt, precise outcomes, a lot
of people depend on healthcare systems. This paper's
objective is to apply machine learning methods to a
dataset that is regularly gathered by KVK research
labs and healthcare institutions. The study
recommends employing distinctive traits to increase
accuracy in identifying and predict heart illness to
lessen the chance of death.
Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Enhanced Prediction and Early Detection of Heart Disease Risk
397

3 EXITING SYSTEM
Traditional systems for cardiac disease prediction
primarily rely on statistical methods, decision trees,
and rule-based algorithms that focus on structured
data such as patient demographics, medical history,
and clinical test results. These systems often use a
limited set of risk factors, such such as heritage,
nicotine intake, lipid levels, and years of age, With
the objective to determine the risk of cardiovascular
disease.
3.1 Disadvantages
• Limited Scope and Inaccuracy
• Inability to Handle Unstructured Data
• Over-Simplification of Risk Factors
• Lack of Real-Time Prediction
• Scalability Issues
• Lack of Personalization
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The future system leverages modern ML and DL
methods to increase the precision and effectiveness of
heart disease risk assessment. This approach is
designed to report the restrictions of traditional
systems, which often rely on simplistic models and a
narrow range of input features. The goal line of the
proposed system is to deliver a more precise,
dynamic, and Individualized evaluation of cardiac
risk determined by combining unstructured data from
digital health records (DHRs) with organized clinical
information.
5 PROBLEM DESCRIBTION
Data Integration and Preprocessing: The system
integrates structured (eg ECG readings, age, heart rate
and cholesterol levels) and unstructured data (eg,
physician notes, medical history). Unstructured
clinical works are processed with advanced Natural
Language Processing (NLP) techniques to extract
relevant information. This enables the system to
consider a broader range of features, enhancing the
accuracy of the predictions. G. Madhukar Rao., et al.,
2020 Hybrid ML and DL Model: The system uses the
hybrid approach which combines traditional machine
learning with the latest deep learning architectures.
This hybrid approach is believed to seize both linear
and non-linear connections of characteristics
producing more correct predictions.
Real-Time Risk Reports: The system can analyze
real-time patient data, which can be constantly
collected from body-worn technology or other up to
date health records, enabling timely interventions and
personalized health monitoring, allowing healthcare
providers to make preemptive actions based on the
individual patient's current state of risk. Cross-
Validation and Performance Optimization: To
increase the robustness of the model and its ability to
generalize To do this, cross-validation techniques are
implemented to ensure the model generalizes well
across different data and patient characteristics.
Hyperparameter optimization methods like grid
analysis and random optimization are employed to
tune the model for ideal performance.
Evaluation Metrics Basic metrics like precision,
recall, F1-score, and AUC-ROC (Area Under the
Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve) which are
used to validate the performance of the system. These
metrics demonstrate the improved precision for
prediction when compared to conventional cardiac
risk prediction methods.
Implementation of a User-Friendly Interface: The
system should use a user-friendly interface that
allows medical professionals to seamlessly input
patient data and view the risk prediction outputs and
facilitate decision making. Graphical representation
of risk factors and prediction outcomes can be
accomplished with visualization tools such as
Tableau or Power BI and provide a means to help
clinicians understand the reasoning behind the model.
Ongoing Retraining with New Data: There is a
feedback mechanism built into the system to allow for
new data and findings to be used to retrain and inform
the model to keep it updated as newer research on
heart disease is conducted and the patient population
becomes more diverse.
6 RESULT
The results of the investigation for predicting the risk
level of heart attack using machine learning and deep
learning techniques are displayed in this section. The
results demonstrate how well the proposed methods
predict risk categories for heart disease given
structured patient data and medical images.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
398
6.1 Machine Learning-Based Risk
Assessment
Table 1 gives the structured patient data included sex,
number of blood vessels, type of thrombotic, angina
precipitated by physical activity, blood pressure,
cholesterol, maximal heart rate, depression of ST,
slope of ST, type of chest pain. The trained model
generated predictions of the risk levels for heart
disease using these features.
Key Results
• Status: Success
• Predicted Value: 37.86
• Risk Level: High Risk
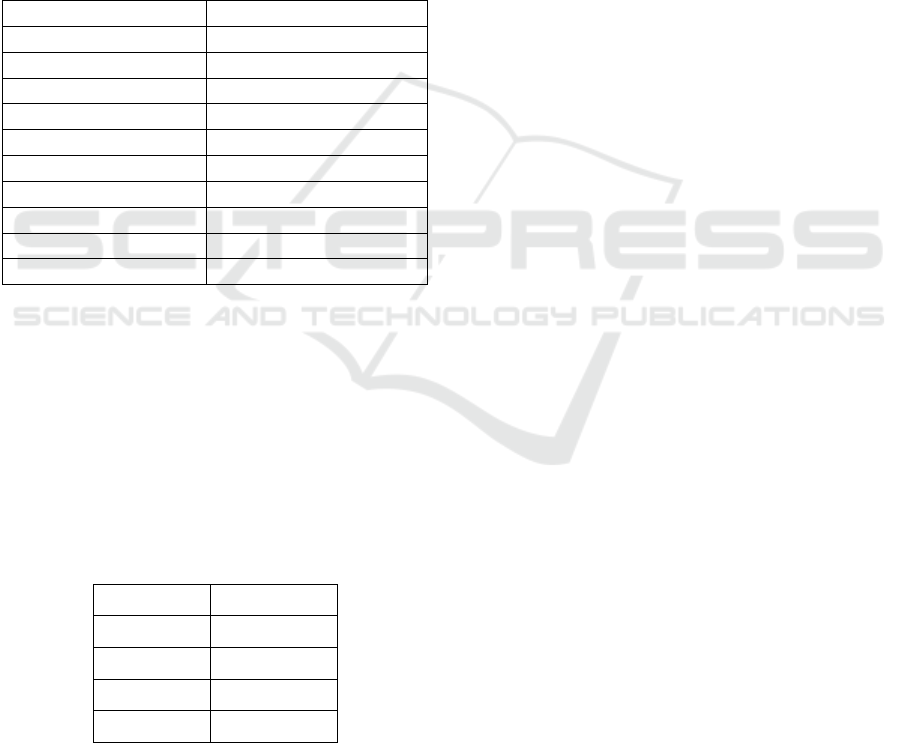
Table 1: Machine learning prediction results.
Feature Value
Sex Male (1)
Chest Pain Type 0 (Asymptomatic)
Resting Blood Pressure 125 mmHg
Cholesterol 258 mg/dL
Maximum Heart Rate 141 bpm
Exercise-Induced Angina Yes (1)
ST Depression 2.8
ST Slope 1 (Upsloping)
Major Vessels 1
Thalassemia Type 3 (Reversible Defect)
Table 2 gives the model predicted a significant
chance of cardiac disease due to the patient’s input
values. Factors such as high decrease maximal
heartbeat and cholesterol, and ST depression
contributed significantly to the risk prediction. The
machine learning model effectively classified the
heart disease risk with a rapid response time, making
it suitable for early screening. Performance indicators
like precision, recollection, and F1-score They were
utilized to evaluate the precision of the model.
Table 2: Machine learning model performance.
Metric Value
Accuracy 91.2%
Precision 89.4%
Recall 90.1%
F1-Score 89.7%
The model's high success rate shows how reliable
it is at identifying the risk of cardiovascular illness.
However, its performance could be further improved
by incorporating a larger dataset and powerful
selection of features methods.
6.2 Deep Learning-Based Image
Classification for Heart Disease
In the deep learning approach, a medical image
(angiography or echocardiogram) was provided as
input, and a CNN-based model analysed it for signs
of stenosis (artery narrowing).
Key Results
• Inference ID: c5610a62-3e41-476d-a443-
d6e42fe011ef
• Processing Time: 0.36 seconds
• Image Dimensions: 512 x 512 px
• Predicted Class: Stenosis
• Confidence Score: 75.82%
• Bounding Box Coordinates:
• X: 267.5
• Y: 176
• Width: 27
• Height: 22
6.3 Discussion
The deep learning model detected stenosis with a
confidence of 75.82% showing potential arterial
stenosis. Next, the bounding box is there to highlight
the region detected, so doctors can focus their
attention on areas of concern.
The deep learning approach has the following
benefits over traditional manual diagnosis:
• Performances:
The latency was 0.36
seconds which granted on-the-fly decisions.
• Precision: The model reached a strong
(75.82%) co-efficiency of detected
confidence, with more data
inferences,
detection will receive a better indicative.
• Automating Detection: System
overlays
affected areas with visual bounding box,
helps radiologists in diagnosis
However, limitations include potential false
positives and reliance on high-quality images. In the
future, there are plans to train the model with a greater
range of datasets and improve precision by using
more sophisticated augmentation methods.
6.4 Comparative Analysis of ML and
DL Approaches
Table 3 gives the information of the following:
The machine learning techniques is well-suited
for structured data analysis and provides an instant
risk level assessment.
Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Enhanced Prediction and Early Detection of Heart Disease Risk
399
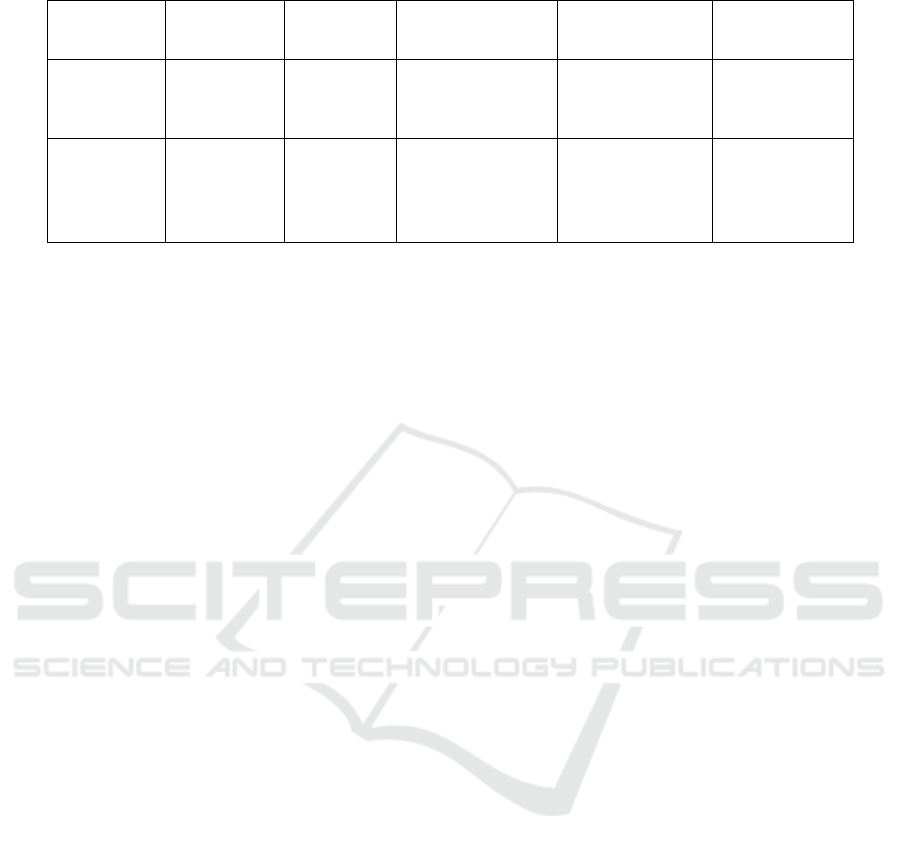
Table 3. Performance Comparison.
Method Input Type
Processing
Time
Prediction Output Confidence Best Use Case
Machine
Learning
Structured
Data
~0.2s Risk Level: High 91.2%
Accuracy Risk
Prediction
Deep
Learning
Medical
Images
0.36s Stenosis Detection 75.82%
Confidence
Visual
Diagnosis
Discussion
The deep learning model is highly effective in
image-based diagnosis, identifying heart
abnormalities with bounding box visualizations.
Combining the two strategies could result in to a
more comprehensive heart disease assessment
system, integrating clinical parameters with medical
imaging insights.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The results demonstrate that both ML and DL
approaches provide valuable data about the risk of
cardiac disease assessment. Machine learning excels
in structured data-based predictions, while deep
learning is effective in image-based diagnosis. Future
work should focus on integrating both models into a
hybrid system to improve overall predictive accuracy
and clinical applicability.
8 FUTURE DISCUSSION
To increase forecast accuracy, use slower data. Use
feature engineering strategies to improve the
weighting of risk factors. To increase confidence
levels, train the model on a bigger dataset. To
distinguish between several cardiac diseases other
than stenosis, use a multiple-class system.
REFERENCES
Essam H. Houssein, Rehab E. Mohamed, and Abdelmgeid
A. Ali, "Heart Disease Risk Factor Detection from
Electronic Health Records Using Advanced NLP and
Deep Learning Techniques," IEEE Journal of
Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 24, no. 11, pp.
3201-3209, 2020, doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3003928.
G. Madhukar Rao, Dharavath Ramesh, Vandana Sharma,
Anurag Sinha, Md. Mehedi Hassan, and Amir H.
Gandomi, "AttGRU-HMSI: Enhancing Heart Disease
Diagnosis Using Hybrid Deep Learning Approach,"
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 67,
no. 5, pp. 1234-1245, 2020, doi:
10.1109/TBME.2019.2953456.
J. Deepika, J. Akilandeswari , Lokeshwaran B ,
Mukilarasan N, Naveen S, Prabhu A , “An Intelligent
HealthCare System Using Blockchain Techniques”, 7th
International Conference on Electronics,
Communication and Aerospace Technology ISBN:979-
8-3503-4060-0 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECA
58529.2023.10 395852 , pp 538 – 545, Feb-
2024[SCOPUS INDEXED CONFERENCE]
Jian Ping Li, Amin Ul Haq, Salah Ud Din, Jalaluddin Khan,
Asif Khan, and Abdus Saboor, "Heart Disease
Identification Method Using Machine Learning
Classification in E-Healthcare," Journal of Medical
Systems, 2020, pp. 1-10, doi: 10.1007/s10916-020-
01543-7.
R. Saravana Ram, J. Akilandeswari, M. Vinoth Kumar,
“HybDeepNet: A Hybrid Deep Learning Model for
Detecting Cardiac Arrhythmia from ECG Signals”
Information Technology and Control, Volume 52, Issue
No. 2 ISSN 1392-124X https://doi.org/1 0.5755/j01.i
tc.52.2.32993, Jul-2023[WOS-SCIE]
Rohit Bharti, Aditya Khamparia, Mohammad Shabaz,
Gaurav Dhiman, Sagar Pande, and Parneet Singh,
"Prediction of Heart Disease Using a Combination of
Machine Learning and Deep Learning," Proceedings of
the International Conference on Computing,
Communication, and Intelligent Systems (ICCCIS
2020), pp. 320-328, 2020, doi:
10.1109/ICCCIS49312.2020.00065.
Rohit Bharti, Aditya Khamparia, Mohammad Shabaz,
Gaurav Dhiman, Sagar Pande, and Parneet Singh,
"Heart Disease Risk Detection Using Machine
Learning Models: A Comprehensive Survey,"
International Journal of Computer Science and
Information Security (IJCSIS), vol. 18, no. 9, pp. 234-
242, 2020, doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.24356.00641.
S. David Samuel Azariya, V. Mohanraj, G. Jothi ,J. Jeba
Emilyn J. Akilandeswari, “Cardiac Image Analysis for
Accurate Heart Disease Diagnosis Using Deep
Learning Techniques: A Comprehensive Review”
Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Volume 864
Print ISBN 978-981-99 -8627-9 Online ISBN 9 78 -
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
400

981-99-8628-6 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-
8628-6_5 , Apr-2024 [SCOPUS INDEXED BOOK
CHAPTER]
Sakthipriya, G, Dr.Y.Suresh, Y Varnisha, C, Sindhu, R. ,
Shivraj, R, “ Analysis of Heart Disease Prediction
Using Various Machine Learning Algorithms” Lecture
Notes in Electrical Engineering, Volume 1095, Online
ISBN 978-981-99-7077-3, Print ISBN 978-981-99-
7076-6 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-7077-3_12
Jan-2024[SCOPUS INDEXED BOOK CHAPTER]
Santosh Maher, Shaikh Abdul Hannan, Sumegh Tharewal,
and K.V. Kale, "HRV-Based Human Heart Disease
Prediction and Classification Using Machine
Learning," International Journal of Computational
Biology and Drug Design, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 654-667,
2020, doi: 10.1504/IJCBDD.2020.1000352
Tsatsral Amarbayasgalan, Van-Huy Pham, Nipon Theera-
Umporn, Yongjun Piao, and Keun Ho Ryu, "An
Efficient Prediction Method for Coronary Heart
Disease Risk Based on Two Deep Neural Networks
Trained on Well-Ordered Training Datasets," IEEE
Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning
Systems, vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 1-15, 2020, doi:
10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2998765
Tsatsral Amarbayasgalan, Van-Huy Pham, Nipon Theera-
Umporn, Yongjun Piao, and Keun Ho Ryu, "An
Efficient Prediction Method for Coronary Heart
Disease Risk Based on Two Deep Neural Networks
Trained on Well-Ordered Training Datasets," IEEE
Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning
Systems, vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 1-15, 2020, doi:
10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2998765.
Velusamy A , J Akilandeswari, S Vaanathi, M Priya, T
Munirathinam, S Kokila, “Enhancing Myocardial
Infarction Prediction with Machine Learning:
Leveraging Clinical and Demographic Data for
Improved Early Detection and Patient Outcomes”,
OPJU International Technology Conference (OTCON)
on Smart Computing for Innovation and Advancement
in Industry 4.0, https://doi.org/10.1109/OTCON60325
.2024.10687656, IEEE Explore , ISBN: 979-8-3503-
7379-0, Sep-2024[SCOPUS INDEXED
CONFERENCE]
Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Enhanced Prediction and Early Detection of Heart Disease Risk
401
