
AI Fashion Assistant-Vogue Vista
Parkavi C, Nimmy Prabha, Mownigaa M, Manigandan G, Soorya R and Vishal K
Department of AIML, SNS College of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Fashion Recommendation, AI-Based Styling, Wardrobe Management, Outfit Suggestions, Machine Learning
in Fashion, Personalized Fashion Assistant.
Abstract: Fashion plays an important role in expressing oneself and picking the right outfit according to personal
characteristics can boost a person's confidence and comfort level. AI-Based Fashion Assistant which helps
Users to choose their best outfits based on their Skin Tone, Body Type, Personal preferences. By utilizing
machine learning algorithms to analyze fashion trends, the system can recall appropriate individual-
characteristic-tailored outfits. Furthermore, the project also includes a wardrobe management system that
suggests outfits based on the clothes a user already possesses, encouraging sustainable clothing habits. The
inclusion of AI-powered suggestions allows this fashion assistant to streamline the decision-making process
and save time when choosing outfits. The new system proposed in this paper resolves the issues of daily
styling in the fashion domain with data-assisted and user-oriented recommendations thus providing a positive
experience of shopping and wardrobe management to the user.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today’s digital age, fashion and personal style play
an increasingly central role in how individuals
present themselves to the world. As society gravitates
towards personalization in all aspects of life, fashion
is no exception. The desire to express one’s unique
identity through clothing choices has never been
more prevalent. However, curating a wardrobe that
reflects personal preferences, aligns with current
trends, and suits different occasions is not always a
straightforward task. Factors such as time constraints,
budget considerations, and an overwhelming number
of fashion choices can make it challenging for
individuals to build and maintain a versatile
wardrobe. This is where the AI Fashion Assistant
project comes into play. By leveraging the power of
artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning
(ML), this innovative solution aims to provide
personalized fashion recommendations and styling
assistance. The intelligent assistant is designed to
simplify wardrobe management, optimize outfit
selection, and enhance the overall user experience in
personal styling. As the fashion industry continues to
embrace digital transformation, the AI Fashion
Assistant stands at the forefront of this evolution,
offering a seamless blend of technology and fashion.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
All the studies reviewed highlight the amazing area
fashion recommendation systems have achieved
through the fusion of machine learning, deep learning
and computer vision methods. These technologies
have pioneered a new personalization experience in
fashion advice, where systems like Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs) learn the performance to
distinguish clothing types from visual data with high
precision. Due to their capability of efficiently
recognizing textured, colorful, or complex shapes in
images, CNNs have become very potent in
classifying fashion categories, thus supporting better
recommendations with context-aware detailed
knowledge. Moreover, Transfer learning (especially
towards pre-trained models from sites like Hugging
Face Smith, J., & Taylor, K. (2022)), further elevated
the ability to reduce training time with significant
amount of classification accuracy.
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
Due to the demand for individual styling and outfit
recommendations, there have been various
approaches and techniques in the area of AI fashion
C., P., Prabha, N., M., M., G., M., R., S. and K., V.
AI Fashion Assistant-Vogue Vista.
DOI: 10.5220/0013913500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
377-381
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
377
recommendations. (2006) to list some early fashion
recommendation systems used rule-based algorithm
and simple filtering methods. With the advent of
artificial intelligence, techniques of the past have
been augmented and improved upon such as image
recognition and machine learning models to study
clothing attributes and analyze user preferences. The
well-known methods include collaborative filtering,
content filtering, and hybrid recommendation
systems, which are based on the combination of
several algorithms. Though, these approaches offer
some degree of personalization, they frequently fail
due to inherent restrictions inflexible styling
recommendations and difficulty to cater individual
style. Some of the shortcomings to date fashion
recommendation systems are lack of style matching
based on the context, color detection accuracy is
limited, real-time outfit suggestions based on the user
uploaded piece of garments in their wardrobe cannot
be provided.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
In the proposed system, we employ advanced
machine learning and image processing techniques to
provide personalized fashion recommendations and
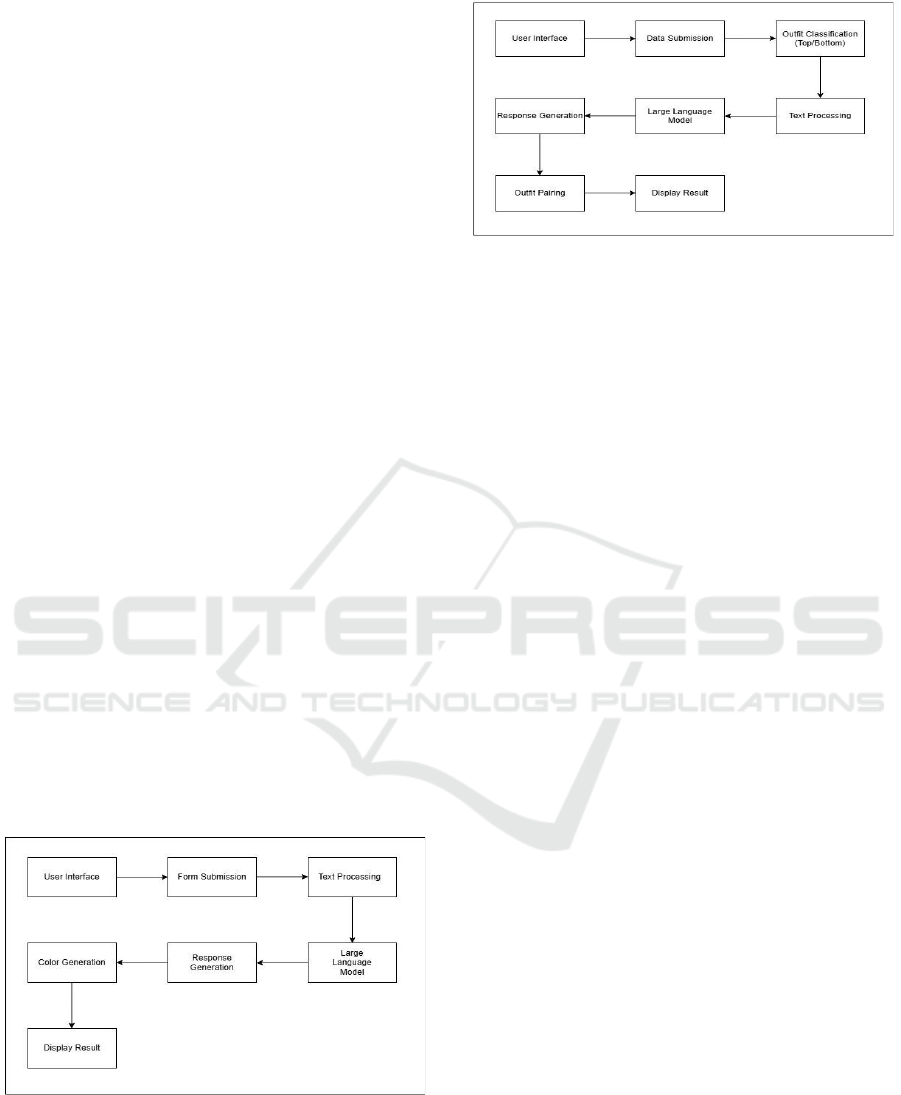
automated wardrobe management. Figure 1 shows
Block Diagram of Outfit Assistant.
The system is
designed to enhance the user experience by offering
tailored outfit suggestions based on individual
preferences and existing wardrobe items, aiming to
improve styling choices and streamline wardrobe
management.
Figure 2 shows Block Diagram of
Wardrobe Assistant.
Figure 1: Block Diagram of Outfit Assistant.
Figure 2: Block Diagram of Wardrobe Assistant.
5 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
AI and ML are revolutionizing numerous sectors by
improving personalization and automating intricate
tasks. In the fashion industry, AI is being utilized with
increasing frequency to provide personalized styling
suggestions, maximize wardrobe organization, and
enhance the overall user experience. AI enables
application in the fashion field through data analysis
and pattern recognition, allowing it to analyze a user's
preferences and recommend a personalized solution
that was previously too difficult to manually handle.
AI technology can customize advice, generate
personalized fashion outfit suggestions, recommend
color combinations, and assist users in wardrobe
planning based on their attributes. AI finds its use in
retail to improve product recommendations, provide
virtual try-ons, and study shopping trends for a better
user experience. Using cutting-edge image
processing and machine learning algorithms, these
apps can manage enormous amounts of visual and
textual data, providing exceptionally relevant and
precision recommendations. (What we’re actually
creating is more along the lines of recommendations
given to a stylist based on the latest trends in addition
to tailoring recommendations based on user inputs
including body shape, skin tone, style preferences,
etc.) AI and ML are integral to streamlining this flow
and other details to provide personalized fashion
recommendations. The models that build up the
system are AI tools and machine learning models that
analyze the user preferences, detect the color and
advise the outfits based on an individual's interests.
Using these technologies, our system allows users to
receive a smooth and highly personalized fashion
experience, creating enhanced convenience and
confidence for daily styling. Through this, we can see
how AI and ML Technology not only boost
personalization but also offer scalable solutions to the
problems of the fashion industry. Incorporating these
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
378

technologies, we propose a system that could
revolutionize the process of wardrobe management
and styling into an interesting, precise, and simple
experience for the user.
6 ALGORITHMS
6.1 Examples of Pretrained Models
(Hugging Face)
Algorithm: Deep Learning Models Based on
Transformers.
Purpose: Hugging Face models are optimized for
complex data, i.e. images and text (mainly
transformer architectures). These models are
optimized for understanding and classifying based on
learned representations of content. To narrow down
this error, you will have to train these models on your
dataset and consequently, you will have new models
that can be used to classify clothing into categories
such as top wear, bottom wear etc. This is the
classification process that helps the assistant to
analyses and categorize a user's wardrobe. The
Hugging Face platform offers many pre-trained
models that save time and computational
requirements when comparing training from scratch
to a pre-trained model, allowing the quick and
efficient use of a fashion assistant with reduced
labeled inputs. Moreover, transformers are capable of
capturing both local and global features in images,
improving their capacity to recognize clothing items
across challenging conditions (e.g., changing light or
perspective).
6.2 Gemini 1.5 Model
Algorithm: proprietary AI/ML model (most likely
using various deep learning techniques)
Intent: It utilizes the Gemini 1.5 model to provide
personalized clothing recommendations based on
user data like body shape, skin tone, and style
preferences. It is likely to incorporate multiple
machine learning techniques such as neural networks
to detect complex relations between clothing item's
features and a user's preferences. Because the model
is flexible enough to use many variables such as
gender, occasion and fashion trends it can give
extremely targeted recommendations. As an example,
it might suggest an outfit based on a user’s body
shape that is proportional and enhances someone’s
personal style. The retraining process allows the
model to better adjust to user feedback and to improve
over time. This helps keep the recommendations fresh
and tailored to the user's evolving taste over time, or
in light of new style trends.
6.3 Image Processing (OpenCV)
Algorithm: Computer Vision Techniques (e.g., Edge
Detection, Contour Analysis)
Functionality: The OpenCV (Open Source Computer
Vision Library) is an important part of the fashion
assistant as this library is used in the assistant to
understand about the images and helps extract the
useful features for clothing recommendations. These
include the image processing algorithms that allow
OpenCV to characterize shape, size, and fabric of
clothing items. For instance, edge detection
techniques assist in determining the contours of an
object, enabling the system to differentiate between
various types of clothing, like dresses, pants, or shirts.
Contour analysis refines this process even further,
aiding in the detection of the outlined edges of
individual clothing pieces in the versions uploaded,
especially beneficial in context with overlapping or
cluttered images. Based on color theory or references
from past experience, Color Detection can be used to
identify colors, this can be a great application of
OpenCV as colors are directly related to the garment
and one can classify various colors of clothes. The
library's real-time processing capabilities make the
fashion assistant efficient, delivering instant
feedback, crucial for an interactive user experience.
This is why real-time tasks like pattern recognition,
object detection, and feature extraction are handled
well by OpenCV.
6.4 Color Detection (K-means
Clustering
Algorithm: K-means (machine learning algorithm)
Purpose: The K-means clustering is an unsupervised
machine learning algorithm used for segmenting
grouping items in data based on similarity by
understanding how K- means clustering works,
fashion clothing color detection could be achieved by
multiple methods of K- clustering. The K- means
clustering algorithm works by clustering pixels in an
image with similar colors, allowing it to identify color
clusters. This is how a fashion assistant would be able
to know what the main colors are in one clothing
piece, such as a dress or a shirt. The primary advantage
of K-means cluster the tone of using mean values for
color detection is its simplicity and efficiency. After
the image has been split into color clusters using the
algorithm, the assistant will identify which cluster is
characteristic of the colors used in the clothing piece.
AI Fashion Assistant-Vogue Vista
379
7 RESULTS
The AI analyses the colors and suggests the best outfit
pairings by matching complementary colors. This
ensures that users receive personalized styling
recommendations and well-coordinated wardrobe
suggestions, enhancing their overall fashion
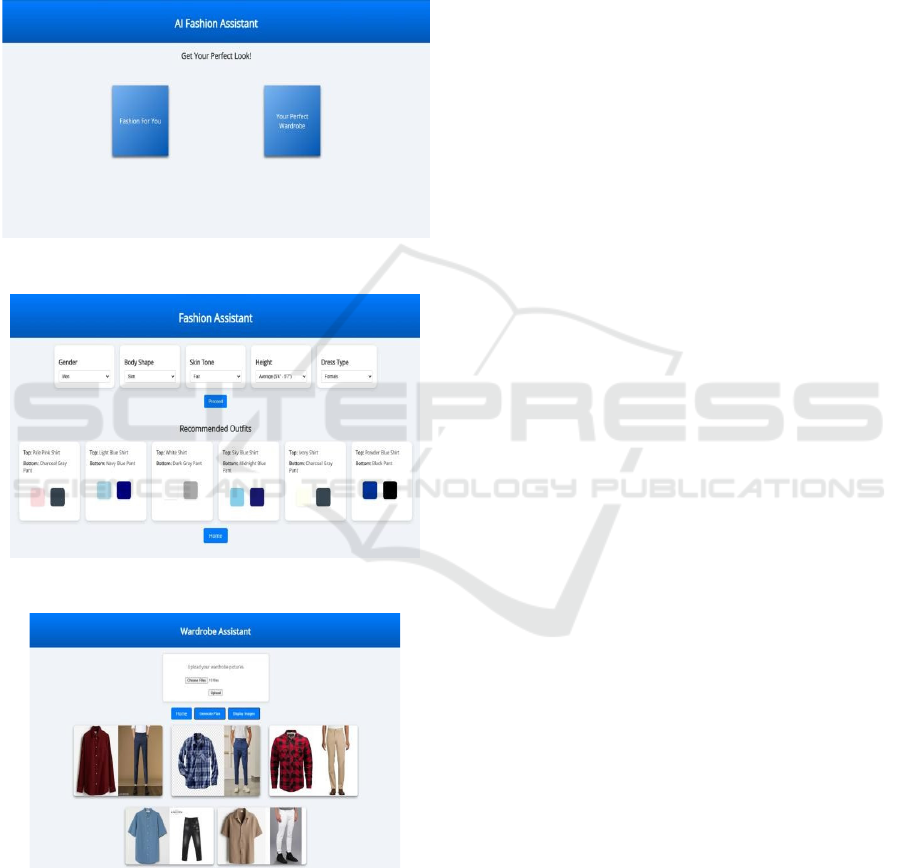
experience. Figure 3 shows the Main Web Page.
Figure 3: Main Web Page.
Figure 4: Web Page of Outfit Assistant.
Figure 5: Web Page of Outfit Assistant.
In our AI Fashion Assistant project, the user interacts
with three main pages. The first page serves as a
navigation hub, providing two buttons: one leading to
the Dress Suggestion page and the other to the
Wardrobe Suggestion page. On the second page, users
can select various features such as gender, dress type,
body shape, skin tone, height, and more. Figure 4
shows Web Page of Outfit Assistant. Upon
submission, the system processes these inputs and
provides color-matching recommendations for
outfits. The third page allows users to upload images
of clothing items (such as tops and bottoms). Based
on the uploaded images. Figure 5 shows Web Page of
Outfit Assistant.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The AI Fashion Assistant reads and uses advanced
machine learning models and AI tools to offer
personalized recipes for fashion. The system provides
personalized outfit recommendations by employing
technologies such as Hugging Face for image
classification, OpenCV for image analysis, and K-
means for color detection, thereby considering user
preferences, body type, and existing wardrobe pieces.
Limitations of fashion recommendation systems are
addressed in order to provide personalized styling,
accurate colors, and dynamic outfit generation in
order to improve user experience. To sum up, our
project tries to connect technology with your
wardrobe and how to interact with it. Unlike other AI
fashion assistants, this one is known for context-
aware recommendations, allowing the app to filter by
tastes. Additional capabilities such as real-time trend
analysis, seasonal wardrobe planning, and social
media integration have the potential to be
incorporated into the tool in the future, further
proving the power of AI to provide tailored and easily
accessible style guidance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We express our deep sense of gratitude and
indebtedness to our institution “SNS COLLEGE OF
TECHONOLGY”, Coimbatore, which provided us
the opportunity to fulfil our cherished goals. We
extend our sincere thanks and regards to Dr. Angel
Latha Mary, Head of the Department, Artificial
Intelligence and Machine Learning, for giving this
opportunity to carry out this work in the college. We
would most heartily like to thank the almighty, our
family members and friends without whom this paper
would be impossible.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
380

REFERENCES
Smith, J., & Taylor, K. (2022). Personalized fashion
recommendations using AI: A review of current
techniques. Journal of Fashion Technology, 15(3), 45-
60.
Johnson, P., & Lee, R. (2021). Color harmony algorithms
in fashion design. International Conference on
Advanced Machine Learning Applications.
Gupta, A., & Sharma, L. (2020). AI-based wardrobe
optimization: Exploring the potential of neural
networks. International Journal of Fashion and AI
Studies, 8(4), 120-135.
Williams, T., & Collins, M. (2021). The impact of AI-
driven outfit selection on consumer behavior. Fashion
Science and Technology Journal, 14(1), 78-95.
Davis, R. (2022, May 10). The role of AI in revolutionizing
the fashion industry.
Patel, S., & Kumar, R. (2020). Machine learning for
sustainable fashion recommendations. Journal of
Green Fashion Technology, 7(2), 99-112.
Thomas, E., & Jones, H. (2021). Using OpenCV for height
detection in personalized fashion assistants.
Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on
Image Processing Applications (ICIPA).
Clarke, D., & Nguyen, V. (2019). Leveraging K-means
clustering for color matching in fashion AI. Journal of
Machine Learning in Design, 12(3), 56-72.
Rodgers, L., & Martin, J. (2018). AI-based style
adaptability: A review of techniques and applications.
Artificial Intelligence in Fashion Technology Journal,
10(5), 145-167.
Harper, C. (2020, September 15). Top AI tools
transforming wardrobe management.
AI Fashion Assistant-Vogue Vista
381
