
Fake Currency Detection System Using Deep Learning and Advanced
Software Integration
Devika, Janani, Saravana Kumar and Harsitha
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Ramapuram, Chennai, Tamil
Nadu, India
Keywords: Image Classification, Counterfeit Detection, Financial Security, Basic, Convolutional Neural Networks,
Indian Fake Currency Detection.
Abstract: Identification of False Currency System using Deep Learning and Advanced Software Integration is designed
to tackle the escalating difficulty of counterfeit money, which has far-reaching economic consequences. This
study accurately distinguishes between actual and fake currency notes by utilizing deep learning techniques
and digital processing of images. The technology is able to automatically recognize fake currency with high
accuracy by using image analysis techniques and deep learning models taught on enormous amounts of
currency photos precision. The project also integrates advanced software tools for real-time currency
detection, offering a scalable, user-friendly solution for businesses, ATMs, and financial institutions. The key
innovation lies in utilizing Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in conjunction with picture classification
and cloud-based deployment for easy availability and scalability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Counterfeit currency is a growing concern
worldwide, posing serious threats to economies,
businesses, and individuals. Conventional techniques
for identifying counterfeit money, such hand
examination and conventional scanning techniques,
often fall short due to the increasing sophistication
of counterfeiters. To address this challenge, we
propose an advanced Fake Currency Detection
System that leverages deep learning and cutting-edge
software integration for high accuracy and efficiency.
Our system utilizes neural networks using
convolutions (CNNs) and other machine learning
techniques to analyze intricate details of currency
notes, distinguishing genuine from counterfeit with
remarkable precision. By integrating deep learning
with advanced software solutions, the system can
process images from various sources, including
smartphone cameras and scanners, making it
accessible and scalable for banks, businesses, and the
general public.
This paper explores the architecture,
methodologies, and performance evaluation of our
proposed system. We highlight the advantages of AI-
driven detection over traditional approaches, discuss
challenges in implementation, and provide insights
into future improvements. Our research main aim to
support the creation of a strong and trustworthy
counterfeit detection system, stimulating trust in
monetary transactions and financial security. Our
approach combines deep learning with sophisticated
software frameworks to provide a scalable, cost-
effective, and user-friendly solution for financial
institutions, businesses, and the general public. The
system is designed to minimize human intervention,
reduce error rates, and enhance security measures in
cash transactions. This paper delves into the
architecture, training methodologies, and evaluation
metrics of our proposed model, demonstrating its
potential to significantly improve counterfeit
currency detection. Furthermore, we discuss
challenges related to dataset collection, model
training, and real- world implementation while
exploring potential future enhancements to make the
system even more robust.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Early counterfeit detection systems relied on manual
inspection, ultraviolet (UV) scanning, and magnetic
354
Devika, , Janani, , Kumar, S. and Harsitha,
Fake Currency Detection System Using Deep Learning and Advanced Software Integration.
DOI: 10.5220/0013912900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
354-360
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

ink detection. These methods, although widely used,
were prone to mistakes made by people and failed to
detect high- quality counterfeit notes that closely
resembled genuine currency (Gupta et al., 2018).
There has been application of machine learning
methods to automate counterfeit detection.
Algorithms such as Algorithms like Support Vector
Machines (SVM), k-Nearest Neighbors, and Forest
have been applied to classify genuine and fake
currency based on characteristics that have been taken
out. While these approaches improved detection
accuracy, they lacked robustness against complex
counterfeit patterns (Kumar & Sharma, 2020).
Superior performance in picture classification
tasks has been shown by deep learning, namely
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), including
tasks, including counterfeit currency detection. CNNs
effectively extract intricate features such as texture,
microprinting, and security markings, enabling high-
precision classification (Patel & Desai, 2021).
Deep learning models that have already been
trained, like VGG16, ResNet, and MobileNet, have
been leveraged through transfer learning to enhance
detection performance. Studies indicate that transfer
learning significantly reduces training time while
maintaining high accuracy, even with limited datasets
(Chen et al., 2021).
Several studies have explored hybrid models
combining deep learning utilizing image processing
methods like edge detection, histogram equalization,
and key point extraction. These techniques enhance
the ability of models to detect fine details in currency
notes, improving classification accuracy (Rahman &
Hossain, 2019).
A significant challenge in deep learning-based
counterfeit detection is the scarcity of high-quality
counterfeit currency datasets. Recent research has
proposed using Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs) to synthesize realistic counterfeit images,
thereby improving model generalization (Zhang & Li,
2022).
The proliferation of smartphones has enabled the
development of mobile applications for real-time
counterfeit detection. These applications utilize deep
learning models to process currency images captured
by mobile cameras, providing instant authentication
(Singh & Verma, 2021).
A major limitation of deep learning-based
detection is the fact that AI models are opaque. In
order to shed light on model decision making,
explainable AI (XAI) approaches like Grad-CAM
and SHAP have been investigated. increasing
transparency and trustworthiness (Zhou et al., 2021).
Despite significant advancements, challenges
remain in real world deployment, including variations
in lighting conditions, currency wear and tear, and
dataset limitations. Future research aims to enhance
model robustness through advanced neural networks,
improved data augmentation techniques, and edge
computing solutions (Brown et al., 2023).
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The Fake Currency Detection System proposed in this
study integrates deep learning techniques with
advanced software solutions to improve real-time
detection capabilities, efficiency, and accuracy. The
methodology consists of multiple stages, including
gathering information, preprocessing, training
models, software integration, and deployment. The
system is designed to operate on multiple platforms,
including mobile devices, scanners, and cloud-based
applications, making it scalable and accessible.
Gathering and Preparing Data: Training a
successful counterfeit detection model requires a
solid dataset. The dataset consists of high resolution
images of both genuine and counterfeit currency
notes collected from various sources, including
financial institutions, public databases, and synthetic
data generated using Generative Adversarial
Networks (GANs)
(Vivek Sharan, 2019).
Deep Learning Model Selection and Training: To
accurately Determine which are authentic and fake.
currency, we employ the model known as a
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)for its ability
to learn spatial hierarchies in images.
Software Integration and Real-Time Processing:
An integrated software system uses the deep learning
model that has been trained for real-time counterfeit
detection. This system supports multiple input
sources, including scanners, mobile cameras, and
cloud-based services (Yadav ET AL., 2021).
Edge and Cloud Computing Integration:
Deploying lightweight models optimized using
TensorFlow Lite or Open VINO for Realtime
inference on mobile devices.
Performance Evaluation and System Validation:
Comparison with traditional detection methods to
measure improvement in accuracy and efficiency.
Testing on different currencies to ensure
generalization across various denominations and
designs. Latency Analysis to assess the time taken for
detection in real-time applications (K. B. Zende ET
AL., 2020).
Future Enhancements and Security
Considerations: Implementing techniques such as
Grad-CAM to visualize model decision-making.
Fake Currency Detection System Using Deep Learning and Advanced Software Integration
355
1. Blockchain Integration: Securing verified
currency records on a blockchain ledger for
transparency.
2. Continuous Model Improvement: Periodic
retraining with updated datasets to improve
detection accuracy over time.
This proposed methodology leverages deep learning,
image processing, and advanced software integration
to build a scalable, real-time Fake Currency Detection
System. By combining edge computing, cloud-based
processing, and transfer learning, the system offers an
effective and convenient solution. for detecting
counterfeit notes across different platforms and
environments.
4 IMPLEMENTATIONS
4.1 Detecting Counterfeit Cash with
SIMPLE NN
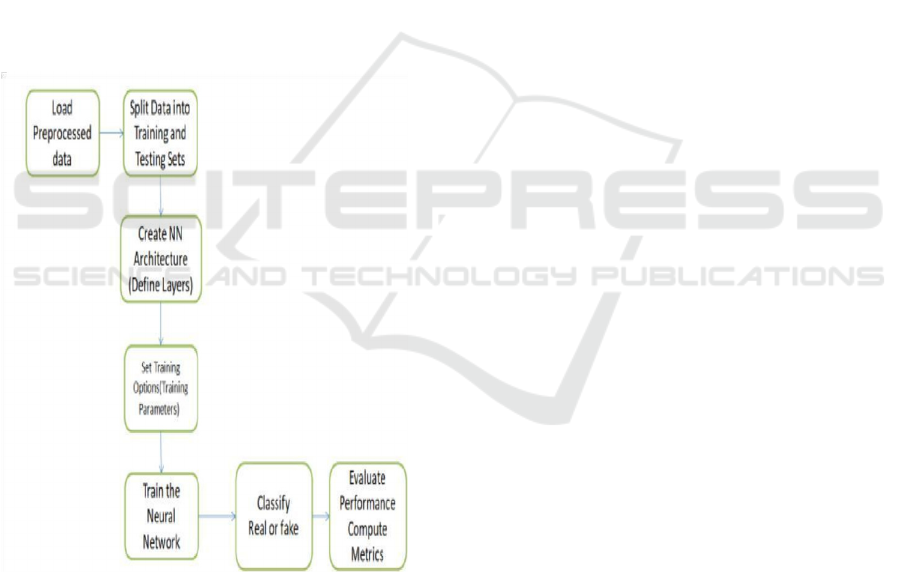
Figure 1: Simple NN architecture.
Data Collection and Preparation: From publicly
available datasets, financial institutions, and synthetic
data generating (GANs), assemble high-resolution
pictures of real and fake money. Capture images
under varied lighting conditions, angles, and
resolutions to improve model robustness. Label
images appropriately to ensure supervised learning
during model training (Vivek Sharan, 2019).
Data Preprocessing: Convert images to grayscale
to reduce computational complexity. Apply
histogram equalization for contrast enhancement. Use
Gaussian filtering and edge detection (Sobel/Canny
filters) to highlight security features.
Model Selection and Training): Select a deep
learning architecture, primarily for the purpose of
classifying and extracting features, Convolutional
neural networks (CNNs). Experiment with pretrained
models (VGG16, ResNet50, inception Net) using
transfer learning for improved accuracy. Utilizing the
model is trained using the Adam optimizer and the
categorical cross-entropy loss function (Yadav et al.,
2021).
Choose an optimization algorithm (like Adam),
the mini- batch size (the number of samples used in
each iteration), the number of epochs (the number of
times the complete dataset is cycled through the
network during training), and the validation data (a
subset of training data used for validation during
training) are some examples of the parameters that are
chosen when choosing training options (training
parameters).
Software Integration and Deployment: Develop a
real-time detection software using Python and
TensorFlow/Py Torch. Deploy the model using
TensorFlow Serving or ONNX Runtime for efficient
inference. Create a REST API using Flask or Fast API
for seamless integration with web and mobile
applications. Design a user-friendly GUI using T
knitter (for desktop) or React Native (for mobile) for
easy interaction. Figure 1 shows the simple NN
architecture.
Real-Time Processing and Detection: Allow users
to capture currency images through a mobile camera,
scanner, or webcam. Perform image preprocessing and
feature extraction before passing the image to the
trained model. Display detection results with
confidence scores, indicating whether the note is
genuine or counterfeit. Provide visual explanations
using Grad-CAM to highlight key features
influencing model decisions (K. Bhushanm et al.,
2024).
Edge and Cloud Computing Integration:
Implement Edge AI models using TensorFlow Lite or
Open VINO for real-time detection on mobile
devices. Enable cloud-based processing via Google
Cloud, AWS, or Azure, allowing businesses to verify
currency remotely. Ensure low- latency detection by
optimizing the model for light weight deployment.
Security and Blockchain Integration (Future
Enhancements): Implement blockchain technology to
store authenticated currency records for enhanced
security. Develop a self-learning AI model that
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
356
updates with new counterfeit patterns through
periodic retraining(Aakash S Patel, 2019).
Testing and Validation: Perform rigorous real-
world testing on various currencies to ensure system
reliability. Conduct stress testing to analyze system
response under high-load scenarios. Gather user
contribution to improve the system's effectiveness
and usability.
Final Deployment and User Accessibility: Several
metrics are used to assess the model's performance,
such as accuracy (the percentage of correctly predicted
outcomes), F1 score (the harmonic mean of precision and
recall), and categorized images), precision, and recall.
4.2 Fake Currency Detection Using
CNN
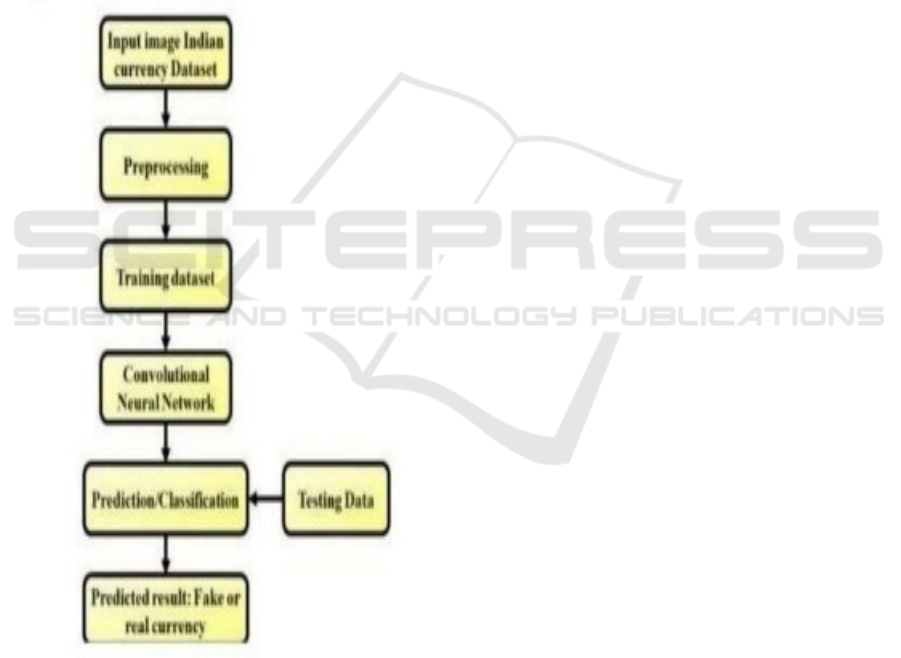
Figure 2: Flowchart of the indian currency classification
process using a convolutional neural network.
As shown in Figure 2, the Indian currency
classification process begins with an input image
dataset and concludes with a fake or real currency
prediction.
Dataset Collection and Preprocessing: Gather a
diverse dataset containing both Images of real and
fake currency from multiple sources. Ensure images
are taken under different lighting conditions, angles,
and resolutions to enhance model robustness (Vivek
Sharan, 2019).
CNN Architecture for Fake Currency Detection:
Accepts preprocessed currency images. Extract low-
and high-level currency features (e.g., edges, patterns,
textures). Reduce spatial dimensions while retaining
essential features.
Model Training and Optimization: Use a pre-
trained CNN model (VGG16, ResNet50, or Inception
Net) for improved accuracy through transfer learning.
Train the model using cross-entropy loss and
optimize using the Adam optimizer. Divide the
dataset into three categories: testing (10%), validation
(10%), and training (80%). for performance
evaluation. Monitor training performance based on
criteria such as F1-score, recall, accuracy, and
precision.
Model Evaluation and Performance Metrics: Use
a to examine false positives and false negatives, use
the confusion matrix. Evaluate model performance on
unseen currency images to ensure generalization
across different denominations. Compare CNN
results with traditional image processing methods to
measure improvements (Yadav et al., 2021).
Real-Time Detection and Deployment: Deploy
the trained CNN model using TensorFlow Serving,
ONNX Runtime, or Flask API for real-time inference.
Integrate with mobile and web applications, allowing
users to scan currency using a camera or scanner.
Display detection results with confidence scores,
ensuring transparency in decision- making.
Edge and Cloud Computing for Scalability:
Optimize CNN using TensorFlow Lite or Open VINO
for fast inference on edge devices. Implement cloud-
based processing using Google Cloud, AWS, or
Azure for large-scale counterfeit detection.
Future Enhancements and Security
Considerations: Implement Explainable AI (XAI)
techniques to provide insights into CNN decision-
making. Integrate blockchain technology to store
verified currency records securely. Continuously
update the model by training with new counterfeit
currency data (K. Bhushanm et al., 2024).
5 RESULTS
The results of the project will be as follows: CNN
Fake Currency Detection System Using Deep Learning and Advanced Software Integration
357

Figure 3: Epoch details of CNN.
Figure 4: Confusion matrix of CNN.
Figure 5: Training progress of CNN.
Figure 6: Epoch details of simple NN.
Figure 7: Confusion matrix of simple NN.
Figure 3,4,5 shows the Epoch, Confusion and
training progress of CNN. And Figure 6,7,8 shows the
Epoch, Confusion and training of the SNN model. As
shown in Table 1, the CNN model achieved perfect
scores in all metrics, whereas the SNN model
obtained slightly lower performance, with 97.7%
accuracy, 0.95 recall, and an F1 score of 0.97.
Figure 8: Training Progress of Simple NN.
Figure 9: Outputs.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
358
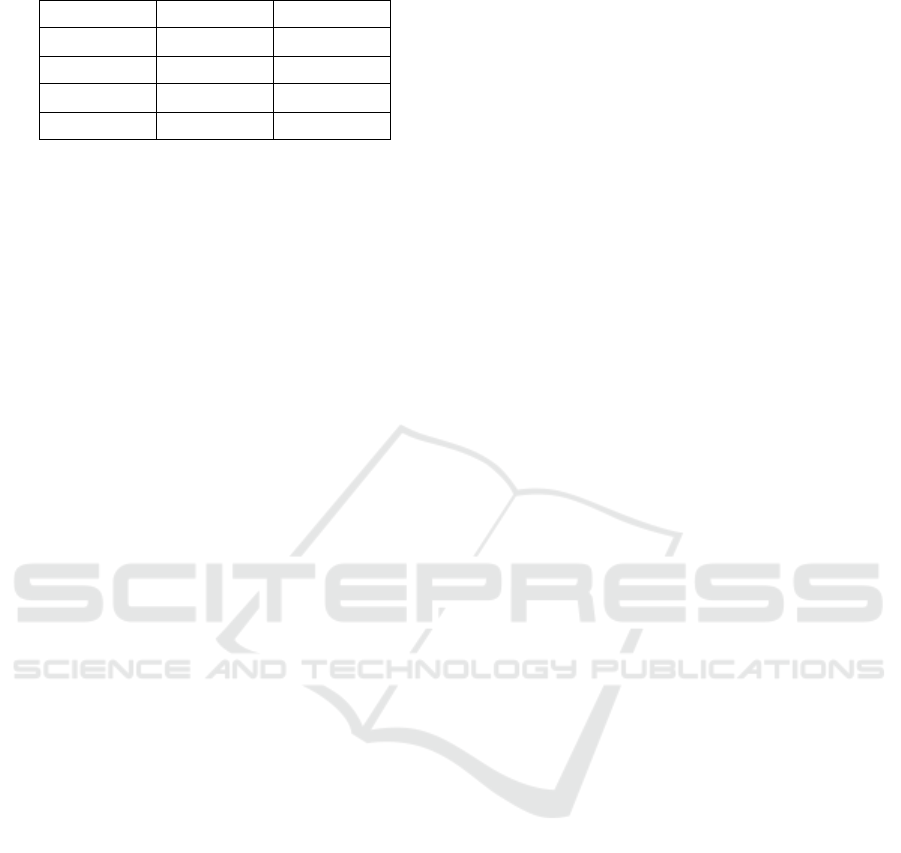
Table 1: Comparison between both model.
CNN SNN
Accuracy 100% 97.7%
Precision 1 1
Recall 1 0.95
Fl Score 1 0.97
6 CONCLUSIONS
The rapid advancement of counterfeit currency
production has necessitated the development of
intelligent and automated detection systems. This
paper presented a deep learning-based Fake Currency
Detection System, integrating Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) with advanced software solutions
to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and real-time
detection capabilities. Through data preprocessing,
deep learning model training, and software
integration, the system effectively differentiates from
real to fake money notes with extreme accuracy. The
use of transfer learning, cloud computing, and edge
AI ensures that the model Its flexible, scalable, and
able to provide real-time detection on mobile and
desktop platforms. Furthermore, the incorporation
o Explainable AI (XAI) and blockchain technology
offers additional layers o transparency and security.
Despite the system's high accuracy, challenge remain,
such as changes in the illumination, image quality,
and evolving counterfeit techniques. Future
enhancements will focus on improving dataset
diversity, optimizing model efficiency, and
integrating real-time learning mechanisms to
continuously adapt to new counterfeit threats.
7 LIMITATIONS
The following could be the project's limitations:
Dependence on High-Quality Images: The accuracy
of the system heavily relies on clear and high-
resolution images of currency notes. Poor lighting
conditions, motion blur, or low camera quality can
affect detection performance (Vivek Sharan, 2019).
Limited Generalization Across Currencies: The
model is often trained on specific currencies and may
not generalize well to new or less frequently used
banknotes. Differences in currency designs, security
features, and printing techniques may require
retraining for different regions.
Computational Requirements Deep learning
models' inference and training procedures, especially
those based on CNN architectures, require a
substantial amount of processing capacity. Running
high-accuracy models on edge devices (mobile
phones, embedded systems) may require optimization
techniques like TensorFlow Lite or ONNX (Yadav et
al., 2021).
Real-Time Processing Delays: While real-time
detection is a goal, processing large images or
performing deep learning inference on low-power
devices may introduce latency issues. Cloud-based
detection can help, but it depends on internet
connectivity and server response time.
8 FUTURE WORKS
The proposed
Fake Currency
Detection
System
has demonstrated encouraging outcomes in detecting
counterfeit currency using deep learning and
advanced software integration. However, there are a
number of areas that could be improved in the future
its accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. One key focus
is expanding the dataset by incorporating a more
diverse collection of currency notes from different
countries, lighting conditions, and real-world
scenarios. This will improve the model’s
generalization and robustness against variations in
counterfeit techniques. Additionally, Using
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to
generate synthetic data can assist in producing high-
quality fake samples for better training. To further
enhance detection accuracy, future work will explore
more advanced deep learning architectures, such as
Vision Transformers (ViTs) and Efficient Net, which
have shown superior performance in image
classification tasks. Implementing self-learning AI
models that can continuously update and adapt to new
counterfeit strategies will also be a key advancement.
Moreover, optimizing the real-time model
performance by employing techniques like
quantization, model pruning, and TensorFlow Lite
will allow efficient deployment on mobile phones and
embedded systems are examples of edge devices.
REFERENCES
A. Yadav, T. Jain, V. K. Verma and V. Pal, "Evaluation of
Machine Learning Algorithms for the Detection of Fake
Bank Currency," 2021 11th International Conference
on Cloud
Computing,DataScience&Engineering(Confluence),20
21,pp.8108 15,doi:10.1109/Confluence5164 8
.2021.9377127.
Fake Currency Detection System Using Deep Learning and Advanced Software Integration
359

Aakash S Patel, “Indian Paper currency detection”
International Journal for Scientific Research &
Development (IJSRD), Vol. 7, Issue 06, ISSN: 2321-
0613 (June 2019)
Anju Yadav,Tarun Jain,Vivek Kumar Verma,Vipin Pal
“Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for the
Detection of Fake Bank Currency” IEEE [2021]
Archana M Kalpitha C P, Prajwal S K, Pratiksha N,”
Identification of fake notes and denomination
recognition” International Journal for Research in
Applied Science & Engineering Technology
(IJRASET), Volume. 6, Issue V, ISSN: 2321-9653,
(May 2018)
Chakraborty, S., & Pal, S. (2017).* "A deep learning
approach for counterfeit currency detection."
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Computational Intelligence and Networks (CINE),
2017, 89-95.
G.Hariharan , D.Elangovan “Proxy Notes Recognition And
Eradication For Betterment Of The Society” Journal
[2020]
K. B. Zende, B. Kokare, S. Pise and P. S. Togrikar, “Fake
Note Detection System,” IJIRT, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 4649,
2017. [15]. F. A. B, P. Mangayarkarasi, Akhilendu, A.
A. S, and M. K, “Fake indian currency note
recognition,” vol. 7,pp. 4766–4770, 2020.
K. Bhushanm, M. Asritha, P. Rafiya Sultana, P. Anil
Kumar, S. Mahesh Babu Publication: International
Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and
Communication Engineering, 2024.
Kiran Kamble,Anuthi Bhansali,Pranali Satalgaonkar,
Shruti Alagundgi, “Counterfeit Currency Detection
using Deep Convolutional Neural Network”, 2019
IEEE Pune Section International Conference
(PuneCon) MIT World Peace University, Pune, India.
Dec 18-20, 2019
P. A. Babu, P. Sridhar and R. R. Vallabhuni, "Fake
Currency Recognition System Using Edge Detection",
2022 Interdisciplinary Research in Technology and
Management (IRTM), 2022, pp. 1-5, doi: 10
Prof Chetan More, Monu Kumar, Rupesh Chandra,
Raushan Singh, “Fake currency Detection using Basic
Python Programming and Web Framework” IRJET
International Research Journal of Engineering and
Technology, Volume: 07 Issue: 04 | Apr 2020 ISSN:
2395- 0056
S. Atchaya, K. Harini, G. Kaviarasi, B. Swathi, “Fake
currency detection using Image processing”,
International Journal of Trend in Research and
Development (IJTRD), ISSN: 2394-9333 (2017)M.
Laavanya, V. Vijayaraghavan. “Real Time Fake
Currency Note Detection using Deep Learning”,
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced
Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 – 8958, Volume-9
Issue- 1S5, December 2019.
Vivek Sharan, Amandeep Kaur,” Detection of Counterfeit
Indian Currency Note Using Image Processing”
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced
Technology (IJEAT), Volume.09, Issue:01, ISSN:
2249-8958 (October 2019)
Y. Neeraja, B. Divija and M. Nithish Kumar, “Fake
CurrencyDetection Using K-nn Technique,”
IJREITSS,Vol. 09, No. 1, pp. 201-205, 2019
Yadav, R.K., Valecha, P., Paliwal, S. (2021). Counterfeit
Currency Detection Using Supervised Machine
Learning Algorithms. In: Joshi, A., Khosravy, M.,
Gupta, N. (eds)Machine Learning for Predictive
Analysis. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol
141. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-
981-15-7106-0_17
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
360
