
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring
Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance
Arun Prasath M M, Govindaraju P, Akash R, Gavinesh P, Jeeva P and Surya S
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Internet of Things, Healthcare, BlockChain, IoT, Wearable Sensors, Emergency Alert, Heartbeat Monitoring,
Air Quality Monitoring.
Abstract: Blockchain technology, which was first made famous by cryptocurrencies, has now attracted a lot of interest
from many different sectors, one of which is healthcare. Examining the potential benefits and drawbacks of
blockchain technology, this article delves into its experimental uses in the healthcare industry. After providing
a brief overview of blockchain technology, this paper explores its potential applications in healthcare,
specifically looking at how it can improve data security, interoperability, and patient empowerment. It also
tackles some of the challenges associated with blockchain technology, such as regulation, scalability, and
privacy. The healthcare business has become more efficient, leading to better patient safety, higher healthcare
expenses, and easier access to healthcare services. This study delves into various computing paradigms, data
processing techniques, and Internet of Things (IoT) architectures. In order to address its numerous healthcare
initiatives and their global advantages, it incorporates a number of communication technologies, often worn
sensors, and healthcare monitoring systems. This study also identifies potential future healthcare facility and
technology implementation strategies, examines the most prevalent problems with wearable sensory systems
that aid in healthcare monitoring, and suggests solutions. This method works well in small towns and rural
areas where doctors' offices can keep in touch with larger hospitals about their patients' health issues.
Nonetheless, should the patient's health deviate from the expected range, the healthcare monitoring system
will promptly alert the attending physician. Healthcare institutions benefit from blockchain technology's
increasing use to connect data storage facilities and secure data transfer by addressing the problem of data
duplication.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the most prominent communication
paradigms, the Internet of things (IoT) is rapidly
expanding across many industries and offers the
prospect of centralized data access and fusion. Data
access permissions may be defined by user and per
authorized staff (e.g., healthcare medics and doctors)
(Lokesh Lodha, et al., 2020), (Soubhagya Ranjan
Mallick, et al., 2024) and (SoonHyeong Jeong, et al.,
2021). Concerns about privacy and confidentiality
make this limited access a must in the healthcare
industry. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables the
interconnection of various devices, such as sensors,
cars, homes, and appliances, over the Internet. This
enables the sharing of data, information, and
resources among users. The result is data fusion,
which has the potential to greatly improve application
usability, accessibility, and data analysis. Many new
trends have emerged as a result of the adaptability of
the Internet of Things (IoT), which aims to increase
data accessibility, resource efficiency, and data
communication across sources in order to boost data
integrity performance generally. Recent
developments in protocol communication
technologies, the prevalence of the Internet, and the
ease with which users may access and use the
underlying infrastructure have made this a reality.
Consequently, people are increasingly looking for
ways to save time and effort through centralized data
collecting and monitoring. Some significant areas
that have been embraced by the Internet of Things
(IoT) are smart cities, smart homes, healthcare, and
environmental monitoring. One of the most talked-
328
M., A. P. M., P., G., R., A., P., G., P., J. and S., S.
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance.
DOI: 10.5220/0013912400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
328-337
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

about issues recently is healthcare, which has risen to
prominence due to factors such as the fast
urbanization, industrialization, and aging populations
in European countries (Pratima Sharma, et al.,2023),
(WAFAA A. N. A. AL-NBHANY, et al., 2024) and
(Lokesh Lodha, et al 2024). Wireless body area
networks (WBANs) link separate nodes such as
sensors and actuators that are embedded in, on, or
beneath a person's skin (Simeon Okechukwu Ajakwe,
et al., 2024) and (Partha Pratim Ray, et al., 2021).
Typically, the network covers the entire human body
and is linked by a wireless communication connection
between the nodes. The implementation specifies a
star or multihop topology for these nodes to be placed
in.
Because of a WBAN's limitless range, various
exciting new uses have emerged in fields as diverse
as medicine, sports, home health care, multimedia,
and remote health monitoring. Wearable wireless
body area network (BAN) sensors can continuously
monitor a patient's vital signs in the medical industry,
including temperature, respiration rate, blood
pressure, heart rate, electrocardiogram (ECG), and
more. Some alternative therapies will enable the
patient to leave the hospital and enjoy fresh air inside
the room or even outside. It will help the hospital's
purse and the patient. The information accumulated
by the patients throughout the years in the natural
environment will give much more data useful for
quick and correct diagnosis (Anichur Rahman, et al.,
2024) and (Yazeed Yasin Ghadi, et al., 2024).
• IoT for Healthcare: Before the advent of
the Internet of Things, patients were limited
to contacting their doctors via home
visitations, via phone, or through text. There
was no way a healthcare provider or a
clinician could monitor the vital signs of a
patient all the time and give advice based on
such observations. Devices enabled by the
Internet of Things (IoT) have enabled
remote monitoring in healthcare, which has
the ability to keep patients safe and healthy
and gives doctors the ability to provide
exceptional care. Because interacting with
clinicians is now easier and faster, it has also
enhanced patient involvement and
happiness. Additionally, re-admissions are
reduced and hospital stays are shortened by
remote monitoring of patients' health.
Improving treatment results and drastically
lowering healthcare costs are two other areas
where the Internet of Things has a big
influence. By re-imagining the role of
devices and human interaction in healthcare
solution delivery, the Internet of Things
(IoT) is undeniably revolutionizing the
healthcare business. Everyone from patients
and their families to doctors, hospitals, and
insurance companies may reap the benefits
of the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare.
• IoT for Patients: Personalization of
treatment is made possible by the use of
wirelessly linked medical devices such as
glucometers, blood pressure monitors, heart
rate monitors, etc., in conjunction with
wearable fitness bands. A person's calorie
intake, exercise routine, appointment
scheduling, blood pressure fluctuations, and
a whole lot more may be programmed into
these gadgets. The ability to continuously
monitor health problems is one way in which
the Internet of Things has improved people's
lives, particularly for the elderly. People
who live alone and their families are greatly
affected by this. An alert mechanism
notifies worried family members and
healthcare providers if there is a disruption
or change in a person's usual activities.
• IoT for Physicians: With the help of
wearables and other IoT home monitoring
devices, medical practitioners may be able to
keep a closer eye on their patients' health. If
patients are adhering to their treatment plans
or if they need immediate medical attention,
they can be tracked by these systems. The
Internet of Things has the potential to make
healthcare practitioners more watchful by
allowing them to proactively engage with
patients. Doctors may use the data collected
by internet of things devices to help their
patients get the best treatment possible.
• IoT for Hospitals: Hospitals may greatly
benefit from IoT devices in many other ways
outside patient health monitoring. Internet
of Things (IoT) devices with sensors can
track medical equipment including oxygen
pumps, defibrillators, nebulizers, and
wheelchairs in real time. Additionally, it is
also feasible to monitor the deployment of
medical workers to different locations in
real-time. The spread of illnesses is a
reasonable concern for hospitalized patients.
Internet of Things (IoT) enabled hygiene
monitoring devices help reduce patient
infections. In addition to assisting with asset
management tasks like pharmaceutical
inventory control, IoT devices may monitor
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance
329

and regulate environmental factors like
temperature and humidity.
• IoT for Health Insurance Companies:
When it comes to intelligent gadgets that are
linked to the Internet of Things, health
insurers have a lot of chances. Health
monitoring gadgets can help insurance firms
with underwriting and claims processes by
collecting data. They can use this
information to spot accusations of fraud and
find potential underwriters. With the use of
IoT devices, insurers and policyholders may
see each other's underwriting, pricing,
claims, and risk assessment procedures in
action. Customers will be able to see the
reasoning behind every decision and the
results of every process thanks to data-
driven decisions made in all operational
processes that are captured by the IoT. To
encourage the use and sharing of health data
provided by IoT devices, insurers may
provide incentives to policyholders. The IoT
features a four-stage design that may be
thought of as process steps. Data is gathered
or processed at one level and then passed on
to the next, with a direct correlation between
the four processes. The incorporation of
values into the process yields intuitive
understandings and exciting new
opportunities for businesses.
• Deploying a network of linked devices, such
as sensors, actuators, monitors, detectors,
video systems, etc. Gathered by these
gadgets is the data.
• We get data in analog form from sensors and
other devices. Then, we need to convert it to
digital form so we can process it further.
• After data is gathered and digitized, the third
step is to preprocess it, standardize it, and
then transfer it to a data center or the Cloud.
• Complete data management and analysis at
the desired level. The use of Advanced
Analytics to this data yields valuable
business insights that can be used to make
smart decisions.
2 RELATED WORKS
Increased privacy and security measures are required
by the healthcare business to comply with legislation
and safeguard sensitive patient information (Sireejaa
Uppal, et al.,2023). Blockchain technology allows
for the incorporation of both of these aspects into the
current systems. A swift solution to the problem of
user-friendliness can be achieved by combining
blockchain technology with the Internet of Things
(IoT). Devices built on the Internet of Things (IoT)
get beyond the low processing power of individual
smart health monitors. There is a storage capacity
constraint for cloud-assisted Internet of Things
devices, such as wearable sensors. It should be
considered, though, that this method is not without its
flaws, which cause it to be inefficient. Data sharing
and data privacy are two of these issues. A solution
based on the Interplanetary File System (IPFS) is
proposed in this study to address these issues. Here,
nodes belonging to other users—doctors,
pharmacists, insurance firms, hospital administrators,
etc are able to access the health data that individuals
continuously upload from their IoT devices and
include in blockchain transactions. Along with this
capability, users may perform transactions on
HealthDote's six blockchains using the system-
specific cryptocurrency DoteCoins to purchase
medical consultations, medicines, insurance authority
payments, and hospital supplies.
With the growth of the IoT, health monitoring
systems have also progressed. This paper focuses on
a four-layer health monitoring system that collects
patient information and provides input to several
medical classifications (Poonam Rani, et al., 2022) as
a secure architecture, providing support from IoT.
When data are collected for computation from
wearable smart sensing devices, the patient ever has
to be considered in both respect of privacy and
security. A lightweight and secure communication
protocol over decentralized IoT networks based on
blockchain architecture is developed as the prime
focus of this communication. The aim is to categorize
these networks into separate classes through transfer
learning. For data integrity, we present a system that
utilizes transfer learning through various pre-trained
models to bind itself with blockchain technology.
Energy consumption reduction and network traffic
minimization have been achieved through a routing
approach that prudently applies node energy,
credibility scores, and link reliability in deciding the
optimal route for data transmission. Classification
accuracy of 92.24% is achieved by the suggested
method, according to the findings.
Technology has allowed the eHealth sector to
expand rapidly, shifting focus away from traditional
hospital settings and toward providing care to patients
in the comfort of their own homes (Aya H. Allam, et
al., 2024). Remote patient monitoring, simplified
electronic medical record (EMR) administration,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
330

medication traceability, and efficient disease control
are just a few of the ways that blockchain and the IoT
are improving healthcare services. This is especially
true in times of crisis, like the recent COVID-19
pandemic. Security issues, such as worries about data
integrity and device authentication, arise from the
increasing use of IoT devices. As a strong option, this
study suggests integrating blockchain technology.
Building trust among varied IoT devices, blockchain
uses its decentralized and tamper-resistant properties
to guarantee the integrity of IoT data. The final part
of this summarizes the issues posed by and potential
solutions offered to the eHealth IoT implementations
regarding blockchain technology. With the results of
this extensive survey, stakeholders will be better
equipped to make decisions that will improve patient
care in an ever-changing industry.
In modern domains including smart cities, smart
homes, schools, hospitals, transportation, and
military operations, the Internet of Things (IoT) plays
a pivotal role (Suliman Abdulmalek, et al., 2022).
When it comes to healthcare, IoT applications really
shine since they allow for safe, real-time remote
patient monitoring, which greatly enhances people's
lives. This article examines the ways in which
healthcare monitoring systems are being impacted by
the IoT. In addition to characterizing healthcare
monitoring sensors, the article delves into Internet of
Things (IoT) monitoring systems that rely on wireless
and wearable sensors. We also go into depth on the
difficulties and unresolved concerns related to
healthcare privacy and security, as well as quality of
service. At last, the study concludes with future
directions connected to several current technological
advances as well as proposals and recommendations
for healthcare IoT applications.
A growing number of entities, including
healthcare institutions, patients, insurance
companies, Internet of Medical Things sensor nodes,
and Internet of Things (IoT) wearable medical
devices, are becoming integral parts of IoMT systems
(Hamed Taherdoost 2023). Because of the need of
scalability in blockchain technology, designing a
blockchain for such applications is challenging. In
light of this insight, we set out to conduct an
exhaustive analysis of all English-language
blockchain-based IoMT solutions created between
2017 and 2022. Bringing together the theoretical
underpinnings of a large corpus of work published in
highly regarded academic journals over the past
decade, this research aims to standardize evaluation
approaches and fully capture the rapidly developing
blockchain area. The mentioned findings support the
identification of several research gaps and possible
future study directions that may benefit both
academics and practitioners.
3 METHODOLOGY
Health protection via prevention and prediction is
progressively replacing conventional medicine's
emphasis on therapy following diagnosis (p2 Health).
In response to this trend, it is essential to continuously
and comprehensively monitor parameters across all
healthcare domains using real-time monitoring and
individual data records. The health care internet of
things is the focal point of this new age of healthcare,
following the successful implementation of e-health
and m-health. Internet of Things (IoT) healthcare
platforms may integrate and combine (on the server
level) important parameters from several domains
which could help with healthcare security. The
second healthcare-related field is environmental
factor monitoring, which encompasses chemical and
physical components as well as vital signs and
physiological parameters. Using this platform, end-
users (approved staff) may alter sampling rates,
synchronize, monitor parameters on Wearables and
applications, and install additional sensor nodes. The
combination of sensor layers at the physical level and
data fusion on the cloud allows for ubiquitous and
centralized data processing, which is used in
healthcare and safety surveillance.
Remote and in-person patient monitoring,
diagnosis, and treatment have all been greatly
enhanced by the fast integration of technology in the
health sector in the past several years. Patients'
quality of life and the capacity to track their data are
both enhanced by this. Most of the injuries
considered focused on chronic illness monitoring as
the primary reason for the use of tele-medical
electrocardiogram systems and the top objective of
remote vital signs monitoring. This is a crucial step in
creating an all-inclusive solution for sequential
patient monitoring, regardless of the ailment, type of
check, or number of units to be managed. Whenever
a medical emergency occurs, the doctor is notified by
a preexisting wireless patient monitoring system that
includes a PIR sensor, temperature, humidity, and
smoke detectors that are attached to the patient's
body. Patient health monitoring network based on
Zigbee wireless sensors. This system is designed to
monitor elderly individuals and patients in coma.
Among its many sensors are those for measuring
heart rate, temperature, saline level, and micro-
electromechanical systems (MEMS). These IoT
systems, among others, provide great advantages to
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance
331
health and medical care in terms of perception,
transfer, and action of data. IoT addressable parts that
emulate smart, accessible, and communicative
systems, for example, non-limiting is medical
equipment, patient information management and
medication control, telemedicine, mobile medical
care, personal health management, and many more.
In modern times, a number of portable sensor
devices have come up to monitor health, fitness, and
levels of activity-a good kind of tech as this
technology has started getting attention over the last
few years. Besides serving the specialized
recreational fitness domain catered by these devices,
researchers have investigated possibilities for their
clinical applications in tele-health monitoring
systems for long-term record-keeping, management,
and clinical access to patients' physiological data.
Every Internet-connected device in the Internet of
Things (IoT) network may communicate with any
other device in the network, and each device can be
uniquely identified and addressed at any moment.
Internet of Things (IoT) based remote health
monitoring systems may automatically exchange data
with healthcare facilities via the web. The following
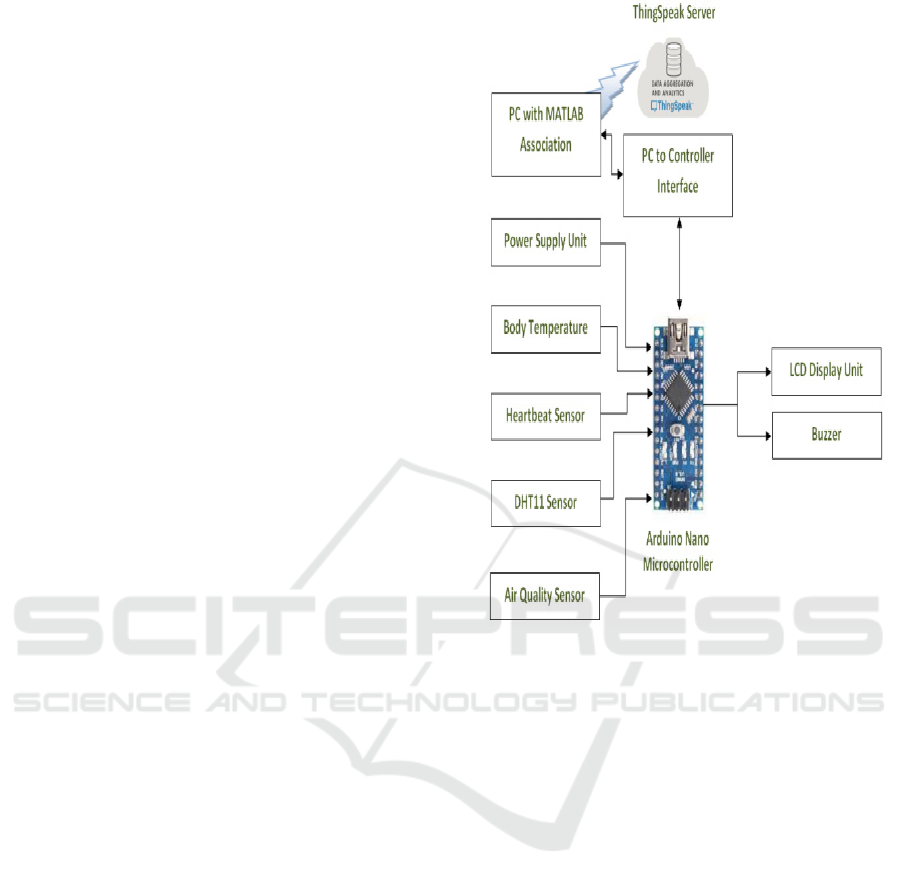
Figure 1 shows the proposed approach block diagram
in clear manner.
• Create an Internet of Things (IoT) based
system that can efficiently measure
environmental, physiological, and behavioral
(partially) variables using a wearable
mechanism;
• Integrate, calibrate, and analyze
environmental and physiological factors in
order to conduct medical research on the
interplay between these variables. Also
included in this is the ability to see data on the
server.
• Launch and refine a modern ambient
monitoring prototype.
• The goal is to create an adaptable Internet of
Things gateway that can use various
commercial devices to measure physiological
indicators. Patients and consumers with a
variety of product ownership may all benefit
from this solution, and the platform is open to
all suppliers.
Figure 1: Block Diagram.
• The user and the medics may communicate in
real-time from beginning to conclusion,
allowing the medics to provide the user with
the advice they need.
• Determine a way to make it work for all types
of workers. By utilizing the end-to-end
connection and adaptable IoT-gateway,
medical professionals are granted the ability to
personalize each patient's monitoring
parameters, including the ability to activate or
deactivate certain sensors and parameters.
• Arduino Nano Microcontroller: Arduino is
a free and open-source software-based
platform for making prototypes. Engineers
may experiment with developing interactive
worlds using this versatile basis. Embedded
systems that can control and detect parameters
in real-time can be created using them,
depending on the application's programming.
It is composed of an ATmega328
microcontroller that can be programmed with
the Arduino software. An Arduino Uno Boot
loader is standard on the Arduino R3/Genuino
R3, which is the board's Indian counterpart.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
332
When written with the Arduino IDE, it
simulates the behavior of the Arduino board.
There are a total of 20 digital inputs and
outputs (I/Os), 16 milliseconds (MHz) of
crystal oscillation, a USB connector, an ICSP
header, a reset button, and 14 digital inputs
and outputs (I/Os), 6 of which may function as
pulse width modulation (PWM) outputs. The
following Figure 2 shows the Arduino nano
microcontroller.
Figure 2: Arduino Nano Microcontroller.
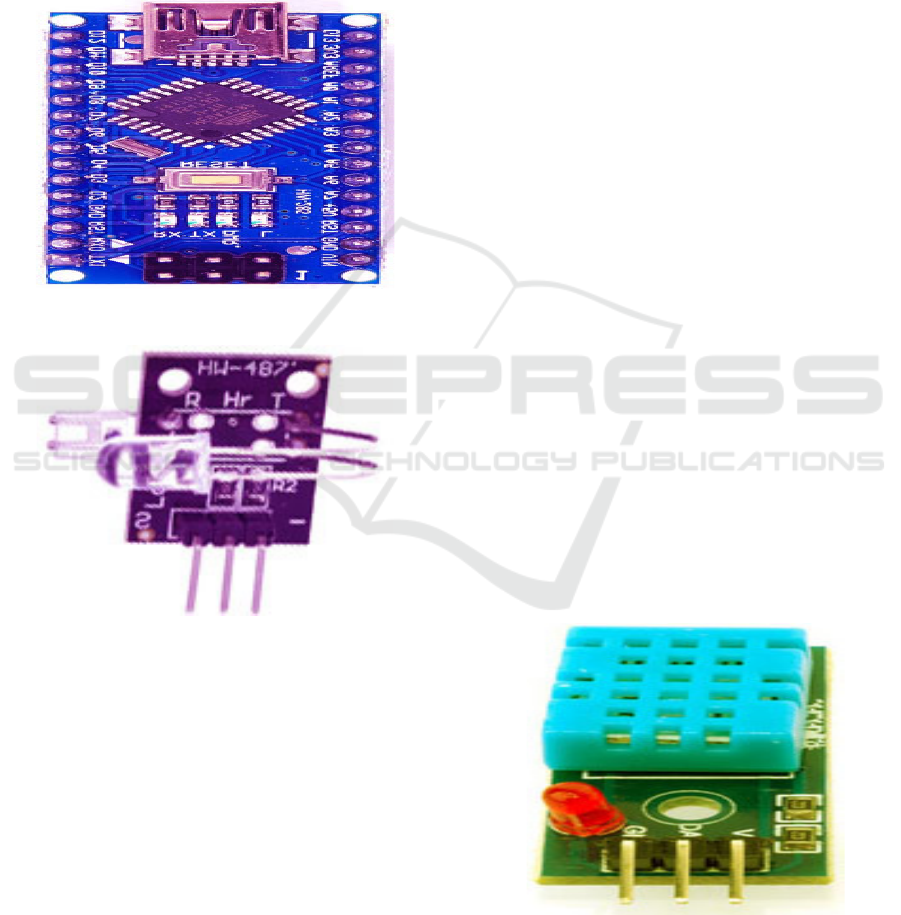
Figure 3: Heartbeat Sensor.
• Heartbeat Sensor: Placing a finger on the
Heart Beat Sensor causes it to produce an
analogue signal that corresponds to the heart
rate. Upon activation, the heart detector will
begin to flash the topmost LED in response to
each heartbeat. In order to measure the heart
rate, the output of this sensor may be directly
linked to the microcontroller. It works on the
premise that light may be modulated by the
constant flow of blood via the finger's nerves
with each pulse. The analog output mode,
which is the module's default, is
straightforward. The following Figure 3 shows
the heartbeat sensor.
• Humidity Sensor: Humidity refers to the
amount of water vapor in the air. Many
industrial processes are sensitive to the
relative humidity of the air, which in turn
affects human comfort. Water vapor affects
many biological, chemical, and physical
processes as well. Because it may have an
impact on product costs and worker safety,
humidity monitoring is essential in industrial
settings. Control systems for industrial
operations and human comfort rely heavily on
humidity sensing. Many industrial and
household applications place a premium on
controlling or monitoring humidity. The
semiconductor industry is ever so reliant on
the measurement and control of relative
humidity and moisture in the fabrication of
wafers. An example of a medical application
of humidity management is pharmaceutical
manufacture, the production of biological
products, sterilizers, incubators, and
respiratory equipment. Some of the most vital
activities involving control of humidity
include dryers and ovens, chemical
purification of gas, humidity control, paper
and textile production, food processing, and
film drying. In agriculture, there are several
reasons for monitoring humidity, including
dew prevention in the plantings and soil
moisture regulation. Humidity management is
essential for residential applications such as
building interiors, microwave ovens, and other
kitchen appliances. To indicate the relative
humidity of a given area, humidity sensors are
used in all of these and countless more
applications. The following Figure 4 shows
the humidity sensor.
Figure 4: Humidity Sensor.
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance
333
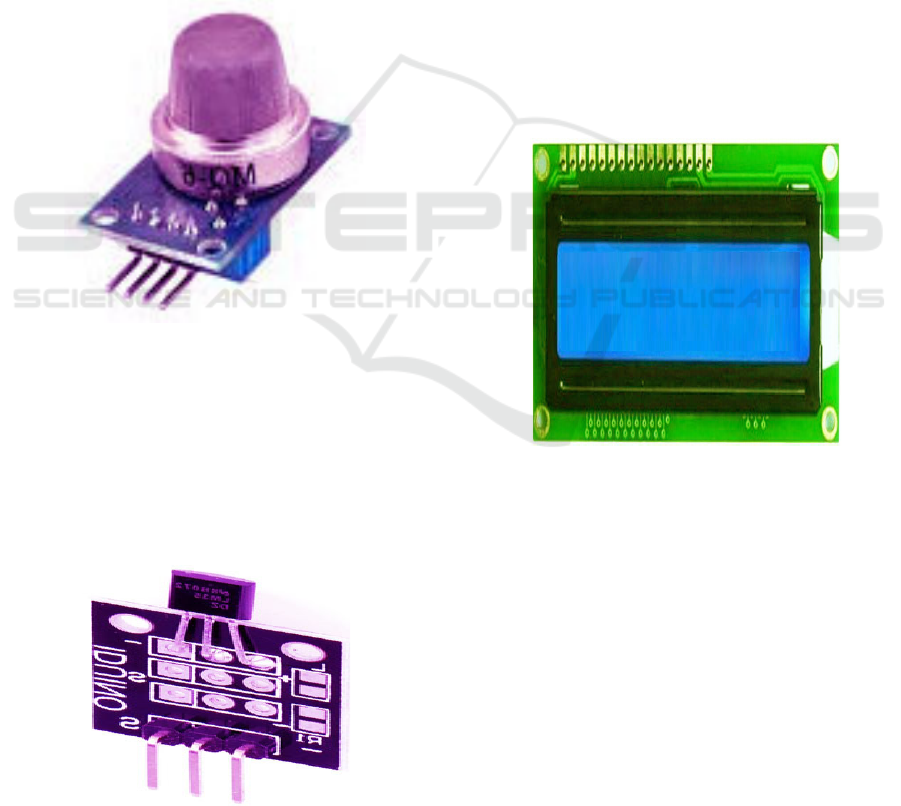
• MQ-6 Gas Sensor: The MQ-6 gas sensor is
designed using SnO2, which has relatively
low conductivity in clean air, as its sensitive
material. With the presence of the target
flammable gas, the conductivity of the sensor
follows the gas concentration. The change in
the conductivity would then be transformed
into an output signal by means of a basic
electronic circuit in order to determine the
concentration. This sensor has extremely high
sensitivity for gases such as natural gas,
butane, propane, and LPG. The sensor is
understood to be a useful product because of
its ability to detect various combustible gases,
including methane, while being versatile and
of low cost. The MQ-6 gas detector is shown
in Figure 5.
Figure 5: MQ-6 Gas Sensor.
• LM35 Temperature Sensor: The ability to
detect when an object is hot or cold is the
primary function of a temperature sensor.
With a proportional output to the temperature
(in °C), the LM35 is a precise integrated
circuit temperature sensor. The LM35 is a
more precise temperature sensor than a
thermistor.
Figure 6: LM35 Temperature Sensor.
Additionally, it has a low coefficient of
thermal expansion and raises the temperature
of still air by no more than 0.1 °C. The
temperature range in which it can function is -
55°C to 150°C. Because of its linear output,
low output impedance, and accurate intrinsic
calibration, the LM35 is ideal for use in
control or readout circuits. An output voltage
proportional to temperature in Celsius is
provided by the LM35. .01V/°C is the scaling
factor. The following Figure 6 shows the
LM35 temperature sensor.
• LCD Display: The liquid crystal display
(LCD) screen is an electrical display module
that has several functions. Many different
kinds of gadgets and circuits make use of the
same basic module: a 16x2 LCD display. This
LCD is called a 16x2 because it has two lines
of sixteen characters each. A 5x7 pixel matrix
displays each character in this LCD.
Command and Data are the names of the two
registers on this LCD. Figure 7 Shows the
LCD Display.
Figure 7: LCD Display.
•
BlockChain and IoT Interfacing:
Blockchain technology is enhancing security,
privacy, and efficiency, skidding giant wheels
in revolutionizing healthcare monitoring. It
provides a decentralized and impossible to
penetrate system for conducting medical data
managements, integrity of data, and
functioning for real-time patient monitoring.
However, some challenges persist, including
privacy, interoperability, and security of data.
Blockchain technology, by providing smart
decentralized immutable frameworks, solves
all these problems in terms of IoT health
monitoring concerning its efficiency, privacy,
and security concerning real-time patient data.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
334
With continuous health data stream from IoT
devices such as smart sensors, medical
implants, and wearables to be stored in the
blockchain, integrity is restored and
minimized access to the information outside
authorized parties. This integration creates
better interoperability, promotes data-sharing
among healthcare providers, and reduces the
chance of central data breaches. Not only does
blockchain technology allow early detection
of diseases and preventive health measures,
but also real-time health monitoring. While
blockchain-based IoT healthcare solutions
promise a safer, more transparent and efficient
digital healthcare ecosystem, they are also
faced with the immense cost of installation,
limited scalability, and regulatory compliance.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Recent developments in healthcare monitoring
technology make it possible for medical equipment to
do real-time assessments hitherto unthinkable for
doctors to execute. It has also enabled healthcare
institutions to operate the lowest cost and
simultaneously service a bigger population. Big data
and cloud computing have also helped to increase
consistency and simplicity of doctor-patient
communication. This resulted in a decreased financial
burden for the patient and more patient participation
in the treatment process. Management has evolved
healthcare monitoring system applications including
personal care for children, old patients and illness
detection. Recent years' notable Internet of Things
effect helps to keep track of chronic illnesses and
enhance health and fitness by means of monitoring.
By tackling a broad spectrum of medical problems,
ideas and service have distorted the healthcare
industry. Growing health-care requirements and
technological developments drive daily service
provision from additional angles. An electronic
healthcare network depends on data interchange
between several medical devices and healthcare
service providers. Block chain technology is one of
the main issues with safe data also promoting
cooperation, sharing, and data fragmentation
nevertheless. Data fragmentation might cause a
knowledge gap between doctors linked to the same
patient. Lack of proper information might hinder the
course of therapy. Block chain technology not only
solves data fragmentation but also helps healthcare
institutions to link the data repositories found in the
network study.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), which interacts with
the Internet of Things, offers age-related support in
expert capacity. The main objective of the suggested
artificial intelligence-based solution is to let elderly
people live comfortably and safely at home. In the
event of a medical calamity, this system offers a
means for closely monitoring patients in real-time and
guarantees that they get help on par with those of
human services. Sophisticated artificial intelligence
techniques, large data analysis, machine learning, and
healthcare sector application help to make this
achievable. Several software tools, like MATLAB
and Arduino IDE, help to empirically evaluate the
suggested method. This MATLAB program is used to
link the whole hardware to PC and obtain the
necessary health data from patients via sensors
thereby enabling the Internet of Things (IoT) help.
MATLAB analyzes and handles the gathered data;
the results are shown to users appropriately. After
that, IoT technology passes the resultant specifics to
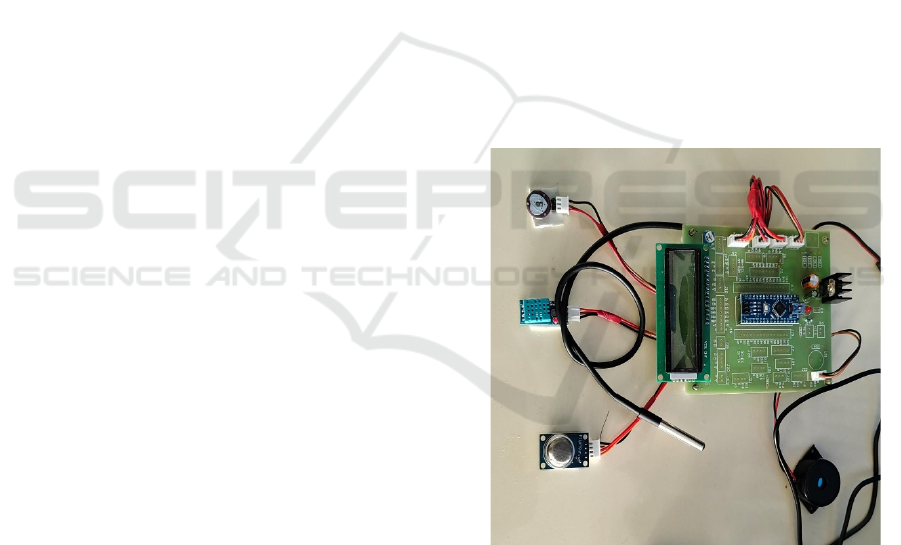
a distant server. Figure 8 displays the hardware design
result of the suggested solution, in which the web
application output pages are clearly shown on further
figures.
Figure 8: Hardware Design.
In the proposed layout, the pages that are
represented by the following figures are the
Homepage, New User Registration, and New Doctor
Registration. These figures are organized 9 through
11 respectively.
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance
335
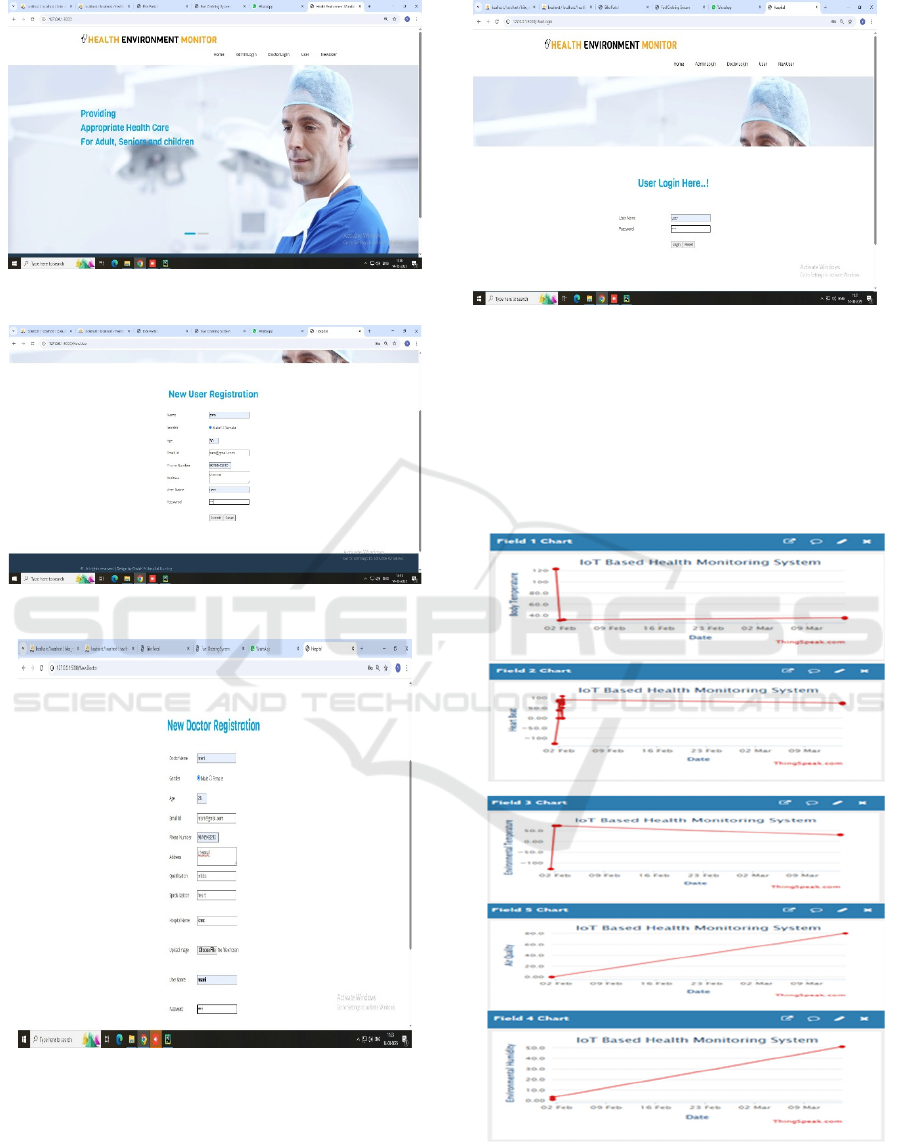
Figure 9: Homepage.
Figure 10: New User Registration.
Figure 11: New Doctor Registration.
The outputs of the suggested system are depicted
in the following Figure 12 These figures reflect the
User Login, Administrator Login, and Doctor Login
results, respectively.
Figure 12: Login User, Administrator and Doctor.
The Matlab output summary of the health
information obtained from sensors such as body
temperature, heartbeat rate, environment
temperature, environment humidity, and air quality
ratio is represented by the following figures, Fig-15
(a), (b), (c), (d), and (e). These figures are described
in more depth below.
Figure 13: Health Records Analysis, Body Temperature,
Heartbeat Rate, Environment Temperature, Environment
Humidity and Air Quality.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
336

5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
SCOPE
The creative health monitoring system that has been
proposed enables physicians to easily identify the
information of each patient on the display monitor
located at their location. Doctors can differentiate
between the data of a specific patient with respect to
their previous values and their current values. In
addition to data recording on the cloud, the Internet
of Things offers the potential to incorporate
additional biomedical sensors and more advanced
features or advantages into this system.
Consequently, the capabilities of IoT technology
render this monitoring system more adaptable and
upgradable in the future. A low-cost, user-friendly
monitoring system for signature signs of highly
sensitive patients is proposed. Vital signs are
accurately sensed, converted into clinical indicators,
and displayed on a central screen and web server, in
a manner that communicates wirelessly with Wi-Fi-
enabled networks or specially-constructed wireless
IoT devices. In summary, blockchain technology has
the capacity to transform healthcare delivery and
outcomes by improving patients' empowerment,
interoperability, transparency, and data security.
Although challenges and constraints persist, ongoing
research and collaboration will foster innovation and
establish a future in which blockchain-enabled
healthcare systems enhance the quality, accessibility,
and equity of care for all. Additionally, this work can
be improved by incorporating certain deep learning
concepts to instantaneously determine the healthcare
status and provide users with the corresponding
information.
REFERENCES
Lokesh Lodha, et al., "Blockchain-Based Secured System
Using the Internet of Medical Things (IOMT) Network
for E-Healthcare Monitoring", International
Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and
Applications, 2020.
Soubhagya Ranjan Mallick, et al., "Blockchain-enhanced
IoT ecosystem for healthcare: Transformative
potentials, applications, challenges, solutions, and
future perspectives", Computers & Industrial
Engineering, 2024.
SoonHyeong Jeong, et al., "A Study on Smart Healthcare
Monitoring Using IoT Based on Blockchain", Wireless
Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021
Pratima Sharma, et al., "Blockchain-Based Privacy
Preservation for IoT-Enabled Healthcare System",
ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2023.
WAFAA A. N. A. AL-NBHANY, et al., "Blockchain-IoT
Healthcare Applications and Trends: A Review", IEEE
Access, 2024.
Lokesh Lodha, et al., "A blockchain-based secured system
using the Internet of Medical Things (IOMT) network
for e-healthcare monitoring", Measurement: Sensors,
2023.
Simeon Okechukwu Ajakwe, et al., "Medical IoT Record
Security and Blockchain: Systematic Review of Milieu,
Milestones, and Momentum", Big Data Cogn. Comput.,
2024.
Partha Pratim Ray, et al., "BIoTHR: Electronic Health
Record Servicing Scheme in IoT-Blockchain
Ecosystem", IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021.
Anichur Rahman, et al., "Internet of medical things and
blockchain-enabled patient-centric agent through SDN
for remote patient monitoring in 5G network",
Scientific Reports, 2024.
Yazeed Yasin Ghadi, et al., "The role of blockchain to
secure internet of medical things", Scientific Reports,
2024.
Sireejaa Uppal, et al., "HealthDote: A blockchain-based
model for continuous health monitoring using
interplanetary file system", Healthcare Analytics, 2023.
Poonam Rani, et al., "Blockchain-based IoT enabled health
monitoring system", The Journal of Supercomputing,
2022.
Aya H. Allam, et al., "IoT-based eHealth using blockchain
technology: a survey", Cluster Comput, 2024.
Suliman Abdulmalek, et al., "IoT-Based Healthcare-
Monitoring System towards Improving Quality of Life:
A Review", Healthcare, 2022.
Hamed Taherdoost, "Blockchain-Based Internet of Medical
Things", Appl. Sci., 2023.
Experimental Evaluation of an IoT Powered Healthcare Monitoring Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology Assistance
337
