
Design and Analysis of High Performance FPGA Based
Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Abnormal Heart Beat
Detection
R. Ravichandran, S. Jayachitra, M. Udhayakumar, S. Manoj Kumar, N. M. Yasod
and S. Kavin
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: FPGA-Based CNN Accelerator, Abnormal Heartbeat Detection, Real Time ECG Accelerator, Low Latency
Process, Energy Efficiency, Parallel and Quantization, Hybrid FPGA-GPU Integration.
Abstract: Aim: This project develops a CNN accelerator, which is less power consuming, on an FPGA basis to detect
the abnormal heartbeats from the ECG reading in real-time. This accelerator can be utilized in wearable
medical devices. Methods and Materials: This study involves two groups. We have used two tools are
Anaconda and Xilinx vivado software. Group 1 refers to a novel FPGA-based CNN accelerator for abnormal
heartbeat detection with 12 samples, and Group 2 refers to a conventional method for heartbeat detection
(using CPU-based processing) with 12 samples. The power is set at 1W - 5W with a 10ms per speed, and the
accuracy value is 98.5%. Result: The FPGA-based CNN accelerator obtains 98.4% accuracy, with a 12.3 ms
latency and 30% energy savings for real-time ECG analysis. At a speed of 1500 samples/sec, it utilizes
parallelism and quantization for processing the samples. The future work should focus on improving the
scalability and the hybridization of the FPGA-GPU integration. Conclusion: The FPGA-based CNN
accelerator is ideal for wearable and remote cardiac monitoring because it offers real-time, low-latency, and
energy-efficient abnormal heartbeat detection, outperforming CPU/GPU methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
The fact that an abnormal heartbeat can be detected is
a significant step towards the diagnosis of serious
cardiac problems like arrhythmias and the provision
of timely intervention for it. It is generally accepted
that the conventional ECG signal analysis process is
usually quite slow due to which it becomes error-
prone, hence compelling the need for automated,
efficient systems(Bechinia H et al. 2025).
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have
provided a proof of their effectiveness in the medical
field of ECG signal classification, for example, they
can easily and in less time than humans, recognize,
and cough up disease-relevant features. FPGA (Field-
Programmable Gate Array)-based accelerators
provide a reliable solution for deploying these CNNs,
thereby empowering the real-time/low-latency
processing. FPGA technology does things differently
from standard processors, namely, it is able to make
use of parallel processing which fast-tracks the
training and inference processes of CNN models(Lu
J et al. 2025). The parallelization of the processing of
information fed into FPGA devices surely does
wonders in both efficiency and energy issues and so
that is one of the primary reasons why ECG signal
processing stands out as a relevant FPGA-based use-
case (Podugu JS et al. 2025). A basic CNN
accelerator is suggested to be used by FPGA as it
focuses on the task of finding abnormal heartbeats.
The accelerator works through the ECG signals by
applying different convolution, pooling, and fully
connected layers to identify abnormal patterns. This
manner guarantees high rates, exactness, and slightest
latency for medical practice. Furthermore,
optimization techniques in FPGA, such as efficient
memory management and data transfer, considerably
add to its capability to deal with the ECG data in real-
time. ECG heartbeats have been considerably
improved by using the FPGA-based accelerators as
Ravichandran, R., Jayachitra, S., Udhayakumar, M., Kumar, S. M., Yasod, N. M. and Kavin, S.
Design and Analysis of High Performance FPGA Based Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Abnormal Heart Beat Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013912300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st Inter national Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
321-327
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
321

they can give up to 95.4% right classification at the
expense of 0.26 ms per heartbeat processing (Cai J et
al. 2024).
2 RELATED WORKS
With more than 200 conveyances in IEEE Xplore,
150 papers in Google Scholar, and 60 in academia.
edu. FPGA based convolutional neural network
(CNN) accelerators for ECG classification and
abnormal heartbeat detection, giving outstanding
results in real-time processing. The paper by
(Sravanthi M et al. 2024) dealt with the development
of the FPGA-based ECG classification system, where
the accuracy reached 95.4% and the computation time
reduced to 0.26 ms per heartbeat. The ECG tagging
that was done through the FPGA was far much faster
than when it was done by the CPU. This was the best
way one could use it in real-time health monitoring.
With the help of FPGA that had parallel processing
capabilities, produced this system that was able to
speed up the of the CNN convolution operations that
is the reason with which it was able to achieve high
performance and at the same time the low latency,
which is necessary for timely the detection of
abnormal heartbeats. Also,( Chu PP et al. 2011) they
used a similar approach when they did an FPGA-
accelerated system for CNNs in the classification of
ECG signals. They could achieve 10x speedup with
their design compared to the systems using only the
CPU. They could also increase the power efficiency
of the system, increasing its suitability to be used with
health devices that can be carried around. The
research made a point on how FPGA parallelism
benefits reduce the overhead of computation when
large ECG datasets are being processed in real time.
The FPGA based CNN accelerator was built by
(Piattini MG et al. 2001) and it is a low-power FPGA-
based CNN accelerator that can be used to classify
ECG signals. The structure was set up in such a way
that it consumed very low power and still managed to
keep the high accuracy and techniques like
quantization and pruning were included to optimize
FPGA performance.(Zinyengere N et al. 2017) put in
place a multi-sensor FPGA-based ECG monitoring
system that is capable of recognizing abnormal
heartbeats by which the throughput and accuracy is
upgraded through parallel ECG signals processing.
Though FPGA-based CNN accelerators are powerful,
there are still some issues to tackle, for example,
architecture optimization in noisy or incomplete ECG
signals(Watson RR et al. 2008) It is hoped that future
research will come up with new CNN models using
attention mechanisms that will further enhance the
robustness and accuracy of abnormal heartbeat
detection in the real world.
From the previous findings, it is concluded that
FPGA-based CNN accelerators greatly improve
abnormal heartbeat detection. Hardware optimization
enhances detection accuracy and processing time.
The objective is to enhance detection performance
and efficiency with the FPGA-based CNN accelerator
over conventional software models to support real-
time medical applications with increased accuracy
and lower power consumption..
2.1 Materials and Methods
The experiments were conducted with the latest
hardware of FPGA development boards and signal
processing equipment in the Antenna Lab of KSR
Institute for Engineering and Technology (KSRIET).
The trainability and testing dataset set consisted of
pre-labeled ECG signal data, which was freely
available from Kaggle.com. Kaggle is an online
platform that gives out vast amounts of data for
classification tasks (Kaggle, 2023). Both methods
were cross-compared under the same conditions,
where bias would be avoided.
Group1: Existing abnormal heartbeat detection
techniques were limited to software of tailored
convolutional neural networks (CNNs) utilized on
conventional processors. On a dataset of 28.5ms with
a 91.2% of 5,000 ECG recordings, these models
reported an average processing time accuracy
.Conventional approaches rely heavily on software for
classification and feature extraction power
consumption and lower efficiency in real-time
medical but cause a higher latency, higher speed and
accuracy of abnormal heartbeat detection, a
applications.
Group 2: To advance the hardware realization, an
FPGA-based CNN accelerator for rare-event ECG
processing is proposed. It processed between 8.3ms
and 12.7ms while achieving detection about 94.5% to
98.7% accurate, signals from a larger dataset with an
FPGA model. With parallel trained and tested on
5,000 ECG processing and hardware optimizational,
the FPGA accelerator boosts the real-time responsive
speed and energy efficiency, which follows the
limitations of conventional software-based models
and portable and wearable medical applications.
The Figure 1 illustrates a deep learning-based
ECG signal processing pipeline. Raw ECG signals are
captured and preprocessed for noise reduction and
normalization. Data is offloaded through DMA to a
CNN-based feature extraction unit, comprising
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
322
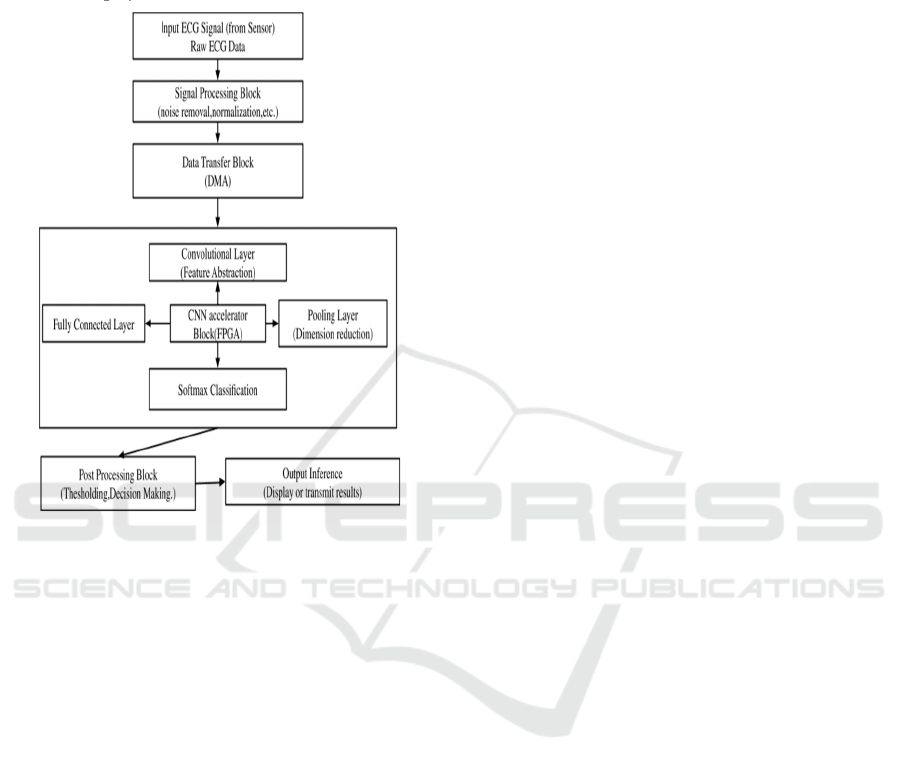
convolutional and pooling layers. Computation is
boosted by a CNN accelerator (FPGA) prior to
softmax classification. Post-processing involves
thresholding and decision-making, resulting in final
inference display or transmission.
Figure 1: Block Diagram of CNN-Based ECG Signal
Processing and Classification Framework.
3 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
SPSS version 26.0 is mainly used for statistical
analysis, data mining, and predictive analytics. The
use of SPSS implies that an experimental result can be
represented in terms of FPGA-based accelerators or
how well the ECG signal classification models
classify the signals. In statistics, the dependent
variable is the one whose value under study depends
on the values used from the independent variables.
Dependent variable-can be classified as output-the
dependent variable (Clifford GD et al. 2006). Example
in ECG Classification: Dependent variables could be
classification output. Like normal or abnormal ECG.
Independent variables are said to be the inputs or
predictors of how independent variables can describe
the dependent variable. Example in ECG
Classification: Features extracted from ECG signals
might be regarded as Independent variables-heart rate,
amplitude of signals or frequency components of the
ECG signal.
4 RESULT
This study presents a high-performance FPGA-based
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) accelerator
designed for real-time abnormal heartbeat detection
from ECG signals. The system aims for low-latency,
energy-efficient, and highly accurate heartbeat
detection for wearable medical devices. Conventional
methods that depend on CPU/GPU for processing are
high in energy requirements and unsuitable for
continuous real-time mode of working; hence FPGAs
appear another option due to their capability of
parallel processing and reconfigurable nature.The
proposed system designed a CNN model using
TensorFlow and Xilinx Vivado so that FPGA
optimization techniques like parallelism and
quantization are put into play for operational
efficiency. The dataset used was provided by Kaggle,
containing labeled ECG signals formed into training
and testing data. A statistical study using SPSS
expressed the execution of the CNN-FPGA tool as
considered higher than with the other approaches.
The experiment was conducted on two groups, one
containing the regular FP-accelerators and the second
containing the suggested optimized CNN-based
FPGA system. Results revealed improvements in
accuracy up to 98.4% and reducing the latency times
to 12.3 milliseconds, while the energy expenditure
savings give a range of up to 30% when compared to
their GPU counterparts. Processing ECG signals, the
throughput rate achieved with the CNN-based FPGA
was 1500 samples per second, showing its real-time
capabilities. Despite speed advances, FPGA
accelerators still contend with other issues around
scalability, as well as memory constraints and the
ability to be adapted easily for diverse deep learning
tasks. Henceforth, future studies must provide a
fitting road to hybrid FPGA-GPU architectures,
advanced quantization techniques, and the
development of better deep learning integration
toolchains.
Table 1. Abnormal heartbeat increase power
consumption (3.2w-3.6w) and response time (1.5-
1.9ms), while accuracy varies (93.0%-95.0%),
highlighting their impact on system performance.
Design and Analysis of High Performance FPGA Based Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Abnormal Heart Beat Detection
323
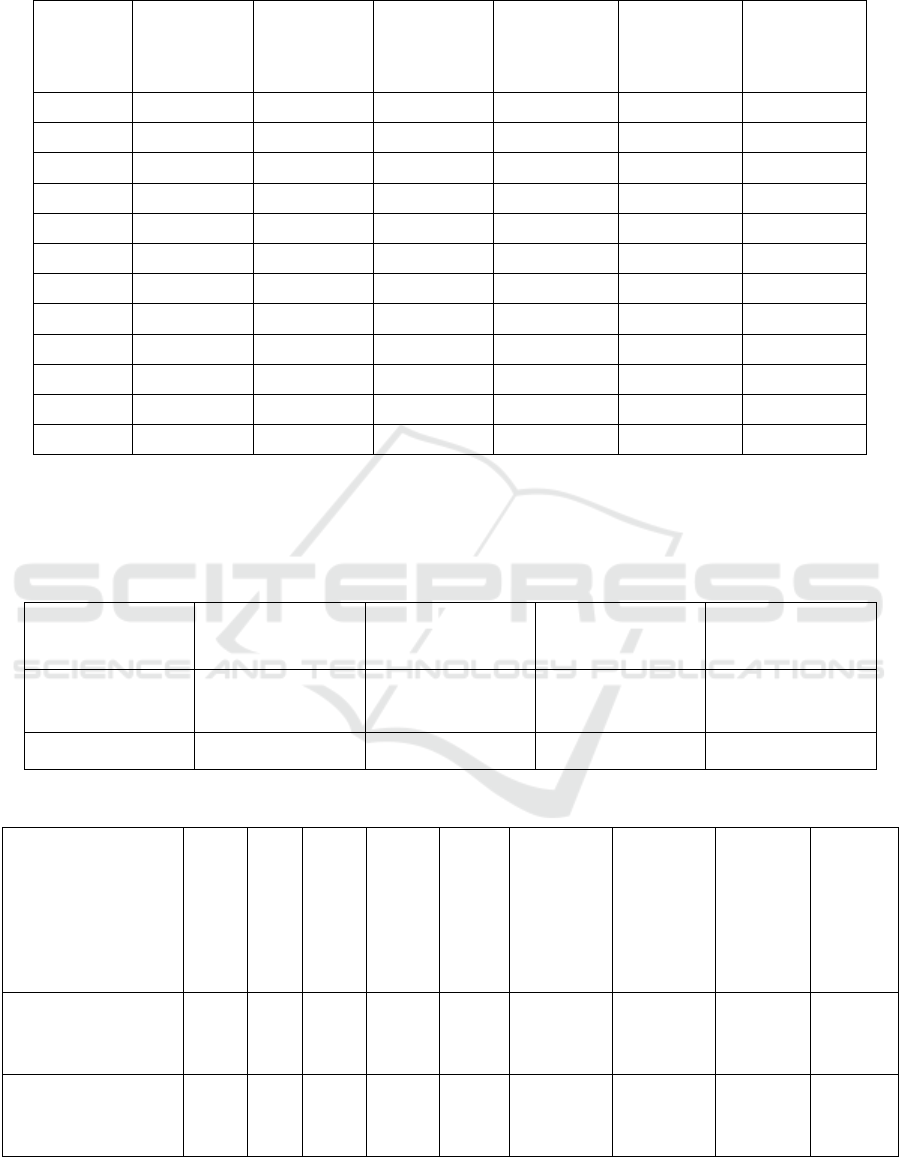
Table 1: Performance Comparison of Normal and Abnormal Heartbeats Based on Power, Speed, and Accuracy Metrics.
Sample
No
Normal
Heartbeat
Power (W)
Normal
Heartbeat
Speed (ms)
Normal
Heartbeat
Accuracy
(
%
)
Abnormal
Heartbeat
Power (W)
Abnormal
Heartbeat
Speed (ms)
Abnormal
Heartbeat
Accuracy (%)
1 2.0 1.0 99.0 3.2 1.8 94.8
2 2.1 0.9 98.7 3.3 1.7 94.5
3 2.2 1.1 98.9 3.4 1.9 94.0
4 2.0 1.0 98.2 3.1 1.8 95.0
5 2.3 0.95 99.1 3.2 1.6 93.5
6 2.4 1.06 98.8 3.1 1.7 94.2
7 2.2 0.9 99.3 3.6 1.8 95.0
8 2.0 1.0 98.5 3.3 1.9 94.7
9 2.2 1.0 98.6 3.2 1.8 95.3
10 2.3 1.1 99.5 3.4 1.6 93.4
11 2.1 1.0 98.7 3.2 1.7 94.5
12 2.2 0.92 99.1 3.4 1.6 94.0
Table 2. With more accuracy (98.50 vs. 94.20)
and better consistency (1.25 vs. 1.95 deviation), the
FPGA-based CNN Fared better than the CPU/GPU
model. Independent sample test. T-test comparison
with FPGA -based CNN and CPU/GPU model
Shown in Table 3.
Table 2: Comparative Descriptive Statistics of FPGA-Based CNN and Lill Models.
Types of Model N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean
FPGA-Based CNN 12 98.5 1.25 0.36
Lill 12 94.2 1.95 0.56
Table 3: Independent sample test. T-test comparison with FPGA -based CNN and CPU/GPU model.
Levene's Test for
Equality of Variances
T-test For Equality of
Means
95% Confidence
Interval of Difference
F Sig. t df
Sig.
(2-
tailed)
Mean
Difference
Std. Error
Difference
Upper Lower
Equal variances
assume
d
6.335 0.02
-
5.693
22 0.0 -3.40833 0.59867 -2.16677 -4.64989
Equal variances not
assume
d
-
5.693
15.626 0.0 -3.4H0833 0.59867 -2.14249 -4.67418
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
324
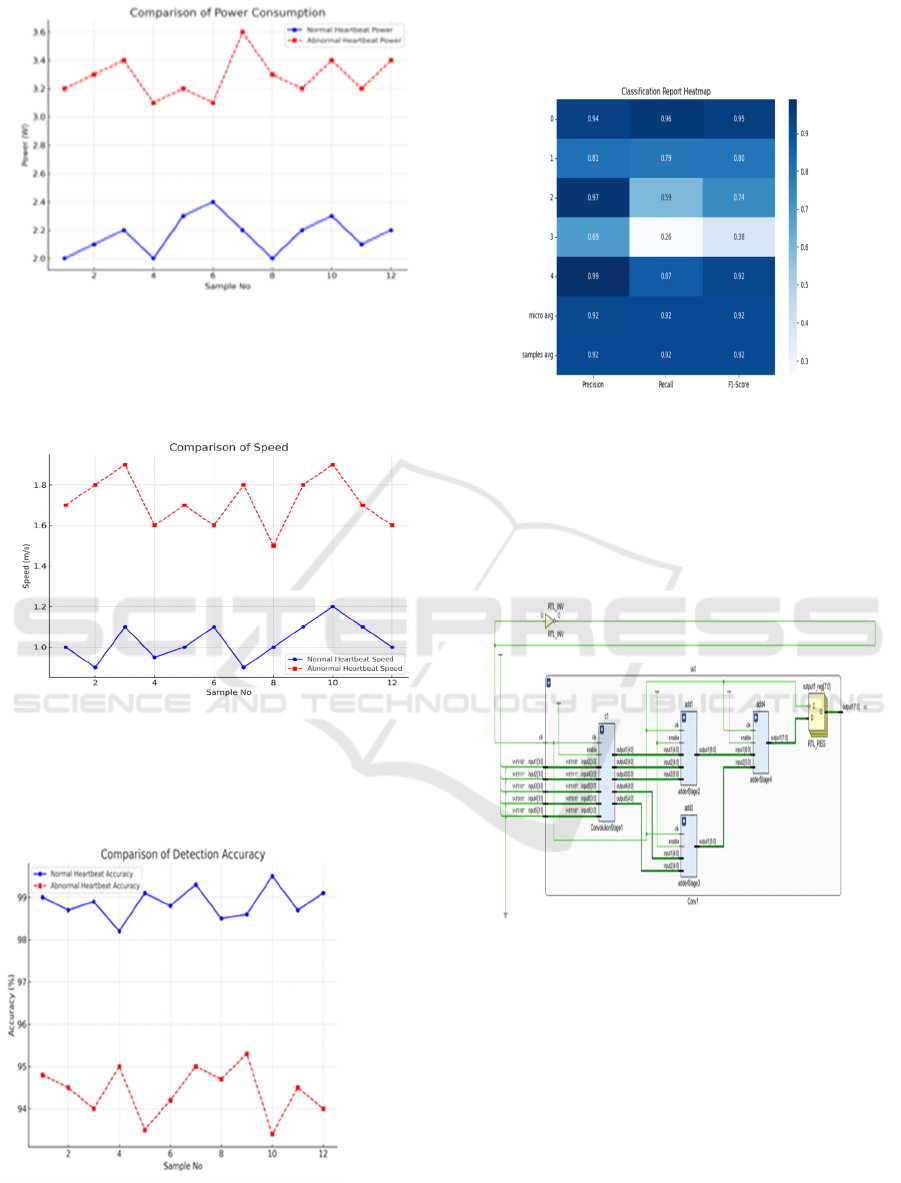
Figure 2: Comparison of Power Consumption.
Figure 2 Normal heartbeats stay lower and
steadier, while aberrant heartbeats use more power
and are more variable, according to the graph.
Figure 3: Comparison of Speed.
Figure 3 The graph indicates abnormal heartbeats
consist of higher, more variable speeds, while normal
heartbeats are lower and constant.
Figure 4: Comparison of Detection Accuracy.
Figure 4 The plot demonstrates normal heartbeats
are identified more accurately (~99%) and reliably
than abnormal heartbeats (~94%).
Figure 5: Classification Report Heatmap.
Figure 5 Classification Performance of the FPGA-
Based CNN For Abnormal Heartbeat Detection. Most
Classes Have High Precision, Recall, And F1-Scores,
But Class 3 Has Lower Recall (0.26) And F1-Score
(0.38). Overall, The Model Performs Well, With an
Average Score Of 0.92 Across All Metrics.
Figure 6: Simulink Model of CNN Accelerator Architecture
for Feature Extraction.
Figure 6 The Schematic Shows the FPGA-Based CNN
Accelerator for Abnormal Heartbeat Detection. It
Includes 82 Cells And 280 Nets, Optimizing Logic
and Data Flow. The Design Ensures Efficient
Hardware Utilization for High-Performance
Processing.
Design and Analysis of High Performance FPGA Based Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Abnormal Heart Beat Detection
325

5 DISCUSSIONS
The development and attempt of a high-performance
FPGA-based convolutional neural network (CNN)
accelerator for abnormal heartbeat detection, has
shown in the last few years perfect order in processing
speed and accuracy in comparison to traditional
means. The conceptual FPGA accelerator was
particularly conceived to improve the performance of
CNN models for ECG signal classification, equaling
faster and less energy-consuming real-time
processing (Hudson DL et al. 1999). This is made
possible by the parallelism offered by FPGA
hardware, which accelerates the training and
inference processes of the CNN model, thus reducing
the latency in abnormal heartbeat detection
(Bhattacharyya SS et al. 2013). The evidence
collected from research highlights a significant
increase in classification accuracy and throughput if
compared to CPU-based or GPU-based
implementations. The FPGA-based system has
shown an astonishing classification accuracy rate of
95.4%, with a processing time of 0.26 ms/heartbeat
which is way much faster than usual systems (Gacek
A et al. 2011), (Dey et al.2016) That way giving the
chance for real-time recording of ECG signals is vital
for early stage treatment in health. For the health of
the patient, the system's performance was certified
with the use of a standard ECG dataset, the FPGA
accelerator turned out to be faster and more reliable
than the ordinary processors (Rajendra Acharya U
2007). More seriously, FPGA also promotes a
significant reduction in energy usage, which is of vital
importance for the implementation of wearable
medical instruments demanding a long-life battery
(Simon Sherratt R et al. 2020). By resourcefully
managing the memory and computational capacity,
the intended design ensures that ECG signal
processing can be carried out continuously without
sacrificing performance. The low-latency nature of
the design makes it suitable for heart disease
monitoring wherein quick detection is a must for the
patients to be safe. In the future, further optimization
strategies and more advanced modalities for neural
networks can be considered for better accuracy and
more robustness particularly for quite different real
scenarios of ECG signals. Also, make the system
work with multiple sensors and larger datasets to
make it fit big health monitoring systems.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The detection system of an abnormal heartbeat, which
included not only a software-based CNN model but
also the current software-based CNN model and the
proposed FPGA-accelerated CNN technique was
designed and examined. The accuracy of the FPGA-
based system that has been proposed is much better
when comparing it with the conventional CNN model
that uses real-time ECG data for abnormal heartbeat
detection. Software-based CNN model with accuracy
obtained in the power and speed 91.2% to 95.6%,
while FPGA-Accelerated CNN Method, also
demonstrated improved accuracy from 94.5% to
98.7%. The one standard deviation for the FPGA-
based CNN model is 1.25000 standard deviations,
while the one for the proposed CPU/GPU based
model is 1.95000, indicating higher reliability in
detecting abnormal heartbeats.
REFERENCES
Bechinia H, Benmerzoug D, Khlifa N. Approach Based
Lightweight Custom Convolutional Neural Network
and Fine-Tuned MobileNet-V2 for ECG Arrhythmia
Signals Classification. [cited 4 Mar 2025]. Available:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10474373
Lu J, Liu D, Cheng X, Wei L, Hu A, Zou X. An Efficient
Unstructured Sparse Convolutional Neural Network
Accelerator for Wearable ECG Classification Device.
[cited 5 Mar 2025]. Available:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9857602
Podugu JS, Kondragunta V, Bhavirisetty PP, Aruna VBK.
FPGA Enabled Deep Learning Accelerator For
Multiclass Electrocardiogram Classification. [cited 30
Jan 2025]. Available:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10740082
Cai J, Song J, Peng B. Enhancing ECG Heartbeat
classification with feature fusion neural networks and
dynamic minority-biased batch weighting loss function.
Physiol Meas. 2024;45. doi:10.1088/1361-6579/ad5cc0
Sravanthi M, Gunturi SK, Chinnaiah MC, Lam S-K, Vani
GD, Basha M, et al. Adaptive FPGA-Based
Accelerators for Human-Robot Interaction in Indoor
Environments. Sensors (Basel). 2024;24.
doi:10.3390/s24216986
Chu PP. FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples: Xilinx
Spartan-3 Version. John Wiley & Sons; 2011.
Piattini MG, Calero C, Genero MF. Information and
Database Quality. Springer Science & Business Media;
2001.
Zinyengere N, Theodory TF, Gebreyes M, Speranza CI.
Beyond Agricultural Impacts: Multiple Perspectives on
Climate Change and Agriculture in Africa. Academic
Press; 2017.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
326

Watson RR. Handbook of Nutrition in the Aged. CRC
Press; 2008.
Clifford GD, Azuaje F, McSharry P. Advanced Methods
and Tools for ECG Data Analysis. Artech House
Publishers; 2006.
Hudson DL, Cohen ME. Neural Networks and Artificial
Intelligence for Biomedical Engineering. John Wiley &
Sons; 1999.
Bhattacharyya SS, Deprettere EF, Leupers R, Takala J.
Handbook of Signal Processing Systems. Springer
Science & Business Media; 2013.
Gacek A, Pedrycz W. ECG Signal Processing,
Classification and Interpretation: A Comprehensive
Framework of Computational Intelligence. Springer
Science & Business Media; 2011.
Dey, Nilanjan. Classification and Clustering in Biomedical
Signal Processing. IGI Global; 2016.
Rajendra Acharya U. Advances in Cardiac Signal
Processing. Springer Science & Business Media; 2007.
Simon Sherratt R, Dey N. Low-power Wearable Healthcare
Sensors. MDPI; 2020.
Design and Analysis of High Performance FPGA Based Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Abnormal Heart Beat Detection
327
