
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card
Fraud
B. Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy
1
, Kawser Naaz Shaik
2
, Neelima Bakkanarappagari
2
,
Jaisnavi Pami Reddy Gari
2
and Jahnavi Reddy Vanna
2
1
Department of CSE, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology (Autonomous), Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of CSD, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology (Autonomous), Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Bank Card Fraud Detection, Machine Learning, LSTM Networks, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN),
Decision Trees, Random Forest, Stacking Classifier, Transaction Data, Fraud Prevention, Real‑Time
Detection.
Abstract: Issues of bank cards fraud detection still represents a huge challenge for financial institutions which
increasingly have to deal with more and more complex actions of crimineity. This work takes up this challenge
by harnessing the power of algorithms to make detection systems more efficient. We use a Kaggle dataset to
develop the following five models and compare them together: LSTM network, CNN-based neural network,
Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Stacking Classifier. CNNs are used to learn complex patterns from
transaction data, while LSTM model sequential relationships and temporal patterns. Decision Trees and
Random Forests offer strong classification through cascaded decisions, combined with ensemble learning.
Furthermore, a Stacking Classifier combines these algorithms well to possibly have better overall
performance. The objective of comparison of these methods is to compares the best method for realtime fraud
detection. It is anticipated that the outcome of the project will make a substantial contribution to making credit
card transaction systems more secure, so as to reduce financial losses and to promote consumer confidence.
1 INTRODUCTION
Credit card fraud detection is an important aspect of
the finance industry as it helps to protect both the
financial institutions and consumers from financial
losses. One of the biggest concerns is the increasing
complexity of fraud.
Requiring sophisticated detection techniques in
order to respond to the evolving threat. There are
various types of credit card fraud which range from
identity theft and account take overs to
manipulations of the transaction. The spread of such
scams has been intensified by the proliferation of
new technologies and methods used by
cybercriminals.
Fraud patterns are constantly changing, and
perpetrators use more sophisticated strategies to
subvert traditional systems. For example, criminals
have evolved to the use of machine learning and AI
to produce and commit the transaction fraud, thus
increasing the difficulty for legacy solutions to
distinguish normal from abnormal. Accordingly,
there is an increasing demand, at deployments with
ideal high security to detect in real time against new
threat.
The financial effect of credit card fraud is
massive. Banks sustain massive losses from
fraudulent activities as well as reputational harm and
loss of consumer confidence. Consumers, for their
part, can face losses of money, stress, and
inconveniences resulting from fraud. The system
costs have direct monetary value which is combined
with intangible costs as efforts to secure systems and
regulatory compliance. Following these challenge
using predictors and developing fraud prevention
system are essential elements in preventing financial
losses, improving public trust, and maintaining the
credibility of the banks’ environment the
trustworthiness of the financial environment. So,
increasing the effectiveness of fraud detection isn't
just a technical need; it's also a flat strategic necessity
for the business of finance.
290
Reddy, B. V. B., Shaik, K. N., Bakkanarappagari, N., Gari, J. P. R. and Vanna, J. R.
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card Fraud.
DOI: 10.5220/0013912000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
290-299
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

1.1 Objective of the Study
Main goal of this investigation is to leverage cutting-
edge ML techniques to enhance the accuracy and
efficiency of detection systems. Fraud remains a
major challenge. For financial institutions because of
their increasing sophistication of fraudulent activities.
Traditional techniques for detecting cheating often
fall short in addressing these evolving threats,
necessitating the exploration of innovative solutions.
To achieve this, the study focuses on applying and
evaluating four distinct machine intelligence
algorithms: CNN, LSTM, Decision Trees, and
Random Forests. Each algorithm offers unique
strengths that can contribute to the detection of
fraudulent transactions. This study seeks to determine
the most efficient method for real-time fraud
detection by evaluating and comparing various
algorithms. The anticipated outcomes should provide
significant insights into enhancing fraud prevention
strategies. security and efficiency of credit card
transaction systems, thereby mitigating financial
losses and enhancing consumer trust.
1.2 Scope of the Study
This research work makes use of a Kaggle Dataset
Create ML models to detect the fraudulent credit card.
one of the essential elements of this work, consists of
transactions along with annotated instances of
fraudulent and non-fraudulent activities. The dataset
is comprised by multiple features types, such as, the
transaction value and the time. and user's specific
information, which is necessary for the training and
testing of the algorithms. Nevertheless, the dataset
could be inherently restricted and not balanced
between transactions of fraud and non-fraud. Such
class imbalance also creates difficulty for the
algorithms to achieve high accuracy and to reduce
both high false positives and negatives. In terms of
scale, the work covers four different machine
intelligence algorithms, CNN, LSTM, Decision Trees
and Random Forest. Every algorithm is picked to
analyse another resides of fraud detection– CNNs for
the identification of complex patterns, LSTM for the
temporal relation of events, Decision Trees &
Random Forests for reliable classification. The goal
is to compare these techniques to see which is the
best for instantaneous fraud detection.
1.3 Problem Statement
Fraud Detection Is Still A Problem Fraud detection
is still one of the key issues in the financial sector and
traditional solutions are perpetually behind the
rapidly evolving fraudulent tactics. Traditional
approaches to fraud prevention often rely on rule-
based systems, where suspicious activities are
identified by predefined criteria and rules. While
such systems are able to be configured to work
against known forms of fraud, they are by nature,
static. They miss new, sophisticated fraud scams,
much of the time that do not adhere to the
predetermined rules. Such a restriction leaves many
spaces open for fraud prevention, and the new types
of fraud cannot be discovered. Another major
challenge is that the dynamic of the Fraudsters is
always changing up their methods, in such a way that
they can conduct their scams. They are constantly
updating and refining their tactics to outpace
detection systems. drill security holes through
detection systems. They are using advanced methods
like social engineering, fictitious identities, and
advanced phishing strategies not effectively
mitigated by traditional systems. This flexibility
results in an ongoing pillow fight between the bad
guys and the detect system, one in which the bad guys
play even more of the game than the detection
systems.
Furthermore, conventional approaches generally
use a few low-quality features or models that are not
able to explain the intricate multiple aspects of fraud.
They may also suffer from undesirable high rates of
False positives increasing operational costs and
customer dissatisfaction. With the development of
fraud, more intelligent and flexible techniques are
urgently required. One potential solution is machine
intelligence, which can be used to analyse vast
amounts of transaction data and trace out subtle,
unobserved patterns that could indicate fraudulent
behaviour. Therefore, added with automatic training
in the traditional identification method mentioned
above, the integration use of the automatic training
ability of M/F and traditional identification method
would fill the gap and improve the overall detection
rate and the detection efficiency.
2 RELATED WORK
Recognizing the card transaction theft. Has
undergone evolutionary development process due to
advancement in fraudulent techniques over the years.
In the past, fraud detection started manually, and only
Rule-based systems that searched for probably
fraudulent transactions, that matched a set of pre-
defined rules were used. Such systems have some
underlying deficiencies; they were not designed to
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card Fraud
291

adapt to new types of frauds that tended to occur more
often, which resulted in increased numbers of false
positives and missed frauds (
Adil et al., 2024).
Techniques for fraud detection began with the use
of statistics and then it advanced to the use of anomaly
detection algorithms. Dynamic identification at the
more detailed level could be achieved through
statistical methods like statistical measures of
transactional behavior such as logistic regression and
statistical outlier detection (
Al Ali et al., 2024)
However, these models have the issues of high
variability and complexity of the fraud transactions
(
Alarfaj et al., 2022)
Some of the changes that characterized the
environment of fraud detection with the help of ML
methods are the following: More algorithms were
introduced, and patterns of fraud identification were
becoming more complex, due to such approaches
searching for patterns in historical data, and adapting
to new trends. These Methods that improved the
effectiveness of the fraud detection systems in
addition to reducing reliance on manual creation of
rules (
Aurna et al., 2024).
CNN and LSTM represent the latest
advancements in fraud detection technology. CNNs
excel at recognizing complex patterns and
irregularities within transaction data, while LSTM are
adept skilled at recognizing time-related
dependencies and patterns in sequences. These
advanced techniques offer promising improvements
in real-time fraud detection, as they can learn complex
relationships within the data and adapt to evolving
fraudulent tactics (
Ghaleb et al., 2024).
In summary, thanks to the continuous progress in
machine intelligence technologies, credit card fraud
detection systems have become more powerful, able
to cope with the ever-transitional nature of credit card
fraud.
Almost all types of ML algorithms are effectively
used for CC fraud detection. Supervised: Different
models like Decision Trees Classifier, Random
Forest Classifier create models and assign new
transactions as fraud or not using old transaction data.
The proposed methods utilise a hierarchical decision-
making and ensemble learning to improve both
discrimination accuracy and robustness of the
system. Deep learning algorithms, including CNN
and LSTM, have also demonstrated potential.
Because CNN model includes convolutional layers,
it can effectively find complex patterns in transaction
data.jpg (796×512). This allows them to capture the
subtle irregularities exhibited in the transaction’s
sequences, which makes them robust for smart
forensic. On the other hand, LSTM are capable of
working with sequential data and are very good at
capturing temporal dependencies, which allow them
to model the chronological order of transactions and
capturing patterns through time
Ileberi, E., & Sun, Y.
(2024).
As we could see from the past Testimonials, these
methods are tremendous help in achieving better
accuracy in detecting the fraud. For instance, CNNs
are used to identify high-precision fraudulent
patterns and LSTM are implemented to store
temporal patterns among transaction sequences.
Ensemble approaches such as the Random Forests
have been proven to enhance the detection
performance by exploiting the joint properties from a
number of decision trees
Kundu, A., Panigrahi, S., Sural,
S., & Majumdar, A. K. (2009).
In summary, ML
represents a strong move forward in fraud detection
with more accurate, efficient and adaptive solutions
than the classical ones. These methods are evolving
and their advancements will ensure even better
defenses for money exchanges and potential
consumers
CNNs which exhibit a decent performance in the
image pattern recognition part is available to use for
financial data analysis such as fraud detection. CNNs
are designed to automatically learn feature pyramids
stacked through layers by means of stacked unit of
convolution, pooling and fully connected network
across layers without any human intervention. This
configuration is especially useful in pattern
recognition and deviations.
From the norm within transactional data set,
which may indicate fraudulent activities
Mienye, I. D.,
& Jere, N. (2024). In the context of fraud detection,
CNNs use their ability to understand spatial relations
within transaction sequences or image of the
transactions data. For instance, CNNs can detect
anomaly or shift in the pattern sequences such as that
of a customer’s transactions that may point towards
fraud. This ability is attained by the network as it
operates concurrently at multiple levels of abstraction
from low to high levels of features
Le, T. T. H.,
Yeonjeong, H., Kang, H., & Kim, H. (2024).
One major use of employing CNN in fraud
identifying is that they are able to properly identify
shapes and anomalies that would otherwise not be
easily recognizable even by other complex
mathematical methods. An advantage over other
models is that CNNs can learn features by themselves
and there is no need for feature selection from the raw
images. This leads to more effective implementation
of a fraud detection system that is more accurate,
efficient in its operations and capable of expanding to
cater for even larger crowds
Shi, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, M.,
& Zhang, L. (2025).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
292

However, CNNs also have limitations. They
demand significant computational power for training,
particularly when dealing with large datasets
Srivastava, A., Kundu, A., Sural, S., & Majumdar, A. K.
(2008).
In summary, while CNNs offer powerful pattern
recognition capabilities that can significantly improve
fraud detection systems, they should be used in
conjunction with other techniques to address their
limitations and achieve optimal performance in
detecting fraud.
LSTM is an expanded version of RNN
particularly developed to tackle the issues arising
from applying usual RNN to sequence data structure.
LSTM are especially suited to model the
dependencies in time and thus can benefit the tasks
that deal with time series data such as credit card
transaction monitoring
Xie, Y., Liu, G., Yan, C., Jiang, C.,
Zhou, M., & Li, M. (2024).
The feature of recurrent neural networks One of the
key benefits for the utilization and maintenance of
long-term dependencies is the use of conventional
RNNs sometimes face the problem of vanishing and
exploding gradients which affects the learning of long
term dependencies. LSTM resolve this problem by
their structure that is comprised of memory cells and
gates. These components also enable the network to
remember information over different sequences and
regulate the data flow within the network so that
temporal information that is relevant is retained and
other redundant information is discarded As for fraud
detection, LSTM is used to scrutinize transaction
sequences to detect an abnormal activity that can be
related to fraud. For example, the fraudulent activities
may appear to have a temporal relationship that may
not be characteristic of normal circumstances. With
LSTM, these sequential patterns are well captured
thereby making it easy to find the inherent time
sequential dependencies which other methods may
not detect. (
Xie, et al., 2023) Hence, LSTM have the
capability of processing sequences with variable
length which is more suitable for transactions which
are often random in nature. Therefore, LSTM is
useful in improving the real time fraud detection
systems due to the importance of timely and accurate
identification of fraudulent transactions based on
temporal data patterns in particular All in all, the
LSTM plays an important role in developing and
improving the performance of fraud detection
systems due to its ability to model complex temporal
data.
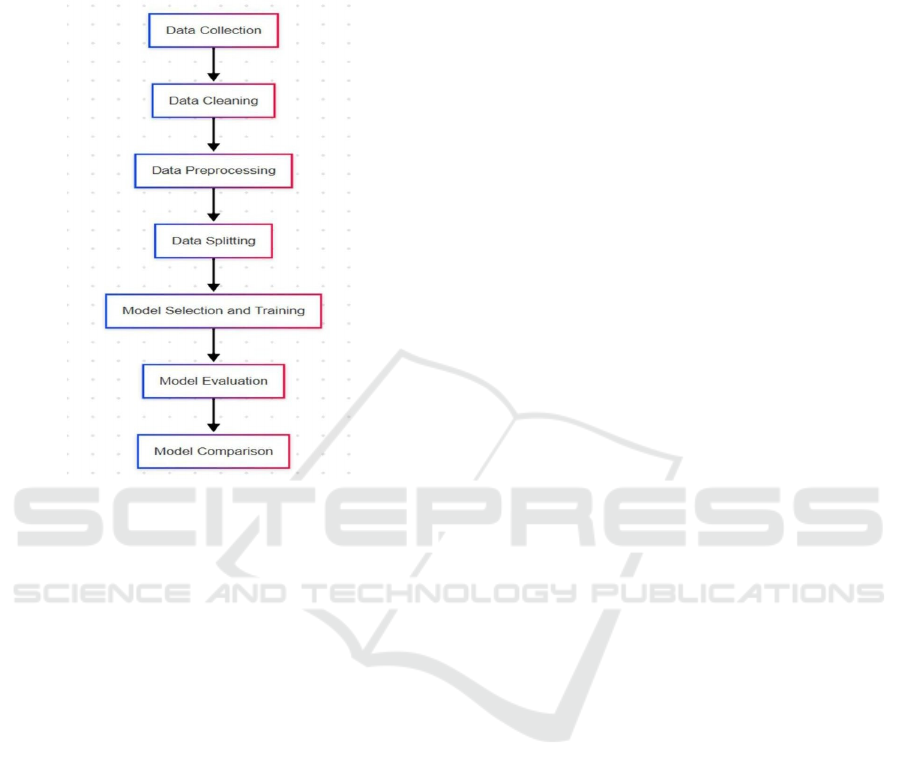
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM
3.1 Problem Definition
Thus, as it is apparent that more and more people are
engaging in online transactions, fraud becomes a very
important issue and a major concern for the financial
institutions. Figure 1 gives the Proposed Methodology
flowchart.
3.2 Data Collection
The dataset for fraud detection is sourced from
various reliable platforms, including banking
institutions, transaction logs, payment gateways, and
fraud investigation reports. The system collects and
analyzes both real-time and historical transaction data
to improve predictive performance.
3.2.1 Key Data Sources Include
• Bank transaction records: Capturing details like
transaction amount, time, merchant details, and
mode of payment.
• Merchant payment logs: Identifying anomalies
in merchant-side transaction behaviors.
• User behavioral data: Tracking spending
patterns, frequency of transactions, and device
usage.
• Fraudulent transaction reports: Learning from
previous fraud cases to identify emerging
fraudulent patterns.
To ensure that the dataset is representative of different
fraud scenarios, diverse sources and different
geographical regions are considered to train the
model on real-world fraud behavior.
3.3 Data Preprocessing
Raw transaction data often contains inconsistencies,
missing values, and redundant information. Before
feeding the data into the machine learning models,
rigorous preprocessing is performed to enhance data
quality and model efficiency.
3.3.1 Data Preprocessing Steps Include
• Removing duplicate transactions and irrelevant
features that do not contribute to fraud
prediction.
• Handling missing values through imputation
techniques like mean, median, or KNN-based
imputation.
• Standardizing transaction logs across different
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card Fraud
293

banks and financial services for uniformity.
• Feature extraction and transformation to
improve fraud detection accuracy, such as
deriving transaction frequency per user or
aggregating spending behavior over time.
This step ensures that the data fed into the model is
well-structured, clean, and optimized for meaningful
analysis.
3.4 Normalization
To maintain consistency across different sources and
scales of data, normalization and standardization
techniques are applied.
3.4.1 Normalization Techniques Include
• Min-Max Scaling: Used to scale numerical
values between a fixed range, ensuring that no
single feature dominates the model.
• One-hot encoding: Converts categorical
variables such as transaction type or location
into numerical form.
• Log transformations: Applied to transaction
amounts and frequencies to reduce skewness
and improve model interpretability.
These normalization techniques help in improving
model convergence and accuracy by reducing
variability and inconsistencies in the dataset.
3.5 Feature Engineering
Feature engineering is a very important process in the
ability of the fraud detection models to accurately
predict cases of fraud. High-quality features are by far
the best elements that help in class distinction
implying real from fake.
3.5.1 Key Features Engineered
• Transaction velocity features: Analyzing how
frequently a user performs transactions in a short
time span.
• Spending behavior trends: Identifying sudden
changes in spending habits that may indicate
fraud.
• Geolocation tracking: Comparing the user’s
current transaction location with historical
locations to detect anomalies.
• Device fingerprinting: Identifying if
transactions are initiated from an unknown
device or suspicious IP addresses.
These engineered features enable the model to make
more informed predictions by leveraging behavioral
and contextual data.
3.6 Model Development
The fraud detection system utilizes both machine
learning and deep learning models to achieve high
fraud detection accuracy.
3.6.1 Machine Learning Models
Implemented
• Decision Trees: Decision trees employ a decision-
making approach to identify fraud transactions
out of the genuine ones.
• Random Forest: It is an enhanced model which
works as an ensemble model and has ability to
reduce variance in the result.
• Stacking Classifier: A class of models that uses an
aggregation of several models to make the best
forecast.
f) Deep Learning Models Implemented:
• Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs):
Extracts complex fraud patterns from
transaction data.
• Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): Captures
sequential dependencies and anomalies in
transactional behavior.
3.6.2 Models
1. LSTM Networks (Long Short-Term Memory)
Definition:
LSTM is a sort of Recurrent Neural
Network that is specially designed to work on
sequences. It provably addresses the vanishing
gradient problem, which means that it is very
effective in learning long temporal dependencies
in time series data.
3.6.2.1 Working Mechanism
1. Input Processing: Sequential data (e.g., timeseries
transactions) is fed into the LSTM model.
2. Cell State & Memory Units: The LSTM cell
maintains an internal memory that allows it to
remember important information across long
sequences.
3. Forget Gate: Decides at which timestep which
information has to be forgotten or rather has to be
remembered.
4. Input Gate: Regulates the addition of new
information into the cell state.
5. Output Gate: He/She shows the output after the
training at each time step and transfers the related
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
294
information to the next state.
6. Training & Optimization: The network is trained
using backpropagation through time (BPTT) to
adjust weights and minimize prediction errors.
Figure 1: Flow chart for proposed methodology.
2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
Definition:
CNN are a subset of deep learning
algorithms that are used for handling data that is
arranged in a grid-based format like the image
and sequential datasets. One of the most
important ideas in CNNs is that convolution
layers learn of spatial hierarchies of features
automatically.
3.6.2.2 Working Mechanism
1.
Convolutional Layer: Applies filters to extract
spatial features from input data.
2.
Pooling Layer: Reduces dimensionality while
preserving essential information (e.g.,
MaxPooling, AveragePooling).
3.
Activation Function: Uses nonlinear functions
(ReLU, sigmoid) to introduce non-linearity.
4.
Fully Connected Layer: Connects neurons to
produce a final classification or prediction.
5.
Softmax Layer: Converts final outputs into
probability scores for classification.
6.
Backpropagation & Optimization: Weights are
updated using gradient descent and loss
minimization functions like cross-entropy.
3. Random Forest
Definition:
Random Forest is an ensemble
learning method that combines multiple decision
trees to improve classification accuracy and
reduce overfitting.
3.6.2.3 Working Mechanism
7.
Bootstrapping: Creates multiple random subsets
of training data.
8.
Decision Tree Construction: Each subset is used to
train a different decision tree.
9.
Feature Selection: A random subset of features is
considered for each tree at split points.
10.
Aggregation (Voting Mechanism): Predictions
from all trees are averaged or majority-voted to
determine the final classification.
4. Stacking Classifier
Definition:
Whereas the stacking classifier is an
ensemble learning technique that combines low
level predictors as a number of base classifiers to
enhance the predictive accuracy. It has a meta-
classifier that is used for combining the results
from different models.
3.6.2.4 Working Mechanism
1.
Base Models: Trains multiple independent models
such as Decision Trees, SVM, and Neural
Networks.
2.
Layered Learning Approach: The predictions
from these models are used as input for a
secondary model (meta- classifier).
3.
Meta-Classifier Training: The final model learns
the best way to combine predictions from base
models.
4.
Final Prediction: The meta-classifier generates
the final output by weighing the strengths of base
models.
Advantages
• Reduces bias by leveraging multiple algorithms.
• Handles complex patterns that single models
may miss.
• Improves classification accuracy and
generalization.
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card Fraud
295
4 DISCUSSION AND RESULTS
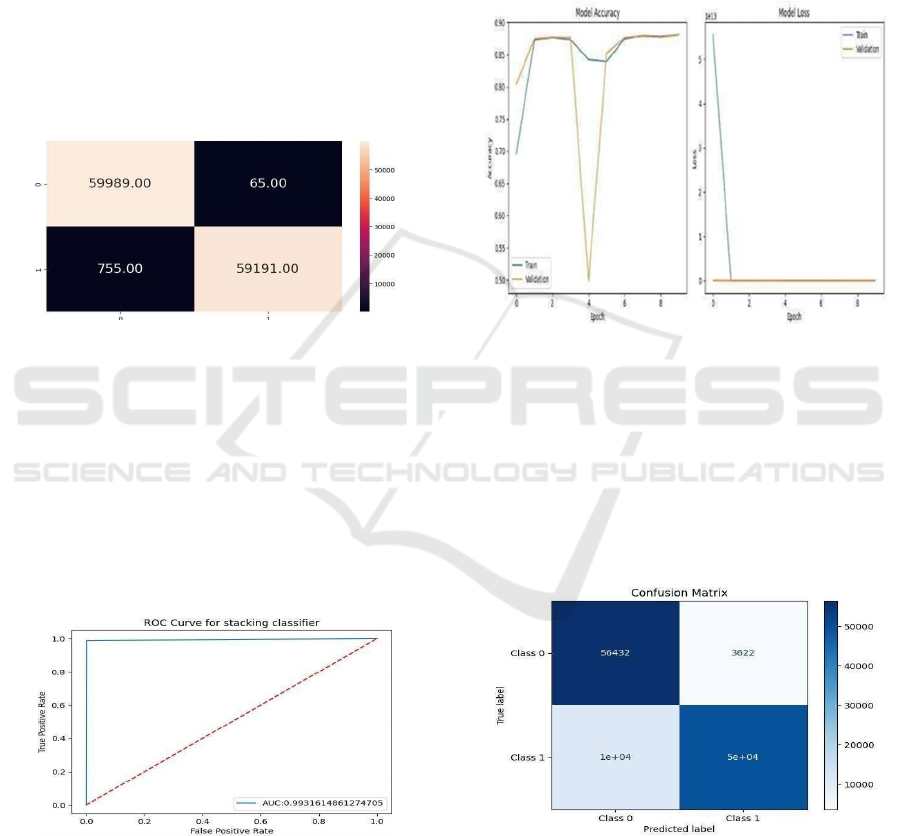
4.1 Stacking Classifier Model Results
This Figure 2 shows how Stacking Classifier recall
score is calculated which is vital in determining its
ability to correctly identify the positive cases that is
fraudulent transactions as in this case. The recall
score () function calculates the measure that
represents what percentage of the actual fraudulent
cases this method identified. The recall of
0.9892236364044774 means that the model for fraud
detection is not missing many of the transactions
which are fraudulent, thus reducing the false
negatives.
Figure 2: Confusion matrix for stacking classifier.
This rather self-explanatory image presents the
confusion matrix of the Stacking Classifier. The
working of the matrix indicates the number of True
Positives, False Positives, False Negatives and True
Negatives which compare the true labels with the
predicted labels. tp = 59,989 means correctly
classified non-fraudulent transactions and tn = 59,191
means correctly classified fraudulent transactions
swhile fn = 755 and fp = 65 means the misclassified
transactions.
Figure 3: ROC curve for stacking classifier.
In Figure 3, ROC curve Receiver Operating
Characteristic curve displayed here depicts the
performance of Stacking Classifier in terms of
distinguishing between the two classes namely
fraudulent and non-fraudulent transactions. The curve
is a graph of the TPR on y-axis and FPR on the x-axis
and the AUC is used to assess the model on a general
scale. The finally calculated value of the AUC =
0.9931614861274705 means a very high model
performance as the AUC closer to 1 means that the
given model is good enough to differentiate between
fraud and genuine transactions.
4.2 CNN Model Results
Figure 4: Accuracy plot for CNN.
This Figure 4 illustrates how the accuracy and loss
of a given model change depending on the training
and validation epochs in machine learning. The
accuracy graph on the left represents performance of
the model, where training accuracy is displayed by
line of blue color while validation accuracy of the
model is displayed by line of orange color; hence the
model is able to learn effectively.
Figure 5: Confusion matrix for CNN.
Figure 5 confusion matrix provides a detailed
overview of the model's predictions for a binary
classification problem. It compares the true labels
with the predicted labels.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
296
4.3 LSTM Model Results
Figure 6: Accuracy Plot for LSTM.
In Figure 6, the left graph in the image is indicating
the performance of the Model Accuracy in terms of
epochs and for Training and validation data. The
Figure 2 also shows the blue line marked as ‘Train’
that represents training accuracy and the orange line
marked as ‘Valid’ for validation accuracy. There is a
slight fluctuation at the beginning of the epochs for
both validation loss and validation accuracy, but
validation accuracy remains at a high level, 0.875 at
this time. The curves indicate no over-learning of the
model as it was learned quite well and generally on
the higher clean data.
Figure 7: Confusion matrix for LSTM.
Figure 7 confusion matrix describes the ability of
the model in predicting two classes: Class 0: Non-
Fraudulent Transactions and Class 1: Fraudulent
Transactions.
•
True Negatives (TN): the number of transactions
that are non-fraudulent were 59771.
•
False Positives (FP): 2,083 transactions out of the
complete transactions that were categorized as
fraudulent were actually normal or nonfraudulent.
•
False Negatives (FN): 6,781 cases of the
fraudulent transactions were classified as
nonfraudulant.
•
[^14] True Positive (TP): Out of actual fraudulent
53,165 transactions, 53,165 of them were identified as
such.
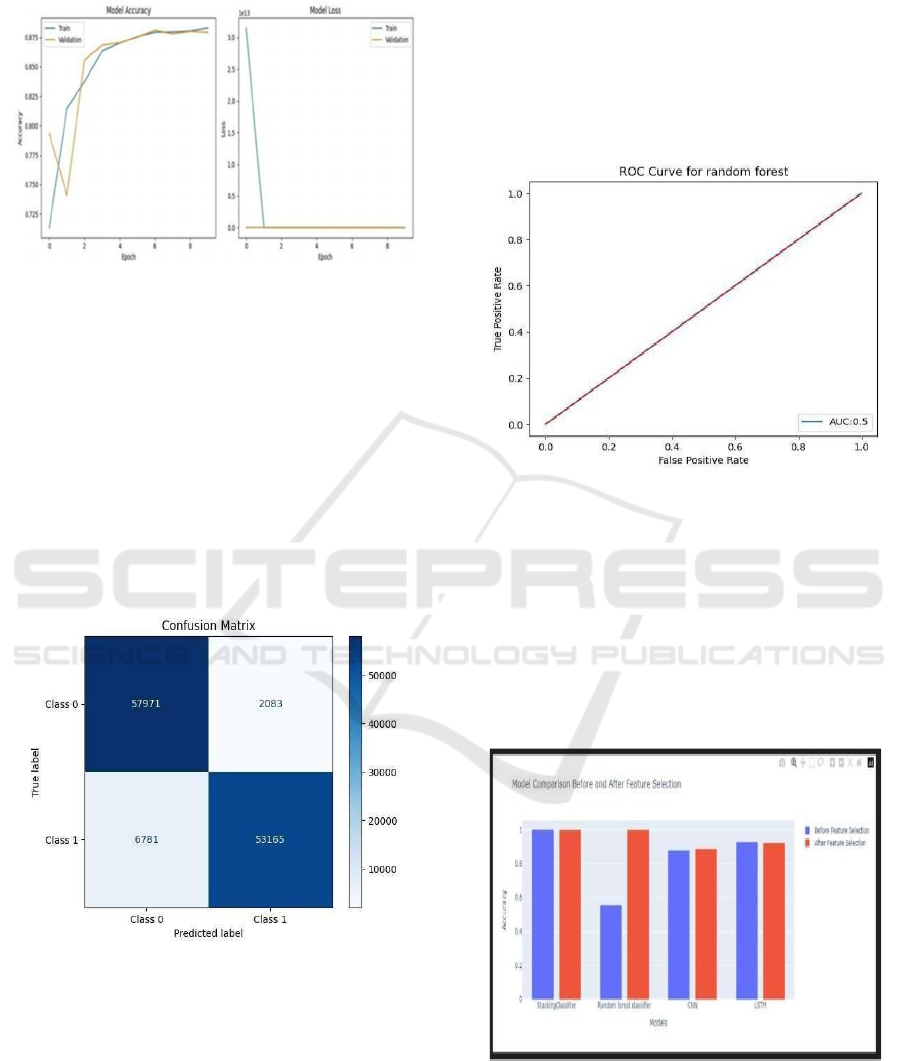
4.4 Random Forest Model Results
Figure 8: ROC curve for random forest.
The Figure 8 involves the representation of a
graph for the Random Forest classifier that is used to
predict whether the transactions are fraudulent or not
fraudulent based on the sensitivity and specificity.
ROC plot depicts TPR or sensitivity rate, which is the
proportion of actual positives among the positive
conclusions drawn while comparing it with FPR, or
the proportion of actual negative among the negatives
concluded.
Figure 9: Accuracy comparison plot for all models.
The Figure 9 image displays a bar chart
comparing the accuracy of different models before
and after feature selection. The models are: Stacking
Classifier, Random Forest Classifier, CNN, and
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card Fraud
297

LSTM. The bars represent accuracy, with the blue
bars showing the performance before feature selection
and the red bars after feature selection, highlighting
performance improvements.
5 DISCUSSION
Among the useful features that are analyzed in the
given paper are as follows: It focuses on the
performance of various machine learning algorithms
in the given dataset. One is the best among all the
other models that is accurate with 99.7% to predict
the meaning of a goal which makes the Decision Tree
and Random Forest models to be the most appropriate
for all complex patterns. This is followed by SVC
with 74.1% and therefore the confusion matrix as an
implication of the areas that should be classified
disparagingly though the two performed badly (
Zhu et
al., 2021).
6 CONCLUSIONS
Therefore, by comparing the various models of the
machine learning one can draw a conclusion as to the
difference in classification of the results. The Decision
Tree and obtained 99.7% accuracy randomly forest
models indicating that the models are capable of
capturing complex patterns and relation that has been
established in the data set.
Altogether, it compared KNN’s effectiveness, and
though it outperformed the last two models, suggested
the optimization of the model. Based on the above
analysis this shows that selecting the correct
algorithms depend on the problem under
consideration.
7 FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
Thus, such consideration of models of ML confirms
that various approaches may lead to a distinct
classification performance. The Decision Tree and
Random Forest models had the highest accuracy of
99.7 percent and the graph thus showing that the
models are capable of capturing complex patterns and
relationship embedded in the data set.
These combined methods utilize the outcomes of
several decision trees, that makes these trees perfect
for problems when overtraining is an important
factor.
REFERENCES
Adil, M., Yinjun, Z., Jamjoom, M. M., & Ullah, Z. (2024).
OptDevNet: An Optimized Deep Event-based Network
Framework for Credit Card Fraud
Detection. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACC
ESS.2024.3458944
Al Ali, A. I., S, S. R., & Khedr, A. M. (2024). Enhancing
financial distress prediction through integrated Chinese
Whisper clustering and federated learning. Journal of
Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and
Complexity, 10(3), 100344.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.J
OITMC.2024.100344
Alarfaj, F. K., Malik, I., Khan, H. U., Almusallam, N.,
Ramzan, M., & Ahmed, M. (2022). Credit Card Fraud
Detection Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning
and Deep Learning Algorithms. IEEE Access, 10,
39700–39715. https://doi.org /10.1109/ACCESS.2022
.3166891
Aurna, N. F., Hossain, M. D., Khan, L., Taenaka, Y., &
Kadobayashi, Y. (2024). FedFusion: Adaptive Model
Fusion for Addressing Feature Discrepancies in
Federated Credit Card Fraud Detection. IEEE Access.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3464333
Ghaleb, F. A., Saeed, F., Al-Sarem, M., Qasem, S. N., &
Al-Hadhrami, T. (2023). Ensemble Synthesized
Minority Oversampling-Based Generative Adversarial
Networks and Random Forest Algorithm for Credit
Card Fraud Detection. IEEE
Access, 11, 89694– 89710 .https: //doi.org/10.1109 /A
CCESS.2023.3306621
Hua, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, X., Zhang, B., & Liang, L. (2007).
Predicting corporate financial distress based on
integration of support vector machine and logistic
regression. Expert Systems with Applications, 33(2),
434–440.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2006.05.006
Ileberi, E., & Sun, Y. (2024). Advancing Model
Performance with ADASYN and Recurrent Feature
Elimination and Cross-Validation in Machine
Learning- Assisted Credit Card Fraud Detection: A
Comparative Analysis. IEEE Access, 12, 133315–
133327.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3457922
Kundu, A., Panigrahi, S., Sural, S., & Majumdar, A. K.
(2009). BLAST-SSAHA hybridization for credit card
fraud detection. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and
Secure Computing, 6(4), 309–315.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TDSC.2009.11
Le, T. T. H., Yeonjeong, H., Kang, H., & Kim, H. (2024).
Robust Credit Card Fraud Detection Based on Efficient
Kolmogorov-Arnold Network Models. IEEE Access.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3485200
Mienye, I. D., & Jere, N. (2024). Deep Learning for Credit
Card Fraud Detection: A Review of Algorithms,
Challenges, and Solutions. IEEE Access, 12,
96893–96910.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3426955
Shi, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, M., & Zhang, L. (2025). Deep
learning for enhanced risk management: a novel
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
298

approach to analyzing financial reports. PeerJ.
Computer Science, 11, e2661.https://doi.org/10.7717/
PEERJCS.2661/SUPP-4
Srivastava, A., Kundu, A., Sural, S., & Majumdar, A. K.
(2008). Credit card fraud detection using Hidden
Markov Model. IEEE Transactions on Dependable
and Secure Computing, 5(1), 37–48. https://doi.org/10
.1109/TDSC.2007.70228
Xie, Y., Liu, G., Zhou, M. C., Wei, L., Zhu, H., Zhou, R., &
Cao, L. (2023). A Spatial– Temporal Gated
Network for Credit Card Fraud Detection by Learning
Transactional Representations. IEEE Transactions on
Automation
Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1109/TA
SE.2023.3335145
Xie, Y., Liu, G., Yan, C., Jiang, C., Zhou, M., & Li, M.
(2024). Learning Transactional Behavioral
Representations for Credit Card Fraud Detection. IEEE
Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning
Systems, 35(4), 5735–
5748. https://doi.org/10.1109/TN NLS.2022.3208967
Zhu, K., Zhang, N., Ding, W., & Jiang, C. (2024). An
Adaptive Heterogeneous Credit Card Fraud Detection
Model Based on Deep Reinforcement Training Subset
Selection. IEEE Transactions on Artificial
Intelligence, 5(8),4026–4041. https://doi.org/10.1109
/TAI.2024.3359568
Advanced Machine Learning Models for Detecting Credit Card Fraud
299
