
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep
Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI
A. Hema
1
, C. H. Hussaian Basha
2
, S. Senthilkumar
3
, B. S. Gopika
4
, R. Muthaiyan
5
and R. Ramanan
6
1
Department of Master of Computer Applications, E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College,
Nagapattinam, 611002, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, SR University, Hanumakonda 506371, Telangana, India
3
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College,
Nagapattinam, 611002, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering, NH-47,
Palakkad mainroad, Navakkarai post, Coimbatore – 641105, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, University College of Engineering,
Thirukkuvalai, 610204, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College,
Nagapattinam, 611002, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Computed Tomography, Convolutional Neural Networks, Early
Detection.
Abstract: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a widespread and debilitating disease of the lungs that
requires the patient to endure, requiring a precise and timely diagnosis to aid in care. In this research, an
innovative method is introduced that combines the classical machine learning methods with feature
extraction based on deep learning to detect and classify the COPD severity from Computed tomography
(CT) scans. We employ CNNs pretrained on large amounts of medical data to extract deep features showing
indicative structural changes in the lung, including emphysema and thickening of airway walls and other
morphological deformations. These features are then used by Support Vector Machine (SVM) to get the
accurate COPD severity classification. This study uses Gradient Weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-
CAM) and Shapley Additive explanations (SHAP) to explain the method prediction with the purpose of
increasing the transparency and interpretability and increasing confidence in AI-driven diagnostics. The
proposed methodology is validated on the LIDC-IDRI (Lung Image Database Consortium Image collection)
dataset for emphysema severity and airway abnormalities. Results of the comparison show that this hybrid
method is more accurate or robust than CNN or traditional ML methods alone. Results show the importance
of explainable and efficient AI in medical imaging in early COPD detection, monitoring of drug efficacy,
and severity assessment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Image processing plays a major role in the research
field in recent years (L. Ramachandran, et al, S.
Senthilkumar, et al). Chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD) is a major global health issue that
contributes in a major way to despair and death and
places a heavy burden on the health system in a
gradual way. This progressive respiratory condition
is associated with persistent symptom and airflow
obstruction and is often caused by prolonged
exposure to harmful substance like cigarette smoke
and environmental pollutants. Delaying the
diagnosis increases the risk of irreversible lung
damage and loss of more than half of the lungs and
their function." Imaging by Computed Tomography
(CT) has an important role in diagnosis and
monitoring of COPD for providing detailed
visualization of lung structures. CT scans are
effective means to analyse key indicators of COPD
such as emphysema, airway wall thickening and
hyperinflation. Unfortunately, the current traditional
diagnostic methods are based mainly on manual
208
Hema, A., Basha, C. H. H., Senthilkumar, S., Gopika, B. S., Muthaiyan, R. and Ramanan, R.
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI.
DOI: 10.5220/0013910500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
208-217
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

interpretation of radiologists, which is a time
consuming, and variable and observer biased
process. The existence of such challenges suggests
that there is a need for an automated accurate and
efficient diagnostic tool to help clinicians analyze
complex medical images exists. Medical imaging
has been revolutionized with the advocacy of image
processing and machine learning (ML)
advancements, which now make it possible to detect
and classify the diseases without the intervention of
physicians. It has been shown that deep learning
methods on Convolution Neural Network (CNN)
can identify complex patterns in medical images
very well. Although CNN based methods lack
interpretability and are complex to overfitting, their
application in specialized areas including COPD
diagnosis is ambiguous. In order to tackle these
limitations, this study presents a hybrid approach
combining deep feature extraction and classic ML
algorithms to improve species classification
accuracy and reliability in the presence of COPD
classification. High level structural features of CT
scan are extracted using pre-trained CNNs, which is
used to detect lung abnormalities related to COPD.
Traditional ML classifiers such as SVMs are applied
to these extracted features using the features and the
features process itself feeds the domain specific to
the short dataset. The above integration of method
integrated the advantages from both deep learning
and classical ML to yield an effective COPD
detection and severity assessment framework.
In the medical field, interpretability is essential
since medical personnel need to have faith in AI-
driven judgements and guarantee their ethical use.
Explainable AI (XAI) methods are integrated into
the diagnostic procedure to accomplish purpose. By
highlighting lung regions that have a major impact
on predictions, these techniques help physicians
assess AI-generated results and comprehend the
reasoning behind automated diagnoses. The LIDC-
IDRI dataset, a publicly accessible collection of
high-resolution CT scans, is used to assess the
suggested methodology. By concentrating on
important characteristics including the degree of
emphysema and changes in the structure of the
airways, this study shows that hybrid machine
learning approaches can provide precise,
comprehensible, and effective diagnostic solutions
for COPD diagnosis and staging.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In (Manoharan, S., 2020.) a new graph cut
segmentation algorithm is proposed, which has been
enhanced to perform lung cancer detection from CT
images. This method has the advantage of better
accuracy of segmenting soft tissues and weak edges
over conventional techniques like watershed and
basic graph cut. They have merits of less energy
consumption and higher accuracy in detecting
nodules, however, they also have limitations of high
memory usage and need further optimization of the
energy function. The proposed algorithm provides
benefit to clinical application by assisting in early
and precise lung cancer detection.
According to research (Immanuel D, J. and Leo
E, S.A., 2024), it proposes a Gradient Descent
Optimization (GDO) model for predicting
cardiovascular disease (CVD) based on machine
learning. The study used data from the UCI
repository and used techniques such as SVM, KNN,
NB, ANN, RF and GDO and the proposed GDO had
an accuracy of 99.62%. The advantages are high
sensitivity (99.65%) and specificity (98.54%) and
good performance in early CVD diagnosis. The
study has; however, some limitations including a
small dataset and need for further feature fusion for
broad application.
In research Kumar, S.,et al, a multimodal
diagnostic approach is presented that uses the CT
scan images and lung sound (cough) data. The study
uses ML and DL techniques like CNNs to reach the
accuracy of 97.5% for early COPD detection. The
merits are high accuracy, the integration of multiple
data modalities, and noise robustness in diagnostic
data. There are, however, limitations that require
large datasets for effective training of the models
and scalability and eventual implementation in
reality. The research Deng, X., et al presents a novel
framework based on the Auto-Metric Graph Neural
Network (AMGNN). Radiomics and 3D CNN
features of CT images are combined towards the
prediction of COPD stages with 89.7% accuracy.
The merits are that superior precision (90.9%) and
AUC (95.8%) are achieved over traditional methods
such as PRM biomarkers. But it is limited by
computational resource requirement and difficulty in
integrating multi-phase CT data. This technique
presents significant improvement in detecting and
managing COPD stage.
Research (Bozkurt, F., 2022) introduces the
HANDEFU framework. The system is innovative in
the combination of handcrafted, deep, and fusion
based feature extraction techniques. The LBP+SVM
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI
209
model for the COVID-19 diagnosis was
demonstrated to have a superior accuracy up to
99.36%. The merits of the framework are flexibility,
dynamic structure and high precision, and
limitations include computational complexity and
execution time in deep and fusion based methods.
Such an approach offers a scalable solution for early
and reliable detection of COVID-19 from medical
images. In Si, et al Hybrid method is presented using
abdominal CT images in its merits, it has rapid
processing (18.6 seconds per patient), high
diagnostic accuracy for specific tumors (e.g., 100%
for IPMN) and the ability to interpret decisions
using saliency maps. It, however, suffers from the
inability to handle imbalanced data and diagnose
normal cases. This has clinical potential for
preoperative decision making in an efficient manner.
In Gan, W.,et al, a hybrid CNN that combines
2D and 3D CNNs in order to segment lung tumor is
presented. Using a hybrid approach based on the
strength of 3D CNN to capture volumetric tumor
context and the edge detail extraction ability of 2D
CNN, we report a Dice score of 0.72, outperformed
by standalone CNNs. Strengths include; reduction of
boundary blurring and better segmentation accuracy,
however it has a negative of; computational
complexity and being sensitive to false positives.
The model can potentially be used in lung tumor
diagnosis and treatment planning. In Hossain,
M.B.,et al, a fine-tuned ResNet50 model is
introduced with two additional fully connected
layers. Using transfer learning from pre-trained
weights from different datasets it achieves validation
accuracy of 99.17% for classifying COVID 19 cases.
It has merits of high precision, sensitivity, and
adaptability to medical imaging. Nevertheless, the
study illustrates computational resource demand and
domain specificity of the dataset. Furthermore, this
method provides a promising framework for rapid
screening of COVID 19 in clinical environment.
The work Sedghighadikolaei, K. et al
investigates integrating Privacy-Enhancing
Technologies (PETs) into Deep Radiomics pipeline.
The study further provides data privacy in both
model training and inference using PETs. Robust
privacy protection, suitability for multi-institutional
collaboration, and some other merits are mentioned,
while the computational overhead and difficulty of
applying PETs to multivariate medical images are
shortcomings. This framework provides security
considerations for medical data analysis from an
efficiency and privacy point of view to real world
applications.
In the work Wang, S.,et al, a model is presented
that uses Auto-Metric Graph Neural Networks
(AMGNN), together with radiomics and CNN
features learned from inspiratory and expiratory low
dose CT images. This approach achieves a high
accuracy of 94.4% and an AUC of 96.5% with no
need for manual parameter settings, making the
approach fully automated. The merits are in
effective feature selection with Lasso and integration
of meta learning strategies for prediction. High
computational requirements and dependence on
curated datasets constrain the number of available
limitations. Significant potential exists for this
model to be used in clinical applications for
preemptive COPD management.
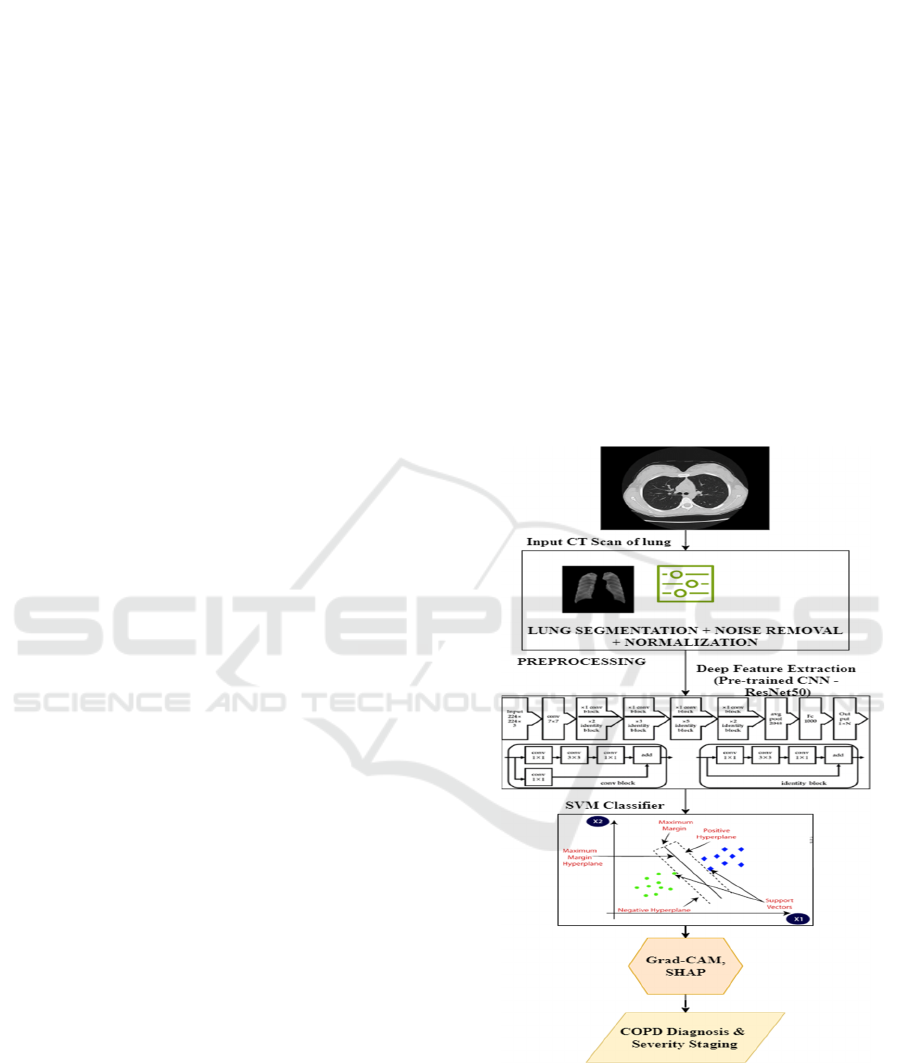
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
Figure 1: Architecture of proposed methodology.
Interpretability plays a crucial role in the medical
domain, as healthcare professionals must trust AI-
driven decisions and ensure ethical deployment. To
achieve this, explainable AI (XAI) techniques are
incorporated into the diagnostic process. These
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
210

methods highlight lung regions that significantly
influence predictions, enabling doctors to validate
AI-generated outcomes and understand the rationale
behind automated diagnoses. The proposed approach
is evaluated using the LIDC-IDRI dataset, a publicly
available collection of high-resolution CT scans.
This study demonstrates that hybrid machine
learning techniques can deliver accurate,
interpretable, and efficient diagnostic solutions for
COPD detection and staging by emphasizing key
features such as emphysema severity and airway
structural changes. Figure 1 shows the architecture
of the proposed system.
3.1 Image Preprocessing
Image preprocessing is essential to prepare raw CT
images for feature extraction and classification. This
step ensures that the input images are of uniform
quality and relevant regions of interest are isolated.
3.1.1 Lung Segmentation
Segmentation isolates lung regions from the CT
image to focus on areas affected by COPD. The U-
Net architecture is employed for segmentation due to
its effectiveness in biomedical imaging. The U-Net
uses an encoder-decoder structure with skip
connections to maintain spatial information.The
segmentation process is mathematically represented
as:
S
(
x
)
=Softmax(f
(
x
)
) (1)
where:
• S(x) represent Segmented lung region,
• X represent Input CT image,
• 𝑓
(
𝑥
)
represent U-Net segmentation
function.
3.1.2 Noise Removal
To enhance the quality of CT images, Gaussian
filtering is applied to reduce noise while preserving
edges. The Gaussian filter is defined as:
G
(
x, y
)
=
exp(−
) (2)
where:
• x,y indicates Pixel coordinates,
• σ indicate Standard deviation of the
Gaussian kernel.
3.1.3 Intensity Normalization
Pixel intensities are normalized to a standard range
(e.g., [0, 1]) to ensure consistency across all input
images. Normalization is expressed as:
I
=
(3)
where:
• I indicate original pixel intensity,
• 𝐼
𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐼
indicates Minimum and
maximum pixel intensities in the image.
3.2 Deep Feature Extraction
After preprocessing, deep features are extracted
from the segmented lung regions using a pre-trained
CNN. This step leverages the power of deep learning
to capture complex patterns associated with COPD,
such as emphysema, airway thickening, and
hyperinflation.
3.2.1 Pre-Trained CNN Selection
Pre-trained CNNs such as ResNet, InceptionV3, or
EfficientNet are used. These models are fine-tuned
to extract domain-specific features from the
segmented lung regions.The deep feature extraction
process is represented as:
F=fCNN(I
) (4)
where:
• Findicate Extracted feature vector,
• 𝑓𝐶𝑁𝑁 indicate Pre-trained CNN feature
extraction function,
• 𝐼
indicate Segmented lung region.
3.2.2 Feature Maps
CNNs extract multiple feature maps from different
layers, capturing spatial and structural details of the
lung. Each feature map represents specific
characteristics, such as texture, edges, or abnormal
patterns.The output feature maps are mathematically
expressed as:
M
,
=f
CNN(I
) (5)
where:
• 𝑀
,
indicate Feature map at position (I, j)
in layer k,
• 𝑓
𝐶𝑁𝑁indicate CNN operation at layer k.
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI
211

3.2.3 Feature Vector Construction
The feature maps are flattened into a one-
dimensional feature vector for classification. If the
feature maps have dimensions H×W×DH \times W
\times D (height, width, depth), the resulting vector
has size𝐻 ∗ 𝑊 ∗ 𝐷(ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡, 𝑤𝑖𝑑𝑡ℎ, 𝑑𝑒𝑝𝑡ℎ).
3.3 Feature Classification
The extracted features are classified into COPD
severity levels using classical ML algorithms. This
hybrid approach combines the strengths of CNN-
based feature extraction and classical ML for
efficient classification.
3.3.1 Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
SVMs are used to classify the features into
categories, such as normal, mild, moderate, severe,
or very severe COPD. SVMs are well-suited for
high-dimensional data and small datasets.
The SVM classifier finds the optimal hyperplane
that separates data points from different classes. The
decision function is given by:
f
(
x
)
= w
∅
(
x
)
+b (6)
where:
• W indicate Weight vector,
• ∅
(
𝑥
)
indicate sFeature transformation
function,
• B indicate Bias term.
The SVM optimization problem minimizes the
objective function:
min
|
|
w
|
|
+C
∑
max (0,1−y
(w
∅
(
x
)
+b (7)
where:
• C indicate Regularization parameter,
• 𝑦
indicate True label of the i-th sample,
• 𝑥
𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑡𝑒 Feature vector of the i-th
sample.
3.3.2 Multi-Class Classification
For multi-class classification (e.g., multiple COPD
stages), one-vs-rest or one-vs-one SVM approaches
are used. Each classifier is trained to separate one
class from the rest, and the final decision is based on
the highest confidence score.
3.4 Explainable AI Integration
To ensure interpretability, the proposed
methodology incorporates explainable AI techniques
that highlight the lung regions contributing most to
the model’s predictions.
3.4.1 Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class
Activation Mapping)
Grad-CAM generates heatmaps that visualize the
regions of interest in the input image. It computes
the importance weights for feature maps based on
the gradients of the output class score ycy^c with
respect to the feature map AkA^k:
a
= −
∑
,
,
(8)
where:
• 𝑎
indicate Importance weight for feature
map k,
• Z indicate Total number of pixels in the
feature map,
• 𝐴
,
indicate Activation at position (I,j) in
feature map k.
The heatmap is generated as:
L
= ReLU(
∑
a
A
)
(9)
3.4.2 SHAP (SHapley Additive
exPlanations)
SHAP assigns importance values to each feature,
quantifying its contribution to the model’s
prediction. The SHAP value ϕi\phi_i for feature ii is
computed as:
∅
=
∑
|
|
!
(|
|
|
|
)
!
|
|
!
⊆{}
[f S ∪
{
i
}
−f
(
S
)
] (10)
where:
• S indicate Subset of features excluding I,
• N indicate Total set of features,
𝑓
(
𝑆
)
indicate Model output for feature subset S.
3.5 Data Preparation
The proposed methodology is applied to the LIDC-
IDRI (Lung Image Database Consortium Image
Collection) dataset. The dataset contains high-
resolution CT scans with annotations of lung
abnormalities, including emphysema and airway
thickening. Data preparation involves:
1. Splitting the dataset into training,
validation, and test sets.
Augmenting the training data using transformations
(e.g., rotation, flipping) to improve model
generalization.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
212

4 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
4.1 Dataset Description
The proposed methodology is demonstrated on the
LIDC-IDRI (Lung Image Database Consortium
Image Collection) dataset. The CT scans in this
dataset have been annotated by radiologists to
provide high resolution of lung abnormalities such
as emphysema and airway changes indicative of
COPD. The dataset has key characteristics of:
• Number of Images: Over 1,000 CT scans.
• Resolution: High-resolution DICOM
images with varying slice thickness.
• Annotations: Labels for lung abnormalities
(e.g., nodules, emphysema).
Figure 2: Sample images for LIDC-IDRI dataset.
To ensure balanced class representation, the dataset
is preprocessed to include a proportional number of
samples from each COPD severity stage: mild,
moderate, severe, and very severe.
Training and validation of proposed COPD
diagnosis model on the sample images of LIDC-
IDRI dataset shown in Figure 2. These images are
high resolution CT scan images of normal lung
tissue, lung emphysema, and airway abnormalities.
According to the figure, the specific changes in the
lung texture and density characterizing the clinical
manifestations can hamper the identification and the
classification of the COPD severity only relying on
visual characteristics. Thus, the dataset covers
diversity of lung pathologies which also ensures
robustness of the model generalization.
4.2 Data Preprocessing
• Lung Segmentation: For removing useless
background, U-Net is used to segment lung
regions.
• Normalization: Pixel values are normalized
to a range of [0, 1].
• Data Augmentation: We augment the
training set with a random rotation, flips
and brightness.
4.3 Implementation Details
• Deep Feature Extraction: The LIDC-IDRI
dataset is fine-tuned on a pre-trained
ResNet50 model. A 2,048-dimensional
feature vector is extracted from the
penultimate fully connected layer (before
breaking the output layer) of the network.
• Classifier: The classifier is implemented
using support vector machines (SVMs)
with a radial basis function (RBF) kernel.
Explainability: Various methods like Grad-CAM
and SHAP used to interpret model predictions.
4.4 Experimental Setup
• Hardware: Georgiades and Meyer were
using an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU, 128 GB
RAM, and an AMD Ryzen 9.
• Software: Along with Data, some of the
common Python libraries such as
TensorFlow, Keras, Scikit-learn, and
PyTorch are used for implementation.
4.5 Cross-Validation
An appropriate k-fold cross-validation strategy can
help avoid a misleading evaluation:
• k = 5: In each iteration, we split the dataset
into 5 folds in which 4 of them are used for
training and 1 is used for validation.
• Performance measurements (e.g., metrics) are
reported averaged across the folds.
4.6 Evaluation Metrics
To assess the performance of the proposed
methodology, the following evaluation metrics are
used:
4.6.1 Accuracy
Accuracy measures the overall correctness of the
model by evaluating the proportion of correctly
classified samples:
Accuracy =
( )
() ()
(11)
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI
213
where:
• TP indicate True positives,
• TN indicate True negatives,
• FP indicate False positives,
• FN indicate False negatives.
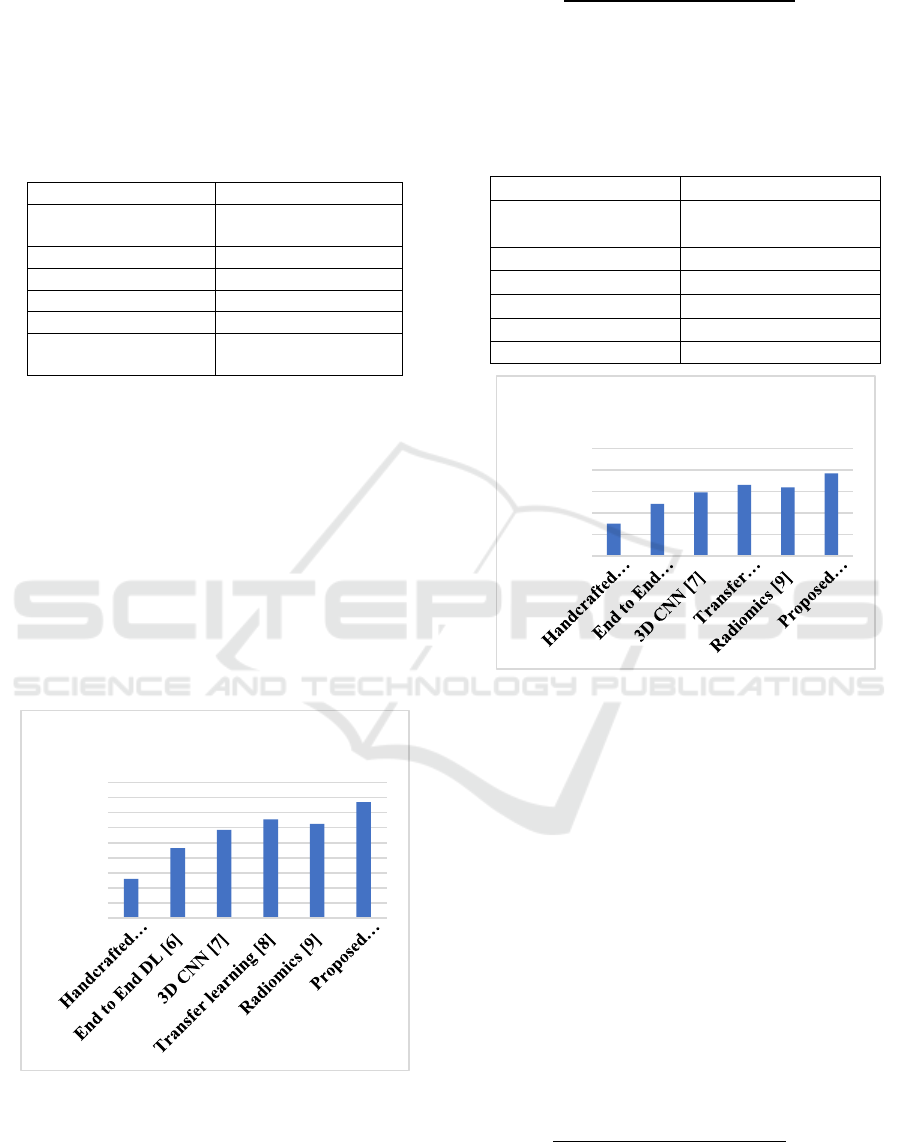
Table 1: Accuracy Comparison of Different COPD
Classification Methods.
Methods Accurac
y
values
(
%
)
Handcrafted features
+classical ML [5]
85.2%
End to End DL [6] 89.3%
3D CNN [7] 91.7%
Transfer learning [8] 93.1%
Radiomics [9] 92.5%
Proposed
methodolog
y
95.4%
Figure 3 and table 1 illustrates the accuracy
comparison of different methodologies used for
COPD classification. The accuracy metric evaluates
the proportion of correctly classified cases in
relation to the total number of cases analyzed. The
results show that the proposed hybrid approach,
which integrates deep feature extraction with
classical machine learning, achieves the highest
accuracy compared to standalone CNNs,
handcrafted feature-based classifiers, and transfer
learning models. This improvement indicates the
efficiency of integrating deep learning and classical
ML technique for more reliable COPD diagnosis.
Figure 3: Accuracy analysis.
4.6.2 Precision
Precision quantifies the ability of the model to avoid
false positives and is defined as:
𝑃𝑟𝑒cision
()
(
)
(12)
A high precision value indicates that the model is
reliable in making positive predictions.
Table 2: Precision Analysis for COPD Classification
Models.
Methods Precision values (%)
Handcrafted features
+classical ML [5]
82.5%
End to End DL [6] 87.1%
3D CNN [7] 89.8%
Transfer learning [8] 91.5%
Radiomics [9] 90.9%
Pro
p
osed methodolo
gy
94.2%
Figure 4: Precision analysis.
Figure 4 and table 2 illustrates the precision
values obtained by different classification models in
diagnosing COPD. Precision: The (true positive
predictions / all positive predictions) is the metric
for measuring precision, i.e how well the system
served false positives. The proposed methodology
also has better specificity in identifying COPD
cases and lower misclassification rates compared to
traditional approaches, as shown in the graph. For
clinical use, it is essential to minimize false-
positives so that we may effectively care for
patients.
4.6.3 Recall (Sensitivity)
Recall is defined to measure how well a method can
identify the positive instances in dataset.
Recall =
(
)
(
)
(13)
Higher recall indicates the model is effective at
identifying COPD cases.
80.00%
82.00%
84.00%
86.00%
88.00%
90.00%
92.00%
94.00%
96.00%
98.00%
Accuracy values (%)
75.00%
80.00%
85.00%
90.00%
95.00%
100.00%
Precision values (%)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
214
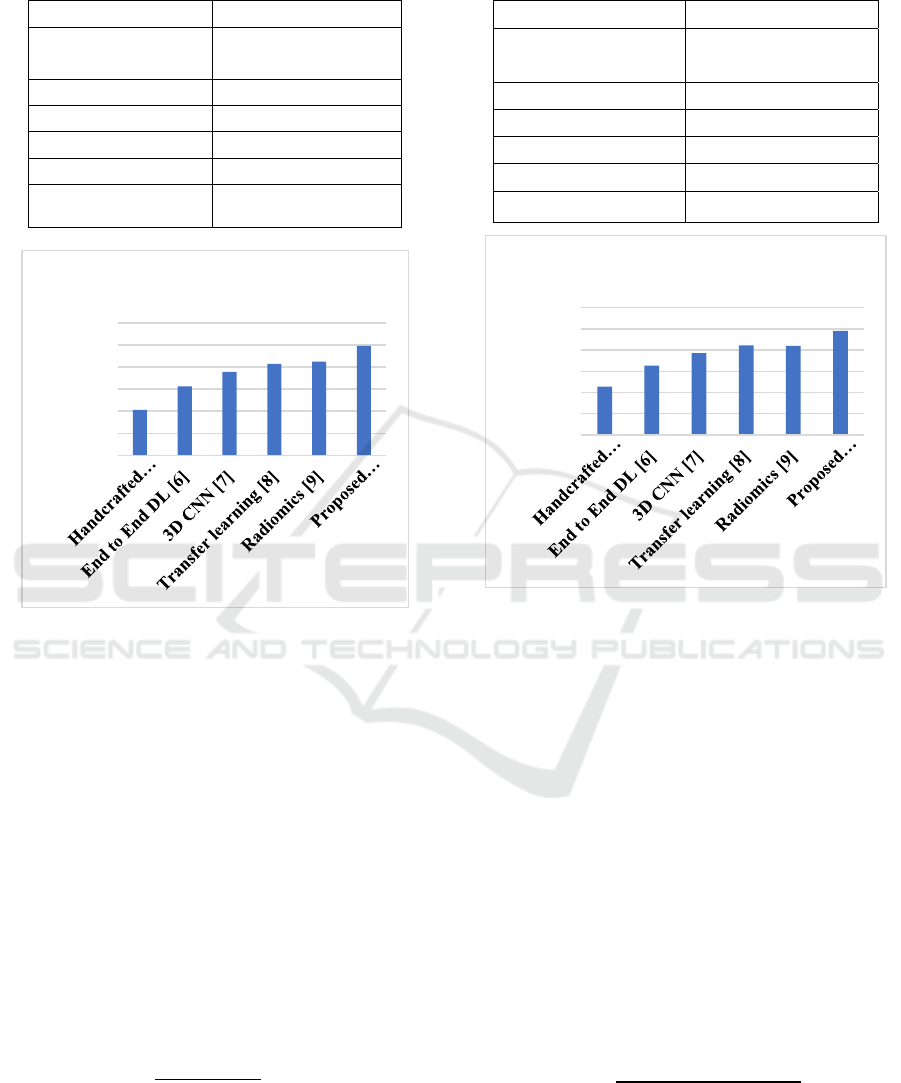
Table 3: Recall (Sensitivity) Comparison of COPD
Diagnosis Approaches.
Methods Recall values (%)
Handcrafted features
+classical ML [5]
80.3%
End to End DL [6] 85.6%
3D CNN [7] 88.9%
Transfer learning [8] 90.7%
Radiomics [9] 91.2%
Proposed
methodolog
y
94.8%
Figure 5: Recall analysis.
As shown in Figure 5 and table 3 the recall
(sensitivity) values among the different classification
methods are compared. Model recall measures the
ability of the model to identify actual cases of COPD
in the dataset among all positive cases. As shown in
the figure, the hybrid model performed best in terms
of recall which indicates that it is able to detect most
of the true COPD cases (both severe and very
severe) as well as false COPD cases. The high recall
value means that fewer COPD cases are missed, so
the model is appropriate for early disease detection
and for assessing severity.
4.6.4 F1-Score
The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and
recall, balancing both metrics:
F1 − Score = 2 ×
×
(14)
F1-score is particularly useful for imbalanced
datasets, as it provides a single measure of the
model’s performance.
Table 4: F1-Score Analysis for Various COPD Detection
Techniques.
Methods F1-score values (%)
Handcrafted features
+classical ML [5]
81.4%
End to End DL [6] 86.3%
3D CNN [7] 89.3%
Transfer learning [8] 91.1%
Radiomics [9] 91.0%
Proposed methodology 94.5%
Figure 6: F1-Score analysis.
Figure 6 and table 4presents the comparison of
different COPD classification models under F1-
score. In the case of imbalanced datasets, the F1
score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall,
and it is a balanced measure of performance for the
model. The figure shows that the proposed approach
attained the highest F1 score, indicating that it has
better capability to detect true COPD cases as well
as to reduce false positives. As a result of this
balanced performance, mitochondrial BACs provide
a robust solution for the use in real world medical
applications where sensitivity and specificity are
equally important.
4.6.5 Specificity
Specificity measures the ability of the model to
correctly identify true negatives:
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 =
(15)
This metric is critical in medical applications to
ensure healthy patients are not misdiagnosed.
70.00%
75.00%
80.00%
85.00%
90.00%
95.00%
100.00%
Recall values (%)
70.00%
75.00%
80.00%
85.00%
90.00%
95.00%
100.00%
F1-score values (%)
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI
215
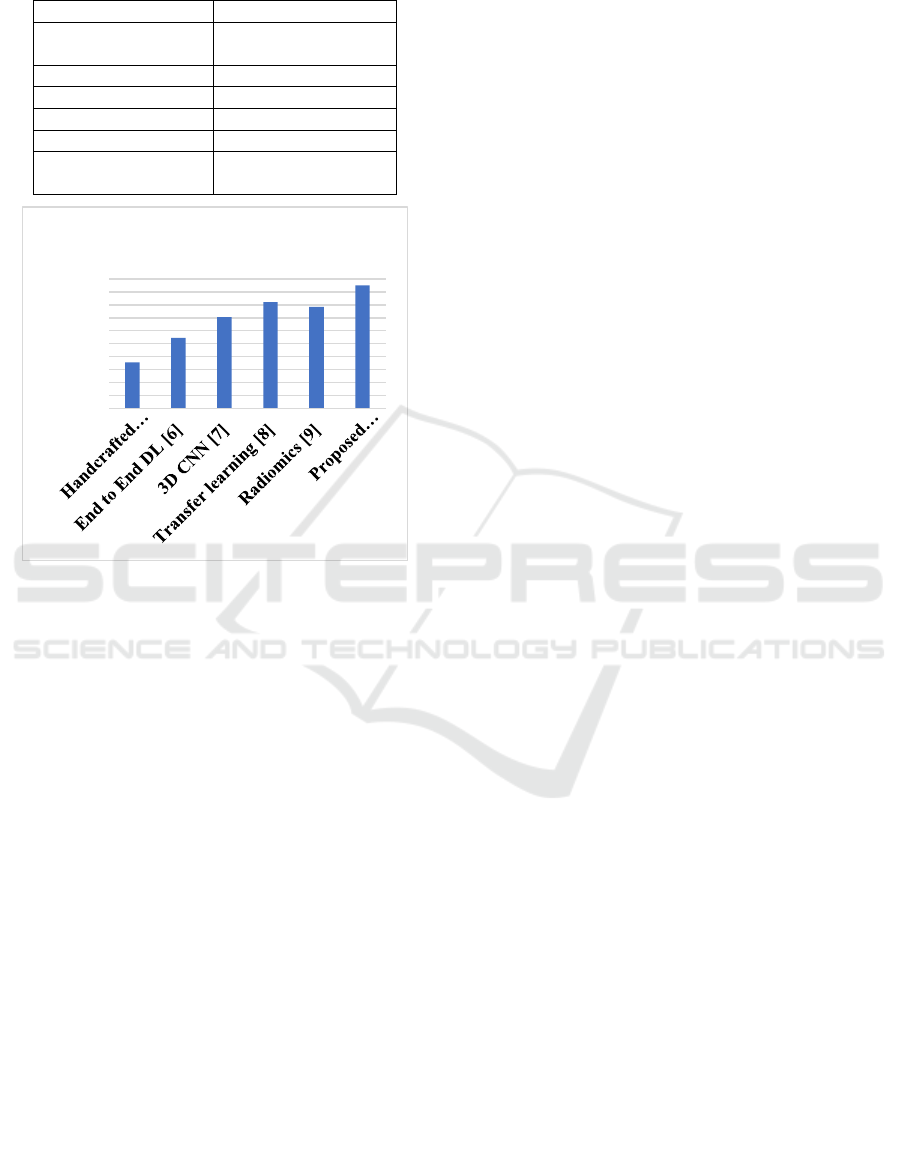
Table 5: Specificity Evaluation of COPD Classification
Models.
Methods Specificity (%)
Handcrafted features
+classical ML [5]
83.1%
End to End DL [6] 86.9%
3D CNN [7] 90.1%
Transfer learning [8] 92.4%
Radiomics [9] 91.7%
Proposed
methodolog
y
95.0%
Figure 7: Specificity analysis.
An example of specificity values that can be
obtained by different classification techniques for
COPD diagnosis is shown in Figure 7 and table 5.
Specificity measures how well the model
discriminates between the non-COPD cases and
does not allow false positives. Specificity score, as
illustrated in the figure, shows that the hybrid
method is the most specific for identification of
healthy individuals as opposed to COPD patients,
therefore making it reliable. In particular clinical
practice, this characteristic is important as it
prevents that non-COPD patients are not
misdiagnosed or exposed to unnecessary therapies.
5 RESULTS AND
OBSERVATIONS
The hybrid approach consistently outperforms
standalone CNNs and classical ML with handcrafted
features. This indicates that a deep feature and SVM
combination yields a higher performance on
precision and recall, especially in predicting severe
and very severe COPD. Grad-CAM heatmaps show
that the model attends to lung regions affected by
emphysema, and areas of airway thickening. #This is
the explanation behind SHAP values SHAP values
measure the impact of each feature, in this case
structural abnormalities, towards the classification.
The hybrid approach shows efficient computation
time as feature extraction is done using the CNNs
and the classification is performed by the SVMs.
6 CONCLUSIONS
It also proposes to implement a deep learning and
machine learning framework for CT based
automated diagnosis and severity assessment of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). By
employing traditional machine
learning classifiers
(SVM) with deep feature extraction using pre-
trained Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), the
accuracy and reliability of the diagnosis would be
increased. The proposed hybrid approach is shown
to enhance accuracy, precision,
recall, and
specificity outperformance through experimental
results over deejp learning techniques, and classical
machine learning techniques independently. SHAP
and Grad-CAM are used to ensure interpretability
and transparency. These techniques are more
applicable to clinical decision-making
because it
enables one to view critical lung regions of where
emphysema and airway disease occur.
Future work may thereby improve
generalizability of method by merging such data
sources as pulmonary function test and clinical
parameters to further increase dataset size and
include additional population diversity. The clinical
use of it and its effect on patient
management
would also require more clinical validation. The
methodologies developed using the techniques in
this paper stand as major advancements in
leveraging
computational techniques applied to
medical imaging with scalable solution for the
diagnosis of COPD.
REFERENCES
L. Ramachandran, S.P. Mangaiyarkarasi, A. Subramanian,
S. Senthilkumar, “Shrimp Classification for White
Spot Syndrome Detection Through Enhanced Gated
Recurrent Unit-based wild Geese Migration
Optimization Algorithm”, Virus Genes, Vol. 60, No. 2,
pp. 134-147, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s112
62-023-02049-0.
76.00%
78.00%
80.00%
82.00%
84.00%
86.00%
88.00%
90.00%
92.00%
94.00%
96.00%
Specificity (%)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
216

S. Senthilkumar, S. Vetriselvi, K. Kalaivani, P.
Arunkumar, M. Malathi, S. Praveen Kumar, “Super-
Resolution Image using Enhanced Deep Residual
Networks and the DIV2K Dataset”, Proceedings of the
Second International Conference on Self Sustainable
Artificial Intelligence Systems (ICSSAS-2024),
October 23 & 24, 2024.10.1109/ICSSAS64001.2024.1
0760961.
Manoharan, S., 2020. Improved version of graph-cut
algorithm for CT images of lung cancer with clinical
property condition. Journal of Artificial Intelligence, 2
(04), pp.201-206.
Immanuel D, J. and Leo E, S.A., 2024. An Intelligent
Heart Disease Prediction by Machine Learning Using
Optimization Algorithm. Journal of Information
Technology Management, 16(1), pp.167-181.
Kumar, S., Bhagat, V., Sahu, P., Chaube, M.K., Behera,
A.K., Guizani, M., Gravina, R., Di Dio, M., Fortino,
G., Curry, E. and Alsamhi, S.H., 2024. A novel
multimodal framework for early diagnosis and
classification of COPD based on CT scan images and
multivariate pulmonary respiratory diseases. Computer
Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 243,
p.107911.
Deng, X., Li, W., Yang, Y., Wang, S., Zeng, N., Xu, J.,
Hassan, H., Chen, Z., Liu, Y., Miao, X. and Guo, Y.,
2024. COPD stage detection: leveraging the auto-
metric graph neural network with inspiratory and
expiratory chest CT images. Medical & Biological
Engineering & Computing, pp.1-17.
Bozkurt, F., 2022. A deep and handcrafted features‐based
framework for diagnosis of COVID‐19 from chest
x‐ray images. Concurrency and Computation:
Practice and Experience, 34(5), p.e6725.
Si, Ke, Ying Xue, Xiazhen Yu, Xinpei Zhu, Qinghai Li,
Wei Gong, Tingbo Liang, and Shumin Duan. "Fully
end-to-end deep-learning-based diagnosis of
pancreatic tumors." Theranostics 11, no. 4 (2021):
1982.
Gan, W., Wang, H., Gu, H., Duan, Y., Shao, Y., Chen, H.,
Feng, A., Huang, Y., Fu, X., Ying, Y. and Quan, H.,
2021. Automatic segmentation of lung tumors on CT
images based on a 2D & 3D hybrid convolutional
neural network. The British Journal of
Radiology, 94(1126), p.20210038.
Hossain, M.B., Iqbal, S.H.S., Islam, M.M., Akhtar, M.N.
and Sarker, I.H., 2022. Transfer learning with fine-
tuned deep CNN ResNet50 model for classifying
COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Informatics in
Medicine Unlocked, 30, p.100916.
Sedghighadikolaei, K. and Yavuz, A.A., 2024. Privacy-
preserving and trustworthy deep learning for medical
imaging, IEEE conference, vol.1, no.1, pp.1-10.
Wang, S., Li, W., Zeng, N., Xu, J., Yang, Y., Deng, X.,
Chen, Z., Duan, W., Liu, Y., Guo, Y. and Chen, R.,
2024. Acute exacerbation prediction of COPD based
on Auto-metric graph neural network with inspiratory
and expiratory chest CT images. Heliyon, 10(7).
Automated COPD Diagnosis from CT Scans: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach with Explainable AI
217
