
AI‑Powered Conversational Assistant for Admission Automation in
Government Educational Platforms
N. Ganitha Aarthi
1
, Thasni Asharif
2
, Shyam Subbiah
3
, Shifa Ashwath
3
,
Sitheshwaran
3
and Narendra Nath
3
1
Department of Computer Science and Design, SNS College of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Computer Science, Dr. SNS. Rajalakshmi College of Arts and Science, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Computer Science and Design, SNS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Government Administration, Rule‑Based Inferencing, Assistant System, Regulatory Information,
Multilingual Support, Decision‑Making Efficiency, Public Sector Automation.
Abstract: The Admission Guru project is an AI-powered assistant integrated into the Rajasthan Education Department’s
website to simplify admission-related processes for engineering and polytechnic institutes. It provides instant,
accurate responses to queries on eligibility, college options, fees, scholarships, and placements using advanced
NLP and AI technologies. Accessible 24/7, the multilingual assistant supports English and Hindi, ensuring
inclusivity for diverse users. By automating responses to frequently asked questions, it reduces administrative
workload and enhances efficiency. Admission Guru streamlines the admission process, improves user
satisfaction, and serves as a transformative tool in Rajasthan’s educational ecosystem.
1 INTRODUCTION
In government administrative departments, officers
often encounter queries requiring reference to
specific rule books and their interpretations. This can
be a time-consuming and error-prone process,
especially when the information is scattered across
various documents and languages. Our proposed
solution aims to streamline this process by developing
a Assistant system that assists officers in providing
accurate and contextually relevant information based
on government rules and regulations. The feedback
for this system comes from real-time interactions with
officers and administrators who frequently deal with
regulatory queries. They have expressed that
answering these queries often relies on their
experience and familiarity with the rules, which can
be challenging and time-consuming. Various rules
and regulations must be consulted, and interpreting
them accurately is crucial to ensure compliance and
informed decision-making. Officers have reported
that the current process is tedious and can lead to
delays in administrative functions.
2 OBJECTIVES
Students and parents in Rajasthan face difficulties in
accessing accurate, up-to-date information about
departmental vacancies, eligibility criteria, and
scholarship opportunities. The existing system is
fragmented, complex, and hard to navigate, leading to
confusion, delays, and missed opportunities. A
solution is needed that simplifies the admission
process, centralizes all relevant information, and is
accessible and user- friendly for all users.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
The rise of digital solutions has transformed
education, with chatbots emerging as efficient tools
for automating processes, addressing inquiries, and
enhancing accessibility. In the context of student
admissions, the Admission Guru chatbots leverages
natural language processing (NLP) and artificial
intelligence (AI) to deliver real-time, multilingual
support for students and parents. Chatbots utilize
NLP to interpret user inputs and generate relevant
responses, as detailed by Jurafsky and Martin (2019)
in Speech and Language Processing. While NLP
170
Aarthi, N. G., Asharif, T., Subbiah, S., Ashwath, S., Sitheshwaran, and Nath, N.
AI-Powered Conversational Assistant for Admission Automation in Government Educational Platforms.
DOI: 10.5220/0013909700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
170-175
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
facilitates language comprehension, implementing it
for Indian languages like Hindi introduces challenges
such as tokenization, syntax parsing, and semantic
analysis (Sharma & Verma, 2021). These challenges
are critical for creating inclusive, multilingual
systems.
Shah and Singh (2020) underscore the role of
chatbots in streamlining administrative workflows
and providing round-the-clock support for admission-
related queries. Tools like the Google Gemini API
enable context- aware interactions and real-time data
integration, essential for systems like Admission
Guru. Frameworks like Streamlit further enhance user
engagement by offering responsive, interactive
interfaces (Kaushik & Gupta, 2022). The scalability
and reliability of chatbots are essential, particularly
during admission peak periods. Cloud-based
infrastructures ensure high traffic handling without
compromising performance (Kaushik & Gupta,
2022). Voice- enabled features and predictive
analytics improve accessibility and personalize user
experiences by anticipating frequently asked
questions (Shah & Singh, 2020; Sharma, 2021).
Security and privacy are vital for protecting
sensitive user data. Russell and Norvig (2021)
advocate encryption protocols and ethical AI
practices to ensure user trust. Analytics also play a
crucial role in identifying performance gaps, refining
chatbot capabilities, and improving user engagement
(Kaushik & Gupta, 2022).
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Existing System
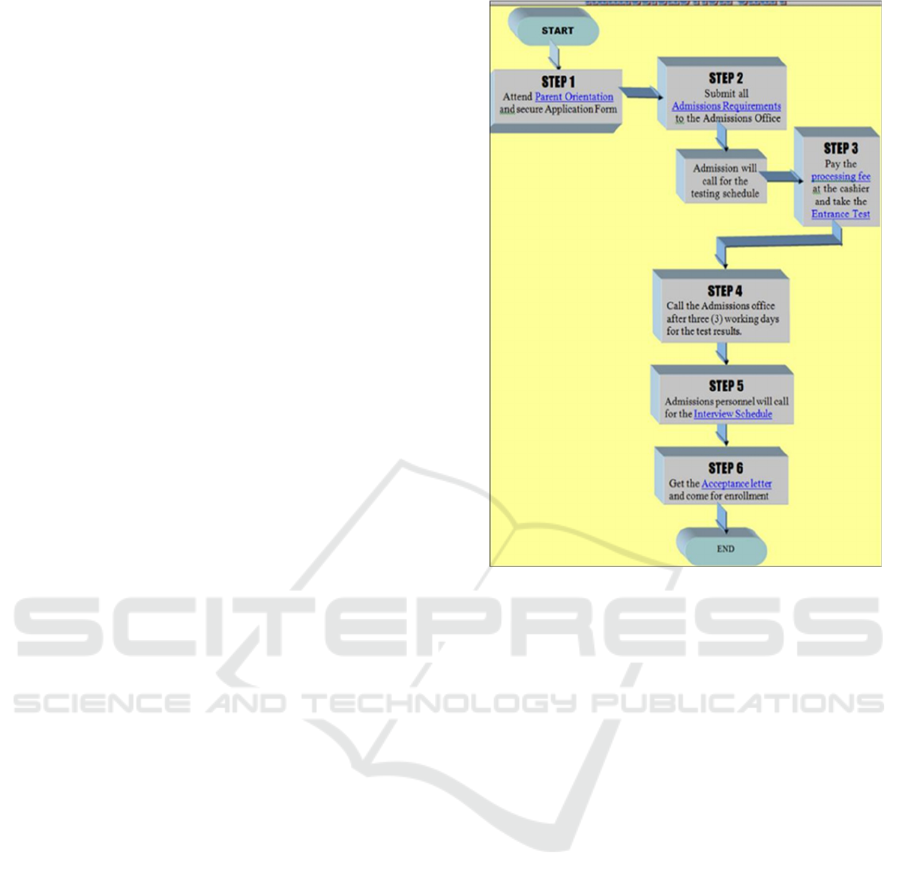
The admission process as shown in figure 1 begins
with Step 1, where applicants are required to attend
the Parent Orientation and secure the application
form. In Step 2, applicants must submit all the
Admissions Requirements to the Admissions Office.
At this stage, admission personnel will contact the
applicant to schedule the entrance test. Moving to
Step 3, applicants need to pay the processing fee at
the cashier and complete the Entrance Test. After
three (3) working days, applicants must contact the
Admissions Office to obtain their test results, as
outlined in Step 4. If successful, the admissions
personnel will call the applicant to schedule an
interview in Step 5. Finally, in Step 6, applicants
receive their Acceptance Letter and proceed to
enrolment.
Figure 1: Existing System Block Diagram.
This process involves approximately six steps,
including two interactions (test and interview) and a
three-day waiting period for test results. By following
these steps, applicants efficiently complete the
admission process.
Pros of Existing System: The structured admission
process offers clarity and transparency, with clear
expectations at each step. Parent orientation ensures
families are informed, while the entrance test and
interview maintain academic standards by admitting
qualified candidates. The defined timeline, including
a three-day waiting period, helps both applicants and
the admissions office prepare for subsequent steps.
Cons of Existing System: The admission process
involves delays, multiple interactions, and waiting
periods, causing anxiety for applicants. The three-day
wait for test results adds uncertainty. Applicants must
manage several steps independently, which can be
overwhelming. Additionally, the process lacks
flexibility for those requiring special
accommodations, reducing accessibility for diverse
applicants.
AI-Powered Conversational Assistant for Admission Automation in Government Educational Platforms
171
4.2 Proposed System
4.2.1 User Interface of Prototype
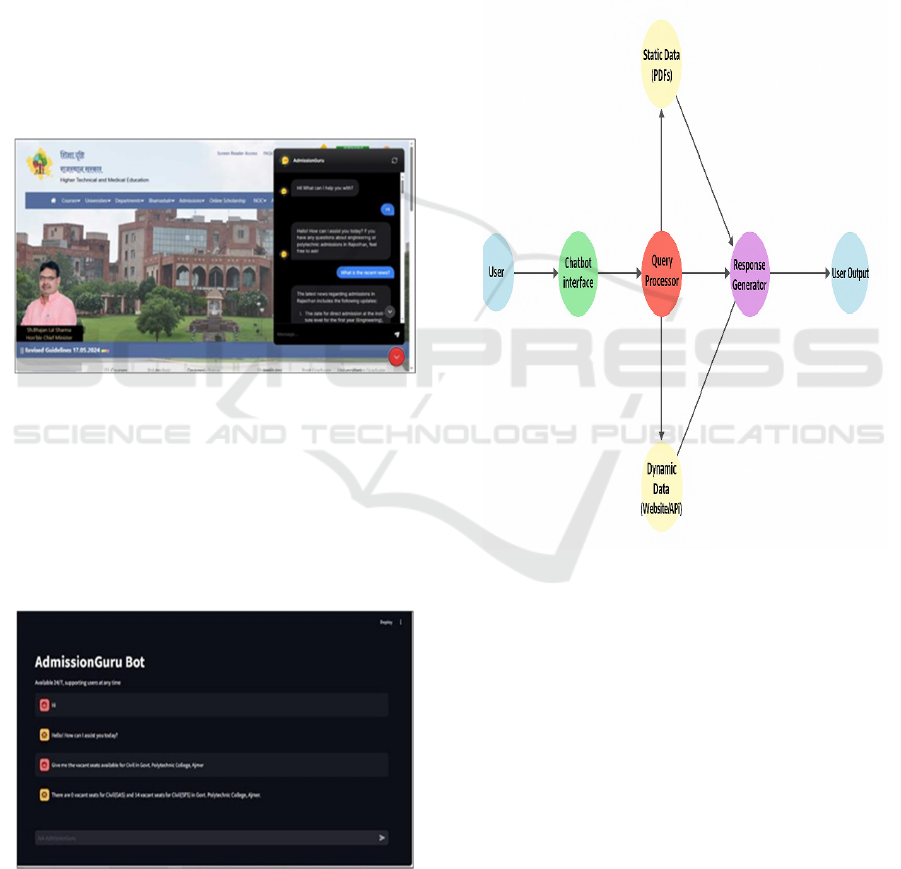
Currently, the Admission Guru chatbot is hosted on
Streamlit Community Cloud (figure 2), a cloud based
platform that enables easy deployment and access to
web applications. This deployment choice makes the
chatbot publicly accessible to users via a provided
link, allowing anyone with an internet connection to
interact with the assistant. The use of Streamlit
Community Cloud eliminates the need for users to
install any software locally, simplifying the process
of accessing the chatbot. Users can directly access the
chatbot through a browser, providing a seamless
experience for anyone looking for admission-related
information, no matter where they are located.
Figure 2: Streamlit Cloud App Ui.
The cloud-based deployment also ensures that the
chatbot is available around the clock. Since the
chatbot is hosted in the cloud, there is no dependency
on local systems or infrastructure. This means that
users can engage with the bot at any time, whether it's
during regular office hours or outside of them. Figure
3 shows the Admission Guru UI in Website.
Figure 3: Admission Guru UI in Website.
When a user clicks the chat icon, a popup window
appears with a simple, intuitive chat interface. The
layout is minimalistic and responsive, keeping the
user focused on the conversation. At the bottom, a
text input field allows users to type their queries,
which can be submitted via the "Enter" key or a
button. The chatbot responds instantly, displaying
answers in a clear, conversational format. The
messages are shown chronologically for easy
understanding. Visual elements, such as avatars or
speech bubbles, may be included to make the
interaction feel more natural and engaging for users.
Figure 4 gives the Data-Flow Diagram.
Figure 4: Data-Flow Diagram.
Upon clicking the icon, a popup window will appear,
displaying a simple and user-friendly chat interface
where users can type their queries and view the
assistant’s responses in a conversational format. After
submitting a query, the chatbot will instantly display
relevant answers retrieved in real-time from live
website data and multiple PDF documents, processed
via the Gemini API. If a query cannot be answered, it
will provide a fallback response, encouraging the user
to refine their question or try another query.
Implementation Stack is shown in figure 5.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
172
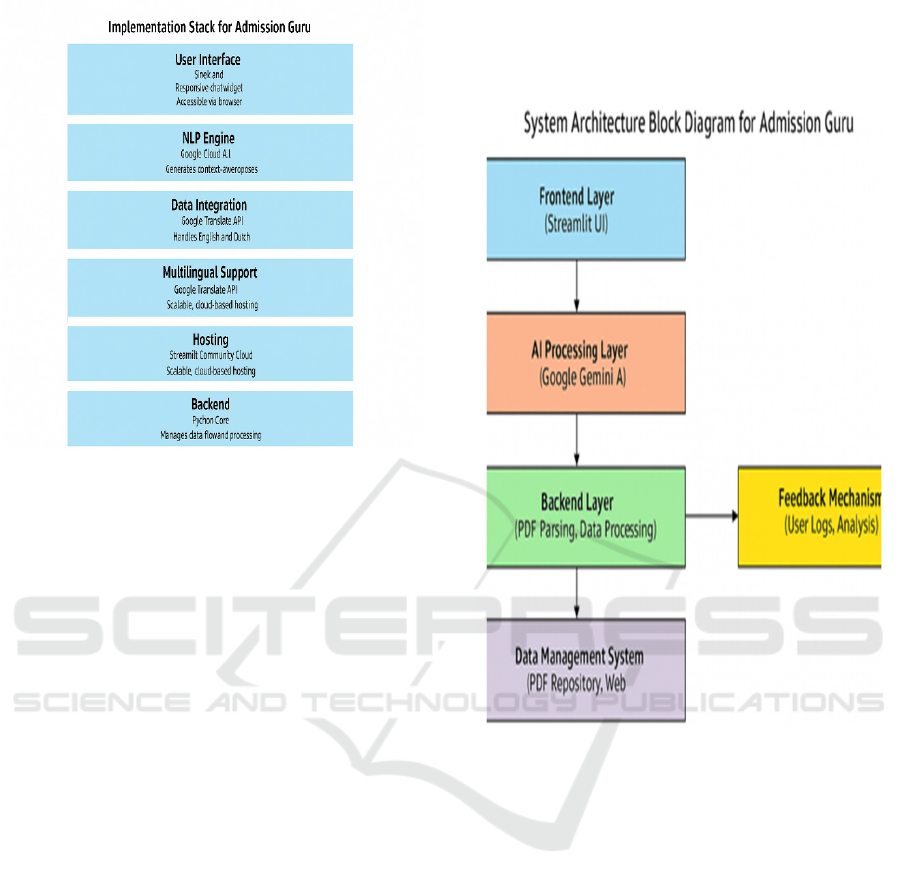
Figure 5: Implementation Stack.
It allows for rapid development of interactive web
applications with minimal effort. Streamlet’s
simplicity makes it a perfect choice for building
intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that don’t require
extensive frontend development expertise. For the
Admission Guru assistant, Streamlit is used to create
the chat interface where users can input their queries
and receive responses from the AI- powered assistant.
The application is embedded into the website, and the
chat interface allows for seamless, real-time
conversations. Streamlit also supports the addition of
multilingual capabilities, ensuring that users can
interact with the assistant in both Hindi and English,
with potential for more languages in the future. The
platform’s flexibility allows the chatbot to be
scalable, handling varying user traffic during peak
periods, such as the admission season. Figure 6 shows
the system architecture block diagram.At the core of
the architecture is the AI Processing Layer, powered
by the Google Gemini API. This layer handles natural
language processing (NLP) tasks, including intent
recognition, context understanding, and response
generation. It ensures that user queries, whether
simple or complex, are accurately interpreted and
addressed. 29 The AI Processing Layer interacts with
a structured Data Management System, which
currently comprises PDF documents containing
frequently asked questions and answers related to
admissions. In the future, this layer will integrate with
live data from the Department of Technical
Education, Rajasthan's website to provide real-time
updates and insights.
Figure 6: System Architecture Block Diagram.
5 RESULTS
In terms of the methods or algorithms used to solve
the problem, ChatGPT-3.5 implements the rational
roots theorem five out of six times and Cardano’s
formula once. ChatGPT-4 attempts to provide a
solution by using the rational roots theorem, a
graphical solution, and a code snippet in python
66.7%, 16.7%, and 16.7% of the time, respectively.
Finally, Gemini AI uses factor lists five times and the
rational roots theorem once. All the implemented
methods or algorithms can correctly lead to a right
answer; thus, it could be said that the chatbots have
chosen a proper way to give an answer. Figure 7
shows the Comparison Chart.
AI-Powered Conversational Assistant for Admission Automation in Government Educational Platforms
173
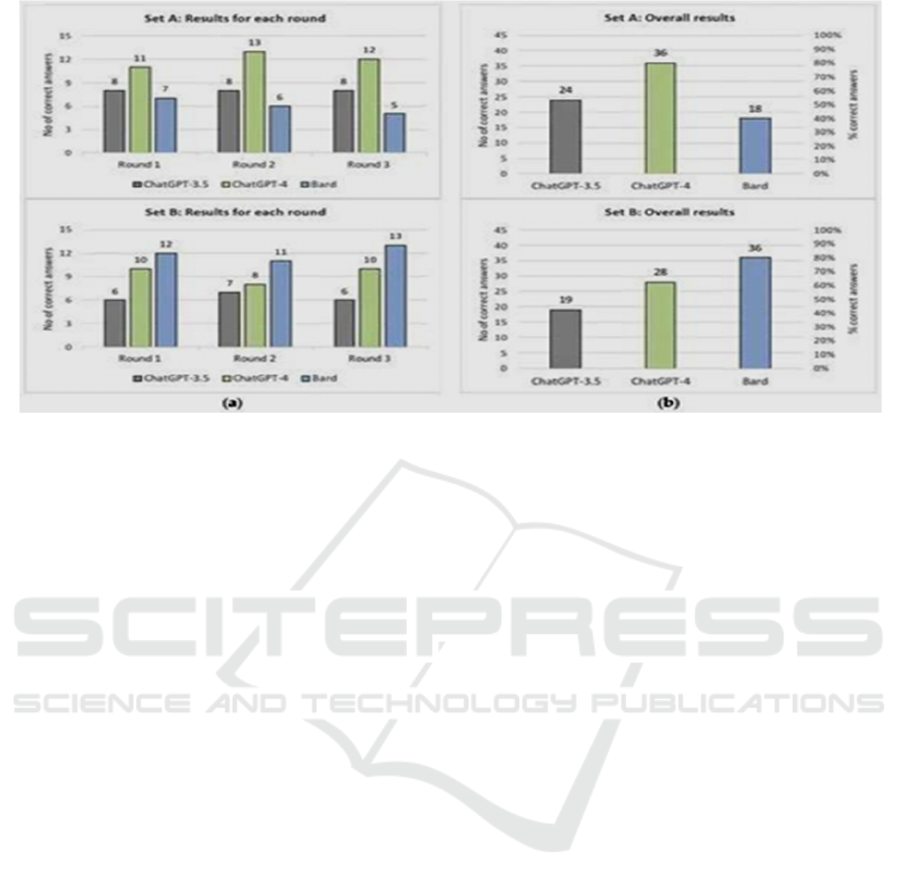
Figure 7: Comparison Chart.
6 CONCLUSIONS & FUTURE
ENHANCEMENT
6.1 Conclusions
The Admission Guru project, developed as an inbuilt
admission assistant for the Rajasthan Education
Department's website, has successfully fulfilled its
objective of streamlining the admission process for
students and parents. By integrating features such as
viewing department vacancies, scholarship details,
and admission guidelines, we have significantly
enhanced user experience. The design thinking
process allowed us to empathize with the target
audience, define their pain points, ideate solutions,
prototype the assistant interface, and test its
functionalities to ensure it meets the needs of
students, parents, and educational administrators.
Our approach began by understanding the
challenges faced by users in navigating the traditional
admission process. These challenges included lack of
timely information, complexity in finding relevant
department vacancies, and confusion regarding
scholarship opportunities. By directly addressing
these issues, Admission Guru was designed to
provide real-time, easily accessible information in a
user-friendly interface. The prototype was validated
with a set of test users, receiving positive feedback
regarding its simplicity and efficiency in guiding
them through the admission journey.
We also incorporated continuous feedback loops,
using real-world data to refine the system's
functionalities and ensure that the platform remains
intuitive and effective. As a result, students and
parents are now able to access critical admission
details seamlessly, making the overall process more
transparent and less stressful. Educational
administrators benefit from the tool as well, since it
automates many manual processes, reducing the
workload and enhancing operational efficiency.
However, while Admission Guru has successfully
met its initial objectives, there is always room for
improvement. The foundation laid in this project can
be further expanded upon to integrate more advanced
features and improve the user experience even more.
6.2 Future Enhancement
The future of Admission Guru holds exciting
possibilities. There are several enhancements that
could elevate the tool to new levels of usefulness for
both users and administrators.
Multilingual Support: As Rajasthan is a diverse
state with a multitude of languages spoken, adding
multilingual support could make Admission Guru
more accessible to a wider audience. This feature
would enable users from different linguistic
backgrounds to interact with the platform in their
preferred language. Integration with Other Systems:
Admission Guru could be integrated with other
education management systems to provide a more
comprehensive service. For example, linking the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
174

assistant to databases that track students' academic
performance and other eligibility criteria could
automate the admission process even further.
Mobile Application: While the tool is accessible via
the website, a dedicated mobile application could be
developed to allow users to easily access the platform
on the go. Given the high mobile penetration in
Rajasthan, this could increase the tool’s adoption
among students and parents.
AI-Powered Guidance: Incorporating AI to provide
personalized advice could enhance the user
experience. The assistant could analyze a student’s
preferences, academic history, and eligibility to
recommend specific departments, courses, and
scholarships.
User Feedback Mechanism: Adding a robust user
feedback mechanism would allow continuous
improvement. Users could report issues or suggest
new features, helping the development team prioritize
future updates based on real user needs.
Enhanced Analytics for Administrators: The
platform could provide educational administrators
with more detailed insights and analytics regarding
admissions, such as trends in application volume,
preferred departments, and common queries. This
could help streamline decision-making and resource
allocation.
REFERENCES
Gupta, S., & Kumar, A. (2020). "Cloud Infrastructure for
Scalable Chatbot Applications." International Journal
of Cloud Computing, 14(1), 75-90.
Jurafsky, D., & Martin, J. H. (2019). Speech and Language
Processing. Pearson.
Kaushik, M., & Gupta, A. (2022). "Optimizing Admission
Processes through Digital Chatbots: A Case Study."
International Conference on Digital Transformation in
Education.
Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2021). Artificial Intelligence: A
Modern Approach. Pearson.
Shah, P., & Singh, K. (2020). "AI-Powered Chatbots in
Education: Enhancing User Engagement and
Accessibility." International Journal of Educational
Technology, 12(4), 215-230.
Shah, P., & Patel, M. (2021). "Voice- Enabled Chatbots:
Bridging the Digital Literacy Gap." Journal of Human-
Computer Interaction, 33(7), 501-520.
Sharma, A., & Verma, R. (2020). "Enhancing
Chatbot Security and Privacy for EducationalApplicati
ons." Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Secure
AI Systems.
Sharma, A., & Verma, R. (2021). "Challenges in
Multilingual NLP: A Focus on Indian Regional
Languages." Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,
45(2), 120-135.
Sharma, A. (2021). "Multilingual Conversational AI
Models for Education: Opportunities and Challenges."
AI in Education Review, 9(3), 132-150.
Verma, R., & Singh, V. (2022). "Real-Time Data
Integration in Chatbots: Techniques and Challenges."
IEEE Transactions on AI Systems, 18(6), 450-462.
AI-Powered Conversational Assistant for Admission Automation in Government Educational Platforms
175
