
Plant Disease Identification and Pesticides Recommendations Using
CNN Deep Learning
Jujaray Vyshnavi, Sangapatnam Sowmya, P. Dhanvitha,
Mandozai Ayesha Khatoon and L. Sandhya Rekha
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE‑AI), Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool,
Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Plant Disease Detection, Deep Learning, CNN, Pesticide Recommendation, Precision Agriculture.
Abstract: Diseases on plants are a major threat to global agricultural productivity and cause great economic losses and
problems of food security. Current disease detection methods employ manual inspection, which is slow,
mistakes prone and aims to disease specific knowledge. Therefore, to mitigate these challenges, there is need
to develop an AI driven Plant disease identification and pesticide recommendation system using convolutional
neural networks (CNNs). Using deep learning techniques, the leaf images are automatically classified to
generate plant disease to a very high accuracy. Thereafter, it offers real-time and disease dependent pesticide
recommendations, maximizing treatment efficiency while reducing pesticides not needed. The model is
trained on the available diseased and healthy plants images after a few preprocessing operations, then feature
extraction and classification using CNN architecture. One main benefit of this method is the availability for
real time disease diagnosis, the decreased dependence of agricultural experts, increased crop yield and usage
of environmentally sustainable pesticides. The system is web or mobile application deployable so it can be
distributed to the farmers. Also, we can further improve the predictive accuracy by tracking environmental
condition like temperature, humidity, and soil health through integrating IoT. The purpose of this research is
to provide an automated, scalable, and cost-effective solution to the problem of plant disease management in
order to enhance precision agriculture. Although this existing system is useful for the future, it may be further
improved this way: multi disease detection, disease affected zone localization, and cloud-based updating for
continuous learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agriculture as a sector is an important sector to assure
food security and stability of the economy globally.
In this way, however, plant diseases are preventing
crop production and significantly decreasing yields,
and ending up farmers frustrated, malleating millions
of dollars to them. Detecting plant diseases
traditionally has been a manual raster that requires
expert inspection and is laborious, costly and quite
often inaccurate. If timely detection is not possible, it
can lead to infections that spread throughout the
place, causing harm to agriculture and food supply.
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning
(DL) technologies have recently advanced, it has
become a promising approach of automated disease
detection. Deep learning model called Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs) are shown to be very
effective for image classification and pattern
recognition and therefore are suitable for leaf image-
based plant disease diagnosis. CNNs have the ability
to learn intricate features from plant images to spot
slight disease symptoms that may not show so clear
to human eye.
In this study, there is a suggestion of an AI
assisted Plant Disease Identification and Pesticide
Recommendation System based on CNNs for real
time disease classification. The system takes plant
leaves images, detects the possible diseases, and then
provides the most adequate pesticides for treatment.
As an automated system, it allows the reduction of
dependency on agricultural specialists as well as
quick and accurate detection of a disease to farmers.
Sustainable pesticide management is one of the
most important advantages of this procedure.
Inappropriate and excessive use of pesticides can be
harmful to the environment, lead to pesticide
resistance and raise the cost to farmers.
Vyshnavi, J., Sowmya, S., Dhanvitha, P., Khatoon, M. A. and Rekha, L. S.
Plant Disease Identification and Pesticides Recommendations Using CNN Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013909500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
153-160
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
153

Recommendation of most appropriate pesticide
according to diagnosed disease is given by the system
such that pest control is efficient with less chemical
exposure, leading to eco-friendly farming.
This system has been implemented via mobile and
web application so that farmers in most remote areas
can easily access to this system. Future ways of
enhancement can be real time IoT based monitoring,
multi disease detection, and cloud-based update to
keep on enhancing the accuracy. This dissertation is
targeted to revolutionize the Precision Agriculture, by
integrating the AI and deep learning in order to
improve the crop health, productivity, and
sustainability.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research methodology of Plant Disease
Identification and Pesticide Recommendation System
using CNN is implemented following a structured
approach so that diseases can be detected accurately
and pesticides can be recommended effectively. The
steps included in the methodology are:
2.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
• A large set of plant leaf images are gathered
from public sources like PlantVillage, Kaggle,
and agricultural research institutes.
• A variety of plant species and disease types are
categorized into healthy and diseased leaves
images.
• Image resizing, noise reduction, contrast
enhancement and data augmentation as
preprocessing techniques make the model
robust and improve the chances of accuracy.
2.2 CNN Model Development
It designs and train a Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN) to classify plant diseases.
• The model includes multiple convolutional
layers, pooling layers, and fully connected
layers for the purpose of extraction of
meaningful features from images.
• The dataset is divided into training, validating
and testing sets; and the model is trained by
minimizing classification errors via Adam
optimizer or Stochastic Gradient Descent
(SGD).
• The model performance is evaluated in terms of
performance metrics like accuracy, precision,
recall, and F1-score.
2.3 Pesticide Recommendation System
• Using expert knowledge, agricultural reports
and guidelines on pesticide usage, a disease to
pesticide mapping database is created.
• Based on the already detected disease, the
system fetches the most appropriate pesticide
recommendations based on factors such as
effectiveness, ecology friendliness and
government regulations
.
2.4 System Deployment and User
Interface
• It is deployed as web based or mobile
application to detect disease in real time using
trained model.
• To mention, farmers can also upload plant leaf
images of a farm and the system gives instant
disease identification which can also suggest
pesticides.
• Methods of combining cloud storage and IoT
integration for real time monitoring of the plant
health or the surrounding environment is
discussed.
2.5 Testing and Validation
• Practical effectiveness of the system is tested
using real world plant images.
• The accuracy, efficiency and usabiltiy of this
paradigm is compared with existing disease
detection methods.
• The system is refined based on feedback
obtained from agricultural experts and farmers
in terms of usability
2.6 Research Area
Plant diseases play an important role in agriculture
and pose serious obstacles to global food production,
while it is of great relevance in the agriculture sector
maintaining the food production sufficient for
humanity. Currently, the joint hands with agricultural
specialists to identify these diseases include manual
inspection, which is time consuming, costly and error
prone. While purpose is logically placed in the
introduction section, another clear reader impression
is that it can also be placed in the conclusion part. In
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
154

this paper, the integration of deep learning methods,
in specific Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs),
is applied toward revolutionizing plant disease
recognition and therapeutic technique.
This study's primary research is sited on precision
agriculture, which entails using AI and data enabled
methods to improve the technique of farming. Image
classification tasks have been made remarkably
successful using deep learning models, in particular
CNNs; thus, they are a wise choice to tackle the
problem of identifying plant diseases from leaf
images. This is done in order to reduce dependency
on human expertise for disease detection while
enhancing its accuracy and speed. The computer
vision algorithms implementation increases the
efficiency of disease classification because it can
identify even the subtle patterns, which can be pure
invisible to the traditional methods.
Second is sustainable pesticide management as
another important aspect of this research. The
excessive and improper use of pesticides can have
negative effects on the environment, contamination
of soil and water and development of pesticide
resistance in the pests. Here, this study includes a
pesticide recommendation system in which
appropriate pesticide treatment is suggested given the
identified disease. Recommendations generated by
the system for the targeted and regulated pesticide use
will be ecofriendly and cost-effective agricultural
practices. This fits with the modern concept of
sustainable farming: to decrease chemical overuse
and to increase crop health.
In addition, the research is also extended to IoT-
based smart farming by incorporating real time
monitoring systems. Environmental factors such as
temperature, humidity, and soil conditions which
would affect disease outbreaks can be tracked by
sensors. The system, by being based on an IoT
technology, can be enhanced through the
incorporation of AI driven disease detection
simultaneously, and can provide predictive insights to
farmers in order to take preventive measures before
the disease spreads widely. Data storage can be cloud
based and update on real time to continuously
improve and adapt the model to new diseases.
This research is poised to make a great innovation
in modern farming, being an interdisciplinary
research at the intersection of AI, agriculture,
computer vision, and environment sustainability.
This study proposes to improve the crop health
management and ensure food security through the
synergism of deep learning with smart sensors and
data processing in real time. There are potential
outcomes of this research to empower the farmers, to
enhance the agricultural efficiency and in general, to
assist a less polluting and stronger farming
ecosystem.
3 LITERATURE SYSTEM
3.1 Plant Disease Detection Using Deep
Learning
• Title: Plant Disease Identification Using
Convolutional Neural Networks.
Author: Mohanty et al.
Abstract: This study applies CNN-based
deep learning models for automatic plant
disease identification using images. The
model was trained on the PlantVillage
dataset, achieving high accuracy in detecting
multiple plant diseases. The study highlights
the advantages of deep learning over
traditional feature extraction methods and
demonstrates the effectiveness of CNNs in
real-time agricultural applications.
3.2 A Deep Learning-Based Approach
for Agricultural Disease Detection
• Title: Deep Learning-Based Plant Disease
Recognition for Smart Agriculture
Author: Ferentinos et al.
Abstract: This research focuses on using
pretrained CNN architectures such as
AlexNet, VGG16, and ResNet for plant
disease classification. The study emphasizes
the importance of transfer learning to
improve detection accuracy and reduce
computational costs. The results
demonstrate that CNN-based models can
outperform traditional machine learning
techniques like SVM and decision trees.
3.3 Smart Agriculture and IoT-Based
Monitoring for Disease Prediction
• Title: IoT-Based Smart Farming System for
Disease Detection.
• Author: Zhang et al.
• Abstract: This paper explores the
integration of IoT and deep learning for real-
time monitoring of plant health. The system
uses environmental sensors to collect
temperature, humidity, and soil moisture
data, which are analyzed alongside leaf
Plant Disease Identification and Pesticides Recommendations Using CNN Deep Learning
155

images using CNNs. The study
demonstrates that combining IoT with AI
can provide early warning systems for
farmers, helping prevent large-scale crop
losses.
3.4 Sustainable Pesticide Management
Using AI-Based Decision Support
Systems
• Title: AI- Driven Pesticide Recommendat-
ion System for Precision Agriculture.
• Author: Kumar et al.
• Abstract: This research introduces a data-
driven pesticide recommendation system
that analyzes disease symptoms and
suggests suitable pesticides. By integrating
plant pathology databases and regulatory
guidelines, the system ensures optimal
pesticide use while minimizing
environmental impact. The study
underscores the potential of AI in reducing
excessive chemical application and
promoting sustainable farming practices.
3.5 Comparative Study of Image
Processing and Deep Learning in
Agriculture
• Title: Traditional Image Processing vs.
Deep Learning for Plant Disease
Classification.
Author: Singh et al.
Abstract: The paper compares traditional
image processing techniques (such as color-
based segmentation and feature extraction)
with deep learning models for plant disease
classification. The results indicate that
CNNs outperform traditional methods in
accuracy, scalability, and adaptability,
making them more suitable for real-world
agricultural applications.
3.6 Key Takeaways from Literature
Survey
• Plant disease detection models based on
deep learning’s CNN models achieve a very
high accuracy, compared to traditional
image processing and machine learning
techniques.
• The combination of IoT with AI based
disease detection gives the farmers real time
monitoring and warnings of early detection
of such diseases that would have meant
major crop losses.
• Pre-trained models (VGG16 and ResNet)
are used in transfer learning for achieving
better classification performance with a
smaller number of training examples.
• The use of AI based pesticide
recommendation systems help in optimizing
the use of chemicals and thus adhering
towards sustainable and eco-friendly
agriculture. Nevertheless, deep learning
presents challenges including high demand
in computation, high dependency on dataset,
and real time deployment which require
more research.
4 EXISTING SYSTEM
Currently, farmers and agricultural experts manually
identify plant diseases and recommend pesticides. In
this system, farmers not only can view the symptoms
of the disease, such as leaf discoloration, spots or
wilting, but also judge the disease and then choose a
pesticide according to experience. But, there are some
deficiencies with this method, which restricts its use
on a large scale.
Therefore, instead, some of the machine learning
(ML) and image processing techniques which are
used for plant disease detection currently need
manual feature extraction which reduces the
precision. Existing methods for plant disease
classification in conventional image processing
process utilize color base segmentation, edge
detection, and feature matching. Performance of these
methods is restricted in terms of complexity of the
plant symptoms, as well as varying lighting
conditions and different angles of leaf images.
A number of agricultural advisory systems make
pesticide recommendations that are based either on
pre-defined datasets or on expert inputs.
Nevertheless, these systems are not adaptive in the
real time and they commonly suggest the application
of pesticide with no consideration to the real time
conditions such as humidity, temperature, and soil
health. On another level, they do not tackle overuse
or misuse of chemical pesticides that results in
degradation of the environmental and heightened
chemical resistance in plants.
To support smart farming, there are some
IoTbased smart farming solutions which are
accompanied by sensors monitoring soil moisture,
temperature and humidity. Although these systems
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
156
address the problems of crop health monitoring and
management of irrigation, they lack in disease
identification and provision of disease treatment
recommendations. The prediction of disease via
cloud-based AI models is still in its infancy stage and
not fully adopted as of yet because of high
computational cost and connectivity problems in rural
areas.
Limitations of the Existing System
• Manual disease identification is error-
prone and time-consuming.
• Traditional image processing techniques
have low accuracy in complex disease
classification.
• Limited real-time adaptability in existing
pesticide recommendation systems.
• Overuse or incorrect use of pesticides,
harming the environment and soil health.
• IoT-based solutions focus mainly on soil
monitoring rather than disease detection
and treatment.
Due to these challenges, there is a growing need
for an AI-powered, automated plant disease
identification system that can provide real-time,
accurate, and sustainable pesticide recommendations
to farmers.
5 PROPOSED SYSTEM
In this approach, we introduce such an AI driven,
automated plant disease detection and pesticide
advisory system that is built on top of Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNN), IoT sensors and cloud-
based decision making. Traditionally available to the
farmers are the generic solutions i.e. manual disease
identification and pesticide application, which comes
with certain limitations and this system works
towards the advancement of the same by providing
real time, accurate and sustainable solutions. It
enables detection of plant disease well in advance and
allows particularly efficient applications of the right
pesticides by using image processing, deep learning
and smart agriculture technologies.
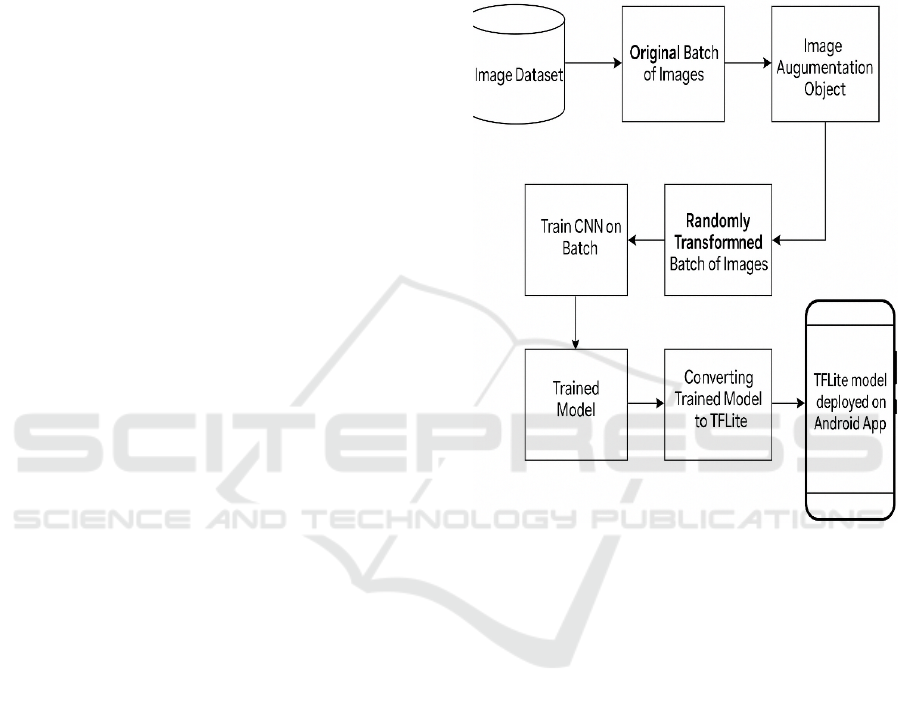
Figure 1 shows the architecture diagram. The
system builds a deep learning model based on
convolutional neural network (CNN) trained on the
dataset of diseased and healthy plant images who are
the core component of the system. A mobile
application or a camera module may be used by the
farmers to capture an image of a plant leaf which will
be analyzed by the system and the diseased plant leaf
will be immediately diagnosed by classifying the
disease. Without manual feature extraction, the CNN
model speeds up and adds more accuracy to the
process. However, unlike traditional machine
learning methods, CNS distinguish different complex
patterns, different colours, and different types of leaf
textures, and thus can help increase disease
classification accuracy.
Figure 1: Architecture diagram.
Besides disease detection through an image-based
system, the system also equipped with IoT sensors to
evaluate environmental factors like temperature,
humidity and soil moisture that also affect the plant
health. A cloud-based AI model analyzes realtime
data to find generated from these sensors. With this
being said, the system considers both image-based
symptoms and environmental conditions to increase
the reliability of disease predictions and prevent the
outbreak from spreading. Farmers can also get alerts
and suggestions for the changing environmental
conditions.
If a disease is known, the pesticide
recommendations are based on the disease type,
severity, and environmental conditions and are
suggested by the system which uses AI. Beyond the
social factors influencing fisher behavior – both on
long and short time scales – there are informative
interactions taking place between the physical
environment and large numbers of daily decisions
made by fishers. Moreover, it offers organic ways of
Plant Disease Identification and Pesticides Recommendations Using CNN Deep Learning
157
treatment to farmers who are embracing the use of
organic practices in farming. The system ensures the
right amount of pesticide is applied at the time it is
needed, to prevent misuse or overuse of your
chemicals, which would lead to resistance.
The system has a web and mobile user interface
with which farmers can upload images, get their
disease reports and receive pesticide treatment
recommendations to improve usability of the system.
By using a platform, real time updates, historical
disease tracking and support for multiple languages
that can be used in multiple regions are available for
use by the farmers. The system constantly gets better
by learning from new cases involving disease and
farmer feedback. An AI powered solution to Smart
Agriculture wherein this AI helps farmers to reduce
crop loss, improve yield quality and advocate the
sustainability in farming.
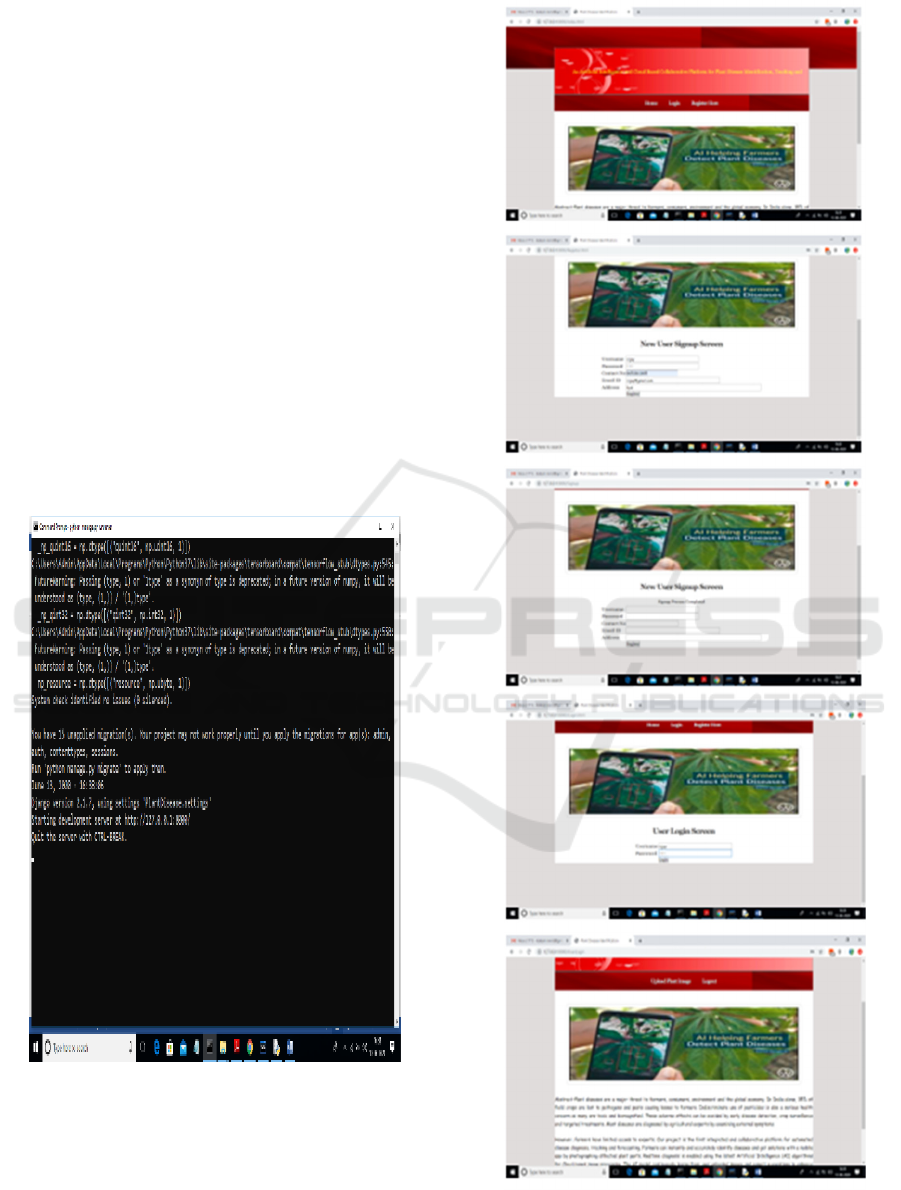
6 RESULTS
Figure 2: Django server running for plant disease detection
web app.
Figure 3: Login & signup flow.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
158

Figure 4: Plant disease detection – image upload flow.
Figure 2 shows the Django Server Running for
Plant Disease Detection Web App. Figure 3 shows the
Login & Signup Flow. Figure 4 shows the Plant
Disease Detection – Image Upload Flow.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, the proposed AI driven plant disease
identification and pesticide recommendation system
provides accurate, real time and automated way to
farmers for detection of plant disease and application
of right treatment. The system integrates
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to predict
disease in images, IoT sensors for environmental
monitoring, and AI driven decision making which
helps in enhancing the precision, efficiency and
sustaining in the process of agriculture.
This system improves diagnostic accuracy
compared to the traditional manual disease
identification and pesticides application, which also
reduces human error chances. With actual time iot
Information, the Plants may be monitored to
Outsmart Where and When They Are Most Liable to
Crop Lysis Caused by Environmental Factors.
Furthermore, the system aids farmers to be better
informed when taking decisions regarding pesticide
usages, in order to allow minimum possible
environmental effect while maintaining maximum
crop health.
This system has user friendly web and mobile
interface where farmers upload their plant images, get
report instantaneously and view AI based pesticide
recommendations. This enables the system to always
be up to date with the new disease case patterns and
environmental patterns and learn continuously.
Through implementing this solution, farmers will
experience increased crop production, less losses, and
better methods of pest control, increase the
productivity of agriculture and food security. A smart
approach to the way this agriculture is done is that it
is a sustainable farming that prevents the use of
excess chemical pesticides and encourages use of eco
– friendly alternatives.
This system can be further increased in the dosage
of information in the future by providing a more
significant dataset cobers more plant species and
diseases, including satellite-based monitoring, and
predictive analytics for plant diseases outbreak. It is
the adoption of such AI powered agricultural
technologies that will become a essential component
in determining the agricultural future in precision
farming and in guaranteeing efficient use of labors,
resources, money, time spent and other variables.
REFERENCES
Abbas, A., Jain, S., Gour, M., & Khanna, A. (2021).
Tomato Plant Disease Detection Using Transfer
Learning with CNN. Artificial Intelligence in
Agriculture, 5, 11-20.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aiia.2021.05.002
Brahimi, M., Arsenovic, M., Laraba, S., Sladojevic, S.,
Boukhalfa, K., & Moussaoui, A. (2018). Deep Learning
for Plant Diseases: Detection and Saliency Map
Visualisation. Human and Machine Learning, 93-117.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90403-0_5
Ferentinos, K. P. (2018). Deep Learning Models for Plant
Disease Detection and Diagnosis. Computers and
Plant Disease Identification and Pesticides Recommendations Using CNN Deep Learning
159

Electronics in Agriculture, 145, 311-318.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.01.009
Kamilaris, A., & Prenafeta-Boldú, F. X. (2018). Deep
Learning in Agriculture: A Survey. Computers and
Electronics in Agriculture, 147, 70-90.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.02.016
Liu, J., Wang, X., & Wang, Z. (2020). A Comprehensive
Review on Plant Disease Detection Using Deep
Learning Techniques. Advances in Intelligent Systems
and Computing, 1021, 27-45.
Lu, J., Hu, J., Zhao, G., Mei, F., & Zhang, C. (2017). An
Improved CNN Model for Recognition of Plant
Disease. International Journal of Engineering Research
& Technology (IJERT), 6(4), 32-38.
Mohanty, S. P., Hughes, D. P., & Salathé, M. (2016). Using
Deep Learning for Image-Based Plant Disease
Detection. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1419.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01419
Picon, A., Alaña, M., Irigoyen, I., Irigoyen, E., &
Bereciartua, A. (2019). Deep Learning for Plant
Disease Detection with Limited Data Sets. Computers
and Electronics in Agriculture, 167, 105093.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.105093
Ramcharan, A., Baranowski, K., McCloskey, P., Ahmed,
B., Legg, J., & Hughes, D. P. (2017). Deep Learning for
Image-Based Cassava Disease Detection. Frontiers in
Plant Science, 8, 1852.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01852
Saleem, M. H., Potgieter, J., & Arif, K. M. (2021). Plant
Disease Classification: A Review of Deep Learning-
Based Approaches. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12,
624094. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.624094.
Sharma, P., Kumar, S., & Shukla, A. K. (2020). Plant
Disease Identification and Classification Using CNN.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
(JAIML), 2(1), 45-57.
Sladojevic, S., Arsenovic, M., Anderla, A., Culibrk, D., &
Stefanovic, D. (2016). Deep Neural Networks Based
Recognition of Plant Diseases by Leaf Image
Classification. Computational Intelligence and
Neuroscience, 2016, 3289801.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3289801
Too, E. C., Yujian, L., Njuki, S., & Yingchun, L. (2019). A
Comparative Study of Fine-Tuning Deep Learning
Models for Plant Disease Identification. Computers and
Electronics in Agriculture, 161, 272-279.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.03.032
Wu, D., Lv, S., Jiang, M., Song, H., Wang, X., & Cheng,
X. (2021). Pest and Disease Detection for Smart
Agriculture Using Machine Learning Techniques.
Smart Agricultural Technology, 1, 100003.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2021.100003
Zhang, S., Zhang, S., Zhang, C., Wang, X., & Shi, Y.
(2019). Cucumber Leaf Disease Identification with
Global Pooling Dilated Convolutional Neural Network.
Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 162, 422-
430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.04.018
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
160
