
EDA: Bank Loan Default Risk Analysis
N. Ramadevi, Vasagiri Sai Kumar, Kondamadugula Dheeraj Reddy, Gandragoli Kasi Viswanath,
Natuva Komal Sai and Bachu Venkata Deepak Kumar
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (Data Science), Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal‑518501,
Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Data Visualization, Statistical Analysis, Credit History, Employment Status, Loan Amount, Default
Probability, Risk Analysis, EDA, Loan Default Risk, Credit Risk.
Abstract: The increasing number of debt lapse presents a large assignment to economic institutions, affecting their
profitability and lengthy-term economic stability. Debt omission occurs whilst the borrower fails to fulfill his
compensation obligations, leading to expanded hazard for banks and creditors. Identification of things
contributing to those omissions is vital to improve credit score danger evaluation and make sure greater
powerful lending practices. This takes a look at focuses on search information analysis (EDA) to research
historical mortgage records and highlight the most important pattern affecting the loan reimbursement
behavior. By analyzing borrower characteristics including income level, employment repute, credit score,
mortgage quantity, hobby rate and reimbursement history, the purpose of this take a look at is to become
aware of critical factors that determine the opportunity of mortgage urge. Using data visualization and
statistical strategies, the research default examines the relationship between various economic and
demographic variables to provide precious insights in chance. Understanding those patterns can assist banks
to make loans and manipulate financial dangers knowledgeable. Analysis curses the importance of credit score
history, as debtors with negative compensation records are more likely to default. Additionally, elements
along with high loan-to-earnings ratio, risky employment and big loan quantity contribute to debt offenses.
By identifying these essential chance indicators, economic establishments can boom their credit evaluation
shape and apply extra powerful hazard mitigation strategies. One of the major goals of this have a look at is
to help banks in developing facts-driven loan approval strategies. By leveraging insights from EDA, monetary
establishments can refine their lending standards, reduce non-acting loans, and optimize risk evaluation
fashions. This, in turn, facilitates in preserving financial balance whilst making sure that eligible borrowers
get hold of get admission to credit score.
1 INTRODUCTION
The growing number of loan defaults has grown to be
an important issue for banks and monetary
establishments global. A loan default occurs whilst a
borrower fails to fulfill the repayment duties, leading
to financial losses for the lender. As the call for loans
maintains to upward thrust, banks should carefully
assess credit hazard to minimize default charges
while ensuring that loans are granted to eligible
applicants. Effective danger control techniques are
essential to preserve economic balance and prevent
monetary disruptions resulting from high default
prices.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) plays a critical
position in understanding the patterns and
developments associated with loan defaults. By
reading historical mortgage facts, financial
establishments can advantage insights into key
factors influencing default danger. Attributes which
include borrower earnings, employment status, credit
score, mortgage amount, interest price, and
compensation records offer valuable indicators of an
applicant's capacity to repay a loan. EDA enables find
hidden relationships among those variables,
permitting banks to make records-driven lending
selections.
One of the number one goals of this take a look at
is to perceive high-chance borrowers based totally on
their economic and demographic traits. Borrowers
with bad credit score history, low earnings, risky
Ramadevi, N., Kumar, V. S., Reddy, K. D., Viswanath, G. K., Sai, N. K. and Kumar, B. V. D.
EDA: Bank Loan Default Risk Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0013909100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
125-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
125

employment, or high debt-to-earnings ratios are more
likely to default. By studying those patterns, banks
can put in force stricter credit score policies, improve
hazard assessment fashions, and minimize monetary
losses. This has a look at also explores how one- of-
a-kind mortgage characteristics, along with mortgage
tenure and interest quotes, effect default prices.
Data visualization techniques, such as histograms,
container plots, heatmaps, and scatter plots, are used
in this evaluation to interpret complex facts
relationships successfully. These visual
representations provide a clearer understanding of
how borrower attributes impact compensation
conduct. Additionally, correlation evaluation helps
determine the electricity of relationships between
exceptional monetary elements, helping in the
improvement of robust risk prediction fashions.
The insights from this evaluation are vital for
monetary establishments to decorate their credit score
approval procedures. By refining lending criteria,
banks can ensure that loans are granted to debtors
with a decrease chance of default. Moreover,
enforcing system mastering models primarily based
on EDA findings can similarly improve the accuracy
of default prediction structures, permitting a proactive
approach to hazard management
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Searching Data Analysis in Debt
Risk Evaluation (EDA)
Ch. Deepika et al. (2024) Integrate searching data
analysis (EDA) with machine learning to assess bank
loan default risks. The proposed system employs
random forest and size values for lecturers,
emphasizing transparency in credit decisions. Python
library such as pandas and
skikit-learns is used for preprocessing and model
training, receive high accuracy through modules for
data division, convenience of importance analysis and
real-time credit prediction. Framework highlights the
role of EDA in identifying repayment patterns and
reducing financial risks for institutions offering
municipal loans.
2.2 An Exploratory Data Analysis for
Loan Prediction Based on Nature of
the Clients
Previous studies in loan prediction have
predominantly employed machine learning and data
mining techniques to assess credit risk. For instance,
Goyal and Kaur (2016) explored ensemble models,
achieving 81.25% accuracy using tree algorithms,
while others utilized J48 (78.38% accuracy) and
Naive Bayes classifiers for loan approval decisions.
Research by Shaath emphasized R-based credit risk
modeling with K-nearest neighbors (KNN) for
handling missing data, and Sudhakar et al. (2016)
applied decision trees to bank datasets for risk
stratification. These works highlight the efficacy of
predictive algorithms but often overlook foundational
data exploration.
2.3 Higher-Compatibility Loan
Approval Using Prediction
Dressing Methods
F.M. Ahosanul Haq and MD. Maheedi Hasan (2024)
acquired 99% accuracy in predicting loan approval
using adbots on a dataset of 148,670 entries. Their job
compares enchanted methods (Random Forest,SVM)
and highlights the strength of the adbots in handling
unbalanced data. Feature selection and encoding
technology streamlines models, while accurate
metrics banking to automate approved procedures in
banking ecosystems.
2.4 Machine Learning for Debt
Classification
Pro. R. Yadgiri Rao et al. (2022) Propose an ML-
based debt prediction system using demographic and
financial characteristics. Their model takes advantage
of trees and logistic regression to classify applicants,
which emphasizes pre -proposing stages such as
external removal and generalization. The study
reports 85% accuracy, highlighting the role of feature
engineering in increasing the future performance for
Indian banking references.
2.5 Nervous Network and Hybrid
Models for Credit Risk Evaluation
Gopinath Mahankali and Mahip Kunagu (2021) focus
on credit risk evaluation using nervous network and
shield promoting. Their work addresses square
imbalance through smoke and receives 89%
accuracy, emphasizing the importance of variables
such as credit history and income. The study
advocates to improve default prediction in retail
banking for hybrid models.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
126

2.6 Comparative Analysis of ML
Algorithm for Loan Approval
Dr. E. Neelima et al. (2022) Compare SVM, Random
Forest and XGBost for loan approval, get 83%
accuracy with feature selection techniques. Their
structure uses the scikit- learn of the python for data
visualization and emphasizes lowering false positive
through hypermeter tuning, demonstrating practical
prevention in the rural banking sector of Andhra
Pradesh.
2.7 Naive Bayes and Ensemble
Learning for Loan Repayment
Prediction
E. Chandra Blassi and R. Rekha (2019) appoints the
methods of the contingent of Bhole Bayes and artists
to predict debt repayment capabilities. Their study
highlights the importance of credit scores and
employment status, acquiring 78% accuracy. This
task underlines the need for real -time monitoring to
update the model with developing financial trends.
2.8 Logistic Regression and Decision
Trees for Automated Loan
Processing
V. Nikhileswar et al. (2019) use logistic regression
and decision trees to automate loan eligibility checks.
By analyzing historical data from Hyderabad-based
banks, their model achieves 81% accuracy, reducing
manual processing time. The study stresses the
scalability of ML models for high-volume loan
applications in urban financial hubs.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Dataset
Collect loan-related data from financial institutions or
publicly available sources. Ensure that the dataset
includes key attributes such as loan amount, applicant
income, credit score, interest rate, employment
status, repayment history, and loan tenure. Perform an
initial inspection of the dataset to check for
inconsistencies or anomalies.
3.2 Data Processing
Handle missing values using techniques such as
mean/median imputation or dropping irrelevant
records. Convert categorical variables into numerical
form using encoding techniques (e.g., one-hot
encoding or label encoding). Standardize or
normalize numerical features to ensure uniformity in
data distribution. Identify and remove duplicate
records to maintain data integrity.
3.3 Train-Test Split
Split the dataset into training and testing sets
(typically 80-20 or 70-30 split). Ensure stratified
sampling to maintain the proportion of loan defaulters
and non-defaulters in both sets. Validate the
distribution of key attributes across training and
testing datasets to avoid bias.
3.4 Training Data
Conduct Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) on the
training dataset to identify trends and correlations.
Use univariate analysis to study the distribution of
individual features (e.g., histograms, box plots).
Perform bivariate analysis to examine relationships
between different attributes (e.g., correlation
heatmaps, scatter plots). Identify key risk indicators
affecting loan defaults, such as high debt-to-income
ratio, low credit scores, or high loan-to-value ratios.
3.5 Testing Data
Use the test dataset for validating insights obtained
from the training data. Cross-check patterns and
ensure consistency in trends observed during EDA.
Assess any significant variations or unexpected
behaviours in the data distribution.
3.6 Statistical Analysis & Visualization
Generate descriptive statistics to summarize data
characteristics, such as mean, median, standard
deviation, and skewness. Create visual
representations, including bar charts, pie charts, box
plots, and distribution curves, to better understand
data patterns. Analyze correlations between different
financial and demographic factors to determine their
impact on loan repayment.
3.7 Result Interpretation
Identify key insights from the EDA, such as common
characteristics of defaulters and successful
borrowers. Highlight significant risk factors
contributing to loan defaults and their potential
impact. Compare findings with existing financial risk
EDA: Bank Loan Default Risk Analysis
127
models or industry standards.
3.8 Visualization & Report Findings
Present the analysis results using dashboards, charts,
and visual reports for better understanding.
Summarize key observations in a structured format,
providing actionable insights for financial
institutions. Propose recommendations for mitigating
loan default risks, such as improved credit scoring
models, stricter approval criteria, or enhanced
borrower monitoring strategies.
Figure 1 shows the
Methodology Flow chart.
Figure 1: Methodology Flow Chart.
4 RESULT AND EVALUATION
4.1 Loan Applicant Data Analysis
Whenever the bank makes decision to give loan to
any customers then it automatically exposes itself to
several financial risks. It is necessary for the bank to
be aware of the clients applying for the loan. This
problem motivates to do an EDA on the given dataset
and thus analyzing the nature of the customer. The
dataset that uses EDA undergoes the process of
normalization, missing value treatment, choosing
essential columns using filtering, deriving new
columns, identifying the target variables and
visualizing the data in the graphical format. Python is
used for easy and efficient processing of data. This
paper used the panda’s library available in Python to
process and extract information from the given
dataset. The processed data is converted into
appropriate graphs for better visualization of the
results and for better understanding. For obtaining the
graph Matplot library is used.
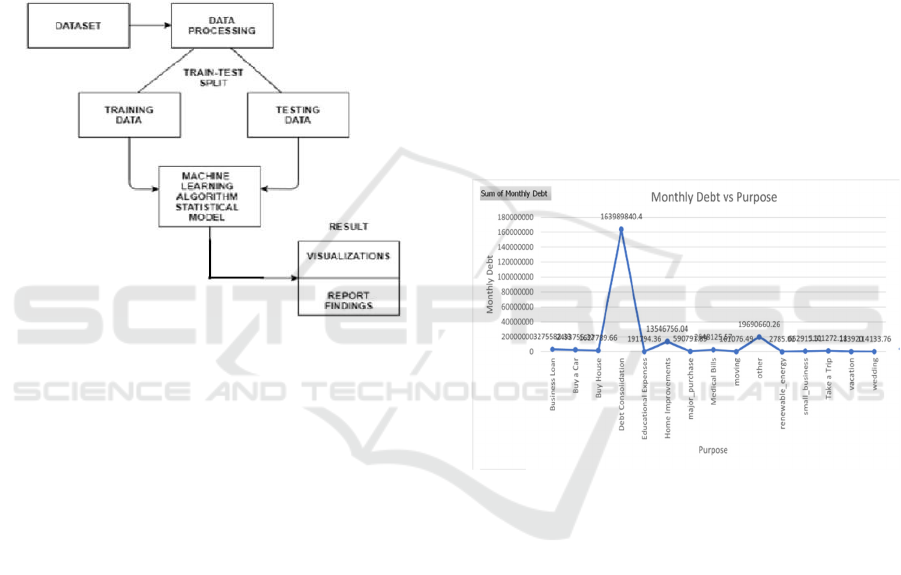
4.1.1 Monthly Debt vs Loan Purpose
• The highest monthly debt is linked to Debt
Consolidation loans, followed by home
buying.
• This suggests that people taking loans for debt
consolidation may already be financially
strained.
• Analyzing the default rates per loan purpose can
highlight high-risk loan categories.
• Debt Consolidation loans dominate,
suggesting many borrowers struggle with
existing debts.
• Home-buying loans also show high debt,
meaning property investments may be risky for
banks.
• Analyzing default rates per loan purpose can
reveal which loan types pose the highest
financial risk.
Figure 2 shows the Monthly Debt
vs Loan Purpose.
Figure 2: Monthly Debt Vs Loan Purpose.
4.1.2 Credit Categories vs Loan ID
• Bad credit borrowers make up the majority,
raising concerns about high default
probability.
• The small number of Excellent and Good
credit loans suggests that banks may prefer
riskier lending strategies.
• Understanding repayment trends per credit
category can help in adjusting loan approval
criteria.
• Most loans belong to the Bad Credit category,
indicating a high-risk borrower pool.
• Very few loans are issued to those with
Excellent or Good credit.
• The high proportion of bad credit loans might
correlate with higher loan default rate.
Figure
3 shows the Credit Categories vs Loan ID.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
128
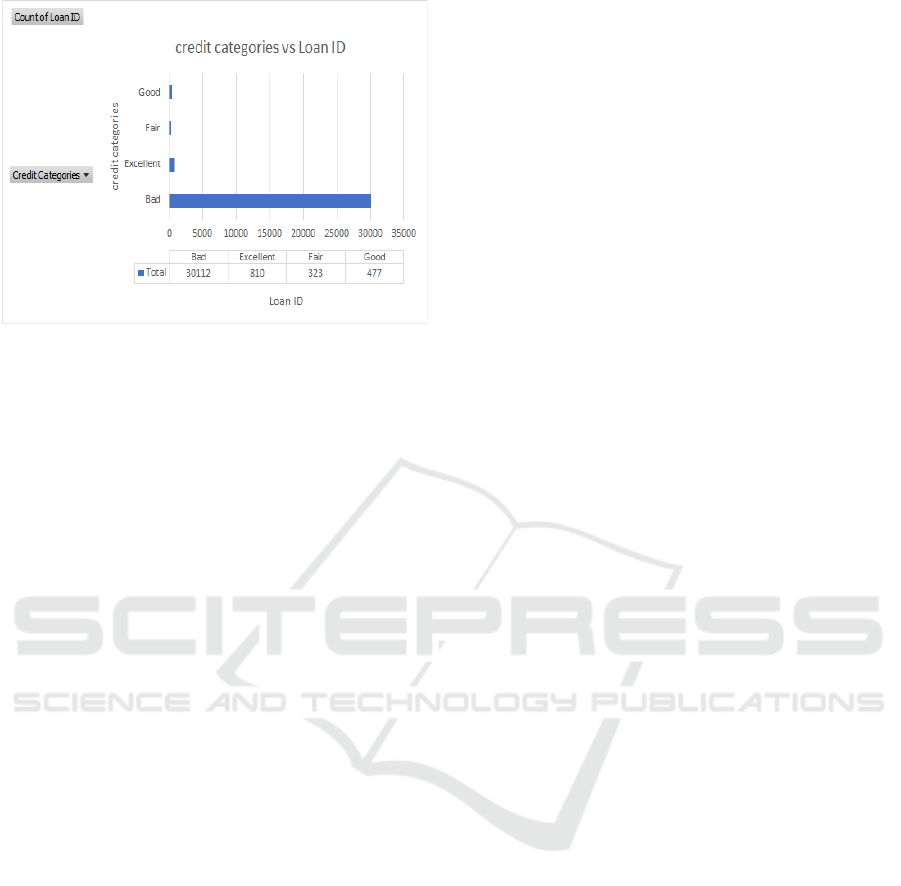
Figure 3: Credit Categories vs Loan ID.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study systematically explores the critical factors
influencing loan default risks through Exploratory
Data Analysis (EDA), offering actionable insights to
enhance credit risk assessment frameworks. Key
findings reveal that debt consolidation and home-
buying loans are associated with higher financial
strain, as borrowers in these categories exhibit
elevated monthly debt levels and default
probabilities. The dominance of bad credit applicants
in loan approvals underscores systemic risks,
suggesting financial institutions may prioritize short-
term gains over long-term borrower stability. Sector-
specific risks, such as freelancers and full-time
workers, emerged as vulnerable groups, necessitating
tailored risk-mitigation strategies. The analysis
identifies credit history, loan-to-income ratios, and
employment stability as pivotal determinants of
repayment capacity. Visualizations like heatmaps and
box plots corroborate these patterns, demonstrating
strong correlations between poor credit scores, high
loan amounts, and default rates.
REFERENCES
Ch. Deepika, Ch. Alekhya, G. Khushi Reddy, Ch. Mounika,
S, Chaitanya Kumar,’ “Eda For Bank Loan Default
Risk Assessment” ‘, Computer Science Department,
JNTUH, Vidhya Jyothi Institute of Technology, India,
International Journal of Progressive Research in
Engineering Management and Science (IJPREMS),
Vol. 04, Issue 12, December 2024, pp: 887-893.
Dr. E. Neelima, Venkata Ayyappa Reddy Maruprolu, Sai
Prasad Penta, and Karthikeya Mallareddy “explored
Loan Approval Prediction Using Supervised Machine
Learning Algorithm” (2022) at GITAM University,
Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India, Vol 13, Issue
04, APRIL/2022 ISSN NO:0377-9254, JES
publication.
E. Chandra Blessie and R. Rekha published “Exploring the
Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction the Loan
Sanctioning Process” (2019) in the International
Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring
Engineering. The research was conducted at the
Department of MCA, Nehru College of Management,
Coimbatore, Tamil Nādu, India, International Journal
of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering
(IJITEE) ISSN: 2278-3075 (Online), Volume-9 Issue-
1, November 2019.
F. M. Ahosanul Haque and Md. Mahedi Hassan authored
“Bank Loan Prediction Using Machine Learning
Techniques” (2024) at the Department of Computer
Science and Engineering, Daffodil International
University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, American Journal of
Industrial and Business Management, 2024, 14, 1690-
1711 https://www.scirp.org/journal/ajibm
Gopinath Mahankali and Maheep Kunagu presented
“Customer Loan Prediction Analysis” (2021) as part of
their Bachelor of Engineering requirements at the
Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
School of Computing, India, IEEE international
conference on advances in computer applications
(ICACA).
Led by Prof. R. Yadagiri Rao, with collaborators K.
Srikanth, S. Ajay Kumar, S. Srinath, Y. Sandeep
Kumar, and B. Rajesh, the project “ML-Based Loan
Prediction” (2022) was executed at the Sri Indu Institute
of Engineering & Technology, Hyderabad, India,
Journal of Education: Rabindra Bharati University Issn:
0972-7175
V. Nikhileswar, Sunil Bhutada, and Mekala Sreenivas
addressed Mitigation of “Banking and Financial
Services Involved Risks” (2019) at the Sreenidhi
Institute of Science & Technology, Hyderabad, India,
Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics
Education Vol.11 No03 (2020), 1073 – 108.
X.Francis Jency, V.P.Sumathi, Janani Shiva Sri developed
“An Exploratory Data Analysis for Loan Prediction
Based on Nature of the Clients “(2018). The work was
conducted at the Department of Mechanical
Engineering, international Journal of Recent
Technology and Engineering (IJRTE) ISSN: 2277-
3878 (Online), Volume-7 Issue-4s, November 2018.
EDA: Bank Loan Default Risk Analysis
129
