
Smart Luggage Theft Detection and GPS Tracking System
Jillella Navya, G. N. Swamy, Siddabattuni Shanmukha Sri, Bhatraju Pujitha and Sasanala Varun
Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College,
Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Luggage Tracking, GPS (Global Positioning System), Arduino Uno, GSM (Global System of Mobile
Communication).
Abstract: Two of the biggest challenges facing the global aviation and transportation industry are lost baggage, luggage
theft, and damage to traveler’s belongings. To address these chronic problems, we have developed and
implemented a luggage tracking system based on the IoT technology. So, in this, the GSM/GPS module is
used for continuous and the Arduino microcontroller is used for data processing. The luggage position is
continuously monitored by the GPS module; it constantly receives relevant position information and sends it
to the microcontroller. The GSM module is responsible for sending the data to the passengers through SMS
and service provided will allow them to easily check on their bags in real time, specifically in the form of a
map. This real-time tracking seeks to minimize the occurrence of lost - misplaced or stolen baggage providing
reassurance for passengers and operational benefits for the aviation sector. This relieves stress, resulting in
passengers knowing the position of their suitcase all the time and has the ability to tracing and reclaiming it
if required. This IoT solution implementation emphasizes the positive happened in the technology of
passenger service, thus trust and satisfaction improvement in the global transports.
1 INTRODUCTION
"Luggage Theft Detection and Tracking System"
prevents theft, and helps in their fast location
tracking. At its heart, a power-fed Arduino Uno
microcontroller keeps track of multiple functions and
alerts. It incorporates an HC-05 Bluetooth module
that communicates wirelessly with a mobile device
owned by the user. For security reasons, users get
their own personalized username and password,
which they enter for Bluetooth pairing. Once the
luggage gets paired with the user’s mobile device, it
stays in range for monitoring (W. Yang and Y. Chen
2022). In case the Bluetooth link is lost from the
luggage moving outside range or being stolen the
system sounds off a buzzer. The Arduino triggers this
alert, for example, if the user moves the luggage out
of Bluetooth range, the system activates its location
mode. A GPS module then receives the precise
coordinates of the luggage and transmits this
information to a GSM module, which establishes a
connection through mobile networks to send the user
location data. Real-time location updates are sent to
the user through a dedicated app called “A-Alert.”
The system is an integration of Bluetooth, GPS and
GSM technologies that enables travelers to track and
find their baggage in a secure manner which will help
them minimise their stress of lost or stolen baggage
(S. Lee, J. Kim, and H. Oh, 2022).
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Mishra and Khare analyze how industry 4.0
technologies, specifically IoT (Internet of Things), can
be adopted to facilitate passenger experience and
operational efficiency in the aviation industry. The
study emphasizes that IoT technologies facilitate real-
time tracking and communication between multiple
stakeholders to minimize delays, optimize resource
management, and enhance safety in airports and
airline companies (D. Mishra and A. Khare, 2023).
Dutta and Park explain the merging of IoT and
Artificial Intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics for
airport operations. Their research demonstrates the
potential of utilizing IoT sensors integrated with AI
algorithms to predict flight delays, anticipate
maintenance requirements, and allocate resources
more efficiently, leading to improved airport
operational performance and reduced disruptions (S.
Navya, J., Swamy, G. N., Sri, S. S., Pujitha, B. and Varun, S.
Smart Luggage Theft Detection and GPS Tracking System.
DOI: 10.5220/0013908800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
101-107
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
101

Dutta and Y. Park, 2023). IoT-based Radio Frequency
Identification (RFID) technology is used in Wang and
Zhang's paper to track the baggage in the airport. They
show how RFID improves the efficiency and accuracy
of baggage handling systems, minimizes lost baggage
situations and increases convenience for passengers
and airport personnel by giving real-time tracking
details (X. Wang and H. Zhang, 2023).
IoT based solutions for baggage tracking and
airport security considering Digital airport ecosystem
Kumar and Rao As demonstrated in their study, IoT
technologies can facilitate real-time tracking of
baggage, enhance security checks, and boost airport
operations, leading to an improved passenger
experience and efficiency of modern airports (Kumar
and V. Rao, 2024). We strive to make sure that lost or
missing luggage problem is eliminated with its
seamless, secure, and cost-effective solution by
combining Bluetooth with other existing
technologies. It outlines several ways to leverage
these technologies in order to enhance overall baggage
handling efficiency, process time and passenger
satisfaction in modern airport (H. A. Adjei et al. 2020).
Pros and cons of the aforementioned models exist
with each. The existing solutions are limited and we
introduce a better solution by utilizing Bluetooth
technology along with other state of the art
technologies. This combination helps to overcome the
shortcomings of existing systems by providing
improved functionality, efficiency, and overall
enhanced user experience in aviation, especially in
baggage tracking, predictive analytics, and overall
operational performance (M. Ö. Demir et al. 2020).
3 PROPOSED METHOD
This System was designed which we named as the
"Luggage Theft Detection and Tracking System" to
overcome the theft problem as well as to quickly
locate luggage if lost. The system utilizes an arduino
uno microcontroller as the main control unit powered
by an external power supply to trigger the necessary
components required for the tracking and alert
functions. A Bluetooth module, the HC-05, may
allow the suitcase to exchange information wirelessly
with the user's mobile device. Unique username and
password for every user for security purpose. The
baggage stays within range of the mobile device once
it is Bluetooth-enabled, making tracking simple. If the
Bluetooth connection is lost, whether because the
luggage has moved out of range or due to a potential
theft, the system triggers an alarm. A buzzer
connected to the Arduino immediately activates,
emitting a loud sound to alert the user of the
disconnection. This audible notification helps the user
quickly detect and retrieve the luggage if it is nearby.
In the case of theft or when the luggage moves beyond
the Bluetooth range, the system switches to location
tracking mode. The system incorporates a GPS
module to deliver accurate position information. The
GSM module is in charge of delivering the data to the
user's mobile device after receiving the baggage's
current coordinates from the GPS module.The GSM
module uses mobile networks to communicate the
luggage’s exact location. The mobile app "A-Alert" is
used to notify the user in real-time, offering instant
updates on the luggage’s whereabouts. This allows
the user to effectively track the luggage (P. Devaki
and M. Karthika, 2019).
The technology guarantees constant monitoring
by fusing GPS and GSM technologies, allowing the
user to trace the position of the luggage at all times.
Connect RX pin of Bluetooth module to TX pin (D2)
of Arduino Uno and TX pin of Bluetooth module to
RX pin (D1) of Arduino Uno*. The ground (GND)
and VCC (VCC) circuits of the Bluetooth module are
connected to the GND and VCC pins of the Arduino
Uno. An input supply of 3.3V to 5V powers the
Bluetooth module. The GPS (Global Positioning
System) module is connected to a Global System for
Mobile Communications (GSM) module. Sending
position data from the GPS (GSM Module) PG via its
TX pin (attached to Arduino Uno's Digital pin 3) to
be processed by the Arduino Uno.
GND and VCC pins of GSM module are
connected to GND and VCC pins of Arduino Uno.
This GSM module needs an input source of around
3.3V to 4V in order to operate its tasks and the
coordinates of location info (longitude, latitude) are
sent from the GSM module to the user mobile device
with the help of A-Alert app. It will display the bag's
location on Google Maps, and forward it to the user's
mobile device. The buzzer will ring if the mobile
device loses Bluetooth connectivity. While the
buzzer's negative pin is linked to GND, its positive
pin is directly attached to the Arduino Uno's Digital
pin 7. The position of the bag is continually sent to
the user's mobile phone using the GSM module. In
addition to offering consumers the ability to retrieve
their baggage in the event that it is lost or stolen, this
technology effectively deters theft. They use
Bluetooth, GPS and GSM technology to give
travelers shady security and minimize that little pang
of anxiety when possessions go missing. If baggage
is lost or stolen, the accurate position tracking of
"Luggage Theft Detection and Tracking System:
provides accurate position tracking, and this prevents
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
102
theft (M. Ghazal et al. 2016).
The heart here consists of Arduino Uno
microcontroller and external powered circuits, which
controls all of tracking and alert parts. To achieve
wireless communication, it uses an HC-05 Bluetooth
module that establishes a secure connection between
the luggage and the owner’s mobile phone. Unique
usernames and passwords are issued to users for
security purposes. To connect, the system uses
Bluetooth technology to keep the luggage within a
defined distance — allowing users to keep an eye on
their luggage when it’s within range. Should the
Bluetooth connection be severed — either from the
luggage moving out of the range of the smart device
or a potential theft — the system sets off an
immediate alert. The buzzer connected to the
Arduino now gets activated making a hard noise to
inform the user that the connection is disconnect. This
sound alert lets the user search and collect the luggage
in case it is near. If the luggage moves outside of
Bluetooth range the system goes into location
tracking mode, employing a GPS module to collect
accurate position coordinates. The coordinates are
transferred to a GSM module, and the real-time
location is dispatched to a user’s mobile. Transport
notification is available by the mobile application
"A-Alert", that can allow the user to gain immediate
updates of the luggage's location and how to find it
(M. Goldstein, 2017).
Travelers have to face this luggage theft where this
advanced solution is coming into the picture which is
known to be the "Luggage theft detection and
tracking system" which is a combination of Arduino
Uno Microcontroller with Bluetooth, GPS, and GSM
module. HC-05 Bluetooth module is used as part of
the system to create a secured wireless connection
between the luggage and users mobile device
authenticated with a unique username and password.
Within a specific range, this Bluetooth connection
enables the user to track the luggage. On
disconnection between the luggage and the mobile
device because the luggage moves beyond range or in
the case of possible theft the system raises an alarm
which rings a buzzer attached to an Arduino and
generates a loud sound to notify and alert the user.
When the luggage is not nearby, the device is
switched to location tracking mode, and a GPS
module provides precise coordinates of the luggage.
This data is transmitted to a GSM module, which uses
the "A-Alert" program to provide real-time position
updates to the user's mobile device. The module then
shows locations on Google Maps for convenient
tracking. The connections are carefully set up such
that the RX and TX pins of the Bluetooth module are
linked to the TX and RX pins of the Arduino, and the
GPS module sends position data to the GSM module,
which relays this information to the Arduino using the
GSM's TX pin. The buzzer, responsible for the alert
sound, has its positive terminal connected to Digital
pin 7 on the Arduino, allowing immediate activation
upon disconnection. Through the integration of
Bluetooth for proximity alerts, GPS for precise
location tracking, and GSM for real-time
communication, the system provides a dependable,
user- friendly solution to safeguard luggage, offering
peace of mind to traveller’s and GSM module, which
sends real-time location updates to the user's mobile
device. Notifications are delivered through the mobile
app "A-Alert," allowing the user to access instant
updates on the luggage’s whereabouts and track it
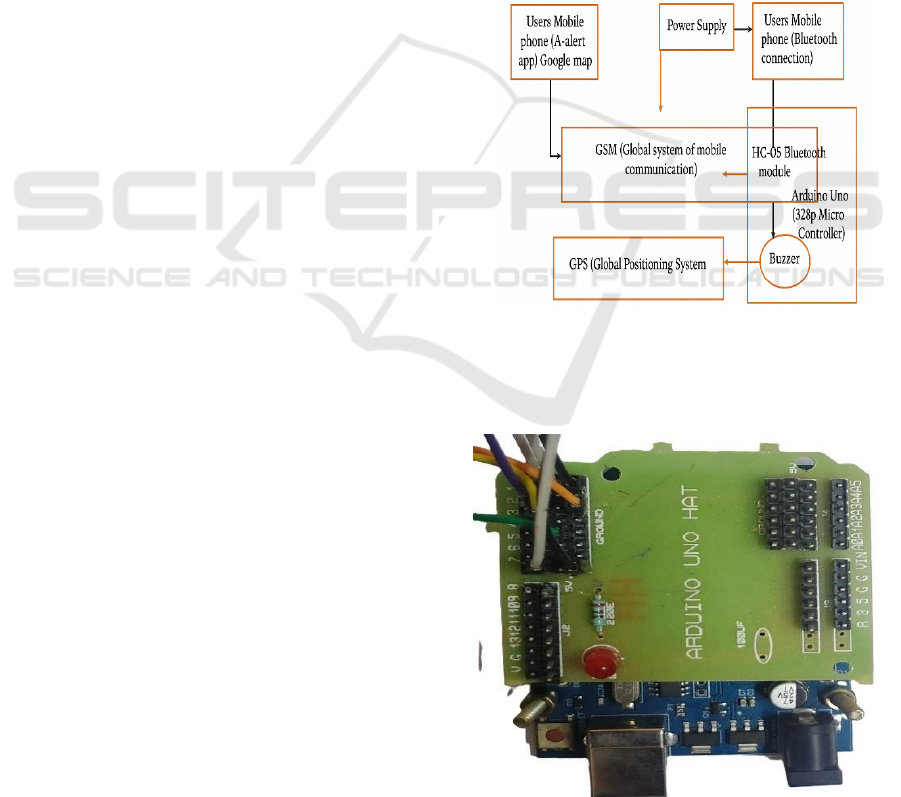
effectively (S. Karthick, 2020). Figure 1 shows the
block diagram of the luggage.
Figure 1. Block diagram of the luggage theft detection and
tracking system.
3.1 Arduino Uno Microcontroller
Figure 2: Arduino Uno microcontroller.
Smart Luggage Theft Detection and GPS Tracking System
103

Figure 2 shows the Arduino uno
microcontroller. In a luggage theft detection and
tracking system, the Arduino Uno serves as the main
controller, managing sensors like accelerometers,
GPS, RFID readers, and proximity sensors to monitor
luggage movement and detect unauthorized handling.
It processes sensor data to identify potential theft
situations, such as luggage movement without the
authorized owner nearby. When theft is suspected, the
Arduino triggers alert mechanisms, like sounding a
buzzer or flashing LEDs, and can send notifications
to the owner’s phone via Bluetooth or GSM modules.
Additionally, if equipped with a GPS module, the
Arduino provides real-time location tracking,
transmitting data to the owner’s device even when out
of Bluetooth range. This integration of sensing,
processing, and communication functions makes the
Arduino Uno the "brain" of the system, ensuring
effective theft detection and tracking (Karvinsky,
2020).
3.2 Bluetooth module
An essential part of the system for tracking and
detecting luggage theft is the HC-05 Bluetooth
module You need 5V DC power supply for it to
work. The serial communication between the
microcontroller and the module's TX and RX pins
allows for data exchange. VCC and GND pins are
connected to power and ground. The EN pin controls
when the module turns on and off, and the STATE
pin indicates its current state. KEY pin is used for
pairing and setup.
Bluetooth module: Choose a compatible
Bluetooth module with microcontroller and
smartphone. An effective serial communication
protocol, such as UART, shall be implemented to
ensure reliable data transmission from the module to
microcontroller and vice versa. Use secure data
transmission techniques to ensure sensitive
information is protected and unauthorized access is
denied. Furthermore, appropriate techniques on
power management are necessary to prolong the
lifetime of system battery (E. Newton, 2020).
Considering these considerations, the HC-05
Bluetooth module can be effectively integrated with
the luggage theft detection and tracking system
enabling robust and reliable wireless communication.
This module is crucial for tracking the luggage in
real time, providing alerts if the luggage is moved
without authorization, and for monitoring the
system's status remotely.
3.3 GPS Module and GSM Module
Figure 3 shows the GPS module is an important part
of many electronic devices that enable accurate
tracking and navigation. GPS modules calculate a
device's latitude, longitude and altitude by receiving
signals from several satellites and calculating the time
difference between the transmission and reception of
the signals. A GPS module consists of an antenna,
GPS receiver, microprocessor, and message
communication means such as UART or I2C. Most
of these modules return data in CSV format, NMEA
data which will contain information about Time,
position and other relevant information about the
device. GPS modules are commonly used in
mapping devices, GPS trackers, and navigation
systems. However, none of these elements, such as air
conditions, signal obstructions and quantity of them
both in the periphery and in high altitude can affect
how well they function. The Ublox NEO series and
Adafruit Ultimate GPS (Purwar et al. 2016) are
common GPS modules.
GSM (Global System for Mobile
Communications) modules are pieces of electronic
equipment used in various electronic devices to
provide cellular connectivity so that they can transmit
data over mobile networks, make voice calls, and
send SMS messages. All these modules typically
include a microcontroller, an antenna, a GSM chipset,
and a SIM card slot. They connect with
microcontrollers using serial protocols like UART.
GSM modules are able to send and receive SMS as
well as voice calls when connected through a SIM
card to a mobile network.
Figure 3. GPS and GSM module.
Applications such as GPS tracking, home
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
104
automation, and remote monitoring frequently
employ GSM modules. They are widely accessible
and reasonably priced, but they depend on the
availability of cellular networks and can use a lot of
power when communicating. The GSM modules
SIM900, SIM800, and SIM5320 are widely used (S.
Safdar et al. 2018. The flow chart for the Luggage
theft detection and tracking system is shown in Figure
4.
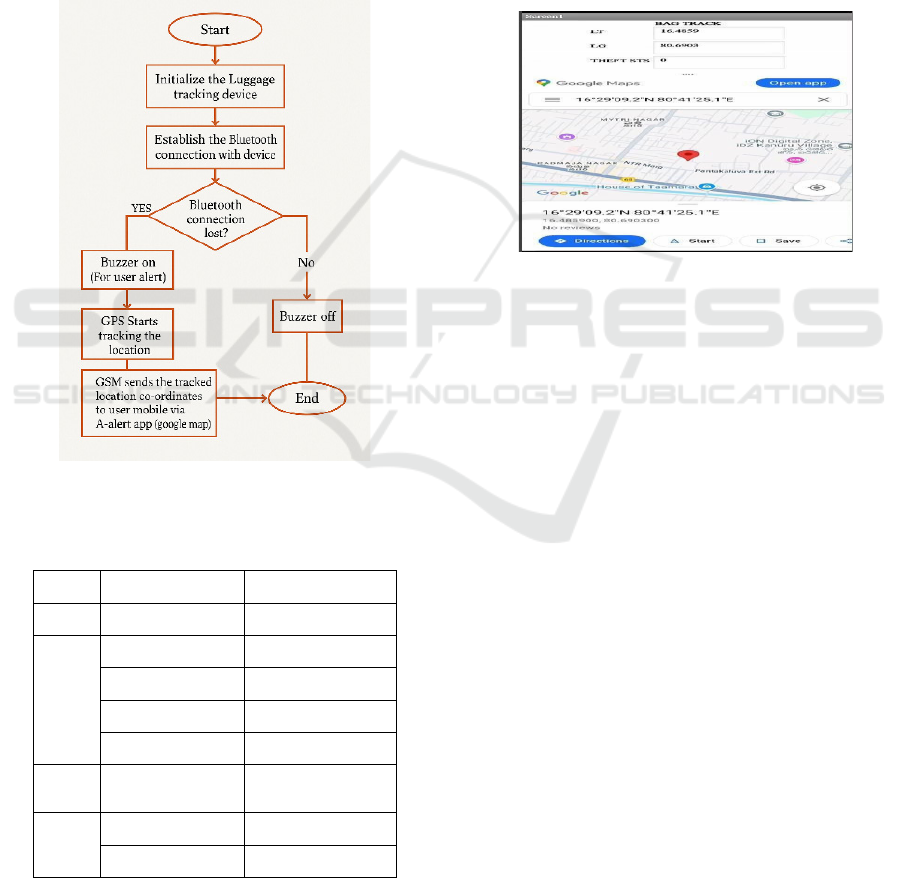
4 WORK FLOW AND METHODOLOGY
Figure 4: Flow chart for the luggage theft detection and
tracking system.
Table 1: Technical specifications of components.
S.NO Components Specifications
1 Microcontroller ATmega328
2
GPS Module Tek MT 3318
Temperature -40 °C to 85 °C.
Power Supply 3.3 – 6 V
Baud Rate 9600bps
3
Bluetooth
module
Hc05
4
GSM Module SIM800
operating voltage 3.7 ~ 4.2V
5 RESULTS
The systems near real time accuracy on luggage
location is precisely measurable. The individual must
assess how precise and accurate the GPS updates are,
and how frequent the location data is. The system
must regularly offer real-time information about the
Luggage’s location (en route, at an airport, or at a
destination) and provide a record of the delivery
speed and correctness of this experience history. This
also evaluates how well the system informs travelers
about their luggage’s location and the speed and
reliability of alerts and notifications sent to users.
Figure 5: Tracking interface of the A-Alert app in mobile
(Google Map).
You may also evaluate the user experience of the
system, encompassing the mobile app UI, how
straightforward it is to pair the baggage tag with it,
and how simple it is to be presented with monitoring
data and status updates. Running tests on the data
handling capabilities of the system, performance of
Bluetooth, and interactions with the cloud can allow
one to analyze the adaptability of the system, the rate
at which it transfers information, and the energy
economy. Another important consideration is
reliability, which involves keeping an eye on how
efficiently the system manages data loss, monitors
luggage, and reacts to mistakes or interruptions.
Discussions may center on the system's scalability,
namely its capacity to handle several baggage tags
and users at once, and how flexible it is in the face of
unforeseen disruptions. The result tracking location
interface is shown in the Figure 5 and figure 6 and 7
luggage tracker hardware prototype and detected
location.
Smart Luggage Theft Detection and GPS Tracking System
105
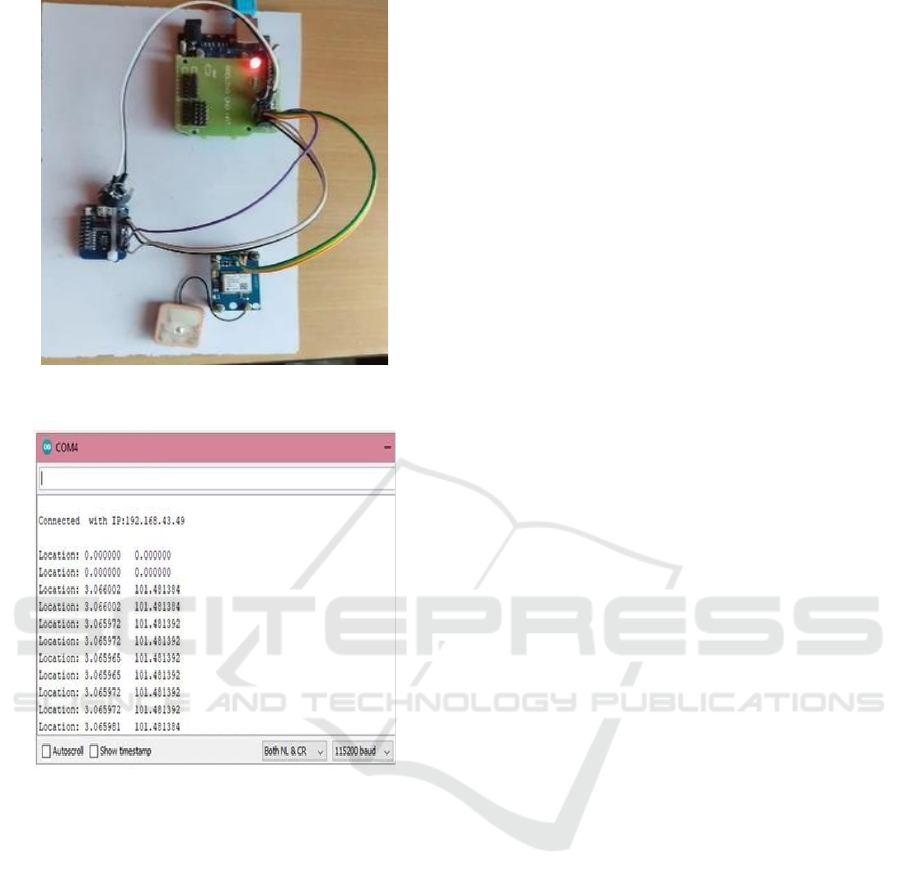
Figure: 6. Luggage tracker hardware protype.
Figure 7: Coordinates of the detected location on serial
monitor.
6
CONCLUSIONS
This Bluetooth-based luggage monitoring device is
quite useful in busy places and on public
transportation, such as buses and trains. When
carrying valuables in their baggage, people frequently
rely on this gadget. This project is a straightforward
but effective way to keep an eye on passenger luggage
and, if needed, offer security by sending an SMS alert
with the position of the luggage and setting off an
audible alarm. The system is a significant
development in access control and security
technology, built on a microcontroller-based security
mechanism that uses a mobile phone. It successfully
addresses security issues that conventional chain-and-
lock techniques are unable to, marking a major
advancement in digital design and technical
advancement. Many applications require security as a
basic necessity, and this gadget works on the tenet
that "prevention is better than cure”. Instead than
tracking baggage just after it has been reported
misplaced, it secures it as soon as it is in the vicinity.
Even if the bag becomes lost, it may still
communicate its location to the user's smartphone,
which will keep updating its position until it is found.
This system uses open-source tools, such as Google
Earth and Google Maps, to provide a GPS-based
tracking solution. It provides a real-time tracking
feature via a client-server architecture, informing
customers of the whereabouts of their luggage as
needed.
7 FUTURE SCOPE
For future development, this study should expand its
focus to incorporate a GPS module to enhance
accuracy in locating luggage. Although the current
system offers useful features, there is room to
improve both the mobile application and the device’s
tracking capabilities. Recommendations for future
work include adding specific location addresses on
Google Maps to help users easily locate their luggage,
as well as implementing a location history feature,
allowing users to monitor past locations of their
luggage over time.
REFERENCES
A. Purwar, J. Divya, and V. K. Chaubey, "GPS Signal
Jamming and Anti-Jamming Strategy - A Theoretical
Analysis," in 2016 IEEE Annual India Conference
(INDICON), pp. 1–6,2016.
A. Kumar and V. Rao, "IoT-based baggage tracking and
security solutions in the digital airport ecosystem,"
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation
Systems, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 2345–2356, 2024.
D. Mishra and A. Khare, "Impact of IoT in modernizing the
aviation industry: From passenger experience to
operational efficiency," International Journal of
Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 14,
no. 3, pp. 45–51, 2023
E. Newton, "Airways Magazine: Airports," Airways
Magazine, December 21, 2021. Available at:
https://airwaysmag.com/airports/iot-airport-baggage-
systems/ NOAA, "What is GPS? "National Ocean
Service, September 4, 2020. Availableat: https://ocean
service.noaa.gov/facts/gps.html
H. A. Adjei, F. K. Oduro-Gyimah, T. Shunhua, G. K.
Agordzo, and M. Musariri, "Developing a Bluetooth
Based Tracking System for Tracking Devices Using
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
106

Arduino," in 2020 5th International Conference on
Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), pp.
1–5 2020.
Karvinsky, "Tracking Based on GPS and the 'Internet of
Things'," IoT Business News, April 16, 2020.
Available at: https://iotbusinessnews.com/2020/04/16/
54510-tracking- based-on-gps-and-the-internet-
ofthings/.
L. Qin, H. Wang, and Y. Fan, "Enhancing airport security
and baggage handling efficiency with IoT technology,
" IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 16,
no. 7, pp. 4321–4330, 2020.
M. Ghazal, S. Ali, F. Haneefa, and A. Sweleh, "Towards
Smart Wearable Real-Time Airport Luggage
Tracking," in 2016 International Conference on
Industrial Informatics and Computer Systems (CIICS),
pp. 1–6 2016.
M. Goldstein, "How To Protect Yourself from Rising
Airport Luggage Theft," Forbes, July 6, 2017.
Availableat:https://www.forbes.com/sites/michaelgold
stein/2017/07/ 06/how to-protect yourself from rising
airport Luggage theft.
M. Ö. Demir, G. K. Kurt, and A. E. Pusane, "On the
Limitations of GPS Time-Spoofing Attacks," in 2020
43rd International Conference on Telecommunications
and Signal Processing (TSP), , pp. 313–316,2020.
Martínez, B. Lanza, "IoT and big data architectures for
airport management and monitoring," IEEE Access,
vol. 8, pp. 20750–20764, 2020.
O. Shobayo, A. Olajube, O. Okoyeigbo, and J. Ogbonna,
"Design and Implementation of an IoT Based Baggage
Tracking System," in Information and Communication
Technology and Applications: Third International
Conference, ICTA 2020, Springer International
Publishing, pp. 618–631,2021.
P. Devaki and M. Karthika, "IoT Based Smart Object
Tracking System," International Research Journal of
Engineering and Technology (IRJET), vol. 6, no. 6, pp.
929–932, 2019.
R. Singh and S. Patel, "Smart baggage tracking and
management using IoT: A case study for aviation
industry," Sensors, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 1102, 2021.
S. Senthilkumar and M. Jain, "Luggage Tracking System
using IoT," International Journal of Pure and Applied
Mathematics, vol. 117, no. 1, pp. 49–55, 2017.
S. Safdar, A. Zeb, A. Khan, and K. Zeeshan, "Android
Based Vehicle Tracking System," EAI Endorsed
Transactions on Energy Web, vol. 5, no. 17, pp. 1–6,
2018. doi: 10.4108/eai.10-4-2018.154447.
S. Karthick, J. Joel, S. Balaji, and T. P. Anish, "Smart
Luggage Tracking and Alert System using Arduino,"
International Research Journal of Modernization in
Engineering, Technology and Science, vol. 2, no. 5, pp.
811–816, 2020.
S. Lee, J. Kim, and H. Oh, "A hybrid RFID-IoT model for
automated baggage tracking in smart airports," Journal
of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 199, pp.
103228, 2022.
S. Dutta and Y. Park, "Integrating IoT and AI for predictive
analytics in airport operations," Journal of Air
Transport Management, vol. 106, pp. 102181, 2023.
W. Yang and Y. Chen, "Optimizing RFID and IoT in airport
logistics for efficient baggage tracking," Journal of
Transportation Management, vol. 54, pp. 98–105, 2022.
X. Yin, L. Zhang, and L. Wu, "Smart airport: IoT-based
real-time baggage tracking system," IEEE Internet of
Things Journal, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 3778–3788, 2021.
X. Wang and H. Zhang, "IoT-enabled RFID technology for
enhanced airport baggage tracking and passenger
convenience," IEEE Systems Journal, vol. 17, no. 1, pp.
182–190, 2023.
Smart Luggage Theft Detection and GPS Tracking System
107
