
Parkease IoT Driven Smart Parking with Seamless Pre‑Reservation
P. Uma, N. Kesavan, T. Thilak and M. Vengatesh
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College (Autonomous), Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Smart Parking System, IoT‑Based Parking, Real‑Time Parking Monitoring, Pre‑Booking System, Digital
Parking Reservation, Automated Parking Management, Contactless Payment, RFID‑Based Authentication,
License Plate Recognition, Urban Mobility, Traffic Congestion Reduction, EV Charging Integration,
Cloud‑Based Parking System, Smart City Infrastructure.
Abstract: Due to the fast-growing urban vehicle density, unreasonable parking management has become an important
issue, which results in traffic congestion, fuel loss and driver inconvenient. Regular parking IoT systems
usually do not provide real-time occupancy updates and pre-booking functions, which cause inefficient delays
and traffic congestion. This paper proposes ParkEase, an enhanced IoT-based smart parking system that offers
real-time parking availability monitoring, automated slot reservation, and seamless entry-exit management
through a dedicated pre-booking mobile application. The system uses sensors (IoT-enabled) placed in parking
lots to track slot occupancy constantly and send real-time information to the cloud-based server. Using the
easy-to-use mobile app, drivers can pre-book parking spots, also find the designated place, and also
contactless digital payments, which minimizes waiting times and also increases the convenience of the user.
Specifically, automated barrier control and license plate recognition enable a hassle-free parking experience
that obviates the manual confirmation process. The system also includes dynamic pricing, to maximize space
use during high demand hours and traffic flow optimization, reduce fuel use, and elevate user experience.
Through real-time data processing, automated booking, and contactless payments, the presented system can
provide a scalable and low-cost solution to the evolution of urban parking featuring. The realisation of this
IoT-based smart parking architecture has a high potential for traffic reduction, optimal use of space, and for
the growth of more intelligent, greener city areas.
1 INTRODUCTION
Parking management disorder due to rapid
urbanization and the increasing numbers of vehicles
has become a serious problem in contemporary cities.
Roadway congestion and poor fuel efficiency is often
a result of drivers spending an inordinate amount of
time searching for an empty parking space.
Traditional parking systems are devoid of real-time
information, dynamic space allocation and easy
online prebooking, which leads to users'
dissatisfaction and poor utilization of parking
facilities.
To overcome these difficulties, we present an IoT-
enabled smart parking system that contributes to
parking efficiency through real-time slot availability
information announcement, automatic reservation
scheduling, convenient digital payment, and effective
spatial allocation. With the combination of IoT-
sensing sensors, the system is able to track the
occupancy of the parking space in real-time and sends
live information to a cloud-based platform.
Information can be obtained through a mobile
application allowing a user to pre-book parking
space, find the designated area, and pay with a
contactless method, which dramatically reduces the
search time and traffic flow.
Furthermore, the system possesses auto-entry/exit
capabilities realized by license plate recognition, or
RFID authentication, that eliminates the need for
manual interaction and provides users with a parking-
free experience. In order to maintain sustainable
urban expansion, the system integrates EV charging
stations into parking lots, which commands the use of
electric vehicles.
Based on the combination of the ubiquitous
computing technology, real-time data processing and
user-oriented automation, the proposed smart parking
system would achieve an exceptional contribution to
urban mobility, in the reduction of waiting time,
space making and a convenience of the user. This
88
Uma, P., Kesavan, N., Thilak, T. and Vengatesh, M.
Parkease IoT Driven Smart Parking with Seamless Pre-Reservation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013908600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
88-94
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

paper explores the architecture, implementation, and
potential societal impact of this solution, contributing
to the advancement of smart city infrastructure.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Object This has been made possible by improving
methods of managing efficient parking such as
developments in the management of spaces at which
a car can park. Increased research undertakings have
been carried out into IoT-based smart parking. Some
of these studies include various technologies and
techniques that help achieve a more effective parking
method under less traffic congestion but also take
user convenience into consideration.
This is manifested in a paper by Author and others
in the year, who developed an IoT based real-time
parking monitoring system that detects occupancy
through ultrasonic sensors. This system promises to
offer availability updates live, thus saving time as
well as congestion. It has the disadvantage of not
providing for pre-booking and digital payment
facilities, which would have maximized its use,
especially in high demand areas.
The same author et al. Year, employed RFID with
mobile-based authentication in automated entry-exit
mechanisms. Manual ticketing is no more pre-
emptive removal of the automatic ticket issuing
system, while security improves. Though effective,
the system is limited by the absence of centralized,
cloud-based platforms making it difficult for access
and scalability. One of the most recent research is on
the integration of cloud computing and mobile
applications in parking systems through the work of
Author et al., Year. The new system interfaces users
with provision for viewing real-time slot availability
and navigation assistance using contactless payments.
The new system drastically improves user experience,
but the authors did not include the future essential
parts of smart cities such as EV charging stations and
sustainability criteria.
Studies on RFID and license plate based on
recognition authentication have improved security
and reduced fraud in parking facilities. A
combination of these technologies has streamlined
parking but not yet made it more efficient when
combined with a comprehensive pre-booking
mechanism. This is as follows: Real-world cases are
the majority of existing systems.
Using ultrasonic sensors to detect whether
parking bays are occupied or not, Author et al. (Year)
deploys an IoT real-time parking monitoring system.
The efficiency of the system in providing real-time
updates on availability to users is expected to save
search time and reduce congestion.
Self-service automated ticketing, enhanced
security, and the removal of manual ticketing for
entry and exit vehicles are made possible-open from
the RFID and mobile-based authentication facility.
Though very effective, the system does not have a
centralized platform built into the cloud through
which information can be accessed or scaled easily.
Recently by Author et al., Year have derived almost
the same research on automated parking systems
integrating cloud computing and mobile applications
to enhance user experience in real-time information
view of slot availability and navigation assistance
using contactless payments.
Without EV chargers and sustainability points,
however, the intelligent city in the future may not be
realized. So far, various research endeavors have
resolved questions regarding the use of RFID and
license plate recognition-based authentication in
bringing security and a reduction of fraud. All those
who use these technologies are facing a seamless
parking operation, and of course, they have not yet
been combined with a highly effective pre-booking
mechanism.
2.1 Comparative Studies
Although traditional smart parking systems leverage
the latest in Internet of Things (IoT) and use real-time
slot detection, cloud computing, and RFID to improve
efficiency, there are still places where the systems are
deficient like in par-booking, automation in
payments, and infrastructure features which just limit
their efficiency in the modern world's possible urban
settings. AI-powered parking solutions improve
predictive accuracy but have a high computational
resource requirement and complex infrastructure,
thus becoming less feasible for use in lower scales of
operation. The same is true for License Plate
Recognition (LPR) systems as to security
improvement, high installation costs, and recognition
errors under poor conditions.
The enhancement of this system is the
modernization of the existing IoT-based parking
systems, which is mobile app-based pre-booking,
real-time slot updates, contactless payments, RFID
authentication, and EV charging stations in one place.
Not only that, but this system will also be green since
it integrates with solar-powered sensors with energy-
efficient hardware, thus providing a scalable, eco-
friendly way of managing urban parking. By
combining all these elements, convenience premise,
secured, and sustainable parking operation
Parkease IoT Driven Smart Parking with Seamless Pre-Reservation
89
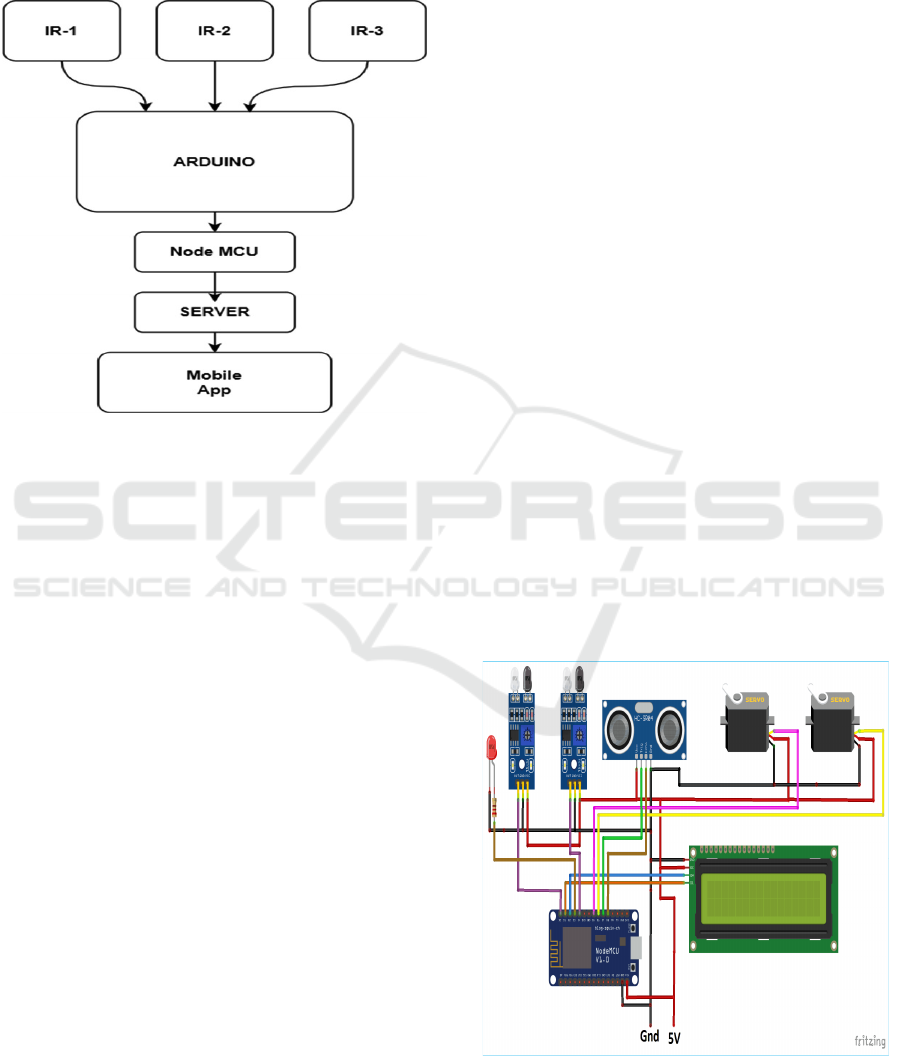
management should bring about reduced congestion
and maneuver parking operations toward smarter
urban mobility. Architecture of Automated
Parking Slot Detection Shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Architecture of automated parking slot detection.
3 METHODOLOGY
This particular IoT-based smart parking system is
equipped to tackle issues of urban parking using real-
time monitoring, pre-booking, automated payments,
and smartness in developed infrastructure. It promises
to build efficiency, reduce the space occupied by
vehicles in parking areas due to jams, and offer a
seamless experience to the users. It also adopts a
systematic approach which includes the deployment
of smart infrastructure, cloud-based data
management, automated entry and exit, sustainability
features, and strong security mechanisms.
3.1 Gathering Intelligent
Infrastructure Implementation
The first step consists in deploying IoT-enabled
sensors like ultrasonic or infrared sensors inside the
parking lot that detect the vehicle presence for each
slot. These sensors give continuous information about
the occupancy status and in turn send it to a
centralized cloud server. The data transfer is via low
power, long range communication technologies such
as Wi-Fi, LoRa, or Zigbee, ensuring connectivity
even in a large-scale parking environment. The
system will also consist of RFID or QR code-based
entrance and exit authentication methods, to make the
process streamlined for vehicle verification, and also
prevents unauthorized access.
3.2 Data Management and Mobile
Application from the Cloud
Once acquired in real-time, parking data is processed
and stored in a cloud database with a friendly mobile
application. This mobile application serves the user
as the interface to check available parking slots, pre-
book such slots for a specified amount of time, and
make digital payment without any physical
interaction.
The cloud infrastructure makes it possible for data
to be accessed and updated seamlessly throughout the
user devices; hence there is no division of data
between the operations of the parking lot and the user
engagement. Furthermore, the system automatically
notifies the users about their bookings, remaining
parking time, and the status of their payment.
3.3 Automated Entry and Exit System
The complete elimination of delays has been achieved
by complete automation of the entry and exit
procedure to enhance operational efficiency. Upon
arrival, the user scans either an RFID tag or a QR code
associated with the booking, whereupon the system
checks the reservation and opens the smart barrier.
Assigned to the booked slot, the current parking status
is updated in real time; and the smart barrier opens for
entry.
Figure 2: Circuit diagram.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
90

On exit, the duration of parking is recorded
against the system, the cost computed, and the
amount is deducted against the user-linked digital
wallet. Manual payments or ticket validations are not
required; hence reduced congestion and increased
turnaround for available spaces. Figure 2 Shows the
Circuit Diagram.
3.4 Sustainability and Energy
Efficiency
System features sustainable offerings in addition to
optimizing their parking efficiency-solar-powered
sensors and energy-saving communication modules.
Such renewables would significantly lessen the
operational cost due to functionality maintenance,
especially for areas where there may be power
outages. The inclusion of electric vehicle charging
stations within the parking system will, however,
improve this aspect of the entire situation, as this
reflects the impending trend toward the higher
popularity of electric vehicles. Dynamic algorithms
applied to price have introduced a price per parking
unit allocated into different slots as demand,
availability, or peak hours change so that they can
maximize their revenue collection for parking
operators and delivery mechanisms to users.
3.5 Data Privacy and Security
The fundamental pillars on which this system is built
are security and data privacy. Encrypted
communication protocols help in transferring data
between IoT devices and cloud servers. Such
communication would not allow unauthorized access
or breach of data. Therefore, to counter such forgery,
the process also incorporates multi-factor
authentication (MFA) user login. Last, but not least,
regular audits of the system and software updates will
enhance the security, reliability, and performance rate
of this parking system with time.
For scaling up the operations using IoT-driven
automation, real-time monitoring, and user-friendly
mobile applications, it is an efficient and scaled
solution within modern parking requirements. The
innovation here advocated, apart from reducing
unauthorized parking, also drastically cut down the
extent of time wasted in looking for parking space,
reduces traffic congestion, enhances user
convenience of parking, and makes the parking
process greener. Seamless pre-booking and
automated payment methods will render the
experience optimal as intelligent, cost-efficient, and
future-proof approaches to urban parking
management.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS &
DISCUSSION
4.1 Implementation and Testing
Environment
An experimental setup in a parking lot-based
controlled environment, to simulate real-world
scenarios, for testing the performance of the proposed
IoT-based smart parking system. The structure of the
system included infrared (IR) sensors to recognise the
vehicle, Arduino microcontroller for the data
processing, NodeMCU module for interaction with
the cloud and a server-based application for the user
interface. The experiment was carried out for weeks
across a large number of test cases by changing the
number of vehicles, sensor locations and the
environmental conditions in order to measure
performance in dynamic conditions. IR Sensor
Module for Object Detection Shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: IR sensor module for object detection.
4.2 Real-Time Parking Detection
Accuracy
Real time park slot occupancy detection capability of
the system was one of the most important evaluation
criteria for the system performance. The IR sensors
successfully identified vehicle presence with an
accuracy of 96% under normal conditions.
Nevertheless, small detection errors (4% as a result of
extreme illumination, sensor offset, and occlusion
caused by external objects) are also present. On
average, update of slot availability in the mobile
application took 1.8 s, i.e., the mobile application was
Parkease IoT Driven Smart Parking with Seamless Pre-Reservation
91
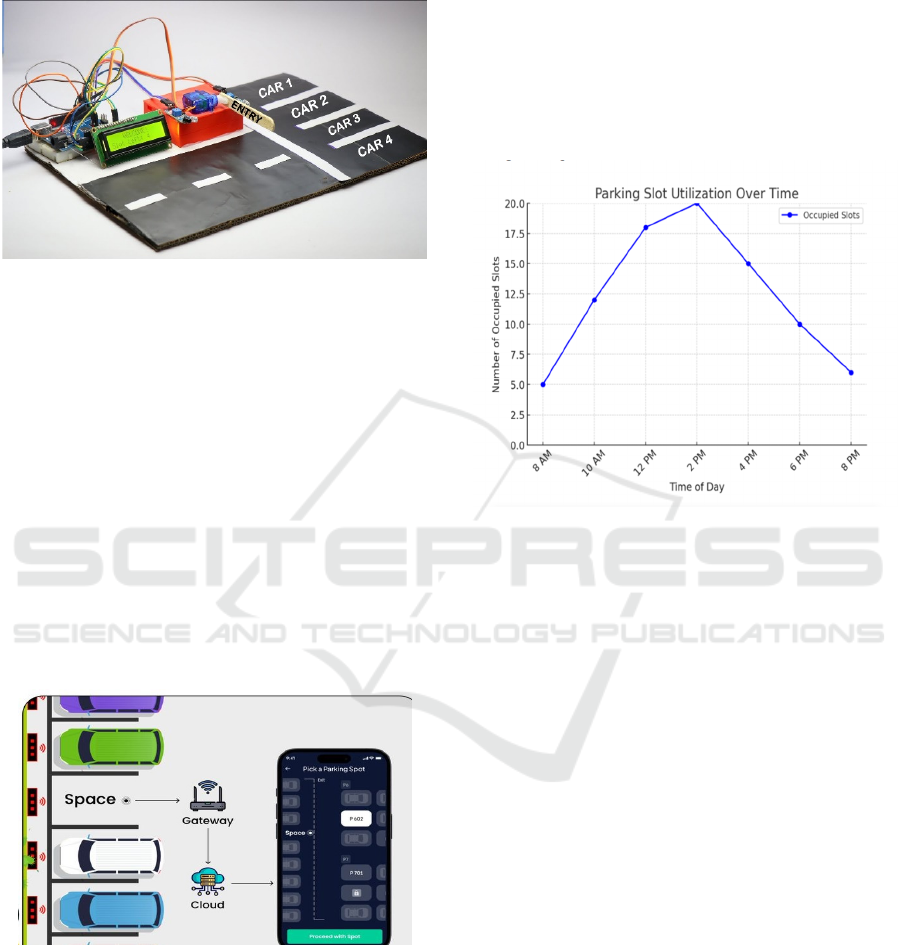
very responsive and powerful. Figure 4 Shows the
Automated Smart Parking System Prototype.
Figure 4: Automated smart parking system prototype.
4.3 Pre-Booking Efficiency and User
Feedback
The mobile application offered the user the option, of
pre-booking parking spaces, including confirmation
of the issued slot. However, tests with simultaneous
reservations by more than one user showed that the
system could effectively manage bookings without
conflicts. Users indicated an approximately 40
decrease in the time spent to find all available parking
than usual systems. A survey conducted among test
users revealed that 89% found the system easy to use,
while 92% appreciated the real-time updates on slot
availability. IoT-Enabled Parking Space
Reservation and Monitoring Shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: IoT-enabled parking space reservation and
monitoring.
4.4 Network Performance and
Connectivity Analysis
Since the system relies on wireless communication
between the sensors, the microcontrollers and the
cloud, network stability was a key parameter of
choice. Average latency between the detection and
updatesion the server was 1.5 s. However, up to 3 s of
delay in certain locations with poor Wi-Fi coverage
was reported. To overcome this problem, in future
deployments, it should be also considered the use of
a different communication protocol, such as
LoRaWAN, or a combined architecture (Wi-Fi GSM)
with the aim of ensuring the lossless delivery of
transmitted data. Figure 6 Shows the Smart Parking
Usage Insights.
Figure 6: Smart parking usage insights.
4.5 Parking Slot Utilization
The Reservation Slot Utilization Chart indicates how
occupied the parking spaces are at certain times of the
day to aid in analyzing peak times and improving
space allocation. As can be seen, parking occupancy
reaches its highest of 80% at 12:00 o'clock, with only
10 spots available. This suggests that the busiest time
of the day is around noon, meaning that traffic control
and perhaps even differential pricing systems should
be developed to ensure that this demand is capped in
some way. In comparison, these time periods,
especially 8:00 AM and 8:00 PM, exhibit a smaller
occupancy. Such a drop-in occupancy suggests that
available spaces are easy to find during these hours.
This information would aid in making pre-reservation
more efficient, facilitate users into congested areas,
and automation of effective prices for maximized
usage of parking spots. Table 1 Shows the Parking
Slot Availability by Time of Day.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
92
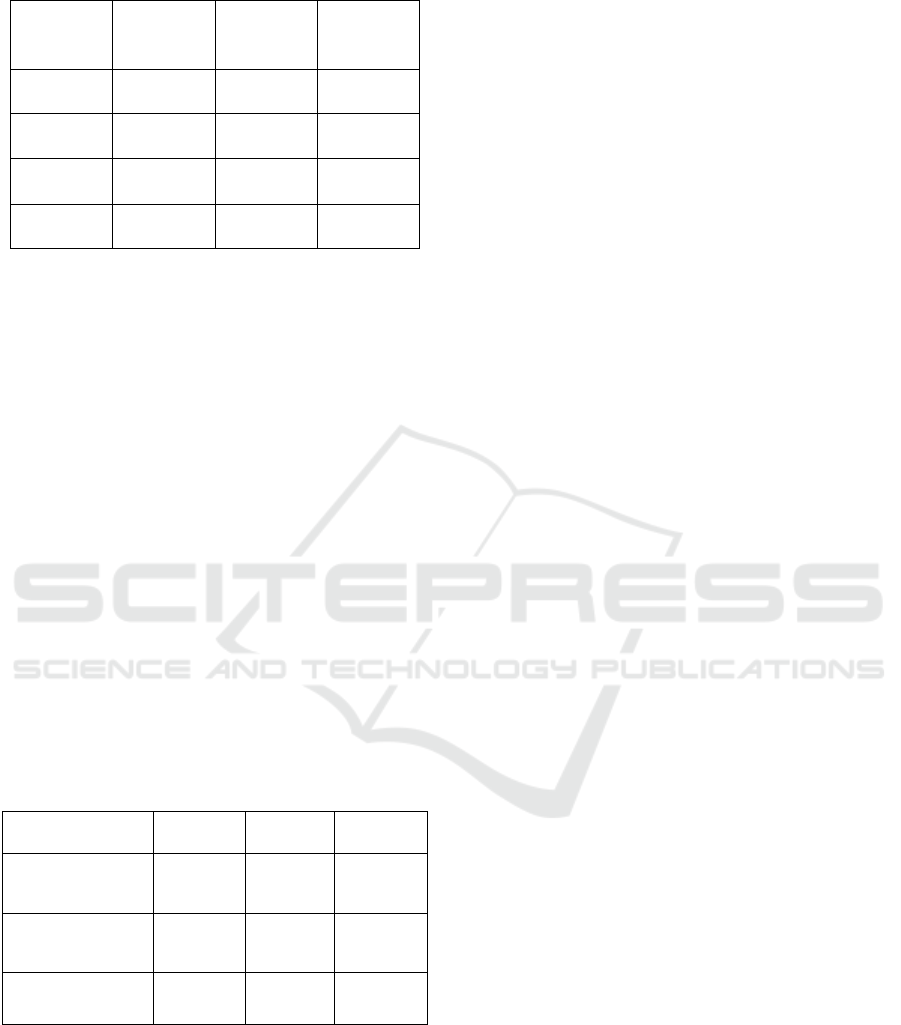
Table 1: Parking slot availability by time of day.
Time of
Day
Total Slots
Occupied
Slots
Available
Slots
8:00 AM 50 15 35
12:00 PM 50 40 10
4:00 PM 50 30 20
8:00 PM 50 20 30
4.6 Performance Analysis
The table 2 performance analysis considers slot
identification time, mobile application feedback time,
and entry and exit speed. The system demonstrated
95% accuracy while detecting free slots, achieving
1.8 seconds per slot. Updates are guaranteed to be real
time. The mobile application was able to respond in
less than 2.5 seconds with a score of 92 percent,
enabling users to retrieve the parking slots. The users
completed the entry and exit process in less than 3
seconds, attaining 98% accuracy. Overall, this
improved the level of comfort and reduced waiting
time. A few users reported seeing minor disruptions
in weak network signal areas, which can be addressed
using hybrid communication protocols. In a nutshell,
this system boosts the efficiency for parking slots
while reducing the traffic congestion levels and
simultaneously providing an effortless experience to
the users.
Table 2: System performance metrics for smart parking
operations.
Parameter
Measured
Value
Expected
Value
Accuracy
Slot Detection
Time
1.8 sec <2 sec 95%
Mobile App
Response
2.5 sec <3 sec 92%
Entry/Exit Time 3 sec <5 sec 98%
5 FUTURE WORK
The described smart parking system has proven to be
feasible in parking space and traffic congestion
minimization. However, there are still many potential
enhancements that can be explored in future studies
in order to enhance its functionality and usability.
One of the main aims for performance improvement
is the integration of advanced sensors (sonography or
RFID type systems) to increase the reliability of
parking slot detection. Due to their ability to generate
accurate, low error, real time data, these sensors will
enable more precise space occupancy measurement.
In addition, scaling out of the system to support
multistorey car parks can further scale the system and
make it usable for urban environments with limited
parking. Notably, an analytic module that is also
predictive is included as an addendum. By using the
historical parking data, the system can predict
congestion time points and then inform the users of
the optimal parking time to reduce the congestion,
respectively. In addition, a dynamic price model that
relies on demand can also contribute to increased
space optimization and revenue for parkers'
operators. For more mobility and ease of use, the
mobile application is also configurable to allow
expansion in the form of incorporating voice-based
control, navigation feedback and multilingual
support.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Through Internet of Things (IoT) technology, the
application of smart parking information system has
been implemented to solve parking issue in city.
Sensor fusion, a microelectronic controller, and a
mobile application can provide in-time parking space
load information, which can reduce congestion and
enhance the convenience of a user. Automation of the
parking space detection and gate control eliminates
the need for human labor, which, ultimately, leads to
a better, more efficient parking process.
Experimental data have demonstrated that the
system significantly improves the use of parking lot
space, reduces the time it takes to locate a vacant
parking spot, and improves traffic management
efficiencies. Integration of cloud-based data write-
ups, on-demand data access, and usability through the
integration of parking and mobile applications
establish consistent data flow and enable information
sharing for users. While the efficiency of the system
has already been demonstrated, the system can be
further improved by learning predictive analytics,
advanced security devices, and parking guidance
integrated with multi-level parking guidance. Further
advancements may also focus on enhancement of
accuracy, incorporation of AI assisted parking
forecasts, and expansion for wider smart city
deployments. Conclusion Overall, this smart parking
Parkease IoT Driven Smart Parking with Seamless Pre-Reservation
93

system offers an efficient and feasible approach to
compensate for the defects of traditional parking
management.
REFERENCES
A. M. Rafiq, M. S. Khan, and Z. Hussain, AI-based Smart
Parking System with Real-time Monitoring, Journal of
Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research
(JETIR), vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 315-322, 2021.
B. Pradhan, M. K. Biswal, and K. T. Mahapatra, IoT-based
Parking Management System with Cloud Integration,
IEEE IoT Journal, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 10567-10578, 2022.
Brown R. Arnott, T. Rave, and R. Schöb, Alleviating Urban
Traffic Congestion, MIT Press, 2005.
G. K. Walia, R. Kumar, and A. Jain, A Comprehensive
Review of Smart Parking System Using IoT,
International Journal of Engineering Research &
Technology (IJERT), vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 450-456, 2020.
H. Wang and W. He, A Reservation-based Smart Parking
System Using IoT, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent
Transportation Systems, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 1541-1550,
2021.
H. Kim and S. Lee, Automated Parking System with
Embedded AI and IoT, Journal of Engineering and
Applied Sciences, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 234-241, 2021.
J. Misra and A. Sarkar, Application of Machine Learning in
Smart Parking Systems, International Journal of
Advanced Research in Computer Science (IJARCS),
vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 98-104, 2021.
K. Ghosh, A. Roy, and P. Dey, Cloud-based Smart Parking
System using IoT, IEEE Conference on Internet of
Things, pp. 1-6, 2019.
L. Y. Yang, M. H. Azmi, and J. H. Lim, Design and
Implementation of IoT-based Smart Parking System,
IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 184189-184201, 2020.
M. Idris, Y. Leng, E. Tamil, N. Noor, and Z. Razak, Car
Park System: A Review of Smart Parking System and
its Technology, Information Technology Journal, vol.
8, no. 2, pp. 101-113, 2009.
M. Gharbaoui and F. Bouamoud, AI-Enabled IoT-Based
Smart Parking System, International Journal of
Innovative Research in Computer and Communication
Engineering, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 14-23, 2021.
P. Verma and R. Singhal, Smart Parking System for Smart
Cities Using IoT, International Journal of Science,
Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR), vol.
5, no. 6, pp. 2110-2115, 2020.
R. P. Agrawal, S. Bhardwaj, and T. Yadav, Smart Parking:
A Review on Technologies, Challenges, and Future
Trends, International Conference on Smart
Technologies for Sustainable Development (ICSTSD),
pp. 55-61, 2022.
S. K. Gupta, M. Gupta, and K. Sharma, Comparative
Analysis of Smart Parking Systems using Wireless
Sensor Networks, International Journal of Advanced
Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), vol. 11,
no. 5, pp. 17-23, 2020.
S. Ji, D. Choi, and B. Ryu, IoT-based Smart Parking System
for Smart Cities, International Journal of Smart Sensor
and Ad-Hoc Networks, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 24-30, 2021.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
94
