
Agricultural Crop Recommendations Based on Productivity and
Season
Boya Ashwini, Gundampalle Mamatha, Ampireddygari Durga Bhavani,
Ediga Gayathri and Vemula Rohini
Department of CSE, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Crop Recommendation System, Decision Tree Algorithm, Climate‑Resilient Agriculture, Geographical
Information Systems (GIS), Machine Learning in Agriculture.
Abstract: Agriculture plays a vital role in ensuring global food security and economic stability. However, the increasing
uncertainty of environmental conditions poses significant challenges to farmers, affecting crop yields and
sustainability. Agriculture and machine learning have a significant relationship, as machine learning can be
applied to various aspects of agriculture to improve efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. To address
this issue, our project aims to develop an innovative agricultural crop recommendation system that integrates
farmer specific data and real-time environmental data to provide personalized, climate-resilient suggestions.
The proposed system leverages decision tree algorithms for interpretability and accuracy. Additionally, it
incorporates Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for spatial analysis of soil and weather patterns. By
integrating farmer- specific data, such as resource availability, and risk tolerance, with real-time
environmental data, including weather patterns, soil moisture, and temperature, the system provides farmers
with sustainable, location-specific crop recommendations. The outcomes of this project include improved
crop yields and productivity, reduced risks associated with climate uncertainty, enhanced economic outcomes
and stability, and the adoption of climate-resilient agricultural practices. The proposed system which is based
on Decision tree algorithm has resulted in 17.46% more accurate than the previous recommender system that
is based on the SVM algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Machine Learning
Machine learning refers to a part of artificial
intelligence that focuses on building systems that can
independently enhance their functionality through
learning- an activity that does not need to be
programmed. The central concept of machine
learning is to allow a computer to take corrective
actions by identifying patterns, drawing inferences,
and resolving issues without relying on detailed input
from a programmer. Machine learning models can
extract information by recognizing associations and
patterns from the past data and experiences. These
insights are progressively used to predict and classify
novel as well as unknown data or even to enhance
decision- making systems. The application of
machine learning is present in many areas such as
natural language processing, computer vision,
recommendation engines, autonomous vehicles,
finance, and healthcare. Machine learning has the
potential to solve difficult problems and foster
creativity in innovative science and technology,
particularly due to the emergence of big data and
powerful computation and machine learning models
and algorithms.
1.2 ML-Based Crop Selection and
Recommendation Systems
An agricultural crop recommendation system is
designed to gather information and provide tailored
crop suggestions to farmers based on the specific
conditions of their farms, historical crop yields, and
current seasonal trends. The goal of this system is to
optimize crop selection, enhance yields, and boost
overall agricultural productivity. By utilizing
machine learning algorithms and Geographic
Information System (GIS) technology, it offers
personalized crop recommendations that consider
Ashwini, B., Mamatha, G., Bhavani, A. D., Gayathri, E. and Rohini, V.
Agricultural Crop Recommendations Based on Productivity and Season.
DOI: 10.5220/0013907200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 4, pages
13-17
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
13

factors like climate conditions, soil characteristics,
and geographical elements. The applications of this
system are extensive, serving everyone from small-
scale farmers to large agricultural businesses. By
adopting this system, farmers can look forward to
better crop yields, lower costs, and increased profits.
Furthermore, it encourages sustainable farming
practices, which play a vital role in food security and
environmental protection.
1.3 Intelligent Data Analysis
Intelligent Data Analysis plays a vital role in
enhancing agricultural practices, especially regarding
crop recommendations. By examining historical
climate data, soil characteristics, and crop yields,
farmers can make well-informed choices about which
crops to plant, the timing of planting, and the best
management practices to maximize productivity.
Climate and weather patterns are essential in
determining the success of crops. Factors like
temperature, rainfall, and soil moisture levels all
influence crop growth and yields. By looking at
historical temperature data, farmers can pinpoint the
optimal temperature ranges for different crops.
Likewise, analyzing rainfall patterns helps identify
the ideal moisture levels for various crops.
Monitoring soil moisture levels can also guide
recommendations for crops that thrive under specific
moisture conditions.
Soil characteristics, including soil type, pH levels,
and nutrient availability, significantly affect crop
productivity. By categorizing soil types, farmers can
suggest crops that are well-suited for each type.
Analyzing soil pH levels aids in recommending crops
that
can
tolerate
certain
pH
ranges.
Evaluating soil nutrient levels allows farmers to
propose crops that align with nutrient needs.
Crop productivity and seasonality are crucial
factors as well. By analyzing historical crop yield
data, farmers can discover high- yielding crops for
particular seasons. Studying seasonal patterns, such
as planting and harvesting times, helps recommend
crops that fit local seasonal cycles. Additionally, crop
rotation strategies can be proposed to enhance soil
health, minimize pests and diseases, and boost crop
yields.
Regional and local factors, including the regional
climate, market demand, and farmer preferences,
must also be considered. By considering regional
climate patterns, farmers can recommend crops that
are resilient to local conditions. Analyzing local
market demand helps suggest crops that cater to
consumer needs in the area. Incorporating farmer
preferences ensures that the recommendations align
with their goals and practices.
To generate accurate and reliable
recommendations, data from various sources can be
utilized, including government agencies, satellite
imagery, and farmers' feedback.
2 BACKGROUNDS
The advent of machine learning algorithms has
allowed for the creation of more advanced models that
can consider various factors and their interactions.
For example, researchers are now able to combine
data on weather patterns, soil quality, crop varieties,
and pest management techniques to develop more
holistic models. As a result, this has led to improved
accuracy in predictions and enhanced decision-
making for farmers and those involved in agriculture.
2.1 Machine Learning Approaches
• Linear Regression (LR): This is one of the
earliest methods in machine learning that has
been applied to predict crop yields.
• Random Forest (RF): This technique uses an
ensemble of decision trees to enhance the
accuracy of predictions.
• Support Vector Machines (SVM): This
method classifies crop yields into various
categories based on the input features.
In summary, the advent of machine learning
algorithms has been a pivotal moment in crop yield
prediction. These algorithms have not only
advanced over time but have also found applications
in other agricultural domains, including precision
farming and agricultural risk management.
3 CURRENT CHALLENGES IN
CROP RECOMMENDATION
SYSTEM
Current crop recommendation systems encounter
several challenges, such as the necessity for more
precise and tailored suggestions, tackling issues
related to data sparsity and cold starts, and
incorporating various elements like climate
conditions, soil characteristics, and geographical
factors. These constraints can result in less than ideal
crop choices, lower yields, and diminished profits for
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
14
farmers.
The current systems depend largely on
conventional approaches, word-of-mouth
communication, and minimal data analysis. They
frequently overlook important issues like climate
change, soil degradation, and water scarcity, resulting
in recommendations that are often inaccurate and
unreliable. Additionally, these systems typically
struggle to incorporate various factors, which can
result in poor crop choices and lower yields.
There is a significant demand for smart crop
recommendation systems that can offer farmers
precise and tailored suggestions. These systems need
to consider various factors, such as climate
conditions, soil characteristics, and geographical
elements, to deliver data-driven insights for the best
crop choices. By utilizing machine learning
algorithms, data analytics, and GIS technology, these
intelligent systems can assist farmers in enhancing
yields, minimizing risks, and boosting profits.
3.1 The Advantages of Intelligent Crop
Recommendation Systems
The benefits of intelligent crop recommendation
systems are extensive.
• These systems assist farmers in choosing the
most suitable crops to cultivate by considering
factors like climate conditions, soil
characteristics, and geographical elements,
which can lead to notable increases in both crop
yields and profits.
• They also help mitigate risks for farmers by
providing insights into the potential challenges
of growing various crops under different
circumstances.
• Furthermore, these systems streamline the
crop selection process, allowing farmers to
save time and energy, enabling them to
concentrate on other important tasks such
as crop management and marketing.
4 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS
In this study, we introduce a new method that utilizes
the Decision Tree algorithm to identify the best crops
for cultivation based on climate and crop data. Our
approach relies on a detailed dataset that includes
historical climate information, soil characteristics,
and geographical elements to train and assess the
algorithm. Additionally, we recommend the most
appropriate fertilizer for the chosen crop, offering
farmers a comprehensive solution for maximizing
crop yields. To ensure our method's accuracy and
reliability, we assess the performance of the Decision
Tree algorithm and compare it with other machine
learning techniques. This thorough evaluation
process allows us to identify the most effective
algorithm for our crop recommendation system. We
also implement strict measures to maintain the quality
and accuracy of our dataset, which is essential for
training and validating our algorithm.
Our approach incorporates Geographic
Information System (GIS) technology to analyze
spatial data and deliver crop recommendations
tailored to specific locations. This integration allows
our system to consider regional differences in
climate, soil, and other environmental factors,
providing farmers with customized guidance for their
particular area. The user interface of our proposed
system is designed to be user-friendly and accessible
to farmers from various backgrounds. Farmers can
easily enter their location, soil details, and other
pertinent information, receiving crop suggestions that
are specifically suited to their conditions. Our system
is built to continuously learn and adapt to new data,
ensuring that its recommendations stay current with
evolving conditions, technologies, and agricultural
practices. This adaptive feature empowers our system
to offer farmers the most relevant and effective
advice, assisting them in optimizing their agricultural
outcomes.
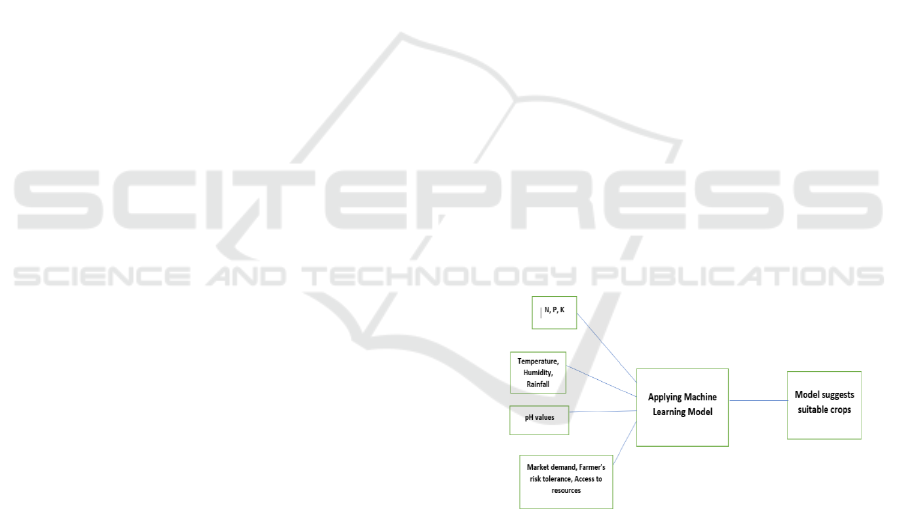
Block Diagram of Crop Recommendation
System Using Machine Learning Shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Block diagram of crop recommendation system
using machine learning.
4.1 Input Data
In our agricultural crop recommendation system, we
consider a wide range of agricultural and
environmental factors that influence crop
productivity. For instance, geographic location,
seasonal data, climate elements such as temperature,
rainfall, and humidity, soil traits like pH and nutrient
levels, altitude, the farmer's risk appetite, resource
availability, and many more factors that impact crop
Agricultural Crop Recommendations Based on Productivity and Season
15

cultivation and productivity are all included. The
system will be validated against various information
like historical data, weather stations, soil examination
results, and satellite photographs to provide the most
accurate and reliable information.
4.2 Data Pre-Processing
Data pre-processing is an essential step in getting our
input data ready for the machine learning model. This
process includes cleaning the data to handle missing
values, outliers, and inconsistencies. We will use
methods like imputation, outlier detection, and data
normalization or standardization to make sure the
data is properly formatted and free from errors or
anomalies.
4.3 Feature Selection
To enhance the performance of our machine learning
algorithm, we need to convert the dataset into an
appropriate format. This includes identifying the most
relevant features that impact the accuracy of our crop
recommendations. We will utilize various feature,
such as converting class attribute values from numeric
to alphabetic and grouping performance classes into
meaningful ranges.
4.4 Crop Recommendation Using
Decision Tree Algorithm
After we finish pre-processing our dataset and
selecting the relevant features, we will train our
Decision Tree algorithm to provide crop
recommendations. This algorithm will consider
various agricultural and environmental factors to
determine the best crops for a specific location.
4.5 System Testing
To ensure that our agricultural crop recommendation
system operates effectively and achieves its goals, we
will perform various types of testing. This will
encompass unit testing, integration testing, functional
testing, and performance testing. Each testing type
will assess different elements of the system, such as its
individual components, the interactions between
modules, overall functionality, and responsiveness.
4.6 System Implementation
The system implementation phase focuses on putting
our agricultural crop recommendation system into
action for farmers and agricultural experts. This
process includes establishing the necessary hardware
and software infrastructure, creating an intuitive user
interface, integrating the trained machine learning
model, and setting up a database to manage historical
agricultural data and user inputs. To maintain the
security and integrity of the system, we will
implement strong security measures to safeguard user
data and prevent unauthorized access.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Agricultural crop recommendation systems that
utilize the Decision Tree algorithm have the potential
to change how farmers choose and grow their crops.
By offering data- driven insights and tailored
recommendations, these systems can assist farmers in
boosting their yields, reducing risks, enhancing
efficiency, and making more sustainable decisions.
The Decision Tree algorithm is particularly
effective for crop recommendations because it can
manage complex relationships between various
factors, is resilient to outliers and noise in the data,
and can scale to accommodate large datasets.
Furthermore, it can analyze the intricate connections
between different variables and the target crop, which
is crucial for effective recommendations.
Our proposed system, which combines the
Decision Tree algorithm with GIS technology, is
designed for farmers of all sizes, whether in developed
or developing nations. By delivering personalized
crop recommendations based on factors like climate,
soil type, and geographical location, our system
empowers farmers to make informed choices,
enhance crop productivity, and boost overall
profitability.
REFERENCES
"A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms for
Crop Yield Prediction" by S. K. Singh et al. (2018)
"Crop Yield Prediction using Weather Data and Machine
Learning" by A. Kumar et al. (2018)
"Crop Yield Prediction using Machine Learning
Algorithms" by A. K. Singh et al. (2019)
"Predicting Crop Yields using Satellite Imagery and
Machine Learning" by J. Liu et al. (2019)
A. K. Singh et al., "Crop Recommendation System using
Machine Learning Techniques," Journal of Intelligent
Information Systems, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 257-273, 2019.
I. H. Witten et al., "Data Mining: Practical Machine
Learning Tools and Techniques," 4th ed., Morgan
Kaufmann, 2016.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
16

J. Han et al., "Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques," 3rd
ed., Morgan Kaufmann, 2011.
K. S. Rao et al., "Crop Yield Prediction using Machine
Learning Algorithms," Journal of Agricultural
Engineering Research, vol. 145, pp. 102-113, 2018.
Latu, (2021). Sustainable Development: The Role of Gis
and Visualisation. The Electronic Journal on
Information Systems in Developing Countries.
EJISDC, 38(5), 1–17.
Medar, et.al., (2020). A Survey on Data Mining Techniques
for Crop Yield Prediction. International Journal of
Advance Research in Computer Science and
Management Studies, 2(9).
Mohebbanaaz, Kumari, L.V.R. & Sai, Y.P. Classification
of ECG beats using optimized decision tree and
adaptive boosted optimized decision tree. SIViP 16,
695–703 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-
02009-x
Oikonomidis, A., Catal, C., & Kassahun, A. (2023). Deep
learning for crop yield prediction: A systematic
literature review. New Zealand Journal of Crop and
Horticultural Science, 51(1), 1–26.
10.1080/01140671.2022.2032213
Palepu. (2021). An Analysis of Agricultural Soils by using
Data Mining Techniques. International Journal of
Engineering Science and Computing,7(10).
R. K. Singh et al., "Agricultural Crop Recommendation
System using GIS and Machine Learning," Proceedings
of the International Conference on Advanced
Computing and Intelligent Engineering, pp. 123-130,
2019.
R. Babu, Mohebbanaaz, T. Lalitha, B. Anjali and U. C.
Sree, "Real-Time Crop Growth Tracking and Disease
Detection using Machine Learning," 2024 IEEE 16th
International Conference on Computational
Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN),
Indore, India, 2024, pp. 457-461, doi:
10.1109/CICN63059.2024.10847369.
S. K. Sahoo et al., "Crop Yield Prediction using Decision
Tree Algorithm and GIS," Proceedings of the
International Conference on Information Technology
and Applied Mathematics, pp. 145-152, 2018.
S. S. Rao et al., "Agricultural Crop Recommendation
System using Decision Tree Algorithm," International
Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science,
vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 234-241, 2018.
Shinde. (2020). Web Based Recommendation System for
farmers. International Journal on Recent and Innovation
Trends in Computing and Communication, 3(3).
Agricultural Crop Recommendations Based on Productivity and Season
17
