
Machine Learning for Heart Disease Identification in E-Healthcare
Shaik Mohammad Riyaz Naik, Anapati Sai Venkat, Kandukuri Dhanush, Potu Mani Kanta,
Palukuru Sumanth Royal and Akula Naveen Kumar
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal‑518501, Andhra Pradesh,
India
Keywords: Cardiovascular Disease, Heart Disease, Machine Learning App, ML Algorithms, SDG 3, SHAP, SMOTE.
Abstract: Heart disease is a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with early detection playing a critical role in reducing
death rates. Accurate prediction of heart disease remains challenging due to complex medical data and the
inability to provide continuous monitoring. Utilizing the heart disease dataset, various feature selection
techniques, including ANOVA F-statistic (ANOVA FS), Chi-squared test (Chi2 FS), and Mutual Information
(MI FS), were employed to identify significant predictors. Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique
(SMOTE) was applied to address data imbalance and enhance model performance. A comprehensive
classification approach was undertaken using diverse machine learning models and ensemble methods.
Among these, a Stacking Classifier combining Boosted Decision Trees, Extra Trees, and LightGBM achieved
superior results, delivering 100% accuracy across all feature selection techniques. The high performance
highlights the effectiveness of advanced ensemble learning in achieving reliable heart disease predictions,
emphasizing the potential of integrating robust feature selection with sophisticated classification models for
precise medical data analysis. This approach demonstrates the capacity to support early diagnosis and
improved patient outcomes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cardiac diseases are one of the leading causes of
mortality worldwide with heart disease having a
major share. The muscular heart is responsible for
pumping blood through the rest of the body as part of
the circulatory system. This complexity is composed
of arteries, veins and capillaries through which
oxygen and nutrients flow to organs and tissues.
CVD: If the normal flow of blood is disturbed, it
leads to different types of heart disorder called
cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Cardiovascular
disease and stroke kill more than 17.5 million people
around the world each year, more than 75% of these
deaths take place in low and middle-income
countries, according to the World Health
Organization (WHO). This alarming statistic
emphasizes the public health challenge of heart
disease that is escalating all around the world, as
myocardial infarctions and strokes result in 80% of
total CVD-related deaths.
The burden of cardiovascular diseases has led to a
global focus on early detection, prevention, and
treatment strategies. In line with the United Nations'
Sustainable Development Goal 3, which emphasizes
the importance of health and well-being, addressing
cardiovascular diseases has become a priority for
improving global health outcomes. Common risk
factors for of heart disease risk factors include
smoking, older age, family history of heart disease,
high cholesterol, lack of exercise, high blood
pressure, obesity, diabetes, and stress. Quitting
smoking, exercising on a regular basis, maintaining a
healthy weight, and managing stress are all lifestyle
choices that can decrease the risk of heart disease. In
addition to lifestyle interventions, you may take tests
like ECGs, echocardiograms, MRIs and blood tests to
find heart disease. Medical procedures such as
angioplasty, bypass, and using implanted devices,
such as pacemakers or defibrillators can also be
necessary for treatment.
Advancements in healthcare technology,
particularly in the realm of Big Data and Electronic
Health Records (EHRs), have made it possible to
leverage vast amounts of patient data for predictive
modeling. Machine learning (ML) techniques are
Naik, S. M. R., Venkat, A. S., Dhanush, K., Kanta, P. M., Royal, P. S. and Kumar, A. N.
Machine Learning for Heart Disease Identification in E: Healthcare.
DOI: 10.5220/0013907000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
861-870
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
861

increasingly being used to analyze large datasets from
healthcare systems, extracting meaningful insights to
predict the likelihood of heart disease. By processing
and analyzing data from various patient
demographics, risk factors, and diagnostic results,
machine learning can assist healthcare professionals
in identifying patients at high risk and enable early
intervention. This approach is transforming the
landscape of healthcare by offering more precise and
efficient methods of diagnosis, prediction, and
personalized treatment plans.
2 RELATED WORK
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including coronary
heart disease, have remained a global health concern,
accounting for a significant proportion of worldwide
mortality. With the rise in healthcare data and
advancements in machine learning (ML) techniques,
there has been a surge in efforts to predict and
diagnose heart disease more effectively. The ability
to analyze large datasets using machine learning
offers new avenues for identifying risk factors,
predicting outcomes, and improving early detection.
This literature survey discusses various studies that
have employed different machine learning models
and techniques to predict heart disease and highlights
their findings.
Yang et al. conducted a study using machine
learning to identify risk factors for coronary heart
disease. Their work focused on big data analysis,
demonstrating that machine learning models such as
decision trees, random forests, and support vector
machines (SVM) could effectively identify key risk
factors from patient data. The study found that high
cholesterol, age, and family history were among the
most significant risk factors contributing to the
prediction of heart disease. Furthermore, the study
underscored the importance of data preprocessing,
feature selection, and the need for a robust dataset in
improving model performance. The results confirmed
that machine learning could be a powerful tool for the
early detection of heart disease, especially when
combined with large, comprehensive datasets.
In a similar vein, Ngufor et al. reviewed several
machine learning algorithms for heart disease
prediction. The authors provided a comparative
analysis of popular techniques like SVM, decision
trees, k-nearest neighbors (KNN), and artificial
neural networks (ANNs). Their findings indicated
that ensemble methods, such as bagging and boosting,
provided superior predictive performance over
individual models. Additionally, the study
emphasized the importance of feature selection, as
irrelevant features can degrade model accuracy. This
review highlighted that while various algorithms
could predict heart disease, the choice of technique
depends heavily on the dataset characteristics, the
computational resources available, and the specific
requirements of the prediction task.
Farag et al. focused on improving heart disease
prediction using boosting and bagging techniques.
Boosting algorithms, such as AdaBoost, and bagging
techniques, like Random Forest, were tested to assess
their ability to enhance prediction accuracy. The
study found that ensemble techniques were more
robust than standalone classifiers in terms of reducing
variance and improving the stability of predictions.
Furthermore, the study suggested that the
combination of boosting and bagging could mitigate
the overfitting problem, which is often encountered in
heart disease prediction models. This work
underlined the importance of using multiple
classifiers in conjunction to achieve optimal
performance.
Zhang et al. investigated the application of
XGBoost, a gradient boosting algorithm, in the
clinical prediction of coronary heart disease. Their
study showed that XGBoost outperformed traditional
methods like logistic regression and SVM in terms of
both accuracy and interpretability. XGBoost’s ability
to handle imbalanced datasets, which is a common
issue in heart disease prediction, made it particularly
suitable for medical data. The study also pointed out
that hyperparameter tuning played a crucial role in
maximizing the model's performance. XGBoost's
superior performance in clinical environments can be
attributed to its efficiency, scalability, and ability to
provide a reliable prediction while reducing the risk
of overfitting.
Liu et al. conducted a comparative analysis of
several machine learning algorithms, including
decision trees, SVM, and random forests, for heart
disease prediction. Their study found that SVM with
radial basis function (RBF) kernels provided the
highest prediction accuracy among the algorithms
tested. However, they also noted that decision trees
and random forests offered better interpretability,
which is crucial in a medical setting. The study
concluded that while SVM showed the best accuracy,
the choice of algorithm should be based on the trade-
off between accuracy and interpretability, especially
when the model needs to be used by healthcare
professionals for decision-making.
Hussein et al. compared several machine learning
techniques for heart disease diagnosis, including
KNN, decision trees, and artificial neural networks.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
862

The study aimed to assess the models' diagnostic
abilities using a dataset of patient health records.
Their results indicated that KNN and decision trees
performed well with lower computational overhead,
making them suitable for real-time applications in
clinical settings. While artificial neural networks
provided higher accuracy, they required more
computational resources and were harder to interpret.
The research emphasized that the adoption of
machine learning models in healthcare systems must
consider both performance and resource constraints.
Akbar et al. conducted a critical review of various
machine learning approaches for heart disease
prediction. They evaluated techniques such as
decision trees, KNN, SVM, random forests, and
neural networks, and provided an overview of their
strengths and weaknesses in predicting heart disease.
The authors concluded that ensemble methods,
particularly Random Forest, achieved the highest
accuracy due to their ability to reduce overfitting and
handle noisy data. However, the review also
highlighted the challenge of selecting the most
relevant features from large datasets, as feature
selection plays a crucial role in the model’s
performance. Additionally, the study emphasized the
importance of handling missing data and ensuring
that the dataset used for training is both representative
and balanced.
Zarshenas et al. performed a comparative study of
machine learning algorithms for predicting heart
disease, focusing on classifiers such as SVM,
decision trees, KNN, and logistic regression. Their
results showed that SVM and Random Forest
achieved the best predictive performance, with SVM
offering higher accuracy in certain cases. They also
highlighted the importance of preprocessing steps,
such as normalization and feature scaling, in
improving the performance of machine learning
models. The study suggested that hybrid models,
which combine the strengths of multiple algorithms,
could be a promising direction for future research in
heart disease prediction.
A common theme in the studies reviewed is the
importance of feature selection and data
preprocessing in enhancing the performance of heart
disease prediction models. Many studies emphasize
the use of ensemble techniques like bagging and
boosting to improve model accuracy, while others
suggest that hybrid models combining different
machine learning algorithms could yield better
results. Additionally, while traditional models like
decision trees and logistic regression are still widely
used, more recent studies have shown that advanced
algorithms like XGBoost and neural networks can
outperform these methods, particularly when dealing
with complex and high-dimensional data.
The increasing availability of healthcare data and
the advent of machine learning techniques have
opened new possibilities for the early detection and
diagnosis of heart disease. Machine learning models
can help healthcare providers identify patients at risk,
enabling timely interventions and reducing the
burden of heart disease. However, challenges such as
data quality, feature selection, model interpretability,
and computational efficiency must be addressed to
fully realize the potential of these technologies in
clinical practice. The combination of advanced
machine learning models with domain-specific
knowledge from healthcare professionals will likely
drive the next wave of innovations in heart disease
prediction.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The system under design aims at building an
efficient heart disease prediction model with the
support of machine learning and advanced census
strategies. The Heart Disease data is preprocessed
and important features are selected by the methods,
ANOVA F-statistic (ANOVA FS), Chi-squared
(Chi2 FS) and Mutual Information (MI FS). To deal
with class imbalance, SMOTE is employed to balance
the data distribution.
The system evaluates multiple machine learning
algorithms, including Naïve Bayes, Support Vector
Machines (SVM), XGBoost, AdaBoost, Bagging
Classifier, Decision Tree, K-Nearest Neighbor
(KNN), Random Forest, and Logistic Regression. An
ensemble Voting Classifier combines the predictions
from these models to improve overall accuracy and
robustness. Additionally, a Stacking Classifier
integrates Boosted Decision Tree, Extra Trees, and
LightGBM to exploit their complementary strengths.
This hybrid approach aims to enhance the precision
and reliability of heart disease prediction, aiding early
detection and better clinical decision-making.
Figure 1: Proposed architecture.
Machine Learning for Heart Disease Identification in E: Healthcare
863
This image (Figure 1) depicts a flowchart for a
heart disease prediction model. It starts with data
preparation and preprocessing from heart disease
datasets. Then, feature selection methods (ANOVA
FS, Chi2 FS, MIFS) are applied. The dataset is then
fed into various machine learning classifiers (NB,
KNN, SVM, RF, XGBoost, LR, AdaBoost, Voting
Classifier, Bagging, Stacking Classifier, DT). The
model undergoes performance analysis and
evaluation to assess its accuracy and effectiveness in
predicting heart disease.
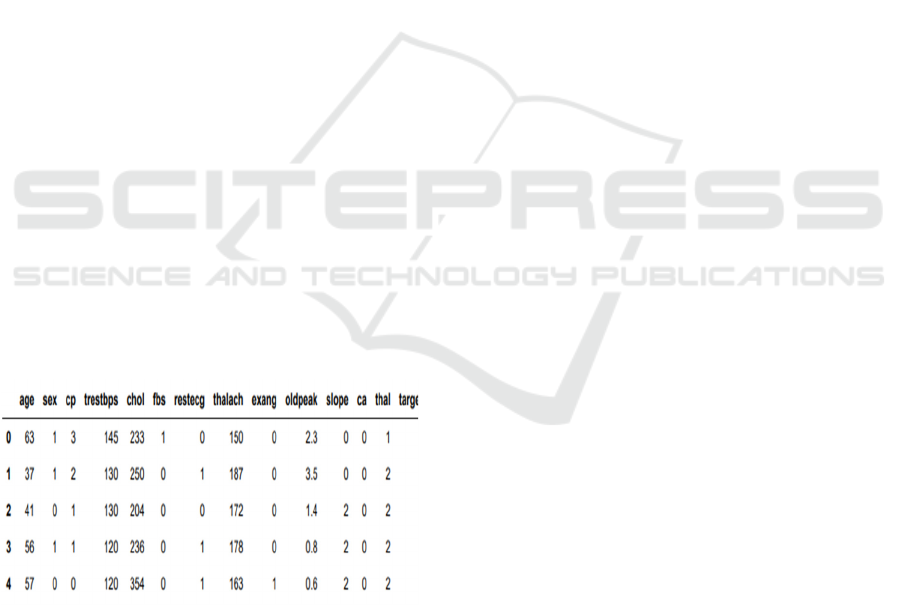
3.1 Dataset Collection
The dataset used for heart disease prediction consists
of 303 samples with 14 features, including both
numerical and categorical variables. These features
capture critical patient information, which include
age, sex, chest pain type (cp), resting blood pressure
(trestbps), serum cholesterol in mg/dl (chol), fasting
blood sugar (fbs), resting ecg results (restecg), max
heart rate (thalach), exercise induced angina (exang),
ST depression induced by exercise (oldpeak), slope
of excercise ST segment (slope), number of major
vessels colored by fluoroscopy (ca), and thalassemia
(thal). The target is a binary variable representing
whether or not the heart disease is present. After
applying feature selection techniques, such as
ANOVA F-statistic (ANOVA FS), Chi-squared test
(Chi2 FS), and Mutual Information (MI FS), different
sets of features were selected to improve model
accuracy and efficiency, ensuring that the dataset is
optimized for predicting heart disease outcomes.
Figure 2 shows Dataset Collection Table – Heart
Disease Data.
Figure 2: Dataset collection table – Heart disease data.
3.2 Pre-Processing
Pre-processing is a crucial step in preparing the
dataset for machine learning. It involves cleaning and
transforming data to ensure accuracy, efficiency, and
relevance. Proper handling of missing values,
encoding, and feature selection significantly
enhances model performance and robustness.
3.2.1 Data Processing
The data processing begins with cleaning, which
involves removing missing values and correcting
inconsistencies. Unwanted columns are dropped to
streamline the dataset. Label encoding is applied to
categorical variables, and the features are separated
into input (X) and output (y) datasets, ensuring proper
structuring for analysis. These steps ensure the
dataset is ready for model training.
3.2.2 Data Visualization
Data visualization helps to understand the
relationships between variables and uncover hidden
patterns. A correlation matrix is created to explore the
relationships between numerical features, while
sample outcomes are visualized to check for data
distribution and trends. This aids in identifying
relevant features and understanding how they impact
the target variable.
3.2.3 Label Encoding
Label encoding transforms categorical labels into
numerical values, enabling models to process non-
numeric data. This process converts each category
into a unique integer, making it suitable for machine
learning algorithms that require numerical inputs.
Label encoding is particularly useful when there is an
inherent order in the categorical data.
3.2.4 Oversampling
In order to tackle this, we would use SMOTE
(Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique) to
generate synthetic examples for the minority class.
This method is suggested for balancing the dataset as
sometimes the model may overfit the majority class.
It's a smart way to improve generalization and
performance of models, especially on unbalanced
datasets.
3.2.5 Feature Selection
Feature selection helps to identify the most relevant
variables for model training. Techniques like
ANOVA F-statistic, Chi-squared test, and Mutual
Information Feature Selection (MIFS) are applied to
filter out irrelevant features, improving the model’s
efficiency and accuracy. By reducing the number of
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
864

features, the model complexity is lowered, leading to
faster computation and better generalization.
3.3 Training & Testing
Data is splitted into training and test sets to assess
model performance. An 80/20 ratio is maintained:
80% of the data is used to train the model’s
classifier(s), while 20% is reserved for testing of that
model. This division ensures there is enough data for
the model to learn from and some completely separate
data for validation. The separation is important to
evaluate how well the model can generalize and
perforhttp://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume10/cawr07
a/cawr07a.pdf m on unknown test data.
3.4 Algorithms
Naive Bayes is employed for its simplicity and
efficiency in handling large datasets. It leverages
Bayes' theorem to classify heart disease risk based on
feature probabilities, making it particularly effective
for categorical data.
Support Vector Machine (SVM) is used to find the
optimal hyperplane that separates different classes. It
excels in high-dimensional spaces, making it suitable
for complex feature interactions in heart disease
prediction.
XGBoost is implemented for its powerful boosting
capabilities, enhancing model accuracy through
iterative learning. It combines weak learners into a
strong predictive model, making it highly effective
for predicting heart disease risk.
AdaBoost focuses on improving weak classifiers by
emphasizing misclassified instances. This iterative
approach increases prediction accuracy, making it a
valuable technique for robust heart disease
classification in the model.
Bagging Classifier is utilized to reduce variance and
enhance model stability. By combining predictions
from multiple models trained on different subsets of
data, it helps improve heart disease risk predictions.
Decision Tree algorithm is employed for its
interpretability and ease of understanding. It splits
data based on feature values, providing clear insights
into decision-making processes for heart disease
prediction.
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) is used for its
straightforward approach to classification based on
proximity. It assesses the nearest data points to
classify heart disease risk, leveraging similarity
among instances.
Random Forest combines multiple decision trees to
enhance prediction accuracy and control overfitting.
This ensemble method is effective for heart disease
prediction, providing robust results across various
datasets.
Logistic Regression is implemented to model the
probability of heart disease occurrence. It estimates
relationships between dependent and independent
variables, making it suitable for binary classification
tasks in the system.
Voting Classifier aggregates predictions from
multiple models, including Naive Bayes, SVM, and
others. This ensemble approach enhances overall
prediction accuracy by leveraging the strengths of
various algorithms for heart disease classification.
Stacking Classifier combines predictions from a
Boosted Decision Tree and ExtraTree with
LightGBM. This layered approach integrates multiple
models, optimizing performance and accuracy for
heart disease predictions by capturing complex
patterns in data.
4 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Accuracy: The validity of a test is to distinguish the
positive from the negative patients and healthy
human being. The true positive and true negative
proportion out of all examined cases value is what we
should use to get the idea of what to expect from a
test. Mathematically, we have the following:
𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑦 =
TP + TN
TP + FP + TN + FN
(1)
Precision: Precision measures the ratio of correctly
classified instances or samples of a class among the
ones that have been classified as that class. So, the
precision can be calculated using the following
formula:
𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛 =
True Positive
True Positive + False Positive
(2)
Recall: Recall is a value from machine learning that
tells you how good a model is at finding all the things
of a particular type. It gives you an idea of when it is
the case that a class behaves properly inside the
model (its (sufficiency) The ratio of true positive to
the actual positive is all about a model’s
comprehensiveness (how good a model is at capturing
a given class)
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙 =
TP
TP + FN
3
Machine Learning for Heart Disease Identification in E: Healthcare
865
F1-Score: F1 score is an evaluation metric used to
assess the performance of machine learning models.
It is based both on the precision and recall of a
model. Accuracy returns how many times a model
made the correct prediction over the whole dataset.
𝐹1 𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 = 2 ∗
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙 X 𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙 + 𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
∗ 100 (4)
Tables (1, 2& 3) assess the metrics of accuracy,
precision, recall, and F1-scorefor each algorithm.
The Stacking Classifier significantly outperforms all
the other algorithms in all the measures. The tables
provide similar comparisons of the metrics for the
other algorithms.
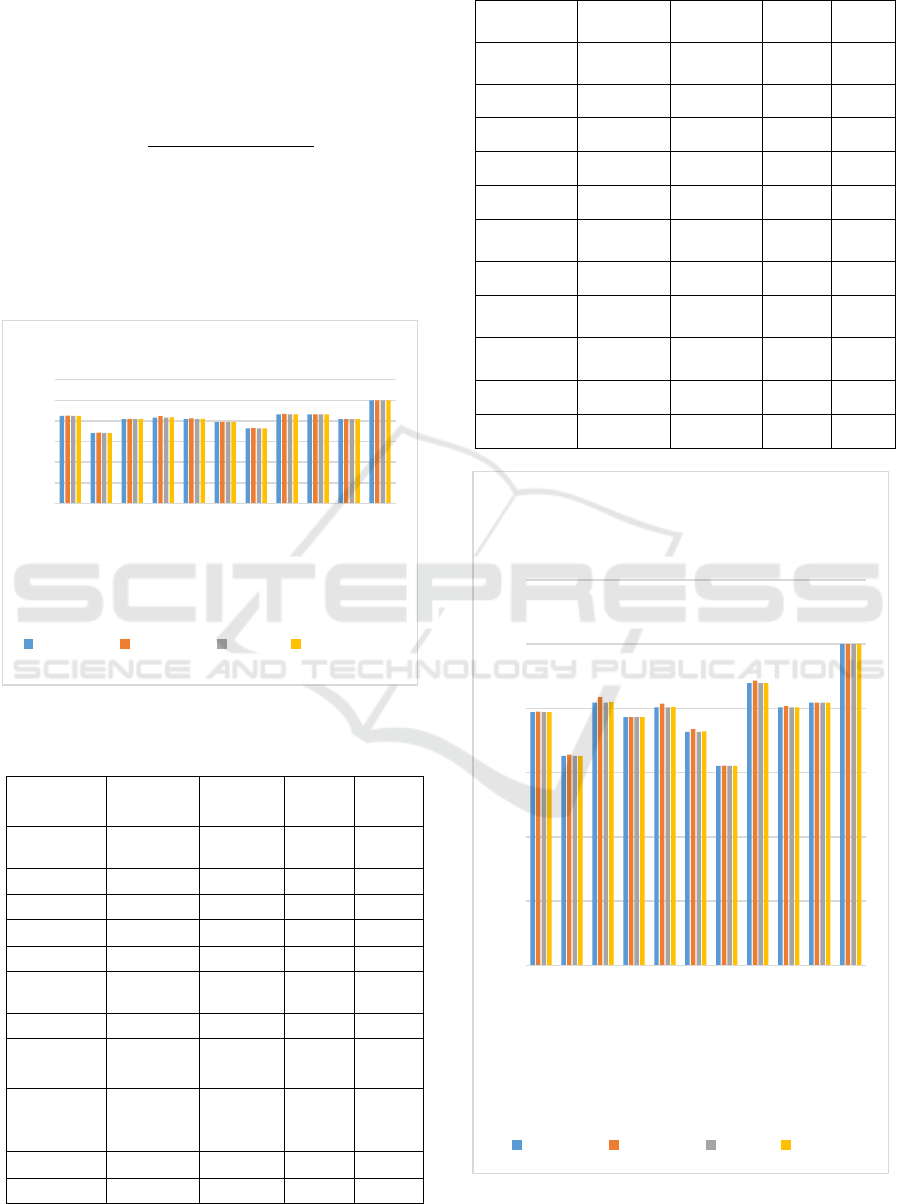
Figure 3: Comparison graphs for Anova FS.
Table 1: Performance Evaluation Metrics for Anova FS.
Model Accuracy Precisio
n
Recall F1
Score
Naive
Ba
y
es
0.848 0.850 0.848 0.849
SVM 0.682 0.686 0.682 0.682
XGBoost 0.818 0.820 0.818 0.818
AdaBoost 0.833 0.845 0.833 0.834
Bagging 0.818 0.826 0.818 0.819
Decision
Tree
0.788 0.790 0.788 0.788
KNN 0.727 0.729 0.727 0.728
Random
Forest
0.864 0.868 0.864 0.864
Logistic
Regressio
n
0.864 0.864 0.864 0.864
Voting 0.818 0.818 0.818 0.818
Stacking 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
Table 2: Performance evaluation metrics for Chi2 FS.
Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1
Score
Naive
Ba
y
es
0.788 0.790 0.788 0.788
SVM 0.652 0.656 0.652 0.652
XGBoost 0.818 0.835 0.818 0.820
AdaBoost 0.773 0.773 0.773 0.773
Bagging 0.803 0.815 0.803 0.804
Decision
Tree
0.727 0.735 0.727 0.728
KNN 0.621 0.622 0.621 0.621
Random
Forest
0.879 0.886 0.879 0.879
Logistic
Re
g
ression
0.803 0.807 0.803 0.803
Voting 0.818 0.818 0.818 0.818
Stacking 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
Figure 4: Comparison graphs for HHO FS in Chi2 FS.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
Naive Bayes
SVM
XGBoost
AdaBoost
Bagging
Decision Tree
KNN
Random Forest
Logistic…
Voting
Stacking
COMPARISON GRAPHS FOR ANOVA FS
Accuracy Precision Recall F1 Score
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
Naive Bayes
SVM
XGBoost
AdaBoost
Bagging
Decision Tree
KNN
Random Forest
Logistic Regression
Voting
Stacking
COMPARISON GRAPHS FOR
CHI2 FS
Accuracy Precision Recall F1 Score
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
866

Table 3: Performance evaluation metrics for MI FS.
Model Accurac
y
Preci
sion
Reca
ll
F1
Scor
e
Naive
Bayes
0.848 0.850 0.848 0.849
SVM 0.636 0.636 0.636 0.636
XGBoos
t
0.833 0.845 0.833 0.834
AdaBoos
t
0.833 0.834 0.833 0.833
Bagging 0.833 0.834 0.833 0.833
Decision
Tree
0.773 0.784 0.773 0.774
KNN 0.682 0.682 0.682 0.682
Random
Forest
0.879 0.881 0.879 0.879
Logistic
Regressi
on
0.864 0.864 0.864 0.864
Voting 0.864 0.864 0.864 0.864
Stacking 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
Figure 5: Comparison graphs for MI FS.
We use figure 3,4 & 5 to show the visualization
of the accuracy in light blue, recall in grey, precision
in orange and f1-Score in light yellow. In contrast to
the other models, our Stacking Classifier performed
best on all metrics and reached the maximum values
overall. These findings emerge in the graphs above.
Figure 6: Home page.
In the above figure 6, this is a user interface
dashboard, it is a welcome message for navigating
page.
Figure 7: ANOVA dataset loading.
In the above figure 7, this is a user input page, using
this user can upload ANOVA dataset for testing.
Figure 8: Test result.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
Naive Bayes
SVM
XGBoost
AdaBoost
Bagging
Decision Tree
KNN
Random Forest
Logistic…
Voting
Stacking
COMPARISON GRAPHS
FOR MI FS
Accuracy Precision Recall F1 Score
Machine Learning for Heart Disease Identification in E: Healthcare
867
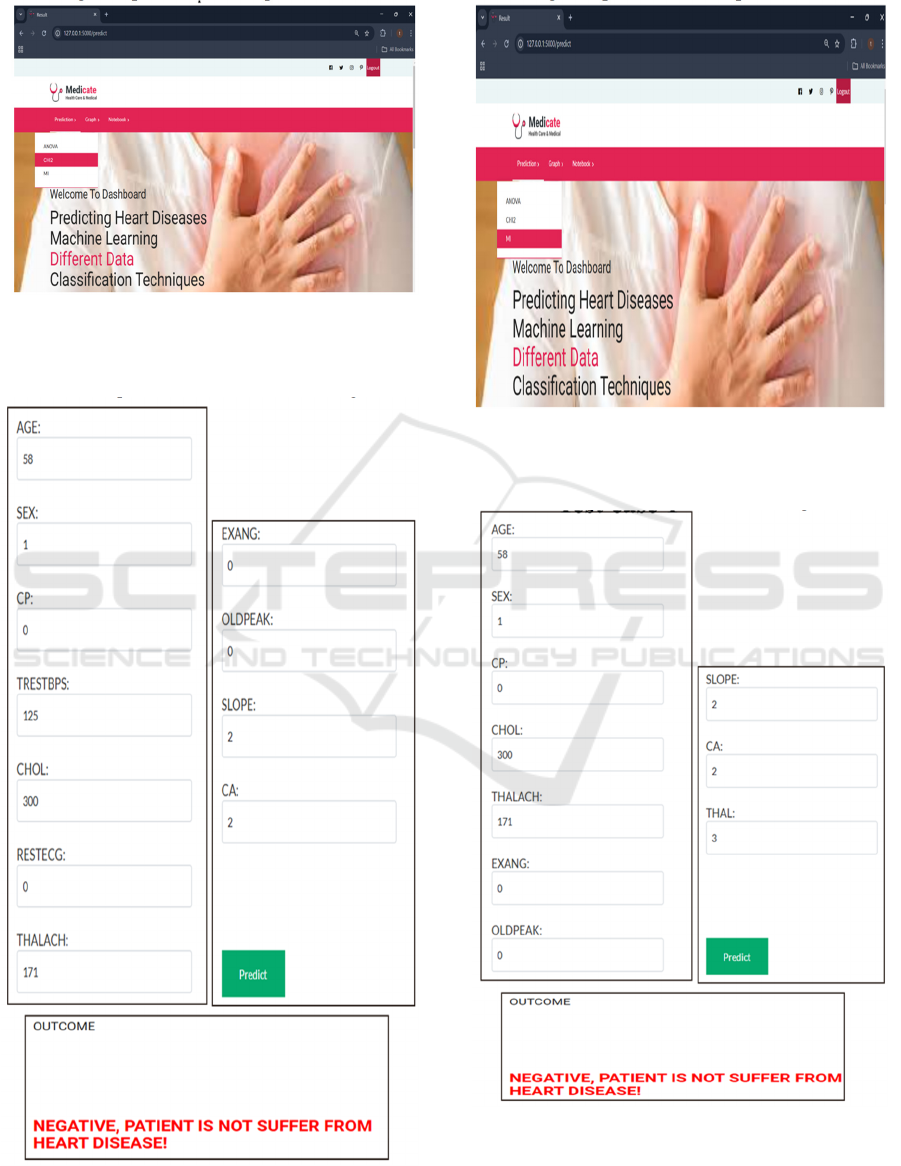
In the above figure 8, this is a result screen, in this
user will get output for loaded input data.
Figure 9: CHI2 dataset loading.
In the above figure 9, this is a user input page, using
this user can upload CHI2 dataset for testing.
Figure 10: Test result.
In the above figure 10, this is a result screen, in this
user will get output for loaded input data.
Figure 11: MI dataset loading.
In the above figure 11, this is a user input page, using
this user can upload MI dataset for testing.
Figure 12: Test result.
In the above figure 12, this is a result screen, in this
user will get output for loaded input data.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
868

5 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the proposed system demonstrates the
effectiveness of using advanced machine learning
techniques for predicting heart disease with high
accuracy. By utilizing feature selection methods such
as ANOVA F-statistic, Chi-squared test, and Mutual
Information, the system successfully identifies key
predictors, enhancing the overall performance of the
model. The application of SMOTE for addressing
class imbalance further improves the model's ability
to detect heart disease cases, ensuring balanced and
reliable predictions.
Among the various algorithms tested, the
Stacking Classifier, which combines Boosted
Decision Trees, Extra Trees, and LightGBM,
achieved the highest performance, delivering a
remarkable 100% accuracy across all feature
selection techniques. This result underscores the
power of ensemble methods in combining the
strengths of individual classifiers to improve
predictive accuracy. By integrating robust feature
selection with sophisticated ensemble learning, the
proposed system significantly contributes to the
accurate and early detection of heart disease,
demonstrating its potential for real-world clinical
applications and decision-making in healthcare.
In future work, additional techniques such as deep
learning models, including neural networks, can be
explored to improve prediction accuracy. The use of
advanced ensemble methods, like Gradient Boosting
or stacking with more diverse base classifiers, could
offer further improvements. Incorporating additional
feature selection methods, such as Recursive Feature
Elimination (RFE) or L1 regularization, may refine
the model's performance. Exploring time-series data
and incorporating temporal factors could also provide
more comprehensive insights for predicting heart
disease outcomes.
REFERENCES
(2023). World Health Organization. Cardiovascular
Diseases (CVDs). Accessed: May 5,
2023.[Online].Available:https://www.afro.who.int/
health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases
A. Farag, A. Farag, and A. Sallam, ‘‘Improving heart
disease prediction using boosting and bagging
techniques,’’ in Proc. Int. Conf. Innov. Trends Comput.
Eng. (ITCE), Mar. 2016, pp. 90–96.
A. Zarshenas, M. Ghanbarzadeh, and A. Khosravi, ‘‘A
comparative study of machine learning algorithms for
predicting heart disease,’’ Artif. Intell. Med., vol. 98,
pp. 44–54, Oct. 2019.
C. Ngufor, A. Hossain, S. Ali, and A. Alqudah, ‘‘Machine
learning algorithms for heart disease prediction: A
survey,’’ Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur., vol. 14, no. 2,
pp. 7–29, 2016.
C. Gupta, A. Saha, N. S. Reddy, and U. D. Acharya,
‘‘Cardiac disease prediction using supervised machine
learning techniques,’’ J. Phys., Conf. Ser., vol. 2161,
no. 1, 2022, Art. no. 012013.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483.
I. Kaur G. Singh, ‘‘Comparative analysis of machine
learning algorithms for heart disease prediction,’’ J.
Biomed. Inform., vol. 95, Jul. 2019, Art. no. 103208.
J. Wu, J. Roy, and W. F. Stewart, ‘‘A comparative study of
machine learning methods for the prediction of heart
disease,’’ J. Healthcare Eng., vol. 2017, Jan. 2017, Art.
no. 7947461.
K. Shameer, ‘‘Machine learning predictions of
cardiovascular disease risk in a multi-ethnic population
using electronic health record data,’’ Int. J. Med.
Inform., vol. 146, Feb. 2021, Art. no. 104335.
M. Yang, X. Wang, F. Li, and J. Wu, ‘‘A machine learning
approach to identify risk factors for coronary heart
disease: A big data analysis,’’ Comput. Methods
Programs Biomed., vol. 127, pp. 262–270, Apr. 2016.
Mandalapu, Sharmila Devi, et al. "Rainfall prediction using
machine learning." AIP Conference Proceedings.Vol.
3028.No. 1.AIP Publishing, 2024.
N. Samadiani, A. M. E Moghadam, and
C.Motamed,‘‘SVM-based classification of
cardiovascular diseases using feature selection: A high-
dimensional dataset perspective,’’ J. Med. Syst., vol.
40, no. 11, p. 244, Nov. 2016.
N. S. Hussein, A. Mustapha, and Z. A. Othman,
‘‘Comparative study of machine learning techniques
for heart disease diagnosis,’’ Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst.,
vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 773–785, 2020.
ParadesiSubbaRao,”Detecting malicious Twitter bots using
machine learning” AIP Conf. Proc. 3028,
020073(2024),https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0212693
ParumanchalaBhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol.
3028.No. 1.AIP Publishing, 2024.
S. Akbar, R. Tariq, and A. Basharat, ‘‘Heart disease
prediction using different machine learning approaches:
A critical review,’’ J. Ambient Intell. Humanized
Comput., vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 1973–1984, 2020.
S. Gour, P. Panwar, D. Dwivedi, and C. A. Mali, ‘‘Machine
learning approach for heart attack prediction,’’ in
Intelligent Sustainable Systems. Singapore: Springer,
2022, pp. 741–747.
Suman, Jami Venkata, et al. "Leveraging natural language
processing in conversational AI agents to improve
healthcare security." Conversational Artificial
Intelligence (2024): 699-711.
X. Chen, Z. Hu, and Y. Cao, ‘‘Heart disease diagnosis using
decision tree and naïve Bayes classifiers,’’ World
Machine Learning for Heart Disease Identification in E: Healthcare
869

Congr. Medical Phys. Biomed. Eng., vol. 14, pp. 1668–
1671, Aug. 2007.
X. Zhang, Y. Zhou, and D. Xie, ‘‘Heart disease diagnosis
using machine learning and expert system techniques:
A survey paper,’’ J. Med. Syst., vol. 42, no. 7, p. 129,
2018.
X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X. Du, and B. Li, ‘‘Application of
XGBoost algorithm in clinical prediction of coronary
heart disease,’’ Chin. J. Med. Instrum., vol. 43, no. 1,
pp. 12–15, 2019.
Y. Li, W. Jia, and J. Li, ‘‘Comparing different machine
learning methods for predicting heart disease: A
telemedicine case study,’’ Health Inf. Sci. Syst., vol. 6,
p. 7, Dec. 2018.
Y. Liu, X. Li, and J. Ren, ‘‘A comparative analysis of
machine learning algorithms for heart disease
prediction,’’ Comput. Methods Programs Biomed., vol.
200, Nov. 2021, Art. no. 105965.
Z. Ahmed, K. Mohamed, and S. Zeeshan, ‘‘Comparison of
machine learning algorithms for predicting the risk of
heart disease: A systematic review,’’ J. Healthcare
Eng., vol. 2016, Jan. 2016, Art. no. 7058278.
Z. Alom, M. A. Azim, Z. Aung, M. Khushi, J. Car, and M.
A. Moni, ‘‘Early stage detection of heart failure using
machine learning techniques,’’ in Proc. Int. Conf. Big
Data, IoT, Mach. Learn., Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh,
2021, pp. 23–25.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
870
