
High‑Performance Computing‑Based Brain Tumor Detection Using
Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
Tummuluri Sree Pujitha, Kolli Rohitha, Karnati Nalini, Guttikonda Madhulatha,
B. Sudharani and Jawad Ahmad Dar
Department of ACSE, VFSTR Deemed to be University, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Brain Tumor Detection, Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Networks (PQDCNN),
High‑Performance Computing (HPC), Deep Learning, Fuzzy Local Information C- Means (FLICM), Fast
Retina Keypoint (FREAK), Gray Level Co- Occurrence Matrix (GLCM), Feature Extraction, Medical Image
Processing, BraTS2020, Figshare.
Abstract: We present a high-performance quantum computing-based model for brain tumor detection based on a Parallel
Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network (PQDCNN) framework. It uses Fuzzy Local Information C-
Means (FLICM) clustering for better segmentation, to execute better than the normal K-means. The data
preprocessing processes are median filtering and data augmentation. Deep fusion of FREAK descriptors,
GLCM texture features, and deep CNN representations Our PQDCNN model achieves high classification
performance on both datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art CNNs on BraTS2020 and Figshare datasets,
showing the potential of quantum-inspired deep learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Brain tumor detection can be a daunting task in
medical diagnostic because of its timeliness and
accuracy. Traditional tumor diagnosis relies heavily
on the manual inspection of magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI) scans, which is an extrapolative and
subjective process associated with inter-observer
variability. With the application of deep learning
specifically, mainly through CNNs, the accuracy of
brain tumor detection has been improved by enabling
automation in identifying and characterizing these
features. However, ordinary CNN models are
computationally rigid since they consume higher
memory and are unable to model long-range spatial
relations in medical images. However, there have
been solutions like quantum-inspired neural
segmentations or high-performance computing
(HPC) frameworks that have emerged to solve these
problems. This paper presents a PQDCN-based brain
tumor detection method. This means that image
pixels are not overlapped and regions through the
image segmentation process can be identified, we
are applying Fuzzy local information c-means
clustering (FLICM), where we use these in the
identification of the image classes. Preprocessing
techniques like median filtering and image
augmentation are employed to enhance the model
generalizability. A hybrid feature representing
tumor scenes is an ensemble of Fast retina key
point (FREAK) descriptors, Gray-level
cooccurrence matrix (GLCM) texture features, and
CNN based deep features. Then, the features obtained
are fed into the PQDCNN model to achieve
multiscale contextual feature extraction with high
inference efficiency using quantum-inspired dilation
strategies.
Utilizing quantum-inspired techniques provides
enhanced analysis of medical images, and quantum
dilated convolutions allow Layer CNN to utilize
receptive field size without losing performance in
comparison to classic versions. This is
advantageous for tumor detection with wide variation
in shape and texture. This model predicts these with
better accuracy by using parallel quantum dilations.
FLICM-based segmentation and multi-feature fusion
complement each other well and provide a potential
solution for automatic brain tumor detection.
The remainder of this paper is as follows: In
Section II, a review of previous work regarding deep
learning of brain tumor detection is provided. Section
III presents the FLICM and the proposed PQDCNN
model. Experimental results, comparison, and
analysis are presented in Section IV.
836
Pujitha, T. S., Rohitha, K., Nalini, K., Madhulatha, G., Sudharani, B. and Dar, J. A.
High-Performance Computing-Based Brain Tumor Detection Using Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0013906600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
836-843
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 RELATED WORK
The QCNN model achieves 99.67% validation
accuracy and shows excellent generalization in brain
tumor classification. Over the 20 epochs, accuracy
increases, yet distinguishing between benign,
meningioma and malignant; glioma is diffi- cult.
Evaluations using real images demonstrate that it can
be integrated into clinics due to its high accuracy and
robustness against overfitting (Khan et al., 2024).
The accuracy of the optimized YOLOv7 model for
detecting glioma, meningioma, and pituitary tumors
from MRI images was 99.5%. With data
augmentation, detection quality im- proved further,
resulting in 497 correct detections, including three
false positive detections. The model achieves 99.5%
precision and 99.3% recall, outperforming state-of-
the-art techniques, though improvement is necessary
for small and noncircular tumors (Abdusalomov et
al., 2023).
In this work, three hybrid CNN-based high-
accuracy clas- sification models are developed for
brain tumor classification. The first one gets 99.53%
on the accuracy, the second one on the
classification of tumors into five types at 93.81%,
and the last one on gliomas grading at 98.56%.
Optimizing these through grid search and with access
to extensive clinical data allows for these models to
greatly outperform traditional practices in early
detection and diagnosis (Srinivasan et al., 2024).
The 16-layer CNN achieved an impressive
accuracy of 98.88% in binary classification and
97.83% in classifying tumors into three categories
using MRI datasets. By in- corporating hybrid
oversampling, we were able to enhance performance
greatly, outshining traditional machine learning
models like random forest, SVM, and k-NN when it
comes to accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and F1
score (Singh et al., 2023).
The PDCNN model showed important results,
hitting 97.33% accuracy on dataset-I, 97.60% on
Figshare dataset-
II, and an impressive 98.12% on
Kaggle dataset-III. By integrating two CNNs with
differing window sizes, we were able to enhance
feature extraction, surpassing the performance of
existing methods (Rahman, T., & Islam, M. S. 2023).
The EDN-SVM classifier demonstrated an
impressive accu- racy of 97.93%, with a sensitivity of
92% and specificity of 98 in MRI brain tumor
detection. By using ACEA, median filtering, fuzzy c-
means segmentation, and GLCM, it not only
surpassed traditional methods in terms of precision
but also greatly improved speed, establishing itself as
a strong tool for automated diagnosis (Anantharajan
et al., 2024).
This study dives into CNN-based brain tumor
classification using a dataset of 7,022 MRI images,
exploring models like VGG, ResNet, DenseNet, and
SqueezeNet. DenseNet deliv- ered an impressive
accuracy of 85% when paired with SVM, while a
hybrid model achieved 83% with LDA (Gu¨ler, M.,
& Namlı, E. 2024).
Saeedi and colleagues took a deep dive into using
deep learning for classifying brain tumors based on
3,264 MRI scans. Their 2D CNN model hit an
impressive accuracy of 96.47%, along with a recall
rate of 95%. Meanwhile, the autoencoder performed
admirably as well, achieving 95.63% accuracy and a
94% recall. On the conventional front, K-NN stood
out with an accuracy of 86% (Saeedi et al., 2023).
The A-GRU model, enhanced with ADAM and
data aug- mentation techniques, achieved a
remarkable accuracy of 99.32% in classifying brain
tumors. It outperformed the CNN, A-CNN, LSTM,
A-LSTM, and GRU models. These results were
further improved through careful hyperparameter
tuning (Saboor et al., 2024).
In this study, we explored using YOLOv3 through
YOLOv7 models for classifying meningioma
firmness. Among these, YOLOv7 stood out with
impressive results: a specificity of 97.95%, a
balanced accuracy of 98.97%, and an F1-score of
99.24%. It outperformed both SVM and KNN
techniques (Alhussainan et al., 2024). By analyzing
3,762 MRI images from Kaggle, we found that
ResNet-50 achieved an impressive 99.82%
accuracy during training and 99.5% during testing
when using the SGD opti- mizer. Through
preprocessing, pixel reduction, and optimizing with
binary cross-entropy, we saw a boost in
performance, finally achieving a 96.10% F1-score,
96.50% precision, and 95.62% recall (Asad et al.,
2023).
In this study, we looked at how deep transfer
learning can help diagnose brain tumors using
models like ResNet152, VGG19, DenseNet169, and
MobileNetv3 on a Kaggle dataset. MobileNetv3
stood out with the highest accuracy, hitting
99.75%, while ResNet152 followed closely with
98.5%. (Mathivanan et al., 2024) The research
achieved an average entropy of 7.32 bits, which
helped in reducing saturation effects. It also recorded
a PSNR of 29.07 dB and a contrast level of 39.47 dB,
surpassing earlier techniques like GHE and BBHE.
With the enhanced Inception V3 model, we reached
an impressive accuracy of 98.89%, outperforming
AlexNet, VGG-16, and GoogLeNet in tumor
classification tasks (Agarwal et al., 2024).
High-Performance Computing-Based Brain Tumor Detection Using Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
837
This research explores deep learning models for
detecting brain tumors using 3,264 MRI images. The
newly developed CNN achieved an impressive
accuracy of 93.3%, an AUC of 98.43%, a recall of
91.1%, and a loss of 0.260. These results surpass
those of established models like ResNet-50, VGG16,
and Inception V3 (Mahmud et al., 2023).
This study emphasizes the impressive capabilities
of U-Net when it comes to segmenting brain tumors,
particularly show- ing superior outcomes in Dice
score, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. Notably,
ACMINet took the top spot on the BraTS2020
leaderboard, which emphasizes how effective U- Net
really is. Between 2020 and 2024, U-Net not only set
new benchmarks but also played an important role in
advancing the diagnostics and treatment of neuro-
oncology (Umarani et al., 2024).
3 METHODOLOGY
In our proposed method, we begin by using FLICM
clustering to effectively segment tumors. After that,
we apply median filtering to reduce any noise, along
with some augmentation techniques aimed at making
our model stronger. For feature extraction, we draw
on a combination of FREAK descriptors, GLCM, and
features derived from deep CNNs to provide a
thorough representation of the data. The PQDCNN
model uses quantum-inspired dilated convolutions to
enhance processing efficiency. We’ve trained our
model on the BraTS2020 and Figshare datasets,
evaluating it based on accuracy, precision, recall, and
F1 score. Plus, by integrating HPC, we ensure that
our approach is scalable and can operate in real time
for medical applications.
3.1 Dataset Description
Datasets The datasets used in this study are medical
images, targeting the detection of brain tumors. We
then split the dataset into training validation and test
sets to train and evaluate the model efficiently
Hence, we utilized the Figshare information suitable
for classification, and we exploited the BraTS2020
information suitable for tumor segmentation to give
an extensive evaluation of our proposed Parallel
Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
(PQDCNN).
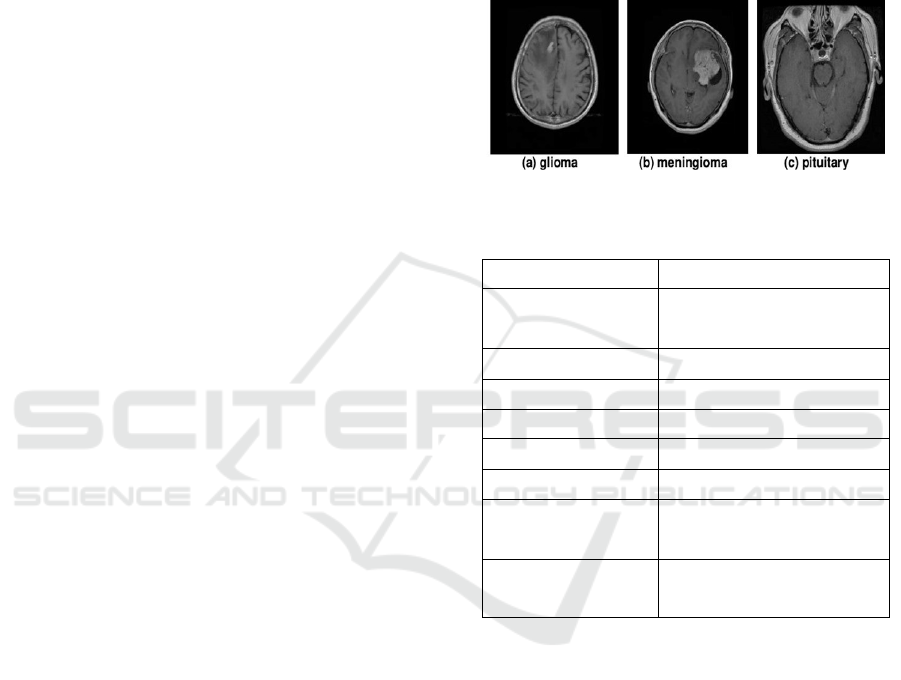
Figshare Dataset:
The Figshare dataset consists
of brain MRI images categorized into three tumor
types:
•
Glioma Tumor
•
Meningioma Tumor
•
Pituitary Tumor
To enhance model performance and consistency, the
dataset undergoes preprocessing, including:
•
Standardizing image dimensions to ensure uniform
input sizes.
•
Normalizing pixel values to improve model
convergence and stability.
•
Applying noise reduction using Median Filtering to
pre- serve tumor structures.
Figure 1: Sample Figshare image dataset.
Table 1: Summary of the Figshare brain tumor MRI dataset.
Attribute Description
Dataset Name
Figshare Brain Tumor MRI
Dataset
Modality Types MRI Images
Target Prediction Brain Tumor Classification
Instances 3,064
Image Dimensions 256 × 256 × 1
Number of Classes 3
Shape of Train Data
Split
(2,451, 256, 256, 1)
Shape of Test Data
Split
(613, 256, 256, 1)
BraTS2020 Dataset: The BraTS2020 dataset includes
multi-modal MRI scans with t1ce and segment
sequences, offering detailed annotations of tumor
regions. This dataset is particularly valuable for
training deep learning models in brain tumor
segmentation. The images in this dataset undergo
preprocessing steps such as:
•
Size standardization for uniform input
representation.
•
Intensity normalization to minimize variations
across different MRI machines.
•
Fuzzy Local Information C-Means (FLICM)
clustering
for effective segmentation of the tumor
region.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
838
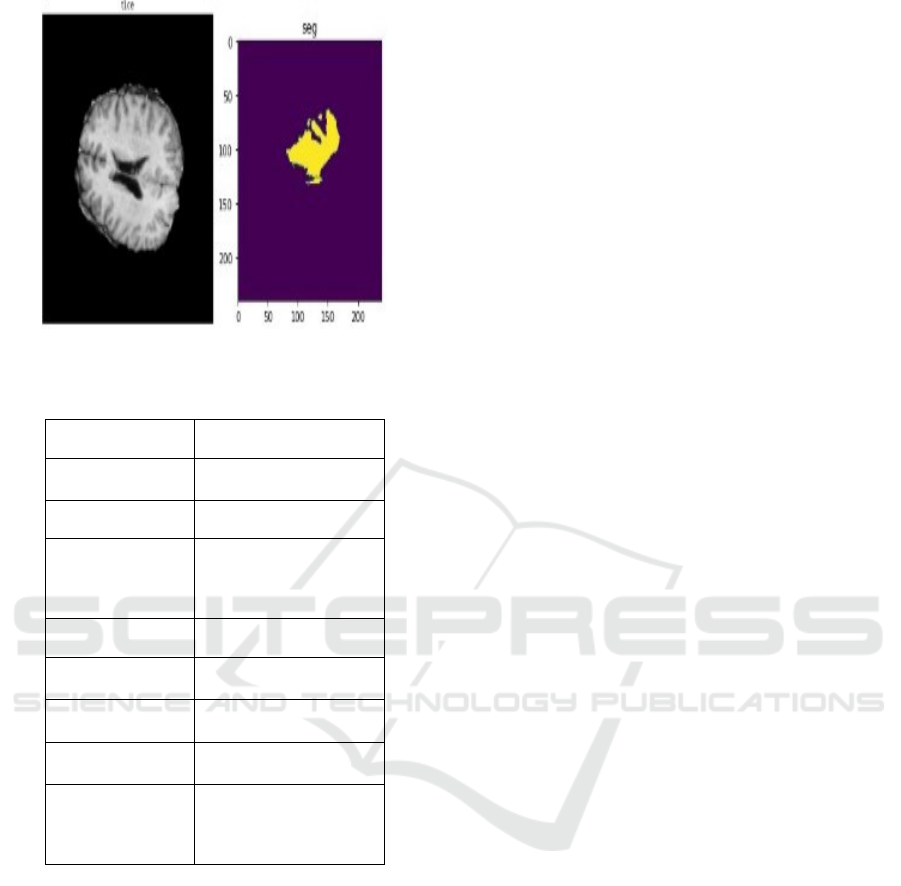
Figure 2: Sample BraTS2020 Image dataset.
Table 2: Summary of the BraTS2020 dataset.
Attribute Description
Dataset Name BraTS2020 Dataset
Modality Types MRI (t1ce, segment)
Target Prediction
Brain Tumor
Segmentation
Instances 369
Image
Dimensions
240 × 240 × 155
Number of
Classes
2
Shape of Train
Data S
p
lit
(293, 240, 240, 155)
Shape of
Validation Data
Split
(76, 240, 240, 155)
Table 1 gives an overview of the FigShare dataset,
while Table 2 details the BraTS2020 dataset used in
this research. By combining these datasets, we ensure
that the PQDCNN model is trained on diverse, high-
quality medical imaging data, achieving the best
accuracy and reliability in automatically detecting
brain tumors.
3.2 Preprocessing
In this paper, we introduce the preprocessing of brain
magnetic resonance images from our PQDCNN. With
the conversion of detailed MRI images to PQDCNN
and passing validation of pre-trained models, we will
get a very accurate training result. Here’s what we
did, step by step:
Image Segmentation: For Image segmentation
we implemented a clustering algorithm called Fuzzy
Local Information c-Means (FLICM). This approach
successfully maintains local spatial context,
diminishes noise, and promotes better feature
extraction which ultimately contributes to the
improved differentiation of tumour from non-tumour
regions.
Noise Reduction: To reduce noise while
preserving the important tumor structures, we
performed median filtering. This initial step of
processing an image not only improves the quality of
the images but also allows us to extract more relevant
features and increase the judiciousness of our
classification efforts with deep learning up to this
point.
Data Augmentation: We applied several data
augmentations to our model to improve
generalization and decrease overfitting. These
included rotating 15-degree rotation, applied shifts,
shear, zooming in and zooming out, flip the images.
With this, we created realistic variations for the
head’s orientation, shapes and sizes of the tumors,
which allowed the model to learn from a wider variety
of MRI scans.
Normalization: All MRI scans were normalized
to the same intensity range [0,1]. This eliminate
difference in intensity which may occur while
different MRI machines are being used or the
machine is under different settings. This also
normalizes the intensity, helping to stabilize the
training process while reducing internal covariate
shifts in deep networks.
Resize: To have a consistency among our dataset
and to achieve the best computational efficiency in
high- performance computing (HPC) setups, we
applied resize to all MRI scans. This should keep vital
tumor-specific information invariant while still
maintaining everything needed for running the
PQDCNN model (the internal structure of the model
does not have to change) as the large amount of rival
information is destroyed.
3.3 Pre-Trained Model Architectures
In this paper, we introduce an innovative deep
learning architecture designed specifically for
identifying brain tumors. This architecture merges
Parallel Convolutional Neural Net- works (PCNN)
with Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural
Networks (QDCNN). Our approach, known as the
Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural
Network (PQDCNN), emphasizes superior feature
extraction, precise tumor localization, and enhanced
High-Performance Computing-Based Brain Tumor Detection Using Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
839
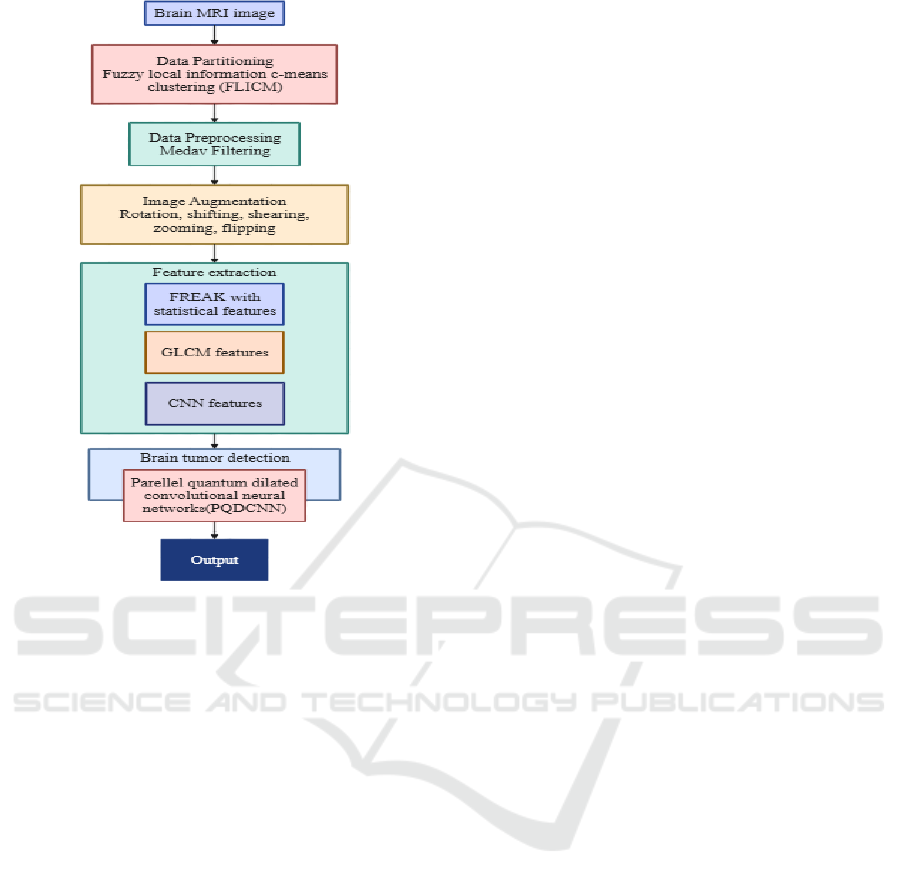
Figure 3: Model Architecture.
classification accuracy. To improve segmentation
efficiency, we use Fuzzy Local Information C- Means
(FLICM) within the model. Besides, we use a
combination of fast retina key point (FREAK)
descriptors, Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix
(GLCM) features, and deep CNN-based
representations for hybrid feature extraction. By
employing a High-Performance Computing (HPC)
strategy, the PQDCNN architecture optimizes the
analysis of brain MRI scans, resulting in highly
efficient and accurate tumor classification.
•
Parallel Convolutional Neural Network (PCNN):
This model employs parallel streams of convolutional
neural network (CNN) to learn hierarchical features
from brain MRI scans. PCNN enhances feature
diversity and classification robustness by parallel
processing of input data by multiple convolutional
streams. The parallel feature extraction function can
be expressed as:
𝑃𝐶𝑁𝑁
𝑥
=
∑
𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑣
𝑥
(1)
Where Conv
i
(x) represents the convolution
operation in the i-th parallel branch.
•
Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural
Network (QDCNN): QDCNN applies quantum-
inspired dilated convolutions to dilate the receptive
field without sacrificing spatial resolution. The
method effectively captures multiscale relations in
brain MRI images, and it results in improved tumor
segmentation and classification. The dilation function
is defined as:
𝑦[𝑖] =
∑
𝑥[𝑖 + 𝑟. 𝑘]
.𝑤[𝑘] (2)
Where x[i] is the input, w[k] is the convolutional
filter, K represents the kernel size, and r denotes the
dilation rate.
•
Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural
Net- work (PQDCNN): The PCNN and QDCNN
together form the PQDCNN model, which employs
the power of parallel convolutional feature extraction
and multi-scale dilated convolutions to achieve
highly accurate detection of brain tumors. The
PQDCNN model is defined as:
PQDCNN(x) = PCNN(x)+QDCNN(x) (3)
where the two components operate in harmony to
enhance classification accuracy without
compromising computational speed.
The PQDCNN model enhances brain tumor
detection by cleverly combining parallel
convolutional layers with quantum dilated
convolutions. This powerful integration allows it to
effectively capture both the local and global features
of tumors. As a result, it greatly improves tumor
localization, feature extraction, and classification
accuracy, making PQDCNN a solid choice for
automatic brain tumor detection.
3.4 Fine-Tuning Pre-Trained Models
for Brain Tumor Detection
To effectively detect tumors, we need to fine-tune our
pre- trained models so they can better recognize
patterns in brain MRI images. In this section, we’ll
explore how we fine-tuned the Parallel Quantum
Dilated Convolutional Neural Network (PQDCNN)
to achieve optimal classification performance.
Loading Pre-trained Weights: The PQDCNN
architec- ture combines Parallel Convolutional
Neural Networks (PCNN) with Quantum Dilated
Convolutional Neural Networks (QDCNN). The
PCNN block is responsible for learning hierarchical
multi-scale features, while the QDCNN boosts
feature representation using quantum- inspired
dilated convolutions. We pre-train these modules on
extensive medical imaging datasets to capture univer-
sal spatial and structural patterns associated with
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
840

brain tumors. After pre-training, we fine-tune the
weights on specific datasets like BraTS2020 and
Figshare to enhance classification performance
representations. This process helps the PQDCNN
pick up on MRI-specific textural and spatial patterns
while keeping valuable pre-trained knowledge from
extensive datasets.
Algorithm: Steps Involved in the Proposed Approach
forBrain Tumor Detection
1. Load the brain MRI dataset (BraTS2020 and
Figshare).
2. Apply data partitioning using Fuzzy Local
Information C-Means Clustering (FLICM).
3. Perform data preprocessing using Median
Filtering to remove noise.
4. Apply image augmentation techniques (Rotation,
shifting, shearing, zooming, flipping) to enhance
model generalization.
5. Extract features using:
FREAK with statistical features.
GLCM features.
CNN-based features.
6. Select the proposed deep learning model:
PCNN if model 1 is chosen,
Model =QDCNN if model 2 is chosen,
PQDCNN if model 3 is chosen.
7. Split the dataset into training, validation, and
testing sets.
8. Train the selected model on the training set.
Tune hyperparameters using the validation set to
improve classification performance.
9. Evaluate the trained model on the test set using
performance metrics such as accuracy, precision,
recall, and f1-score.
Freezing Layers: To maintain the valuable feature
rep- resentations we’ve already trained and to prevent
overfit- ting, we start by freezing the entire set of
convolutional layers during the early training phase.
We kick things off by initializing the new fully
connected layers with a higher learning rate,
allowing the model to grasp the specific patterns
present in brain MRI scans. Once we see some
progress, we gradually tune the earlier layers at a
slower rate.
Progressive Unfreezing: After training the output
layer, we gradually unfreeze the deeper layers,
allowing the model to improve its low-level and
mid-level feature representations. This process helps
the PQDCNN pick up on MRI-specific textural and
spatial patterns while keeping valuable pre-trained
knowledge from extensive datasets.
The PQDCNN uses both parallel and
quantum dilated convolutions to effectively
capture the local and global spa- tial
relationships in brain MRI images. This leads to
better accuracy in segmentation and
classification. The fine-tuning strategy we’ve
introduced helps the model generalize well with
fewer chances of overfitting while also ensuring
it runs efficiently on high-performance
computing systems.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Let’s dive into the outcomes of using the Parallel
Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
(PQDCNN) for brain tumor classification. This
model employs FLICM for data splitting and
incorporates various feature extraction techniques like
FREAK descriptors, GLCM features, CNN-based
embed- dings, and of course, PQDCNN itself for an
accurate diagnosis of brain tumors. We evaluate how
well PQDCNN performs in classifying these tumors
and explore whether applying Progressive Unfreezing
in transfer learning can enhance its effectiveness.
4.1 Performance Comparisons
Figshare Dataset: PQDCNN outperforms both PCNN
and QDCNN across all metrics, hitting an impressive
accuracy of 93.53%. It also achieves precision at
93.48%, recall at 93.53%, and an F1-score of 93.46%,
displaying its effective- ness in tumor classification.
Besides, its ROC AUC score of 0.9924 emphasizes
its superior ability to distinguish between different
outcomes. While QDCNN does surpass PCNN in
precision (88.38%) and F1-score (88.34%), it still
lags when
compared to PQDCNN. These results
underline the major advantages of quantum
dilation and parallel computation in medical
imaging. Table 3 gives the dataset comparison of
Figshare while table 4 gives the comparison of
BraTS2020 dataset.
Table 3: Comparing PCNN, QDCNN, and PQDCNN
models for Figshare dataset.
Metric PCN
N
QDCNN PQDCNN
Accurac
y
84.39% 88.64% 93.53%
Precision 85.44% 88.38% 93.48%
Recall 84.39% 88.664% 93.53%
F1 Score 84.75% 88.34% 93.46%
ROC AUC 0.9551 0.9753 0.9924
High-Performance Computing-Based Brain Tumor Detection Using Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
841

Figure 4: PCNN, QDCNN and PQDCNN confusion
matrices.
Figure 5: ROC Curve.
BraTS2020 Dataset: When we look at how the three
models perform, PCNN, QDCNN, and PQDCNN, it
turns out that all have an accuracy of 75%. However,
PQDCNN stands out with a better recall rate (75%)
and an F1-score of 70.59%, suggesting it strikes a
better balance between precision and recall. While
PCNN and QDCNN are a tad more precise (71.43%),
their lower recall (62.5%) brings down their F1- score
(66.67%). This tells us that PQDCNN does a better
job of identifying positive cases, making it the
preferred model when recall is a key factor.
Table 4: Comparing PCNN, QDCNN, and PQDCNN
models for BraTS2020 Dataset.
Metric PCN
N
QDCNN PQDCNN
Accurac
y
84.39% 88.64% 93.53%
Precision 85.44% 88.38% 93.48%
Recall 84.39% 88.664% 93.53%
F1 Score 84.75% 88.34% 93.46%
ROC AUC 0.9551 0.9753 0.9924
Figure 6: PCNN, QDCNN and PQDCNN Confusion
Matrices.
Figure 7: ROC curve.
5 CONCLUSIONS
When comparing the performance of the PCNN,
QCNN, and PQDCNN models on two datasets,
Figshare and BraTS2020, it is clear that PQDCNN
stands out consistently. For the Figshare dataset,
PQDCNN achieves the highest accu- racy at 93.53%
and excels in other metrics as well, including
precision (93.74%), recall (93.53%), F1-score
(93.46%), and ROC AUC (0.9924). Thus, it emerges
as the top performer for this dataset. Similarly, in the
case of the BraTS2020 dataset, all models show
identical accuracy at 75%; however, PQDCNN has a
higher recall rate at 75% and a better F1-score of
70.58%. This points to a more favorable balance
between precision and recall. Overall, these findings
suggest that PQDCNN is the strongest model,
particularly in scenarios where recall and F1-score
play critical roles in classification performance.
REFERENCES
Abdusalomov, A. B., Mukhiddinov, M., & Whangbo, T. K.
(2023). Brain tumor detection based on deep learning
approaches and magnetic resonance imaging. Cancers,
15(16), 4172.
Agarwal, M., Rani, G., Kumar, A., Kumar, P., Manikandan,
R., & Gandomi, A. H. (2024). Deep learning for
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
842

enhanced brain tumor detection and classification.
Results in Engineering, 22, 102117.
Alhussainan, N. F., Ben Youssef, B., & Ben Ismail, M. M.
(2024). A deep learning approach for brain tumor
firmness detection based on five different YOLO
Versions: YOLOv3–YOLOv7. Computation, 12(3), 44.
Anantharajan, S., Gunasekaran, S., Subramanian, T., &
Venkatesh, R. (2024). MRI brain tumor detection using
deep learning and machine learning approaches.
Measurement: Sensors, 31, 101026.
Asad, R., Rehman, S. U., Imran, A., Li, J., Almuhaimeed,
A., & Alzahrani, A. (2023). Computer-aided early
melanoma brain-tumor detection using deep-learning
approach. Biomedicines, 11(1), 184.
Gu¨ler, M., & Namlı, E. (2024). Brain tumor detection with
deep learning methods’ classifier optimization using
medical images. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 642.
Khan, M. A. Z., Innan, N., Galib, A. A. O., & Bennai, M.
(2024). Brain tumor diagnosis using quantum
convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2401.15804.
Mahmud, M. I., Mamun, M., & Abdelgawad, A. (2023). A
deep analysis of brain tumor detection from mr images
using deep learning networks. Algorithms, 16(4), 176.
Mathivanan, S. K., Sonaimuthu, S., Murugesan, S.,
Rajadurai, H., Shivahare, B. D., & Shah, M. A. (2024).
Employing deep learning and transfer learning for
accurate brain tumor detection. Scientific Reports,
14(1), 7232.
Rahman, T., & Islam, M. S. (2023). MRI brain tumor
detection and classification using parallel deep
convolutional neural networks. Measurement: Sensors,
26, 100694.
Saboor, A., Li, J. P., Ul Haq, A., Shehzad, U., Khan, S.,
Aotaibi, R. M., & Alajlan, S. A. (2024). DDFC: deep
learning approach for deep feature extraction and
classification of brain tumors using magnetic resonance
imaging in E-healthcare system. Scientific reports,
14(1), 6425.
Saeedi, S., Rezayi, S., Keshavarz, H., & R. Niakan Kalhori,
S. (2023). MRI-based brain tumor detection using
convolutional deep learning methods and chosen
machine learning techniques. BMC Medical In-
formatics and Decision Making, 23(1), 16.
Singh, K., Kaur, A., & Kaur, P. (2023). Computer Aided
Detection of Brain Tumors using Convolutional Neural
Network based Analysis of MRI Data.
Srinivasan, S., Francis, D., Mathivanan, S. K., Rajadurai,
H., Shivahare, D., & Shah, M. A. (2024). A hybrid deep
CNN model for brain tumor image multi-classification.
BMC Medical Imaging, 24(1), 21.
Umarani, C. M., Gollagi, S. G., Allagi, S., Sambrekar, K.,
& Ankali, S. (2024). Advancements in deep learning
techniques for brain tumor segmentation: a survey.
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 101576.
High-Performance Computing-Based Brain Tumor Detection Using Parallel Quantum Dilated Convolutional Neural Network
843
