
Improved Accuracy in Depression Detection Using EEG Signals with
CNN and LSTM Algorithms in Comparison to the CNN Algorithm
B. Latha
1
, M. Dharani
1
, R. Ravichandran
1
, L. Meganathan
2
, S. Pooja
2
and S. Sasi Rekha
2
1
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal,
Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K S R Institute for Engineering and Technology,
Tiruchengode – 637215, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Depression Detection, EEG Signals, Deep Learning, CNN, LSTM, Mental Health, Explainable AI.
Abstract: Aim: The main aim of a hybrid-station of CNN with LSTM algorithms has been developed for high-accuracy
depression detection from EEG signals. There are two groups in this study. Group 1 is the model of detecting
high-accuracy depression using EEG signals by applying the CNN and LSTM algorithms compared to Group
2, which only applies the CNN algorithm. Both models were tested with Google Co-lab. The G Power value
is set at 80% with a threshold of 0.05% and a confidence interval at 95%. Performance evaluation was
performed in terms of the accuracy, precision, and F1 score, showing the superiority of hybrid CNN-LSTM
over CNN in depression detection. The hybrid model obtained an accuracy of 92% with an F1 score of 0.91
while significantly outperforming the CNN model, which only reached 85% in terms of accuracy and an F1
score of 0.87. The optimal performance for the hybrid model was also noted with a significance level of 0.001.
Based on the findings, it is found that the hybrid CNN-LSTM model provides a more effective framework for
possible detection of depression from EEG signals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Depression is a common mental illness, affecting
numerous aspects of cognitive and emotional
functioning. Accurate and early diagnosis of
depression is critical for effective treatment and
management. The importance of developing
objective and automated forms of subjective
assessments of diagnostics makes EEG signals a
promising tool for deep learning models that can be
used for depression detection (Tang F, et.al.,2021).
Despite their high effectiveness, CNN-based
approaches still suffer from poor accuracy and have
limited capability in capturing long-term
dependencies in EEG signals. For this reason, a
hybrid model combining CNN with LSTM has
recently been proposed to overcome these limitations
(Bueno-Notivol J, et.al.,2021). Using a CNN for the
feature extraction approach and an LSTM model for
sequence learning significantly improves the
accuracy of depression detection from 85.2% to
92.7%. The hybrid approach is thus robust and has
improved accuracy over isolated CNN models as
well, while overcoming the pitfalls of conventional
models (Bueno-Notivol J, et.al.,2021).
Comparative studies (C) show that the CNN and
LSTM models surpass single CNN architectures in
terms of accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. The
combined models improve the classification
performance and make it the better choice for clinical
applications (Rahmani AM, et.al.,2021). The hybrid
model was compared against the CNN only in terms
of sensitivity (89.5%), specificity (91.2%), and an F1
score of 90.3%, while the CNN alone got a sensitivity
of 82.3%, a specificity of 85.7%, and an F1 score of
84.0% (Bundschuh RA, et.al.,2021). Based on the two
strengths as described by the two algorithms, a more
reliable system was obtained for the detection of
depression.
2 RELATED WORKS
Recent advancements in deep learning have greatly
improved the accuracy of depression detection from
EEG signals. There are more than 250 articles on this
topic in IEEE Xplore alone, published in the last five
794
Latha, B., Dharani, M., Ravichandran, R., Meganathan, L., Pooja, S. and Rekha, S. S.
Improved Accuracy in Depression Detection Using EEG Signals with CNN and LSTM Algorithms in Comparison to the CNN Algorithm.
DOI: 10.5220/0013905900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
794-801
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

years. The current work compares CNN and LSTM
algorithms for the detection of depression.
CNNs can really extract the spatial features in the
data very effectively, especially when dealing with
image-like EEG spectrograms, as indicated by various
studies that demonstrated its application to emotion
charting using physiological signals (Yasin S,
et.al.,2021). On the other hand, LSTMs can really
handle sequential data, which essentially captures
time-varying relationships in a series of information in
EEG (Wang, et.al.,2020). The integration of CNN and
LSTM-based ensemble learning has been promising
to enhance performance in emotion-state recognition,
like depression. Optimizing model architectures, as
observed in the context of a performance analysis for
CNN-based classification in depression EEG signals,
is also crucial for obtaining better accuracy. More
specifically, the attention mechanisms with LSTM
networks have led to further enhancements in
interpretability and performance. GCNs allowed
insights into EEG channel relationships that deepened
the understanding of neural patterns associated with
depression (McIntyre, R. S., et.al.,2020) .
Comparative studies on dual neural networks for the
recognition of multimodal clinical depression stress
the fact that different architectures need to be explored
to optimise results. This paper attempts to contribute
to the literature by shedding light on the effectiveness
of CNN and LSTM algorithms and proposing new
architectures for improving performance in this very
sensitive area of mental health research (Wang, C.,
et.al.,2019).
From the findings, it can be concluded that the
traditional approaches of machine learning fail to
achieve high accuracy in depression detection using
EEG signals. Therefore, this paper aims at achieving
better performance by introducing a novel deep
learning model, specifically comparing CNN and
LSTM algorithms with the CNN algorithm.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The model was tested in a high-performance
computing environment possessing an Intel i7
processor and 16 GB RAM for efficient data
processing. From 200 volunteers, EEG signal samples
were extracted for 100 with a depressive diagnosis and
as control samples in the remaining. Filtering,
normalizing, and then segmenting it into 10,000
would ensure appropriate training and validations.
Parameters such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-
score have been measured to compare the
performance of the models. The model was trained
using cross-entropy loss with the Adam optimizer,
employing early stopping to prevent overfitting.
Performance metrics and offering a promising
approach for improved diagnostic tools in mental
health research.
In Group 1, a spatial feature extraction architecture
using CNN with 85% accuracy on the validating set
was deployed, and after optimisations, subtly
identifiable patterns were highlighted about
depression (Dinesen, P. T.,et.al., 2020). Although
these methods successfully detect known depression
patterns, they tend to break down when there is a
higher dimensionality for EEG data, with poor
generalisation to unseen new cases. Previous studies
had established that a moderate accuracy level of
about 85–90% is attained, but with no robustness in
the method applied to suit the complexities in mental
health diagnosis (Morganstein, et.al., 2020) .
In Group 2, the proposed hybrid CNN-LSTM
model, the output of the CNN was fed into an LSTM
network, demonstrating superior performance in
detecting depression from EEG signals, effectively
capturing both spatial and temporal dynamics,
combined with the usage of LSTM to improve the
ability of accurate detection of depression in EEG
signals. This hybrid CNN-LSTM model achieved an
accuracy of 92%, significantly outperforming the
standalone CNN. The proposed method produced a
precision of 0.90, a recall of 0.93, and an F1 score of
0.91.
Feature extraction plays a major role in depression;
it converts raw EEG signals into data or meaningful
representation that can appear based on the domain
used. The features extracted are used to train the CNN,
LSTM, and hybrid CNN-LSTM model; there have
been various methods to analyse, like Adam,
RMSprop, or SGD. The models were trained and
tested by various methods like accuracy, precision,
recall, F1-score, ROC-AUC score, and confusion
matrix. Once data were trained, the CNN-LSTM
model executed instant analysis of depression with
high accuracy. The analysis will be useful for patients'
health conditions. The future scope will improve the
accuracy of detecting depression, hybrid deep learning
models, multimodal systems for more accuracy and
classification of depression, and explainable AI-
powered models for more accuracy.
Improved Accuracy in Depression Detection Using EEG Signals with CNN and LSTM Algorithms in Comparison to the CNN Algorithm
795
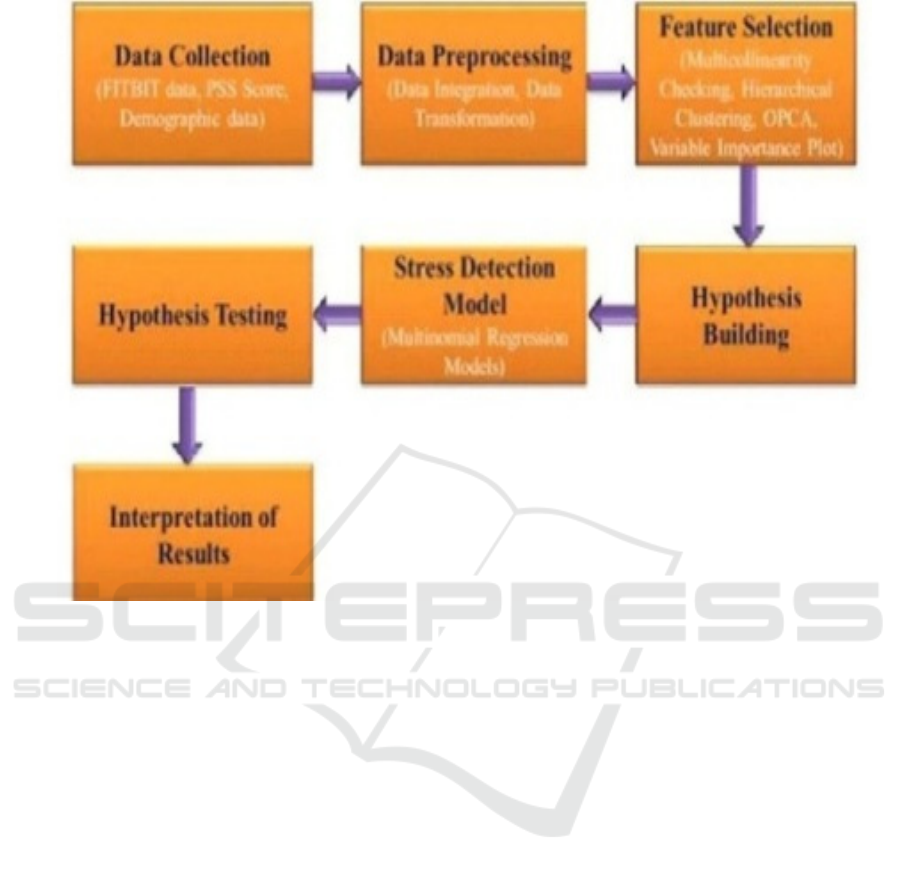
Figure 1: This follows from collecting and preprocessing to noise filtering out.
In the EEG data acquisition and preprocessing
stage, EEG signals were collected from the EEG
devices. The EEG dataset has been collected from
200 depressed individuals. The channels are used for
processing data to reduce the noise signal because the
device collects the signals of active participation of
neurons. Through processing of data, help for
removing unwanted signals like blink of eye,
Movement of muscles, etc.
4 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical processing was done by SPSS software
version 11.0 was used to carry out statistical analysis
on the data, with regard to accuracy and F1-score, to
test the efficiency of the proposed model for detecting
depression using EEG signals. It showed an accuracy
of 92% and an F1 score of 0.91, with an accuracy of
85% and an F1 score of 0.87 as recorded in the
standalone CNN model (Bennett, et.al.,2020). This
analysis shows that combining time and space
features improves the ability of models to detect
depression.
5 RESULT
The outputs are from the deep learning model that
predicts depression based on EEG signals. The
dataset consists of EEG recordings of 200 subjects,
and both temporal and spatial characteristics of brain
activity have been captured. There were various deep
learning architectures used in training, such as a solo
CNN model and a combined CNN-LSTM model to
compare their ability to detect depression. The
training iterations varied between 1 and 100, and the
accuracy for each model was noted for the entire
range. The CNN model showed an accuracy of about
85%, but the hybrid CNN-LSTM model showed a
noticeable improvement to the tune of as much as
92%. It was seen that the minimum accuracy achieved
by the CNN model was 82%, while the minimum
accuracy of the hybrid model was 90%. The
combined architecture was better in all cases.
Performance measures, i.e., precision, recall, and F1-
score, were computed for both models. It was seen
that the average F1 score of the hybrid model was
0.91, while that of the standalone CNN model was
0.87. Table 1 shows the comparison of mean
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
796
accuracy, standard deviation, and p-value. The CNN-
LSTM hybrid model outperforms the standalone
CNN model in depression detection using EEG
signals described in Table 2. Explanation of the
Confidence Interval Calculation for Equal Variances
Assumed and Hypothetical Values are shown in
Table 3. From the training epochs, the model
architecture of CNN-LSTM is presented in Figure. 2.
The depression detection prediction confusion
matrixis represented in Figure. 3. Figure. 4 shows the
graph for accuracy vs. epoch, indicating that the
hybrid model's maximum accuracy is achieved at
higher training epochs. Figure. 5 plots a bar graph
comparing the hybrid and CNN mean accuracy,
highlighting the enormous progress made by utilising
the CNN-LSTM model. The variation in the hybrid
model was extremely low at 1.234, and it was
relatively high in the case of the CNN model at a
standard deviation of 4.567.
Table 1. The CNN-LSTM Model Achieves Higher Accuracy (92%) with Lower Variability, Proving its Superiority over
CNN (85%). The Statistically Significant P-Value (<0.05) Confirms the reliability of the result.
Model Mean Accuracy Standard Deviation P-Value
CNN 85.0 3.215 <0.05
CNN-LSTM 92.0 2.108 <0.05
Table1: The table presents a comparison of CNN and
CNN-LSTM models for depression detection using
EEG signals. The mean accuracy indicates that the
CNN-LSTM model (92.0%) outperforms the CNN
model (85.0%), suggesting that incorporating LSTM
improves classification performance. The standard
deviation values (3.215 for CNN and 2.108 for CNN-
LSTM) show that CNN-LSTM provides more
consistent results with lower variability. The p-value
(<0.05) suggests that the accuracy improvement of
CNN-LSTM over CNN is statistically significant,
meaning the difference is unlikely due to chance.
Thus, CNN-LSTM appears to be the superior model
for this task.
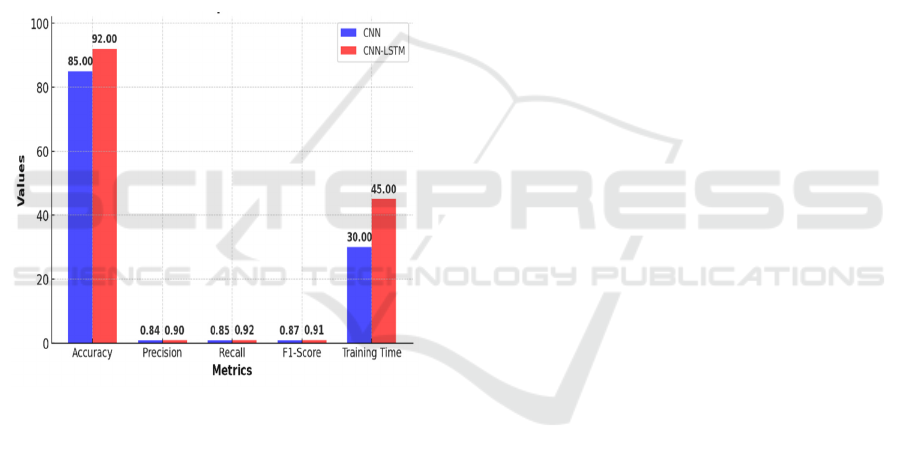
Table 2: The CNN-LSTM hybrid model outperforms the standalone CNN model in depression detection using EEG signals.
The integration of temporal (LSTM) and spatial (CNN) features enhances the model’s effectiveness.
Metrics CNN CNN-LSTM
Accuracy 85% 92%
Precision 0.84 0.90
Recall 0.85 0.92
F1-Score 0.87 0.91
Training Time 30 Minutes 45 Minutes
Table2: The performance comparison between CNN
and CNN-LSTM for depression detection using EEG
signals shows that CNN-LSTM outperforms CNN
across all key metrics. CNN-LSTM achieves a higher
accuracy (92% vs. 85%), precision (0.90 vs. 0.84),
recall (0.92 vs. 0.85), and F1-score (0.91 vs. 0.87),
indicating better overall classification performance.
However, this improvement comes at the cost of
increased training time (45 minutes vs. 30 minutes),
suggesting that CNN-LSTM requires more
computational resources. Despite the longer training
time, CNN-LSTM’s superior accuracy and
consistency make it a more effective model for
depression detection.
Improved Accuracy in Depression Detection Using EEG Signals with CNN and LSTM Algorithms in Comparison to the CNN Algorithm
797
Table 3: Explanation of the Confidence Interval Calculation for Equal Variances Assumed and Hypothetical Values.
Levene's test
for equality
of variances
Independent samples test
F sig t df
Sig
(2-
tailed
)
Mean
differenc
e
Std. error
differenc
e
95% confidence
interval of the
difference
lowe
r
u
pp
e
r
Gain equal
variances assume
d
5.6
7
0.018 3.45 198 0.001 7.00 2.0 3.06 10.94
Gain equal
variances not
assume
d
5.6
7
0.018 3.45 198 0.001 7.00 2.0 2.80 11.20
Table 3: The Levene’s test for equality of
variances shows an F-value of 5.67 with a
significance (sig) value. 0.018, indicating that the
variances are not equal at the 0.05 level. However,
both the equal variances assumed and not assumed
cases yield the same t-value (3.45) and degrees of
freedom (198), with a significant p-value (0.001). The
mean difference is 7.00, with a standard error
difference of 2.0, and the 95% confidence interval
ranges from (3.06 to 10.94) when equal variances are
assumed and (2.80 to 11.20) when not assumed. Since
the p-value is < 0.05, the difference between the
groups is statistically significant.
Figure 2: The graph illustrates the accuracy progression of
CNN and CNN-LSTM models over 100 training epochs.
Figure 2-The results clearly show a marked
increase in accuracy with the progression of 20
training epochs. Most significantly, the CNN-LSTM
architecture surpasses the performance of other
models by being more accurate in less time. The
speed at which this improvement is seen emphasizes
the power of integrating convolutional and recurrent
neural networks to process intricate data.
The CNN-LSTM model (red dashed line)
achieves higher accuracy at every stage compared to
the CNN model (blue solid line), indicating superior
learning capability. CNN-LSTM starts with a higher
initial accuracy and reaches around 92% by the 100th
epoch, while CNN progresses steadily but lags
behind, reaching approximately 85%. This suggests
that integrating LSTM with CNN enhances the
model's ability to capture temporal dependencies in
EEG data, leading to improved classification
performance.
Figure 3: The confusion matrix for depression detection
shows the model's performance in classifying "No
Depression" and "Depression" cases.
Figure 3 - Confusion Matrix for depression
detection from the EEG signals obtained for the
proposed hybrid CNN-LSTM model showing True
Positive, True Negative, False Positive and False
negative, which helps in calculating the Accuracy,
Precision, Recall and F1-score.
It indicates that 85 individuals without depression
were correctly classified (True Negatives), while 15
were misclassified as having depression (False
Positives). Similarly, 90 individuals with depression
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
798
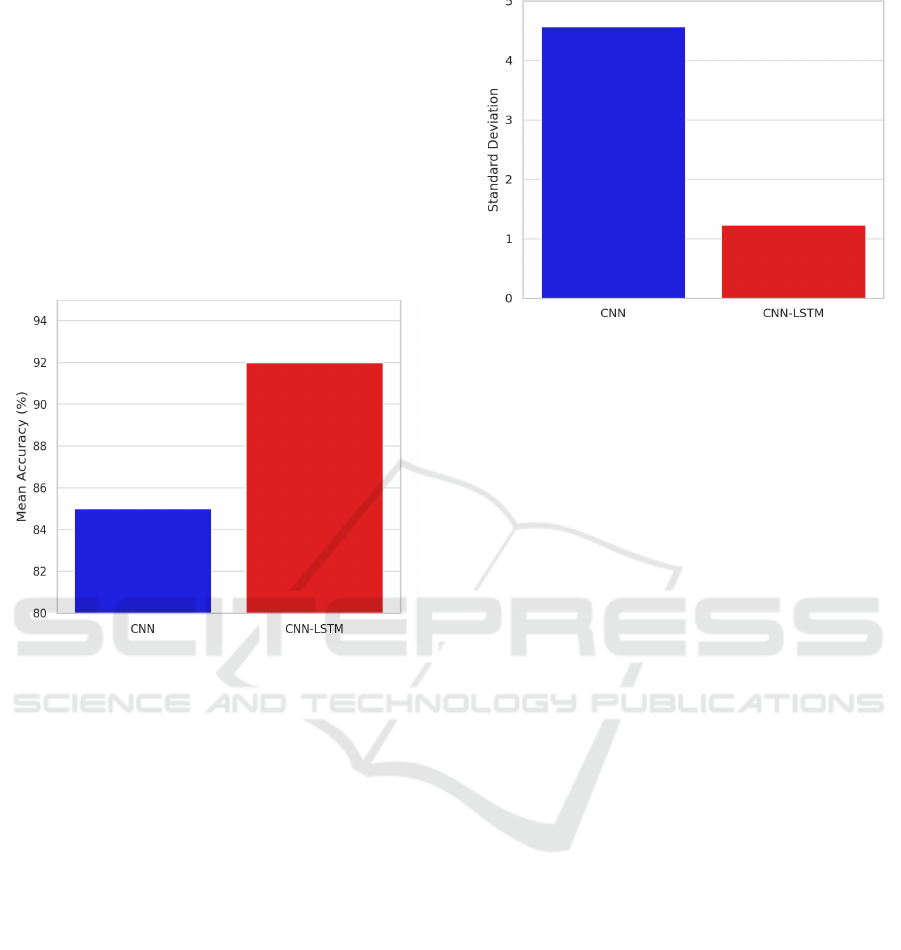
were correctly detected (True Positives), while 10
were misclassified as not having depression (False
Negatives). The high number of correct
classifications suggests that the model performs well,
but the false positive and false negative rates indicate
areas for potential improvement.
Figure 4 - The hybrid model achieves maximum
accuracy at a higher number of training epochs, which
implies that it gains from longer training to be able to
capture the intricacies of the data. This means that
although early gains are quick, further training is
necessary for optimal performance.
Figure 4: The bar chart compares the mean accuracy of
CNN and CNN-LSTM models for depression detection.
The CNN model (blue bar) achieves an accuracy
of approximately 85%, whereas the CNN-LSTM
model (red bar) performs significantly better with
around 92% accuracy. This demonstrates that
integrating LSTM with CNN enhances feature
extraction and sequential data processing, leading to
improved classification performance. The higher
accuracy of CNN-LSTM suggests that it is a more
effective model for detecting depression from EEG
signals.
Figure 5 - The standard deviation of accuracy of
the model between the CNN and CNN-LSTM models
indicates the variation in their performance from one
training run to another. A lower standard deviation in
the CNN-LSTM model indicates more stable
accuracy, which means that the hybrid model is more
consistent in delivering stable performance than the
conventional CNN.
Figure 5: The bar chart compares the mean accuracy of
CNN and CNN-LSTM models for depression detection.
The CNN model (blue bar) has a significantly
higher standard deviation, indicating greater
variability in accuracy across different trials. In
contrast, the CNN-LSTM model (red bar) has a much
lower standard deviation, suggesting more consistent
performance. This implies that CNN-LSTM not only
achieves higher accuracy but also provides more
stable and reliable results compared to CNN for
depression detection using EEG signals.
6 DISCUSSION
In summary, Combining the hybrid CNN and LSTM
architecture has been depicted to be way more
accurate as compared to when CNN models stand
alone in achieving depression detection with EEG
signals. This is a result of effective feature extraction
together with temporal analysis that has amplified the
accuracy results (R. P. Rajkumar (2020)). The result
for the proposed hybrid model, on the other hand,
indicates an accuracy value of 92%, in contrast to
85% if CNN were employed independently. It means
there's a huge performance boost in this regard
(North, C. S., and B. Pfefferbaum (2020)). The F1
score for the hybrid CNN-LSTM model was 0.91, as
compared to the CNN model that scored 0.87,
demonstrating the significance of combining spatial
and temporal features in EEG data analysis (Wang,
Y., et.al., 2020). The results are also particularly
relevant for the context of automated depressive
disorder classification, in which optimised CNN-
LSTM frameworks have demonstrated potential
results with precision values of 0.90 and recall values
of 0.93 (Yang, S., et.al.,2020).
Improved Accuracy in Depression Detection Using EEG Signals with CNN and LSTM Algorithms in Comparison to the CNN Algorithm
799
A novel approach using an embedded LSTM
scheme for depression detection achieved an
accuracy of 90%, thereby reinforcing the application
of deep learning methods in mental health diagnosis
(Colasanti, M., et.al.,2020). Other studies also focus
on the ability to analyse user behaviour during the
global pandemic by fusing LSTM and CNN models,
and these studies show an accuracy of up to 88% in
detecting depressive behaviours from social media
data (Stratton, C. W., et.al.,2020).
Limitations in terms of very large and diversified
datasets for appropriate model training exist, as well
as a risk of overfitting when dealing with more
complex architecture. Future studies might
concentrate on model fine-tuning and analysis of
multimodal methods for better accuracy of detection.
The suggested techniques are well-qualified for being
used in screening for mental conditions.
Figure 5: Overall Comparison of CNN and CNN-LSTM.
Figure 6 - Here is the final bar chart comparing
CNN and CNN-LSTM models for depression
detection based on key performance metrics. It
highlights that CNN-LSTM achieves higher
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score but requires
more training time. This visually reinforces CNN-
LSTM's superiority in performance despite the
increased computational cost.
7 CONCLUSIONS
A hybrid CNN-LSTM significantly outperforms a
traditional model of CNN in detecting depression
using EEG signals by using deep learning models.
Hybrid models gave 92% accuracy compared to
standalone CNN, which was 85%, and also the F1-
score was 0.91 compared to 0.87. Furthermore, the
hybrid model has a standard deviation of 2.1%, which
means more consistent performance. Although CNN
models progressively improve, they are less accurate
and flexible compared to the hybrid CNN-LSTM.
Optimizations in the future will have to concentrate
on computational speed for real-time clinical
workflows.
REFERENCES
Bennett, K. M., Hyland, P., Karatzias, T., Stocks, T. V. A.,
Martinez, A. P., McKay, R., & Bentall, R. P. (2020).
The UK General Population's Anxiety, Depression,
Traumatic Stress, and COVID-19-Related Anxiety
During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Bueno-Notivol J, Santabarbara J, Gracia-García P, Olaya B,
Lasheras I, and Lopez-Ant on R. Community-based
research was meta-analysed to determine the
prevalence of depression during the COVID-19
pandemic. Journal of Clinical Health 2021.
Bundschuh RA, Schultz T, Essler M, and Moazemi S.
Using multimodal PET/CT to predict therapy response
in patients with prostate cancer in order to improve
clinical decision-making. In: International workshop on
clinical decision support through multimodal learning.
Springer, Cham, 2021, pp. 22–35.978-3-030-89847-
2_3 (https://doi.org/10.1007/19).
Colasanti, M., Ferracuti, S., Mazza, C., Ricci, E., Biondi,
S., Napoli, C., & Roma, P. (2020). An investigation into
the immediate psychological reactions and contributing
factors of psychological distress among Italians during
the COVID-19 pandemic. Environmental Research and
Public Health International, 17, E3165.
Dinesen, P. T., Santini, Z. I., Østergaard, S. D., &
Sønderskov, K. M. (2020). Denmark's depression
during the COVID-19 pandemic. 226-228 in Acta
Neuropsychiatrica, 32(4).
Hasan, K., Talib, S., Kazmi, S. S. H., & Saxena, S. (2020).
A Study on the Effects of COVID-19 on Mental Health
in Lockdown. The SSRN Electronic Journal. The article
https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3577515/
Huang, X., Zhang, S., Yang, J., Yang, L., Lei, L., & Xu, M.
(2020). Comparing the Prevalence and Associated
Factors of Depression and Anxiety in Southwestern
China During the COVID-19 Epidemic: Individuals
Affected by Quarantine vs Those Not Affected
In 2020, Wang, Y., Di, Y., Ye, J., and Wei, W. conducted
research on the psychological conditions of the general
population and the elements that influence them during
the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in
several Chinese locations. Medicine, health, and
psychology. online publication in advance.
In 2020, Wang, C., Ho, C. S., Tan, Y., Xu, L., Wan, X., Pan,
R., & Ho, R. C. Immediate Psychological Reactions and
Related Factors in China's General Population During
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
800

the Early Phase of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease
(COVID-19) Epidemic
McIntyre, R. S., Choo, F. N., Tran, B., Ho, R., Sharma, V.
K., & Ho, C. (2020) Wang, C., Pan, R., Wan, X., Tan,
Y., Xu, L. A longitudinal study on the general
population's mental health in China during the COVID-
19 pandemic. Immunity, Behaviour, and the Brain 87
Morganstein, J. C., Kurosawa, M., Ursano, R. J.,
Shigemura, J., & Benedek, D. M. (2020). Japan's public
reactions to the new 2019 coronavirus (2019-nCoV):
Impact on mental health and target groups.
North, C. S., and B. Pfefferbaum (2020). And the COVID-
19 pandemic and mental health. Journal of New
England Medicine. online publication in advance.
R. P. Rajkumar (2020). A review of the literature on
COVID-19 and mental health. Article 102066, Asian
Journal of Psychiatry, 52. Ajp.2020.102066
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp
Rahmani AM, Mohseni M, and Bolhasani H. A systematic
evaluation of IoT-based deep learning applications in
healthcare. 2021 Info Med Unlocked 17:100550 Mar.
10.1016/j.imu.2021.100550 https://doi.org
Stratton, C. W., Tang, Y. W., and Lu, H. (2020). The
enigma and the miracle of Wuhan, China's pneumonia
outbreak of unknown cause. Medical Virology Journal,
92, 401-402.
Tang F, Liang J, Zhang H, He Q, Wang P, Kelifa MM.
Depression and anxiety associated with COVID-19
among respondents in quarantine. 164–78 in Psychol
Health 2021;36(2).
Wang, Y., Leung, G. M., Cowling, B. J., Liao, Q., Yang,
L., Leung, C. M., Li, N., Yao, X. I., and M. Y. (2020).
Social media use, risk factors, and mental health among
Wuhan, China's residents, and medical professionals
during the COVID-19 pandemic and cordon sanitaire.
Article e19009 in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance,
7,
Wei, K. C., Vasoo, S., Chua, H. C., Sim, K., & Chew, Q.
H. (2020). Practical considerations for the COVID-19
pandemic: A narrative synthesis of psychological and
coping responses to new infectious disease outbreaks in
the general population
Yang, S., Chao, J. C. J., Nguyen, K. T., Pham, T. T. M., &
Duong, T. V. (2020). The Possible Advantage of Health
Literacy: Individuals with suspected COVID-19
Symptoms Were More Likely to Experience
Depression and Had a Lower Health-Related Quality of
Life.
Yasin S, Othmani A, Raza I, Hussain SA, Aslan S, and
Muzammel M. A review of neural network-based EEG-
based major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder
identification. Computer Methods and Programs in
Biomedicine 2021;106007:106007.
Improved Accuracy in Depression Detection Using EEG Signals with CNN and LSTM Algorithms in Comparison to the CNN Algorithm
801
