
Fake News Detector in Social Media Using AI
K. E. Eswari, Harshini S, Kaaviyadharshini M and Kavinnagul S
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College Erode,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Fake News, Block chain, and Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Abstract: Natural language processing (NLP), blockchain technology, and reinforcement learning (RL) are all
employed within this new method for detecting fake news. It begins by gathering a large set of news articles
and accompanying data, which is then cleaned and tokenized through the use of natural language processing
(NLP) methods. A key feature set that is extracted, including word counts and readability scores, is used to
train an RL agent. The agent is provided with the skills to distinguish authentic and false news through a
reward- punishment framework. In the post-training process, the RL agent makes decisions based on these
features in determining whether novel articles are valid or fake ones. While blockchain technology's
operation is described, more details must be provided. This approach works to prevent false and misleading
content dissemination in digitalnews.The explosive expansion of online social networks within the last few
years has promoted the spread offake news for political and commercial purposes. The consumers of these
sites are easily influenced by fake news using deceitful language, which impacts offline societygreatly.
Detection offake news quicklyis one of the key objectives in enhancing the accuracy of information on
online social networks. The algorithms, methods, and rules for detection of false news stories, authors, and
entities in web-scale social networks are investigated in this work, in addition to measuring their efficacy.
The sheer magnitude of web-scale data complicates detection, estimation, and correction offtake news,
particularly considering the increasing importance of correct information, particularly social media. In this
paper, we introduce a method of identifying false information andtalkabout howtoapplyit on Facebook, one
of the most used social networking websites.Rather than relying on typical news websites that typically
involve source verification, most smartphone users prefer to read news on social networking sites.
Authenticating news and articles posted on social networking platforms such as Facebook, Twitter,
WhatsApp, and other microblogs is challenging, though. If rumors are used as factual news, it is not good
for society. Emphasis on verifying and sharing authentic, verified news is the need of the time in countries
like India where false news may spread easily. In this study, a machine learning andnatural language
processing-based model and methodology for detecting fake news are introduced. The technique employs a
Support Vector Machine (SVM) tocompilenews reports and evaluate their validity. Compared to other
models, the performance of this proposed model with 93.6% accuracy demonstrates how efficiently it can
identify false news.
1 INTRODUCTION
Un supervised model-based on fake information
detection is an important novel approach to
combating epidemic spreading of misinformation in
today's cyber-age digital world (Augenstein, T et al.,
2020). However, with the rise of social media and
other online platforms, the issue of the spread of
false or misleading information has risen to
prominence since it could be harmful for public
debate, democracy and public safety. Unsupervised
fake news detection methods rely on inherent
pattern and features of textual data so as to be able to
distinguish between generated news and real news
without the support of pre-label training data (P.
Rosso et al., 2017). These models attempt to
automatically detect fake news and even dangerous
content through techniques such as natural language
processing, clustering, and anomaly detection. This
provides a proactive and scalable mechanism to
address the epidemic of misinformation.
788
Eswari, K. E., S., H., M., K. and S., K.
Fake News Detector in Social Media Using AI.
DOI: 10.5220/0013905800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
788-793
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

1.1 Natural Language Processing
(NLP)
A branch of software engineering referred to as
"natural language processing"(NLP)is intended to
provide computers with the capacity to understand
written and verbal languagein a manner that
simulates human capability. NLP combines
computational etymological rule-based human
language presentation with facts, artificial
intelligence, and sophisticated learning models. With
these developments, computers are now able to fully
"comprehend" human language as messages or
auditory data, including the expectations and
perspectives of the writer or speaker. Computer
programmers use natural language processing (NLP)
to reply to verbal requests, translate text from one
language to another, and summarize huge amounts
of information quickly and even continuously.
Natural language processing (NLP) is utilized by
virtual assistants, customer service chatbots, speech-
to-message transcription applications, voice-
controlled GPS navigation and other shopping
conveniences. But NLP also plays a key role in
massive commercial initiatives that enhance
important corporate operations, enhance employee
efficiency, and automate operations.
1.2 Block Chain Technology
Blockchain technology can be employed to safely
store information, making it extremely hard, if not
impossible, for fraud, hacking, or system alteration
to occur. A block chain is simply a computer
network that spreads and replicates a digital record
of transactions across the network. Each new
transaction is replicated into the ledger of each
member, and there are a number of transactions in
every block of thechain. Several
usersmanagethisdistributeddatabasesystem, referred
to as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). A
constantly expanding set of immutable,
cryptographically locked transactional records
shared by all the users of a network is referred to as
a blockchain (T. Cignarella et al., 2020). Authorized
individuals are able to trace any transactional event
back to its historical moment due to the time stamps
and pointers to earlier transactions in every record.
One specific application of the general concept of
networked ledgers is blockchain.
1.3 Fake News
The spread off fake news has appeared as a serious
and alarming issue in the age of digital information
and social media. Deliberately in corrector
misleading information reported in the guise of
genuine news with the aim to deceive or manipulate
popular thinking is refer red to as fake news.
Unsubstantiated or obviously erroneous stories
spread quickly because information on the internet
can be circulated with such ease, resulting in the
creation of false news (B. Riedel et al., 2018). This
ultimately results in miscommunication, strife, and
the possibility of influencing people's opinions and
choices. Theubiquityofmisinformation is
aseriousrisktoinformationaccuracyinthetechnological
era, raising essential questions regarding media
literacy, ethical journalism, and the implications of
disinformation on society S. Ochoa et al., With
information being more accessible than ever, this
world-wide problem has implications for public
health, politics, and other elements of society.
2 RELATED WORK
With the enormous increase of communication
technologies and intelligent devices, the data traffic
also increased dramatically and huge volume of data
has been generated per second from different
applications, users and devices. For this reason, the
need for methods to address changes in data over
time or concept drifts has been growing. El Stream
Ahmad Abbasi et al proposed the El Stream, a novel
technique that combined real and synthetic data, and
both ensemble and nonensemble classifier in both
on-line and off-line stages to identify concept drifts
J. Vijay et al., (2021). While processing, in decision-
making, El Stream uses a majority vote to choose
the best classifier. Experimental results indicate that
our ensemble learning approach performs well better
than conventional machine learning algorithms and
state-of-the-art approaches in both simulated and
real datasets in terms of higher accuracy. In the past
decade, there has been a tremendous amount of
interest in big data, due to potential benefits that can
be gained from valuable insights and advantages,
including cost saving, quicker decision-making and
innovations in varied applications. However, the
analysis of such data is hard if it is delivered to the
analyst as a continuous stream (D. Mouratidis,
2021).
The amplified utilization of social networking sites
has taken fake news from zero to sixty in the modern
era. It is important to validate information available
on social network websites, including valid sources,
however with online news, there is no way to
Fake News Detector in Social Media Using AI
789

confirm source veracity. In this paper, we introduce
the FNU-Bi CNN model for data pre-processing
using the basic features from NLTK like stop words
and stemming. We also use batch normalization,
dense layers, LSTM, and WORDNET Lemmatizes
to calculate TF-IDF and select the features. The data
sets are trained by Bi-LSTM with ARIMA and
CNN then classification performed by using several
Machine Learning Algorithms. This method
constructs an ensemble model which captures news
article, author and title representations from text data
to derive credibility scores. We benchmark two
data classifiers including SVM, DT, RF, KNN,
Naive Bayes and K-NN in an effort to maximize the
prediction accuracy. Chang Li et al. Put forth the
suggestion that we argument provide rich evidence
form an if old views (Y. Wang et al., 2020). Yet, it is
hard to comprehend the positions within the
discussions because modeling both textual content
and user interactions is required. Current methods
typically dis regard the connection between various
issues of argumentation and favor a general
categorization strategy. In this paper, we consider
the issue as a collaborative representation learning
problem in which we embed authors and text based
on their interactions. We evaluate our model on the
Internet Argumentation Corpus and compare various
structural information embedding methods.
Experiment results show that our model performs
superior to competitive models. Social media
platforms have become increasingly important
powerful forces on political debates,
allowinguserstoexpresstheirvoicesandinteractwithco
ntrasting opinions. This leads to examination of
public opinion, political rhetoric, and argument
forms, calling for extensive research to find out how
argumentation dynamic works and writers interact
with whattheywrite. U mar Mohammed A bacha et
al. broke new ground in researching report grouping,
an elementary task in computer programming and
database administration Chokshi and R. Mathew’s,
(2021). It is a process of classifying papers in to
some classes, a basic process fin formation
classification because the number of reports
continues to rise with the rise in personal computers
and technology. Classification of such papersbased
on their content is essential. Text classification is
widely used to classify text into different categories
and involves a number of steps, each category
having a proper method enhancing the performance
in processing. Effective content-based classification
is essential for data experts and researchers and is an
important role in handling and sorting through
massive datasets (C. Dulhanty et al., 2019). Aparna
Kumari et al. introduced a newfeature selection
technique employed with a real dataset. This
methodology develops attribute subsets based on
two factors: (1) selecting discriminantattributes with
high classifying abilityand distinct from one another,
and (2) ensuring that the attributes in the sub set
complement each other by correctly classifying
distinct classes. The process uses confusion matrix
data to consider each attribute independently. It is
necessary to choose attributes with high
discrimination power, especially in the case of large
datasets, like brain MRI scans, where feature
selection significantly impacts classification
performance. As data get sparser when the number
of features rises, more training data are required to
effectively describe high-dimensional datasets,
leading to the" curse of dimensionality."
2.1 Previous Research
Individuals today use social media for consumption
and spreading of news to a larger extent, which is
the primary reason for the spread of both genuine
and fake news throughout the nation. Spread of fake
news on platforms like Twitter is a significant
danger to society. One of the major challenges to an
effective identification of false news on platforms
like Twitter is sophistication in distinguishing
between accurate and false content. Scientists have
managed this by focusing on methods of fake news
detection. Thestudy will utilize the FNC-1 dataset,
which has four features for identifying fakenews.
Wewillutilizebigdatatechnology (Spark) and
machine learning to compare and analyze the latest
techniques for detecting fake news. The approach
involvesemployingadecentralizedSparkclustertodeve
lop a stacked ensemble model.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The engineering that the solution to fake news relies
on is a mixture of blockchain, reinforcement
learning (RL), and natural language processing
(NLP). The workflow collects a vast volume of
news articles and also metadata, such as the author,
date and source. In the pre- processing step, the
collected data are tokenized and cleaned by NLP
techniques. Sentence length, readability and word
frequency constitute, in turn, features derived from
the processed text. These features are used as
training data to the RL agent, which learns about the
patterns that separate real news and false news.
When trained, the agent can then check whether it is
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
790

true or fake for a new news story on the extracted
features.
3.1 News organization
Technologies such as blockchain and NLP can help
to curb misinformation and fake news, including
fake media content. One of those tactics is to dissect
news articles (headline, lead, body, conclusion). By
examining those structures more closely, signs of
fake media could be detected. NLP is a computer
artificial intelligence, originally trying to study the
speech of the computers with human language, can
be used to analyze the content of news stories for the
presence of FF. For example, NLP approaches can
enable the investigation of the use of words in the
news and the discovery of inconsistencies that tell us
lies are being told.
3.2 Data Authentication
These blockchain and natural language processing-
based methodologies of fake media detection can
also be further modified by incorporating the data-
authentication systems. For the detection of fake
media the trustworthiness and genuineness of the
content under consideration need to be verified. the
computerized mark is one such best approach to give
information validation by guaranteeing the source
of a news article. These digital signatures, used to
authenticate the information, are generated by
cryptographic algorithms. The unforgeability of the
digital signature is ensured by including it in the
news report and recording it on a blockchain, where
anyone can easily check it.
Table1: Comparison table.
Algorithm accuracy precision Recall F1 score
NLP 88.66 86.78 89.18 87.67
RL 95.78 93.86 92.39 94.56
BlockChain 94.63 94.89 93.33 92.68
Additionally, inconsistencies in the data can be
detected via machine learning techniques. For
example, linguistic differences between the title of a
fake news piece and its body can be exposed
through teaching these algorithms. If so, these
inconsistencies may be annotated as suspicious
media. Table 1 shows the comparison table.
3.3 Proof-Of-Authority (POA)
A Proof of Authority (PoA) system involves another
set of trusted validators to validate the transactions
on the blockchain. The validators are often
companies or persons of high reputation for honesty
and honor. They verify that news reports are
authentic before they are added to the blockchain.
The PoA enables the creation of the first proven-
resistant and efficient detection of fake content. "
The validators are hesitant to violate the protocol's
integrity, depending on their trust and reputation,
and are probably not cooperating with other players
to form a cheating coalition. Natural language
processing can be used while evaluation of the
language the news story is constructed from and if it
is likely to have fake media. After the data is
formatted, the resulting data set is transmitted to
validators for validation. If news report is confirmed
by the validators to be true, the news report is added
to the blockchain, otherwise the news report is
rejected.
3.4 Fake Media
NLP can be exploited to explore the text of the
articles, identifying possible cases of manipulated
media. For example, NLP may identify linguistic
disparities, such as a mismatch in tone between the
headline and the body of the article. It can read the
sentiment of the article to know if there's any bias,
misinformation or fake news. The use of natural
language processing (NLP) solutions and the Cloud.
The FCTs can perform real-time provide a practical
method to detect false media by leveraging NLP
solutions and cloud computation capabilities. Fake
media is a term used to define article, images or
videos created with the intent to deceive or deceive
people secure and tamper-proof authentication and
storage for news stories. And any news story could
be tied to a single digital signature on the
blockchain, which we can use to trace its properness.
Using a blockchain and therefore an auditable and
tamper-evident way of securing the integrity of
processed data.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Certain metrics, such as F1 score, precision, and
recall, canbe applied to quantify how effective the
Fake News Detector in Social Media Using AI
791
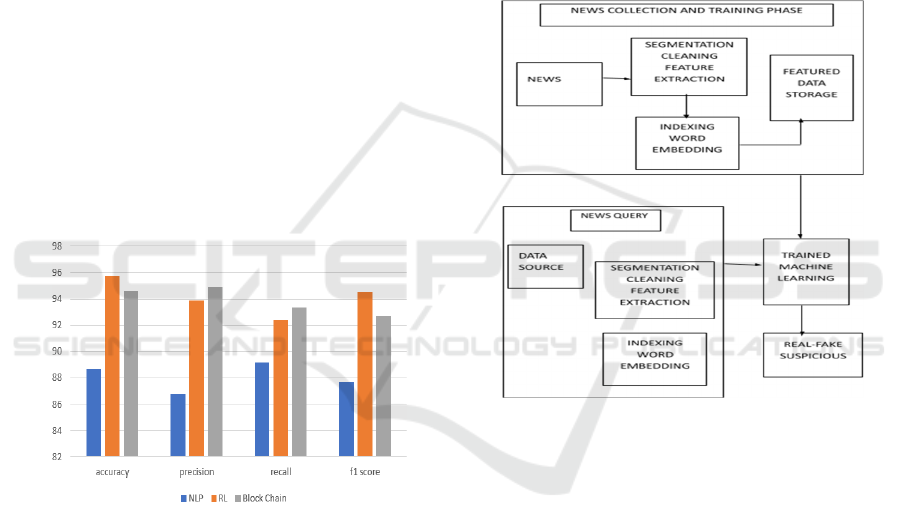
proposed method isin detecting fake news. Recall
determines the ratio of true positives to all
positiveactuals, whereasprecision determines the
ratio of true positives to all predicted positive values.
F1 score, as the mean of precision and recall
inversely weighted bythe measure, determines the
general performance whereby higher values indicate
better accuracy.
A labeled dataset of real and false news articles
can be usedto evaluate the performance of the
proposed system by comparing its predictions. The
accuracy, recall, and F1 measure of the system can
then be calculated based on its predictions. The
performance of the system can also be evaluated by
comparing it with other existing state-of-the-art fake
news detection methods. The overall performance of
the suggested system in identifying false news is
determined by several factors, including the purity
of the dataset, the effectiveness of the utilized NLP
methods in preprocessing data, thearchitecture of
theRL agent, and theaccuracyof the utilized
blockchain technology in providing security for data.
Ongoing testing and evaluation are important to
examine the performance of the system and identify
what needs to be improved. Figure 1 shows the
blockchain.
Figure 1: Comparison of accuracy, precision, recall, and
F1 score for NLP, RL, and Blockchain.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
SCOPE
To sum up, recognizing news as fake has an
important role in the current society with the
potential to produce a wide range of effects. The
offered solution based on blockchain, reinforcement
learning, and natural language processing is a
possible way to resolve this problem. By pre-
processing and feature extraction for news text with
NLP methods, the RL agent can be trained to learn
the patterns to distinguish between real news and
fake news. In the future, the method might be used
for anything that's communicated in text and could
become a powerful tool for halting the spread of
fake news and facilitating the spread of real news.
There are a number of directions that future work
could take in order to improve the proposed false
news detection technique. One possible
improvement is feature extraction, where more
features can further tune the RL agent to better
differentiate between real and fake news. Moreover,
the adoption of deep learning models combined with
other NLP advanced techniques for enhancing the
overall performance of the system could provide a
great potential. Figure 2 shows the flowchart of the
proposed system architecture.
Figure 2: Flowchart of the proposed system architecture.
REFERENCES
In a report published in 2020 on arXiv:1606.05464,
Augenstein,T. Rocktaschel, A. Vlachos,and K.
Bontcheva studied posture identification using
bidirectional conditional encoding. AtIberEval2017,
M.Taule,M.A.Martí,F.M.Rangel,
P. Rosso, C. Bosco, and V. Patti gave a summary of the
gender and stance recognition job in tweets about
Catalan independence. The 2017 2nd Workshop on
Evaluating Human Language Technologies for Iberian
Languages (CEUR-WS), volume 1881, included this
paper as one ofits proceedings.
Multilingual stance detection in political conversations on
social media was the subject of research by M. Lai,
T. Cignarella, D. I. Hernández Farias, C. Bosco, V.Patti,
and P. Rosso. Their study was published in September
2020 under the publication number 101075 in the
journal Computational Speech and Language.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
792

A baseline strategy was put forth by B. Riedel,
Augenstein,GeorgiosSpithourakis,and S. Riedelfor the
Fake News Challenge posture identification challenge.
Their study was published in May 2018 and offered a
straightforward but efficient method.
Fake Chain: A blockchain architecture to ensure trust in
social medianetworks was published byS. Ochoa, G.D.
Mello, L. A. Silva, A. J. Gomes, A.M.R. Fernandes,
and V.R.Q.LeichhardtinProc.Int.Conf.Qual,Inf.
"A Dynamic Technique for Identifying theFalse News
Using Random Forest Classifierand NLP," J. Vijay,
H.Basha, and J. A. Nehru, Computational Methods
and Data Engineering, 2021, Springer, pp. 331-341.
In a “Deep learning for fake news identification,” a
matched textualin put structure, Written by D.
Mouratidis and published in February 2021 in
Computation, vol. 9, no. 2, p. 20.
Weak supervision for false news detection via
reinforcement learning was published by Y. Wang, W.
Yang, F. Ma, J. Xu, B. Zhong, Q. Deng, and J. Gao in
Proc.AAAIConf.ArtificialIntelligence,vol.34,2020,pp.
516-532.
Chokshi and R. Mathew’s study, “Deep learning and
natural language processing for fake news detection:
research.” SSRN Electronic Journal, January 2021.
[Online]. Available with abstract id=3769884 at
papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm
Inresearchreleasedin2019, C.Dulhanty,J.L.Deglint, I.b.
Daya, and A. Wong investigated automatic
misinformation assessment using deep bidirectional
transformer language models for stance identification.
Fake News Detector in Social Media Using AI
793
