Smart Mental Health Prediction for Employees Using Ensemble
Learning
K. Manikanda Kumaran, S. Aljesirabanu, M. Anushree and B. Gowthami
Department of Information Technology, E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College, Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Mental Health, Employees, Ensemble Learning, Machine Learning.
Abstract: Internal heartiness is defined as the lack of internal health problems. Instead, internal health is a state of well-
being that allows employees to manage their work, accomplish their goals, learn and work efficiently, and
positively influence their working environment. Employers' internal problems have a variety of detrimental
effects on the association. Their ability to think, act, feel, socialize, and form relationships is also adversely
affected. Therefore, it is imperative to promptly address the underlying health situation and implement
appropriate treatments. This study's primary goal is to develop a machine literacy model that can predict
employees' internal health conditions and the need for treatments. For this study, employees from non-
technical, specialized businesses were used. Using techniques like Decision Tree (J48), Support Vector
Machine (SVM), Random Forest, and Ensemble Learning, the gathered data samples are pre-processed and
analysed. The delicacy position of the ensemble literacy that merged the algorithms below was 93.16.
Ensemble literacy is the fashionable algorithm to read the position of the need for therapies for workers'
internal health when compared to the J48.
1 INTRODUCTION
The problem of mental health disorders, such as
anxiety, depression, and stress-related conditions is a
pressing concern in healthcare. Assessments, leading
to delays in diagnosis and treatment. To address this,
a model is proposed to predict whether an employee
needs mental treatments.
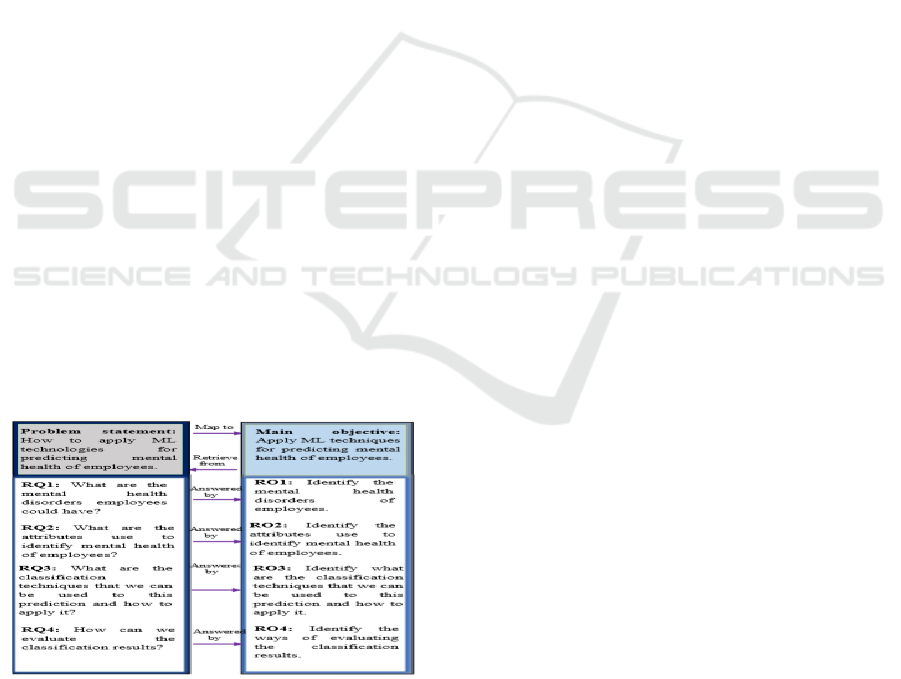
Figure 1: Mapping of the research questions and objectives.
This model uses advanced technologies like EEG
for brain activity analysis, NLP for sentiment
analysis, and facial recognition for emotion detection.
The goal is to enhance early detection, provide timely
interventions, and promote overall well-being.
However, the challenge lies in integrating diverse
data sources into a unified prediction model, which
can be challenging due to the lack of comforting
careers, job insurance, and job.
Figure 1 shows the mapping of the research
questions and objectives. This study aims to identify
employees with mental health disorders using
machine learning and develop a model for assistance,
with the research questions and objectives outlined in
Section II and Section III.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Brain Chemistry & Mental Illness – Imbalances in
brain chemistry contribute to mental disorders like
depression and ADHD. Depression in Daily Life
Depression is frequently portrayed as brief sadness,
but it can have significant emotional and financial
consequences. Mental Health and Public Perception
Understanding public perceptions of mental health
aids in funding and policymaking (DelPozo-Banos et
Kumaran, K. M., Aljesirabanu, S., Anushree, M. and Gowthami, B.
Smart Mental Health Prediction for Employees Using Ensemble Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013905700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
781-787
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
781

al., 2024). Data Mining in Mental Health – Machine
learning methods analyse and classify mental health
data for better insights. Social and cognitive skill
development is slowed down in both ADHD and
PDD (Kothari, R., & Kanchana, R. (2024)). Mental
Well-Being and the Environment a person's mental
well-being is influenced by their mindset and the
environment around them (Xu et al., 2023).
Definition of Mental Illness – Mental illnesses are
diagnosable conditions affecting thoughts, emotions,
or behaviour (Pourkeyvan et al., 2023). Impact of
Clinical Depression: Clinical depression affects one
in ten people and has an impact on society and
finances. Machine Learning in Diagnosis – AI models
help classify and predict depression using patient data
(Alanazi et al., 2022). Language & Mental Health –
Language patterns can indicate psychological states
with over 80% accuracy (Maniyar et al., 2022).
Virtual Training for Clinicians – AI-based virtual
training improves clinicians’ empathy skills
(Espinola et al., 2022). Workplace & Depression –
The workplace environment significantly affects
employees’ mental health (Alanazi et al., 2022).
Healthcare Worker Stress – Psychological distress is
high among healthcare workers due to socio-
demographic factors (Maniyar et al., 2022).
Generalized Prediction Models – Large datasets and
optimization techniques improve mental health
predictions (Espinola et al., 2022). Workplace Mental
Health Benefits – Companies offering mental health
benefits see better employee well-being (Manikanda
Kumaran et al., 2021). Technology’s Role in Society
– Rapid advancements in technology and policies
affect mental health (Prabha et al., 2024). Data
Mining for Disease Prediction – Machine learning
aids in predicting diseases, including mental disorders
(Katarya, R., & Maan, S. (2021).). Proposed Model
for Employees – A new model using EEG, NLP, and
facial recognition predicts employees needing mental
health treatment. Challenges in Data Integration –
Combining different data sources for prediction is
difficult due to job security and insurance issues.
Impact of Work Pressure – Employee stress leads to
missed interventions and reduced workplace
productivity. Algorithms for Mental Health – J48,
Random Forest, and Naïve Bayes help analyse
employer mental health data. Personality Disorders
and Substance Abuse: KNN and Naive Bayes are
used in studies to predict these disorders, with KNN
providing the highest level of accuracy
(Oktafiqurahman et al., 2022). Audio-Based Mental
Health Detection – Using noise-cancelled recordings,
studies analyse voices for mental disorder detection
(Rundensteiner, E., et al. 2022). SVM & Random
Forest in WEKA – These models are used in WEKA
for mental health classification (Singh, A., et al.
2021). DASS-21 for Stress, Anxiety & Depression –
Decision Trees, Random Forest, and SVM classify
mental health conditions using survey data (Chung,
J., & Teo, J. 2022). Stacking Ensemble Models –
Multi-layered ML models improve accuracy by
optimizing classifiers (Chung, J., & Teo, J. 2022).
Super Learner Ensemble – This method selects the
best-performing model based on accuracy and
prediction time (Kessler, R. C., et al. 2020). Research
Gap – There is a lack of supervised machine learning
models for predicting employees needing mental
health treatment. Study Objective – The study aims to
develop a machine learning model integrating diverse
data sources for early mental health detection.
Summary of literature is given in table 1.
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
Existing mental health systems rely on manual
assessments and basic HR metrics, lacking predictive
analytics to identify mental health needs proactively.
Inefficient use of employee data and poor resource
allocation hinder personalized interventions,
negatively affecting workplace well-being and
productivity. A predictive model using machine
learning can improve early identification and targeted
support for better mental health outcomes.
Disadvantages
• Data Quality Issues: Incomplete or
inconsistent input data can reduce prediction
accuracy, leading to biased and unreliable
outcomes.
• Complexity: Handling large, high-
dimensional datasets increases model
complexity, requiring more computational
power and making maintenance difficult.
• Overfitting: The model may perform well
on training data but poorly on new data by
learning irrelevant patterns, reducing
generalization.
• Interpretability: Complex models, like
deep learning, may lack transparency,
making it hard for professionals to
understand predictions.
• Data Privacy Concerns: Sensitive mental
health data requires strict privacy and
security measures to prevent unauthorized
access and data breaches.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
782
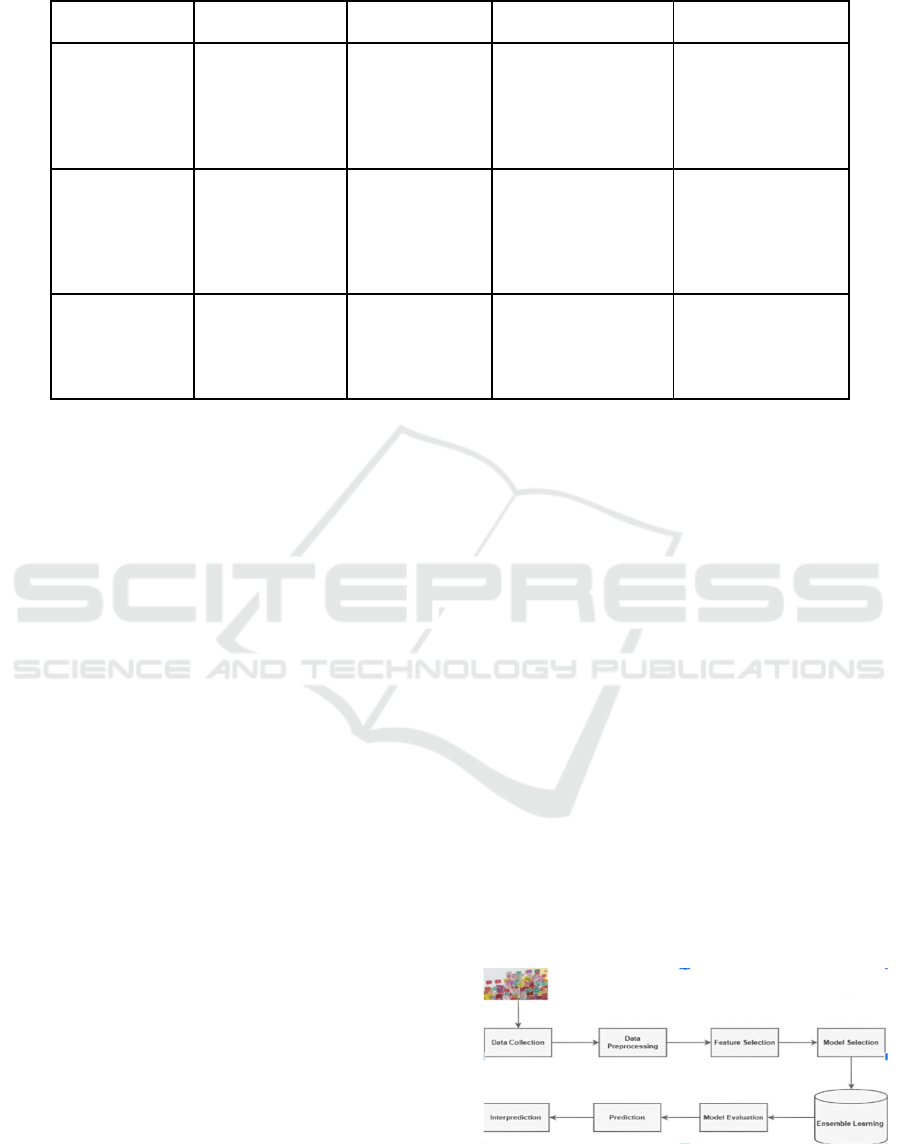
Table 1: Summary of Literature.
Ref Data Methodolo
gy
Ob
j
ective
(
s
)
Limitations
Singh et al.,
2024
Online
questionnaire
IoT, ML (KNN,
Naive Bayes,
Decision Tree)
Identify work
pressure and detect
employees needing
mental health
assistance.
Needs testing with
different ML
algorithms to detect
stress attacks.
Rundensteiner,
E., et al. (2022)
Online social data
(smartphones,
smartwatches)
Pilot study,
SVM, Random
Forest
Develop Short-Term
Depression Detector
for group
classification and
design implications.
Hard to calculate
actual sleep time;
low co-relation due
to insufficient data
on social activeness.
Espinola et al.,
2020
Psychiatric ward
data (78 patients)
Vocal acoustic
analysis, ML
Support diagnosis of
mental disorders and
anxiety using vocal
data and ML.
Small sample size;
insufficient for ML-
based research
.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The designed model integrates multi-modal data
sources facial expressions, EEG data, and text
analysis to enhance mental health prediction
accuracy. Facial expressions will be analysed to
detect emotional states and behavioural patterns
linked to stress, anxiety, and depression. EEG data
will assess brain activity patterns to identify
emotional and cognitive stress. Text analysis using
sentiment analysis and NLP will extract emotional
tones and psychological patterns from written
communications. The combined data will improve
prediction accuracy and enable early intervention. A
chatbot will provide customized mental health
treatment suggestions based on predictions, handling
multiple employees simultaneously and offering
tailored support.
Advantages
• Improved Data Quality and Accuracy: The
proposed system enhances mental health
assessment by continuously monitoring
emotional states, brain activity (EEG), and
sentiment from text, leading to faster and more
targeted intervention
• Reduced Complexity through Data
Integration: It simplifies data processing and
improves model efficiency by integrating
diverse data sources into a unified framework,
overcoming the complexity of high-dimensional
data.
• Minimized Overfitting: The system reduces
overfitting by using a balanced combination of
facial, EEG, and text data, helping the model
focus on meaningful patterns rather than noise.
• Enhanced Interpretability: Unlike existing
black-box models, the proposed system
improves interpretability by providing clear
insights from facial expressions, brain activity,
and text analysis, helping healthcare
professionals make informed decisions.
• Early Detection and Faster
Intervention: Real-time processing and
analysis of facial expressions enable early
detection of mental health issues, leading to
timely interventions.
• Better Privacy and Data Security: Secure data
handling and encryption methods protect
sensitive mental health information from
unauthorized access and breaches.
4.1 System Architecture
Figure 2: System architecture.
Smart Mental Health Prediction for Employees Using Ensemble Learning
783
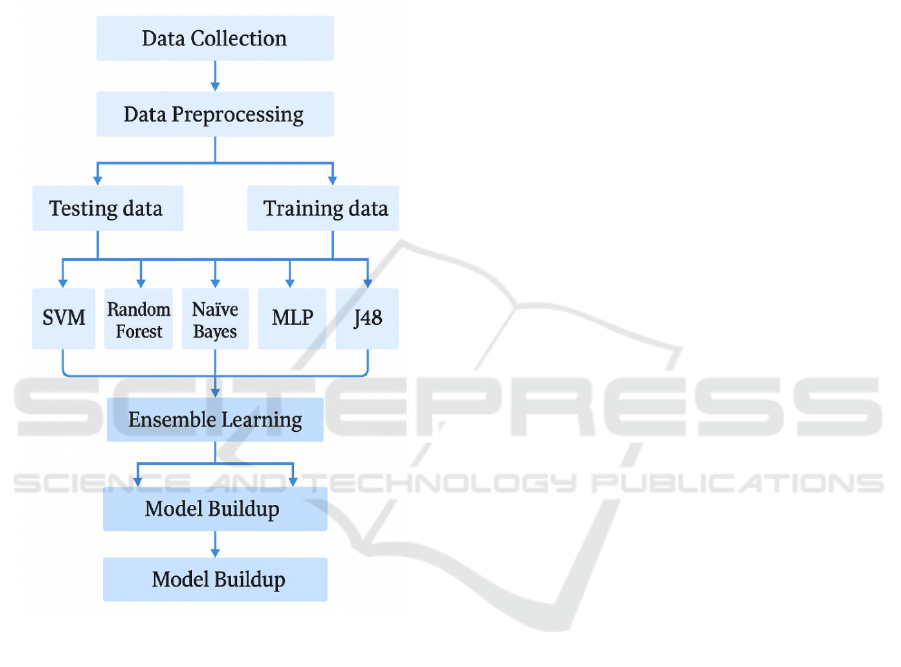
Figure 2 illustrated the System Architecture and
figure 3 shows the conceptual framework.
4.2 Methodology and Techniques
The proposed system for mental health prediction
uses advanced techniques such as facial expression
analysis, brain activity monitoring through EEG
devices, text analysis, and machine learning models.
Figure 3: Conceptual framework.
The Haar Cascade Classifier and OpenCV are
used for real-time face recognition and expression
classification, while EEG devices like Emotiv and
NeuroSky measure brainwave patterns associated
with mental health conditions. The XGBoost machine
learning model is used for predictive analysis,
efficiently managing missing data and outliers. The
BERT algorithm is used for text data analysis,
extracting sentiment, tone, and emotional context
from text, identifying signs of mental distress or
emotional imbalance. ChatGPT is integrated to
provide personalized suggestions and
recommendations to help employees manage stress,
anxiety, and other mental health challenges
effectively.
4.3 Ensemble Learning Algorithm
Ensemble Learning is used in a model for predicting
mental health treatments for employees. It combines
multiple machine learning models, such as Decision
Trees, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and
Random Forest, to analyse various data. Bagging and
boosting techniques are applied to aggregate outputs
and minimize prediction errors. Bagging reduces
variance and improves model stability by averaging
or voting on outputs. Boosting creates a series of
models, each correcting previous one, enhancing
model accuracy. XG Boost, a powerful boosting
algorithm, is integrated to handle complex
relationships and missing data. This ensemble-based
approach enhances generalization capability,
capturing diverse patterns in employee data and
improving decision-making.
5 IMPLEMENTATIONS
Data Collection: High-quality, multi-modal data is
gathered from facial expressions (using Haar Cascade
Classifier and OpenCV), EEG signals (from Emotiv
and NeuroSky), and text data (using BERT) to analyse
emotional, neurological, and psychological states.
Data Preprocessing: Data is cleaned, normalized,
and scaled to improve learning efficiency. Text data is
processed using tokenization and stemming, and
categorical data is encoded numerically for consistent
model input.
Feature Selection: Key features are extracted from
facial expressions (smile intensity, eye movement),
EEG patterns (alpha, beta, theta waves), and text data
(sentiment polarity, emotional tone). PCA reduces
dimensionality to focus on the most meaningful data.
Model Selection: XGBoost is selected for its
predictive strength. Other ensemble models like
Random Forest and Bagging are also tested for
improved generalization.
Ensemble Learning Method: Bagging averages
multiple models to reduce variance, while Boosting
(using XGBoost) corrects errors from previous
models, improving accuracy and consistency.
Training: The models are trained using processed
data, with hyperparameter tuning and cross-validation
to enhance accuracy and prevent overfitting.
Evaluation: Performance is evaluated using
accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and confusion
matrix to measure prediction reliability and identify
improvement areas.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
784
Interpretation: ChatGPT generates personalized
recommendations based on emotional states,
providing visual reports for better decision-making
and addressing specific mental health issues in the
workplace.
6 RESULT & DISCUSSION
Figure 4: Registration page.
Figure 5: Login page.
Figure 6: Facial expression analysis.
Figure 7: EEG expression analysis.
Figure 8: Text data analysis & ChatGPT is integrated to
provide personalized suggestions and recommendations.
Figure 4 shows the Registration Page, Figure 5
presents the Login Page, Figure 6 displays the Facial
Expression Analysis, Figure 7 illustrates the EEG
Expression Analysis, and Figure 8 integrates Text
Data Analysis using ChatGPT for personalized
recommendations.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The HR system utilizes Haar Cascade Classifier,
BERT, EEG, and sentiment analysis to predict
employees' mental health. This ensemble learning-
based system enhances predictive accuracy and
reduces error rates by combining multiple models. It
helps identify stress patterns, emotional states, and
cognitive health issues, enabling HR departments to
design targeted interventions, improving employee
well-being and productivity.This innovative
approach demonstrates the potential of machine
Smart Mental Health Prediction for Employees Using Ensemble Learning
785

learning and AI in enhancing mental health care and
promoting a healthier work environment.
8 FUTURE WORK
The mental health prediction system for employees
uses ensemble learning techniques and multi-modal
data analysis to identify and address mental health
challenges. Future work will focus on improving data
quality, expanding the model's capabilities,
enhancing real-time analysis, and incorporating
additional mental health indicators. Data
enhancement and diversity are key areas for future
work, including incorporating physiological data,
contextual data, and real-time analysis.
Real-time analysis and monitoring will be crucial,
enabling the system to detect stress and emotional
distress as they occur. Personalized models can be
created for different job roles and stress levels,
improving the relevance and effectiveness of the
recommendations. Integration with mental health
support systems, such as employee assistance
programs, therapy platforms, and mental health
hotlines, will facilitate immediate support for
employees. Advanced algorithms like XGBoost,
Bagging, and Boosting can further improve accuracy,
especially for complex patterns in time-series data
like EEG signals and facial expressions. Enhanced
privacy and data security will be a critical focus, with
advanced encryption methods and secure data storage
protocols. Ethical considerations and bias reduction
will also be prioritized, with the system regularly
audited for potential biases based on race, gender,
age, and other factors.
REFERENCES
"Machine learning-based prediction of mental well-being
using health behavior data from university students."
(2023). Bioengineering, 10(5), 575.
"Machine learning and deep learning models for predicting
mental health." (2024). European Journal.
"Machine learning techniques to predict mental health
diagnoses: A systematic review." (2024). Clinical
Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health, 20,
e17450179315688.
Alanazi, S. A., Khaliq, A., Ahmed, F., Alshammeri, N.,
Hussain, I., Zia, M. A., Alruwaili, M., Rayan, A.,
Alsayat, A., & Afser, S. (2022). "Public's mental health
monitoring via sentiment analysis of financial text
using machine learning techniques." IEEE Access, 10,
12745–12758.
B. V. Prabha, K. Manikanda Kumaran, S. Manikandan and
S. P. Murugan, "A Comparative Analysis of Machine
Learning Algorithms for Healthcare Applications,"
2024 4th International Conference on Advancement in
Electronics & Communication Engineering (AECE),
GHAZIABAD, India, 2024, pp. 214-218.
Chung, J., & Teo, J. (2022). Single classifier vs. ensemble
machine learning approaches for mental health
prediction. Applied Computational Intelligence and
Soft Computing, 2022, 1–10.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9970363
Chung, J., & Teo, J. (2022). Mental health prediction using
machine learning: Taxonomy, applications, and
challenges. Applied Computational Intelligence and
Soft Computing, 2022, 1–19.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9970363
DelPozo-Banos, M., Stewart, R., & John, A. (2024).
"Machine learning in mental health and its relationship
with epidemiological practice." Frontiers in Psychiatry,
15, 1347100.
Editorial: "Mental health, epidemiology and machine
learning." (2024). Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15, 1536129.
Espinola, C. W., Gomes, J. C., Pereira, J. M. S., & dos
Santos, W. P. (2020). Detection of major depressive
disorder using vocal acoustic analysis and machine
learning. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/
2020.06.23. 20138651ResearchGate+1Academia+1
Espinola, C. W., Gomez, J. C., Pereira, J. M. S., & Santos,
W. P. D. (2022). "Detection of major depressive
disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and
generalized anxiety disorder using vocal acoustic
analysis and machine learning." Journal of Psychiatric
Research, 148, 69–78.
K. Manikanda Kumaran, M. Chinnadurai, S. Manikandan,
S. Palani Murugan, E. Elakiya, "An IoT based Green
Home Architecture for Green Score Calculation
towards Smart Sustainable Cities", KSII
TRANSACTIONS ON INTERNET AND
INFORMATION SYSTEMS VOL. 15, NO. 7, Jul.
2021, https://doi.org/10.3837/tiis.2021.07.005.
Kannan, K. D., Jagatheesaperumal, S. K., Kandala, R.N.V.
P. S., Lotfaliany, M., Alizadehsanid, R., & Mohebbi,
M. (2024). "Advancements in machine learning and
deep learning for early detection and management of
mental health disorders." arXiv preprint
arXiv:2412.06147.
Katarya, R., & Maan, S. (2021). Predicting mental health
disorders using machine learning for employees in
technical and non-technical companies. International
Journal of Information Technology, 13(3), 1021–1028.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00642-0
Kessler, R. C., et al. (2020). Developing algorithms to
predict adult onset internalizing disorders: A super
learner approach. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 123,
1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.01.001
Kothari, R., & Kanchana, R. (2024). "Mental health
prediction using machine learning techniques and
comparison with existing works." AIP Conference
Proceedings, 3075(1), 020228.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
786

Maniyar, A. A., SH, J. K., N, N., HK, R., & T, A. (2022).
"Machine learning techniques for stress prediction in
working employees." International Journal of
Computer Science and Engineering, 10(4), 102–109.
Oktafiqurahman, A., Kusrini, & Nasir, A. (2022).
Personality prediction based on Facebook media social
status using the method Naïve Bayes and KNN.
International Journal of Artificial Intelligence
Research, 6(1), 1–10.
https://doi.org/10.29099/ijair.v6i1.123
Pourkeyvan, A., Safa, R., & Sorourkhah, A. (2023).
"Harnessing the power of Hugging Face Transformers
for predicting mental health disorders in social
networks." arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.16891.
Rundensteiner, E., et al. (2022). Mental illness detection
through audio signal processing. BBRC Research
Communications, 15(4), 45–52.
https://www.academia.edu/97500672/Mental_Illness_
Detection_Through_Audio_Signal_Processing
Singh, A., et al. (2021). Mental illness prediction using
machine learning algorithms. International Research
Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 10(8),
1–6. https://www.irjet.net/archives/V10/i8/IRJET-
V10I833.pdf
Singh, A., Singh, K., Kumar, A., Shrivastava, A., & Kumar,
S. (2024). Machine learning algorithms for detecting
mental stress in college students. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2412.07415. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.07415
Xu, X., Wang, D., & Dey, A. (2023). "Mental-LLM:
Leveraging large language models for mental health
prediction via online text data." arXiv preprint
arXiv:2307.14385.
Smart Mental Health Prediction for Employees Using Ensemble Learning
787
