
Intelligent Plant Disease Diagnosis with Explainable AI Methods and
Lightweight Model
Ishan Joshi, Naman Mardia and R. Vidhya
CTech, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Plant Disease Detection, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep Learning, Explainable AI (XAI), Sustainable
Agriculture.
Abstract: Agriculture is a most important contributor to a country economy and especially in India, as majority of rural
people, its only source of livelihood. Plant diseases are among the most significant challenges to agriculture,
which can be caused by pathogen, synthetic fertilizers, outdated farming practices, and environmental
conditions. The yield for crops can be greatly reduced by these diseases that lead to substantial coronavirus
economic impact. AI and Machine Learning techniques for outbreak detection have become widely used by
researchers to tackle this issue. This survey examines prevalent plant leaf diseases, explores traditional and
deep learning methods for disease detection, and reviews available datasets. It also addresses the use of
Explainable AI (XAI) applied to deep learning to enhance the transparency of the models, leading to
understandable decisions for the user. Drawing on this expertise, the survey provides insights for researchers,
practitioners, and other stakeholders, informative the creation of effective and transparent biosolutions to plant
diseases, resulting in sustainable agricultural systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Even with the advancement of agricultural
technology, plant disease continues to be a pressing
challenge, leading to increasing annual crop losses
globally and posing a significant threat to food
security (Shirahatti et al.; Ko Ko Zaw et al.;
Owomugisha et al.). Conventional methods for
detecting plant diseases heavily depend on expert
knowledge, which may introduce errors, biases, and
inefficiencies, especially in large-scale agricultural
practices (Hasib et al.; Singh et al.). These limitations
often delay treatment, allowing diseases to spread
further and reduce yields. The growing field of
machine learning and computer vision offers a
solution through automated systems for disease
detection (Cap et al.; Amin et al.). However, many
existing models’ function as black-box systems,
offering little to no insight into their decision-making
processes (Baehrens et al.; Lundberg and Lee). This
lack of transparency can reduce trust and hinder
adoption among farmers and agronomists who require
clear and verifiable recommendations (Wei et al.;
Daglarli). Additionally, such models may perform
poorly in varying visual environments (Rajeena et al.;
Sapura et al.). This underscores the need for intelligent
plant disease diagnosis systems that not only achieve
high accuracy but also incorporate explainability
through Explainable AI (XAI) methods (Arvind et al.;
Tabbakh and Barpanda). These systems must provide
interpretable outputs to empower users in making
informed decisions about disease management (Wei et
al.; Baehrens et al.). Furthermore, the solutions should
be robust, scalable, and adaptable to different
agricultural contexts to ensure widespread usability
(Cap et al.; Amin et al.). Therefore, this survey paper
presents a comprehensive overview of common leaf-
based plant diseases, available datasets, and state-of-
the-art detection techniques (Shirahatti et al.; Singh et
al.; Ko Ko Zaw et al.). It also highlights the application
of XAI techniques, especially in CNN and
Transformer models, to enhance interpretability and
model transparency in disease classification tasks
(Tabbakh and Barpanda; Arvind et al.; Lundberg and
Lee; Wei et al.). The paper emphasizes the importance
of XAI in this domain and outlines potential directions
for future research (Daglarli; Baehrens et al.; Amin et
al.).
Joshi, I., Mardia, N. and Vidhya, R.
Intelligent Plant Disease Diagnosis with Explainable AI Methods and Lightweight Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0013904700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
739-744
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
739

2 OVERVIEWS ON LEAF BASED
PLANT DISEASE DETECTION
All living organisms, including plants, animals, and
humans, are vulnerable to diseases. Researchers and
professionals in agricultural science and management
are actively searching for advanced solutions to
mitigate plant disease outbreaks, which can cause
significant damage to agricultural productivity
(Shirahatti et al.; Owomugisha et al.). To address this,
various scientific disciplines collaborate to control
the spread of plant leaf diseases and ensure a stable
food supply for the world’s growing population (Ko
Ko Zaw et al.; Sapura et al.; Rajeena et al.).
Plant diseases can manifest through various
symptoms that affect a plant’s structural components
such as leaves, stems, and roots, ultimately
influencing its growth and yield (Singh et al.; Cap et
al.). The occurrence of these diseases varies
seasonally, influenced by changes in weather
conditions and the presence of specific pathogens
(Amin et al.; Tabbakh and Barpanda). Recent
approaches using convolutional neural networks and
vision transformers show promising results in
improving detection rates (Arvind et al.; Wei et al.).
The integration of Explainable AI (XAI) further
enhances these models by offering transparent
insights into classification decisions, promoting trust
among end-users like farmers and agronomists
(Baehrens et al.; Lundberg and Lee; Daglarli).
Furthermore, research demonstrates that XAI models
such as SHAP, LIME, and attention-based techniques
are helping interpret deep learning decisions in
agriculture and beyond (Hasib et al.; Wei et al.). This
section thus surveys common leaf diseases, key
datasets, and notable contributions in the area of leaf-
based plant disease detection.
2.1 Common Leaf Diseases in Plants
Plant diseases predominantly affect the leaves, but
can also impact the roots, stems, and fruits.
Among these, leaf diseases are the most prevalent
and are typically managed using fungicides,
bactericides, or resistant plant varieties. Below are
some of the most common leaf diseases:
• Blight: One of the most destructive plant
diseases, Blight has historically caused
significant damage, such as during the 1840s
potato famine. This fungal disease spreads in
warm, humid conditions through wind-borne
spores.
• Scab: This fungal disease is host-specific
and can infect individual plants. It is
prevalent in apple trees, where it initially
causes olive green spots on the leaves, which
eventually turn yellow before the leaves fall
off.
• Powdery Mildew: Common in shaded
areas, Powdery Mildew is easily
recognizable by the white powdery coating
on the upper surface of the leaves. This
disease spreads in humid conditions with
low soil moisture.
• Mosaic Virus: The mosaic virus affects
plants at a molecular level, commonly
infecting tomatoes, tobacco, and other
horticultural plants. Infected leaves develop
yellowish and whitish stripes.
• Marssonina Blotch: Caused by the fungus
• Marsonina Caronaria, this disease occurs in
high rainfall areas. Infected leaves develop
circular dark green patches that can turn dark
brown in severe cases.
• Black Spot: Another fungal disease, Black
Spot, creates round black spots on the upper
surface of leaves. It thrives in prolonged wet
conditions or when leaves remain moist for
extended periods.
• Frogeye Spot: Caused by the fungus
Cercospora Sojina, Frogeye Spot manifests
as purple spots on leaves during early spring,
which later develop into brownish rings
resembling a frog's eye.
• Rust: This easily identifiable fungal disease
causes brownish rusty spots on leaves and is
commonly found on apples, roses, and
tomatoes, especially during wet weather in
early spring.
Plant leaf diseases are one of the growing
challenges in agricultural productivity due to a wide
range of pathogens such as fungus, bacteria, viruses,
etc. These pathogens have different lifecycles and
environmental triggers, making disease management
a potentially complex and multi-factors challenge.
Exploring the conditions specific to diseases such
as Blight and Rust for example to focus methods of
intervention. For example, these diseases can cause
significant changes in plant physiology, and impede
photosynthesis and nutrient uptake, resulting in
reduced growth and yield, or even death in some
cases if not properly managed.
The dataset includes various plant diseases, such
as Apple Scab (Figure 1), Rose Black Spot (Figure 2),
Powdery Mildew (Figure 3), Blight (Figure 4),
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
740

Mosaic Virus (Figure 5), Marssonina Blotch (Figure
6), Frogeye Spot (Figure 7), and Rust (Figure 8), each
of which presents unique visual characteristics aiding
in accurate classification.
Figure 1: Apple scab.
Figure 2: Rose black spot.
Figure 3: Powdery mildew.
Figure 4: Blight.
Figure 5: Mosaic virus.
Figure 6: Marssonina blotch.
Figure 7: Frogeye spot.
Figure 8: Rust.
3 OVERVIEWS ON
EXPLAINABLE AI (XAI)
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is the talk of the town, and
with good reason, for almost every subtype of
research is either moving towards AI or refactor their
already existing rule-based system to AI systems. But
many of today’s AI systems, such as those that
employ deep learning and machine learning, are very
opaque, meaning that users cannot tell what is
happening inside the system or what drives important
decisions. This lack of source transparency creates
mistrust and discourages users from adopting your
final product.
Certain AI researchers claim that explanations do
not need to be an area of focus in AI research as it is
either not necessary or too ambitious, whereas others
have stated that rather than hinder human
intelligence, explanations accompanying AI outputs
can facilitate it and can build trust in these systems.
In this way, closing this gap would enhance trust on
Intelligent Plant Disease Diagnosis with Explainable AI Methods and Lightweight Model
741
AI systems and unleash opportunities for AI led
products & services.
AI systems need to explain things to users in
critical areas such as law, medicine, agriculture,
finance and defence so that they can apply them
safely and confidently. Explanations provide a useful
layer of human-computer interaction, enabling users
to get more value from AI-based services. AI has
been advancing rapidly, made possible in no small
part by machine learning methods ranging from
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) and Random
Forests (RF) to probabilistic models to Deep Learning
(DL) neural networks, all of which work as blackbox
models. These models require little to no human input
in order to run, and can be employed right away in
multiple environments with little tailoring.
But according to the tradition we have been
trading off the performance of machine learning
models such as predictive accuracy with model
interpretability. For example, deep learning is often
highly accurate models, but not very explainable,
while decision trees are very explainable, but not very
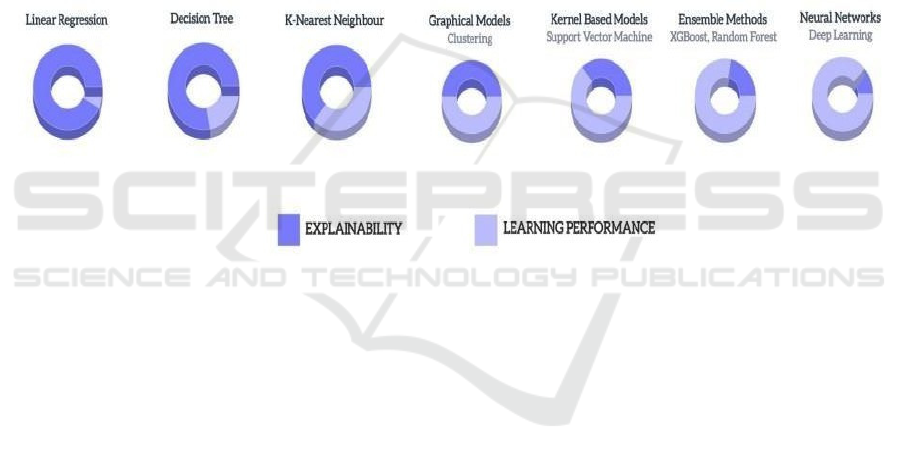
accurate. A hypothetical graph (Figure 2) illustrates
this performance-explainability trade-off,
demonstrating that explainability typically decreases
while model performance increases. Figure 9 Shows
Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning
Algorithms: Explainability vs Learning Performance.
To address this challenge and make AI solutions
more transparent and trustworthy, a research domain
called Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has
emerged. XAI aims to enhance the interpretability of
AI systems, making them easier for users to
understand and trust. A. What is XAI?
Figure 9: Comparative analysis of machine learning.
That said, artificial intelligence (AI) has become
a hot new commodity, bringing about a considerable
change in numerous environments, from automatic
vehicles to medical diagnostics. Yet users who are not
technical often do not understand the systems on
which they depend, and therefore, trust in AI-
generated decisions cannot be taken for granted. In
industries as sensitive as defences, healthcare, and
safety, this issue is being cast in an even graver light,
given the extent of AI's integration into these
domains. As AI becomes more prevalent in
supporting or even replacing human supervisors in
these domains, it is imperative to do more than show
how the AI reached a given decision; it is a
prerequisite of any responsible AI system to ensure
the users can verify how the system works and how
the AI works.
Concerns like these are why Explainable
Artificial Intelligence (XAI), a sub field of machine
learning, was created. These XAI techniques are
finding applications for improving the transparency
and reliability of AI systems by exposing their inner
workings in a manner that users can appreciate and
also be confident in the model’s decisions. By
implementing ethical considerations, XAI minimizes
the chances of unintentional bias while boosting
confidence in the system's results. XAI is mainly
focused on providing humans a set of rules for XAI
decisions and making AI systems more user and
efficient friendly according to some similar
principles.
For example, consider a healthcare scenario where
a patient with breathing issues is placed on a ventilator.
A doctor monitors the patient's heart rate through an
AIenabled system, which displays fluctuating heart
rates on the screen.
The AI algorithm is designed to predict the
patient's heart rate for the next 15 seconds based on
previous and current data. However, this system, like
many "black-box" models, provides highly accurate
predictions without explaining the factors influencing
these heart rate variations. In this case, the doctor is
relying on an AI system that offers no insight into its
decision-making process, making it risky to trust such
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
742
a system without understanding the internal factors
driving the predictions.
This hypothetical example highlights the need for
explainable AI systems in high-stakes environments,
where users must be able to trust and understand the
decisions made by AI in order to use them effectively
and safely. By making AI more transparent, XAI can
bridge this gap.
4 MODEL ARCHITECTURE
In this work, we used the LAAMA (Lightweight
Attention-
Augmented Mobile-friendly Architecture),
alongside EfficientNetV2L, MobileNetV2, and
ResNet152V2 for comparison, to detect 38 diseases
across 14 plant species. LAAMA incorporates
lightweight attention modules to improve feature
extraction and focus on important regions in the
images while keeping the model suitable for
deployment on mobile and edge devices.
The LAAMA architecture is designed with depth
wise separable convolutions and attention
mechanisms that reduce computational complexity
and make it mobile-friendly.
We pertained LAAMA on the ImageNet dataset,
fine-tuned it for plant disease detection, and followed
the same steps for the other models to ensure a fair
comparison.
We used the Adam optimizer with a learning rate
of 0.0001, categorical cross-entropy as the loss
function, and a softmax activation function in the
output layer, which has 38 neurons due to the
multiclass classification nature of this task. All
models, including LAAMA, were trained for 50
epochs, using a dropout function to mitigate
overfitting.
Table 1: Performance Metrics Comparison of Deep Learning
Models for Classification Tasks.
Model
LAA
MA
EfficientNe
tV2L
MobileN
etV2
ResNet1
52V2
Accur
acy
99.25
%
99.63% 98.86% 98.44%
Precis
ion
99.13
%
99.63% 98.68% 98.19%
Recall
98.94
%
99.63% 98.03% 97.53%
F1
Score
99.03
%
99.63% 98.29% 97.82%
5 RESULT ANALYSIS
We have tested our models on quantitative
performance evaluation metrics: accuracy (1),
precision (2), recall (3), and f1 score (4) by their
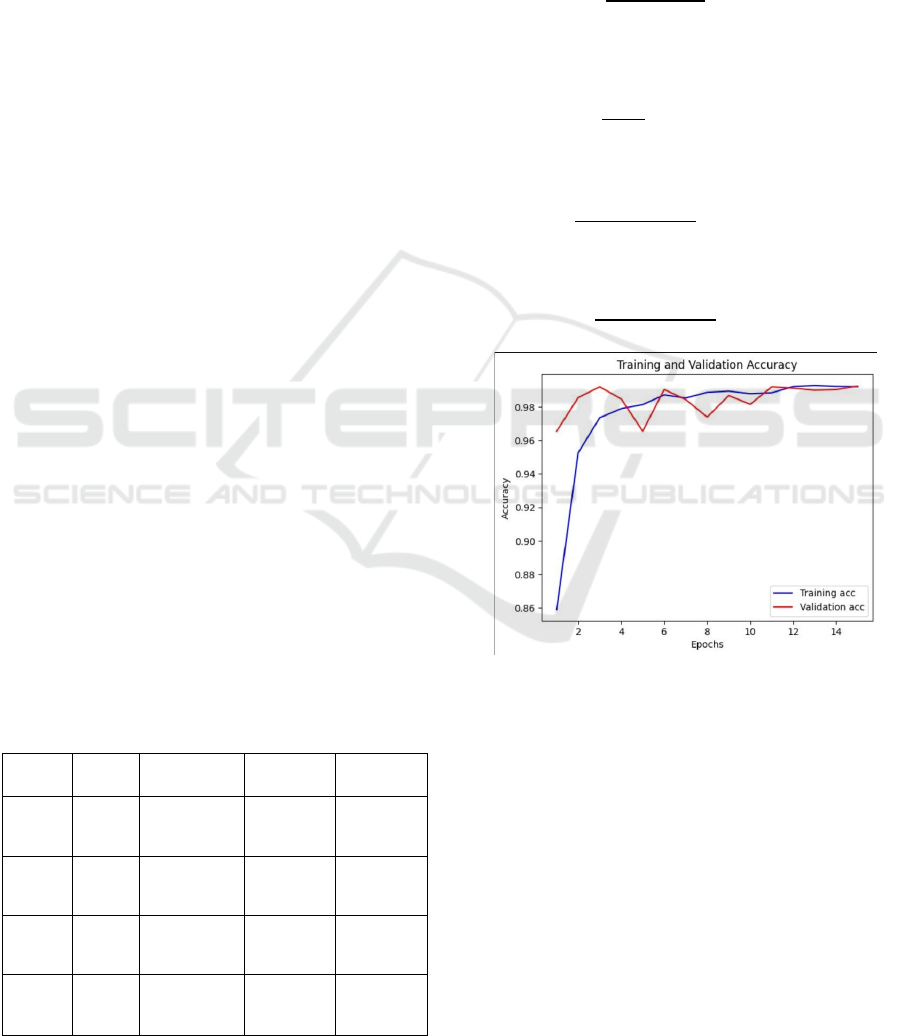
predictions on our test set. Figure 10 Shows the
Training and Validation Accuracy.
𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑦 =
(1)
Here, TN = True negative, TP = True positive, FN =
False negative, FP = False positive.
𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛 =
(2)
Here, TP = True positive, FP = False positive.
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙 =
∗∗
(3)
Here, TP = True positive, FN = False negative.
𝐹1𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 =
∗∗
(4)
Figure 10: Training and Validation Accuracy.
From Table 1, we observe that EfficientNetV2L
achieved the highest performance across all metrics,
but LAAMA provided competitive results while
maintaining a lightweight architecture suitable for
mobile deployment:
• Accuracy: LAAMA scored 99.25%, which is
0.38% lower than EfficientNetV2L but higher
than both MobileNetV2 and ResNet152V2.
• Precision: LAAMA achieved 99.13%
precision, 0.5% lower than EfficientNetV2L
but higher than MobileNetV2 and
ResNet152V2.
• Recall: LAAMA had a 98.94% recall, 0.69%
lower than EfficientNetV2L but still higher
Intelligent Plant Disease Diagnosis with Explainable AI Methods and Lightweight Model
743

than MobileNetV2 and ResNet152V2.
• F1 Score: LAAMA's F1 score was 99.03%,
just 0.60% lower than EfficientNetV2L and
higher than the other two models.
• Thus, while EfficientNetV2L outperformed in
raw accuracy and precision, LAAMA
provides a strong trade-off between
performance and mobile-friendliness, making
it highly suitable for applications requiring
real-time processing on edge devices.
REFERENCES
Adi Dwifana Sapura, Djarot Hindarto, Handri Santoso,
“Disease Classification on Rice Leaves using
DenseNet121, DenseNet169, DenseNet201”,
Sinkyone: Jurnal dan Penelitian Teknik Informatika
Volume 8, Issue 1, January 2023, DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33395/sinkron.v8i1.11906
Amer Tabbakh and Soubhagya Sankar Barpanda. “A Deep
Features Extraction Model Based on the Transfer
Learning Model and Vision Transformer “TLMViT”
for Plant Disease Classification”. In: IEEE Access 11
(2023). Conference Name: IEEE Access, pp. 45377–
45392. ISSN: 2169-3536
CS Arvind et al. “Deep Learning Based Plant Disease
Classification with Explainable AI and
Mitigation Recommendation”. In: 2021 IEEE
Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence
(SSCI). Dec. 2021, pp. 01– 08
D. Baehrens, T. Schroeter, S. Harmeling, M. Kawanabe, K.
Hansen, and K. R. Müller, “How to explain individual
classification decisions,” J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 11,
pp. 1803–1831, 2010
Daglarli, Evren, “Explainable Artificial Intelligence (xAI)
Approaches and Deep Meta-Learning Models for
Cyber-Physical Systems”, Artificial Intelligence
Paradigms for Smart Cyber-Physical Systems, edited
by Ashish Kumar Luhach and Atilla Elçi, IGI Global,
2021, pp. 42-67.
Fathimathul Rajeena, Aswathy S, Mohamed A. Moustafa
and Mona A. S. Ali, “Detecting Plant Disease in Corn
Leaf Using EfficientNet Architecture An Analytical
Approach”, Electronics 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/
electronics12081938
Godliver Owomugisha, Friedrich Melchert, Ernest
Mwebaze, John A Quinn and Michael Biehl, “Machine
Learning for diagnosis of disease in plants using
spectral data”, Int'l Conf. Artificial Intelligence (2018).
Godliver Owomugisha, Friedrich Melchert, Ernest
Mwebaze, John A Quinn and Michael Biehl, “Machine
Learning for diagnosis of disease in plants using
spectral data”, Int'l Conf. Artificial Intelligence (2018).
HASSAN AMIN, ASHRAF DARWISH (Member, IEEE),
ABOUL ELLA HASSANIEN AND MONA
SOLIMAN. “End-to-End Deep Learning Model for
Corn Leaf Disease Classification”, IEEE Access, “,
Volume 10, 2022, Digital Object Identifier
10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3159678
J. Shirahatti, R. Patil, and P. Akulwar, “A survey paper on
plant disease identification using machine learning
approach,” in 2018 3rd International Conference on
Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES).
IEEE, 2018, pp. 1171–1174.
K. M. Hasib, F. Rahman, R. Hasnat, and M. G. R. Alam,
“A machine learning and explainable ai approach for
predicting secondary school student performance,” in
2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and
Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC),
2022, pp. 0399– 0405.
Kaihua Wei, Bojian Chen, Jingcheng Zhang, Shanhui Fan,
Kaihua Wu, Guangyu Liu and Dongmei Chen,
“Explainable Deep Learning Study for Leaf Disease
Classification”, Agronomy 2022, 12, 1035,
https://doi.org/ 10.3390/agronomy12051035
Ko Ko Zaw, Dr. Zin Ma Ma Myo, Daw Thae Hsu Thoung,
“Support Vector Machine Based Classification of Leaf
Diseases”, International Journal of Science and
Engineering Applications, 2018.
Quan Huu Cap et al. “LeafGAN: An Effective Data
Augmentation Method for Practical Plant Disease
Diagnosis”. In: IEEE Transactions on Automation
Science and Engineering 19.2 (Apr. 2022). Conference
Name: IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and
Engineering, pp. 1258–1267. ISSN: 1558-3783.
S. M. Lundberg and S. I. Lee, “A unified approach to
interpreting model predictions,” Adv. Neural Inf.
Process. Syst., vol. 2017-Decem, no. Section 2, pp.
4766–4775, 2017
Uday Pratap Singh et al. “Multilayer Convolution Neural
Network for the Classification of Mango Leaves
Infected by Anthracnose Disease”. In: IEEE Access 7
(2019). Conference Name: IEEE Access, pp. 43721–
43729.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
744
