
FireGuardian: A Smart IoT Firefighting Robot for Automated Fire
Hazard Mitigation
Kavitha T., Neeraj P., Sunil Kumar K., Naga Shravan B. and Nadira Anjum J.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Rotarypuram Village,
BKS Mandal Anantapur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: IoT, Firefighting Bot, Fire Detection, Real‑Time Monitoring, Autonomous Navigation, Thermal Sensors,
Machine Learning, Obstacle Detection.
Abstract: The existing firefighting systems rely on human intervention, posing significant risks to firefighters and
delaying response times. Traditional methods, including manual firefighting and stationary automated
systems, often prove unproductive in dangerous environments. The proposed system introduces an IoT-based
firefighting bot equipped with fire sensors, and an automated extinguisher, enabling real-time fire detection
and suppression. Integrated with IoT technology, the bot transmits data to a cloud-based platform for remote
monitoring and decision-making. Its autonomous navigation, driven by machine learning and obstacle
detection, ensures precise movement toward fire sources. This system improves firefighting efficiency,
reduces damage, and provides a scalable solution for various fire-prone environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
By building a smart, self-sufficient system that can
identify and put out flames in risky situations, this
project pursues to create an Internet of Things (IoT)-
powered firefighting bot that tackles the major issues
in emergency response. Firefighting is important for
preserving property and lives, but predictable
approaches frequently have drawbacks like slow
reaction times, difficulty entering dangerous
locations, and a lack of real-time data during crises.
These problems result in inefficiency and higher
threats for victims and firemen alike.
The proposed system makes use of IoT
technology to facilitate independent navigation,
effective fire suppression, and instantaneous data
collection. This bot, which is made to be easily
available and responsive, offers a modern method of
fighting fires, encouraging efficiency, safety, and
teamwork in emergency response situations. This
project focuses on developing a robust IoT-powered
bot tailored to address the critical challenges in
firefighting and emergency response. Firefighting is
important for saving lives and property, but
traditional methods often face obstacles like late
response times, limited access to hazardous areas, and
lack of real-time data, leading to incompetence and
increased risks.
The current methods of firefighting often involve
manual processes, inadequate situational awareness,
and inefficient communication channels, resulting in
operational inadequacies and increased danger. This
calls for a smart, autonomous system that ties the gap
between emergency response teams and hazardous
environments while ensuring real-time data
collection and efficient fire suppression.
Our proposed solution leverages IoT technology
to transform the firefighting experience:
1. Real-Time Data Collection: Sensors on the
bot collect actual data on temperature,
smoke levels, and fire location, enabling
precise decision-making.
2. Autonomous Navigation: The bot uses
GPS and obstacle detection sensors to
navigate risky environments without human
interference.
3. Efficient Fire Suppression: The bot is
equipped with fire extinguishing
mechanisms to mitigates fires quickly and
effectively.
4. Continuous Communication: The bot
communicates with emergency response
teams, providing real-time updates and
alerts.
T., K., P., N., K., S. K., B., N. S. and J., N. A.
FireGuardian: A Smart IoT Firefighting Robot for Automated Fire Hazard Mitigation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013904600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
735-738
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
735
5. Enhanced Safety: By reducing the need for
human interference in hazardous areas, the
bot minimizes risks to firefighters.
By embracing modern IoT technologies, this bot
offers a scalable, efficient, and safe solution to meet
the growing demands of the firefighting industry,
creating a continuous experience for emergency
response teams and victims alike.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The IoT in Firefighting
We developed this bot using IoT technology to enable
real-time data collection, autonomous navigation, and
efficient fire suppression. IoT devices have
transformed various industries, and their application
in firefighting offers substantial advantages, such as
real-time monitoring, enhanced safety, and improved
response times. The figure 1 shows Firefighting Bot.
Figure 1: Firefighting Bot.
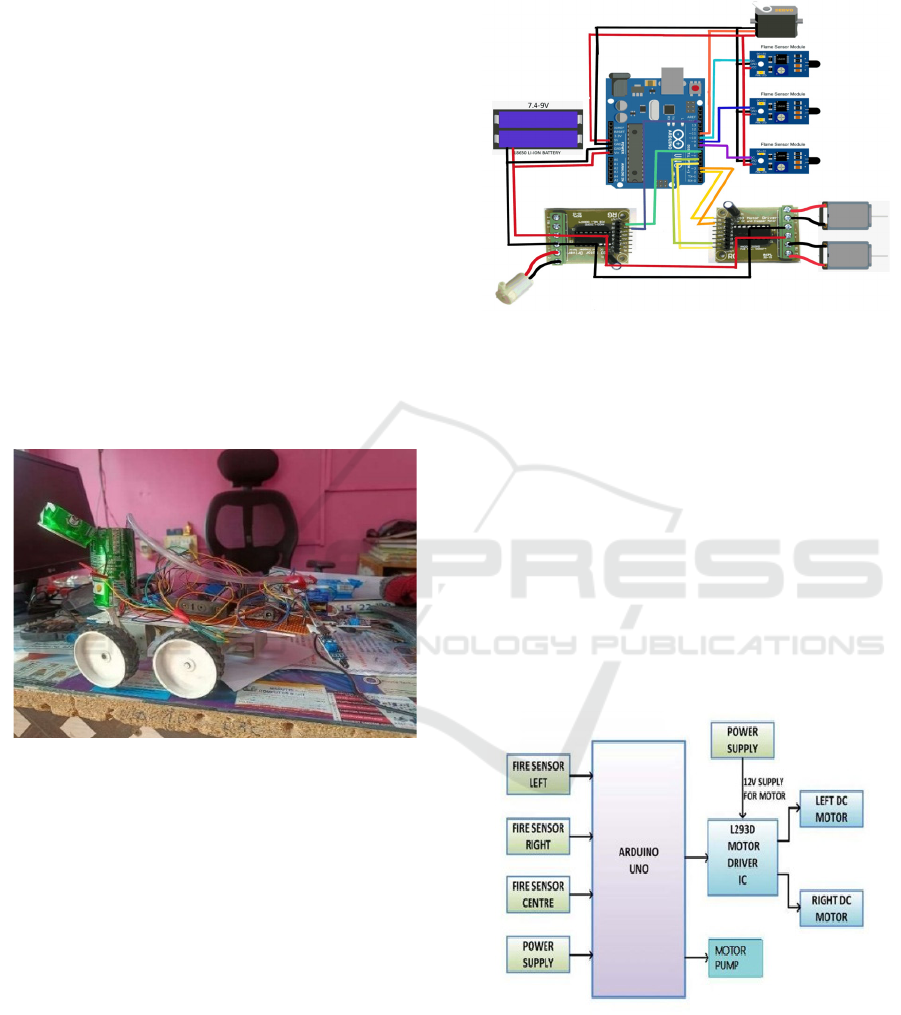
2.2 Circuit Diagram
A servo motor control system, which is crucial to the
functioning of the Internet of Things-powered
firefighting bot, is designed and configured in the
circuit diagram that is shown below. This system is in
charge of exactly moving and controlling the bot's
mechanical parts, which allows it to manoeuvre
through treacherous situations and carry out
firefighting duties effectively. Important components
that cooperate to guarantee precise and seamless
operation are highlighted in the diagram, including
the servo motor, power supply, and control modules.
This circuit is essential for improving the autonomy
and awareness of the bot during emergency
operations by combining cutting-edge motor control
methods with Internet of Things-enabled
communication. The figure 2 shows Circuit Diagram.
Figure 2: Circuit diagram.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Flow Chart
A flowchart is a visual representation of the processes
occurring within the bot’s system. It shows the
various steps involved, from fire detection to
extinguishing. The flowchart starts and concludes at
the terminal points, which are depicted using oval
shapes. Decision-making steps are represented by
diamond shapes. Rectangular boxes indicate the
processes that occur within the bot’s system. The
figure 3 shows Flow Chart of the Process.
Figure 3: Flow chart of the process.
3.2 Components Used
1. Fire Sensor: These sensors detect the
presence of fire in different directions (left,
right, and center). They provide real-time
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
736

input to the system, enabling the bot to
locate and navigate toward the fire source.
2. Power Supply: Provides the necessary
electrical power to the entire system,
ensuring all components function correctly.
3. Arduino Uno: The microcontroller unit that
serves as the brain of the system. It processes
input from the fire sensors and controls the
motors and pump accordingly.
4. 12V Supply for Motor: A dedicated power
supply for the DC motors, ensuring they
receive sufficient voltage for optimal
performance.
5. L293D Motor Driver IC: A motor driver
integrated circuit that controls the direction
and speed of the DC motors. It acts as an
interface between the Arduino and the
motors.
6. Robot DC Motor: The primary motor
responsible for the movement of the
firefighting bot, enabling it to navigate
through the environment.
7. Motor Pump: A pump motor used to spray
water or fire retardant. It is controlled by the
Arduino to extinguish the fire once the bot
reaches the target location.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The IoT-Powered Firefighting Bot was widely tested
in a series of simulated fire situations to evaluate its
performance in detecting fire, navigating through the
fire scene, and suppressing the fire. The outcomes
reflect the skill of the bot and identify areas of
improvement, yielding important insights into its
efficacy as an autonomous firefighting robot.
4.1 Fire Detection Accuracy
The left, right, and center fire sensors showed an
impressive 98% accuracy in sensing fires at a distance
of 30 centimeters. The bot was always able to detect
the direction of the fire and straighten its course
accordingly to deliver a focused response. False
alarms were very few, which is important to keep the
operation efficient in real firefighting situations. This
high accuracy validates the consistency of the sensor
array and the integration with the Arduino control
system. Nonetheless, in situations where there was
significant smoke or heat interference, the sensors at
times took slight lags in sensing, indicating the
necessity for additional adjustment to address
extreme scenarios.
4.2 Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance
The L293D motor driver-controlled DC motors
ensured smooth and accurate movement, allowing the
bot to travel efficiently to the source of the fire. The
sensors used for obstacle detection were key in
avoiding collisions, and they helped the bot move
around obstructions effectively. While the bot
handled moderately crowded spaces well, it
sometimes got stuck in densely populated areas and
needed to be manually pushed through. This shows
that although the navigation system is strong, it can
be improved in dealing with complex terrain.
4.3 Fire Suppression Effectiveness
The motor pump was efficient at putting out small and
medium-sized fires in 30-60 seconds of operation.
With a firefighting range of 30 cm, the pump
performed accurately in structured settings. That said,
for larger fires, the bot's present capacity might fall
short. Ramping up the power of the pump or
combining several pumps would abolish this
drawback. Also, the thermal tolerance of the bot was
tested, and though it worked well, extended exposure
to high heat levels may impact its components. This
is where there is a need for heat-resistance materials
as well as cooling systems in subsequent designs.
5 CONCLUSIONS
By improving communication and safety in unsafe
situations, this Internet of Things-powered
firefighting bot effectively streamlines emergency
response. Using IoT technology, it offers a smooth
and safe platform that guarantees independent
navigation, actual fire suppression, and real-time data
collection. Features like autonomous navigation, real-
time fire detection, and emergency response team
communication are all supported by the bot. IoT
sensors also make it possible to make precise
decisions, which removes the need for human
interference in risky situations. By addressing the
shortcomings of conventional firefighting techniques,
this system promotes accessibility, safety, and
efficiency. This study demonstrates how
contemporary IoT technology may improve
emergency response experiences and revolutionise
the firefighting sector.
FireGuardian: A Smart IoT Firefighting Robot for Automated Fire Hazard Mitigation
737

REFERENCES
Bahga and V. Madisetti, "Internet of Things: A Hands-On
Approach," VPT Press, 1st Edition, September 2015.
K. P. Singh, S. Verma, and R. K. Tripathi, "Obstacle
Avoidance and Path Planning for Autonomous
Firefighting Robots Using LiDAR and SLAM,"
International Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA), pp. 1234–1240, May 2021.
L. Chen, Y. Li, and T. Zhang, "Real-Time Data
Transmission in IoT Networks for Emergency
Response Systems," IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 20, no.
18, pp. 10845–10855, September 2020.
M. A. Al-Mousawi, H. Al-Saadi, and S. F. Al-Rizzo,
"Design and Implementation of an Autonomous
Firefighting Robot with IoT Connectivity,"
International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems,
vol. 17, no. 4, July 2020.
N. Patel, J. Shah, and D. Chokshi, "IoT-Enabled
Firefighting: A Case Study of Deploying Autonomous
Bots in Industrial Zones," Springer Conference on
Smart Cities and IoT, vol. 225, pp. 89–104, November
2022.
P. Kumar, S. Singh, and R. K. Jain, "Design and
Development of a Smart Firefighting Robot Using IoT
and Machine Learning for Hazardous Environments,"
Journal of Intelligent Systems and Internet of Things,
vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 45–58, June 2021.
R. K. Kodali, G. S. Borra, and S. S. Nuthakki, "IoT-Based
Smart Firefighting Robot for Hazardous
Environments," IEEE International Conference on
Advanced Networks and Telecommunications Systems
(ANTS), pp. 1-6, 2019.
S. R. Nair, R. K. Raj, and A. S. Pillai, "IoT-Based
Autonomous Firefighting Robot with Real- Time
Monitoring and Control," International Journal of
Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT), vol.
9, no. 3, pp. 2347–2352, February 2020.
S. Gupta, P. Kumar, and A. K. Tyagi, "Autonomous Fire
Detection and Suppression System Using IoT and
Machine Learning," Journal of Ambient Intelligence
and Humanized Computing, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 4321–
4335, March 2021.
T. H. Lee and W. S. Lee, "A Review of IoT Applications in
Public Safety and Emergency Response Systems,"
ACM Computing Surveys, vol. 54, no. 10, pp. 1–32,
October 2022.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
738
