
IoT Based Autonomous Solution for the Maintenance of Public Toilet
A. Joyce, V. Sharmili, S. Shivani and J. Malathika
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, PSNA College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul, Tamil Nadu,
India
Keywords: Autocleaning, Monitors, Environmental Condition, Control System, Optimizing Water Usage, Hygiene
System.
Abstract: Automated restroom system integrates IoT for water control and real-time occupancy detection to optimize
resource usage efficiently. The system uses ultrasonic sensors for person detection and Ammonia sensors for
detecting bad odors in restrooms. Water motor activates automatically when ultrasonic sensor detects a
person, ensuring timely and efficient cleaning of the restroom. Fog maker dispenses sanitizing mist when
hands are placed under it, enhancing hygiene and reducing manual intervention. LCD and IoT enable real-
time monitoring of restroom conditions, providing data for efficient management and maintenance. UV light
is incorporated for germ cleaning, ensuring a hygienic environment by eliminating harmful microorganisms
in the restroom.
1 INTRODUCTION
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in
automated restroom systems has significantly
improved hygiene, resource management, and user
convenience.
The absence of proper sanitation facilities
increases the spread of bacterial and viral infections
such as diarrhea, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and
skin diseases. heavy odor, it creates multiple
problems like headaches, nausea, and respiratory
discomfort. Environmental issues in public toilets
stem from excessive water wastage due to leaking
taps and inefficient flushing systems.
Traditional restroom maintenance relies on
periodic cleaning schedules and manual intervention,
often leading to inefficiencies in water usage, hygiene
maintenance, and real-time monitoring. The
development of smart restroom systems aims to
address these challenges by incorporating advanced
sensors and automation techniques to enhance
efficiency and cleanliness. By utilizing IoT, these
systems ensure optimal resource utilization while
reducing the dependency on human effort for
maintenance and monitoring.
A key component of the automated restroom
system is real-time occupancy detection, which plays
a crucial role in optimizing water and energy
consumption. The system employs ultrasonic sensors
to detect human presence and trigger necessary
actions such as water flow control and sanitation
processes. This feature ensures that water is used only
when required, minimizing wastage while
maintaining a clean and hygienic restroom
environment. Additionally, an MQ6 gas sensor is
integrated to detect unpleasant odors, allowing
immediate corrective actions, such as activating
ventilation or air-purification systems, to maintain
fresh restroom conditions.
To further enhance hygiene, the system includes a
fog maker that dispenses a sanitizing mist when hands
are placed under it. This eliminates the need for
physical contact with sanitation devices, reducing the
risk of germ transmission. Moreover, an ultraviolet
(UV) light sterilization mechanism is incorporated to
disinfect restroom surfaces, effectively eliminating
harmful microorganisms. These features work
collectively to ensure a safer restroom environment,
particularly in high-traffic public spaces where
maintaining hygiene is crucial to preventing the
spread of infections.
Real-time monitoring and data analytics further
enhance the efficiency of automated restrooms. An
LCD display and IoT connectivity enable facility
managers to track restroom conditions remotely,
allowing timely intervention and maintenance. By
Joyce, A., Sharmili, V., Shivani, S. and Malathika, J.
IoT Based Autonomous Solution for the Maintenance of Public Toilet.
DOI: 10.5220/0013904500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
729-734
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
729

leveraging IoT-driven automation, these smart
restroom systems not only promote hygiene but also
contribute to sustainability by conserving water and
reducing excessive cleaning resource consumption.
With continuous advancements in sensor technology
and automation, the implementation of such
intelligent restroom systems is expected to become
increasingly widespread, revolutionizing restroom
management across various sectors, including public
facilities, corporate spaces, and healthcare
institutions.
2 RELATED WORKS
Explores the use of IoT-enabled smart toilets for
elderly care, enabling health monitoring at home,
particularly for infection tracking (K. Dheeraj, S. S.
Kumar, and K. R. Singh). Smart restroom monitoring
system for residential colleges, using IoT sensors to
track restroom conditions and send alerts for
maintenance, ensuring hygiene and user satisfaction
(J. Smith, A. Brown, and L. Taylor).
Sensors monitor cleanliness and usage, alerting
maintenance teams in real time via an IoT-enabled
system aimed at maintaining public toilets in smart
cities, reducing the risk of disease transmission
(Wang Yunhe and Wang Bingbing). Smart public
toilets within the context of a smart city, aiming for
efficiency and sustainability (QIN Doudou, GUO
Kairui, LI Yuhao et al.).
Focuses on how IoT can be applied in the design
of public toilets, optimizing hygiene, maintenance,
and user convenience (M. Patel and R. Sharma).
Smart washroom cleaning system using hub
technology to streamline cleaning operations. Sensors
detect usage patterns and cleanliness levels,
triggering alerts for cleaning staff, improving hygiene
efficiency (Nayana B. Chide and Nilesh P. Bobad).
Smart toilet capable of analyzing excreta for real-
time, personalized health monitoring. Highlights its
potential in early disease detection through non-
invasive methods (Seung-min Park, Daeyoun Won,
Jung Ho Yu, Sanjiv Gambhir, Brian Lee, Andre
Esteva, et al.). IoT-enabled smart washrooms,
focusing on user convenience, water conservation,
and maintenance optimization (R. Sujeetha, D.
Abhinav, R. Rithik, and S. Abishek).
Toilet system for monitoring health by analyzing
excreta, offering personalized health feedback
(Cristina Balaceanu, Ioana Marcu, George Suciu,
Carina Dantas, and Peter Mayer). Washrooms in
general and lacks integration with advanced
healthcare or personalized services (K. Nakamura, S.
Takahashi, and Y. Honda).
IoT-based toilet management system,
emphasizing automated maintenance and real-time
monitoring to ensure cleanliness and efficiency (R.
Gupta, S. Mehta, and V. Deshmukh). Smart toilet
system designed for elderly individuals and people
with disabilities, emphasizing usability, health
monitoring, and enhanced accessibility (D. Lopez and
J. Garcia).
IoT sensors to detect human presence in smart
toilets. It discusses potential improvements and
strategies to enhance sensor accuracy and reliability
(F. Rossi, L. Bianchi, and P. Conti). Smart toilet
system for optimizing resource usage like water and
energy. Sensors collect usage data to help manage
resources more efficiently (C. Lee and M. Park).
Public toilets as either potential health facilitators
or pathogen transmitters, emphasizing design and
hygiene management for public health (Clara Greed).
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
Existing research on IoT-enabled smart toilets has
significantly evolved, focusing on hygiene,
maintenance, health monitoring, and resource
optimization. Early studies examined public toilets as
potential health facilitators or pathogen transmitters,
emphasizing hygiene management and design
considerations. With technological advancements,
IoT integration became a key focus, leading to the
development of smart toilet systems that optimize
resource usage, such as water and energy, through
sensor-driven data collection.
Research has also introduced IoT-based toilet
management systems aimed at automated
maintenance and real-time cleanliness monitoring,
ensuring efficient restroom operations. Additionally,
studies have explored the challenges of using IoT
sensors for human presence detection in smart toilets,
highlighting concerns related to accuracy and
security.
In recent years, smart toilets have been
increasingly explored for healthcare applications.
Some advancements in this field have introduced
smart toilets capable of analyzing excreta for real-
time, personalized health monitoring, with potential
applications in early disease detection. Similarly,
research has focused on the use of IoT-enabled smart
toilets for elderly care, particularly in infection
tracking, allowing health monitoring at home.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
730
Other studies have proposed smart restroom
monitoring systems for residential colleges to ensure
cleanliness and user satisfaction. Additionally, IoT-
enabled systems have been developed to maintain
public toilets in smart cities, reducing disease
transmission risks. These studies highlight the
growing integration of IoT in sanitation and
healthcare, paving the way for future innovations in
smart toilet technology.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system integrates IoT for real-time
monitoring and control, optimizing water usage and
improving restroom hygiene. Ultrasonic sensors
detect human presence and Water level from tank,
triggering automated cleaning mechanisms like water
motors to ensure timely restroom maintenance.MQ6
sensors monitor air quality, detecting bad odors and
initiating cleaning processes to maintain a pleasant
restroom environment with Spryer. Fog makers
dispense sanitizing mist when hands are placed under
them, enhancing hygiene and reducing the spread of
germs. LCD and IoT enable real-time monitoring of
restroom conditions, providing data for efficient
management and maintenance. UV lights are
integrated for germ cleaning, ensuring a sanitized
restroom environment by eliminating harmful
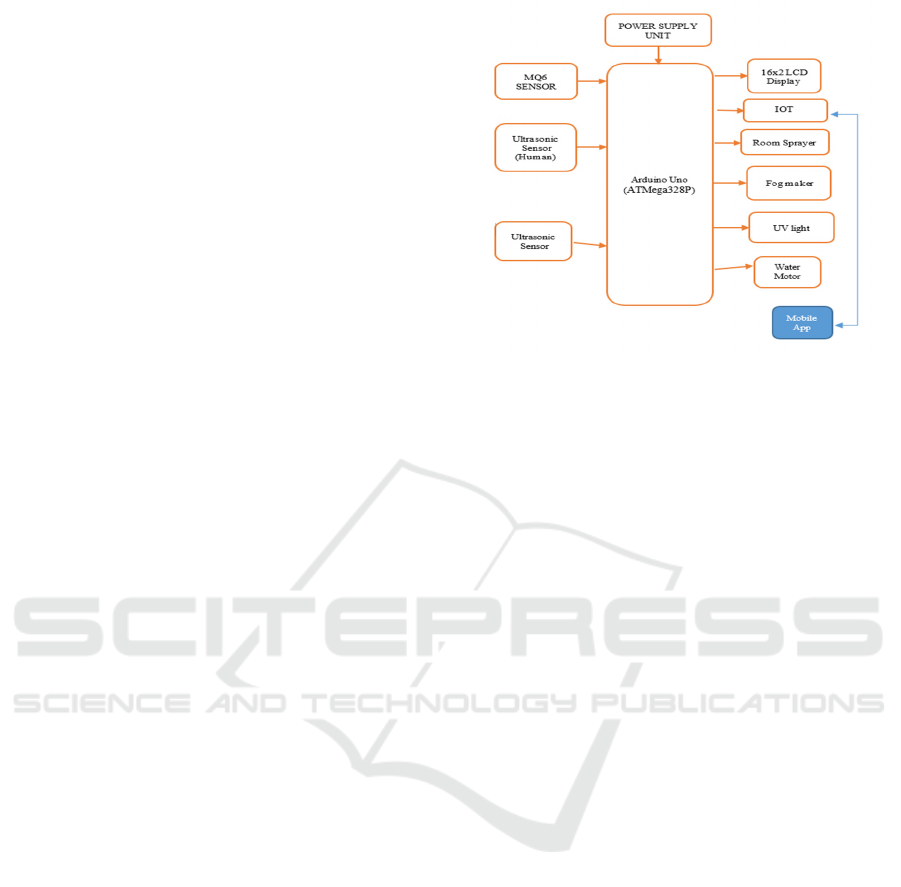
microorganisms effectively. Figure 1 shows the
IoT-
Based Smart Sanitization and Environmental Monitoring
System Using Arduino.
• User Detection & Monitoring Module
• Air Quality & Odor Detection Module
• Automated Cleaning & Water Management
Module
• Sanitization & Hygiene Enhancement
Module
• IoT-Based Remote Monitoring & Control
Module
• Power Supply & Connectivity Module
Figure 1: IoT-based smart sanitization and environmental
monitoring system using Arduino.
UNO (ATMega328P) – Acts as the main Arduino
controller, processing sensor inputs and controlling
output devices such as the water motor, fog maker,
and display.
NodeMCU (ESP8266) – Provides Wi-Fi
connectivity for remote monitoring and control,
allowing users to access data or send commands
wirelessly.
Water Motor – Operates based on sensor readings,
turning on or off to regulate water flow as needed,
controlled by the Arduino.
Fog Maker – Uses ultrasonic vibrations to convert
water into mist, controlled by the microcontroller for
humidity control or visual effects.
16x2 LCD – Displays real-time sensor readings,
system status, or any necessary information processed
by the Arduino.
UV Light – Turns on for sterilization or specific
applications, controlled via relays or transistors based
on programmed conditions.
MQ6 Sensor – Continuously detects gas leaks (LPG,
propane, butane) and sends signals to the Arduino,
which can trigger alerts or safety actions.
Ultrasonic Sensor – Measures distances or levels by
emitting ultrasonic waves and detecting reflections,
useful for obstacle detection or liquid level
monitoring.
Power Supply Unit – Provides regulated power to all
components, ensuring stable operation of
microcontrollers, sensors, and output devices.
Jumper Wires – Facilitate electrical connections
between components, enabling communication and
power distribution within the system.
IoT Based Autonomous Solution for the Maintenance of Public Toilet
731
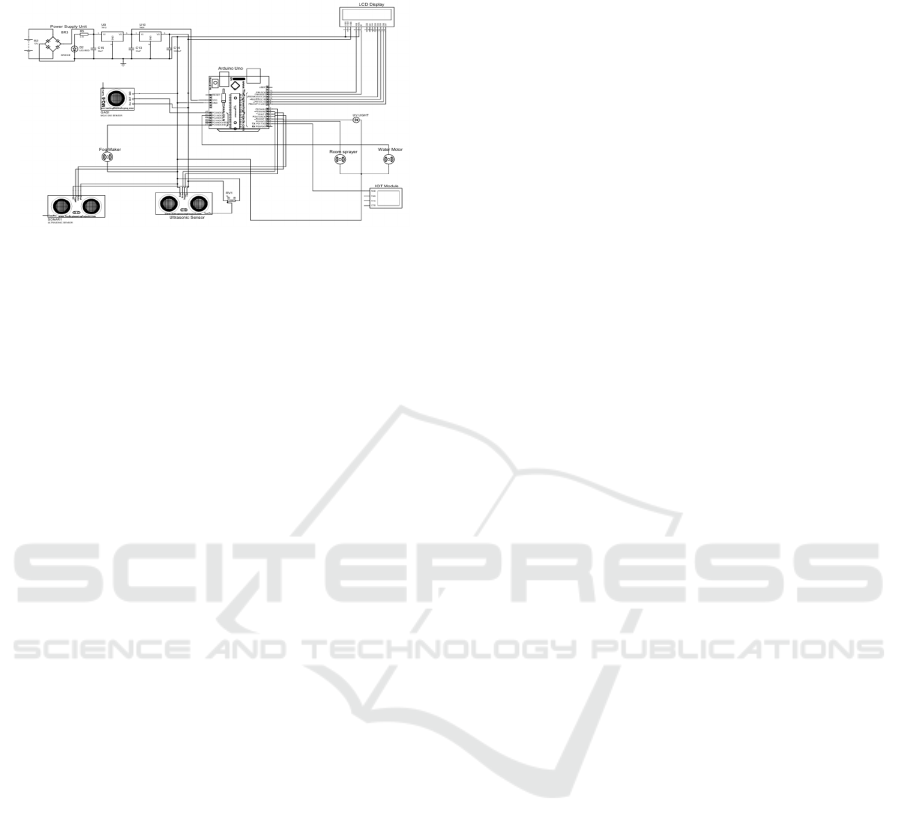
5 IMPLEMENTATIONS
Figure 2: Smart waste management system using Arduino
and IoT.
Figure 2 gives the smart waste management system
using Arduino and IoT.
These are the algorithms we are using in this process.
• Event-Driven Algorithm: The system
continuously listens for inputs from ultrasonic
sensors (person detection), MQ6 sensors (odor
detection), and hand detection for the fog maker.
Whenever an event (sensor trigger) occurs,
corresponding actions (water motor activation,
sanitation, etc.) are executed.
• State Machine Algorithm: The system
transitions between different states (Idle,
Occupied, Cleaning, Ventilation, Disinfection)
based on sensor data.
• Loop-Based Control Algorithm: A continuous
loop runs to check sensor inputs and update
restroom conditions in real-time, ensuring
efficient monitoring.
• IoT-Based Monitoring Algorithm: Data from
sensors is sent to an IoT dashboard, enabling
remote tracking and maintenance alerts.
5.1 User Detection & Monitoring
Utilizes ultrasonic sensors to detect human presence
in the restroom. Activates water motor only when a
user is detected, reducing water wastage. Tracks
water level in the storage tank to ensure optimal water
availability.
• Air Quality & Odor Detection
Uses MQ6 gas sensors to detect bad Odors and
monitor air quality. Triggers automatic cleaning
mechanisms when Odor levels exceed a
threshold. Ensures a pleasant restroom
environment by eliminating foul smells
efficiently.
• Automated Cleaning & Water Management
Controls water motor to spray and clean surfaces
based on sensor inputs. Reduces manual
intervention and ensures consistent hygiene
levels. Monitors and optimizes water usage,
preventing unnecessary wastage.
• Sanitization & Hygiene Enhancement
Integrates fog makers to dispense sanitizing mist
when a user places hands under them. UV light
system eliminates harmful microorganisms,
ensuring germ-free restrooms. Enhances user
hygiene and reduces the risk of infections.
• IoT-Based Remote Monitoring & Control
Utilizes NodeMCU (ESP8266) for cloud-based
real-time monitoring of restroom conditions.
Displays restroom status and sensor data on an
LCD screen. Sends data to Arduino IoT Cloud
for remote management and maintenance alerts.
• Power Supply & Connectivity
Ensures uninterrupted power for components
like Arduino UNO, sensors, and actuators. Uses
jumper wires for connectivity between hardware
components. Manages power distribution to
optimize energy efficiency.
6 SAMPLE OUTPUT
The system comprises an Arduino-based smart safety
circuit integrating IR, ultrasonic, and gas sensors for
real-time environmental monitoring. As shown in
Figure 3, the sensors detect obstacles, distance, and
toxic gases, with data processed by Arduino to trigger
appropriate actions like exhaust fan activation. In
Figure 4, the circuit identifies motion and hazardous
gas presence, displaying alerts on the LCD and
activating safety mechanisms through relays. Figure
5 highlights the regulated power supply and relay-
driven control for managing detected risks. Together,
these configurations ensure a responsive and
automated safety solution for hazardous
environments.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
732
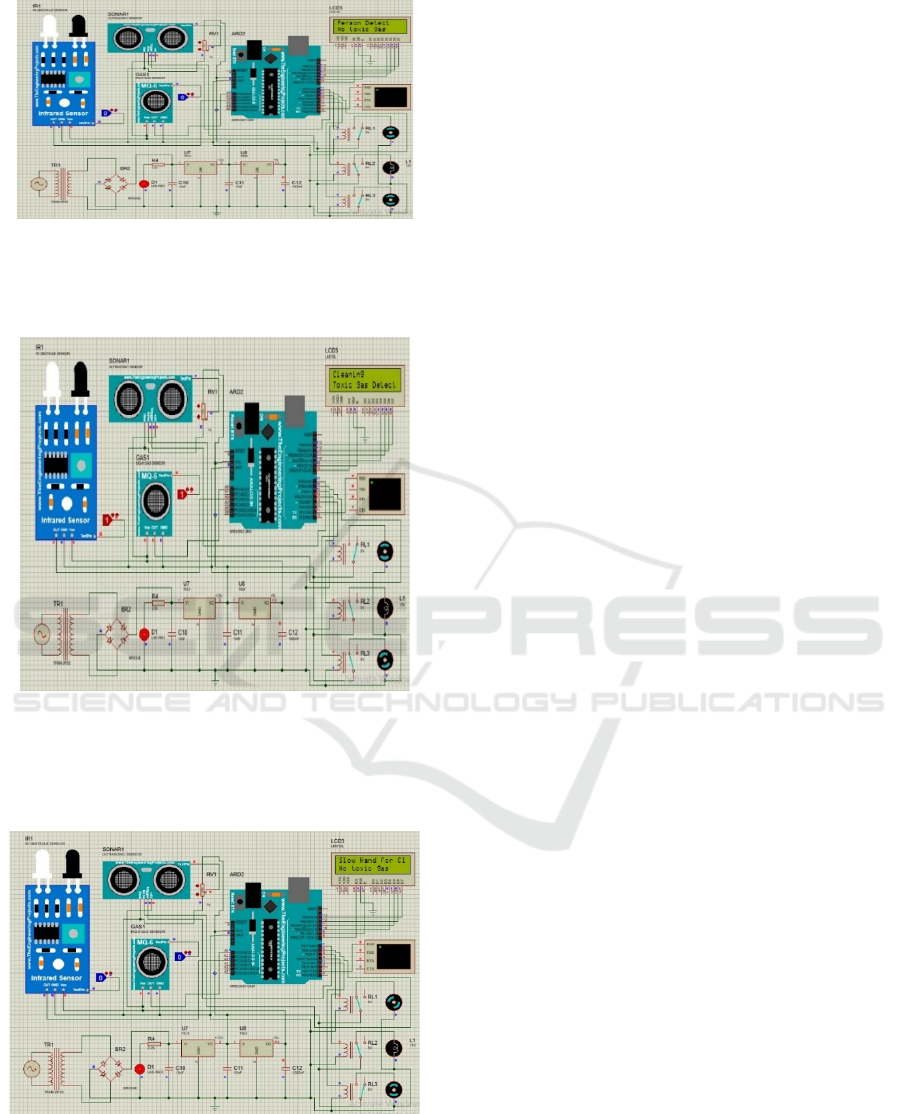
Figure 3: Sensor (IR, Ultrasonic, gas) detect obstacles,
distance, and toxic gases, sending data to Arduino. Arduino
processes signal, display status on LCD, activates relays to
trigger exhaust fan or alert system.
Figure 4: Sensor detect obstacle, motion and gas level,
sending data to Arduino which processes and display status
on LCD. Based on the input, Arduino activates relays to
trigger alarm or exhaust system for safety.
Figure 5: This circuit use Arduino to monitor gas, distance
and obstacles via sensor, displaying status on an LCD and
control devices through relays a regulated power supply to
the entire system.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The automated restroom system optimizes water
usage and improves hygiene through IoT-enabled
real-time monitoring and control. Ultrasonic sensors
ensure accurate person detection, triggering
automated cleaning mechanisms and reducing
manual intervention in restrooms.MQ6 sensors detect
bad odors, initiating cleaning processes to maintain a
pleasant and hygienic restroom environment. Fog
makers enhance hygiene by dispensing sanitizing
mist, reducing the spread of germs and improving
user convenience. LCD and IoT enable real-time
monitoring of restroom conditions, providing data for
efficient management and maintenance. UV lights
ensure germ-free restrooms by eliminating harmful
microorganisms, providing a sanitized environment
for users.
REFERENCES
C. Lee and M. Park, "IoT-Enabled Smart Toilet Cleaning
and Maintenance System for Urban Areas," Smart City
Technologies Journal, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 25-30, 2016.
Clara Greed, "The role of the public toilet: Pathogen trans-
mitter or health facilitator?", Building Services Engi-
neering Research Technology - build serving res tech-
nol., vol. 27, pp. 127-139, 2006.
Cristina Balaceanu, Ioana Marcu, George Suciu, Carina
Dantas and Peter Mayer, Developing a Smart Toilet
System for ageing people and persons with disabilities,
pp. 1-4, 2019.
D. Lopez and J. Garcia, "Public Toilet Waste Management
and Hygiene Improvement Strategies Using IoT," Ur-
ban Sanitation Research Journal, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 35-
42, 2018.
F. Rossi, L. Bianchi, and P. Conti, "Enhancing Public Re-
stroom Sanitation with Smart Maintenance Technolo-
gies," Hygiene and Public Health Review, vol. 12, pp.
77-85, 2017.
J. Smith, A. Brown, and L. Taylor, "IoT-Based Smart Re-
stroom Monitoring System for Public Hygiene
Management," International Journal of Smart Cities
and Infrastructure, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 45-52, 2022.
K Dheeraj, S S Kumar and KR Singh, "Empowering elderly
care with intelligent IoT-Driven smart toilets for home-
based infectious health monitoring [J]", Artificial Intel-
ligence in Medicine, pp. 144102666102666, 2023.
K. Nakamura, S. Takahashi, and Y. Honda, "A Sensor-
Based Smart Public Toilet System for Real-Time
Cleanliness and Maintenance," IEEE Transactions on
Smart Infrastructure, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 67-75, 2019.
IoT Based Autonomous Solution for the Maintenance of Public Toilet
733

L. Zhang, X. Wang, and H. Chen, "Automated Cleaning So-
lutions for Public Toilets: A Technological Perspec-
tive," Building Maintenance and Hygiene Science, vol.
9, pp. 54-61, 2015.
M. Patel and R. Sharma, "Automated Public Toilet
Cleaning System Using IoT Sensors," Journal of
Environmental Health and Sanitation, vol. 15, no. 4, pp.
89-95, 2021.
Nayana B. Chide and Nilesh P. Bobad, "Review: IoT based
Smart Washroom", International Research Journal of
Engineering and Technology (IRJET), vol. 07, no. 01,
Jan 2020.
P. Roberts and G. Williams, "Public Restroom
Maintenance: Challenges and Innovations," Journal of
Urban Hygiene and Sanitation, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 12-18,
2014.
QIN Doudou, GUO Kairui, LI Yuhao et al., "Design of in-
telligent public toilets based on internet of things tech-
nology[J]", Electronic Technology and Software Engi-
neering, no. 15, pp. 25-26, 2021.
R. Gupta, S. Mehta, and V. Deshmukh, "AI-Driven Predic-
tive Maintenance for Public Restroom Hygiene," Inter-
national Conference on Smart Sanitation Systems Pro-
ceedings, pp. 150-155, 2019.
R. Sujeetha, D Abhinav, R Rithik and S Abishek, "Toilet
Management System Using IoT", international journal
of scientific technology research, vol. 8, no. 12, decem-
ber 2019, issn 2277-8616.
Seung-min Park, Daeyoun Won, Jung Ho Yu, Sanjiv Gam-
bhir, Brian Lee, Andre Esteva, et al., "A mountable
toilet system for personalized health monitoring via the
analysis of excreta", Nature Biomedical Engineering,
2020.
T. Chen, H. Wu, and Z. Li, "Sustainable Public Toilet
Maintenance Through IoT-Based Resource Optimiza-
tion," Smart Cities and Sustainable Development, no.
07, pp. 102-110, 2020.
Wang Yunhe and wang Bingbing, "Exploration of smart
public toilet design under the vision of smart city[J]",
Intelligent Building and Smart City, no. 01, pp. 96-98,
2021.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
734
