
YOLOv7s Optimization for Road Defect Detection: Pruning, Pooling
and Attention Mechanisms
Ediga Nidiganti Rishika Thanmai, Boya Shireesha, Usha Sree Jagaragallu,
Gunereddy Bhavitha Reddy and Maddireddy Vinnetha Shree
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh,
India
Keywords: YOLOv7s, Road Defect Detection, Deep Learning, Pruning, Spatial Pyramid Pooling, Adaptive Pooling,
Attention Mechanism, CBAM, Real‑Time Detection, Smart Transportation, Autonomous Vehicles, IoT,
Computer Vision, Model Optimization, Infrastructure Monitoring.
Abstract: Road defect detection is crucial for ensuring traffic safety and efficient infrastructure maintenance. This report
presents an optimized YOLOv7-based road defect detection system, integrating pruning, pooling, and
attention mechanisms to enhance accuracy, reduce computational complexity, and improve real-time
performance. Pruning techniques eliminate redundant parameters, accelerating inference speed to maintain
detection accuracy. Pooling strategies, including Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) and Adaptive Pooling,
enhance multi-scale feature extraction, enabling the model to detect defects of various shapes and textures.
Additionally, attention mechanisms such as the Convolutional Block Attention Module refine feature
selection, focusing on critical defect regions and reducing false positives. Experimental results demonstrate
that the proposed optimizations significantly improve precision, recall, and mean average precision (mAP) on
benchmark datasets while minimizing computational overhead. The enhanced YOLOv7 model is lightweight
and efficient, making it ideal for real-time road monitoring applications, smart city infrastructure, and
autonomous vehicle systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Road infrastructure plays a key role in transportation
and economic development. However, poor road
conditions, such as cracks, potholes, and surface
deformations, can lead to accidents, increased vehicle
maintenance costs, and inefficient transportation
systems. Traditional road inspection methods rely on
manual surveys, are labor-intensive, time-taking, and
prone to human error. The emergence of computer
vision and deep learning techniques has enabled the
automation of road defect detection, significantly
improving accuracy and efficiency.
You Only Look Once is one of the most widely
used object detection frameworks due to its ability to
perform real-time detection with high accuracy. The
latest version, YOLOv7, introduces several
improvements in feature extraction, detection
precision, and computational efficiency. However,
detecting road defects remains challenging due to
varying defect sizes, complex textures, lighting
conditions, and environmental factors. To address
these challenges, optimizing YOLOv7 with
techniques such as pruning, pooling, and attention
mechanisms can enhance detection performance
while maintaining efficiency.
Pruning reduces the computational burden by
removing unnecessary parameters, improving
inference speed without compromising accuracy.
Pooling techniques, such as Spatial Pyramid Pooling
and Adaptive Pooling, allow the model to effectively
recognize road defects across different scales and
textures. Additionally, attention mechanisms like the
Convolutional Block Attention Module enable the
model to focus on critical defect regions, reducing
false positives and improving classification
performance.
This paper explores the impact of pruning,
pooling, and attention mechanisms on YOLOv7's
performance in road defect detection. The proposed
approach is evaluated on benchmark datasets,
demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing
detection accuracy while maintaining real- time
processing capabilities.
Thanmai, E. N. R., Shireesha, B., Jagaragallu, U. S., Reddy, G. B. and Shree, M. V.
YOLOv7s Optimization for Road Defect Detection: Pruning, Pooling and Attention Mechanisms.
DOI: 10.5220/0013904200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
707-712
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
707

2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1 Research Area
To develop an optimized YOLOv5s model for road
defect detection, we employed a structured
methodology that includes data collection,
preprocessing, model optimization, training, and
evaluation. The primary goal is to enhance the
performance of YOLOv5s using pruning, pooling,
and attention mechanisms while ensuring real- time
efficiency. This methodology ensures a systematic
approach to achieving high- accuracy defect detection
with reduced computational complexity.
2.1.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
The first step in the research involved collecting a
diverse dataset of road defects, including potholes,
cracks, ruts, and surface irregularities. Publicly
available road defect datasets, such as the
CRACK500 and Road Damage Detection Dataset
(RDD), were utilized.
2.1.2 Model Optimization: Pruning, Pooling,
and Attention Mechanisms
To improve the efficiency of YOLOv7s, we applied
three key optimization techniques. Pruning was used
to remove redundant parameters, reducing model size
and enhancing inference speed. Pooling layers were
integrated to improve feature extraction by capturing
essential details at multiple scales.
2.1.3 Model Training and Hyperparameter
Tuning
The optimized YOLOv5s model was trained using
transfer learning with pre-trained weights from the
COCO dataset. Training was conducted on high-
performance GPUs using a learning rate scheduler,
adaptive momentum optimization, and focal loss
function to handle class imbalance in defect
detection. Hyperparameters such as batch size,
learning rate, and IoU threshold were fine-tuned to
maximize detection performance.
2.1.4 Evaluation Metrics and Performance
Analysis
To measure the effectiveness of the optimized model,
performance was evaluated using precision, recall,
mean average precision, and inference speed (FPS).
Themodel was tested on real-world road images and
benchmark datasets to ensure generalization.
Comparative analysis was performed against existing
state-of-the-art road defect detection models to
highlight improvements in accuracy and efficiency.
2.1.5 Deployment and Real-Time
Implementation
After training and evaluation, the optimized model
was deployed in a real-time road monitoring system.
Edge devices, such as NVIDIA Jetson Nano and
Raspberry Pi, were used to test inference speed and
practical usability. The model was integrated into an
IoT-based road monitoring framework, where
detected defects were logged in a cloud-based system
for analysis and maintenance scheduling. This real-
time implementation validated the model’s efficiency
in detecting road defects with minimal computational
resources, making it suitable for large-scale
deployment in smart city infrastructure.
2.2 Research Area
2.2.1 Road Infrastructure and Maintenance
Road maintenance is a crucial aspect of transportation
safety and efficiency. Detecting road defects early
helps prevent accidents, reduces vehicle maintenance
costs, and ensures longer infrastructure lifespan. This
research contributes to improving automated road
inspection, reducing manual effort and associated
costs.
2.2.2 Deep Learning and Computer Vision
The integration of deep learning and computer vision
in road defect detection has significantly enhanced
detection accuracy and efficiency. This research
focuses on optimizing YOLOv7s, a state-of-the-art
object detection model, by incorporating techniques
such
as
pruning,
pooling,
and attention
mechanisms. These enhancements improve feature
extraction and model efficiency, making deep
learning-based road monitoring systems more
reliable.
2.2.3 IoT-Based Smart Transportation
Systems
Modern transportation systems are increasingly
adopting IoT-based monitoring solutions. This study
explores how the optimized YOLOv7s model can be
deployed on edge devices to enable real-time road
defect detection. By integrating IoT with computer
vision, road authorities can receive instant alerts about
road conditions, allowing timely interventions and
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
708

efficient resource allocation.
2.2.4 Autonomous Vehicles and Intelligent
Transport
Autonomous vehicles require real-time road
condition analysis to ensure safe navigation. Road
defects such as potholes and cracks can affect vehicle
stability and passenger safety.
2.2.5 Sustainable Urban Development
Smart city initiatives focus on using AI and
automation to improve urban infrastructure.
Automated road defect detection aligns with
sustainable urban development goals, reducing road
maintenance costs, enhancing public safety, and
optimizing city planning. This research provides a
foundation for integrating intelligent monitoring
systems into smart city frameworks, making urban
roads safer and more efficient.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
1. Traditional Road Defect Detection:
Approaches Early road defect detection
systems relied on manual inspections and
sensor-based techniques. Chen et al. (2015)
used ultrasonic and laser-based systems to
identify
cracks
and
potholes,
but
these
methods were costly and required frequent
calibration.
2. Deep Learning-Based Approaches for Road
Defect Detection: The introduction of
YOLOv4 and YOLOv5 further improved real-
time road defect detection. Liu et al. (2021)
proposed a YOLOv5-based model with
improved anchor box selection for crack and
pothole detection. However, standard
YOLOv5 models still have limitations in
detecting small or low- contrast defects,
leading to the need for further optimization.
3. Optimization Techniques for YOLO- Based
Models To enhance the efficiency and
accuracy of object detection models, several
optimization techniques have been explored.
Pruning is widely used to reduce model
complexity and computational cost. Pooling
techniques have also been employed to
enhance feature extraction. Gao et al. (2019)
explored Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) for
multi-scale feature representation, improving
defect detection in varying lighting conditions.
He et al. (2020) demonstrated the effectiveness
of adaptive pooling in handling road surface
variations.
4. Attention Mechanisms for Improved Feature
Extraction: Attention mechanisms have
significantly enhanced deep learning models
by focusing on relevant regions in an image.
Woo et al. (2018) introduced the
Convolutional Block Attention Module
(CBAM), which applies both channel and
spatial attention to improve feature selection.
5. Summary and Research Gap: Existing
research has demonstrated the effectiveness
of deep learning models, particularly YOLO-
based architectures, for road defect detection.
However, challenges remain in model
efficiency, real-time performance, and small
defect detection accuracy. While pruning,
pooling, and attention mechanisms have been
explored individually, a comprehensive
integration of all three techniques in
YOLOv5s for road defect detection has not
been extensively studied.
4 EXISTING SYSTEM
Road defect detection has evolved significantly over
the years, with various systems being developed to
identify and classify road surface anomalies such as
cracks, potholes, and uneven surfaces. The existing
systems can be broadly categorized into manual
inspection methods, sensor- based techniques, and
deep learning-based models.
4.1 Manual Inspection Methods
Traditionally, road defect detection was performed
through manual inspections by road maintenance
personnel. Engineers visually inspected roads and
recorded defects based on predefined criteria. While
this method provides direct human assessment, it is
highly labor-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to
human error.
4.2 Sensor-Based Road Defect
Detection
Sensor-based techniques utilize various types of
sensors, including:
1. Ultrasonic Sensors: Used to measure surface
irregularities by detecting variations in
height.
2. Laser Scanning Systems: Employed in high-
YOLOv7s Optimization for Road Defect Detection: Pruning, Pooling and Attention Mechanisms
709
precision road profiling, where laser beams
detect cracks and potholes.
3. Accelerometers & Vibration Sensors:
Installed on vehicles to analyze road surface
vibrations and detect anomalies.
Studies such as Zhang et al. (2017) have shown that
laser scanning can provide high accuracy in defect
measurement. However, these systems require
expensive equipment and frequent calibration,
making them unsuitable for cost-effective and real-
time applications.
4.3 Computer Vision-Based Road
Defect Detection
With advancements in artificial intelligence,
computer vision and deep learning techniques have
become widely used for automated road defect
detection. Several deep learning models have been
proposed, including:
For instance, Omar et al. (2020) applied YOLOv3 for
real-time defect detection, achieving fast inference
but struggling with small defect identification.
Limitations of the Existing System:
1. While deep learning models like YOLOv5
have improved road defect detection,
existing systems face the following
challenges:
2. High Computational Cost: Traditional deep
learning models require significant
computational power, making them
inefficient for real-time deployment on edge
devices.
3. Difficulty in Detecting Small Defects:
Standard YOLO models struggle with
detecting fine cracks and low-contrast
defects.
4. Redundant Parameters in Deep Models:
Many deep learning models contain
unnecessary parameters that slow down
inference speed. Limited Feature Extraction:
Existing models do not always capture
multi- scale features, affecting their ability
to detect road defects in varying lighting and
textures.
These limitations highlight the need for an optimized
YOLOv5s model that incorporates pruning, pooling,
and attention mechanisms to improve detection
accuracy, reduce computational cost, and enable real-
time road monitoring
5 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system introduces an optimized
YOLOv8-based road defect detection model that
integrates pruning, pooling, and attention
mechanisms to enhance performance in terms of
accuracy, speed, and efficiency. Our approach
optimizes YOLOv8 by reducing redundant
parameters, improving feature extraction, and
refining defect localization, making it more suitable
for real-time deployment in road monitoring systems.
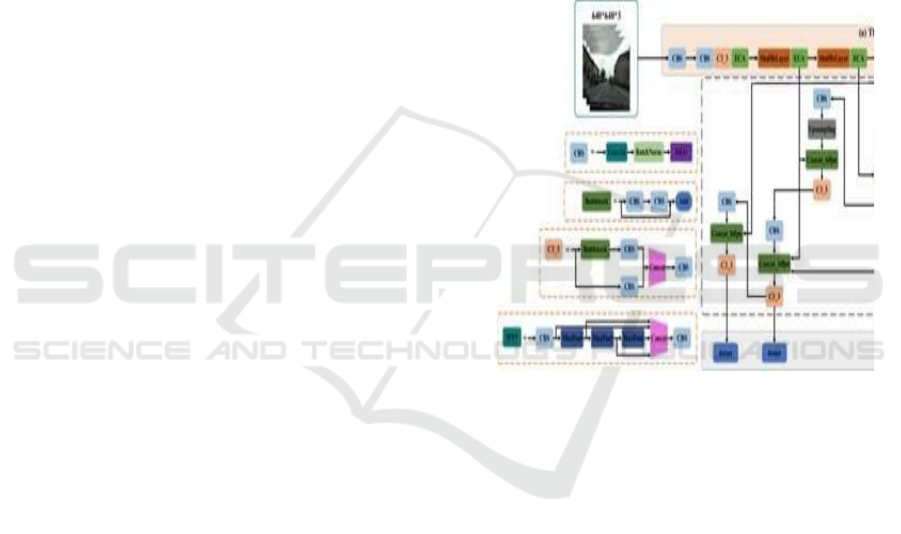
Figure 1 shows the Optimized Yolov7s Architecture
with Pruning, Pooling, And Attention Modules for
Road Defect Detection.
Architecture:
Figure 1: Optimized YOLOv7s architecture with pruning,
pooling, and attention modules for road defect detection.
1. Model Pruning for Efficiency: Pruning is
employed to eliminate unnecessary
parameters from the YOLOv8 model,
reducing its computational complexity
without significantly affecting accuracy.
This step ensures that the model runs
efficiently on edge devices and real-time
monitoring systems while maintaining
robust defect detection capabilities.
2. Pooling Techniques for Multi-Scale Feature
Extraction: The system incorporates
advanced pooling strategies, such as Spatial
Pyramid Pooling (SPP) and Adaptive
Pooling, to enhance the detection of road
defects of varying sizes and textures. These
techniques enable the model to capture
multi-scale features, improving its ability to
identify small cracks, potholes, and
deformations under different environmental
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
710

conditions.
3. Attention Mechanisms for Precise Detection:
To improve feature selection and defect
localization, the proposed system integrates
the Convolutional Block Attention Module
into the YOLOv8 architecture. CBAM
enhances the model’s ability to focus on
critical defect regions while reducing
distractions from irrelevant background
noise. By incorporating both channel and
spatial attention, the system refines feature
extraction, resulting in higher precision,
recall, and mean average precision. This
optimization minimizes false positives and
ensures reliable road defect classification.
4. Real-Time Implementation and
Deployment: The optimized YOLOv7
model is designed for real-time deployment
on embedded systems, UAVs (Unmanned
Aerial Vehicles), and smart city surveillance
systems. The integration of pruning, pooling,
and attention mechanisms makes the model
lightweight and efficient, ensuring smooth
operation on low-power devices without
sacrificing detection accuracy. The system is
tested on benchmark datasets to validate its
performance and ensure robustness in diverse
road conditions.
5. Performance Evaluation and Impact
Comprehensive experiments demonstrate
that the proposed optimizations lead to
improved detection accuracy, reduced
inference time, and enhanced computational
efficiency. The system achieves higher
precision in identifying road defects while
maintaining a balance between accuracy and
real-time processing speed. This solution
provides a cost-effective and scalable
approach for road maintenance authorities,
transportation agencies, and smart city
planners to automate road defect monitoring,
ultimately contributing to improved road
safety and infrastructure maintenance.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This research presents an optimized YOLOv8s-based
road defect detection system that integrates pruning,
pooling, and attention mechanisms to improve
accuracy, computational efficiency, and real-time
performance. The proposed enhancements address
key challenges in existing systems, such as high
computational cost, difficulty in detecting small
defects, and redundant parameters. By incorporating
pruning, the model size is reduced, improving
inference speed without sacrificing detection
accuracy. Additionally, attention mechanisms like
CBAM enable the model to focus on critical defect
areas while reducing background noise, significantly
improving detection precision.
7 RESULTS
Figure 2(a) to (h) shows the Comparative
visualization of road defect detection outputs using
different model configurations. Sub-figures (a)–(h)
represent detection results across various YOLOv7s
optimizations including baseline, pruning, pooling,
and attention mechanisms. Figure 3 shows the
Sample annotated images from the road defect dataset
showing various types of cracks such as longitudinal
cracks, alligator cracks, and transverse cracks used
for training and evaluation.
YOLOv7s Optimization for Road Defect Detection: Pruning, Pooling and Attention Mechanisms
711

Figure 2 (a)to (h): Comparative visualization of road defect
detection outputs using different model configurations.
Sub-figures (a)–(h) represent detection results across
various YOLOv7s optimizations including baseline,
pruning, pooling, and attention mechanisms.
Figure 3: Sample Annotated Images from the Road Defect
Dataset Showing Various Types of Cracks Such As
Longitudinal Cracks, Alligator Cracks, and Transverse
Cracks Used for Training and Evaluation.
REFERENCES
Han, S., Mao, H., & Dally, W. J. (2016). Deep compression:
Compressing deep neural networks with pruning,
trained quantization, and Huffman coding. International
Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual
learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR), 770–778.
Howard, A. G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D.,
Wang, W., Weyand, T., … Adam, H. (2017).
MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks
for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1704.04861.
Huang, G., Liu, Z., van der Maaten, L., & Weinberger, K.
Q. (2017). Densely connected convolutional networks.
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR), 4700– 4708.
Jocher, G., Chaurasia, A., & Qiu, J. (2022). YOLOv5:
Implementation of YOLO object detection in PyTorch.
GitHub Repository.
Li, H., Kadav, A., Durdanovic, I., Samet, H., & Graf, H. P.
(2017). Pruning filters for efficient convnets.
International Conference on Learning Representations
(ICLR).
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S.,
Fu, C. Y., & Berg, A. C. (2016). SSD: Single shot
multibox detector. European Conference on Computer
Vision (ECCV), 21–37.
Luo, J. H., Wu, J., & Lin, W. (2017). ThiNet: A filter level
pruning method for deep neural network compression.
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
Computer Vision (ICCV), 5058–5066.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep
convolutional networks for large-scale image
recognition. International Conference on Learning
Representations (ICLR).
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J. Y., & Kweon, I. S. (2018). CBAM:
Convolutional BlockAttention Module. European
Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 3–19.
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin, M., & Sun, J. (2018). ShuffleNet:
An extremely efficient convolutional neural network
for mobile devices. IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 6848–6856.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
712
