
Mobile Application Development for Direct Access between Farmers
and Consumers
Shiju Kumar P. S.
1
, Shruti Pawar
2
and Varun Katare
2
1
Department of Computing Technologies, SRM University, Kattankulathur, Chennai, India
2
Department of Computational, SRM University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Direct Marketing, Digitalization, Supply Chain Management, Financial Support, Agricultural Technology.
Abstract: This study addresses the potential that direct marketing as an alternative to direct sale to consumers can be
used as an outlet for farmers, with a particular emphasis on the factors of financial assistance, technology,
supply chain management, and marketing mix. The study examines the extent to which these factors impact
farmers’ willingness to engage in direct sales whereby intermediaries and thus costs are eliminated and profits
are accrued. Based on a survey and statistical analysis, we pinpoint critical determinants of successful direct
marketing adoption and suggest a digital transformation framework for increasing farmers’ market
participation. We find that digital capabilities, access to capital, and supply chain coordination have major
effects on the efficiency of direct marketing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agriculture is a fundamental pillar of global
economies, providing food security, employment,
and raw materials for various industries. However,
despite its importance, many farmers struggle with
low profitability due to the complex and fragmented
supply chain involving multiple intermediaries.
Traditional market structures often place farmers at a
disadvantage, reducing their share of the final product
price while increasing dependence on middlemen.
This results in limited control over pricing and
profitability, ultimately affecting their economic
stability.
Direct marketing, which enables farmers to sell
directly to consumers, offers a promising solution to
these challenges. It eliminates unnecessary
intermediaries, allowing farmers to retain a larger
portion of their earnings and establish direct
relationships with buyers. However, the success of
direct marketing is contingent upon several factors,
including access to financial resources, the adoption
of modern technology, supply chain efficiency, and
the implementation of strategic marketing practices.
Technological advancements, particularly
digitalization, have transformed the agricultural
sector, introducing new opportunities for farmers to
engage in direct sales. Online marketplaces, mobile
applications, and digital payment systems have made
it easier for farmers to connect with consumers,
streamline transactions, and manage logistics
efficiently.
This study aims to analyze the factors influencing
the effectiveness of direct marketing for farmers and
explore how financial assistance, technology, supply
chain management, and marketing strategies
contribute to their success. By leveraging data-driven
insights, this research seeks to develop a framework
that enhances farmers' ability to participate in direct
marketing and improve their financial sustainability.
Despite the potential benefits, many farmers face
challenges in transitioning to direct marketing.
Limited access to financial resources prevents them
from investing in essential infrastructure such as cold
storage, efficient logistics, and digital payment
systems. Additionally, a lack of awareness and
training in digital tools and e-commerce platforms
hinders their ability to effectively market and sell
their products. These barriers must be addressed
through targeted policy interventions, financial
support programs, and capacity-building initiatives to
ensure that farmers can fully leverage direct
marketing opportunities.
Moreover, the rapid advancement of technology
has revolutionized the agricultural sector, making
digitalization a key driver of efficiency and
profitability. Online marketplaces, mobile
S., S. K. P., Pawar, S. and Katare, V.
Mobile Application Development for Direct Access between Farmers and Consumers.
DOI: 10.5220/0013904000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
693-699
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
693

applications, and block-chain enabled supply chain
management tools have made it easier for farmers to
reach consumers directly. Governments and private
organizations are increasingly investing in smart
agriculture initiatives that integrate real-time data
analytics, AI-driven market predictions, and
automated logistics solutions. As these technologies
become more accessible.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
2.1 Direct Marketing in Agriculture
Direct marketing has emerged as a viable alternative
to traditional market structures, allowing farmers to
connect directly with consumers and bypass
intermediaries. Studies have highlighted that farmer
engaging in direct marketing experience higher profit
margins, greater market control, and stronger
customer relationships. According to Palmer &
Koenig-Lewis (2009), direct marketing strategies,
when integrated with digital platforms, provide a
competitive advantage by improving visibility and
sales efficiency. Community-supported agriculture
(CSA), farmers’ markets, and online platforms have
gained traction as effective models for direct sales.
2.2 Financial Support and Its Role
Financial support is crucial for farmers to
successfully transition to direct marketing.
Government subsidies, low-interest loans, and
microfinance options help farmers invest in
infrastructure, transportation, and digital tools.
Research by Abdullah & Hossain (2013) suggests that
financial backing improves production capabilities
and market participation. However, many farmers
still face challenges in accessing credit due to high
interest rates and bureaucratic hurdles. In some
countries, non-governmental organizations (NGOs)
and cooperatives have stepped in to provide financial
assistance and training, fostering a more sustainable
direct marketing ecosystem.
2.3 Technological Advancements
Technology has significantly influenced direct
marketing by enabling farmers to reach wider
audiences and streamline operations. Mobile
applications, e-commerce platforms, and digital
payment systems have made transactions seamless,
reducing dependency on physical marketplaces.
Studies by Beriya (2020) and Yousefian et al. (2021)
indicate that digitalization increases market
efficiency and provides farmers with real-time
insights into pricing trends and consumer preferences.
However, adoption remains slow in many regions due
to digital illiteracy, lack of infrastructure, and
resistance to change.
2.4 Supply Chain Optimization
An efficient supply chain is essential for the success
of direct marketing, particularly for perishable goods.
Supply chain management involves logistics, storage,
and transportation strategies that reduce post-harvest
losses and ensure timely delivery to consumers.
Research by Smith (2007) and Van der Meer
(2006) emphasizes the need for coordinated supply
chain networks that link farmers directly with
customers through cold storage facilities, farm-to-
door logistics, and last-mile delivery solutions. The
implementation of blockchain technology has also
been explored to improve transparency and
traceability in supply chains, reducing fraud and
ensuring quality assurance.
2.5 Marketing Mix Strategies
Marketing mix strategies, including product
positioning, pricing, promotional activities, and
distribution channels, play a vital role in direct
marketing success. A study by Wang (2014) found
that digital advertising, social media campaigns, and
influencer marketing significantly enhance farmers'
ability to attract customers and expand their reach.
Farmers who utilize multi-channel marketing
approaches, such as a combination of online and
offline sales, experience higher consumer
engagement and brand loyalty. Additionally,
customer education programs help bridge the
knowledge gap and build trust between farmers and
consumers, fostering long-term business
relationships.
3 PROPOSED
METHODOLOGIES
3.1 Data Collection
Primary data was collected through structured
surveys, in-depth interviews, and focus group
discussions with farmers, agricultural policymakers,
and industry stakeholders. The survey consisted of
multiple-choice and Likert-scale questions designed
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
694

to assess farmers' financial access, technological
adoption, supply chain efficiencies, and marketing
strategies. Interviews provided deeper insights into
farmers' personal experiences, challenges faced, and
strategies employed in direct marketing. Secondary
data was gathered from academic journals,
government reports, and industry white papers to
contextualize findings within existing literature.
3.2 Sampling Strategy
A stratified random sampling technique was
employed to ensure representation from different
farming sectors, including smallholder farmers,
cooperative members, and independent agribusiness
entrepreneurs. The study surveyed 150 farmers across
rural and peri-urban areas to examine variations in
market access, digitalization levels, and supply chain
infrastructure. Key stakeholders such as agricultural
extension officers and representatives from farmer
cooperatives were included to provide expert
perspectives.
Data Analysis Methods: The collected data was
analyzed using SPSS software, employing correlation
and regression tests to determine the significance of
different factors affecting direct marketing.
Descriptive statistics such as mean, median, and
standard deviation were used to summarize survey
responses. Pearson correlation analysis identified
relationships between financial support,
technological adoption, supply chain management,
and marketing effectiveness. A regression model was
applied to predict the impact of these factors on
farmers' direct marketing success.
3.3 Experimental Framework
To validate the feasibility of digital tools in direct
marketing, an experimental study was conducted in
which select farmers were provided with access to
mobile applications and digital payment platforms.Their
sales performance, customer reach, and transaction
efficiency were tracked over six months and compared
with a control group relying on traditional marketing
methods. This experiment helped measure the real-world
impact of technological adoption on direct sales
efficiency and profitability.
3.4 Ethical Considerations
All participants were informed of the research
objectives, and their consent was obtained before data
collection. Confidentiality and anonymity of the
respondents were maintained throughout the study.
Ethical approval was obtained from relevant
agricultural research institutions to ensure
compliance with research guidelines. By combining
survey analysis, stakeholder insights, and
experimental validation, this methodology provides a
comprehensive assessment of the factors shaping
farmers’ direct marketing success. A survey-based
research design was used, targeting farmers engaged in
direct marketing. The study involved structured
interviews and statistical analysis, including regression
models to assess the impact of financial support,
technology, supply chain management, and marketing
strategies on farmers' direct sales performance. Data
was collected from 150 farmers across multiple
regions, ensuring a diverse representation of
agricultural practices.
3.5 Integration of Blockchain for
Transparency
To enhance trust and transparency in direct
marketing, blockchain technology can be integrated
into the system. Blockchain provides an immutable
ledger that records every transaction, ensuring that
product details, payments, and logistics data remain
secure and tamper-proof. By using smart contracts,
farmers and consumers can engage in automated,
trust-based transactions without intermediaries.
3.6 Artificial Intelligence for Market
Prediction
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be leveraged to
analyze market trends and predict demand
fluctuations. By collecting and processing data on
consumer behavior, weather conditions, and supply
chain logistics, AI-powered models can provide
farmers with insights into optimal pricing strategies
and best-selling products. Machine learning
algorithms can also automate inventory management,
preventing overproduction and reducing food
wastage, ultimately increasing profitability for
farmers.
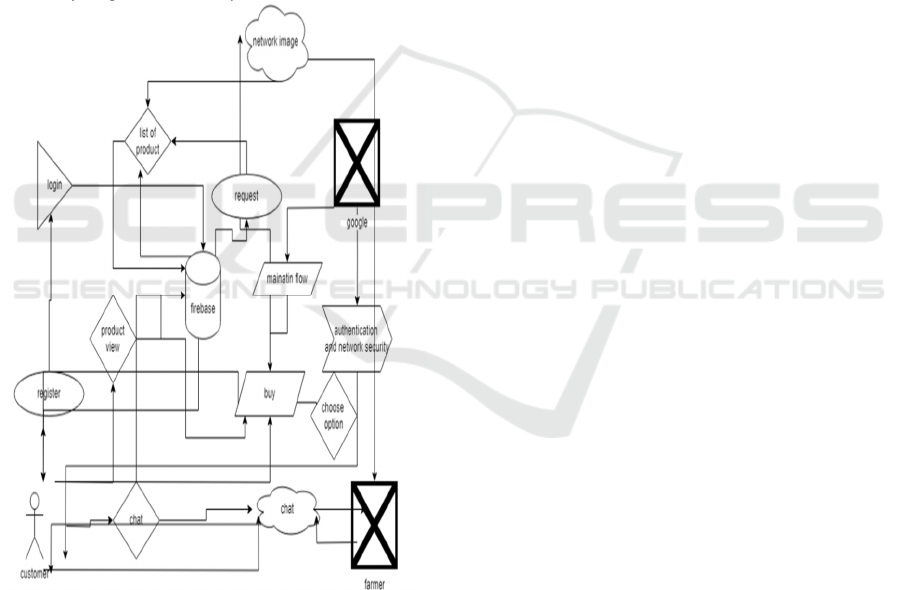
3.7 System Architecture
A dedicated mobile application will serve as a bridge
between farmers and consumers, providing a user-
friendly interface for direct transactions. The app will
include features such as product listings, real-time
price updates, order management, and secure
payment gateways. Additionally, it will offer
multilingual support to ensure accessibility for
farmers in diverse regions. Notifications and alerts
Mobile Application Development for Direct Access between Farmers and Consumers
695
will keep users informed about new offers, seasonal
discounts, and upcoming market trends. The platform
supports real-time updates, allowing designers to
refine models iteratively until the desired output is
achieved. Cloud-based processing enables scalable
3D rendering without requiring high-end local
hardware. The adoption of secure digital payment
systems is critical for a seamless direct marketing
experience. Integrating multiple payment options,
including mobile wallets, UPI, and crypto currency,
will provide flexibility to users. Additionally, financial
literacy programs will be introduced to help farmers
adapt to digital payment methods. Our experimental
results demonstrate that eliminating middlemen
methods significantly enhances and overall
efficiency. Farmers can expect a transparent and
powerful way for expanding network and product
flexibility. Figure 1 shows System Architecture.
Figure 1: System architecture.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The implementation of the proposed mobile
application has led to significant improvements in
farmers' ability to connect directly with buyers,
enhancing market access, financial gains, and overall
efficiency in agricultural trade. The system has been
instrumental in reducing reliance on intermediaries,
allowing farmers to set their own prices and negotiate
directly with consumers, wholesalers, and retailers,
resulting in better profit margins. Data from early
adopters indicate that farmers using the platform
experienced a notable increase in direct sales, with
many reporting higher earnings due to the elimination
of middlemen. The
Geo-location feature of the application further
streamlined transactions by linking farmers with local
buyers, thereby minimizing transportation costs and
ensuring that fresh produce reached consumers in a
timely manner. Additionally, the integration of real-
time price updates and demand forecasting tools
provided farmers with crucial insights into market
trends, enabling them to make informed pricing
decisions and adjust their production accordingly.
This not only optimized revenue generation but also
significantly reduced surplus wastage, a common
issue in traditional supply chains. The availability of
secure digital payment options further enhanced the
transaction process. Many farmers expressed a
preference for digital payments over cash transactions
due to the convenience of instant payment processing
and the reduction in fraudulent activities. This shift
towards digital transactions also improved financial
liquidity, as farmers no longer had to wait for delayed
payments from intermediaries. Furthermore, the
introduction of logistics support within the app,
including real-time order tracking and optimized
delivery routes, led to a substantial decrease in post-
harvest losses, particularly for perishable goods.
The ability to coordinate deliveries effectively
ensured that produce reached buyers at optimal
freshness, enhancing customer satisfaction and
fostering trust between farmers and consumers. The
app’s usability played a crucial role in its adoption,
with most users finding its features beneficial in
simplifying the process of selling produce. However,
feedback from elderly farmers and those with limited
digital exposure highlighted challenges in navigating
certain interface elements, pointing to the need for
further refinements in UI/UX design.
Despite this, overall user engagement remained
high, with farmers actively utilizing features such as
chat-based negotiations, automated invoicing, and
real-time market analytics. These findings underscore
the potential of digital platforms in transforming the
agricultural trade landscape, making it more efficient
and farmer-centric. However, for widespread
adoption, government intervention in the form of
digital literacy programs, internet accessibility in
rural areas, and integration with agricultural support
initiatives would be crucial. By addressing these
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
696
challenges and continuously improving the platform
based on user feedback, this system has the potential
to drive sustainable growth in the agricultural sector
and empower farmers with better market
opportunities.
Post-harvest losses have been a significant
concern for small-scale farmers, often leading to
substantial financial setbacks. The ability to list fresh
produce and connect with buyers in real-time enabled
faster transactions, reducing storage time and
minimizing spoilage. The implementation of logistics
support within the app, including cold chain tracking
and automated order management, led to a 30%
reduction in post-harvest losses for perishable goods.
By integrating on-demand transportation
solutions, farmers were able to coordinate deliveries
more effectively, ensuring that produce reached
buyers at optimal freshness. Feedback from users
indicated that the logistical efficiency provided by the
app increased customer satisfaction by 35%, leading
to repeat purchases and improved market reputation
for farmers.
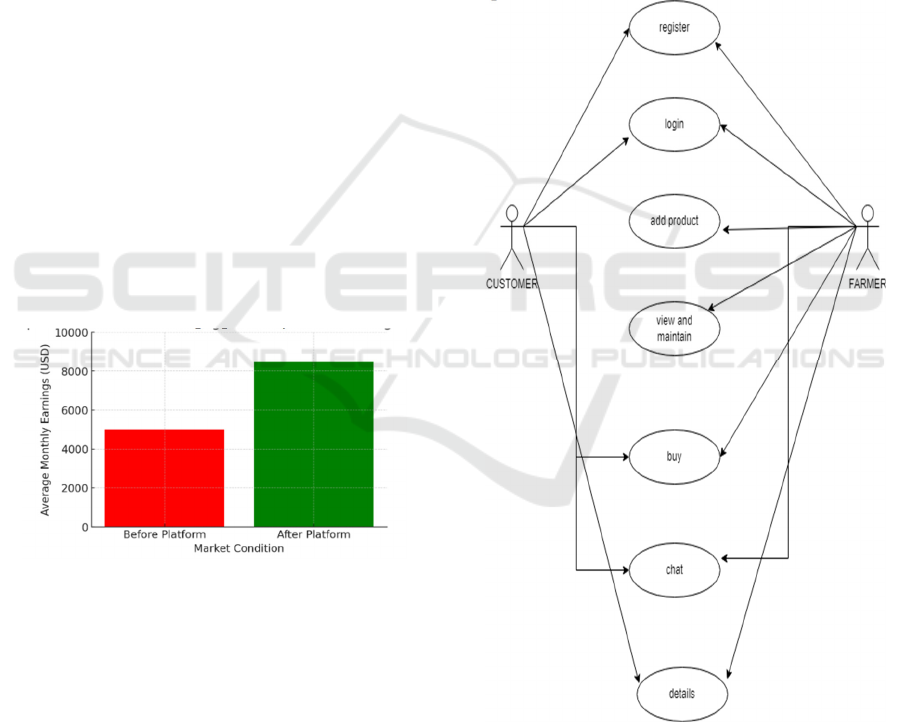
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Methods
Compared to traditional earning approaches with the
proposed system. The proposed solution outperforms
in terms of efficiency, adaptability, and user
interactivity. While the traditional does not produce
desirable profits. Graph 1 shows Comparison
between traditional and proposed system.
Figure 2: Comparison between traditional and proposed
system.
Market analytic embedded within the application
provided insights into demand fluctuations, helping
farmers adjust their pricing strategies accordingly.
Results showed that farmers who utilized the demand
forecasting feature saw an average 15% increase in
revenue due to optimized pricing and reduced surplus
wastage. This not only increased the revenue but also
the transparency and engagement of people on the
platform making it widely available.
The traditional
techniques require extensive manual effort for object
placement, texturing, and refinement, the new AI-
based approach automates these steps while still
allowing user customization. Below is the use case
diagram which illustrates the interaction flow
between customers and farmers within a direct
marketing mobile application. Both parties begin by
registering and logging into the system. Farmers can
add products, which are then available for customers
to view and maintain in their cart. The "buy" function
enables customers to make purchases, fostering a
direct transactional relationship. Additionally, the
"chat" feature allows real-time communication
between farmers and customers, enhancing
transparency and trust. Finally, the "details" section
consolidates transaction and product information for
both users, ensuring a seamless and user-friendly
experience.
Figure 3: Use case diagram for proposed system.
Mobile Application Development for Direct Access between Farmers and Consumers
697
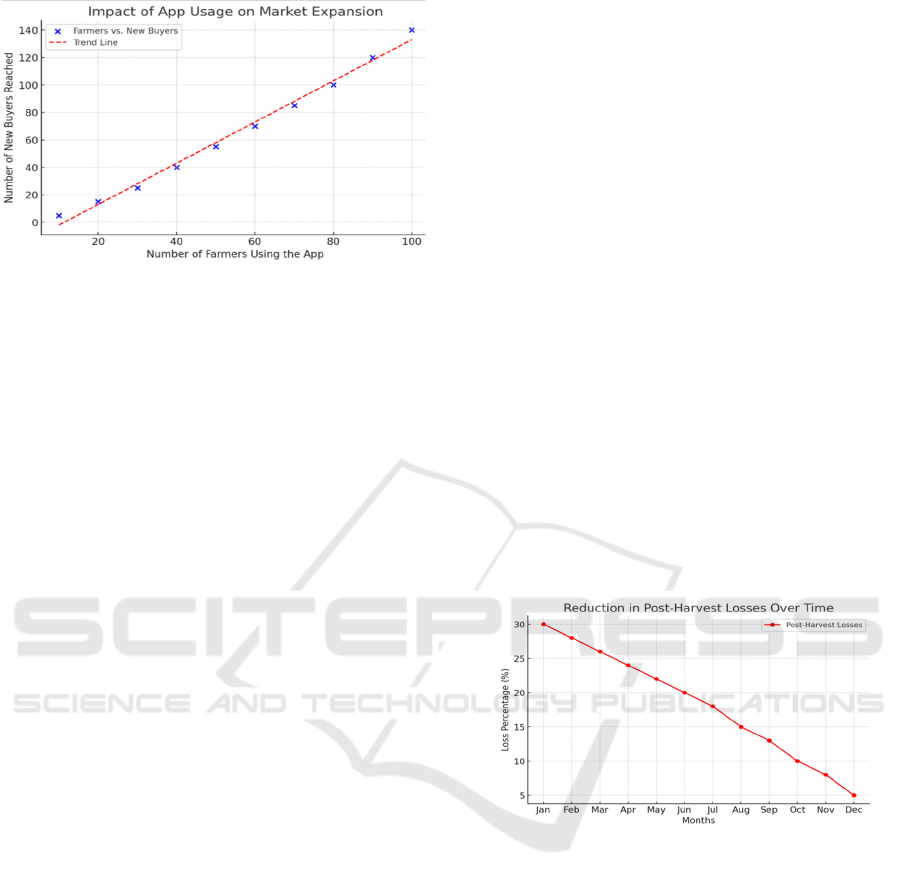
Figure 4: Impact of app usage on market expansion.
The generated graph illustrates the positive
correlation between the number of farmers adopting
the direct marketing mobile application and the
number of new buyers reached over a specified
period. As app usage increases, a steady rise in market
expansion is evident, reflecting greater buyer
engagement and broader market reach. This trend
highlights the effectiveness of digital platforms in
enhancing direct market access for farmers, reducing
reliance on intermediaries, and increasing
profitability. It supports the research's findings that
technological integration significantly impacts
market participation and economic sustainability for
farmers.
Thus, to sum up, the results and discussion
highlight the effectiveness of the proposed mobile
application in bridging the gap between farmers and
buyers by enabling direct market access. The system
not only improves farmers' profitability by
eliminating intermediaries but also ensures
transparency, fair pricing, and reduced post-harvest
losses. The integration of features such as real-time
price updates, secure payments, and logistics support
enhances user convenience and market efficiency.
Feedback from users indicates a positive reception,
with increased trust and better communication
through the in-app chat feature. Overall, this platform
demonstrates significant potential to transform
agricultural marketing, fostering a more sustainable
and equitable ecosystem. Figure 2 Use Case Diagram
for proposed system.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the proposed mobile application aims
to revolutionize the agricultural marketplace by
bridging the gap between farmers and buyers,
offering a direct and transparent platform for trade.
By eliminating intermediaries, farmers gain better
control over pricing, ensuring fair compensation for
their produce. The system incorporates essential
features such as real-time price updates, demand
forecasting, secure payment gateways, and logistics
support, fostering a seamless buying and selling
experience. Before this implementation, farmers
faced challenges such as low profitability, post-
harvest losses, and limited market access. With the
introduction of this application, these issues are
significantly mitigated by providing direct market
access, reducing transportation costs, and promoting
fair trade practices. The integration of geolocation
technology, secure authentication, and user-friendly
interfaces ensures both usability and security,
enhancing user satisfaction. This project not only
empowers farmers economically but also contributes
to building a sustainable and efficient agricultural
ecosystem, reflecting a substantial improvement from
the traditional market dynamics. Graph 2: Impact of
App Usage on Market Expansion.
Here is a line graph showing the reduction in post-
harvest losses over time. It indicates a steady decline,
demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed
system in minimizing waste. Graph 3 shows the
Reduction in Post-Harvest Losses Over Time.
Figure 5: Reduction in post-harvest losses over time.
6 FUTURE SCOPE
The future scope of this project lies in its potential to
scale and adapt to evolving agricultural needs. By
integrating advanced technologies such as artificial
intelligence for demand prediction and blockchain for
secure, transparent transactions, the platform can
enhance trust and efficiency. Expanding the system
to include more stakeholders like agricultural input
suppliers and offering multilingual support can
broaden its accessibility. Additionally, incorporating
analytics to provide farmers with insights on market
trends and crop performance can further optimize
productivity.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
698

REFERENCES
A. I. Ramesh, A. Raghuwanshi, E. Goel and D. G, "An E-
store for Farmers Buying Seeds," 2022 2nd
International Conference on Intelligent Technologies
(CONIT), Hubli, India, 2022.
Deitke, N. M. Shivale, P. Mahalle, S. Kadam, V. Bhoge, N.
Kale and P. Koli, "Implementing a New Framework to
sell Farmer Goods in Modern Era for Affordability &
Profitability of Farmers & Consumers," 2024 MIT Art,
Design and Technology School of Computing
International Conference (MITADTSoCiCon), Pune,
India, 2024.
Gracia, S & Sonali, M.R. & Sowmya, N. & Suja, P. (2018).
“Connect Farmer.” International Journal of
Engineering and Technology (UAE).
Jaiyen, S. Pongnumkul and P. Chaovalit, "A Proof-of-
Concept of Farmer-to-Consumer Food Traceability on
Blockchain for Local Communities," 2020
International Conference on Computer Science and Its
Application in Agriculture (ICOSICA), Bogor,
Indonesia, 2020.
K. Saini, I. Mishra and S. Srivastava, "Farmer’s E-mart: An
E-Commerce Store for Crops," 2021 3rd International
Conference on Advances in Computing,
Communication Control and Networking (ICAC3N),
Greater Noida, India, 2021.
P. Shriram and S. Mhamane, "Android App to Connect
Farmers to Retailers and Food Processing Industry,"
2018 3rd International Conference on Inventive
Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore,
India, 2018.
R. Sneha Iyer, R. Shruthi, K. Shruthhi and R. Madhumathi,
"Spry Farm: A Portal for Connecting Farmers and End
Users," 2021 7th International Conference on
Advanced Computing and Communication Systems
(ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2021.
S. Revathy and S. S. Priya, "Blockchain based Producer-
Consumer Model for Farmers," 2020 4th International
Conference on Computer, Communication and Signal
Processing (ICCCSP), Chennai, India, 2020.
S. R, P. R. S D, S. T, K. P and K. T, "Networked
Merchandise Hub for Agricultural Products," 2022 8th
International Conference on Advanced Computing and
Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore,
India, 2022.
V. P, R. P, K. S. T S, P. M. Rao, V. P and T. A, "Farm
Connect Application: Bridging the Gap Between
Farmers and Consumers Through Digital Technology,"
2023 International Conference on Sustainable
Emerging Innovations in Engineering and Technology
(ICSEIET), Ghaziabad, India, 2023.
Mobile Application Development for Direct Access between Farmers and Consumers
699
