
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI
D. R. Shreya
1
, Vasa Vidhyadhari
1
, B. Naga Divya
2
,
Vadisela Lakshmi Chandrika
1
and Patnam Shetty Bhoomika
1
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (DS), Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Venkayapally,
Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Venkayapally, Kurnool,
Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: MFCC, DenseNet121, CNN, Analysis of Images, PSNR, SSIM.
Abstract: This research aims to use a multidimensional dataset (MELD, Multimodal Emotion Lines Dataset) to develop
a web-based model for spoken emotion recognition. The dataset comprises text, audio, and image, and is used
for identifying emotions in conversational data. Before we generate the final results like image scaling,
reducing noise, incoming data. Natural language data is tokenized using basic text tokenization, and various
audio-feature extraction techniques are used, including Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC). After
pre-processing, the data is split into training and testing data and used to classify the emotion with deep
learning models, including CNN and DenseNet121. The aim of this study is creating of web interface-based
model of spoken emotion recognition with the help of multidimensional dataset (MELD: Multimodal Emotion
Lines Dataset). The dataset utilized is Emotions Dataset which detects emotions in conversational data in the
form of text, audio, and images. Then, the entering data are pre-processed using some techniques such as
picture scaling, noise removal, gray conversion, normalization etc. MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral
Coefficients), an algorithm for audio features extraction, and text tokenization for natural language data are
used. Data for pictures are collected, pre-processed, and separated to train and test, then further used to classify
the emotions using CNN, DenseNet121 and so on, deep learning models. Using the MELD (Multimodal
Emotion Lines Database), a multidimensional dataset, this study aims to create a web-based model for spoken
emotion recognition. It is used to extract emotion from the conversational data comprising text, audio, and
pictures. The incoming data is pre-processed using techniques such as picture scaling, noise removal, gray
conversion, and normalization. We use Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) for extracting audio
features and tokenization for language data. The data set is split into training and testing post pre-processing,
and the emotions are classified using deep learning models CNN and DenseNet121.
1 INTRODUCTION
Emotion recognition has become an important area
that contributes to human-computer interaction with
the advent of AI-powered systems designed to
understand human emotion. Correctly detecting
emotions across different media types, such as text,
audio, or pictures, has important implications in
areas like sentiment analysis, virtual assistants, and
even healthcare. The cognitive task required to
comprehend verbal and even non-verbal
communication to detect these subtle cues is not only
a challenging one but also a complex task that
requires emotion recognition. Emotion detection
relies heavily on contextual information, and this
gets especially complicated by the need to express
emotions in the course of a conversation.
Recent advances in deep learning have increased
the use of multimodal emotion identification system.
To best understand human feelings, these systems
aim to combine multiple sources of data such as
sentiment and meaning from text, intonation and
pitch from voice, and facial expressions from photos.
They can be trained and evaluated on different
datasets, including MELD (Multimodal Emotion
Lines Dataset), which provides conversational data in
the form of text, audio, and images labeled for seven
emotional states (anger, disgust, fear, happiness,
sadness, surprise, neutral). This study aims to
implement an emotion detection model with the help
of deep learning techniques that can be accessed
568
Shreya, D. R., Vidhyadhari, V., Divya, B. N., Chandrika, V. L. and Bhoomika, P. S.
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI.
DOI: 10.5220/0013902100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
568-578
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

online using the MELD dataset.
By integrating multiple senses, the system aims
to enhance classification accuracy and build a more
nuanced understanding of emotional states. The
recognition of emotions is less subjective and more
accurate in terms of interpretation compared with the
traditional single-modality approaches that use just
one type of data, i.e., image, audio, or text.
Ultimately, though, the project's goal is to build a
scalable system capable of real-time recognition of
emotions by interplays in the multimodal
conversational data.
2 PROJECT OBJECTIVES
The primary objectives of this project are to build an
online emotion detection engine that, given
multimodal input, e.g., text, vocal, visual can
accurately classify multimodal models into one of the
seven unique emotional classes known as features,
namely anger, disgust, fear, happy, sorrow, surprise
and neutral. Using deep learning approaches and the
MELD dataset, the research aims to create a solid
model that can fuse three modalities to reach a wide
opinion about the human emotions. The system's
ability to decode multimodal information will be a
critical part of the heart of the system for more
accurate emotion detection. Text tokenization would
help with basic detection from text, while the
combining of DenseNet121 and CNN model would
help in efficiently managing images and audio.
The project is intended to assist in the
development of emotion-aware AI systems, which
can be used in sentiment analysis, health-care, and
human-computer interaction.
3 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
Emotional recognition algorithms have a range of
challenges especially in multimodal data. Because
real-world datasets can vary widely, one of the
biggest challenges lies in synchronizing the various
input types, as not every dataset will have text, voice,
and images aligned. Each modality carries its own set
of feature extraction and interpretation challenges,
which can add a layer of difficulty to the performance
of emotion detection systems. However, while deep
learning methods have shown promising results in
relation to emotion classification, there still remains a
void to bridge the gap that accounts for multimodal
data integration for real-time applications.
Ensuring that the model can consistently classify
emotions across diverse sources of data without
sacrificing performance or effectiveness remains
quite a challenge.
4 PROJECT SCOPE
To create an online emotion recognition system
which is trained and evaluated with the dataset
MELD. Scope will include multimodal data
preprocessing (picture scaling, noise reduction,
audio MFCC feature extraction, and text
tokenization). Then CNN and DenseNet121 deep
learning models will be used for emotion
categorization. The algorithm will try to classify
seven emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness,
sorrow, surprise and neutral based on the input data.
Model performance will be measured using accuracy,
precision, recall, F1 score, ROC curves for the image
data, and image quality metrics.
The MELD dataset will be the system’s main
focus, but the ideas and approaches developed could
subsequently be applied to other multimodal emotion
recognition problems.
5 ALGORITHMS
The deep learning models utilised in this study
include Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for
the classification of image and audio data and
DenseNet121 for the extraction of image feature. The
ability of these models to handle large and complex
datasets makes them suitable for multimodal
emotion recognition tasks. We will also use text
tokenization methods for natural language
processing, and MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral
Coefficients) for audio feature extraction as a
supplement to the deep learning models.
6 EXISTING SYSTEM
Most of the existing emotion identification schemes
focus on identifying emotions in uni-modal (text,
voice or image) data. Audio-based methods extract
audio features, such as Mel Frequency Cepstral
Coefficients (MFCC), to identify emotion based on
the tone, pitch, and tempo of a person's voice,
whereas image-based techniques often utilize
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) to analyze
facial expressions. Text-based emotion identification
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI
569

systems typically employ Natural Language
Processing (NLP) techniques such as sentiment
analysis or tokenization to derive emotional
information from text. Although there has been
sufficient accuracy in these systems in their
respective domains, they still struggle with speech in
real-world scenarios where emotion is conveyed
simultaneously in dozens of modalities.
However, these modalities are rarely integrated,
and existing systems tend to evaluate each modality
independently, which ignores the potential
information hidden in multimodal data. Moreover,
existing systems often struggle with ambiguous or
noisy input especially when the modalities are
misaligned or filled with errors. Affect-based
approaches may struggle with recognition in noisy
environments, or identifying facilities that are
obscured or in different illuminate. Thanks to deep
learning, a new era of emotion analysis systems has
been opened, but current systems still often lack the
support of a transparent, real-time application in real-
world scenarios where multiple modalities need to be
processed together.
7 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system aims to overcome the
limitations of existing emotion identification systems
by utilizing a multimodal approach. To build a more
dependable and precise model for emotion
recognition, this system merges three distinct types of
data, specifically text, audio, and images. Using
sophisticated deep learning architectures like CNN
for image and audio classification and DenseNet121
for image processing, the system will be able to
analyse and integrate data from these diverse sources.
The data pretreatment pipeline is going to handle the
methods to clean and pre-process the data to train out
the model, like text tokenization, feature extraction
(MFCC for audio), image scale, noise removal etc.
Note that emotions are often expressed through
multiple modalities simultaneously, and so by
combining these different modalities they can create
a more true-to-life representation of the complexity
of human emotions. This holistic approach gives the
model a better chance of detecting emotions more
accurately in adverse real-world scenarios where one
modality might be noisy or limited. Also, suggesting
a solution capable of performing these emotion
predictions in a short period of time will allow
optimizing this whole system to work in real time.
This opens the door to live interaction or other
applications that require immediate responses, such
as customer service queries or interactive AIs.
8 LITERATURE SURVEY
focuses on, CNNs for image analysis, Transformer
models for text analysis, and Long Short- Term
Memory (LSTM) networks for audio processing (J.
Patel, S. Lee, R. Garcia). The authors use the MELD
dataset to evaluate their multimodal emotion
identification system. A pre-trained DenseNet
architecture is employed for the image modalities,
and an LSTM-based model is employed to process
the MFCC-audio features that were obtained. The
textual input is tokenized and passed to a transformer-
based sentiment analysis algorithm, to extract
contextual meaning from the conversation. For
example, A. Kumar, V. Sharma, and M.Dissertation
Tan use CNNs for facial expression identification,
CNN-based models for audio feature extraction and
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers) for analysis in a deep learning
framework. which gives a sentiment of the text of the
chat. The authors propose a late fusion approach
predicting emotional states by fusion techniques
fusing the output of all three models on popularly
known EmotiW dataset for validation.
9 METHODOLOGY
9.1 Data Selection
Data Preprocessing Module: Preparation of MELD
dataset for further analysis and training of the model
is an important feature. It handles the transformation
of raw input data text, audio, images and so on into
forms that machine learning model can leveraged
effectively. Image data preprocessing methods, in
order to enhance computational rate and model
accuracy, consist of scaling to a predefined size,
changing the image to grayscale and normalizing the
pixel values. During the preprocessing steps, Mel-
frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) are extracted
from the audio data, representing the spectral
properties of the sound which allows the model to
understand the emotive tones present in speech. Noise
removal techniques are also used to ensure that the
audio input is clear and background noise that could
obscure emotion recognition. Tokenization is the
process of converting raw text into a list of words or
tokens that a natural language processing (NLP)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
570
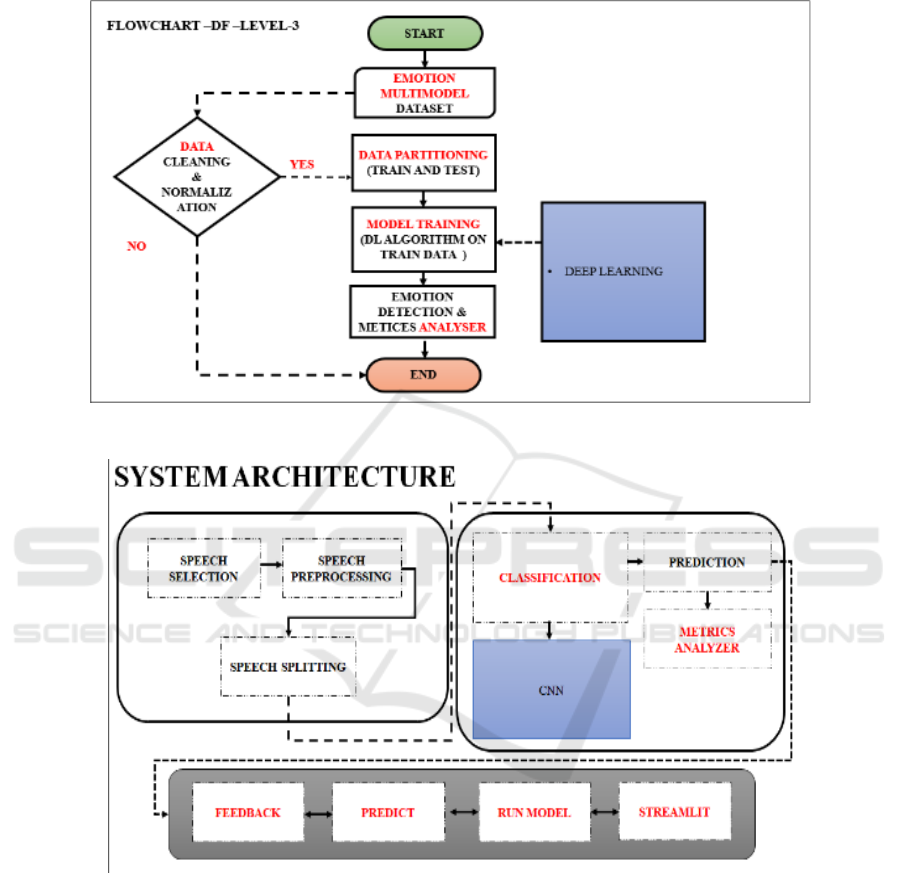
model can read. Figure 1 shows the block diagram of
proposed system and the figure 2 illustrate the
implementation methodology of the data selection.
Figure 3 show the Run project in spyder env of the
result and the Figure 4 show the Get fear data.
Figure 1: Block Diagram of proposed system.
Figure 2: Implementation methodology.
9.2 Feature Extraction Module
Description
The Feature Extraction Module is responsible for
extracting important features from text, audio, and
image processed multimodal data that can be used
for emotion classification. Deep learning techniques
such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) or
more complex methods for feature extraction are
employed to screen relevant patterns from visual data,
such as environmental cues or facial expressions, that
could indicate an emotional state. For speech emotion
recognition, MFCCs are used in audio to characterize
raw audio signals and provide the main features based
on rhythm, tone, and pitch, which are crucial
components for recognizing speech emotion. Textual
data is processed into its vector representation using
NLP technologies, such as tokenization and
embedding techniques like Word2Vec or BERT, that
can convey the emotional undertones and semantic
meaning of the dialogue.
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI
571
9.3 Module for Model Development
In the Model Development Module, the deep
learning models for emotion classification are
designed, built and trained. Multimodal data
complexity is handled by implementing two core
models in this study CNN & DenseNet121.
DenseNet121 which utilizes the visual features
retrieved from the photographed to process through
this as it is a deep neural network that is particularly
well suited for learning hierarchical representation of
images. The CNN architecture extracts patterns from
audio, image, and video data. Together, these models
allow the system to make better informed predictions
by considering aspect of the temporal and spatial data
linkages. Backpropagation and gradient descent
optimization algorithms are used through training
with a large dataset containing examples with tagged
emotional states.
10 RESULTS
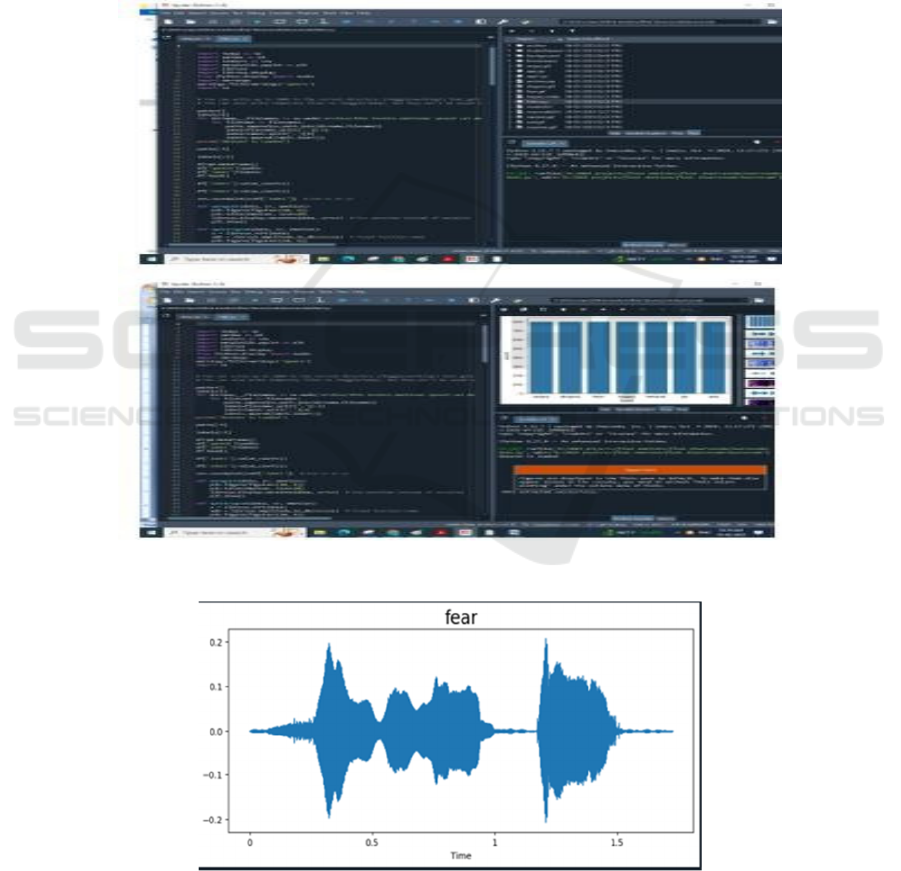
Figure 3: Run project in spyder env.
Figure 4: Get fear data.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
572
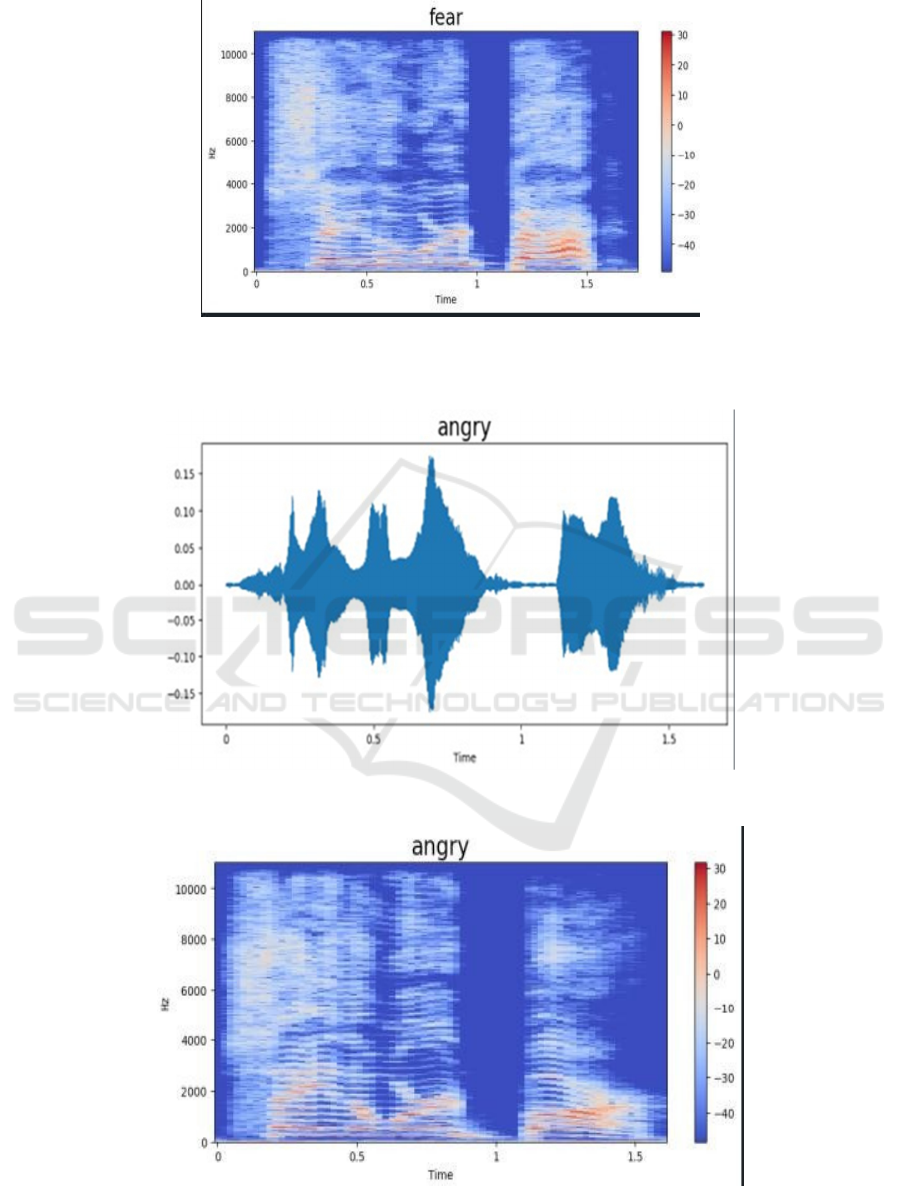
Figure 5: Get decibels data.
Figure 5 show the Get decibels data for the result and the figure 6 shows the get angry data.
Figure 6: Get angry data.
Figure 7: Get angry decibels data.
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI
573
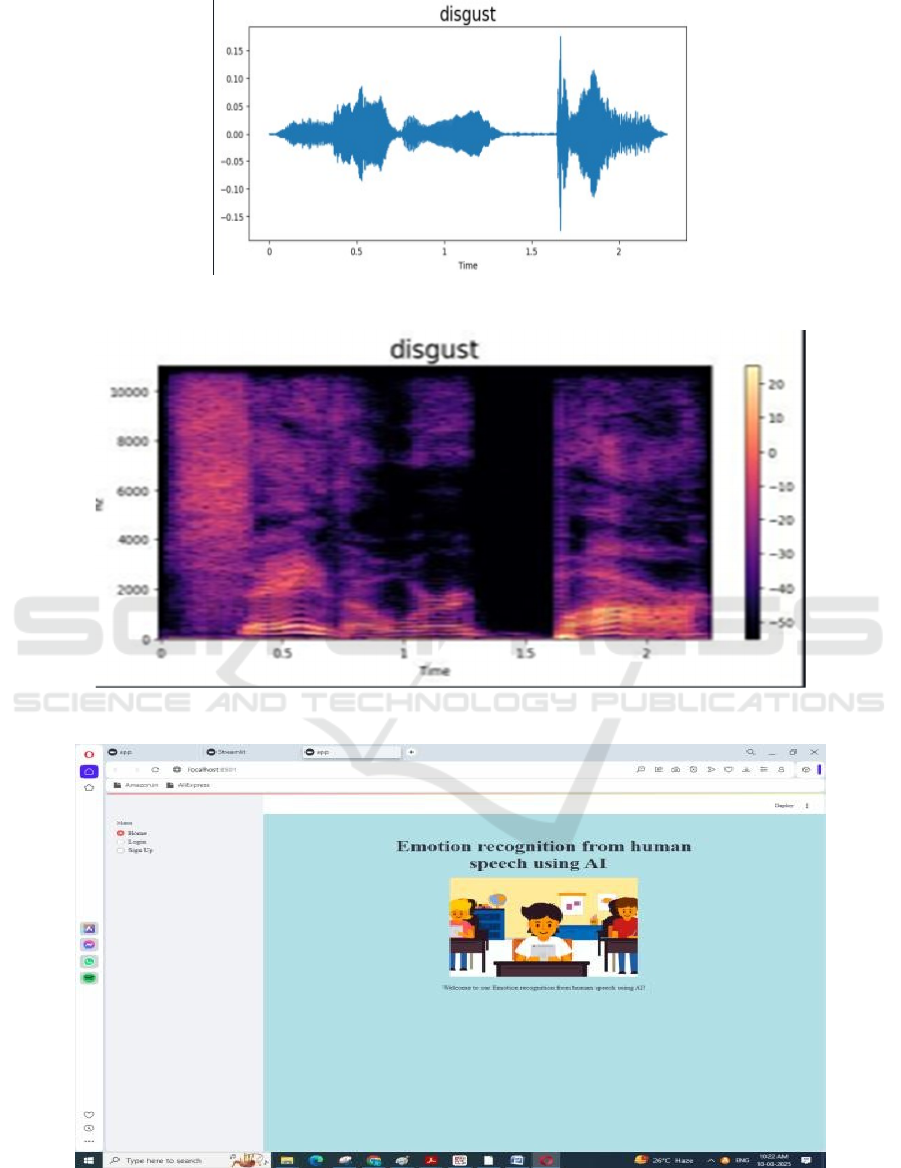
Figure 8: Get disgust data.
Figure 9: Get disgust decibels data.
Figure 10: Dashboard of login page.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
574
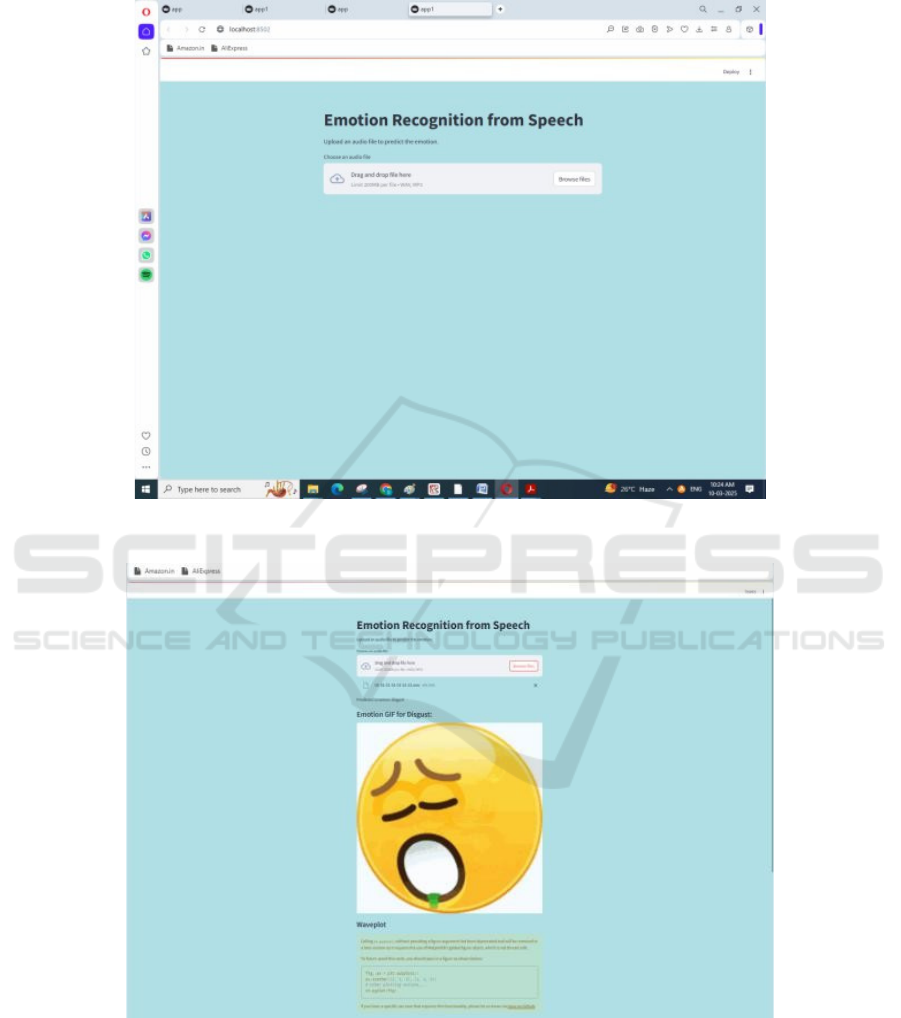
Figure 7 show the Get angry decibels data and the Figure 8,9,10 shows the get disgust data, get disgust decibels data and
dashboard of login page.
Figure 11: Upload audio data.
Figure 12: Get results of emotion.
Figure 11 view the upload audio data and Figure 12 show the get results of emotion.
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI
575
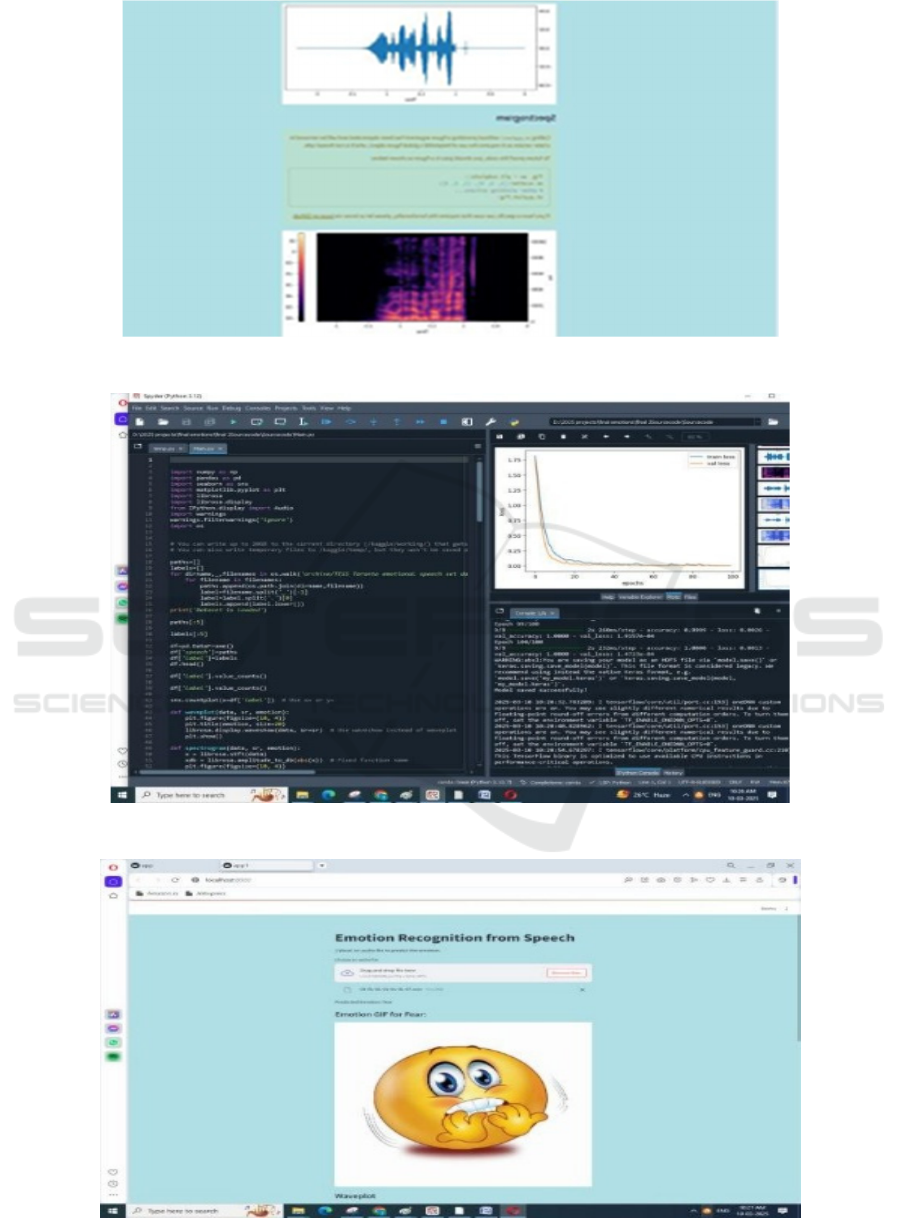
Figure 13: Get DB of data.
Figure 14: Results of test datasets.
Figure 15: Final result of emotion.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
576
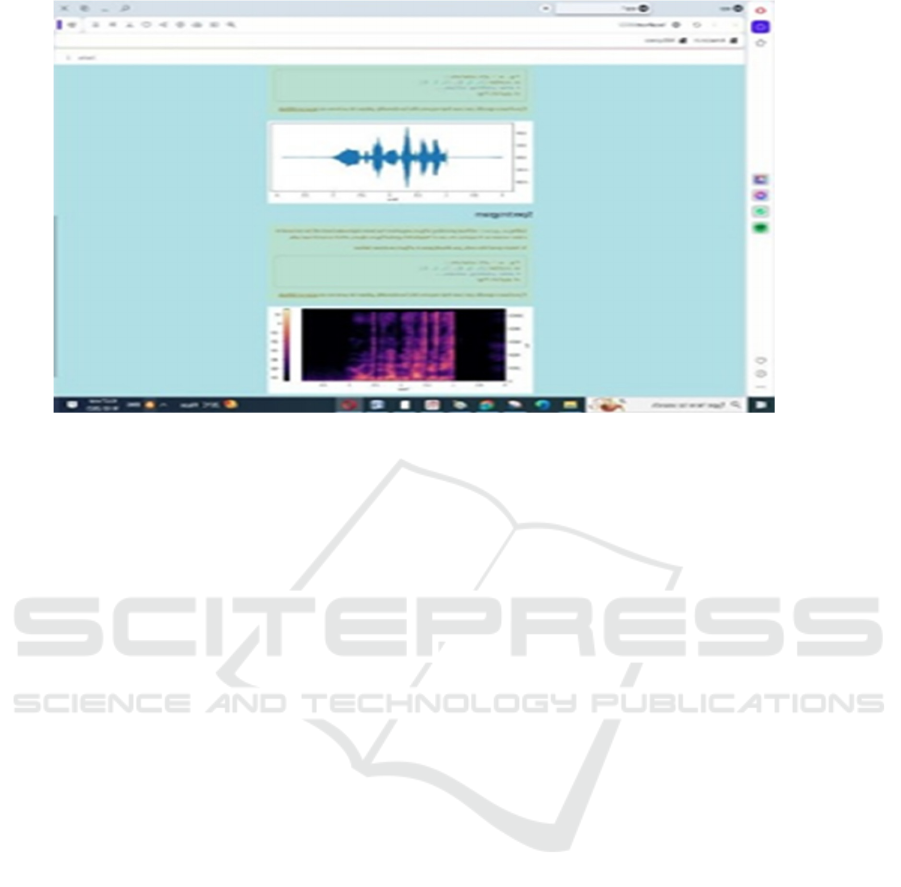
Figure 16: Get real time DB.
Figure 13 show the get DB of data, Figure 14 show the
results of test datasets, Figure 15 show the final result of
emotion and Figure 16 shows the Get real time DB.
11 CONCLUSIONS
Overall, this experiment demonstrates that a
multimodal approach utilizing text, audio cue and
visuals may provide an effective means of emotion
recognition. Deep learning Models like CNN and
DenseNet121 in creating the system could categorize
the emotions into happy, sadness, fear, and surprise
appropriately. Using preprocessing techniques and
feature extraction techniques, such as MFCC for the
audio and GLCM for the images, every modality is
more suitable to the need of the task. The fusion of
multiple sources of data results in a more accurate and
better comprehension of human emotions than
traditional single- modality methods, which enhance
the reliability of the systems.
The proposed system operates in real-time with
commendable accuracy, offering potential
applications across diverse sectors such as customer
support, entertainment, and healthcare. This
experiment's successful implementation shows the
importance of developing multimodal emotion
detection in the context of designing intelligent
systems that can better understand and respond to our
feelings. By combining different data types, each one
contributing their unique perspectives, it facilitates a
more detailed and dynamic emotion classification
process.
12 FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
A better understanding of emotional states is also
possible if more data modalities, such as
physiological signals (e.g., heart rate, skin
conductivity, or facial electromyography), are
included in the proposed system which would help
further improve the proposed system in future. What
is needed is to complement the existing components
(image, audio, and text) with physiological signals,
those frequently used in emotional computing, to
strengthen emotion recognition performance.
Additionally, further advanced natural language
processing may be applied to textual data with
advances in transformer-based models such as BERT
or GPT, allowing the system to identify and cluster
more complex emotions that are coded through
language.
REFERENCES
Advancements in Emotion Recognition Using Multimodal
Deep Learning – 2023.
Combining Deep Learning and Multimodal Data for
Enhanced Emotion Recognition – 2024.
Combining Facial and Acoustic Features for Emotion
Detection in Virtual Assistants – 2024.
Cross-Modal Approaches to Emotion Recognition in
Interactive Systems – 2024.
Deep Learning Models for Emotion Recognition from
Visual, Acoustic, and Textual Data – 2023.
Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using AI
577

Deep Multimodal Learning for Emotion Recognition: An
Empirical Study on Dataset Diversity – 2024.
Emotion Detection Using Facial Expressions, Speech, and
Text for Virtual Assistants – 2023.
Emotion Recognition in Conversations: A Deep Learning
Approach – 2023.
Emotion Recognition from Multimodal Data Using Multi-
Scale Convolutional Networks – 2024.
Enhancing Multimodal Emotion Recognition with
Attention Mechanisms – 2023.
Fusion of Multimodal Features for Emotion Detection in
Real-Time Systems – 2023.
Fusion of Audio-Visual-Textual Features for Robust
Emotion Recognition in Conversational AI – 2023.
Improving Accuracy in Emotion Recognition by
Leveraging Multimodal Features – 2024.
Leveraging Multimodal Fusion Techniques for Cross-
Domain Emotion Recognition – 2024.
Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition Using Deep
Neural Networks – 2023.
Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Healthcare Using
Convolutional Neural Networks and Text Analytics –
2024.
Multimodal Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning for
Real-Time Applications – 2024.
Real-Time Emotion Detection from Multimodal Data
Using Deep Neural Networks – 2024.
Real-Time Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Virtual
Reality Environments – 2024.
Understanding Emotions Through Multimodal AI Models
– 2022.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
578
