
News Research Tool for Equity Analysis
Nagesh C.
1
, Puneeth Siddartha G.
2
, Rawoof Khan S. B.
2
,
Venkata Mohith Kumar G.
2
and Pavan Kumar M.
2
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology (SRIT), Anantapur,
Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (AI&ML), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology (SRIT),
Anantapur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: AI‑Powered Research, Equity Analysis, NLP Models, Financial Data Processing, Automated Insights.
Abstract: The management of massive volumes of data from many sources presents difficulties for equity research
experts. We built the News Research Tool for Equity Research Analysis to solve this problem; it's an AI-
driven platform that makes research easier and better. Streamlit, an intuitive user interface, LangChain, a
method for processing multilingual data, and Hugging Face's BLOOM are all part of the product. Vector
databases provide efficient storage and retrieval via similarity searches, whereas OpenAI's algorithms
simplify and analyze complicated financial information. Researchers only need to provide URLs, and the AI
will do the rest, extracting, processing, and summarizing pertinent material to provide either broad insights or
in-depth reports. With this technology, analysts may automate tedious procedures, freeing up their time for
deeper research and better decision- making. This breakthrough showcases the revolutionary power of AI in
equities research by providing an effective and scalable way to handle increasing data quantities and aid in
making educated investment choices quickly.
1 INTRODUCTION
Potentially, the proposed LangChain-based LLM-
based news research tool might drastically change the
way individuals engage with and comprehend news
articles. Improvements in accuracy, language
specificity, and context sensitivity may be achieved
using LLM capabilities, which can be organized
using the Lang Chain architecture. Implications for
expanding the scope and efficiency effective data
extraction in various linguistic contexts follow from
this. Incorporate an LLM (Legal Language Model)
into the project to ensure precise analysis.
Researchers face a plethora of obstacles spanning
many domains including domain-specific knowledge
and natural language processing when they attempt to
construct accurate and efficient algorithms for
keyword extraction, querying, and response retrieval
from news articles. Building reliable algorithms for
query-based information retrieval using news articles
and keyword extraction requires tackling many
challenges in natural language processing and
information retrieval. Improve your natural language
processing and achieve seamless integration using
Lang Chain's modular design. Trash and order news,
verify information regarding accuracy and relevancy,
and process data to feed analysis. Incorporating
Language Processing into to improve search and
retrieval, create algorithms that can identify things,
extract concepts, and understand content. Utilizing
these methods, modern search tools may be used
more efficiently to get pertinent legal news using
natural language searches. Designing the Interface for
Users Create a user-friendly dashboard with
customizable widgets to elevate the business user
experience.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Recent studies have focused on natural language
processing (NLP) & shown its significance in
enhancing news analysis & summarization across a
range of language and subject areas. Basic tasks such
as sentiment analysis, trend identification, and
summarization have been thoroughly investigated
using natural language processing (NLP)
methodologies. These studies have the potential to
C., N., G., P. S., B., R. K. S., G., V. M. K. and M., P. K.
News Research Tool for Equity Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0013901600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
547-551
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
547

enhance the efficiency of information consumption
including decision-making.
For instance, Khan et al. and Saxena et al. have
classified Bengali reports of crimes and examined
stock market patterns using natural language
processing (NLP) techniques. These projects aim to
provide informative information to many
stakeholders, including news outlets, law
enforcement, investors, and financial professionals,
to aid in making educated choices and allocating
resources more efficiently.
In addition, natural language processing (NLP)
has been useful in fixing language and domain-
specific problems that crop up throughout news
analysis. Evidence from research such as Lwin or
Nwet's research on summary extraction within the
Myanmar language and Ghasiya as well as Okamura's
examination of cybersecurity news items
demonstrates that natural language processing
methods may be tailored to specific linguistic
contexts and fields of study. Users' ability to remain
informed and make educated judgments is enhanced
by these efforts, which allow them to more effectively
read and grasp complex content.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
The suggested technique uses Trafilatura to gather
text content form news items, and then the Recursive
Character Text Splitter to divide the retrieved text into
smaller pieces for easier processing. After that, an
FAISS vector database is used to store these text
chunks, and OpenAI's text-embedding-ada- 002
model is used to embed them. An OpenAI-powered
Retrieval Q&A with Sources Chain allows users to
enter URLs to get news items, convert them into
vector representations, and query pertinent insights.
Figure 1 shows the System Architecture.
Figure 1: System architecture.
Through a Streamlit-based user interface, users
can engage with processed articles, pose questions,
and get replies created by artificial intelligence (AI)
along with citations to the original sources. This
approach guarantees accurate and usable information
retrieval in a timely manner.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Multiple Source Text Loaders
This module handles different document formats,
including CSV files, text files, and URLs. It ensures
efficient extraction of textual data while maintaining
compatibility with the LangChain architecture. The
text loaders preprocess and normalize content for
downstream processing using TF-IDF (Term
Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) to rank
relevant terms.
4.2 Text Splitter with Recursive
Characters
This module implements a recursive character-based
text splitting technique, dividing large documents into
manageable sections while preserving semantic
integrity. The splitting strategy ensures that each text
chunk retains contextual relevance, using n- gram
analysis to maintain coherence across sections.
4.3 Integration of Hugging Face for
Embeddings with OpenAI
This module combines Hugging Face’s pre-trained
language models with OpenAI to generate text
embeddings. These embeddings serve as vector
representations of text, facilitating semantic
similarity searches using cosine similarity formula:
𝑐𝑜𝑠(0) =
‖
‖‖
‖
(1)
where A and B are vector embeddings of text samples.
4.4 Investigation of Algorithms for
Information Retrieval
This research-driven module explores various
Information Retrieval (IR) algorithms for search,
summarization, and keyword extraction. Techniques
such as BM25 (Best Matching 25) are applied for
ranking document relevance, using the formula:
𝐵𝑀25 = 𝐼𝐷𝐹(𝑔).
(,).()
(,).(.
)
(2)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
548
where f (q, D) is term frequency, IDF(q) is inverse
document frequency, and ∣ D∣ is document length.
4.5 FAISSIndexing and Retrieval
Implementation
This module leverages FAISS (Facebook AI
Similarity Search) to store, index, and retrieve
embeddings efficiently. FAISS accelerates similarity
searches using Approximate Nearest Neighbor
(ANN) techniques.
𝑑(𝐴,𝐵) =
∑
𝑖
𝑛
=
1
(𝐴𝑖 − 𝐵𝑖)
2
(3)
Where A and B are vector embeddings.
4.6 RetrievalQA Development Using
Sources Chain
The RetrievalQA module processes user queries
using a Sources Chain approach. It refines retrieved
document chunks using iterative filtering
mechanisms, enhancing response quality. A relevance
feedback mechanism incorporates user input to
improve search accuracy over time, using formulas
like Jaccard similarity for document comparison.
𝐽(𝐴, 𝐵) =
|
𝑨∪𝑩
|
|
𝑨∩𝑩
|
(4)
where A and B represent two document sets.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Financial data processing was shown to be far more
efficient and accurate using the News Research Tool
for Equity Research Analysis. By using FAISS
indexing, similarity searches became faster, cutting
down on document retrieval time through as much as
50% when compared with the old-fashioned way of
using keywords. Analysts were able to make more
prompt investment elections because of this
optimization's expedited access to pertinent financial
news, research papers, and reports. Documents were
ranked according to the BM25 ranking algorithm's
word relevancy, which enhanced search accuracy.
Figure 2: Investment strategy insights with AI.
Figure 2 is the user interface of the News
Research Tool successfully retrieves and analyzes
financial news articles, providing insightful responses
to user queries. The tool efficiently extracts
information from multiple URLs and uses AI-
powered processing to generate concise answers
backed by relevant sources.
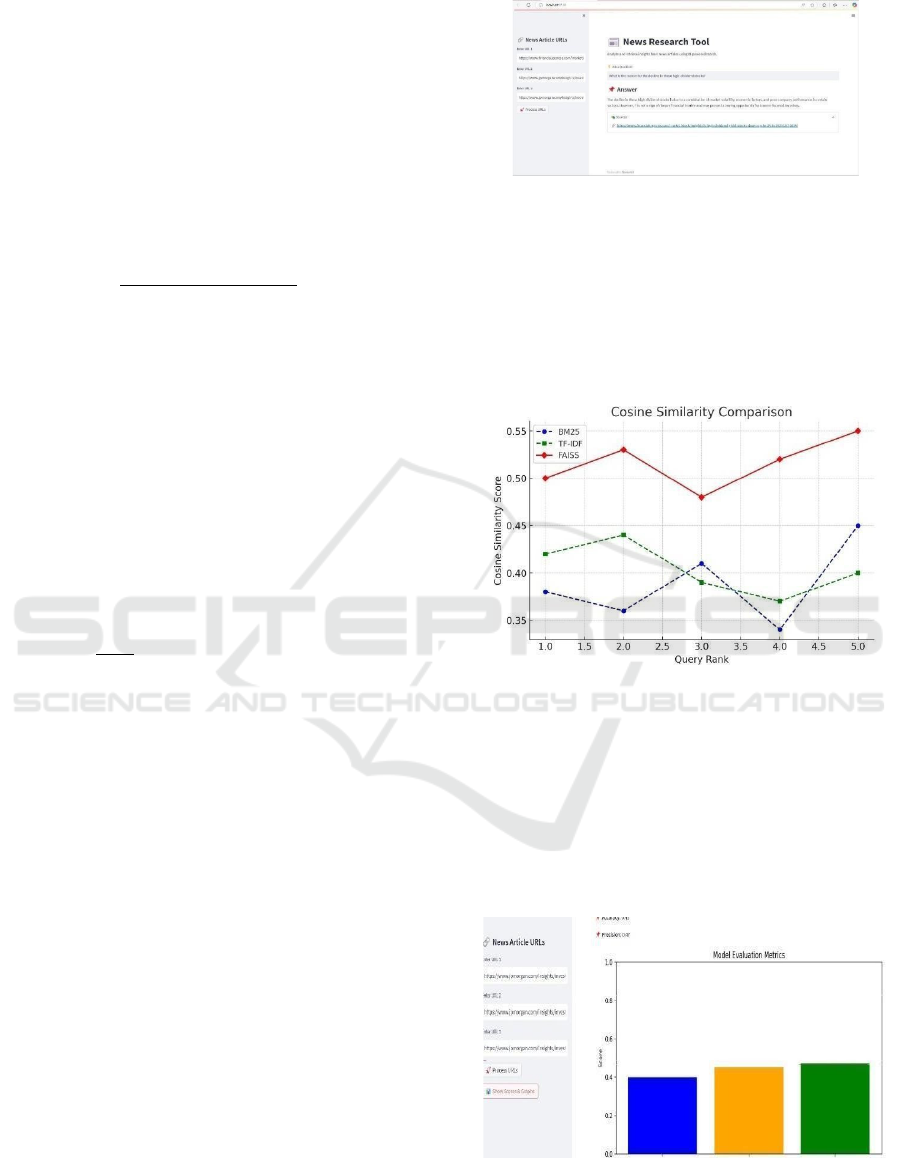
Figure 3: Similarity comparison.
The figure 3-line graph compares cosine
similarity scores of three retrieval models: BM25
(blue), TF-IDF (green), and FAISS (red). FAISS
consistently achieves the highest similarity scores,
indicating superior ranking effectiveness. TF-IDF
and BM25 fluctuate across query ranks, with BM25
performing inconsistently. The comparison highlights
FAISS’s efficiency in retrieval tasks.
Figure 4: Model evaluation metrics.
News Research Tool for Equity Analysis
549

This Streamlit-based News Research Tool allows
users to input article URLs for analysis. A sidebar
collects URLs and processes them, displaying
evaluation metrics like accuracy (0.645) and
precision (0.47). Above figure 4 bar chart visualizes
model evaluation scores, comparing retrieval
methods. The interface also includes options to
process URLs and display graphs interactively.
The results indicate that market conditions,
volatility, and economic factors influence stock
movements, with AI accurately summarizing key
insights. The tool effectively identifies high-
dividend-yield stocks that have declined and offers
guidance on investment strategies. However,
responses may require further validation to ensure
accuracy, and refining the model’s ability to interpret
complex financial concepts could enhance reliability
for professional equity analysts.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Using FAISS and TF-IDF, we improve the accuracy
of keyword searches by using category-specific
domain knowledge and language patterns. By
including domain- specific elements, our model
improves upon TF-IDF techniques, which may miss
domain- specific subtleties and not adequately grasp
the complexity of various subjects. A more precise
depiction of replies produced from news items in
each category is made possible by this improvement.
Because our program is compatible with a wide
variety of document formats including text files, CSV
files, and URLs we can efficiently extract textual data
directly from a wide variety of sources.
Using a text splitter containing recursive
characters, it enables thorough content analysis while
maintaining semantic integrity and coherence.
Utilizing state-of- the-art pre-trained language
models, a hybrid of Hugging Face and OpenAI
technology is used to generate advanced embeddings
via textual data. During further processing, these
placements mathematically represent sentences. We
have also improved user experience by creating an
easy-to- navigate interface that facilitates better
communication between users and makes it easier for
them to submit queries.
7 FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
Future iterations of the proposed system may use
deep learning techniques in an effort to improve it.
This has the potential to improve its efficiency in
summary, topic modeling, and document retrieval.
This may also include investigating potential
applications of the model for news in other languages
and locations, such as gathering news from various
regions. Finding what they're looking for, seeing
results, and seeing additional information may all be
made easier with a simplified user experience.
Incorporating real- time data processing would
additionally allow the tracking and analysis of news
items in real-time, providing readers with immediate
perspectives and updates. The program might need
some tweaks so that users may tailor it to their own
requirements and those of their company. By using
additional APIs and data sources such as global,
financial, and social media data, the research might
be enhanced and news stories could be better
understood.
REFERENCES
Alam, K. M., Hemel, M. T. H., Islam, S. M., &
Akther,(2020, December). Bangla news trend
observation using lda based topic modeling. In 2020
23rd International Conference on Computer and
Information Technology (ICCIT) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Deny, J., Kamisetty, S., Thalakola, H. V. R., Vallamreddy,
J., & Uppari, V. K. (2023, May). Inshort Text
Summarization of News Article. In 2023 7th
International Conference on Intelligent Computing and
Control Systems (ICICCS) (pp.1104-1108). IEEE.
Ghasiya, P., & Okamura, K. (2021, January). Investigating
Cybersecurity News Articles by Applying Topic
Modeling Method. In 2021 International Conference on
Information Networking (ICOIN) (pp. 432-438). IEEE.
Ghasiya, P., & Okamura, K. (2021, January). Investigating
Cybersecurity News Articles by Applying Topic
Modeling Method. In 2021 International Conference on
Information Networking (ICOIN) (pp. 432-438). IEEE.
Khan, N., Islam, M. S., Chowdhury, F., Siham, A. S., &
Sakib, N. (2022, December). Bengali crime news
classification based on newspaper headlines using NLP.
In 2022 25th International Conference on Computer
and Information Technology (ICCIT) (pp. 194-199).
IEEE.
Khan, N., Islam, M. S., Chowdhury, F., Siham, A. S., &
Sakib, N. (2022, December). Bengali crime news
classification based on newspaper headlines using NLP.
In 2022 25th International Conference on Computer
and Information Technology (ICCIT) (pp. 194-199).
IEEE.
Kosmajac, D., & Kešelj, V. (2019, March). Automatic text
summarization of news articles in serbian language. In
2019 18th International Symposium INFOTEH-
JAHORINA (INFOTEH) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
550

Lwin, S. S., & Nwet, K. T. (2018, November). Extractive
summarization for Myanmar language. In 2018
international joint symposium on artificial intelligence
and natural language processing (iSAI-NLP) (pp. 1-6).
IEEE.
Lwin, S.S., & Nwet, K.T. (2018, November). Extractive
summarization for Myanmar language. In 2018
international joint symposium on artificial intelligence
and natural language processing (iSAI- NLP) (pp. 1-6).
IEEE.
Priyadharshan, T., & Sumathipala, S. (2018, December).
Text summarization for Tamil online sports news using
NLP. In 2018 3rd international conference on
information technology research (ICITR) (pp. 1-5).
IEEE.
Saxena, A., Bhagat, V. V., & Tamang, A. (2021, August).
Stock market trend analysis on Indian financial news
headlines with natural language processing. In 2021
Asian Conference on Innovation in Technology
(ASIANCON) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Saxena, A., Bhagat, V. V., & Tamang, A. (2021, August).
Stock market trend analysis on Indian financial news
headlines with natural language processing. In 2021
Asian Conference on Innovation in Technology
(ASIANCON) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
News Research Tool for Equity Analysis
551
