
Enhancing Database Security through Multi‑Layered Cryptographic
Techniques
Gayathri Ramasamy, Gurupriya M., Govindu Lvn Sridhar, Unnam Aditya and Nalla Shreyas
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Amrita School of Computing, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Bengaluru,
Karnataka, India
Keywords: Advanced Substitution Cipher, Encryption, Database Security, Cryptography, Homomorphic Cipher.
Abstract: In light of the computer age, the rise in the number of unauthorized access and cyber security threats makes
use of reliable forms of encryption a must in protecting people’s data. This paper demonstrates the
enhancement of an elaborate cipher system to include advanced forms of substitution ciphers besides the
classic Caesar Cipher, Homomorphic Cipher, and Napoleon Cipher. The research work focuses on the use of
the concept of unique keys aimed on increasing crypto- graphic security and the safety of the database data
kept, transferred and retrieved from the database. The study also looks into the working of multi-layered
cipher integration in light of real word data security and draws out the benefits and drawbacks of such
encryption methods against data manipulation. The results extend knowledge about the possibilities of
complex cryptographic solutions for the database protection and indicate the prospects for further research
aimed at strengthening cryptographic protection against new kinds of threats.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern citizens are living in an informational world
where the amount of information increases with the
speed of light as a consequence of storing and using
it in digital mode, which, with all the advantages, has
led to substantial existential threats, first of all,
concerning data storage and processing. Primary data
storage systems commonly implement simple data
security measures to protect the information;
nevertheless, these measures could be insufficient in
low-impact databases as they do not employ elaborate
security models typical to the databases of high
impact. Small level databases which are used in
narrowed areas with poor economy or simple
applications have become more and more likely to be
attacked because they have poor encryption ability.
This growing risk puts demands to design
sophisticated cryptographic solution more suited to
improve the security on those databases while not
compromising much on performance and
functionality.
The proposed Advanced Cipher System addresses
the shortcomings of the traditional encryption
methods through the development of a new multiple
layer since low-level databases are the target.
Contrary to ordinary approaches to encryption that
involves the use of a single layer of security, this work
combines multiple ciphers to develop a strong
Substitution Cipher System. By encrypting using
unique keys the system adds an extra layer of security
and makes it way harder to crack compared to other
attacks such as using brute force or cryptography
attack. In contrast to the general encryption solutions,
the proposed framework considers the peculiarities of
low-level DBs: low computational overhead and
increased flexibility in terms of scenario for resource-
limited scenarios.
This is a complete secure system intended to
afford data storage, transmission and even access.
What the research is able to show through a structured
evaluation is that the integrated advanced ciphers are
attained in their objectives of thwarting the
unauthorized access or alteration of the information
in question. Probabilistic analysis of the solution in
conjunction with its actual application allows for not
only solving the current problem related to the
encryption of the database at the application level but
also to put the basis for further development of
cryptographic methods, especially for lower-level
database applications.
532
Ramasamy, G., M., G., Sridhar, G. L., Aditya, U. and Shreyas, N.
Enhancing Database Security through Multi-Layered Cryptographic Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0013901400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
532-540
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

The following are the objectives of the proposed
work:
• Establish a secure multilayer encryption model
using sophisticated alphabetic substitution
techniques such as Caesar Cipher and advanced
Homo- morphic Cipher and Napoleon Cipher to
encode the database data.
• Proposed an encryption framework that
addresses an important class of databases,
leveraging low-level models while providing
significant protection in fractionated
environments while keeping intensive security
services costs low.
• Provide a concise and readable design of the
chat application interface and do not interrupt
the user with issues related to encryption, which,
nevertheless, occurs at the time of
communication.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Ritwic et al. (2022) introduced a new encryption
technique combining modified versions of the
Vigen`ere and Polybius ciphers, offering enhanced
security over traditional classical ciphers vulnerable
to modern cryptographic attacks. Noor A. et al.
(2020) introduced a cryptosystem combining
Homophonic and Polyalphabetic Substitution
Ciphers using a circular queue and four keys,
providing fast encryption for personal and network
communication security. Carlson et al.2022)
demonstrated that permutation-substitution-
permutation (PSP) ciphers using regular byte-block
boundaries are as insecure as multi-byte substitution
ciphers, proposing counter measures and introducing
isomorphic cipher reduction. Aiman Al- Sabaawi
(2021) surveyed cryptanalysis techniques for classic
ciphers Caesar, transposition, and Hill demonstrating
how simple algorithms can break them, enhancing
understanding of cryptanalysis and its application in
securing information systems.
Dhavare A. et al. (2013) in his article discussed an
algorithm for breaking homo- phonic substitution
ciphers using a nested hill climb approach, tested on
various substitutions, with a special focus on the
unsolved Zodiac 340 cipher. Anuj Gu- rung et al.
(2024) presented a new encryption algorithm based
on the Caesar cipher, enhanced by random number
generation. It uses two random number lists as keys,
making decryption harder and improving security.
Srivastava et al. (2023) re- searched about the
transformation of data into an unreadable format,
encrypted, and decrypted; steganography is hiding
information within a file. The concept of this paper
will be to combine two technologies. With the use of
image steganography technology along with
cryptography, which is Caesar Cipher encryption,
data security will be improved. Akbar Serdano et al.
(2021) proposed a combined algorithm for the Hill
Cipher and the Caesar Cipher, increasing security
level in data. The research led to improvements in
both encryption and decryption times, especially as
the size of the matrix varied from one size to another.
Increasing the size of the matrix to 5x5 increased the
decryption time.
Oleksandr et., al. (2021) proposed work on
homophonic encryption which seems to have the
advantage of mapping any number of ciphertext
symbols to every plaintext character for improving
security, drawbacks seem to exist for modern
cryptograms. This paper will analyze the Z408 and
Z340 ciphers with emphasis on points of attack
against them. Manjunath S. et., al. (2024) proposed
work on the Pigpen cipher, also known as the
Freemason cipher, is somewhat limited: no key and
cannot encrypt numbers. The AlphaMeshX or AMX
improves it by making a key-based encryption
version using ASCII encoding and mathematical
substitution of 13 alphabetic and 18 numeric versions
for added security.
A recent work of B. Murugadoss et al. (2021)
discusses how watermarking intellectual property
rights over multimedia contents is safeguarded using
digital image watermarking exploiting the spatial and
frequency domains technique- DWT, DCT, and SVD.
Chaotic maps, such as Henon and Logistic maps, are
used for embedding the watermark securely as these
are sensitive to initial conditions. Cryptographic
techniques, such as RSA and Elliptic Curve
Cryptography (ECC), are used for secure keys.
Hybrid schemes are the recent ones that use DWT-
SVD for decomposition and chaos-based encryption
that resist cropping, compression, and noise addition
attacks. This provides strong watermarking as well as
secure multimedia content protection. The work by
Dhanyashree et al. (2021) talks about how graph
theory strengthens the security in the communication
net- work, especially in cryptography. In this study,
the methods of graph labeling are explored, including
both vertex and edge labeling that encodes secure
information. L (3,2,1)-path coloring is one of the
powerful encryption methods that is the extension of
the traditional method of vertex distance-based
labeling.
H. S. Chinta et al. (2024) have presented the work
on how the hybrid approach of deep learning-
cryptography ensures the confidentiality of medical
Enhancing Database Security through Multi-Layered Cryptographic Techniques
533

images and the risk of unauthorized access and
breaches. The study focused on DNA-based AES
encryption for strong data encoding and the LSB
embedding technique for effective data concealment
in steganographic contexts. Discrete Wavelet
Transform is used for compression, saving the storage
and transmission cost while not losing the image
quality.
A. S. Reddy et al. (2024) presented work about the
security of multimedia data, especially audio files,
because of risks in unauthorized access and
manipulation. The article focused on AES as an
efficient means for digital data protection but was
susceptible to attacks based on pattern recognition
attacks. Cellular automata have been emphasized on,
particularly Rule 30, due to its chaotic behavior and
generation of pseudo-random numbers, providing a
better layer of encryption. In addition, XORing
between the cellular automata sequence and AES-
encrypted data increases randomness while
eliminating any patterns. Loss- less compression
formats like WAV are used for the audio file so that
encryption and decryption maintain integrity and
quality during reconstruction. This hybrid approach
on AES and cellular automata has provided audio
data secure transmission and storage through an
efficient way. The work by M. Saraswathi et al.
(2022) discussed the application of graph labeling
techniques, particularly radio mean labeling, in
cryptography. In encrypting, radio mean numbers are
used to determine how key matrices should be
created. Using path graphs maximizes a given order’s
graph diameter and cycle graphs improve a
generator’s key so robust schemes of encryption may
develop from it. By combing graph labeling
techniques and those based on matrices within
cryptology, the given technique ensures that
communications become a challenge for an opponent
simply through the inherent complexity presented in
its radio mean labeling scheme.
Long et al. (2023) examined the application of HE
to multi-layer graph databases that enable secure
computations on encrypted data without revealing the
plain- text. It identifies trade-offs between HE’s
unparalleled security and its computational overhead,
demonstrating that the current HE systems are
practical for low-volume queries but are not scalable
for large-scale operations. This paper shows an
extensive performance evaluation that clearly shows
a quadratic growth of execution time against the data
size and a linear improvement due to parallelism.
Radhakrishnan and Akila (2021) extended the
research in RSA algorithm to be applicable in the
distributed database. Scalability data security and
efficiency problems solutions improved. In this
modified RSA algorithms, key sizes are modified,
and factorization ways are changed such that systems
be- come stronger while fighting off hacking threats.
Fatima et al. (2023) proposed an advanced encryption
technique for protecting facial biometric databases
using bit-plane scrambling with diffusion generated
from chaotic maps. This ensures that the data left in
the database is protected against several forms of
attacks, such as brute force and statistical attacks. The
encryption process consists of several rounds of
transformation and diffusion, resulting in a ciphertext
that is highly diffused, hence counter to known
cryptanalytic techniques.
Rao et al. (2021) addressed the concept of a hybrid
approach for encryption that incorporates Diffusion
Oriented Cryptography in the protection of both rest
and transit data through Diffie-Hellman for safe key
sharing among different entities. Diffusion would
actually make the data more random in nature, hence
the information cannot be easily reversed in any form
of cryptanalysis; therefore, Diffie Hellman technique
is used for ensuring the safe sharing among entities
that are authorized for use. The goals of the project
being considered are aligned with emphasizing
stratification and protection both for data and critical
transactions. Ryandika and Prabowo (2023)
discussed the implementation of integrating AES-256
with RSA to harden web-based databases from SQL
injection attacks. Using AES-256 is done because it
will efficiently encrypt sensitive information; the
incorporation of RSA is there to supplement a more
sophisticated key mechanism in that decryption will
only be made available through use of a
corresponding public and private key. Results show
some performance trade-offs, namely increased
response times for big datasets and RSA overhead
involved in generating its key pair. level database
operations. This survey done by Abood and Guiguis
(2018) reviewed various cryptographic algorithms,
including AES, DES, and RSA. The output may help
to mix together Caesar cipher and homophonic
encryption for your use case. This combination ties
simple methods together with security, forming a
powerful, multilevel encryption system. For instance,
Caesar cipher data can change in the quickest way
while homophonic encryption combats frequency
analysis. These together offer a complete security
mechanism.
Awadh et al. (2023) introduced a multi-tiered
security framework, particularly designed for cloud
computing environments, using the integration of
RSA, AES, and steganographic techniques, which
ensure data integrity and confidentiality. The
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
534
proposed model stresses layered security, where
encryption is used to protect data, steganography to
hide data, and compression to increase storage
capacity and transmission. It addresses some of the
shortcomings of standalone encryption strategies and
promotes a holistic approach to security. The depth
study done by Mushtaq et al. (2024) assessed the
security features of widely used cryptographic
techniques like AES, DES, and RSA. Highly relevant
to the integration of Caesar and homophonic
encryption is the fact that such an analysis
underscores the necessity for the balance of overhead
on computations with robustness to security. Drawing
from such findings, Caesar cipher may thus be
positioned as an easy method for quick obfuscation;
the more serious needs to ensure secure operation are
catered for by homophonic encryption. Nurhayati et
al, (2024) designed an instant messaging Android
application using the AES mode for message
confidentiality. The vulnerability of being an open
platform and susceptible to sniffing with
unauthorized access into the conversation platforms
that this article discusses has been addressed in the
E2EE model. Applying the emphasis placed upon
method on cryptographic efficiency on databases-
especially in relation to the layering of encryption
algorithms- the application of Caesar cipher design
could serve to provide a light initial obfuscation layer,
with homophonic encryption heightening complexity
to improve against frequency analysis attacks.
Goel et al. (2024) stressed the importance of secure
communication by using AES-256 encryption in a
Node.js-based application. The highly robust crypto-
graphic system with ease of implementation assures
the reliability of communication in real-time. The
paper focuses on primary cryptographic aspects like
data encryption, decryption procedure, and key
management strategy. Chat systems demonstrate that
AES-256 is strong enough for secret information to
protect it against unauthorized access. The Double
Layer Password Encryption algorithm is the next
stride in the research into strengthening safety in
cloud-based password administration systems.
Loganathan and Saranya (2024) integrated one- time
password generation technique using public-private
key cryptography for the process of dual encryption
for safe and secure authentication. DLPE af- firms
that its multi-level security approaches significantly
mitigate these risks of unauthorized access, hostile
intrusions, and data breach. This susceptibility focus
of cloud environments encompasses inadequate
authentication methods and session hijacking, and it
also addresses a robust encryption-centric mitigation
strategy. A. V. Kumar et al. (2024) explored the
importance of FHE in cloud computing and
particularly in its capacity to support computations on
encrypted data without decryption. The study puts
much importance on the use of FHE to protect data
privacy while the organization is carrying out
operations like mathematical operations and queries
in cloud contexts, the issue of third parties coming in.
It presents FHE’s four step procedure outsource,
query, computation, and decryption demonstrating
how it can protect organizational data even as it
processes it. The advantages found are data privacy
from breaches and the possibility of securely working
on outsourced data, and the disadvantages found are
computational overhead, consumption of memory
and infeasibility in some cases for some queries.
3 METHODOLOGY
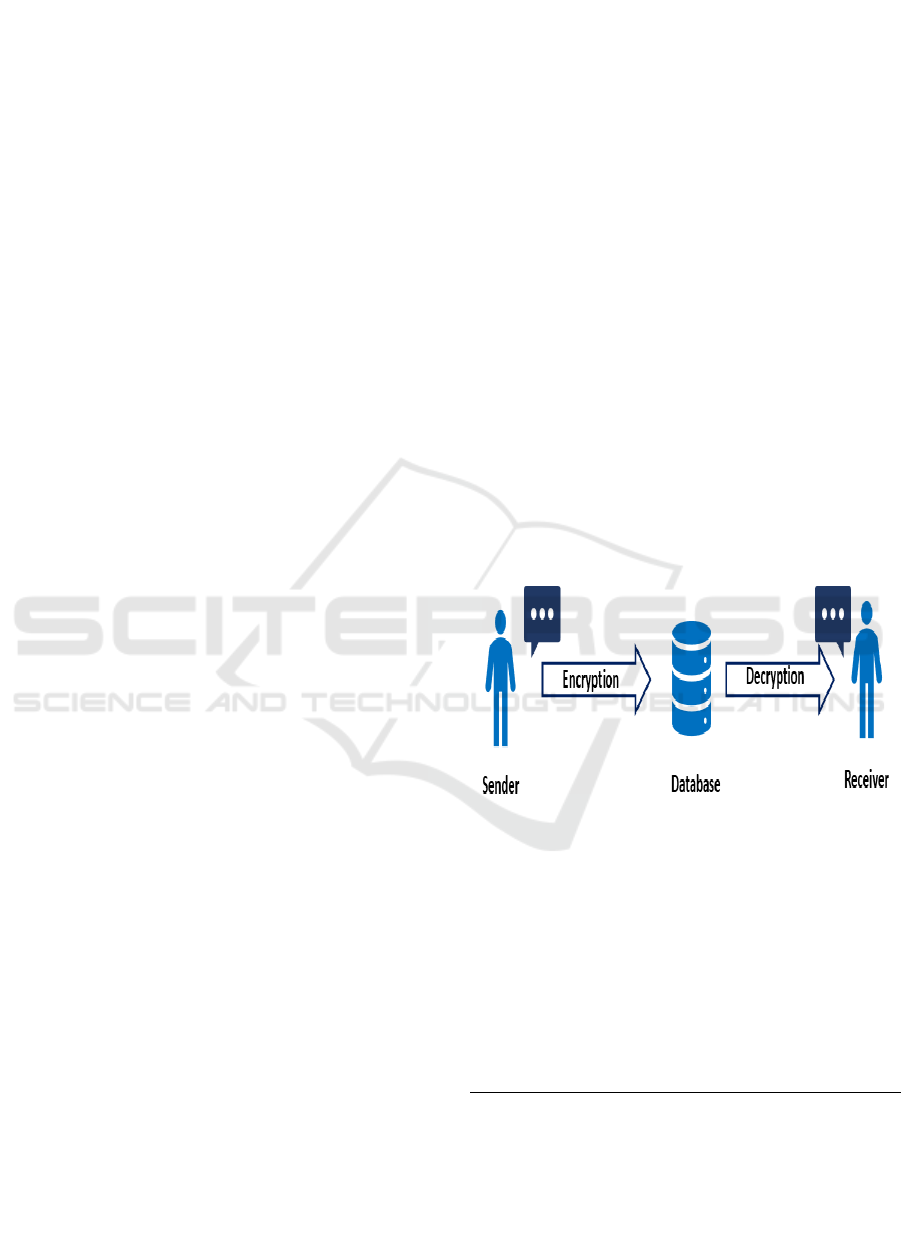
This Figure 1 represents the general flow of
operations in the Advanced Cipher System with an
emphasis on status while reroute to be stored in
database and after being stored it is send to receiver
by performing decryption algorithms.
Figure 1: Work flow of cipher system.
The encryption and decryption process workflows in
the given algorithm 1 and algorithm 2 is a linear
process, which in detail undergoes the Sequential
Special Character Replacement, Caesar Cipher,
Homomorphic Substitution, Napoleon Cipher and
Rail Fence Cipher and vice versa. Earlier steps
increase the complexity of data in each iteration and
guarantee safe conversion of the plain text into the
cipher text with strong resistance to the attack on the
cipher text and other types of invasions.
Algorithm 1: Encryption Workflow.
Require: Plaintext P, Rail Fence Key K
Ensure: Encrypted Ciphertext C
1: Replace special characters in P using predefined Unicode
mapping
2: Apply Caesar Cipher on P with shift S to get intermediate
Enhancing Database Security through Multi-Layered Cryptographic Techniques
535
ciphertext C1
3: Perform Homomorphic Substitution on C1 using a
predefined dictionary to get C2
4: Substitute numbers in C2 with corresponding alphabetic
characters using Napoleon Cipher to get C3
5: Apply Rail Fence Cipher on C3 with key K to get the
final ciphertext C
6: return C
Algorithm 2: Decryption Workflow.
Require: Encrypted Ciphertext C, Rail Fence Key K
Ensure: Decrypted Plaintext P
1: Apply Rail Fence Decipher on C using key K to get
intermediate ciphertext C3
2: Reverse Napoleon Cipher on C3 to substitute alphabetic
characters back to numbers, producing C2
3: Perform Homomorphic Desubstitution on C2 to get C1
4: Reverse Caesar Cipher on C1 with negative shift S to
obtain intermediate plaintext P1
5: Replace special Unicode characters in P1 with original
special characters to get the final plaintext P
6: return P
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
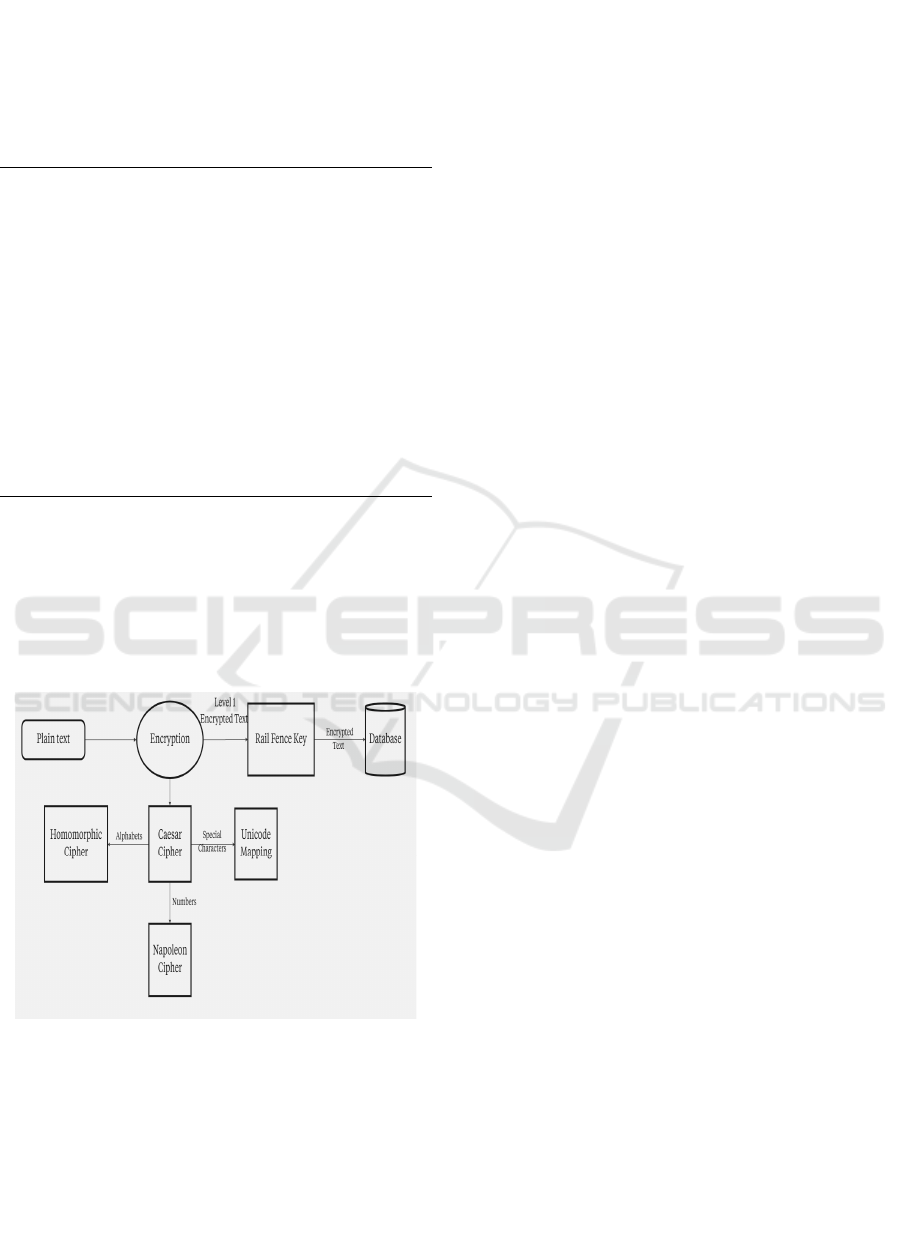
The flow of proposed system is shown in Figure 2
which resembles the flow of Encryption and how are
we going to perform it in the Database.
Figure 2: Work flow of encryption.
User Interface (UI).
In this way, the interface of the application offers
clear and simplified navigation for secure messaging.
UI is created by using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
since the user interface has to be responsive. It
includes:
• Chat Interface: live chat window allows a user
to send messages back and forth in real-time and
offers such options as time stamps and chat log.
• Login and Registration: The system contains a
login so one has to login in order to use the
system, new users are expected to register on the
system. All user credentials that are provided are
securely encrypted before they are stored.
• Minimal User Interruption: The application of
the encryption and decryption processes is such
that there are no any prompt messages in the
application
so as to indicate whether or not the
encryption is being applied.
4.1 Backend and Server
The backend is in PHP and this is hosted on a
XAMPP framework to maintain the server system
locally. XAMPP is perfect for developing and testing
locally as it integrates Apache, MySQL, and PHP so
easily within the platform. The backend is responsible
for:
• Handling Requests: Producing modules for
user registration, login and logout, chat
interaction and message getting.
• Encryption and Decryption: To provide end
to end secured communication, all messages
stored in the database are encrypted and
decrypted when read.
4.2 Database
As for the storing of user details and chat
conversation the chat application employs the use of
XAMPP MySQL database. The key features of the
database include:
• User Data Storage: User information which
include, usernames password and the likes
are well stored in the database through a
strong encrypted format.
• Encrypted Message Storage: All the chat
messages are stored in an encrypted format
using the discussed multi-fold encryption
mechanism. The encrypted messages
include sender id, recipient id along with
message id.
4.3 Encryption Mechanism
One of the most significant components of the design
is the layered encryption complex which guarantees
the protection of the text messages of the application
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
536

users. The encryption process involves the following
steps:
Unicode Mapping.
The steps of operation of an encryption workflow
consist of the first step of substituting some characters
in the plaintext with Unicode symbols in accordance
with the mapping. This transformation makes sure
that special characters are encoded in a standard
format which ease the encryption exercise and at the
same time, avoid some of the complications that may
be occasioned by non-standard encoding Instruction:
What are the complications that may be occasioned
by the non-standard encoding of these characters?
This step also increases the code complexity of the
ciphertext by reverting some of the characters to their
Unicode equivalents as part of its security
enhancement strategy to discourage a possible attack
by revealing or attempting to extract a
particular
pattern.
Caesar Cipher the Caesar Cipher is the simplest of
all encipherment techniques comprises of shifting the
letters in the plaintexts by a fixed number of times in
the alphabet. In this system, after the Unicode
translation of the text, a Caesar Cipher transformation
of the text is applied under which each character is
shifted by a shift value (S). This substitution ensures
that the characters are disguised, this is in a way that
they give an initial encryption. The Caesar Cipher is
also useful in hiding text given that when practiced
together with other methods the plain structure of the
text is not easily recognizable. While the basic Caesar
Cipher is fairly uncomplicated, it definitely deserves
to be applied, as used in combination with other
techniques in a cascading manner forming a multiple
level strong ciphering system.
Napoleon Cipher Napoleon Cipher technique is
used for managing the alphabets followed by numeric
characters in the text. The Napoleon Cipher, in this
case, replaces each number character with an
alphabetical character depending on mapping. It is
important for the purpose of hiding numerical data
within the ciphertext. Because with the translation of
numbers into letters it becomes more difficult for the
attackers to define and strike on the numerical values,
which in their turn are usually included into the key
parameters of the protected in- formation. The added
transformation not only serve the function of
obscuring numerical values but also contributes to the
augmentation in the given level of complexity of a
certain encryption system against frequency analysis
as well as brute force attacks.
Homomorphic Cipher Subsequent to the Caesar &
Napoleon Ciphering the latter is encrypted using a
Homomorphic Ciphering. Homomorphic encryption
may be described as an innovative cryptographic
concept that enables computations to be conducted
over encrypted data without having to decrypt such
data in the first instance. This property makes
homomorphic encryption especially beneficial in
areas that demand secure processing on anonymized
data, as secure computations on the data in cloud
services. In the given encryption process,
homomorphic substitution makes the task more
intricate than simple swapping so as to disguise
plaintext while allowing certain computations on the
encrypted information. This additional step
guarantees the security of the data, as well as
functionality when called upon for particular uses in
the process.
Rail Fence Cipher It needs to be pointed that the
Rail Fence Cipher is a transposition cipher used as the
final layer of encryption. In this process the encrypted
text from the above-mentioned step is then written in
a series of rows one below the other as is shown in the
figure following the given key (K). Finally, to
encrypted the last ciphertext the characters are then
read off row by row. This move of characters has
another feature of putting more difficulty in
deciphering of the ciphertext in that; changing the
structure of characters makes it even hard for an
attacker to logically decipher the plaintext without the
help of key and structure used. When used on its own
the Rail Fence Cipher is much less sophisticated in
the way it works than previous substitution
techniques: but when the order of the letters is
combined with previous substitutions then the Rail
Fence Cipher provides a higher level of security to the
encryption process.
5 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
5.1 MD5 Hashing
In the chat application the passwords that are created
by users they are encrypted using the MD5 hash
encryption as shown in Figure 3 before storing them
in the database. This makes sure that there will be no
plain text password saved, adding to security and
converting it into fixed length irreversible hashes
values. This makes user credentials secure from
access by unauthorized people even if the database is
infiltrated.
Enhancing Database Security through Multi-Layered Cryptographic Techniques
537
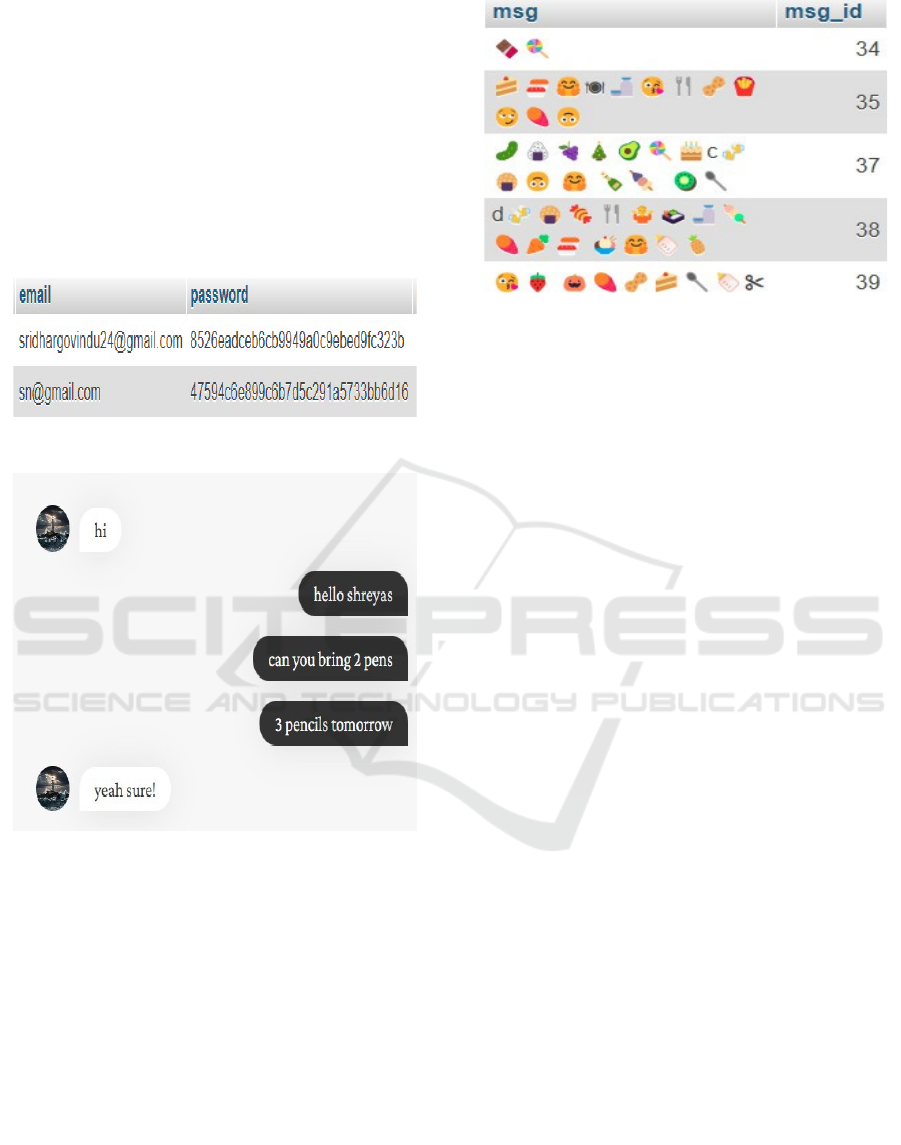
5.2 Chat Window
The Figure 4 shows the friendly chat or a dialogue
window where the interlocutors are the users. The
chat window layout is simplistic with user interface
design to the minimalistic level and switching
between the sender and the receiver’s interfacing
balloons. Every message has a timestamp and
formatted in a way that makes it easy to understand
and maintain communication without compromising
its encrypted status.
Figure 3: User password hashing using MD5.
Figure 4: Image displaying chat window.
5.3 Encrypted Message Inside the
Database
This Figure 5 shows the encrypted chat message
storage in the database. As mentioned above, to each”
msg id” there corresponds an encrypted message in
the form of emoji sequences as a consequence of
homophonic substitution. This de- sign guarantees
the messages stored in it are safe and meaningless to
a third party without decryption hence protecting
privacy of users.
Figure 5: Image displaying chat database.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed system presents a highly secure system
of chat application that employs multilevel high-
secured encryption for the user’s data including
storage of data, sending and even retrieving of data.
Combining processes of substitution and
transposition ciphers promotes the security of
conveyance and resistance to most present-day
modern attack types. Because the system is aimed at
low-level databases, it has an optimal combination of
computational characteristics and the highest level of
data protection. This makes it an acceptable method
of maintaining privacy of user credentials through use
of MD5 hashing from passwords and of messages by
use of homophonic substitution. It thus paves the way
for the realization of layered encryption practice in
other mature and future secure database systems.
REFERENCES
A. V. Kumar, K. Bhavana and C. Yamini, “Fully
Homomorphic Encryption for Data Security Over
Cloud,” 2022 6th International Conference on
Electronics, Communication and Aerospace
Technology, Coimbatore, India, 2022, pp. 782-787,
doi: 10.1109/ICECA55336.2022.10009404.
A. S. Reddy, D. N. Achar, M. S. Mol and N. Panda, “Audio
Encryption Using AES and Cellular Automata,” 2024
15th International Conference on Computing
Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCC
NT), Kamand, India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/ICCCNT61001.2024.10724851.
Abood, Omar & Guirguis, Shawkat. (2018). A Survey on
Cryptography Algorithms. International Journal of
Scientific and Research Publications. 8. 495-516.
10.29322/IJSRP.8.7. 2018.p7978.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
538

Al-Sabaawi, A., 2021, June. Cryptanalysis of Classic
Ciphers: Methods Imple- mentation Survey. In 2021
International Conference on Intelligent Technologies
(CONIT) (pp.1-6). IEEE.
Awadh, Wed & Alasady, Ali & Hashim, Mohammed S..
(2023). A multilayer model to enhance data security in
cloud computing. Indonesian Journal of Electrical
Engineering and Computer Science. 32. 1105.
10.11591/ijeecs. v32.i2. pp1105-1114.
B. Murugadoss, S. N. R. Karna, J. S. Kode and R.
Subramani, “Blind Digital Im- age Watermarking using
Henon Chaotic Map and Elliptic Curve Cryptography
in Discrete Wavelets with Singular Value
Decomposition,” 2021 International Symposium of
Asian Control Association on Intelligent Robotics and
Industrial Automation (IRIA), Goa, India, 2021, pp.
203-208, doi: 10.1109/IRIA53009.2021.9588744.
Bhagat, K., Kumar Das, A., Kumar Agrahari, S., Aanand
Shah, S., RT, D., & Ramasamy, G. (2024). Cross-
Language Comparative Study and Performance
Benchmarking of Sorting Algorithms. Available at
SSRN 5088751.
Carlson, A., Mikkilineni, S.R., Totaro, M.W., Wells, R.B.
and Hiromoto, R.E., 2022, July. Equivalence of Product
Ciphers to Substitution Ciphers and their Se- curity
Implications. In 2022 International Symposium on
Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC)
(pp.1-6). IEEE
D. G. Ryandika and W. A. Prabowo, “Two-Stage
Encryption for Strengthening Data Security in Web-
Based Databases: AES-256 and RSA Integration,”
2023 IEEE International Conference on Communicat-
ion, Networks and Satellite (COMNETSAT), Malang,
Indonesia, 2023, pp. 486-492, doi: 10.1109/COMNET-
SAT59769.2023.10420796.
Dhanyashree and K. N. Meera, “An Illustration of L (3, 2,
1)-path Coloring in Cryptography,” 2021 IEEE 3rd
PhD Colloquium on Ethically Driven Innovation and
Technology for Society (PhD EDITS), Bangalore,
India,
2021, pp. 1- 2, doi: 10.1109/PhDEDITS53295.2021.96
49559.
Dhavare, A., Low, R.M. and Stamp, M., 2013. Efficient
cryptanalysis of homo- phonic substitution ciphers.
Cryptologia, 37(3), pp.250-281.
Gurung, A., Gupta, S. and Varshney, S., 2024, April.
Advanced Caesar Cipher Encryption Algorithm Using
Random Key Generation. In 2024 IEEE 9th
International Conference for Convergence in
Technology (I2CT) (pp.1-5). IEEE.
H. S. Chinta, M. A. U. Sai and K. C.R, “A Deep Learning-
Cryptography Hy- brid Approach for Ensuring Medical
Image Confidentiality,” 2024 Third International
Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Information and
Communication Technologies (ICEEICT), Trichirapp
alli, India, 2024, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ICEE-
ICT61591.2024.10718617.
Ibraheem, N. and Hasan, M., 2020. Combining several
substitution cipher algorithms using circular queue data
structure. Baghdad Science Journal, 17(4), pp.1320-
1320.
J. Long, R. Dantu and J. White, “Performance Analysis of
Homomorphically- Encrypted Heterogeneous Multi-
Layer Graph Databases,” 2023 5th IEEE Inter- national
Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Intelligent
Systems and Applications (TPS-ISA), Atlanta, GA,
USA, 2023, pp. 324-334, doi: 10.1109/TPS-
ISA58951.2023.00047.
Kisan Daule, Viraj, Sanay Santh V, Keshav Padmakumar,
Gayathri Mohandas, and Gayathri Ramasamy.
"Optimized System for Crowd Management Using
Encryption and Decryption Techniques." Available at
SSRN 5089076 (2024).
M. S. Rao, K. Venkata Rao and M. H. M. Krishna Prasad,
“Hybrid Security Approach for Database Security using
Diffusion based cryptography and Diffie-Hellman key
exchange Algorithm,” 2021 Fifth International
Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile,
Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India,
2021,
pp. 1608- 1612, doi: 10.1109/I- SMAC52330.2021.96
40762.
M. Saraswathi and K. N. Meera, “Radio mean labeled paths
in Cryptography,” 2022 IEEE 4th PhD Colloquium on
Emerging Domain Innovation and Technology for
Society (PhD EDITS), Bangalore, India, 2022, pp. 1-2,
doi: 10.1109/PhDED- ITS56681.2022.9955298.
Majumder, R., Datta, S. and Roy, M., 2022, March. An
enhanced cryptosys- tem based on modified classical
ciphers. In 2022 8th International Conference on
Advanced Computing and Communication Systems
(ICACCS) (Vol. 1, pp.692- 696). IEEE.
Mamro, O., Lagun, A. and Dupak, B., 2021, May.
Investigation of Homophonic En- cryption on Zodiac
Z408 and Z340 Ciphers. In 2021 IEEE 12th
International Con- ference on Electronics and
Information Technologies (ELIT) (pp.109-112). IEEE.
Mandapati and Sankar, Divity Mani and Sri Hanish Kumar,
Meka Sai and Ramasamy, Gayathri, Intelligent
Innovations in Personal Security: A Smarter Approach
for Enhanced Protection (November 15, 2024).
Manjunatha, S. and Thenmozhi, S., 2024, May. Extended
Pigpen Cipher with New Variations using ASCII and
Division Substitution. In 2024 4th International
Conference on Pervasive Computing and Social
Networking (ICPCSN) (pp.785- 789). IEEE.
Naga Sudha, D. K. S., Hari Priya, C., Bindu Sree, M.,
Sankar, D. M., Sri Hanish Kumar, M. S., & Ramasamy,
G. (2024). Intelligent Innovations in Personal Security:
A Smarter Approach for Enhanced Protection.
S. Radhakrishnan and A. Akila, “Securing Distributed
Database Using Elongated RSA Algorithm,” 2021 7th
International Conference on Advanced Computing and
Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore,
India,
2021, pp. 1931- 1936, doi: 10.1109/ICACCS51430.20
21.9441962.
S. F. Raza, S. Deshmukh, A. Kulkarni and D. Pradhan,
“Face Database Protection Using Encryption
Enhancing Database Security through Multi-Layered Cryptographic Techniques
539

Technique,” 2023 IEEE Pune Section International
Conference (PuneCon), Pune, India, 2023, pp. 1-5, doi:
10.1109/PuneCon58714.2023.10450006.
Serdano, A., Zarlis, M. and Nababan, E.B., 2021, April.
Performance of combining hill cipher algorithm and
caesar cipher algorithm in text security. In 2021
International conference on artificial intelligence and
mechatronics systems (AIMS) (pp.1-5). IEEE.
Sri Hanish Kumar, M. S., BG, S., Mahithi Reddy, T., Bindu
Sree, M., & Ramasamy, G. (2024). Optimizing Job
Shop Scheduling: A Comparative Study of
Metaheuristic Algorithms.
Srivastava, M., Srivastava, U. and Srivastava, S., 2023,
March. Modified Caesar Cipher with image
steganography. In 2023 6th International Conference on
Information Systems and Computer Networks
(ISCON) (pp.1-6). IEEE.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
540
