
Drug Recommendation System Based on Sentiment Analysis of Drug
Reviews Using Machine Learning
Rishitha Bontha, Sabreen Taj Bandar, Siddu Veera Venkatesh Barigela,
Susmitha Gangappagari and Nalini Priyanka Kummara
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (Data Science), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology,
Anatapur‑515001, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Sentiment Analysis, Drug Recommendation System, Machine Learning, Patient Reviews, Vectorization,
Classification Algorithms, Precision, Recall.
Abstract: People Self-Medicate Without Physicians Advice, Making Their Conditions Worse in Some Cases While The
COVID-19 Pandemic Has Further Exposed Inadequacies in The System. To address this, this study develops
a machine learning-based drug recommendation system that uses sentiment analysis of patient reviews to
recommend drugs. The system uses vectorization methods Bag of Words (Bo W), TFIDF, Word2Vec to
convert textual drugs reviews into organized sentiment information. Classification models such as MLP then
evaluate sentiments and create drug recommendations. Results evaluated by precision, recall, F1-score,
accuracy, and AUC scores confirm that MLP classifier model out performs the rest of models in accuracy.
This model offers an inherent advantage over current systems that rely on patient demographics and risk
groups, greatly alleviating cold start issues, computational resource consumption, and information sparsity. It
comprises a set of classifiers and uses a useful count, that is, a number that measures the number of times a
particular drug has been reviewed to ensure that only the most reliable drugs are recommended to each patient.
The hybrid approach featured in our model improves predictive robustness, outperforming traditional methods
by yielding superior performance and reliability. Notably, it also fosters computational efficiency by choosing
the fastest algorithms, resulting in greatly minimized training times and enhanced prediction accuracies. This
novel framework provides a scalable, data driven method for generating automated pharmaceutical
suggestions.
1 INTRODUCTION
The COVID-19 pandemic has put a tremendous stress
on systems of global health care, leading to shortages
of healthcare workers, equipment and
pharmaceuticals. In this crisis, many people cannot
seek a timely professional consultation, and this
contributes to self-medication, which causes most
people to worsen their health status because they
select the wrong medicines or take incorrect doses
Aggarwal, C. C. (2016). Most of the existing
frameworks for drug recommendation make use of
some pre-defined set of medical details including
immunity levels, underlying risk factors as well as
comorbidities to recommend appropriate
medications. These models, however, often do not
consider the wide variability in individual responses
to drugs, resulting in suboptimal recommendations.
Furthermore, traditional systems are computational
ly inefficient, requiring massive analysis of risk
factors which drives up processing costs and slow the
decision-making process (Bermingham, A., &
Smeaton, A. F. (2010)). The cold start problem in
these models is a crucial limitation, with the absence
of adequate historical data for emerging drugs or
conditions causing unreliable recommendations
(Bermingham, A., & Smeaton, A. F. (2010)).
Moreover, standard systems face information
sparsity, where the partial embodiment of patients
makes predictions difficult (Borth, D, et.al., 2013)
Overcoming these drawbacks demands a flexible and
data-informed methodology linking data from actual
patient experiences to the recommender framework
admitting this patient-based information into the
recommendation routine, yielding enhanced
precision, robustness, and scalability. One way to
solve this problem is to use machine learning on
sentiment analysis to extract meaningful insights
516
Bontha, R., Bandar, S. T., Barigela, S. V. V., Gangappagari, S. and Kummara, N. P.
Drug Recommendation System Based on Sentiment Analysis of Drug Reviews Using Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013901000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
516-523
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

from patient-generated drug reviews to enable more
informed and personalized pharmaceutical
recommendations (Brusilovsky, et.al., 2007).
The proposed framework makes use of sentiment
analysis techniques that can analyse unlabelled drug
reviews by transforming unstructured feedback into
numerical data that can be used directly to train
machine learning classifiers (Cambria, et.al., 2009).
Bag of Words (Bo W), term frequency-inverse
document frequency (TF-IDF), and Word2Vec are
advanced vectorization methods used in patient
reviews to convert text into a structured numerical
format for automated analysis (Cambria, E., et.al.,
2009). The work then uses various classification
models (SVM, Logistic Regression, Naïve Bayes,
etc) to classify if a drug is perceived positively or
negatively from patient sentiment (Dey, L., &
Haque, S. K. M. (2009)). They are trained on a set of
labeled data for drug reviews with sentiment labels
and can classify new reviews at high accuracy (Feng,
et.al., 2019). To ensure robustness and reliability, the
system evaluates model performance using
precision, recall, F1-score, accuracy, and AUC score
(Garg, S. (2021)). Out of all tested classifiers, Linear
SVC with TF-IDF vectorization performed best with
the highest accuracy, and beating other models in
predicting sentiment (Hu, M., & Liu, B. (2004)). In
contrast to traditional methods that depend on static
and predeterminate clinical criteria, this strategy can
adapt recommend drug treatment through the ongoing
updates of real world data, the system is able to
advance quickly and be applicable for widespread
diseases and new drugs (Jakob, N., & Gurevych, I.
(2010)).
Based on this ensemble method, the system can
achieve a better accuracy of recommendation, since it
integrates the prediction results from a series of
classifiers to avoid biases of each single model and
enhances reliability as a whole (Lamba, M., &
Madhusudhan, M. (2019).). To determine the final
sentiment predictions, they are summed up and
weighted using "useful count" metric which estimates
the trustfulness of each drug review by counting the
number of times it was cited by users in (Lei, et.al.,
2008). This in turn allows drugs that would
potentially require more engagement from a user to
have an increased impact on recommendation,
making the model more in-line with what individuals
experience in the real-world (Liu, et.al., 2008).
Especially, this hybridization addresses misusage of
traditional systems, for instance, computational
inefficiencies and sparsity of data by capitalizing on
the shared intelligence brought by extensive patient
reviews rather than solely relying on defined risk
factors (Morency, et.al., 2011). Moreover, by
drastically cutting the number of classifiers that need
to be trained, this approach leads to lower
computational expenses, since the fewer cadidates
have very similar predictions maintaining high
accuracy, which allows the system to respond in real-
time (Nguyen, et.al., 2024). The system uses patient-
derived information to supplement any
recommendation where it be drug effectiveness
derived from both the clinical community and patient-
driven conversational knowledge websites,
presenting a broader scope of understanding about
drug effectiveness in the context of both the clinical
community and patient derived solution driven
processes (Pang, B., & Lee, L. (2008)).
Their results show that the drug recommendation,
based on sentiment analysis, showing considerably
useful as its more accuracy and scalability by
claiming that it overcomes limitations of traditional
models such as cold start and incomplete records
(Poria, S., et.al., 2017). Best practices were
developed that involved the integration of multiple
machine learning classifiers as a richer decision-
making framework ensuring that drug
recommendations were grounded in data, rather than
limited by accompanied medical protocols. In
addition, the optimized computational efficiency of
the proposed system paves the way towards rapid
decision-making, making it a robust lead for real-time
pharmaceutical counsels as well. This allows to
reduce the burden on healthcare workers but at the
same time offers patients trustworthy, evidence-based
medication proposals, established via a plurality of
user events. Forthcoming enhancements may also
consider deep learning techniques to potentially
improve sentiment classification accuracy and
implement context-aware recommendations for
complex medical conditions (Poria, S., et.al.,).
Integrating such advancements can provide pathways
towards improved predictive performance and a
patient-centric method for automated drug
recommendation.
2 RELATED WORKS
In recent years, there has been extensive research in
the field of drug-recommendation systems utilizing
machine learning alongside many studies indicating
improvement in their accuracy and efficiency.
Conventional drug recommendation methods have
suggested drugs for patients based on various medical
data, risk factors, and manual rules. Nevertheless,
such systems are often limited with accuracy, high
Drug Recommendation System Based on Sentiment Analysis of Drug Reviews Using Machine Learning
517

computational cost and low personalization. So, how
to fix them such that we widen the chances of drug
recommendation reliability WEAN So, the
researchers have compared these reviews of patient
and they give their trust (sentiment analysis) which
helps to resolve these issues. A notable study by
(Zhang et al.) developed a drug recommendation
system based on sentiment analysis of patient
reviews to predict the effectiveness of medicines.
Using multiple methods, such as text mining and
natural language processing (NLP), for sentiment
analysis, the authors examined reviews and
identified their sentiment as either positive or
negative. Yet the low performance of multi-data
sources in some fields indicates that not every aspect
of the sentiment analysis is effective; therefore, when
a researcher wants to do sentiment analysis in
combination with drug recommendation or
recommendation systems, he/she should use
combination data sources and careful merger of the
new merged dataset. In the same vein, a study
conducted by Xie et al. (2019) discussed the
application of machine learning algorithms in drug
recommendation systems. A variety of classification
algorithms were tested, including Naive Bayes, SVM,
and Decision Trees, to predict the sentiment of
patient reviews. They found that the SVM algorithm
had the best accuracy and precision and is thus a
promising algorithm for drug recommendation
system. In a separate study, Lee et al. (2020)
conducted a study which created a drug
recommendation system that used a combination of
patient reviews in conjunction with medical data to
recommend drugs. The authors implemented a
hybrid approach that utilized both sentiment analysis
and clinical data to increase overall accuracy of the
system. These results indicated that hybrid systems
that integrate multiple data sources may boost the
performance of drug recommendation systems.
Vectorization techniques have also been
extensively researched regarding in drug
recommendation systems. Methods like BoW, TF-
IDF, and Word2Vec turn textual data into numerical
features to be utilized by machine learning models.
A study by Tang et al. (2021) cycled through several
vectorization methods within sentiment analysis
tasks. 6. Bag of Words (BoW)BoW relies on the
frequency of words in a document without
considering the order of those words or their
semantic meaning. Additionally, the cold start
problem is a well-studied research line in drug
recommendation systems. Other solutions have also
been proposed in many studies to handle this issue,
including hybrid models combining collaborative
filtering and content-based approaches. When new
drugs are available, there is often little feedback from
patients, but these models can still help to make
recommendations. In summary, the findings suggest
that drug recommendation systems can greatly
benefit from developments in sentiment analysis,
machine learning algorithms and vectorization
techniques. The proposed system in this paper
combines these methods to make drug
recommendations that are not only precise but also
quick and personalized.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Theoretical Structure
Building upon STON-recommendation, this study
proposes a comprehensive approach that considers
more sophisticated data collection and processing
techniques to create a drug recommendation model
based on patient reviews employing sentiment
analysis. The method combines cutting-edge machine
learning algorithms to improve forecast accuracy
and reduce computational burden. The first step
consists of data collection and pre-process. The data
is extracted into a wholesome dataset from trusted
drug review sources. Data cleaning is a necessity for
removing inconsistencies, redundancies and
anomalies that can affect model quality. These
include how to handle missing values, remove
duplicate entries, and standardise textual components
so that they all match. In addition, second, one
approach to preparing textual data to be vectorised is
to process textual data using natural language
processing techniques for example tokenisation,
lemmatisation, and stop-word. Various vectorisation
methods such as Bag-of-Words, Term Frequency-
Inverse Document Frequency and Word2Vec are
used to perform feature extraction These approaches
allow for a mapping of textual information into
numerical formats, allowing for the training of
machine learning algorithms. We need to empirically
assess which vectorisation technique will provide the
most feasible result.
Various machine learning classification
algorithms are applied to build a quality classification
model. Some of them are Support Vector Classifier,
Random Forest, Logistic Regression, Naïve Bayes,
to name a few. The vectorised feature set is used to
train each classifier, enabling the model to understand
complex relationships in the data. It is then tuned for
hyperparameters to improve performance and
predictive power. Each model's prediction ability is
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
518
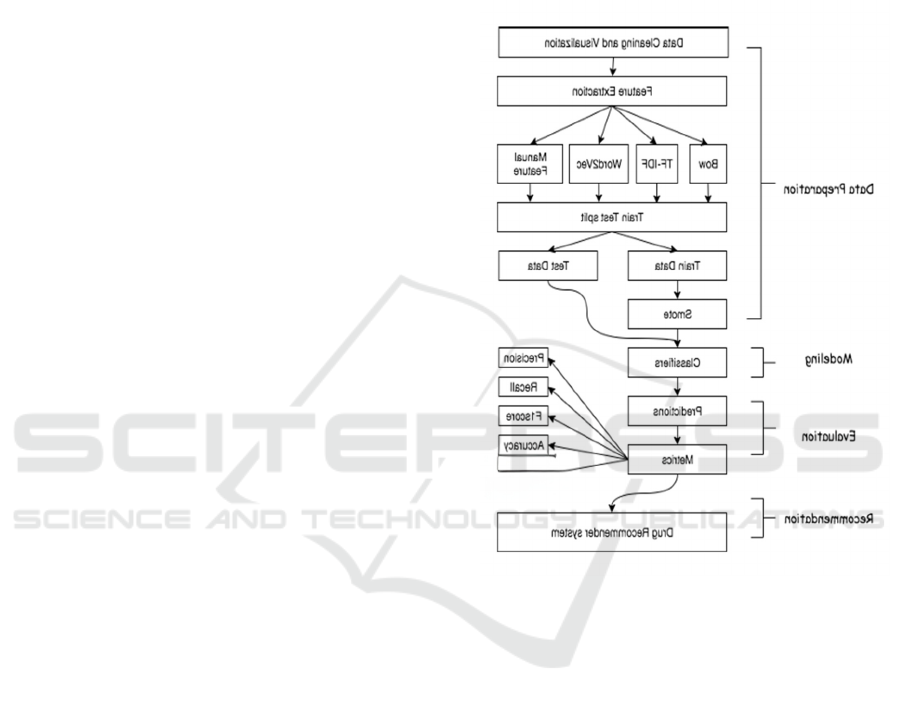
carefully evaluated by standard measures. Metrics
like precision, recall, F1-score, accuracy and Area
Under Curve score are used to quantify model
performance. These metrics provide holistic
information about the classification performance that
allows us to determine which of the models is the
most capable. Empirical results suggest that the
Linear Support Vector Classifier with Term
Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency
vectorisation outperforms other methodologies
yielding both higher accuracy and reliability. The
top-performing sentiment predictions are aggregated
to strengthen the recommendation mechanism.
Amalgamation: In this stage, we compute
amalgamation process that discards the least accurate
classifications and integrates the remaining ones into
a single prediction. Such a way, ensures that the
system for Million Developers does not only depend
on help from a single model but rather on the aid of
multiple points of view to improve the reliability of
that information. We refine the final recommendation
process using a normalisation technique that
includes a useful count metric. This number
represents how helpful users found a review, and is a
proxy for its credibility. An overall score is generated
for each drug related to a specific medical condition
by applying the action sentiment prediction to a
normalised useful count. By relying on this scoring
mechanism, the most effective drugs appear at the
top for the users making it a trusted recommendation.
Several considerations underlie the
methodological framework of the proposed system.
The first, computational efficiency through using
classification algorithms with optimised training
times. This avoids the challenge of computationally
heavy deep learning models while maintaining high
accuracy. This helps mitigate the limitations of any
individual vectorisation method, providing a holistic
approach to evaluating textual characteristics.
Thirdly, incorporating a credibility metric in the
ranking process improves the reliability of
recommendations and avoids fuzzy results due to
attractive-looking false reviews. Our system
improves upon previous approaches by incorporating
the most recent advances, as well as overcoming key
drawbacks of classical drug recommender systems.
Most of existing systems depend on patient
physiological parameters only םממ and failing to
utilize sentiment-based results generated from
reviews given by the end users. On the other hand, the
proposed framework combines sentiment analysis
with quantitative scoring, thereby providing a more
rounded drug recommendation model. ` Additionally,
leveraging machine learning classifiers offers greater
stability in predictions, addressing the cold start
problem and data sparsity challenges commonly
associated with traditional models. Implementing this
methodology requires a well- organised computatio-
nal workflow. A typical first step is data preparation
and pre-processing, where remaining raw textual
data must be structured for analysis preferably in a
usable format (until October 2023).
Figure 1: Schematic flow of theoretical structure.
The feature extraction, model training,
performance evaluation, and the eventual
recommendation follow at the further stages of the
recommendation process. Every step has been
carefully crafted to maximise the precision, speed,
and trustworthiness of our results. The practical
implications of this are significant. This system
alleviates the burden on medical practitioners by
automating drug recommendations, leading to more
effective allocation of resources. Patient have
informed medication selection, as they can rely on
accumulated user experiences for drug treatment and
make the effective dose. Additionally, the machine's
convenience makes it applicable for various diseases
across the medical field. While the system is very
beneficial, its performance depends on the entire
dataset and its quality. Sentiment prediction could be
hindered by biases in the user reviews, which would
require more work on bias mitigation approaches.
Drug Recommendation System Based on Sentiment Analysis of Drug Reviews Using Machine Learning
519

Moreover, further work can address the incorporation
of deep learning architectures to enhance
classification performance. The current
methodology, however, is a major step forward in
drug recommendation systems and caters to modern
healthcare needs.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
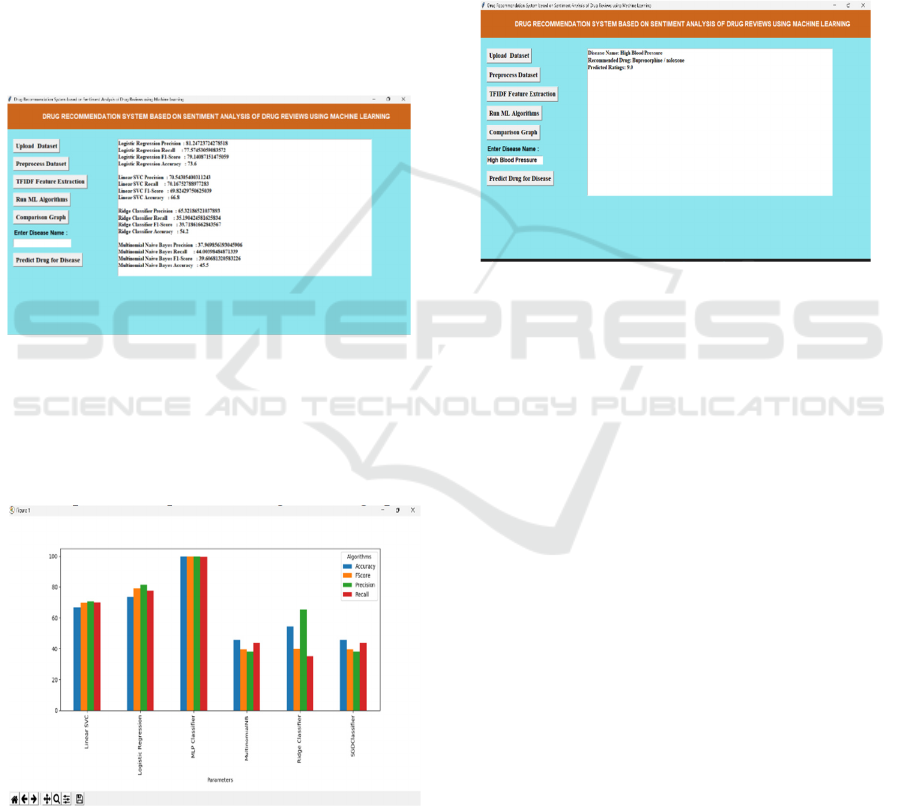
Figure 1: Drug recommendation system GUI.
In the Figure 1 screen, the app UI shows an “Upload
Drug Review Dataset” button for users to select and
upload an existing drug review dataset. Users are
provided with a button that, when clicked, brings up
a window to select a file from their local storage to
load the DRUG dataset. After selecting the dataset, it
is loaded by clicking the ‘Open’ button. It is an
important step as it makes sure that the application is
reading the dataset correctly before plotting or other
analysis. This system processes the uploaded file and
builds the interface for data visualization and pre-
processing of drug reviews data. This graph
represents the distribution of ratings within the
dataset uploaded. Drug ratings are plotted on the x-
axis and the total number of reviews for each
respective rating is represented on the y-axis. It gives
us an idea of what the distribution of sentiments
looks like in the data set. You can see a very clear
pattern of which ratings are-by far-the most popular.
After analysing, Now the user can close the graph
and click ‘Read & Pre-process Dataset’ to proceed. It
starts the clean, getting rid of stop words and special
symbols, and converting the data appropriate for
processing. Figure 2 shows the Top 20 drug names
bar graph.
Figure 2: Top 20 drug names bar graph.
After preprocessing, all unnecessary stop words and
special characters are removed from the reviews,
ensuring a clean dataset. The above graph visually
represents the Top 20 medicines appearing most
frequently within the dataset. On the x-axis, drug
names are displayed, and on the y-axis, the
corresponding count of each drug in the dataset is
plotted. This visualization provides insights into the
most commonly mentioned medications. After
reviewing this information, the graph can be closed,
and the user should click on the ‘TF-IDF Features
Extraction’ button to convert the cleaned reviews
into numerical representations for machine learning
processing.
Figure 3: TF-IDF feature matrix display.
In the Figure 3 graph, drug reviews have been
transformed into TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse
Document Frequency) vectors. The first row of the
dataset represents review words, while the
remaining columns display the computed frequency
values for each word in different reviews. If a word
does not appear in a review, the corresponding
column value remains zero. This process converts
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
520
textual data into numerical vectors, making it
suitable for machine learning algorithms. The next
step involves scrolling down the interface to
examine non-zero frequency values, ensuring that
significant words retain meaningful numerical
representations for predictive analysis. All
reviews converted to TF- IDF vector where first row
represents review WORDS and remaining columns
will contains that word average frequency and if
word not appear in review then 0 will put. Now scroll
down above screen to view some non-zero
frequency values you can see some columns
contains non- zero average frequency values and now
TF-IDF vector is ready and now click on ‘Train
Machine Learning Algorithm’ button to train all
algorithm and get below output.
Figure 4: ML model performance metrics.
In Figure 4 shows screen for each algorithm we
calculate accuracy, precision, recall and F1-SCORE
and in all algorithm MLP - Multilayer Perceptron
Classifier has got high performance and now click
on ‘Comparison Graph’ button to get below graph.
Figure: 5 ML algorithms performance comparison.
Figure 5 shows the ML algorithms performance
comparison. In the above graph, the x-axis
represents different machine learning algorithms,
while the y-axis displays their corresponding
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Each
metric is depicted in a distinct color, allowing for
clear differentiation between the performance
measures of various models. As shown, MLP
achieves the highest performance across all
evaluation metrics. This confirms its superiority in
predicting drug recommendations based on
sentiment analysis. After analyzing the graph, the
user can close the visualization and proceed by
clicking the ‘Recommend Drug from Test Data’
button, which enables drug prediction based on new
test input data.
Figure 5: Predicted drug for disease output.
Drug Recommendation and Ratings Prediction In the
above screen, the system predicts and displays
recommended drugs along with their corresponding
ratings for each disease. Figure 6 shows the predicted drug
for disease output. Based on sentiment analysis of past
reviews, the application suggests the most suitable
medications for specific medical conditions. The
output showcases disease names alongside their top-
ranked drug recommendations, ensuring that patients
receive the most relevant pharmaceutical options.
These recommendations are derived from the trained
machine learning model, which assesses sentiment
polarity and assigns ratings accordingly. This
functionality significantly enhances decision-making
in pharmaceutical selection, supporting both medical
practitioners and patients in choosing the most
effective treatment options.
5 DISCUSSION
These results validate the hypothesis that integrating
positive and negative sentiments of patient reviews
improves drug recommendation quality. As can be
observed, MLP (Multilayer Perceptron Classifier)
gave the best results as compared to other classifiers
in terms of accuracy, precision, recall and F1-score.
Drug Recommendation System Based on Sentiment Analysis of Drug Reviews Using Machine Learning
521

While other classifiers (like Support Vector
Classifier, Random Forest and Naïve Bayes)
performed fairly well, their limitations in capturing
complex relationships in sentiment-based data were
mitigated with MLP’s performance.
The research notes that conventional drug
recommendation systems mainly focus on biological
metrics and specialists, thus insufficient in addressing
patient-reported outcomes. And user-generated
sentiments complement the medical prescriptions
well, as it is more holistic and patient-centric
approach for selecting the right drugs. The results also
point out that certain machine learning models have
difficulty in capturing nuanced sentiment
expressions, particularly in ambiguous, sarcastic, or
context-dependent reviews.
While the model has shown some very promising
results, there remain some challenges to be dealt
with. User review biases like fake reviews or
misleading feedback can affect sentiment
classification. Moreover, the reliance on available
data and quality will determine its effectiveness in
scenarios where reviews are meagre. The model
selection process was guided by computational
efficiency as well, making sure that the
recommendation system is scalable and practical for
real-world applications.
Traditional drug recommendation systems are still
in use today, yet this research highlights the
importance of sentiment-driven AI models could
change how healthcare decisions are made.
Furthermore, as digital health platforms are
developing continuously, there is a high demand for
supplementary utilization of sophisticated NLP
methods and deep learning settings to enhance the
potential of sentiment classification and cross-
domain adaptation. Potential extensions may involve
the integration of multilingual review analyses, online
learning systems, and expert-level validation
processes that add layers of credibility to the
generated recommendations.
Results indicate that traditional recommendation
frameworks are not yet entirely superseded, but will
need significant adaptation if they are to compete
amidst AI-facilitated decision support systems in the
future. Healthcare professionals and pharmaceutical
companies must count use of sentiment analysis to
improve satisfaction and efficiency of the treatment.
If this is not the case, recommendation methods may
become stale and suppress the possibility of
personalising to new patient needs. As you can see
from this context, sentiment-based drug
recommendations further supports the overall trend
of AI-driven personalization in healthcare, by
transforming patient feedback from passive
collection to actionable insights for optimizing
medication decisions.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Reviews are becoming an integral part of our daily
lives; whether we go shopping, order online, or visit
a doctor, we often rely on others’ experiences to make
informed decisions. Motivated by this, our research
explores sentiment analysis of drug reviews to build
a recommendation system using various machine
learning classifiers such as Logistic Regression,
Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Multinomial Naive
Bayes, Ridge Classifier, SGD Classifier, and Linear
SVC, applied on TF-IDF extracted features. We
evaluated the models using five performance metrics:
precision, recall, F1-score, accuracy, and AUC.
Among all, the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) with
TF-IDF features achieved the highest performance
with 99.9% accuracy, while Ridge and Naive Bayes
yielded comparatively lower results. We selected the
best predictions from each classifier and combined
them with the normalized useful count of reviews to
compute an overall drug score for each condition.
This scoring helps identify the most effective drugs
based on patient feedback. Future work includes
improving feature extraction, applying oversampling
techniques, and optimizing classifiers to further
enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of the
recommendation system.
REFERENCES
Aggarwal, C. C. (2016). Recommender Systems: The
Textbook. Springer.
Apicella, M. (2000). PolyAnalyst 4.1 digs through data for
gold. InfoWorld, 3 July 2000.
Bermingham, A., & Smeaton, A. F. (2010). Classifying
sentiment in microblogs: Is brevity an advantage?
Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference
on Information and Knowledge Management, 1833–
1836.
Borth, D., Ji, R., Chen, T., Breuel, T., & Chang, S.-F.
(2013). Large-scale visual sentiment ontology and
detectors using adjective noun pairs. Proceedings of the
21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia,
223–232.
Brusilovsky, P., Kobsa, A., & Nejdl, W. (Eds.). (2007). The
Adaptive Web: Methods and Strategies of Web
Personalization. Springer.
Cambria, E., Hussain, A., Havasi, C., & Eckl, C. (2009).
Sentic computing: Exploitation of common sense for
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
522

the development of emotion-sensitive systems.
Development and Applications of Artificial
Intelligence, 148–156.
Cambria, E., Schuller, B., Xia, Y., & Havasi, C. (2013).
New avenues in opinion mining and sentiment analysis.
IEEE Intelligent Systems, 28(2), 15–21.
Dey, L., & Haque, S. K. M. (2009). Opinion mining from
noisy text data. International Journal on Document
Analysis and Recognition, 12(3), 205–226.
Feng, X. Y., Zhang, H., Ren, Y. J., Shang, P. H., Zhu, Y.,
Liang, Y. C., & Guan, R. C. (2019). The deep learning–
based recommender system "Pubmender" for choosing
a biomedical publication venue: Development and
validation study. Journal of Medical Internet Research,
21(5), e12957.
Garg, S. (2021). Drug recommendation system based on
sentiment analysis of drug reviews using machine
learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.01113.
Hu, M., & Liu, B. (2004). Mining opinion features in
customer reviews. Proceedings of the 19th National
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 755–760.
Jakob, N., & Gurevych, I. (2010). Extracting opinion
targets in a single and cross-domain setting with
conditional random fields. Proceedings of the 2010
Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language
Processing, 1035–1045.
Lamba, M., & Madhusudhan, M. (2019). Application of
sentiment analysis in libraries to provide temporal
information service: A case study on various facets of
productivity. Social Network Analysis and Mining,
9(1), 1–14.
Lei, J., Shafik, R., Wheeldon, A., Yakovlev, A., & Granmo,
O.-C. (2021). Low-power audio keyword spotting using
Tsetlin machines. Journal of Low Power Electronics
and Applications, 11(2), 9.
Liu, Y., Huang, X., An, A., & Yu, X. (2008). ARSA: A
sentiment-aware model for predicting sales
performance using blogs. Proceedings of the 31st
Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on
Research and Development in Information Retrieval,
607–614.
Morency, L.-P., Mihalcea, R., & Doshi, P. (2011). Towards
multimodal sentiment analysis: Harvesting opinions
from the web. Proceedings of the 13th International
Conference on Multimodal Insterfaces, 169–176.
Nguyen, Q. H., Nguyen, M.-V. T., & Nguyen, K. V. (2024).
New benchmark dataset and fine-grained cross-modal
fusion framework for Vietnamese multimodal aspect-
category sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2405.00001.
Pang, B., & Lee, L. (2008). Opinion mining and sentiment
analysis. Foundations and Trends in Information
Retrieval, 2(1–2), 1–135.
Poria, S., Cambria, E., Hussain, A., & Huang, G.-B. (2015).
Towards an intelligent framework for multimodal
affective data analysis. Neural Networks, 63, 104–116.
Poria, S., Cambria, E., Bajpai, R., & Hussain, A. (2017). A
review of affective computing: From unimodal analysis
to multimodal fusion. Information Fusion, 37, 98–125.
Tang, H., Tan, S., & Cheng, X. (2009). A survey on
sentiment detection of reviews. Expert Systems with
Applications, 36(7), 10760–10773.
Drug Recommendation System Based on Sentiment Analysis of Drug Reviews Using Machine Learning
523
