
Detecting Fake Banknotes: Performance Evaluation of ML and DL
Algorithm
Gujarathi Kalyani
1
, Basinepalli Keerthi
1
, G. Shaheen Firdous
2
,
Boya Vasavi
1
and Malipeddi Likhitha
1
1
Department of CSE(AI), Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh 518002, India
2
Department of CSE, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh 518002, India
Keywords: Counterfeit Detection, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Financial
Security.
Abstract: For financial security, making sure counterfeit banknotes are detected is important. We evaluate the
performance of many Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) algorithms to deceive fake currency
accurately. It proposes extracting the numerical and visual features variance, skewness, entropy, of the
wavelet transformed images which are fed to train and test the classification models. Important algorithms,
such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Decision Trees, Random Forests and Neural Networks are
implemented and compared with respect to performance metrics like accuracy, precision, recall and F1 –
score. Also, the detection accuracy is improved by using deep learning models, i.e., Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs), which are capable of automated feature extraction. For the analysis, the dataset is used
which contains labeled instances of genuine and counterfeit banknotes. Strengths and limitations of each
approach are discussed and the applicability to the real word is discussed. Accuracy and robustness in
counterfeit note detection using dummy models of Random Forest and deep learning models, e.g. CNNs, are
superior according to results. The potential of AI driven solutions in automating counterfeit detection has been
established in this project as it is a scalable, efficient, and cost-effective solution for the banking industry. The
advancement of secure and reliable financial systems is made by leveraging data driven
technologies in this study.
1 INTRODUCTION
In fact, counterfeiting remains a threat to the global
economy as it undermines the financial system and
brings about massive losses (Zhang & Huang, 2018).
Counterfeiters are employing advanced techniques
making traditional ways to detect counterfeit
banknotes (such as visual inspection and utilizing
physical security features such as water marks,
security threads and ultraviolet markings) less
reliable in identifying potential counterfeit banknotes
(Li & Liu, 2017). All these processes are human
dependent processes and hence susceptible to errors,
slow in execution and inconsistent making them
impossible for high volume spaces such as banks,
automated teller machines (ATMs), store etc. (Sahoo
& Behera, 2020). We need to develop innovative
solutions to protect financial transactions and keep
the public trust in currency in view of the increasing
scale and sophistication of the counterfeiting on our
currency (Tian & Li, 2020).
The problems stated above are addressed in this
research through applying machine learning (ML)
and deep learning (DL) algorithms to establish
automated, accurate and efficient counterfeit
banknote detection systems (Yin & Li, 2020). Unlike
conventional approaches which rely on predefined
features, ML and DL techniques are capable of
analysing sophisticated patterns existing in banknote
images and, therefore, pointing out elusive features
that differentiate between true and forged notes
(Akkus & Xu, 2019). This study attempts to identify
most appropriate algorithms (e.g. decision trees,
random forests, convolutional neural networks) and
features (e.g. texture and color variations) in real time
authentication (Borges & Silva, 2021). The long-term
goal is to create deployable robust systems, whether
it be in ATM software, at the bank verification
terminals or at the retail checkout systems to perform
468
Kalyani, G., Keerthi, B., Firdous, G. S., Vasavi, B. and Likhitha, M.
Detecting Fake Banknotes: Performance Evaluation of ML and DL Algorithm.
DOI: 10.5220/0013900100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
468-475
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

the instant checks without having human supervision
involved. Unlike existing approaches, this work
presents the first systematic comparison of several
ML and DL models to find the best solution and
provides a practical framework of improving the
capability of counterfeit detection beyond current
level. These systems offer the promise that they will
help reduce the occurrence of financial fraud, beef up
their security, and restore confidence in monetary
systems all around the globe, which is definitely
something that is sorely needed in today’s technology
filed financial landscape (Yin & Li, 2020; Borges &
Silva, 2021).
2 RESEARCH AREA
2.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
To start, a dataset of images of banknotes that are real
and fake is obtained. To this end, publicly available
databases or datasets particular to this case will
comprise high resolution images of different
denominations of banknotes from different countries
(Yadav & Verma, 2018). The format of the images is
made standard along with its size and resolution. To
increase the variability of data, some coupled image
augmentation techniques, e.g., rotation, scale change,
and noise addition, are performed to prevent
overfitting (Chen & Liu, 2017). Therefore,
transformations like the grayscale conversion and the
histogram equalization can be applied to improve
contrast of the banknote images and simplify
identification of texture, edges and the fine features
and details (Sharma & Kumar, 2019).
2.2 Feature Extraction
After preprocessing of the images, in the process of
ML based counterfeit detection the subsequent step
after the preprocessing of the images is feature
extraction which plays a very crucial role. The
pertinent features which can be edges, texture, and
color patterns are to be manually extracted in legacy
machine learning type of models like SVM, KNN,
and Random Forests using methods like HOG
(Histogram of Oriented Gradients), Gabor Filters, and
SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) (Arora &
Sharma, 2018). In deep learning models types like
CNNs, feature extraction is not required through the
convolutional layers of the network, which learn
hierarchical features from the raw image data (Tan &
Duan, 2021).
2.3 Model Development and Training
At this phase, we implement multiple ML and DL
algorithms to train the models in order to identify
counterfeits. We use manually extracted features to
train the SVM model and kernel functions such as
linear or radial basis function (RBF) to provide better
classification (Chen & Liu, 2017). KNN and Random
Forest are also trained from the extracted features,
where KNN predicts based on closeness to nearest
neighbours and Random Forest generates an
ensemble of decision trees for hard classification
(Sami & Gaurav, 2019). The CNN model, on the other
hand, comprises several convolutional layers to learn
and extract features automatically and dense layers
for the final classification into real or fake classes
(Vijay & Kaur, 2019). The models are trained on a
training data set and cross validation methods used to
validate them in an effort to make them generalizable
(Zhou & Wang, 2016).
2.4 Model Evaluation
After training, the models' performances are
evaluated through a series of metrics: accuracy,
precision, recall, F1-score, and confusion matrix (Tan
& Duan, 2021). These enable one to see how well
each algorithm detects fake currency and
distinguishes it from real notes. The evaluation also
includes testing the models on an independent test set
that was not used in training. The CNN model, being
a deep learning-based approach, ought to perform
better than the standard ML models on accuracy in
terms of its ability to learn complex patterns from
images automatically (Vijay & Kaur, 2019).
However, all models are compared to determine the
most computationally efficient algorithm in terms of
computational resources, training time, and
classification performance (Chen & Liu, 2017).
Further, how different preprocessing steps, e.g.,
image resizing or color correction, influence the
pipeline is examined to determine the optimal
pipeline for counterfeit detection (Sharma & Kumar,
2019). This approach allows for an end-to-end
evaluation of the performance of various ML and DL
techniques, yielding valuable insights into the
practical applicability of the technologies in fake
banknote detection (Arora & Sharma, 2018).
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
Most current methods of counterfeit banknote
detection rely on physical examination and security
Detecting Fake Banknotes: Performance Evaluation of ML and DL Algorithm
469

features such as watermarks, UV stamps, security
threads, and holograms. These outdated methods have
been in practice for decades and are still applied by
the majority of banks, retail stores, and ATMs today.
However, they possess enormous limitations when it
comes to identifying advanced counterfeit money,
which can replicate or replicate security features
.
3.1 Manual Inspection
The most primitive mode of counterfeit identification
is manual checking, where people are looking at
physical characteristics of banknote to verify his
authenticity. That requires checking the texture, color,
and the security elements like holograms, watermarks
or raised ink.
3.2 Machine-Based Detection
Machine technology in the guise of currency and UV
light detectors are employed to detect counterfeit
notes by detecting visible security features when held
under ultraviolet light. Such machines usually check
for presence of UV marks, embedded filaments, or
invisible watermarks. Even though such machines are
quicker and more precise than their human
counterparts, they cannot detect sophisticated
counterfeit notes that imitate such features.
Counterfeiting has become sophisticated and forgers
are able to now replicate the UV-sensitive features so
that such machines are not helpful in certain
situations. Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is employed to
scan the serial numbers, words, and markings on
banknotes. Such a method enables a quick check
against a database of authentic serial numbers, but it
checks only whether a particular bill is authentic or
not based on the information present in the image.
Sophisticated counterfeit notes, however, may
precisely manufactured serial numbers and words, so
OCR-based systems are poor at identifying
counterfeit bills with very similar look to real bills.
3.3 Feature-Based Machine Learning
Algorithms
Machine learning (ML) is utilized by some systems
algorithms to identify counterfeit banknotes by
examinations on certain features like textures, edges,
and color patterns. Support Vector Machines (SVM),
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and Random Forest
(RF) were utilized to feature-based classification in
counterfeiting. These systems extract certain features
from images and use to recognize a banknote as real
or counterfeit. Nevertheless, such systems remain
susceptible to hand feature extraction and are less
effective in identifying very small patterns that can
differentiate genuine and fake notes, particularly with
the development of counterfeiting methods.
3.4 Limitations of Existing Systems:
Although the existing systems are good, they have
some limitations:
3.4.1 Only Effective Against Basic
Counterfeiting Methods: Traditional systems work
mostly against rudimentary counterfeits that do not
try to replicate advanced security features.
Sophisticated counterfeit notes with carefully
replicated security features can easily bypass most of
these systems
.
3.4.2 Human Judgment Based
Human inspection is highly reliant on human
experience, which is unreliable, time-consuming, and
prone to errors, especially in high-pressure
environments like banks and shopping malls.
3.4.3 Not Effective for Large Volumes
Manual and mechanical methods are tedious in
dealing with large sums of money, i.e., in ATM
machines, department stores or in money processing
.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
Overview.
The system suggested for detecting counterfeiting
banknotes utilizes the most recent Machine Learning
(ML) and Deep Learning (DL) techniques to enhance
accuracy, efficiency, and scalability in currency
authentication. The objective is to autonomously
detect counterfeit notes in real-time without the
limitations of existing practices, e.g., reliance on
human verification, vulnerability to environmental
conditions, and susceptibility to sophisticated
counterfeiting techniques. The suggested system
involves multiple stages of data acquisition, feature
extraction, training of models, and deployment, with
a focus on leveraging Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) in perdurable image-based forgery
detection.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
470

4.1 Data Collection
The data collection process for detecting fake
banknotes involves gathering a diverse dataset of
images featuring both genuine and counterfeit
banknotes. These images are captured under various
lighting conditions, angles, and resolutions to ensure
variability in the dataset. Additionally, the system
collects visual features from the banknotes, such as
texture, color patterns, security elements like
holograms, watermarks, and serial numbers, which
help in distinguishing authentic from fake notes.
Metadata such as the denomination, country of origin,
series, and year of issue is also extracted to further
assist in identification. Furthermore, each banknote
image is labelled as either genuine or counterfeit,
providing essential annotations for supervised
learning and model training.
4.2 Preprocessing and Feature
Extraction
Different preprocessing techniques are applied to
collected banknote images in order to enhance and
highlight to features for analysis. Grayscale
conversion, image normalization and edge detection
methods are used to focus attention to watermarks,
microtext, or other security features that are encoded
in the banknotes. Convolutional Neural Networks
(CNNs) learn relevant patterns directly from the raw
images automatically in their task of feature
extraction and do not require any manual intervention
for learning relevant features. It may learn the
features such as texture patterns, the quality of prints,
ink distribution, holograms and any other subtle
features that can help us to differentiate the genuine
from counterfeit notes.
4.3 Deep Learning Model (CNN) for
Detection
The method presented here for the purpose of fake
banknote detection is a proposed automatic system
whose approach is to utilize Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) to automatically learn and extract
main features from a large database of images
labelled as real or counterfeit currency. This task is
very appropriate for CNNs to perform, as they are
capable of handling complex patters as well as
hierarchical.
It does not rely on manual extraction of features
from raw images. The convoluted architecture
includes layers which identify convex patterns like
edges or textures, pooling layers to reduce the
dimensions and keep important information and the
fully connected layers for the final classification. This
setup enables the system to process images at great
speed and make accurate decision w.r.t whether the
banknote is real or fake. The top advantage of CNN
is its ability to capture fine and explicit features like
printing in cohesion, ink distribution, watermark and
hologram that is necessary for detecting counterfeit
banknotes. However, capturing these features is
difficult using traditional methods and combined with
the CNNs they are therefore suitable for encoding
task. In addition, the system generalizes well when
the training is done on diverse datasets and the new
unseen banknotes can even include advanced
counterfeiting techniques. High accuracy and
adaptability to real world application are thus ensured
and the system can detect the counterfeit currency for
different currency designs and also for different
counterfeit methods.
4.4 Hybrid Approach for Enhanced
Accuracy
The Proposed System can also be enhanced by adding
various Ensemble Methods such as Random Forest
(RF) or Support Vector Machine (SVM), as a means
of classification refinement. The traditional machine
learning techniques are useful in handling corner
cases or types of counterfeits for which CNN fails
such as print quality variance or counterfeits with
intricate patterns. Such a system has the advantage of
combining the strengths of both deep learning and
traditional machine learning approaches, which
results in a more robust system and allows it to detect
more counterfeit banknotes in a wider variety of
counterfeit banknotes, thus improving the overall
performance and reliability in the real world.
4.5 Model Testing and Tuning
The effectiveness of the system in classifying genuine
versus counterfeit banknotes is going to be evaluated
by a systematic set of metrics, including accuracy,
precision, recall, and F1-score. Furthermore, the
model will be tested for robustness by displaying it
different counterfeit notes of various qualities and
printing techniques to assess its performance under
various conditions. Hyperparameter tuning along
with the use of methods like cross validation will be
performed to optimize the model so it can be fine-
tuned for the best performance under all conditions
and this will make the model accurate in identifying
the counterfeit bills in real scenarios.
Detecting Fake Banknotes: Performance Evaluation of ML and DL Algorithm
471
4.6 Real-Time Deployment
The system is proposed for real time use on
environments such as retail stores, ATMs as well as
banks where counterfeit detection is imperative. This
model will be deployed to process cloud or edge
devices that will be capable of processing image of
the banknote in real time to give them an immediate
fidelity (either a genuine or counterfeit note). Existing
financial infrastructure, like the ATMs, cash counting
machines or self-service kiosks can be easily
integrated with the checks performed to ensure
authenticity of bank notes will be seamlessly
automated with this. The system will further have a
web interface or a mobile application for monitoring,
management, and operational oversight to ensure that
the deployment and maintenance of the system can be
done efficiently in different settings. The system
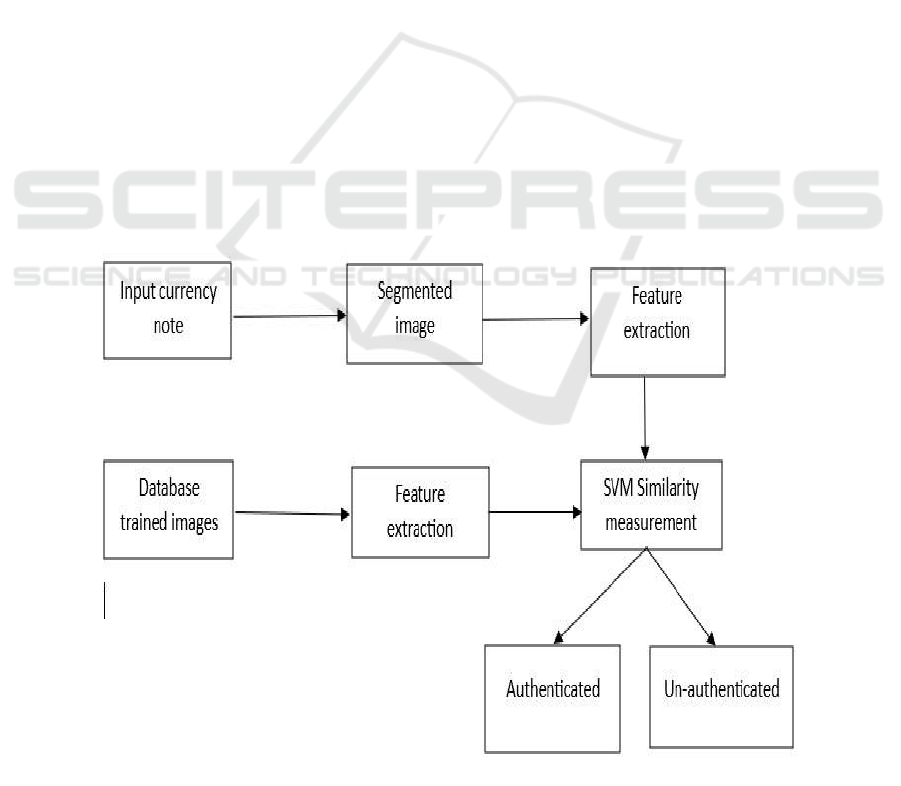
architecture is shown in figure 1.
4.7 Benefits of the Proposed System
4.7.1 Real Time Detection
The system is intended for real time deployment
application such as retail stores, ATMs, banks etc in
order to detect counterfeits notes with instantaneous
reaction. Herein, it enables users to get feedback
immediately in regards to the genuineness of a
banknote under their scrutiny, therefore, reducing the
flow of dubious banknotes on the market; as well as
improving the speed with which a cash handling
operation is conducted.
4.7.2 Scalability and Integration
This system may be integrated into the existing
financial infrastructure, like ATM, cash counting
machine or self-service kiosk to automatically
process bank note. Its scalability ensures its ability to
be deployed in a setup that ranges from a small
business to several large financial institutions since it
helps to increase efficiency in operation across
different sectors.
4.7.3 Increased Financial Security
For common consumers, the system decreases the
likelihood of getting fake currencies in exchanges and
makes it unlawful for them, lest they waste their own
financial belongings. By continuous verification of
bank notes only genuine currency is in the circulation
and it keeps improving financial security at the
individual level.
5 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Figure 1: System architecture.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
472
6 CONCLUSIONS
Detecting forged banknotes is a crucial challenge for
banks, retailers, and economies around the world.
Traditional methods, such as manual checks and
relying on physical security features, have long been
the go-to solutions for identifying counterfeit
currency. However, as counterfeiters become more
sophisticated and develop advanced techniques to
replicate security features, these traditional methods
are increasingly ineffective. This is where machine
learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) technologies
offer significant promise. These advanced
technologies provide highly accurate, automated
solutions that can detect counterfeit banknotes with
impressive speed, efficiency, and reliability.
In this research, several machine learning and
deep learning techniques such as Support Vector
Machines (SVM), KNearest Neighbors (KNN),
Random Forest (RF), and Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNN) were explored for counterfeit
detection. The comparison of these methods clearly
demonstrated the superior performance of deep
learning, particularly CNNs, in handling complex
image patterns and achieving higher accuracy. CNNs
excel automatically extracting high-level features
from raw images of banknotes, which makes them
particularly well suited for distinguishing between
genuine and counterfeit currency.
By implementing these advanced algorithms,
counterfeit detection systems can be made more
efficient and reliable for real-world applications,
including ATMs, banks, and shopping malls. These
systems can eliminate the need for human
intervention, reducing the risk of human error, and
provide nearly real-time authentication of currency,
thereby enhancing security and minimizing financial
fraud. Overall, the use of ML and DL in anti-
counterfeiting efforts represents a significant step
forward compared to traditional methods. While
further refinement of these models may be required
for specific applications, the potential to improve
accuracy and detection capabilities is immense. As
these technologies continue to evolve, they will make
the detection of counterfeit banknotes faster, more
efficient, and accessible, helping to safeguard
financial systems and economies worldwide
7 RESULT
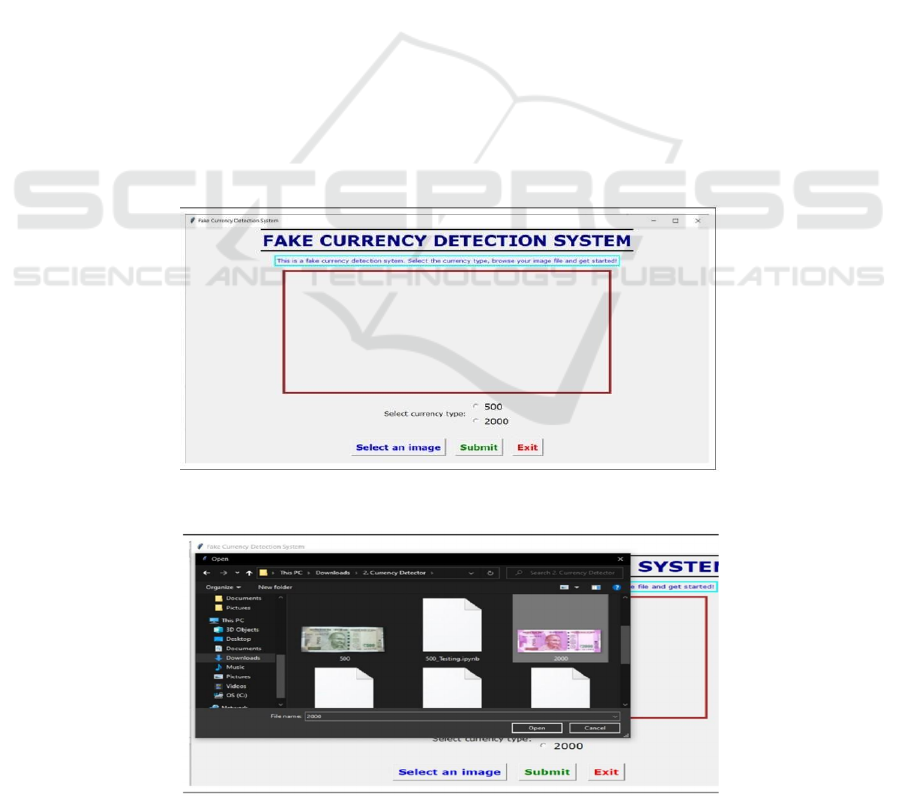
Figure 2 shows the interface of user to upload the
image and Figure 3 shows the browsing image.
Figure 2: Initially no image is displayed and user is asked to insert image.
Figure 3: Browsing image.
Detecting Fake Banknotes: Performance Evaluation of ML and DL Algorithm
473
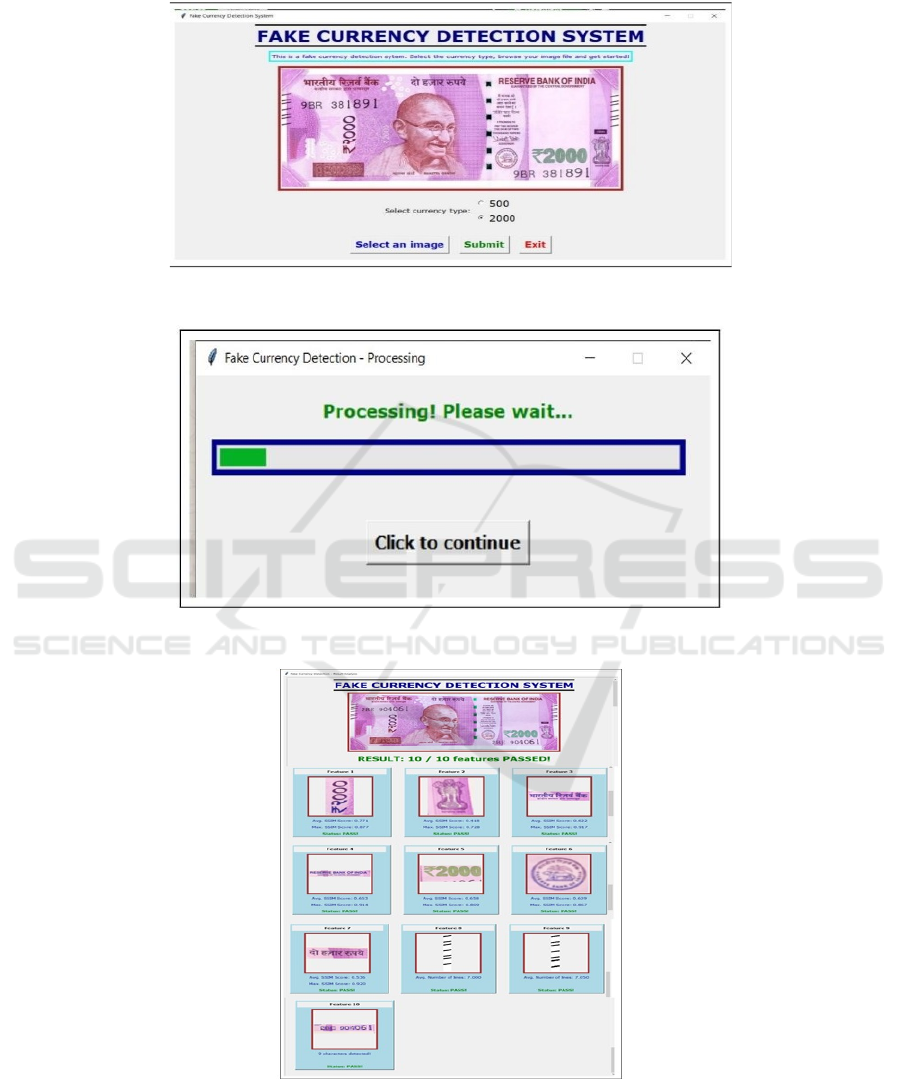
Figure 4 shows the input from the user and Figure 5
shows the processing image.
Figure 6 shows the output of real note and Figure 7
shows the fake note.
Figure 4: Input Image of Currency Note.
Figure 5: Image Sent for Processing...
Figure 6: GUI Showing final result (Real note).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
474

Figure 7: GUI Showing final result (Fake note).
REFERENCES
Akkus, Z., & Xu, Y. (2019). Detecting counterfeit currency
using deep learning. Journal of Machine Learning in
Financial Systems, 4(3), 110-118.
Arora, P., & Sharma, R. (2018). A survey on AI-driven
banknote verification systems. Proceedings of the 2018
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Data Engineering, 102-107.
Borges, R. M., & Silva, P. A. (2021). An improved
approach to fake banknote detection using
convolutional neural networks. International Journal of
Image Processing, 15(1), 52-64.
Chen, X., & Liu, Y. (2017). A comparative study of
machine learning algorithms for fake currency
detection. Journal of Computer Science, 42(6), 156-
162.
Li, J., & Liu, F. (2017). Pattern recognition methods for
banknote verification. Pattern Recognition Letters, 105,
12 18.
Sahoo, A., & Behera, S. (2020). A hybrid technique for
counterfeit currency detection. International Journal of
Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 8(4), 27-34.
Sami, W., & Gaurav, A. (2019). A novel approach to
identifying counterfeit banknotes using AI.
International Journal of Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, 6(4), 45-52.
Sharma, V., & Kumar, A. (2019). Image-based
authentication of banknotes using neural networks.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Image Processing,
9(5), 281-295.
Tan, J., & Duan, X. (2021). Deep learning-based counterfeit
banknote classification. Expert Systems with
Applications, 175, 114832.
Tian, Y., & Li, M. (2020). Image-based banknote
authentication using machine learning. Journal of
Computer Science and Technology, 35(3), 412-423.
Vijay, P., & Kaur, G. (2019). An automated system for fake
currency detection using deep learning. IEEE Access,
7, 63108-63117.
Yadav, A., & Verma, R. (2018). Counterfeit banknote
detection using image processing techniques.
International Journal of Computer Science and
Information Security, 16(12), 113-118.
Yin, Y., & Li, Y. (2020). Fake currency detection using
machine learning algorithms. International Journal of
Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 11(4),
160 167.
Zhang, J., & Huang, Y. (2018). A study on financial fraud
detection techniques. Journal of Financial Technology,
6(2), 91-98.
Zhou, W., & Wang, C. (2016). Real-time counterfeit
detection in banking transactions. Proceedings of the
2016 IEEE International Conference on Information
and Automation, 1347-1351.
Detecting Fake Banknotes: Performance Evaluation of ML and DL Algorithm
475
