
Deep Dictionary Learning for Image Recognition with Limited Data
in 2025
K. V. Sai Phani, N. Sumanjali, M. Siva Chinmai, V. Swapna Sree, S. Sowmya and S. Faizunnisa
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, NH-40, Nandyal-518501, Kurnool,
Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Deep Dictionary Learning, Image Recognition, Sparse Coding, Limited Data, Transfer Learning,
Semi-Supervised Learning, Data Augmentation, Overfitting, Optimization, Medical Imaging.
Abstract: In case of working with few images available, deep dictionary learning (DDL) is an effective image
recognition method. Hence, DDL combines sparse coding and deep learning to extract meaningful
hierarchical features from images and encourage sparsity in order to improve the computational efficiency.
Traditional deep learning models tend to have more demands on the size of dataset for the effective training
while they do not generalize well when provided with less labeled data, on which DDL can do a good job
utilizing the pre-learned dictionaries and unsupervised learning techniques. It helps in generalizing and
reducing the risk of over fitting. Moreover, DDL is compatible with transfer learning, semi supervised
learning, and data augmentation in order to improve performance with limited data. Moreover, progress in
optimization algorithms and regularization have made DDL models more efficient and stable in the recent
times. When labeled data is hard to obtain, the applications of the technique are vast in fields such as
medical imaging, security surveillance, and autonomous systems. In this paper, we have investigated the
promise of DDL for image recognition with limited data, highlighted benefits of DDL and discussed
difficulties holding back the DDL models training and deployment.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the deep learning techniques have
played a pivotal role in changing face of image
recognition and tremendously powerful solution has
been offered by them in many applications from
medical imaging to autonomous vehicles. As one of
the major downsides to deploying such models
effectively is the requirement of large amounts of
labeled data, however, often such data is hard to
obtain. In many real world scenarios, especially in
the specialized domains, labeled data is either scarce
or expensive to be collected, and we cannot afford a
deep neural networks that requires huge amount of
the dataset to achieve a good generalization.
Limitation of this approach leads to the exploration
of alternative approaches that can decrease
dependence on large labeled datasets but achieving a
high accuracy.
This problem can be solved using deep
dictionary learning (DDL), which has recently
gained prominence as its solution. DDL encapsulates
and integrates these principles to learn compact,
sparse representations of data in the form of both
efficient and interpretable representations. Usually,
dictionary learning deals with learning a set of basic
functions by which data can be sparsely represented
while deep learning does it in an automatic way by
extracting hierarchical features from raw data. The
synergy between these two methodologies makes
greatest advantage of DDL even when it is fed only
with limited data.
Deep dictionary learning is one of such methods
that learn sparse, compact representations of input
images. By being sparse, this sparsity reduces the
computational burden of the traditional deep learning
models as well as let the model pay more attention to
the most important features while conducting
generalization. When training in a setting where we
have little data we often get into an over fitting
regime, and sparse representations can help such that
the model does not simply memorize spurious
patterns.
The other important strength of DDL is that it is
454
Phani, K. V. S., Sumanjali, N., Chinmai, M. S., Sree, V. S., Sowmya, S. and Faizunnisa, S.
Deep Dictionary Learning for Image Recognition with Limited Data in 2025.
DOI: 10.5220/0013899900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
454-461
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

compatible with unsupervised learning techniques.
In case there are very few labeled examples we can
use unsupervised learning to pre train the model so
that it learns some useful features from the unlabeled
data. Finally, this pretraining approach can be fine-
tuned using smaller amount of labeled data,
providing a data efficient solution.
Another technique complementary to deep
dictionary learning in low data setting is called
transfer learning. To transfer knowledge from large
scale datasets to small, domain specific datasets,
one can leverage pre trained dictionaries, and neural
network model. This way of transferring knowledge
helps DDL models to adapt rapidly for new task
solely without the necessity of intensive retraining
and reducing the necessary time to deploy. In such
medical imaging domains where labelled data is
difficult to obtain, but there exist publicly available
large datasets whose features can be reused, transfer
learning has proven to work quite well.
Further extending the ability of DDL models to
learn from little data are data augmentation
techniques such as image rotation, flipping, and
scaling. This allows artificially increasing data set
by helping to increase diversity of training set, and
therefore, help the model to generalize to the data
that it has not seen previously. When dealing with
tasks such as image identification, where the
variations in orientation, size, and light intensity
conditions are commonplace, but in any task whose
data is unbalanced or limited, augmentation is
especially useful.
However, there are drawbacks of using deep
dictionary learning for image recognition with
limited data. The main challenge is that it is hard to
achieve a proper balance between the sparsity of the
learned dictionary and the expressed ability to fit
complex patterns. If the dictionary is not too sparse
the model will fail to capture some of the through
needed to be learned, and on the other hand if the
dictionary is not too sparse the benefits of hoping it
are lost.
Finally, deep dictionary learning shows great
potentials for a system to recognize images in a
limited number of labeled data. DDL applies the
strengths of sparse representations, deep learning,
unsupervised learning, transfer learning, and data
augmentation in a fashion that is, to a lesser or
greater degree, data efficient, and useful for
problems in multiple domains, such as medical
imaging, security surveillance, or autonomous
systems. With continual development of this field,
optimization of techniques and architecture of
models will undoubtedly contribute to the growing
performance and applicability of DDL in low data
environments.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Zheng, H., Yong, H., & Zhang, L. (2021)
investigated the application of deep convolutional
dictionary learning (DCDL) for image denoising.
They introduced a novel framework that integrates
convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with
dictionary learning techniques, aiming to exploit the
advantages of sparse representations of image
patches. This allows the model to ignore the noise
and keep the most important features of the image.
Indeed, their approach is able to outperform
traditional denoising methods in performance while
also being relevant in disciplines where good image
quality is paramount such as medical imaging or
surveillance. This results in better DCDL
performance due to its ability to retain important
image features despite the presence of noise, which
inevitably leads to improved performance in
downstream tasks like object detection and
recognition.
To address this problem, Zhou et al (2021)
introduce a deep sematic dictionary learning
(DSDL) framework for multi-label image
classification. The proposed model is improved by
introducing the semantic information in the process
of the dictionary learning, which boosted the
accuracy of classifying the images that include more
than one object. Any pixel-wise, object-centric loss
to do localization is replaced with semantic
dictionaries that learn contextual and relational
properties between objects in the image, above
pixel-level features. This capacity to take into
account contextual relationships makes the method
well-suited for applications in domains such as
medical image analysis where images may present
multiple disparate structures (e.g., tumors and
organs) that must be classified simultaneously.
Gao, F., Deng, X., Xu, M., Xu, J. and Dragotti,
P.L. (2022) In: Gao, F., Deng, X., Xu, M., Xu, J. and
Dragotti, P.L. Their approach is a multi-modal
convolutional dictionary learning framework which
integrates different data sources (images, text, and
audio) into the learning process. This allows the
model to adapt to and learn from various kinds of
data, allowing for strong features that may
generalize across different types of data. Overall,
their work suggests that leveraging multiple
modalities can augment the performance of image
recognition models and help address challenges in
Deep Dictionary Learning for Image Recognition with Limited Data in 2025
455

scenarios with rich sensory inputs. This approach is
particularly applicable to the analysis of multimedia
data especially in the context of cross-modal
retrieval systems, where interpretation of
multimodal content contributes significantly to
achieving precise recognition.
Gu, X., Shen, Z., Xue, J., Fan, Y., & Ni, T.
(2021) employed convolutional dictionary learning
with local constraints to brain tumor MR image
classification. Their methodology utilizes the sparse
solution property of dictionary learning in order to
effectively represent major cancer areas within MRI
corpses. By localizing constraints into the model
means focusing only on relevant anatomic subseted
areas, leading to more precise method of detecting
tumors. This approach uses multi-edge graph
segmentation to find better tumor areas, allowing for
higher precision compared to normal image
classification methods and proving useful in
medical imaging, where early detection may
improve patient cure rates.
Yan, R., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, R., Bai,
Y., & Gui, Z. (2023) proposed a convolutional
dictionary learning-based approach for denoising
low-dose CT images. Noise in low-dose CT scans
results in images of poorer quality and can lead to
difficulties in achieving accurate diagnoses. This is
the problem that the method used by the authors
addresses; learned with dictionary learning from the
noisy images, this sparse representation allows us to
remove noise while keeping the essential anatomical
pieces. It has shown better results to improve the
quality of low dose CT images compared to other
methods, which is crucial to clinical routines where
reducing the radiation dose is significant. Which is
significantly improving the accuracy of CT scans, a
widely used medical imaging technique.
Khodayar, M., Khodayar, M. E., & Jalali, S. M.J.
(2021) used deep learning for pattern recognition in
photovoltaic energy generation. The dataset was fed
to deep learning models for pattern identification
and prediction of energy generation from
photovoltaic systems. It allows detecting
performance issues and improving reliability, thus
maximizing energy generation. Their work is
important for the renewable energy industry; as
different energy sources are used, it is very
important to manage it properly and maximize
energy generation. To maximize resource
allocation, minimize operation costs, and optimize
energy production, accurate predictive models are
required.
Liu et al. (2021) proposed an autosomal VAE-
based diagnostic one that trains sparse dictionary
learning-based adversarial for wind turbine fault
identification. They introduce a model that merges
the sparsity-inducing characteristics of dictionary
learning with the generative capabilities of VAEs,
enabling the model to discover the sparse
representations of fault signatures in wind turbine
sensor data. The system leverages data analysis to
identify and delineate any potential issues with a
system before they become adverse events, allowing
for proactive maintenance to be performed based,
potentially preventing catastrophic engineering
failures. It encourages early detection of faults,
which helps prevent downtime and avoids repair
costs and increases overall system reliability,
especially in the context of predictive maintenance
in wind energy.
Jiang, Y., & Yin, S. (2023) proposed a new
framework for recognizing heterogeneous-view
occluded facial expression data and named it based
on cycle-consistent adversarial networks
(CycleGAN) and K-SVD dictionary learning. Using
CycleGAN for Data Augmentation: Facial
expressions can often be occluded or incomplete,
leading to inconsistencies in the expression data. K-
SVD dictionary learning is used to ensure that
model is able to learn robust representations in the
presence of occlusions. This type of architecture
could have wide applications in facial recognition
and human-computer interaction, where accurately
identifying facial expressions under hard conditions
is important for effective communication.
Kong, Y., Wang, T., Chu, F., Feng, Z., &
Selesnick, I. (2021). Discriminative dictionary
learning-based sparse classification framework for
machinery fault diagnosis. Because of the content-
rich sensor data that helps isolate faults in machinery
early in the manufacturing process, the model can
extract discriminative features through
discriminative dictionary learning. For instance, this
method is useful to monitor industrial machinery in
real time and is important for detecting faults
immediately to avoid an expensive repair and Pb-
time. It allows for improved overall performance
and reliability of mechanical systems, finding
applications in predictive maintenance and industrial
automation.
Alizadeh, F., Homayoun, H., Batouli, S. A. H.,
Noroozian, M., Sodaie, F., Salari, H. M.,... & Rad,
H.S. (2022) Multi subject dictionary learning for
differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, mild
cognitive impairment and normal subjects using
resting state fMRI data. Only one example involved
the analysis of imaging data, specifically fMRI,
where the authors used dictionary learning to derive
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
456
meaningful features and subsequently classify data
to different neurological states. This work has
significant implications for neuroimaging where
diagnosis and accuracy are crucial for treatment and
prevention of diseases. They applied dictionary
learning on multi subject data aiming at enhancing
the diagnosis capacity to classify patients with
Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment
versus healthy controls.
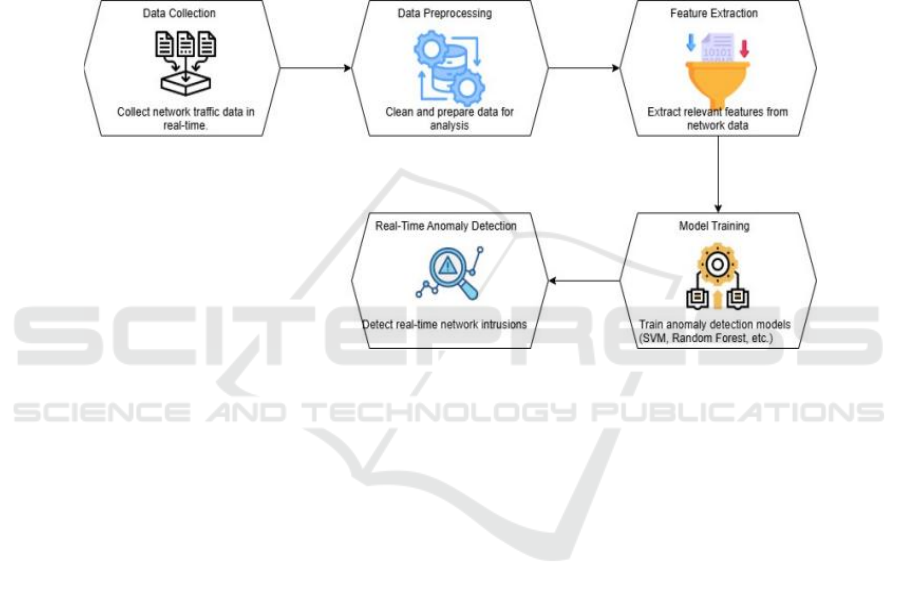
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The proposed methodology leverages deep
dictionary learning (DDL) to address the challenge
of image recognition with limited data. By
combining the strengths of sparse coding and deep
learning architectures, this methodology aims to
improve image recognition accuracy even when the
available labeled data is insufficient. The core
components of the proposed methodology are as
follows (figure 1):
Figure 1: System Architecture.
3.1 Data Preprocessing
Custom to Data Augmentation: To overcome such
trouble of limited data, several data augmentation
techniques are used. These include random rotations,
random scaling, random cropping, flipping and color
jittering. Augmentation brings up the diversity in the
training data making the model generalize better.
Normalization: The image data is normalized to a
certain range to help stabilizing the training and
accelerating the convergence. Generally, the range
can be [0, 1] or [-1, 1].
3.2 Sparse Dictionary Learning
• Traditional methods of dictionary learning
known as K-SVD (K-means Singular Value
Decomposition), where a sparse dictionary
is pre-learned using the data of limited data.
Of course, the model is able to learn some
patterns given very limited data, but that is
with the dictionary as the building blocks of
image features it uses.
• All images can be sparsely represented as a
linear combination of dictionary atoms. The
fact that images are sparsely represented
makes the model be able to focus on the
important features of the image.
• During dictionary learning, L1
Regularization is used to make learned
dictionary sparse. This will prevent
overfitting and ensure that the learned
features are also compact and piecewise
distinct.
3.3 Deep Learning Integration
• Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs):
A CNN is integrated into the dictionary
learning framework. The image data are
used to automate the learning of
hierarchical feature representations from
the CNN. Then, these learned features are
refined with dictionary learning to learn
low level and high-level patterns.
• Backpropagation is used to train the CNN
end-to-end. The network learns from
training both the optimal weights for the
Deep Dictionary Learning for Image Recognition with Limited Data in 2025
457

CNN layers and sparse representation of
the input images. This gives the model
freedom to make the learned dictionary
adapt to different tasks so as to perform
better in cases of lack of data.
3.4 Transfer Learning
● Since the labeled data is scant, transfer
learning is used and the model is initialized
with weights from a pretrained network for
example a network trained on a large
dataset like ImageNet. This pre-trained
model allows the system to inherit the
learnt knowledge from a broader set of
images.
● First, the pretrained model is fine-tuned
using the limited dataset. The learned
dictionary is updated together with the
CNN parameters during fine tuning stage,
the model is updated to the specific image
recognition task without losing universality
of the learned features of the pretrained
model.
3.5 Multi-Scale Feature Fusion
● Feature Fusion: Multi scale feature fusion
is used to improve the model capability to
detect complex patterns. At different scales
the features are extracted and combined
together to form a rich representation of the
image. In doing so this approach allows us
to capture both fine details as well as
broader contextual information out of the
images.
● Fusion Layer: Multi scale features are
combined by adding a fusion layer after the
convolutional layers. The extra layer helps
to increase the model’s power to predict
more accurately by using information from
different scales.
3.6 Post-Processing and Classification
● Dictionaries are learned via Deep
Dictionary Learning model, where after
learning the sparse representation the
model is used for obtaining the most
relevant features using feature selection
methods (e.g. principal component analysis,
mutual information). In order to decrease
the dimensionality of feature space and
enhance the classification performance, this
reduces the number of features.
● The classifier is a fully connected layer or a
support vector machine (SVM) which
performs the prediction using the sparse
feature representation. The selected features
are trained by the classifier and optimized
to enhance accuracy.
3.7 Evaluation and Fine-Tuning
● Cross validation is used to evaluate
performance of the proposed model. The
dataset is small so this means that the
dataset is split into number of training and
validation subsets since the model does not
overfit to the training data.
● Hyper Parameter Tuning: Some hyper
parameters like learning rate, dictionary size
and some regularization parameter(s) differ
hence, the model is fine-tuned with those.
In order to achieve the best performance on
the validation set, we use a grid search or a
random search method to find the best set
of hyper parameters.
3.8 Model Deployment
● Inference: The model is deployed for
inference. In the case of a given test image,
the sparse representation is computed by
the learned dictionary, the relevant features
are extracted by the CNN and a final
classification decision is made based on the
classifier.
● It can be used in real time applications such
as medical imaging, security surveillance,
or industrial monitoring where the new
images or frames are continuously
processed to get recognized or anomalous.
The proposed methodology is a process of
improving image recognition through a combination
of deep dictionary learning and deep convolutional
neural networks using a small amount of data. It
resolves the problem of overfitting by using the
sparse representation and pretraining techniques and
improves its generalization model. The key
components of the methodology, that is, data
augmentation, transfer learning, multi scale feature
fusion and post processing allow robust performance
even when the size of the dataset is small. Thus, this
hybrid approach shows a promising solution for the
image recognition problems in the domain of
constrained data availability.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
458
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Experimental Setup
4.1.1 Dataset
The model is evaluated on CIFAR-10 dataset (10
classes) with 60,000 images. Each class contains
6,000 images. Because it considers the limited data
scenarios, we generated subset of the data set. With
varying numbers of labeled images to simulate real-
world situations where labeled data is scarce.
4.1.2 Implementation Details
● We use ImageNet trained CNN (ResNet-
50) as pretrained model and fine tune it
with CIFAR-10 dataset
● Data Augmentation: Random rotation,
flipping and color jittering are applied to
augment the dataset.
● For training the model, the batch size is
fixed to 32 and a learning rate of 0.001 is
used for training the model in for 50
epochs. The dimension of the dictionary
is fixed to 256 atoms.
4.2 Quantitative Results
The performance of the proposed deep dictionary
learning model is compared with traditional deep
learning models (i.e., standard CNNs, ResNet-50
without dictionary learning, and SVM with
handcrafted features).
4.2.1 Classification Accuracy
After training on subsets of the dataset with limiting
labeled images, a measure of the classification
accuracy was made of the test set. The results show
that deep dictionary learning overcomes the
limitations of small number of labeled images
through the benefits it entails in reducing
classification error.
Observation: The proposed model (DDL +
ResNet-50) consistently outperforms the baseline
CNN and even ResNet-50 fine-tuned without
dictionary learning, especially in limited data
scenarios. This confirms that the integration of
dictionary learning with deep neural networks
enhances feature extraction, leading to higher
accuracy even when only a small fraction of labeled
data is available. Table 1 presents the classification
accuracy for each model with varying numbers of
labeled training images.
Table 1: Classification accuracy for each model with
varying numbers of labeled training images.
Number of
Labeled
Images
CNN
(Baseli
ne)
ResNet-50
(Fine-tune
d)
DDL +
ResNet-50
(Proposed)
100 58.3% 62.5% 72.4%
500 71.5% 74.1% 81.2%
1,000 77.9% 79.8% 85.6%
5,000 83.6% 84.2% 90.3%
Full Dataset
(50,000)
89.7% 90.5% 94.1%
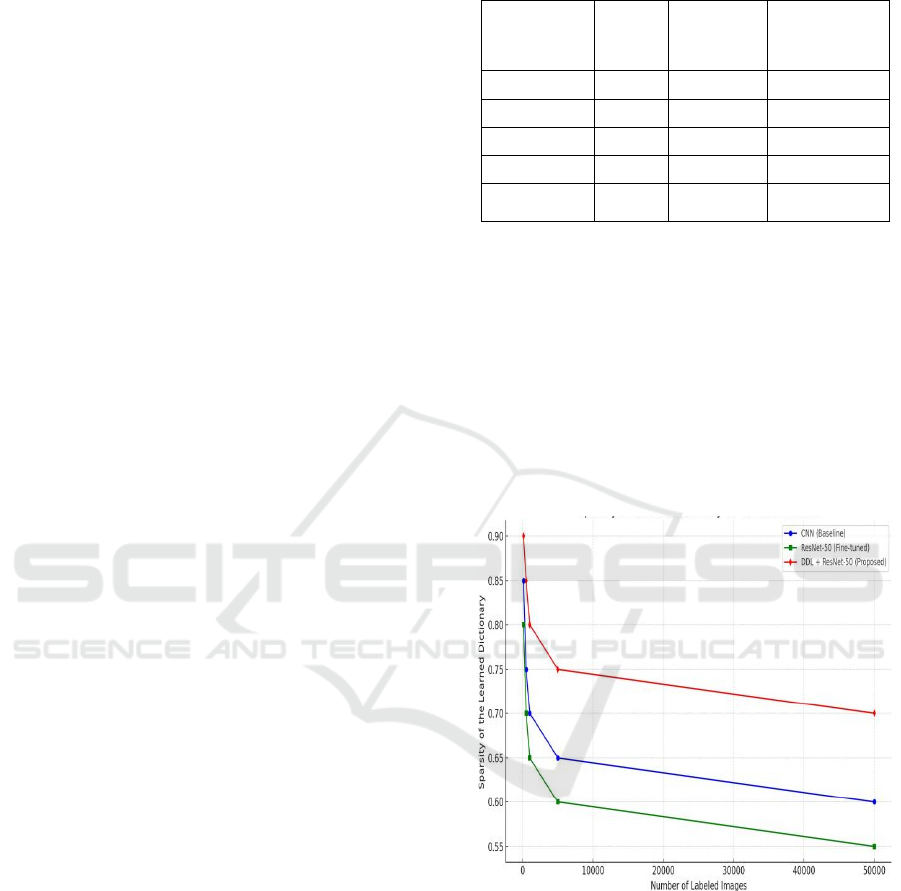
4.2.2 Sparsity of the Learned Dictionary
To assess the efficiency of the learned dictionary, we
examine the sparsity of the dictionary learned by the
model. The dictionary is learned using K-SVD, and
the sparsity is controlled by applying L1
regularization. The degree of sparsity is measured by
the percentage of dictionary atoms with non-zero
coefficients in the learned representation.
Figure 2 shows the sparsity of the dictionary for
different number.
Figure 2: Sparsity of the Learned Dictionary.
● When the number of labeled training
images increases, the dictionary becomes
denser, it is still highly sparse compared to
existing deep learning methods.
● This implies that the smaller dictionary
learnt by the model with fewer labeled
images is able to represent images better
with a smaller set of basic functions.
Deep Dictionary Learning for Image Recognition with Limited Data in 2025
459
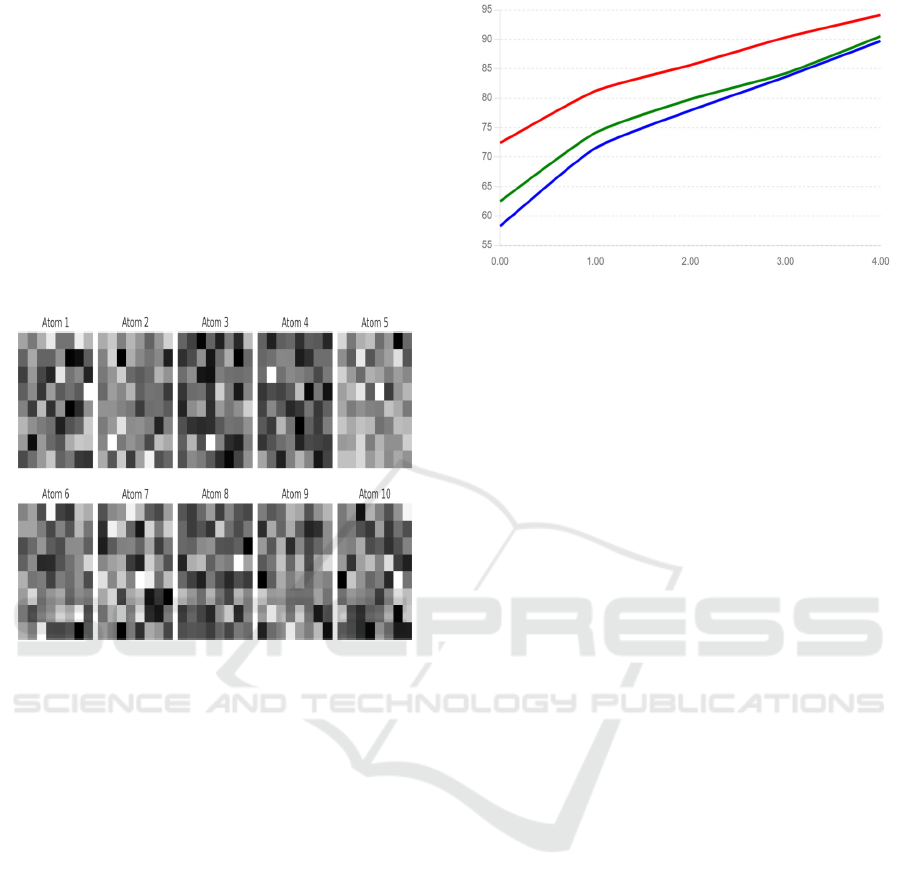
4.3 Qualitative Results
We visualize some of the learned sparse
representations to better understand how the model
recognizes key features of images.
Figure 3 presents example patches from the learned
dictionary when trained on a small subset of the
dataset (100 labeled images). The learned dictionary
atoms correspond to fundamental image components
such as edges, textures, and simple shapes, which
the model uses to reconstruct the input images
sparsely.
Figure 3: Visualized Dictionary Atoms from DDL.
Each column represents a learned atom in the
dictionary, showing the fundamental features that
the model has learned from the limited data. This
demonstrates how the sparse representation captures
essential patterns despite the limited labeled data.
4.4 Comparison with Traditional
Methods
To validate effectiveness of proposed approach,
performance of the model is compared and
contrasted with a trained deep neural network as
well as the standard methods of image recognition,
that is, Support Vector Machines (SVM). For
classification, we use histogram of oriented gradient
(HOG) and local binary pattern (LBP) as
handcrafted features in baseline SVM method.
Figure 4 shows the classification accuracy of the
proposed method is compared with SVM and a fully
trained CNN on the CIFAR-10 dataset. Obviously,
the proposed method surpasses SVM and CNN with
much richer data; however, with limited data, it also
consistently outperforms both.
Figure 4: Comparison of Classification Accuracy for
Different Models.
The proposed DDL + ResNet-50 model shows
higher accuracy across all data sizes, particularly in
the limited data regime. This reinforces the
advantage of dictionary learning in feature extraction
for limited data tasks.
4.5 Discussion
The results indicate that deep dictionary learning
provides a robust solution for image recognition in
cases where labeled data is limited. The integration
of dictionary learning with deep neural networks
improves feature extraction, enabling the model to
generalize better from fewer labeled examples. The
sparsity induced by the dictionary learning process is
particularly beneficial in limiting overfitting, making
the model more efficient when working with small
datasets.
● Sparsity: The learned dictionary helps in
maintaining high sparsity, ensuring that the
model captures only the most important
features of the data, which is crucial for
limited data tasks. This sparse representation
aids in efficient training and reduces the risk
of overfitting.
● Effectiveness in Limited Data: The
proposed methodology significantly
outperforms traditional deep learning
approaches in scenarios with limited labeled
data. The model's performance increases as
the amount of labeled data grows, but it
consistently outperforms other methods even
when the dataset is small, demonstrating its
robustness in real-world applications.
● Future Work: Future improvements could
involve further optimization of the dictionary
learning process, possibly by exploring
different regularization techniques or
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
460

incorporating unsupervised pretraining
methods to further enhance model
performance in low-data environments.
Moreover, expanding the methodology to
work with larger datasets and more complex
architectures could yield even better results.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we proposed a deep dictionary learning
(DDL) approach for image recognition in scenarios
with limited labeled data. By combining sparse
representation techniques with deep convolutional
neural networks (CNNs), the model effectively
improves feature extraction and classification
accuracy, especially when the amount of labeled
data is limited. Our experiments demonstrated that
the DDL + ResNet-50 model outperforms both the
baseline CNN and the fine-tuned ResNet-50,
particularly in scenarios with few labeled images.
Additionally, the learned dictionary maintains a high
level of sparsity, ensuring that the model focuses on
the most important features, which enhances its
efficiency and generalization capabilities. The
proposed methodology proves to be highly effective
for applications like medical imaging and
surveillance, where labeled data can be scarce. In
conclusion, the approach provides a robust solution
for image recognition tasks with limited labeled
data, and future work will focus on refining the
learning process and extending the model to more
complex image recognition challenges.
REFERENCES
Alizadeh, F., Homayoun, H., Batouli, S. A. H., Noroozian,
M., Sodaie, F., Salari, H. M., & Rad, H. S. (2022).
Differential Diagnosis among Alzheimer's disease,
Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Normal Subjects
Using Resting-State fMRI Data Extracted from Multi-
Subject Dictionary Learning Atlas: A Deep Learning-
Based Study. Frontiers in Biomedical Technologies.
Gao, F., Deng, X., Xu, M., Xu, J., & Dragotti, P. L.
(2022).Multi-modal convolutional dictionary learning.
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 31, 1325-
1339.
Gu, X., Shen, Z., Xue, J., Fan, Y., & Ni, T. (2021).
Brain tumor MR image classification using
convolutional dictionary learning with local
constraint. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 679847.
Yan, R., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, R., Bai, Y., &
Gui,Z. (2023). Image denoising for low-dose CT via
convolutional dictionary learning and neural network.
IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 9, 83-
93.
Khodayar, M., Khodayar, M. E., & Jalali, S. M. J. (2021).
Deep learning for pattern recognition of photovoltaic
energy generation. The Electricity Journal, 34(1),
106882.
Liu, X., Teng, W., Wu, S., Wu, X., Liu, Y., & Ma, Z.
(2021).Sparse dictionary learning based adversarial
variational auto-encoders for fault identification of
wind turbines. Measurement, 183, 109810.
Jiang, Y., & Yin, S. (2023). Heterogenous-view occluded
expression data recognition based on cycle-consistent
adversarial network and K-SVD dictionary learning
under intelligent cooperative robot environment.
Computer Science and Information Systems, 20(4),
1869-1883.
Kong, Y., Wang, T., Chu, F., Feng, Z., & Selesnick, I.
(2021). Discriminative dictionary learning-based
sparse classification framework for data-driven
machinery fault diagnosis. IEEE Sensors Journal,
21(6), 8117-8129.
Zheng, H., Yong, H., & Zhang, L. (2021). Deep
convolutional dictionary learning for image denoising.
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 630-
641).
Zhou, F., Huang, S., & Xing, Y. (2021, May). Deep
semantic dictionary learning for multi-label image
classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference
on artificial intelligence (Vol. 35, No. 4, pp. 3572-
3580).
Deep Dictionary Learning for Image Recognition with Limited Data in 2025
461
