
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain
Disorders
Ahobila Sashank Sarma, Shaik Allabakash and S. Thenmalar
Department of Networking and Communications, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Deep Learning, Convolution Neural Network, Deep Learning, Graph Based Fusion, Neurological Disorder,
ADNI, PPMI.
Abstract: Neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and stroke present
significant challenges in early diagnosis and management. Deep learning has shown great potential in
analyzing multi-modal neurological data, including medical imaging and genetic information. However,
traditional deep learning models struggle with effective multi-modal data integration. Existing graph learning
techniques address inter-subject relationships but face difficulties in optimally fusing imaging, genetic, and
clinical data. To overcome these challenges, we propose an advanced deep learning-based Convolutional
Neural Network (CNN) framework that enhances the Graph-Based Fusion (GBF) approach by incorporating
convolutional and transformer-based models for multi-modal feature extraction and classification. Our
imaging-genetic fusion module employs attention mechanisms to derive meaningful representations, while a
multi-graph fusion module integrates imaging, genetic, and clinical features for improved diagnostic
accuracy. Extensive validation using the ADNI and PPMI datasets demonstrates that the proposed deep
learning- enhanced GBF model achieves an accuracy of 88%, outperforming traditional GBF techniques. This
integration of deep learning with graph-based fusion provides a more precise and early detection framework
for neurological disorders. The proposed deep learning-enhanced GBF model leverages attention mechanisms
and multi-graph fusion to integrate imaging, genetic, and clinical data, achieving 88% accuracy on ADNI and
PPMI datasets. This approach enhances diagnostic precision and facilitates early detection of neurological
disorders.
1 INTRODUCTION
Neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease
(AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), present
significant challenges in clinical practice due to their
overlapping symptoms and complex
neuropathological characteristics. These conditions
affect millions worldwide, leading to cognitive
decline, motor impairments, and reduced quality of
life. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for
timely therapeutic intervention, effective disease
management, and improved patient outcomes.
Recent advancements in medical imaging
techniques, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging
(MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT), have
greatly enhanced our ability to visualize structural
and functional abnormalities in the brain. Structural
MRI (sMRI) provides detailed anatomical
information, functional MRI (fMRI) captures brain
activity patterns, and diffusion-weighted imaging
(DWI) characterizes white matter integrity. While
these imaging modalities offer valuable insights the
manual interpretation of complex neuroimaging data
remains a significant bottleneck in accurate diagnosis
To overcome these limitations, artificial
intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL)
methodologies have gained prominence in medical
image analysis. In particular, Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) have demonstrated exceptional
capability in feature extraction and pattern
recognition, making them well- suited for automated
neurological disorder classification. By leveraging
large-scale neuroimaging datasets, CNN-based
models can learn discriminative features that
facilitate precise differentiation between various
neurological conditions.
This research proposes a novel deep learning
framework integrating multimodal neuroimaging
data sMRI, fMRI, and DWI to enhance the
classification of neurological disorders. The proposed
Sarma, A. S., Allabakash, S. and Thenmalar, S.
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain Disorders.
DOI: 10.5220/0013899600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
431-442
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
431

system employs CNNs to analyze brain imaging data,
capturing intricate structural and functional
differences associated with different disorders.
Experimental evaluations on extensive datasets
validate the model’s effectiveness, demonstrating
high accuracy in distinguishing between AD, PD, and
other neurological conditions.
Furthermore, to improve interpretability and
transparency, attention mechanisms are incorporated
into the framework. These mechanisms highlight
critical brain regions that contribute to classification
decisions, thereby increasing trust in AI-driven
diagnoses and providing valuable insights into the
underlying pathological processes. By bridging the
gap between AI and clinical decision-making, this
approach has the potential to assist neurologists in
more precise diagnostics and personalized treatment
planning, ultimately leading to improved patient care
and therapeutic outcomes.
2 RELATED WORKS
Recent advancements in deep learning, graph-based
learning, and multimodal data integration have
significantly improved disease prediction and
medical image analysis. Researchers have explored
various techniques, including multimodal graph
learning, convolutional networks, and self-attention
mechanisms, to enhance predictive accuracy and
interpretability in medical applications. Graph-based
learning has shown promise in modeling complex
relationships among medical data modalities.
Zheng et al. proposed a multi-modal graph
learning approach for disease prediction, leveraging
structured data fusion. Liu et al. introduced Mtfil-Net,
an automated model for Alzheimer’s disease
detection and MMSE score prediction based on
feature interactive learning. Du et al. employed a joint
multitask sparse canonical correlation analysis for
identifying genotype–phenotype associations. Zhang
et al. developed a hypergraph-based manifold
regularization framework for multi-modal imaging
genetics data fusion, specifically applied to
schizophrenia studies. Another work by Du et al.
explored adaptive sparse multi-view canonical
correlation analysis for associating genomic,
proteomic, and imaging biomarkers.
Fu et al. presented a multimodal medical image
fusion method incorporating a Laplacian pyramid and
a convolutional neural network-based reconstruction
strategy. Xu and Ma introduced EMFusion, an
unsupervised enhanced medical image fusion
network. Song et al. designed a multi-center and
multi-channel pooling graph convolutional network
(GCN) for early Alzheimer’s disease (AD) diagnosis
based on a dual-modality fused brain network. Zhu et
al. proposed a multimodal triplet attention network
for brain disease diagnosis, enhancing feature
interactions. Ko et al. developed a deep generative–
discriminative learning framework for multimodal
representation in imaging genetics. Wang et al.
tackled multimodal learning with incomplete
modalities through knowledge distillation.
Zhu et al. introduced a dynamic hypergraph
inference framework for neurodegenerative disease
diagnosis. Li et al. proposed DARC, a deep adaptive
regularized clustering approach for histopathological
image classification. Yi et al. provided a survey on
hippocampal segmentation in brain MRI using
machine learning techniques. Parisot et al. employed
graph convolutional networks for disease prediction,
particularly focusing on autism spectrum disorder and
AD. Huang and Chung developed edge-variational
graph convolutional networks to enhance
uncertainty-aware disease prediction.
Du et al. associated multi-modal brain imaging
phenotypes with genetic risk factors using a dirty
multi-task learning model. Another work by Du et al.
introduced adaptive structured sparse multi-view
canonical correlation analysis for identifying
multimodal brain imaging associations. Pahuja and
Prasad designed deep learning architectures for
Parkinson’s disease detection using multi-modal
features. Huang et al. leveraged a temporal group
sparse regression and additive model for biomarker
detection in AD. Kim et al. applied joint-
connectivity-based sparse canonical correlation
analysis to detect biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease.
Lei et al. developed a multi-scale enhanced GCN for
detecting mild cognitive impairment. Zhang et al.
proposed local-to-global GCNs for classifying brain
disorders using resting-state functional MRI (rs-
fMRI).
Devlin et al. introduced BERT, a deep
bidirectional transformer model for language
understanding, which has been influential in medical
text analysis. Cheng et al. presented a fully automated
multi-task learning model for glioma segmentation
and IDH genotyping using multimodal MRI. Yang et
al. proposed a unified hypernetwork model for
multimodal MR image synthesis and tumor
segmentation, addressing missing modalities. Kazi et
al. integrated self-attention mechanisms into graph
convolutions for disease prediction.
Wang et al. developed Mogonet, a GCN-based
framework that integrates multi-omics data for
patient classification and biomarker identification.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
432
Ying et al. introduced an ensemble model combining
imagery and genetic features for AD diagnosis.
Finally, Song et al. reinforced the efficacy of multi-
channel pooling GCNs in early AD diagnosis by
utilizing dual-modality fused brain networks.
Finally, Wang et al. presented an improved GCN-
based model for early AD diagnosis using dual-
modality fused brain networks. Their study highlights
the importance of integrating multimodal information
to improve classification accuracy.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Working Methodology
The proposed system using deep learning algorithms
that would improve the diagnosis of the brain disorder
by tapping into the fast-growing impact of deep
learning and AI technologies across different sectors
of industries. Technologies affect the industries not
just in altering the process and changing the decision-
making process. In this project, the focus on deep
learning to support the accurate diagnoses of
disorders in the brain.
In an attempt to achieve that, gathered a vast
dataset containing the clinical records of brain
disorder patients, healthy people, and those who are
showing very early symptoms. The deep learning
model aggregates these data to identify patterns and
correlations of symptoms of a brain disorder with
images. The algorithms that used in deep learning are
complex calculations and pattern recognition to
interpret those medical images. It analyses the unique
features on the dataset then learns how to identify the
underlying patterns that are associated with various
brain disorders. On extensive training of the model,
the model will become effective in its predictions of
the likelihood about a brain disorder over new, unseen
data. When an input image is presented, our algorithm
applies the learned patterns and analysis techniques in
determining whether the subject is suffering from a
brain disorder (see Figure1). Over time, it becomes
finer and more accurate, hence very reliable within its
domain of application, especially useful in early
diagnosis.
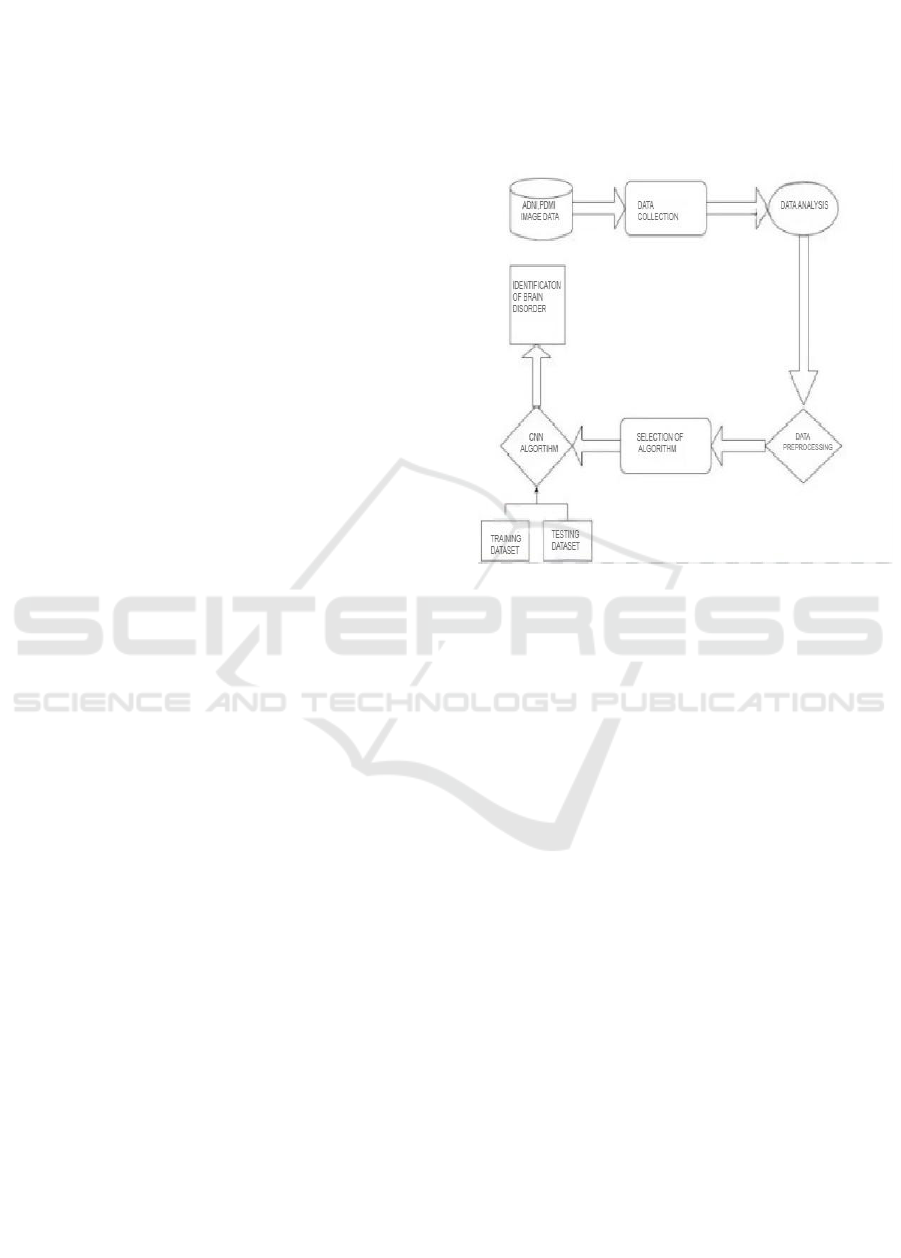
Figure 1 states a flowchart representing the
process of identifying brain disorders using a
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) algorithm.
The process begins with Data Collection, followed by
Data Analysis to extract meaningful insights. The
data then undergoes Preprocessing to enhance quality
and remove noise before being fed into the CNN
Algorithm for feature extraction and classification.
The system then proceeds to Accuracy Selection,
where the model’s performance is evaluated. If the
accuracy meets the desired threshold, the model is
Deployed, leading to the Identification of Brain
Disorders based on medical imaging data. This
structured approach ensures efficient and accurate
diagnosis of neurological disorders.
Figure 1: Working Methodology.
3.1.1 Data Collection
Where the first brain imaging datasets were sourced
during the course of this project. It is also a good site
to look for datasets since it receives a lot of datasets
from either researchers or institutions which are nice
when training machine- learning models. In this
instance, brain images that were useful in diagnosing
a number of neural ailments were sought out. Once
obtained, the images proceed to the next step where
they are preprocessed for uniformity and quality.
Preprocessing includes operations like resizing of
images, the use of standard pixel normalization
techniques, expanding the dataset using image- based
activities like rotation and flipping which create some
diversity, and using noise filtering techniques to make
the images clearer. This stage minimizes model
training time and enhances the accuracy of the model
as the noise in the input data is minimized.
3.1.2 Manual Review and Image Quality
Control
Such inefficiencies could have been avoided at the
previous stage if training dataset images that were
irrelevant or incorrectly labelled images were
reviewed manually after performing the pre-
processing phase. This is particularly important in the
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain Disorders
433

field of medical imaging, where performance of a
model is highly dependent on how accurate the
training data is Therefore, if there is no such tolerance
for substandard images, it means that training can be
done on data that is of high quality, hence making the
system less prone to incorrect predictions and more
efficient in its operations.
3.2 Convolutional Neural Networks
After removing outliers from the dataset, it is further
utilized within the structure of the Convolutional
Neural Network (CNN). CNNs are especially
effective in image classification tasks because the
model itself can learn how to detect and extract
important features from raw input data. Within this
project, the CNN will be constructed in a manner that
focuses on distinguishing patterns of brain scans
which depict varying neurological conditions. The
architecture of the model includes several
convolutional structures that assist in determining
specific features’ filters, pooling structures for
dimensionality reduction, and fully connected layers
for the ultimate classification. The model, through
dozens of touchdowns exactly where he should look
for the critical changes which may indicate the
probability 0.
Even when inputs are normalized, substantially
larger activations are seen. After this, the network’s
output and the lower layers will become completely
irrational. Batch normalization allows for an output
standard deviation of around 1 and a mean of about 0.
The Conv2d layer applies filters to the input
image, detecting features such as edges, textures, and
patterns. It performs an element-wise multiplication
between the filter and the image patch, summing the
result to produce a feature map. MaxPooling2D
reduces the spatial dimensions of the feature maps,
selecting the maximum value within a defined
window (e.g., 2x2).
This down-sampling retains the most important
information while reducing the computational load
and overfitting risk.
Training Dataset: This subset is used to train the
CNN model, allowing it to learn patterns from labeled
images of normal and diseased brains. The model
adjusts its parameters through backpropagation and
optimization techniques
Testing Dataset: After training, the model is
evaluated on an unseen testing dataset to assess its
generalization ability and ensure it can accurately
classify new images.
During this phase, data augmentation techniques
such as flipping, rotation, and brightness adjustments
may be applied to increase dataset diversity and
improve the model's robustness. The trained CNN
model is then fine-tuned using hyperparameter
optimization to achieve the best possible accuracy
We begin with the following lines of importing
the data generator function in Keras and then setting
a few parameters including dimensions, rescaling
factors, value range and zoom parameters, as well as
horizontal flipping. We further use the data generator
function to load our image dataset from the given
directory, set up the training and test sets with
validation, retrieve the target dimension, batch size,
and turn on the classification mode. This allows
training using a network which have constructed by
stacking together several layers of CNN.
3.3 Data Analysis
3.3.1 Non-Demented Dataset
The Non-Demented Data set consists of the MRI scan
of volunteers who are without any symptoms of the
disease and do not bear cognitive impairment or
neurodegenerative diseases. They are needed in deep-
learning structures that try to detect diseases like
dementia. They therefore act as the control group. In
this manner, this model employs scans of the brains
of healthy individuals to establish a structural
representation of its conceptions of what constitutes a
healthy brain. This provides a baseline comparison
from which it can then compare the dementia-
exhibiting patients. Therefore, the model is now able
to determine differences between what arises from
normal aging compared with changes observed early
in cognitive decline.
The No Impairment dataset consists of MRI brain
scans of people that have no signs and symptoms of
cognitive decline and neurological disorders. This is
our control group in our deep learning framework;
this will be used to have a benchmark when compared
with those individuals who have cognitive
impairments. These images enable the model to
recognize structures within the brain that are to be
associated with normal brain functionality. These
images will be organized as follows:
• Total Images 501 Image Resolution:
• Minimum width: 128 pixels
• Max width: 128 pixels
• Minimum width: 128 pixels
• Maximum Height: 128 pixels.
All of the images are the same size. In this
manner, the network processes them properly.
Representative images of the No Impairment dataset
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
434
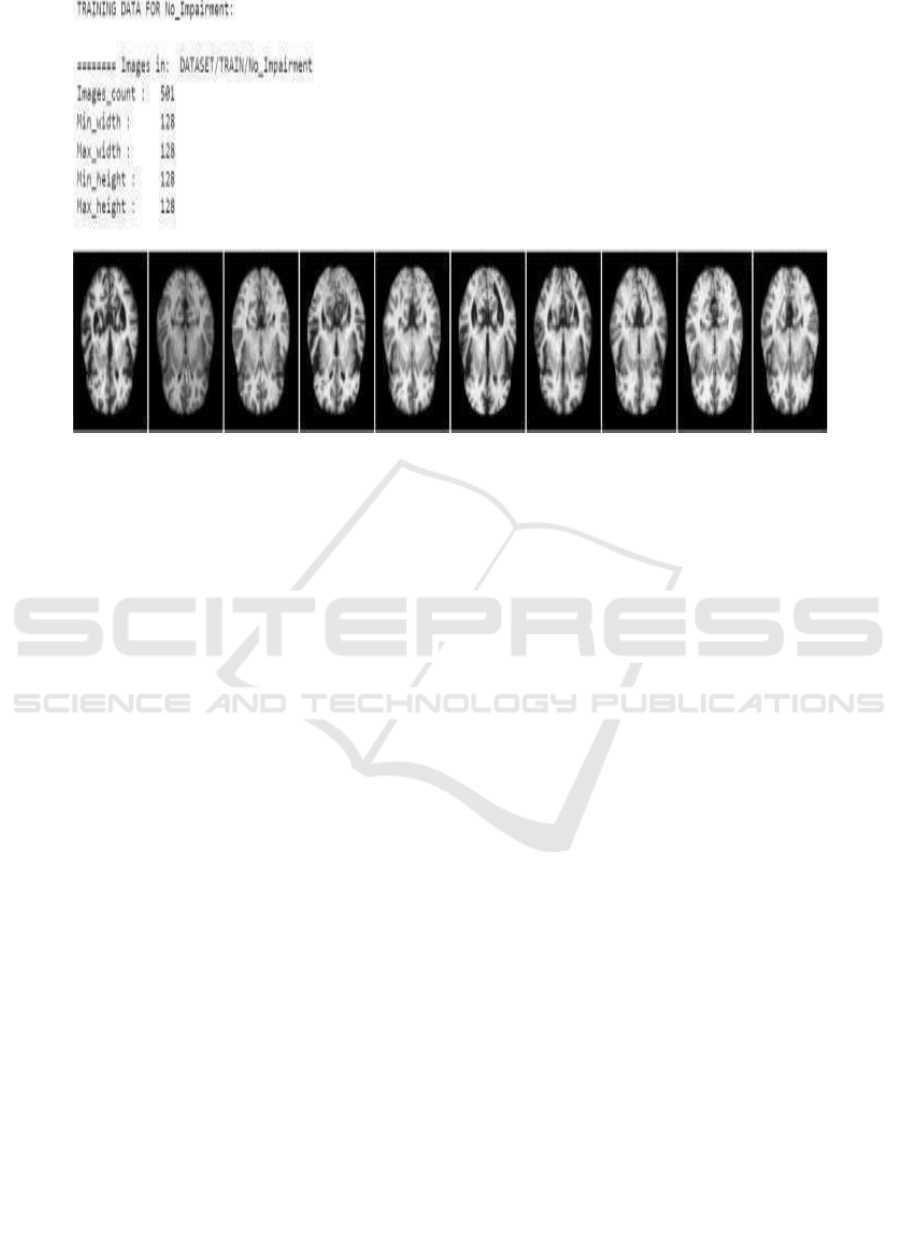
Figure 2: No Impairment.
Figure 2 states a set of brain MRI scans obtained
from the category labeled” No Impairment.” (Figure.
3 depicts). Below are cross-sectional images of the
brain, mainly showing structural features available in
a healthy functioning brain.
3.3.2 Demented Dataset
Demented Dataset contains brain scans-it contains
MRI and CT images of a patient that has been
diagnosed with dementia. Images range from mild
memory impairment to serious cognitive degeneracy.
Subclassifications enable researchers to create
models that can predict, identify, monitor, and treat
the medical conditions of the patients.
Types of Images and Data Structure: There are
evident detailed MRI and CT scans within the brain
set. Images indicate form and size alterations
resulting from the disease inside the brain. Each
image in the collection has a tag indicating the stage
of dementia. This setup helps train computer models
in the recognition of patterns from diseases.
• Imaging Types: MRI and CT scans.
• Image size: 128x128 pixels, in a grey-scale.
Data Annotation Images are annotated for these
subtypes of dementia:
3.3.3 Mild Cognitive Impairment
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) is considered the
initial stage of cognitive decline, often serving as a
transitional phase between normal aging and more
severe neurodegenerative conditions such as
Alzheimer’s disease. Individuals diagnosed with MCI
typically experience noticeable difficulties with
memory, attention, and problem-solving skills,
although these impairments are not severe enough to
interfere significantly with their ability to carry out
daily activities. One of the hallmark signs of MCI is
a decline in episodic memory, which affects the
ability to recall past events, recent conversations, or
appointments.
Neuroimaging studies of individuals with MCI
often reveal subtle structural changes in the brain,
particularly in regions responsible for memory and
cognitive processing. A common finding is a mild
reduction in brain volume, especially in the
hippocampus, a structure deeply involved in memory
formation and spatial navigation. These changes,
while not as pronounced as in later stages of cognitive
impairment, indicate an underlying
neurodegenerative process that, if left unaddressed,
may progress to more severe conditions such as
Alzheimer’s disease or other dementias.
The training dataset which comes from Mild
Impairment and which has been used in machine
learning for the purpose of brain image classification.
There are 500 images, all at 128x128 pixel resolution.
These are MRI scans from patients diagnosed with a
condition called Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI),
often the precursor to worse forms of dementia.
These images reveal diffuse brain atrophy,
especially in regions construed to be with memory
and intellectual functions such as the hippocampus.
The time of detection in alteration of the brain is
important so that this early diagnosis and intervention
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain Disorders
435
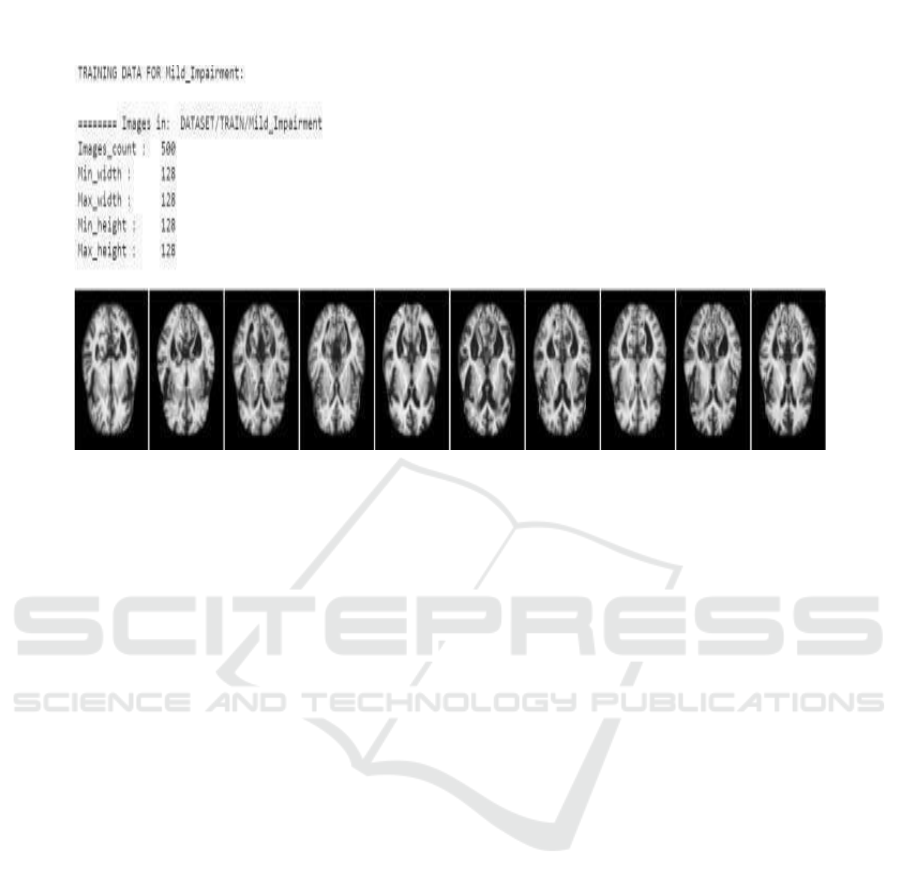
may be done, thereby eventually slowing the
progression to worse kinds of dementia.
Figure 3: Mild Impairment.
3.3.4 Moderate Dementia
Modern Dementia Now, thinking problems worsen,
and patients face hard times while working around the
house. Their memory is much worse, and they also
find it hard to pay attention, talk, or solve problems.
Brain images show a huge decline in gray matter
coupled with more brain shrinkage mostly in the
temporal and parietal parts. This is the point at which
dementia brings extreme disturbance to life because
patients will start asking for help to do everything-
control money, cook food, or even to go to familiar
places.
Brain imaging studies of patients in this stage
reveal significant atrophy and shrinkage, particularly
in the gray matter of the temporal and parietal lobes
regions responsible for memory, language
processing, and spatial awareness. These structural
changes further contribute to disorientation and
confusion, making it difficult for individuals to
navigate even familiar environments
Figure 4 depicts from a Moderate Impairment
dataset. Prepared in this manner, the model learns
toward the identification of more developed stages of
cognitive decline. It includes 501 images, drawn from
MRI pictures with a resolution of 128x128 pixels.
Each shows different sections of the brain of patients
diagnosed with moderate cognitive impairment.
There is definite eroding of memory, reasoning,
and thought capacity, and it has been connected with
the reduction in brain volume and loss of grey matter.
The images of the brain clearly show visible
shrinkage in parts of very critical regions such as
hippocampus, frontal lobes or ventricles, which
expand with deteriorating brain tissue.
Dementia is characterized by a progressive
deterioration of memory, reasoning, and overall
cognitive function, which is closely linked to a
decline in brain volume and the loss of gray matter.
As the disease advances, patients experience
increasing difficulty with retaining new information,
recalling past events, solving problems, and making
decisions. Their ability to process complex thoughts
diminishes, leading to confusion, disorientation, and
a reduced capacity for logical reasoning.
Neuroimaging studies provide clear evidence of
structural brain changes associated with this decline.
Significant shrinkage is observed in critical regions
responsible for memory, executive function, and
emotional regulation. One of the most affected areas
is the hippocampus, a structure crucial for forming
and retrieving memories. As hippocampal neurons
deteriorate, individuals struggle with memory
retention, eventually leading to severe amnesia.
The frontal lobes, responsible for decision-
making, problem- solving, and personality regulation,
also show noticeable atrophy. As these regions
degenerate, patients may experience behavioral
changes, impaired judgment, and difficulty managing
emotions. Additionally, the ventricles fluid-filled
spaces in the brain expand as surrounding brain tissue
deteriorates, reflecting the extensive loss of neurons
and connections within the brain
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
436
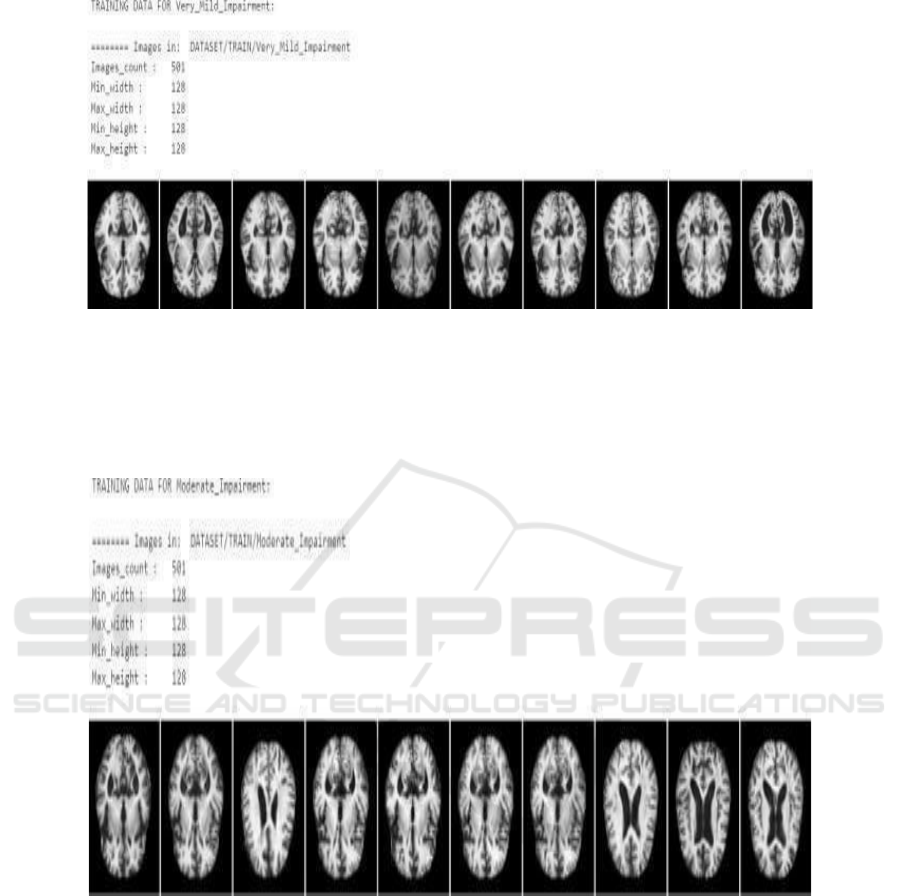
Figure 4: Moderate Impairment.
The Figure 4 states that in the given set can also
provide some critical information to train models
directed toward dis- covering and analyzing brain
structure abnormalities responsible for moderate
dementia. On observing structural changes,
researchers and models can move towards
understanding these better and maybe slowing down
the progression of the disease.
Figure 5: Very Mild Impairment.
3.3.5 Very Mild Dementia
Figure 5 states that there is an overall loss of all
capacities for thinking and physical in severe
dementia. Most patients cannot identify family
members, talk, or even take care of themselves. Much
gray matter is missing and there is considerable
thinning of the outer layer due to widespread
shrinkage and damage in a vast majority of the brain.
Such patients need continuous time care. The
treatment focuses on comfort and symptom
management.
Neuroimaging studies reveal severe brain
atrophy, with widespread loss of gray matter and
significant thinning of the cerebral cortex. These
structural changes result from extensive neuronal loss
and damage affecting nearly all regions of the brain,
leading to complete functional decline. The brain’s
ability to process information, store memories, and
control bodily functions is severely compromised. As
the disease progresses, self-care becomes impossible,
and patients require round-the-clock assistance for
even the most basic daily activities. They are unable
to dress, eat, or bathe independently, making full-time
caregiving essential. Mobility declines significantly,
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain Disorders
437
leading many individuals to become bedridden or
completely dependent on others for movement. In this
stage, patients are also at a high risk for infections,
particularly pneumonia, as their weakened immune
systems and decreased physical activity contribute to
complications.
There is only one MRI image per brain scan.
Examples include 501 images, 128x128 pixels for
each part of the brain of the patients diagnosed with
VMCI. An example of a very mild impairment dataset
in training models to detect early signs of cognitive
decline is furnished as follows. The hallmark of early-
stage dementia, or Very Mild Cognitive Impairment,
is that patients may exhibit some minimal alteration
in their memory and cognitive functions but still be
able to care for themselves. The brain images would
reveal subtle morphological changes typically located
in areas that may include the hippocampus, thus
exposing early onset brain atrophy to the machine
learning models.
These data will prove helpful at the earlier stages
of progression of dementia and will enable
researchers and practitioners to train their AI models
so that such models can distinguish between healthy
brain states and slight impairments, thus enabling
earlier intervention and management of the
conditions related to dementia.
Training Data for Dementia Classification: The
dataset hugely impacts the training of machine and
deep learning algorithms in a way to classify different
types of dementia. These algorithms can even detect
and classify early, midlife as well as late stages of
dementia based on the images of brains collected
from patients with mild, moderate, or advanced levels
of cognitive declination. Researchers have highly
used CNN as well as other deep learning architectures
to work with this data set to work in.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The deep learning model was implemented using a
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) integrated
techniques to enhance feature extraction and
classification of neurological disorders. The dataset
used for training and validation consisted of multi-
modal brain imaging data, including structural MRI
(sMRI), functional MRI (fMRI), and diffusion-
weighted imaging (DWI) sourced from the ADNI and
PPMI datasets. The dataset size included 501 non-
demented images and an equal number of dementia-
classified images, further categorized into mild,
moderate, and advanced stages based on cognitive
impairment. The data underwent preprocessing
techniques such as normalization, augmentation
(rotation, flipping), and manual quality control to
remove noise and ensure high-quality training input.
During model training, accuracy and loss metrics
were analyzed over 100 epochs. The training
accuracy steadily increased, peaking at 88.54%, while
test accuracy fluctuated initially due to potential
overfitting before stabilizing at 84%.
4.1 Training and Test Accuracy over
Epochs
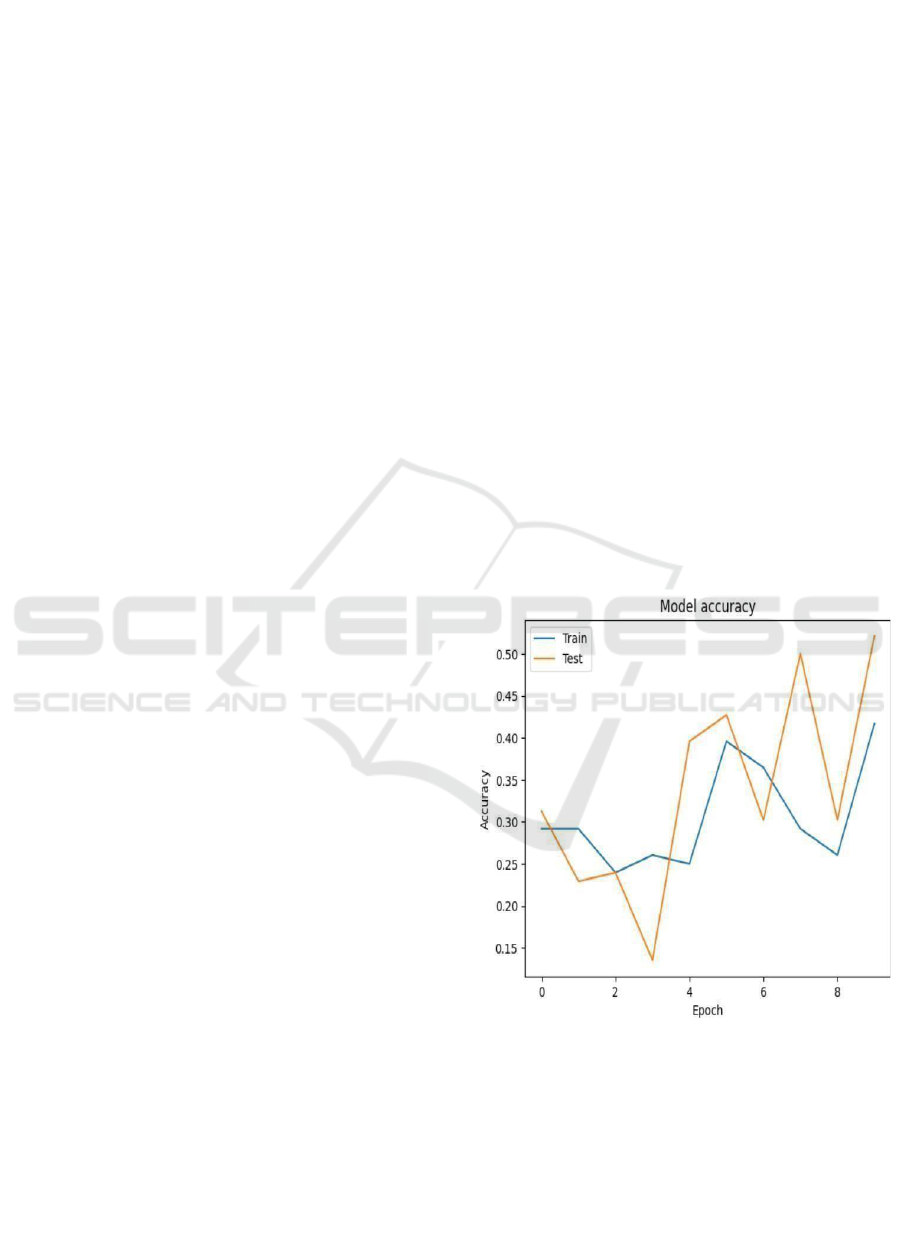
Training and Test Accuracy over Epochs: Fig. 6
states that the curve gives an idea of how the
performance of the model through accuracy for the
epochs in training and test sets is going on. Here, the
epochs are given along the x- axis and the accuracy
along the y-axis (Figure 6). The blue color represents
training accuracy while the orange color depicts test
accuracy. The test accuracy fluctuates wildly in
training; it could be overfitting or instability in this
experiment. The train accuracy increased very
slowly, and it was very low perhaps much more work
is needed by the model for this to get more in tune or
adjusted.
Figure 6: Accuracy Over Epochs.
This means that in details, it oscillates around
30% and stays constant until epoch 2 but then
oscillates and finally at epoch 9 around 35%.
Oscillations of the test accuracy begin around 30%,
quickly fall to epoch 2, and oscillate substantially
between epochs 4 to 9, peaking to approximately 50%
during the last epoch. Oscillations in such curves
indicate the model is not very good at generalization
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
438
since test accuracy spikes and drops while training
accuracy is mostly stable.
4.2 Training and Test Loss over
Epochs
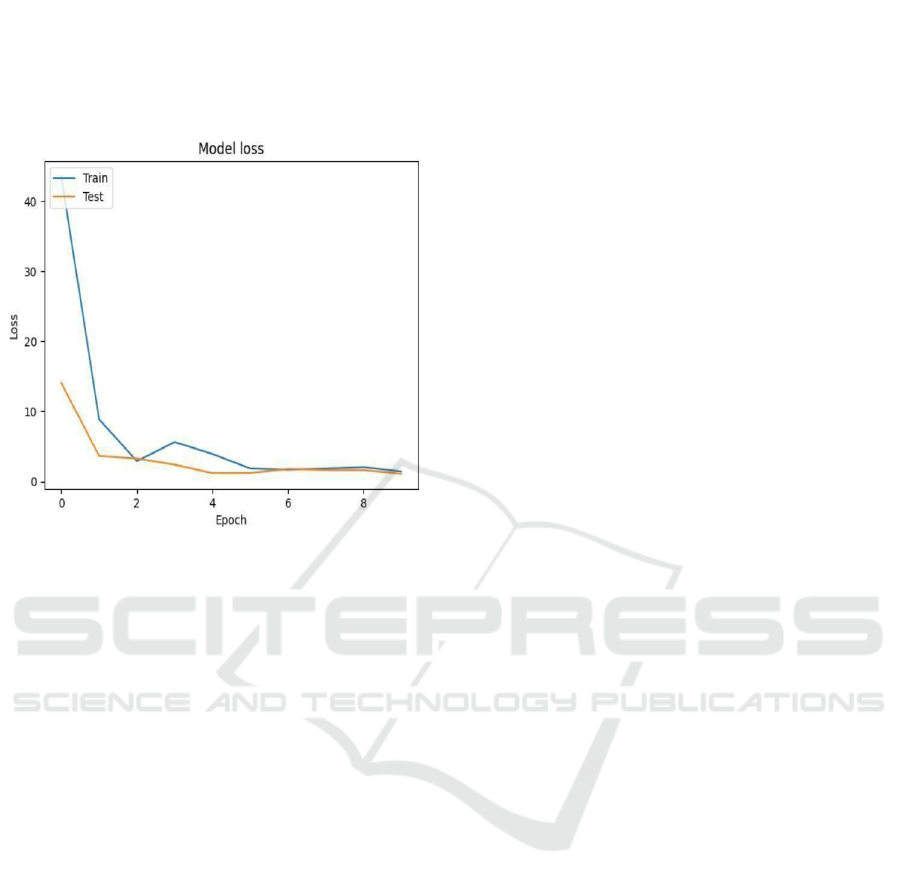
Figure 7: Loss Over Epochs.
The figures 6 and 7 states that the accuracy and loss
for the model over epochs by both training and test
datasets. Accuracy plot Fig. 10 states Accuracy goes
erratic and wildly fluctuates between about 30% at
the beginning to peaks at around 50% at epoch 9,
when the training accuracy, relatively low, is still
increasing steadily from about 30% to 85%. This
discrepancy between training and test accuracy seems
promising for overfitting or instability in the model
that might need further tuning or regularization.
The plot of loss, figure 7 states the steep decline
in the loss values for both the data. Training loss is
around 40 and drops sharply to approximately 5 by
epoch 4 and rises steadily. The test loss is around 12,
fades a little but gets stable steadily near 1 after the
initial few epochs in training. The sharp drop of the
loss indicates learning by the model but the
fluctuating accuracy shows that there are still some
headspaces for improvement to further improve the
generalization of the model. There’s a reason why
Shuffle Net has been chosen as a lightweight
architecture; it is very effective at orchestrating.
Very complex computations with minimal
resource consumption. The model was trained over
100 epochs and accuracy and loss formed the
evaluation metrics, interlaced, which might shed
some light upon even deeper insights into model
behavior during the training process.
The accuracy plot shows that, beginning with the
training and test accuracies, they are initially on a
fluctuating path- particularly for the case of the test
accuracy, whose pattern is quite kaleidoscopic. It
could thus represent overfitting: the model performs
well on the training data but does not generalize. The
model peaks at a good accuracy of about 50% within
the test dataset, though this is still below the desired
level and shows that the model certainly captures
some of the essential features of the brain disorder
images but needs further refinement. Conversely, the
loss plot weaves a much more textured tapestry.
The loss of the training graph begins with a very
high value greater than 40 and then, in subsequent
epochs, the training as well as test losses show a
luscious downward curve to nearly 0 at epoch 10. It
is phenomenal loss because it shows how the model
learns over time and decreases the errors of the
prediction. Underlying weight and parameter puzzle
of Shuffle Net was able to cross the intricate mosaic
of brain neurological disorder classification at some
cost due to problems encountered.
The most interesting findings from the results
revolve around the model’s behavior related to test
data. This kind of oscillations in test accuracy,
especially after epoch 5, encourage a more detailed
look into data augmentation techniques or potential
class imbalance or even the quality of the used
images. The cross-road is exactly that where the
opportunity lies to reimagine traditional data
preprocessing techniques or to look for methods of
regularization that would really thwart overfitting.
4.2.1 Model Performance Highlights
Training Accuracy: Peaked at about 35% after a
number of epochs. Test Almost reached 50% with
high variance probably owing to overfitting. Train
and Test Loss: Losses drop drastically, timing a very
complex drop almost to 0 that depicts although the
model reduces error very well, its generalization
abilities can improve. This model’s journey through
the crucible of model training, where layers
intertwine to grab patterns in such neurological
disorders, remains mystical and fascinating. Further
work will include enhancements towards the dataset,
optimization techniques, and fine-tuning of
architecture to the optimum degree in performance to
deliver crucial medical image classification tasks in
this important field of medicine.
Model Training Performance Visualization:
Model training and validation curve the logged values
are accuracy, precision, loss, and validation loss. A
total of 100 epochs were trained on the model. The
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain Disorders
439
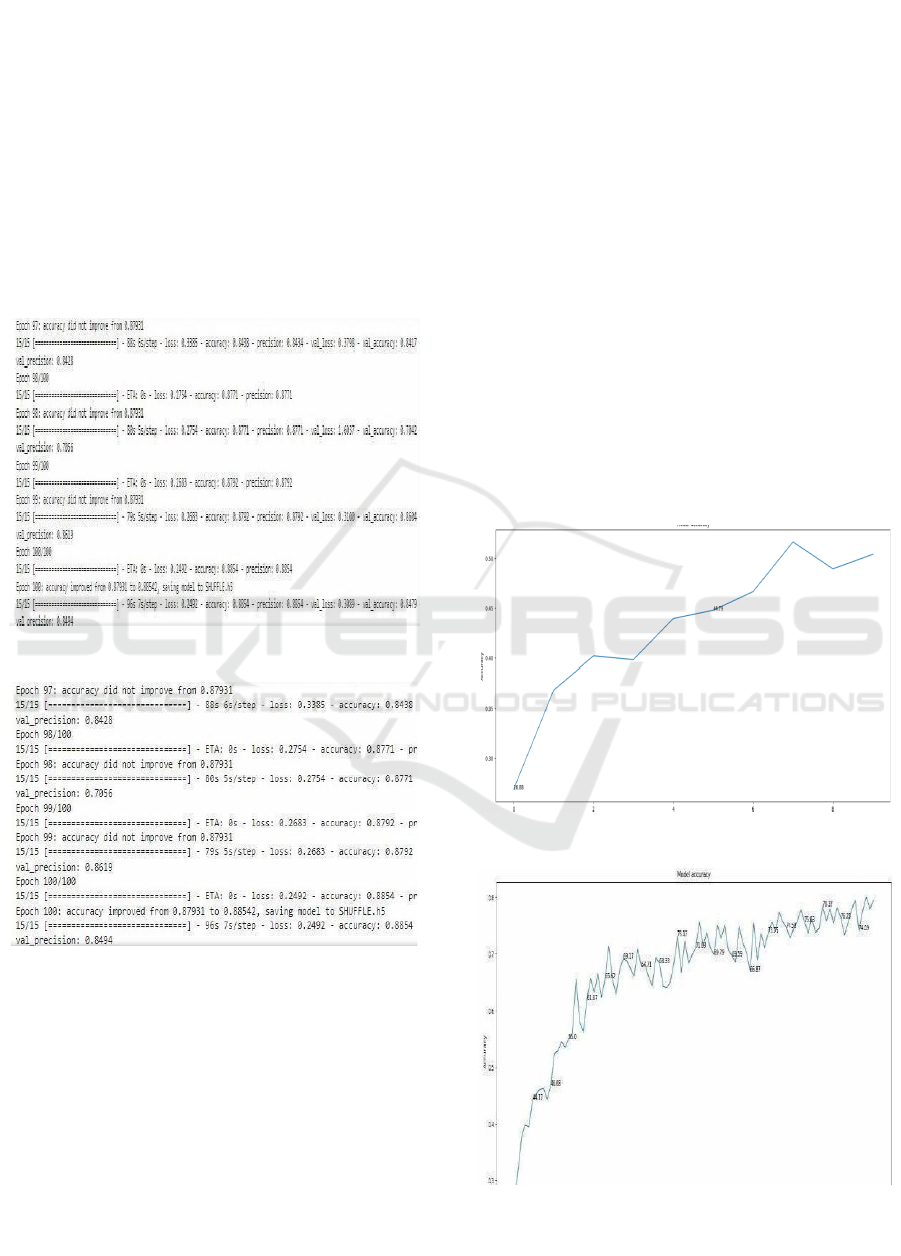
performance metrics during the different steps of the
training process are plotted. Figs. 12&13 states Note
how val accuracy oscillates from epoch to epoch;
however, the general trend is upward. Epoch 100: The
model had given the best validation accuracy at
0.8854 with a corresponding validation loss, val loss
of 0.2492 and validation precision, val precision as
0.8496. For further usage purposes, after epoch 100,
the model was saved as” SHUFFLE.H5” because it
had been optimized. Final Training Accuracy
Reached: 0.8854 suggests the potential that the model
might have in order to classify the brain neurological
diseases.
Figure 8: Model Training Performance Visualization.
Figure 9: Model Training Performance Visualization.
Model Accuracy Progression Over Epochs: It
depicts the improvement in the accuracy of the model
over time on successive epochs with multiple
trainings. The x-axis Figure 8 & 9 states are epochs
while the y-axis is indicated by the corresponding
accuracies obtained during successive training
processes. From the graph shown, there is an apparent
rise beginning from the starting accuracy of
approximately 0.34 to go rising gradually to the final
accuracy of roughly 0.84. This smooth growth
indicates a learning capability of the model over time
as it learns parameters to minimize the error at every
epoch. It saw oscillations to grow across epochs,
trying to balance between learning and
generalization; this had rapid spikes in certain phases-
the most pronounced at around epoch 15 and epoch
60. The accuracy peaks over 0.8 at these epochs,
which indicates that it is efficiently picking up the
major patterns to classify brain neurological diseases.
That is to say, this progressive precision
improvement. Figure 10 states that although with
some fluctuations, demonstrates that the model is able
to generalize at training. The above- mentioned
disparities are very common in deep models,
particularly when the models have architectures with
complexity in refinements; it depicts the model to be
exploring multiple minima in the optimization
framework. The last accuracy Figure 11 states of
about 0.84 shows that the model had reached a highly
high-performance level and thus was acceptable for
steady operations within robust classification
exercises in the domain of neurologic disorders of the
brain.
Figure 10: Model Accuracy Progression Over Epochs.
Figure 11: Model Accuracy Progression Over Epochs.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
440
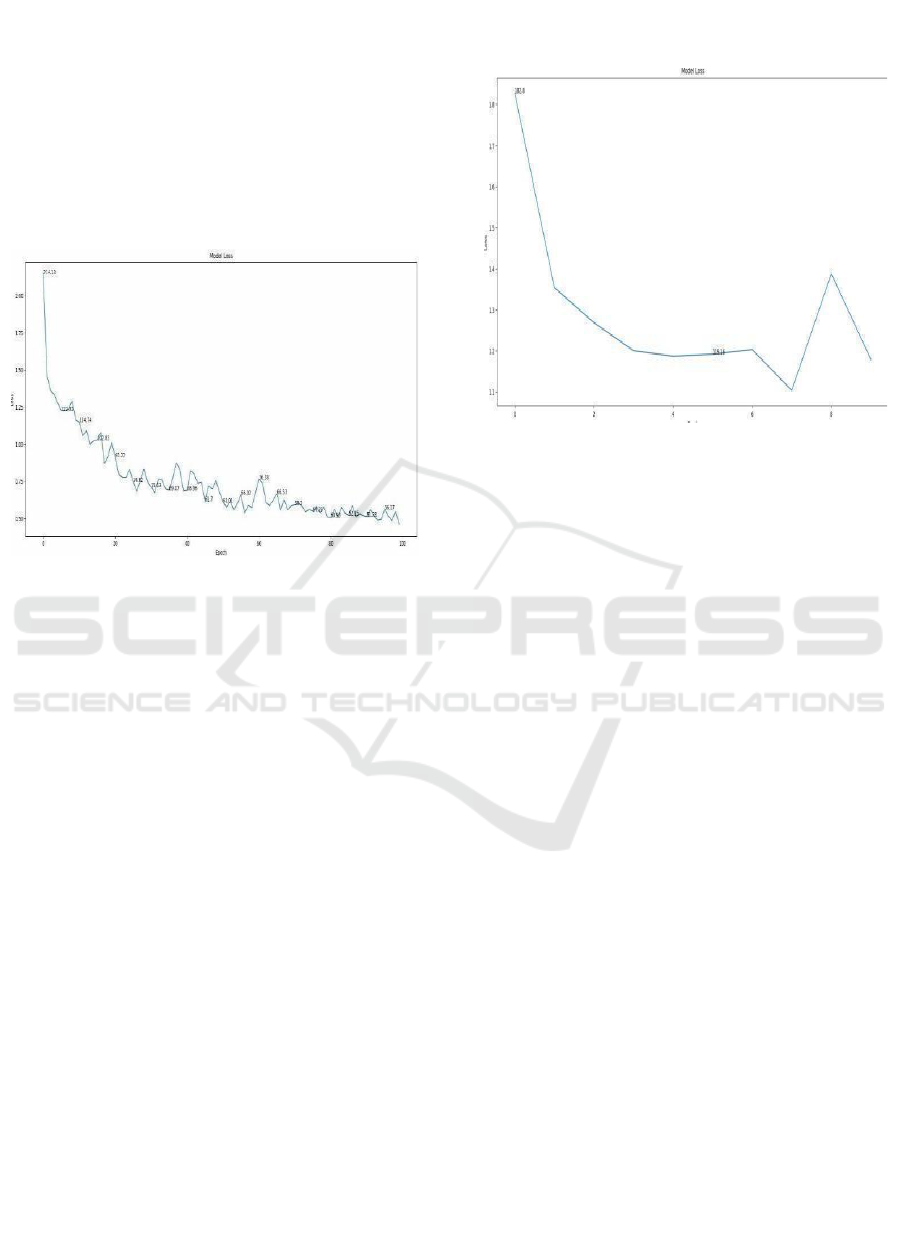
Model Loss Progression Over Epochs: Figure 12
states the loss that the model suffered during the
training period and therefore contains all information
about its capacity to learn and generalize. The
abscissa there represents epoch number, and ordinate
represents the value of the loss related to the capacity
of the model to minimize error disorders using deep
learning methods. It shows how the model has
improved with time properly decrementing errors
with time.
Figure 12: Model Loss Progression Over Epochs.
The second curve Figure 12&13 states the curve
of loss with regard to a deep-learning-based model
applied in the context of a classifying task on
challenging medical data. In that curve, the x-axis is
represented by the number of epochs whereas the y-
axis is representing the loss-a measure of fitting error
by the model for predictions.
The training process is a huge loss of
approximately 1.8, meaning that the net starts grossly
underfitting since the model still learns the hidden
patterns of the data. Sudden Drop: The fall of the loss
drops drastically in the initial epochs into around 1.2
by epoch 3 showing steep descent. This, thus, shows
that the model is actually learning and tending its
parameters to minimize error. Plateau and
Fluctuations: Almost no changes in the loss curve
after epoch 6 suggest that the model has stabilized its
trajectory of learning to a large extent. However, a big
sharp increase of the loss at around epoch 8 can be
interpreted as showing overfitting to the data, or this
model is not able to find tougher patterns. Conclusive
Loss: The loss at the end of the training phase is 1.1,
which indicates successful learning and a powerful
generalization ability concerning the training dataset.
The loss curve in this figure is from one of my
projects, where I designed a deep learning model that
predicts a condition concerning neurological issues
based on medical imaging data. It indicated an
excellent rate of optimization and accuracy with the
predictions since the model showed uniform loss
reduction during epochs.
Figure 13: Model Loss Progression Over Epochs.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The application of deep learning techniques,
particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs),
presents significant potential for enhancing the
accuracy of neurological disorder classification. By
leveraging advanced algorithms, researchers can
improve the detection of subtle patterns within
complex brain imaging datasets, facilitating early
diagnosis and deeper insights into conditions such as
Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Multiple Sclerosis.
This progress not only strengthens diagnostic
capabilities but also establishes a foundation for
developing personalized treatment strategies,
ultimately advancing patient care and therapeutic
outcomes.
REFERENCES
A. Kazi et al., “Self-attention equipped graph convolutions
for disease prediction,” in Proc. IEEE 16th Int. Symp.
Biomed. Imag., 2019, pp. 1896 – 1899.
B. Lei et al., “Multi-scale enhanced graph convolutional
network for mild cognitive impairment detection,”
Pattern Recognit., vol. 134, 2023, Art. no. 109106.
G. Pahuja and B. Prasad, “Deep learning architectures for
Parkinson’s disease detection by using multi-modal
features,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 146, 2022, Art. no.
105610.
H. Xu and J. Ma, “EMFusion: An unsupervised enhanced
medical image fusion network,” Inf. Fusion, vol. 76, pp.
177– 186, 2021.
Deep Learning Approaches for Early Diagnosis of Neurological Brain Disorders
441

H. Yang, J. Sun, and Z. Xu, “Learning unified hyper-
network for multimodal MR image synthesis and tumor
segmentation with missing modalities,” IEEE Trans.
Med.Imag., to be published, doi:
10.1109/TMI.2023.3301934
H. Zhang et al., “Classification of brain disorders in rs-
fMRI via localtoglobal graph neural networks,” IEEE
Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 42, no. 2 , pp. 444–455, Feb.
2023.
J. Fu, W. Li, J. Du, and B. Xiao, “Multimodal medical
image fusion via laplacian pyramid and convolutional
neural network reconstruction with local gradient
energy strategy,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 126, 2020,
Art. no. 104048.
J. Liu, X. Tian, J. Wang, R. Guo, and H. Kuang, “Mtfil-Net:
Automated Alzheimer’s disease detection and mmse
score prediction based on feature interactive learning,”
in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Bioinf. Biomed., 2021, pp.
1002–1007.
J. Cheng, J. Liu, H. Kuang, and J. Wang, “A fully
automated multimodal MRI-based multi-task learning
for glioma segmentation and IDH genotyping,” IEEE
Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 1520–1532, Jun.
2022.
J. Li et al., “DARC: Deep adaptive regularized clustering
for histopathological image classification,” Med. Image
Anal., vol. 80, 2022, Art. no. 102521.
J..Devlin,M.W.Chang,K.Lee,andK.Toutanova,“BERT:Pre
- trainingof deep bidirectional transformers forlanguage
understanding,” 2018, arXiv: 1810.04805.
L. Du et al., “Identifying diagnosis-specific genotype–
phenotype associations via joint multitask sparse
canonical correlation analysis and classification,”
Bioinformatics, vol. 36, no. Supplement_1, pp. i371–
i379, 2020
L. Du et al., “Associating multi-modal brain imaging
phenotypes and genetic risk factors via a dirty multi-
task learning method,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol.
39, no. 11, pp. 3416–3428, Nov. 2020
L. Du et al., “Identifying associations among genomic,
proteomic and imaging biomarkers via adaptive sparse
multi- view canonical correlation analysis,” Med.
Image Anal., vol. 70, 2021, Art. no. 102003
L. Du et al., “Adaptive stuctured sparse multiview
canonical correlation analysis for multimodal brain
imaging association identification,” Sci. China Inf. Sci.,
vol. 66, no. 4, 2023, Art. no. 142106.
M. Huang, X. Chen, Y. Yu, H. Lai, and Q. Feng, “Imaging
genetics study based on a temporal group sparse
regression and additive model for biomarker detection
of Alzheimer’s disease,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol.
40, no. 5, pp. 1461– 1473, May 2021.
M. Kim, J. H. Won, J. Youn, and H. Park, “Joint-
connectivity-based sparse canonical correlation
analysis of imaging genetics for detecting biomarkers
of Parkinson’s disease
P. Yi, L. Jin, T. Xu, L. Wei, and G. Rui, “Hippocampal
segmentation in brain MRI images using machine
learning methods: A survey,” Chin. J. Electron., vol. 30,
no. 5, pp. 793– 814, 2021.
Q. Wang, L. Zhan, P. Thompson, and J. Zhou, “Multimodal
learning with incomplete modalities by knowledge
distillation,” in Proc. 26th ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf.
Knowl. Discov. Data Mining, 2020, pp. 1828–1838.
Q. Zhu, H. Wang, B. Xu, Z. Zhang, W. Shao, and D. Zhang,
“Multimodal triplet attention network for brain disease
diagnosis,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 41, no. 12, pp.
3884–3894, Dec. 2022
Q.Ying,X.Xing,L.Liu,A.L.Lin,N.Jacobs,andG.Liang,“Mul
ti-modal data analysis for Alzheimer’s disease
diagnosis: An ensemble model using imagery and
genetic features,” in Proc. 43rd Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE
Eng. Med. Biol. Soc., 2021, pp. 3586–3591.
S. Parisot et al., “Disease prediction using graph
convolutional networks: Application to autism
spectrum disorder and Alzheimer’s disease,” Med.
Image Anal., vol. 48, pp. 117–130, 2018.
S. Zheng et al., “Multi-modal graph learning for disease
prediction,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 41, no. 9, pp.
2207 2216, Sep. 2022.
T. Wang et al., “Mogonet integrates multi-omics data using
graph convolutional networks allowing patient
classification and biomarker identification,” Nature
Commun., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–13, 2021.
W. Ko, W. Jung, E. Jeon, and H.-I. Suk, “A deep
generative– discriminative learning for multimodal
representation in imaging genetics,” IEEE Trans. Med.
Imag., vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 2348–2359, Sep. 2022
X. Song et al., “Multicenter and multichannel pooling GCN
for early AD diagnosis based on dual-modality fused
brain network,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 42, no. 2,
pp. 354–367, Feb. 2023.
X. Song et al., “Multicenter and multichannel pooling GCN
for early AD diagnosis based on dual-modality fused
brain network,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 42, no. 2,
pp. 354–367, Feb. 2023.
Y. Zhu, X. Zhu, M. Kim, J. Yan, D. Kaufer, and G. Wu,
“Dynamic hypergraph inference framework for
computer- assisted diagnosis of neurodegenerative
diseases,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 38, no. 2, pp.
608–616, Feb. 2019.
Y. Huang and A. Chung, “Edge-variational graph
convolutional networks for uncertainty-aware disease
prediction,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Med. Image Comput.
Comput.- Assist. Intervention, 2020, pp. 562–572.
Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, L. Xiao, Y. Bai, V. D. Calhoun, and
Y.-P. Wang, “Multi-modal imaging genetics data
fusion via a hypergraph-based manifoldregularization:
Application to schizophrenia study,”IEEETrans.Med.
Imag., vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 2263–2272, Sep. 2022
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
442
