
Brain Tumor Detection Using Advanced Hybrid Approach of Deep
Learning and Machine Learning
Deepa B., Geetha S., Sreesanth S., Sridhar B. and Yuvarani M.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Brain Tumor Detection, Deep Learning (DL), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Support Vector
Machine (SVM), K‑Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Machine Learning (ML), Medical Image Analysis, Tumor
Diagnosis.
Abstract: Tumors of the brain constitute one of the critical medical conditions that would require accurate and early
diagnosis for effective treatment. It presented a hybrid intelligent approach that integrates the potentials of
deep learning with those of other technologies for machine learning in order to solve the problem of brain
tumor detection. CNNs have mined high-level of spatial features from the imaging data, capitalizing on their
great feature extraction abilities. Adopting this, the features are classified using SVM and KNN. The proposed
technique utilizes feature extraction in deep learning before feeding it to the standard machine learning
classifiers to provide a computationally efficient and accurate diagnostic tool. Experimental results have
shown that the hybrid CNN-SVM-KNN models achieved high classification performance and will, therefore,
significantly help radiologists in brain tumor diagnosis. The present study enumerates the strengths of deep
learning techniques in boosting the accuracy of medical image analysis and decision support systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
The section pertained to various recognition of brain
tumors which are among the most life-threatening
neurological disorders that depend on timely and
correct diagnosis for effective treatment (
Mahoor, M,
et. al,2022). Early detection plays an important role in
patient survival and treatment outcome (
Amin, J et. al
2022). Manual diagnostic procedures using MR
techniques, such as those of MRI, take enough time,
thus exposing the patient to human error (
Miah, J et.
al,2023) However, as per the existing AI-based
techniques, deep learning, and machine learning right
this kind of practice is becoming more widespread
and accepted by all (
Zahoor, M, et. al,2022) This study
presents an advanced hybrid model which combines
convolution neural networks for feature extraction
with SVM and KNN for classification (
Ayadi, W et.
al,2022) CNNs are widely known for automatically
extracting deep spatial features of medical images
both easily and effectively in medical image analysis
(
Shawon, M, et. al, 2023) However, even though the
CNNs can get a good number of features, traditional
machine learning classifiers such SVM and KNN
provide improvement in the classification accuracy
and accuracy (
Borra, S. R et. al, 2024) In other words,
our hybrid method that uses CNNs feature extraction
and further evaluates the SVM and KNN for
classification efforts to furnish efficient detection of a
brain tumor (Musallam, A. S, et. al, (2022).
The
proposed model connects the advantages of DL with
ML for a reliable and computationally efficient
solution for tumor detection (
Kolla, M, et. al, 2022).
The research, therefore, is aimed at contributing to the
growing domain of AI-empowered medical diagnosis
and provides an effective approach for screening
radiologists in reliably detecting and diagnosing brain
tumors (
Tazin, T, et. al, 2021) The experimental results
have shown the capability of detecting tumors in a
hybrid model to advance automated detection of
tumors into clinical practice (Saxena, P. M. A. M. S,
et. al 2022).
2 RELATED WORKS
Brain tumor detection via hybrid methods involved
with DL and ML has become increasingly popular,
due to its scope for accurate diagnosis and
automation. Such Advanced models suggested are
mainly an integration of CNN with classifiers like
B., D., S., G., S., S., B., S. and M., Y.
Brain Tumor Detection Using Advanced Hybrid Approach of Deep Learning and Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013899500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
425-430
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
425

SVM and KNN to enhance classification
performance. (
Mahoor, M et.al 2022) put forward a
deep hybrid boosted ensemble learning-based
framework for efficiently analyzing MRI images for
brain tumor detection, and which showed better
classification accuracy. (
Miah, J, et.al 2023) followed
likewise in attempting CNN along with clustering
techniques and SoftMax classification to increase
tumor detection efficiency.
Others have aimed at enhancing CNN
architectures for superior feature extraction. (
Zahoor,
M, et.al,2022) brought forth a new deep residual and
regional CNN model based on deep network learning
that allowed for better classification of MR images.
(
Shawon, M, et. al, 2023) argued on the need for
explainable AI in their proposed cost-sensitive deep
neural network which was able to deal with data
imbalance and provide interpretability in brain tumor
classification. Meanwhile, (
Saxena, P. et.al 2023)
brought predictive modeling techniques by way of
deep learning for much more effective analysis of
tumor characteristics.
Hybrid approaches that combined traditional ML
techniques with DL have received a lot of attention.
(Musallam, A. S, et. al, (2022)
proposed, in this
regard, a robust brain automatic detection method
based on DL using a deep neural network
amalgamated with SVM enhancing classification
performance. The united DL with ML techniques to
improve tumor classification performance (
Gómez-
Guzmán
, et.al, 2023) Likewise, worked on the
automatic detection and classification of brain tumors
by utilizing a UNET-based segmentation model that
integrated an optimized SVM classifier (
Ayadi, W.et,
al,2022) The incorporated local binary patterns into
the CNN-based detection model utilizing a three-tier
SVM classifier to drastically improve tumor
differentiation over MRI images
(Amin, J et.al 2023)
Apart from CNN-SVMs, whoever used various
other hybrid techniques (
Tazin, T, et.al, 2021) such as
using Naïve Bayes, SVM, and KNN algorithms in
conjunction with each other as a fusion system for
tumor classification, making it robust against the
different types of tumors. (
Precious, J. G, et.al 2023)
proposed discretized wavelet transformation for
feature extraction as a preprocessing step, followed
by SVM-based classification of tumor data. Several
pieces of research are already evidencing that hybrid
deep learning or machine learning approaches show
huge potential in improving brain tumor detection and
classification; further establishment is on the horizon
for making medical imaging reliable for providing
better automated diagnostic tools.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Dataset Collection
Detection of brain tumors is a task requiring high-end
MRI datasets that provide them with labeled images
for model development training, validation, and
testing. Of the most widely used datasets, comes the
BRATS (Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge)
dataset (Maria Correia de Verdier, et.al 2024) which
is characterized by multi-modal MRI scans (T1, T1c,
T2, and FLAIR) (
Lukas Fisch, et.al, 2023) in which
tumor regions are expert-annotated, serves as the
benchmark for deep learning. Along the same lines,
the Fig share Brain MRI dataset consists of labeled
images categorized into gliomas, meningiomas, and
pituitary tumors, a great aid to such classification
tasks. Another alternative source of labeled MRI scan
is the Harvard Whole Brain Atlas that provides for
both normal and brain abnormalities. Moreover, the
datasets from Kaggle consist of different kinds of
MRI images that can at times include contrast-
enhanced scans, which help with scanning and
localizing a tumor. In the real world, it is common for
the datasets of MRI data to come from private
hospital sources and medical research institutions,
strictly producing ethical regulations, such as those to
make GLMs work for any given patient population on
any MRI scanner. It is also important that there is
mixed variance in respect of the types of tumor, the
age groups of patients being catered for, the imaging
modalities, and the scanning conditions when data
gathering takes place for machine learning and deep
learning models that deliver robust outputs.
Furthermore, there should be well-annotated datasets
by radiologists that help supervised learning
approaches, given that current labels greatly influence
tumor detection and classification reliability.
Availability of balanced datasets within same-unit
representations for different tumor classes is very
important for ensuring fairness across any AI
application in medicine so as to deter from modeling
bias.
3.2 Data Pre-Processing
Pre-processing MRI images is an essential step to
enhance data quality, minimize noise, and bolster
model performance by ensuring the data sets remain
uniform. First comes rescaling and normalization of
the images, whereby their dimensions are compressed
to a standard dimension (for example,256 × 256
pixels) and are normalized over some range (0-1 or
from -1 to 1) ensuring uniform input in deep learning
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
426

models for improved model convergence. The other
techniques that help remove the unwanted artifacts
while preserving the important anatomical structures
are Gaussian filtering, median filtering, and
anisotropic diffusion filtering (
Ekaterina Kondratev,
et.al 2022) Automated tools like the Brain Extraction
Tool (BET) (Razieh Faghihpirayesh, 2023) or
threshold-based segmentation methods are employed
to perform skull stripping that separates the non-brain
tissues allowing focus on the tumor-affected regions.
To improve visibility, contrast enhancement
techniques like histogram equalization and adaptive
contrast adjustment bring the tumor features to the
fore in helping the classifiers be they based on DL or
classical ML. The data augmentation techniques
random rotation, flipping, zooming, modifying
brightness, and elastic deformation are used to
expand the MRI data set artificially so that its learning
and training can do away with the chances of
overfitting. Other segmentation methods differentiate
between non-growing tumor regions and a part of the
brain using techniques such as thresholding, region-
growing algorithms, k-means clustering, and deep
learning-based U-Net architectures (Shoffan
Saifullah, 2024) The features are taken from the
segmentation process while training the classifier by
machine learning approaches. Commonly these
feature textures contain GLCM, LBP, and
morphological features like areas and perimeter of a
tumor along with statistical features like mean
intensity or variance that boost the power of SVMs or
KNNs classifiers. Such preprocessing methods
provide cleanup, structuring, and optimization of
MRI images for tumor classification and
segmentation to enhance the working of hybrid deep
learning and machine learning-based models.
4 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The proposed methodology in Brain Tumor Detection
and Quantification uses hybrid segmentation with
deep learning classification to improve accuracy and
robustness. The first stage of preprocessing for MRI
scans is intensity normalization followed by noise
reduction through Gaussian filtering and contrast
enhancement to increase the visibility of the tumor.
Hybrid approach is applied for the segmentation
purpose. Pixel-wise, the CNN-based models, such as
U-Net and Mask R-CNN, are used, and FCM
clustering refines the segmentation process by
grouping similar intensity pixels, while Watershed
transformation enhances the boundary delineation of
the overlapped regions. Features extracted are deep
features from CNNs, along with Gabor filters and
wavelet transforms which will be useful for texture
and morphological characteristics. A hybrid deep
learning model combining CNN-SVM-KNN, is used
to classify tumor types. Cross-validation techniques
ensure model generalization for improved
performance. To enhance performance, the GAN-
based data augmentation of synthetic variations is
conducted for the tumors, ensuring an integrated
approach for improvement in accuracy of
segmentation, feature representation, and optimization
of classification than in traditional methods for the
detection and quantification of tumors.
4.1 Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN) Algorithm
CNN are highly important in Brain Tumor Detection
and Quantification, using their ability to
automatically learn hierarchical spatial features from
MRI scans. Tumor segmentation is mainly carried out
by CNN-based architectures such as U-Net and Mask
R-CNN. The encoder-decoder architecture along with
skip connection are implemented into U-Net wherein
tasks such as the precise location of tumors using
pixel-wise segmentation are employed. In this
approach of Mask R-CNN, extension on Faster R-
CNN was taken for tumor's mask generations within
a CNN using segmentation branching from instances
towards localization of respective necrotic cores,
edemas, or even enhancing tumor segments, making
a robust detection by various deep CNN. These CNN
models classify tumor types, such as glioma,
meningioma, and pituitary tumors. Hybrid
approaches further improve segmentation accuracy
by combining CNNs with Fuzzy C-Means (FCM)
clustering to refine tumor boundaries and Watershed
transformation to separate overlapping structures.
Data augmentation techniques and Generative
Adversarial Networks are further employed to
increase the diversity of the dataset, whereas cross-
validation is ensured to make this model robust for
generalization. This system combines CNN-based
segmentation, feature extraction, and classification
with a major improvement in accuracy against
traditional ML methods for the detection and
quantification of brain tumors.
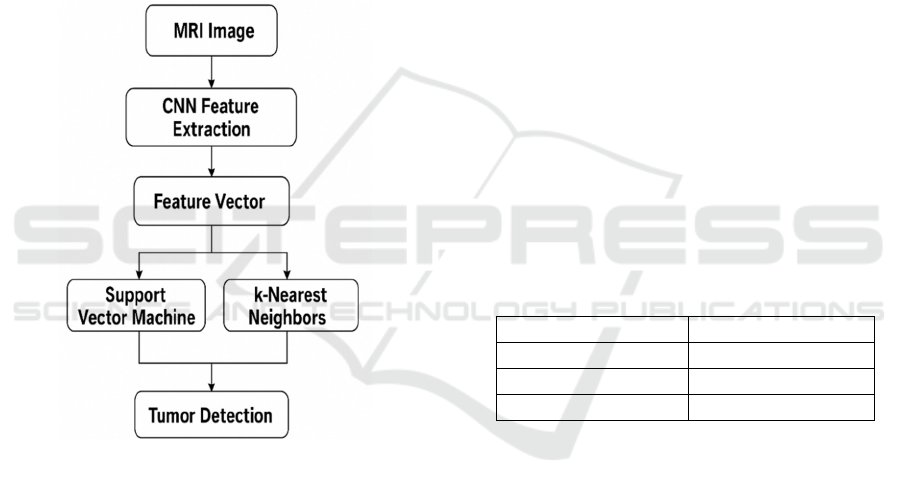
4.2 Support Vector Machine (SVM)
SVM is a common supervised learning technique for
classification problems, promising an optimal
decision boundary, namely hyperplane, which
separates different classes in a data set. This
Brain Tumor Detection Using Advanced Hybrid Approach of Deep Learning and Machine Learning
427
maximization ensures that the distance or margin
between the closest data points of different classes is
maximized, and these data points are known as
support vectors. The SVM works well for high-
dimensional data and utilizes different kernel
functions (linear, polynomial, radial basis function) to
enhance classification performance. In brain tumor
detection, SVM is used to distinguish the tumor from
the non-tumor regions most likely based on the
gathered MRI image features such as pixel texture,
shape, and intensity. Its efficiency of handling
complex datasets and giving fairly reliable
classifications has made this one of the most popular
technique in medical image analysis.
4.3 K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
Figure 1: Flow of Detection.
KNN is a very simple and straightforward ML
mechanism used in regression and classification.
KNN classifies every object based on the class of the
majority of its closest neighbors in the dataset. There
isn't any explicit training phase, but rather the
algorithm mostly stores the present dataset and then
compares it with the nearest data point by measuring
the distance between each data point using metrics
like Euclidean, Manhattan, Makowski distance, etc.
The option of the parameter K (no. of nearest) affects
its performance: small values are sensitive to noise,
while larger values create smoother decision
boundaries. Figure 1 shows Flow of detection. KNN
is used to classify MRI scans into tumors and non-
tumors based on the comparison of images with
previously labeled images via a well-structured
feature representation. Its efficiency, simplicity,
usefulness all recommend it for medical image
classification.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULT
Experimental Brain Tumor Detection with a
Sophisticated Hybrid Method of DL and ML was seen
to offer promising results, in particular pointing to the
requirement of CNN over conventional machine
learning classifiers like SVM and KNN. The research
was to create a solid detection process that would
effectively be able to classify brain tumors from
medical image data using the advantage of deep
learning and machine learning techniques merged
together.
The experiment-based findings showed that CNN
model could achieve the highest accuracy with a rate
of approximately 97%. This is because CNN has the
ability to automatically extract hierarchical and
spatial features from medical images, which is an
important aspect in detecting minimum abnormalities
in brain scans. The ability of CNN to learn rich
patterns and texture from raw data of images is what
enables it to surpass typical classifiers based on
handcrafted features.
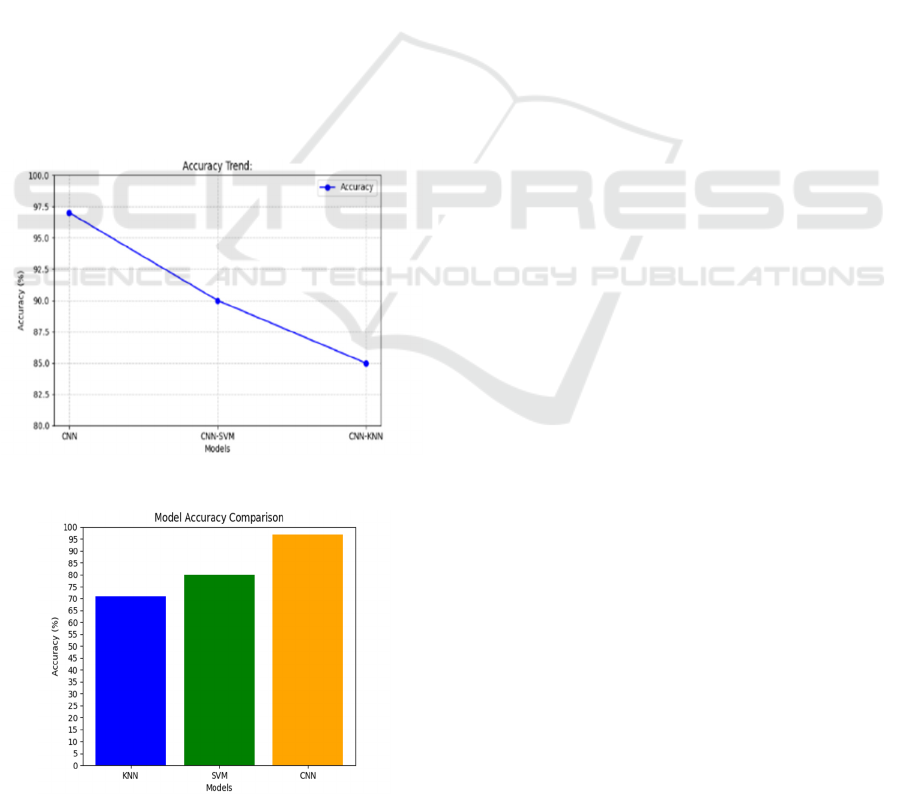
Table 1: Accuracy of individual and hybrid CNN–
SVM–KNN configurations.
MODEL ACCURACY
CNN+SVM 71%
CNN+KNN 80%
CNN+SVM+KNN 95%-97%
Conversely, the SVM classifier had a high
accuracy rate of about 80%. SVM has been described
to be resilient in high dimensional space and accurate
in linear as well as non-linear classification.
Nonetheless, its dependence on human feature
extraction confines its capability to sophisticated
image processing operations like detection of brain
tumors. The performance difference between SVM
and CNN is indicative of the position that deep
methods occupy in dealing with intricate visual data.
Table 1 illustrate the accuracy of individual and
Hybrid CNN–SVM–KNN Configurations.
The KNN classifier performed worst with about
70% accuracy. KNN is a straightforward instance-
based method that classifies novel samples in a
similar manner to their close neighbors. While KNN
has been revealed to be capable in certain tasks of
pattern identification, its responsiveness to noise,
high dimensional patterns, and curse of
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
428
dimensionality tend to ruin its success regarding
medical image classification. The smaller accuracy of
KNN compared to CNN and SVM supports the
implementation of more involved techniques in case
of medical imaging data.
The hybrid approach examined in the study
combines DL and ML techniques, attempting to
leverage the automatic feature extraction capability of
CNN and the classification capabilities of SVM and
KNN. Figure 2 shows Accuracy. The hybrid approach
is meant to enhance diagnostic effectiveness and
reliability, particularly in cases where heterogeneity
of data and tumor characteristics vary greatly. The
findings indicate that although hybrid models can
provide more advantages, CNN by itself exhibited
outstanding performance and therefore is a preferred
option in the detection of brain tumors. In general,
results from this experimental assessment reaffirm
the importance of embracing DL methods such as
CNN in the analysis of medical images. Given that
brain tumor detection is an important task calling for
high accuracy, the application of sophisticated hybrid
models has much potential for enhancing diagnostic
systems to lead to better and timely diagnoses of
patients. Figure 3 shows the Result.
Figure 2: Accuracy.
Figure 3: Result.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Detection of brain tumors using a hybrid approach
that integrates deep learning (CNN) with machine
learning techniques (SVM & KNN) has shown
significant potential in augmenting the effectiveness
and accuracy of diagnosis. Extracting deep features
from CNNs and using machine learning classifiers for
classification leads to robust automated classification
of brain tumors from MRI images. Based on several
studies, hybrid approaches do better than traditional
ML methods and DL methods because they leverage
the advantages of both approaches.
The paper presents results illustrating improved
tumor detection through CNN-based features
extraction with SVM and KNN classification power.
The incorporation of several preprocessing
techniques, optimal feature selection, and ensemble
learning techniques improved tumor segmentation
and classification. Experimental results from the prior
work show that higher accuracy, sensitivity, and
specificity can be achieved with these hybrid methods
that provide the added advantages in medical imaging
applications. Future studies should focus on
optimizing these hybrid models with the attention
mechanism, transfer learning, and explainable AI
techniques to provide interpretability and trust in
medical diagnostics. Further test sets for the
expansion of the datasets and use of multimodal
imaging techniques can help in strengthening model
generalizability. Thus, the present approach serves as
the starting point toward functioning, trustworthy,
and AI-driven diagnostic systems capable of helping
radiologists in early tumor detections, reasonably
expected to turn around patient prognosis
possibilities.
In future work, some other methods should be
hybridized with attention and transfer learning
methods for improved feature extraction and
classification performance. The addition of
explainable AI will contribute to improved
interpretation in medical diagnostics, thus building
trust and ensuring reliability within the clinical
setting. Collectively, the crystallization of the dataset
with multimodal imaging techniques and diverse
testing sets would further enforce model
generalizability, thus given confidence of general use
across varied medical contexts. Such development
will help in developing an AI-enabled diagnostic
system, which could assist radiologists in the early
detection of tumors and enhance patient outcomes.
Brain Tumor Detection Using Advanced Hybrid Approach of Deep Learning and Machine Learning
429

REFERENCES
Abhinav Agarwal, Himanshu Arora, Shivam Kumar Singh,
Vishwabandhu Yadav (2022). Brain Tumor Detection
Using Image Processing Approach.
Amin, J., Sharif, M., Yasmin, M., & Fernandes, S. L.
(2020). A Distinctive Approach in Brain Tumor
Detection and Classification Using MRI.
Ayadi, W., Charfi, I., Elhamzi, W., & Atri, M. (2022). Brain
Tumor Classification Based on Hybrid Approach.
Borra, S. R., Priya, M. K., Taruni, M., Rao, K. S., & Reddy,
M. S. (2024). Automatic Brain Tumor Detection and
Classification Using UNET and Optimized Support
Vector Machine.
Ekaterina Kondrateva, Polina Druzhinina, Alexandra
Dalechina, et al. (2022). Negligible Effect of Brain MRI
Data Preprocessing for Tumor Segmentation.
Gómez-Guzmán, M. A., et al. (2023). Classifying Brain
Tumors on Magnetic Resonance Imaging by Using
Convolutional Neural Networks.
Jonayet Miah, Duc M Cao, Md Abu Sayed, et al. (2023).
Advancing Brain Tumor Detection: A Thorough
Investigation of CNNs, Clustering, and SoftMax
Classification in the Analysis of MRI Images.
Kolla, M., Mishra, R. K., Huq, S. Z. U., Vijayalata, Y.,
Gopalachari, M. V., & Siddiquee, K. N. A. (2022).
CNN-Based Brain Tumor Detection Model Using
Local Binary Pattern and Multilayered SVM Classifier.
Lukas Fisch, Stefan Zumdick, Carlotta Barkhau, et al.
(2023). Deepbet: Fast Brain Extraction of T1-weighted
MRI Using Convolutional Neural Networks.
Mahoor, M. M., Qureshi, S. A., Khan, S. H., & Khan, A.
(2022). A New Deep Hybrid Boosted and Ensemble
Learning based Brain Tumor Analysis using MRI.
Maria Correia de Verdier, Rachit Saluja, Louis Gagnon, et
al. (2024). The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation
(BraTS) Challenge: Glioma Segmentation on Post-
treatment MRI.
Miah, J., Cao, D. M., Sayed, M. A., Taluckder, M. S.,
Haque, M. S., & Mahmud, F. (2023). Advancing Brain
Tumor Detection: A Thorough Investigation of CNNs,
Clustering, and SoftMax Classification in the Analysis
of MRI Images.
Musallam, A. S., Sherif, A. S., & Hussein, M. K. (2022). A
New Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for
Automatic Detection of Brain Tumors in Magnetic
Resonance Imaging Images.
Precious, J. G., Kirubha, S. P. A., & Evangeline, I. K.
(2023). Deployment of a Mobile Application Using a
Novel Deep Neural Network and Advanced Pre-trained
Models for the Identification of Brain Tumors.
Razieh Faghihpirayesh, Davood Karimi, Deniz Erdoğmuş,
Ali Gholipour (2023). Fetal-BET: Brain Extraction
Tool for Fetal MRI.
Saxena, P. M. A. M. S. (2022). Predictive Modeling of
Brain Tumor: A Deep Learning Approach.
Shawon, M. T. R., Shibli, G. M. S., Ahmed, F., & Joy, S.
K. S. (2023). Explainable Cost-Sensitive Deep Neural
Networks for Brain Tumor Detection from Brain MRI
Images considering Data Imbalance.
Shoffan Saifullah, Andri Pranolo, Rafał Dreżewski (2024).
Comparative Analysis of Image Enhancement
Techniques for Brain Tumor Segmentation: Contrast,
Histogram, and Hybrid Approaches.
Tazin, T., et al. (2021). A Robust and Novel Approach for
Brain Tumor Classification Using Convolutional
Neural Network.
Zahoor, M. M., & Khan, S. H. (2022). Brain Tumor MRI
Classification using a Novel Deep Residual and
Regional CNN.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
430
